Boost搜索引擎 查找并去重(3)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、InitSearcher
- 二、Search
- 摘要函数GetDesc
- 测试
- 总结
前言
要结束喽,嘻嘻~
我们现在已经完成了数据清洗与去标签、建立索引的工作,接下来就是要编写服务器的任务了!!
一、InitSearcher
接下来我们就是要根据索引去进行搜索了,分别是 InitSearcher() 和 Search()
#include "index.hpp"namespace ns_searcher
{class Searcher{private:ns_index::Index *index; // 供系统进行查找的索引public:Searcher() {}~Searcher() {}public:void InitSearcher(const std::string& input){// 获取或者创建index对象(单例)// 根据index对象建立索引}// query: 搜索关键字// json_string: 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结果void Search(const std::string& query, std::string* json_string){//...}};
}
- query: 搜索关键字
- json_string: 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结果
我们的目标流程:
- 分词:对搜索关键字 query 在服务端也要分词,然后查找 index
- 触发:根据分词的各个词进行 index 查找
- 合并排序:汇总查找结果,按照相关性(权重 weight )降序排序
- 构建:将排好序的结果,生成json串 —— jsoncpp
- 服务器要去构建索引,本质上就是去构建一个 Index 对象,然后调用其内部的方法
- 我们知道构建正排索引和倒排索引本质就是将磁盘上的数据加载的内存,其数据量还是比较大的(可能本项目的数据量不是很大)
- 从这一点可以看出,假设创建了多个 Index 对象的话,其实是比较占内存的,我们这里就可以将 Index 类设计成为单例模式
namespace ns_index
{class Index{private:std::vector<DocInfo> forward_index; // 正排索引std::unordered_map<std::string, InvertedList> inverted_index; // 倒排索引// 将 Index 转变成单例模式private:Index() {} // 这个一定要有函数体,不能deleteIndex(const Index &) = delete; // 拷贝构造Index &operator=(const Index &) = delete; // 赋值重载static Index *instance;static std::mutex mtx; // C++互斥锁,防止多线程获取单例存在的线程安全问题public:~Index() {}public:// 获取index单例static Index *GetInstance(){// 这样的【单例】 可能在多线程中产生 线程安全问题,需要进行加锁if (nullptr == instance) // 双重判定空指针, 降低锁冲突的概率, 提高性能{mtx.lock(); // 加锁if (nullptr == instance){instance = new Index(); // 获取单例}mtx.unlock(); // 解锁}return instance;}DocInfo* GetForwardIndex(uint64_t doc_id){//...}};// 单例模式Index* Index::instance = nullptr;std::mutex Index::mtx;
}
这样的话 InitSearcher() 就很明了了
void InitSearcher(const std::string &input)
{// 获取或者创建index对象(单例)index = ns_index::Index::GetInstance(); // 根据index对象建立索引index->BuildIndex(input);
}
二、Search
- 对用户的输入的【关键字】,我们首先要做的就是【分词】,只有分成不同的词之后,才能按照不同的词去找文档;
- 分词完毕后,我们就要去触发这些分词,本质就是查找建立好的正排索引和倒排索引;
- 我们的每个文档都是设置了权重字段的,我们就应该在触发分词之后,进行权重的降序排序,达到权重高的文档靠前,权重低的文档靠后;
- 根据排序完的结果,构建 json 串,用于网络传输。
这个序列化和反序列化的工作就交由我们的 jsoncpp 来完成吧
好,现在我们开始第一步流程:分词!
- 我们 index 模块 中的 正排索引 中已经做了分词操作,这只能说明服务器已经将数据准备好了,按照不同的词和对应的文档分好类了
- 但是用户输入的关键字,我们依旧是要做分词操作的
- 设想一下,如果没有做分词,直接按照原始的关键字进行查找,给用户反馈的文档一定没有分词来的效果好,甚至有可能匹配不到文档
就像我在Edge里面搜索 “中南大学计算机学院” ,肯定也是被拆词来匹配的
// query ---> 搜索关键字
// json_string ---> 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结果
void Search(const std::string& query, std::string* json_string)
{// 1.分词 --- 对 query 按照 Searcher 的要求进行分词 std::vector<std::string> words; // 用一个数组存储分词的结果 ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words); // 分词操作
}
就是这样,很轻松惬意地完成了第一步的流程,现在开始第二步,查找!
- 分词完成以后,我们就应该按照分好的每个词(关键字)去获取倒排拉链
- 我们将获取上来的倒排拉链进行保存到 vector 当中,这也就是我们根据用户关键字所查找的结果
但是这里我们要思考一个很严肃的问题:我们搜索出来的文档是不是有重复?
很显然是的,原理在于,我们的倒排拉链节点 InvertElem 只能保证一个文档对应一个关键字,那么我们的输入 input 被拆成很多关键字后,可能对应到了同一个文档ID,也就是说,一个文档可能包含不止一个我们的关键字,但是我们肯定不是想要这个结果,我们自己搜索的时候也不会同一个结果出现两次,这种体验感是很差的
可能我描述的出现重复的原因不是很好,没事,让DeepSeek来!
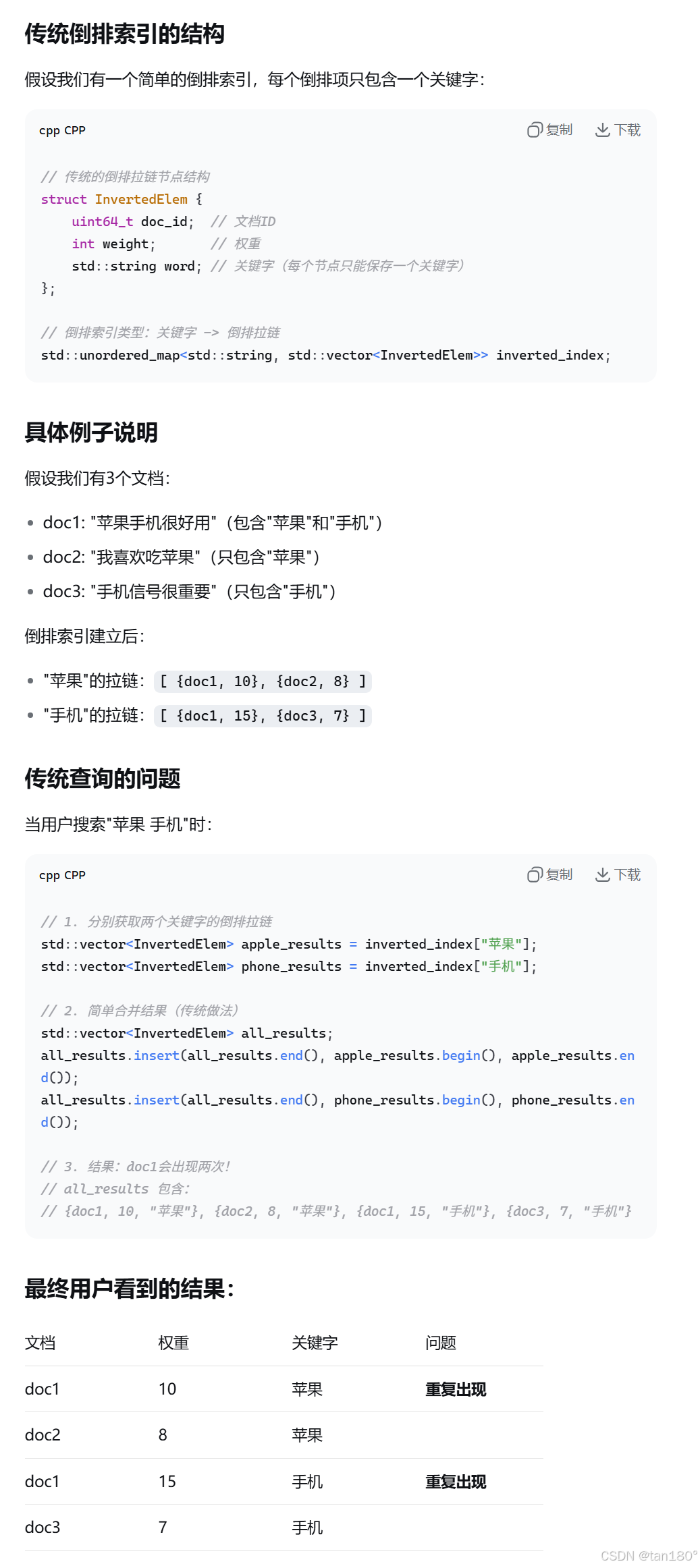
理想情况下,应该是只显示一个文档,并且所有关键词的权重应该相加,再排序显示
所以我们现在定义一个新的倒排拉链节点来存储,如下:
// 该结构体是用来对重复文档去重的结点结构
struct InvertedElemPrint
{uint64_t doc_id; // 文档IDint weight; // 重复文档的权重之和std::vector<std::string> words; // 关键字的集合,我们之前的倒排拉链节点只能保存一个关键字InvertedElemPrint() : doc_id(0), weight(0) {}
};
好了,接下来有了这样铺垫,我们可以来编写触发分词的代码了
// query ---> 搜索关键字
// json_string ---> 返回给用户浏览器的搜索结果(jsoncpp)
void Search(const std::string& query, std::string* json_string)
{// 1.分词---对query按照Searcher的要求进行分词std::vector<std::string> words; // 用一个数组存储分词的结果ns_util::JiebaUtil::CutString(query, &words); // 分词操作// 2.触发---就是根据分词的各个"词",进行index查找,建立index是忽略大小写,所以搜索关键字也需要std::vector<InvertedElemPrint> inverted_list_all; // 用vector来保存std::unordered_map<uint64_t, InvertedElemPrint> tokens_map; // 用来去重for (std::string word : words) // 遍历分词后的每个词{boost::to_lower(word); // 忽略大小写ns_index::InvertedList* inverted_list = index->GetInvertedList(word); // 获取倒排拉链if (nullptr == inverted_list){continue;}// 遍历获取上来的倒排拉链for (const auto &elem : *inverted_list){auto &item = tokens_map[elem.doc_id]; // 插入到tokens_map中,key值如果相同,这修改value中的值item.doc_id = elem.doc_id;item.weight += elem.weight; // 如果是重复文档,key不变,value中的权重累加item.words.push_back(elem.word); // 如果是重复文档,关键字会被放到vector中保存}}// 遍历tokens_map,将它存放到新的倒排拉链集合中(这部分数据就不存在重复文档了)for (const auto &item : tokens_map){inverted_list_all.push_back(std::move(item.second));}
}
好了,最精华的一步结束了,现在我们开始进行降序排列,因为相关性高的肯定排前面,所以我们按 weight 降序排列
// 3. 合并排序---汇总查找结果,按照相关性(weight)降序排序
std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(),[](const InvertedElemPrint &e1, const InvertedElemPrint &e2){ return e1.weight > e2.weight; });
最后就是返回结果了,按照搜索结果构建 json 字符串,当然了你得先安装一下
#(Ubuntu)
sudo apt-get install -y libjsoncpp-dev
// test_json.cpp
// 可以先来看看效果,感受一下第三方库的强大!
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>// Value Reader(反序列化) Writer(序列化)
int main()
{Json::Value root;Json::Value item1;item1["key1"] = "value1";item1["key2"] = "value2";Json::Value item2;item2["key1"] = "value3";item2["key2"] = "value4";root.append(item1);root.append(item2);// 两种序列化方式// 序列化方式1// Json::StyledWriter writer; // 序列化方式2Json::FastWriter writer; std::string s = writer.write(root);std::cout<< s << std::endl;return 0;
}// // 序列1
// [
// {
// "key1" : "value1",
// "key2" : "value2"
// },
// {
// "key1" : "value3",
// "key2" : "value4"
// }
// ]// // 序列2,很明显实际网络传输中这种方法会更快一点
// [{"key1":"value1","key2":"value2"},{"key1":"value3","key2":"value4"}]
好了,现在我们开始最后一步
#include "index.hpp"
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>namespace ns_searcher
{class Searcher{void Search(const std::string& query, std::string* json_string){// ...// 4.构建---根据查找出来的结果,构建json串---jsoncppJson::Value root;for (auto &item : inverted_list_all){ns_index::DocInfo* doc = index->GetForwardIndex(item.doc_id);if (nullptr == doc){continue;}Json::Value elem;elem["title"] = doc->title;elem["desc"] = GetDesc(doc->content, item.words[0]); // content是文档去标签后的结果,但不是我们想要的,我们要的是一部分elem["url"] = doc->url;// 调试// elem["id"] = (int)item.doc_id;// elem["weight"] = item.weight;root.append(elem);}// Json::StyledWriter writer; //方便调试Json::FastWriter writer; // 调式没问题后使用这个*json_string = writer.write(root);}}
}
摘要函数GetDesc
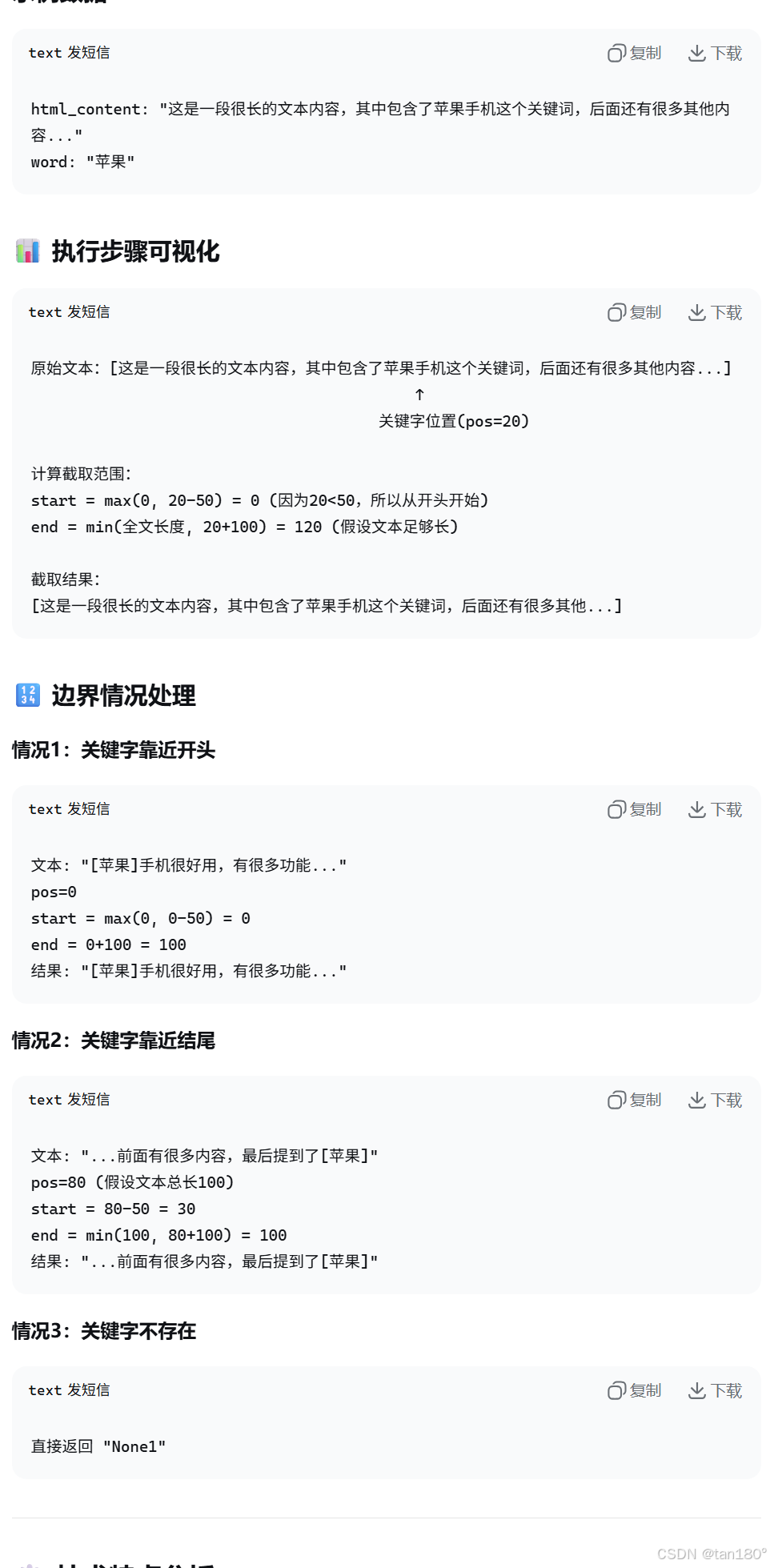
很显然我们搜索的时候,内容并不会完全展现,最多展示一些字数,所以我们并不用传给 elem[“desc”] 文档的全部内容 “doc.content” ,所以我们现在来解决一下摘要函数问题
std::string GetDesc(const std::string& html_content, const std::string& word)
{// 找到word(关键字)在html_content中首次出现的位置// 然后往前找50个字节(如果往前不足50字节,就从begin开始)// 往后找100个字节(如果往后不足100字节,就找到end即可)// 截取出这部分内容const int prev_step = 50;const int next_step = 100;// 1.找到首次出现auto iter = std::search(html_content.begin(), html_content.end(), word.begin(), word.end(), [](int x, int y){ return (std::tolower(x) == std::tolower(y)); });if (iter == html_content.end()){return "None1";}int pos = std::distance(html_content.begin(), iter);// 2.获取start和end位置int start = 0;int end = html_content.size() - 1;// 如果之前有50个字符,就更新开始位置if (pos > start + prev_step)start = pos - prev_step;if (pos < end - next_step)end = pos + next_step;// 3.截取子串,然后返回if (start >= end)return "None2";std::string desc = html_content.substr(start, end - start);desc += "...";return desc;
}
测试
做好了代码总得来个测试一下吧,现在我们来个 debug.cc
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>#include "searcher.hpp"const std::string input = "data/raw_html/raw.txt";int main()
{ns_searcher::Searcher *search = new ns_searcher::Searcher();search->InitSearcher(input); // 初始化search,创建单例,并构建索引std::string query; // 自定义一个搜索关键字std::string json_string; // 用json串返回给我们char buffer[1024];while (true){std::cout << "Please Enter You Search Query: "; // 提示输入fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1, stdin); // 读取buffer[strlen(buffer) - 1] = 0;query = buffer;search->Search(query, &json_string); // 执行服务,对关键字分词->查找索引->按权重排序->构建json串->保存到json_string->返回给我们std::cout << json_string << std::endl; // 输出打印}return 0;
}
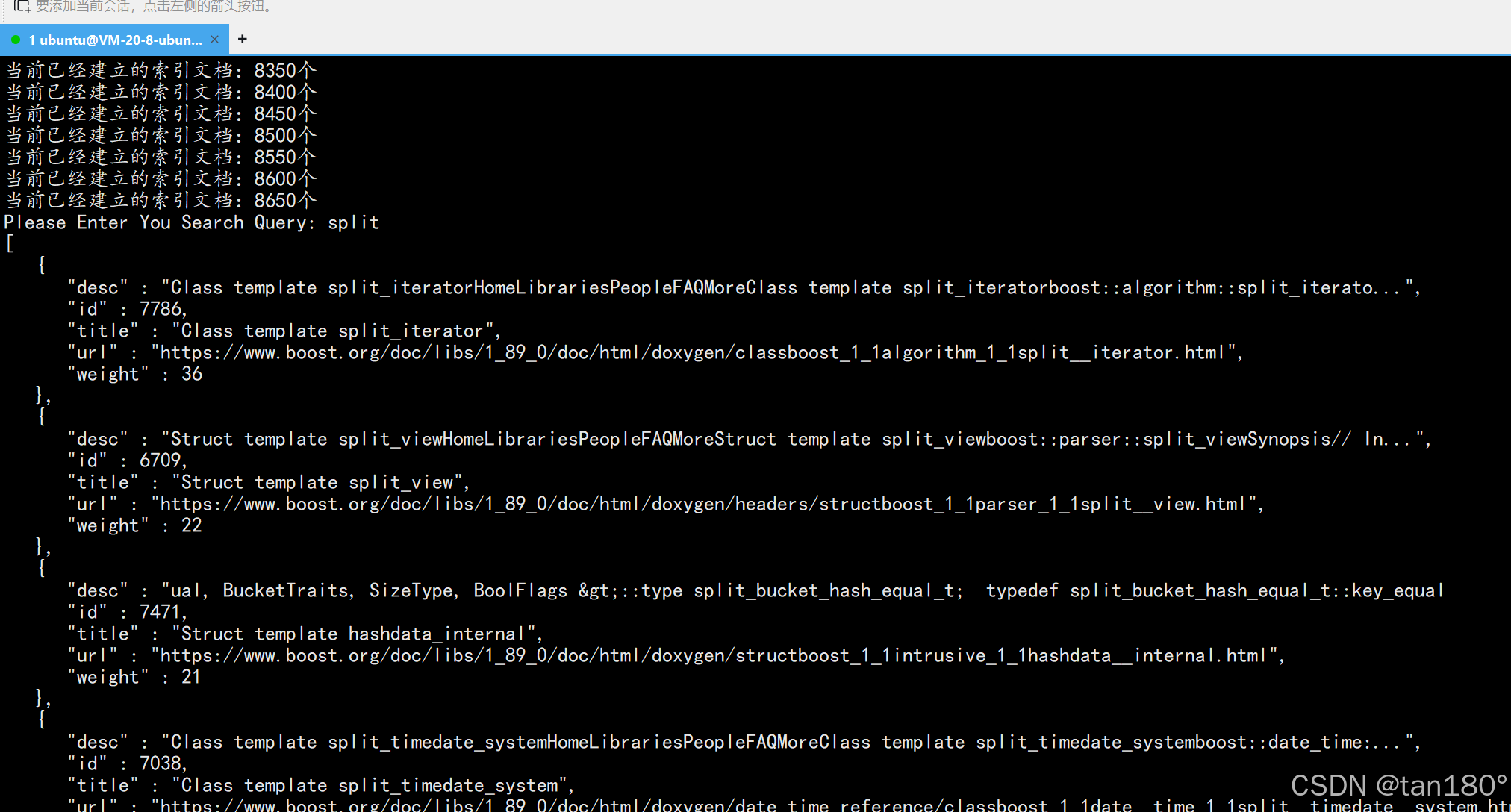
我们尝试复制一个网址,看下权重到底是否一样,就选第一个吧
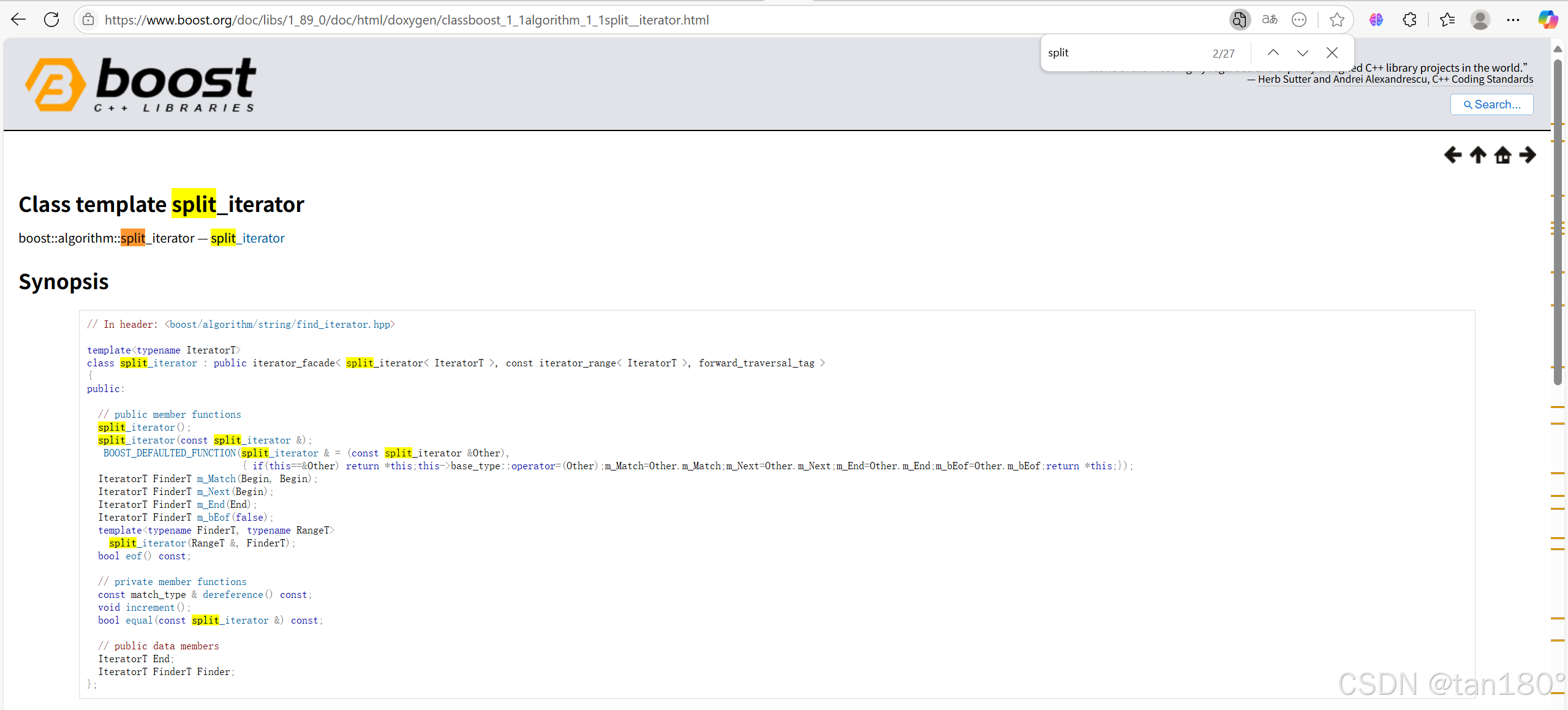
我们发现确实 split 的数量 标题有1个,内容有26个,加起来刚好36,没错,真棒!!!
当然我自己私底下又自己测试了几个,有些搜索出来的可能会多或者少那么一两个,我猜测这可能是分词的问题
总结
马上就要迎来我们的最后一篇喽,嘻嘻,谢谢大家!
