Linux Shells
目录

Task1 Introduction to Linux ShellsLinux Shell 简介
图片版

文字版
As regular users of operating systems, we all extensively use the Graphical User Interface (GUI) to carry out most operations. It takes a few clicks on different options, and your task is done. However, you can perform almost every task by writing commands in the CLI of your operating system rather than using the GUI. The shells give you some great features for the commands you write in your CLI. This way of interacting with the OS is more efficient and resource-friendly.
作为操作系统的常规用户,我们都广泛使用图形用户界面 (GUI) 来执行大多数操作。它只需要点击几下不同的选项,你的任务就完成了。然而,你几乎可以通过在操作系统的 CLI 中编写命令来执行任何任务,而不是使用 GUI。shell 为你在 CLI 中编写的命令提供了一些很棒的功能。这种与操作系统交互的方式更加高效,资源更加友好。
Suppose you are in a restaurant and have two options for your food. The first option is to order food from the menu, and the waiter will serve it. The second option is to cook your desired dish yourself in the kitchen. In terms of a Linux system, the kitchen here is the OS, and using the GUI of the OS is just like ordering the food from the menu, and the waiter will serve it for you. However, using the CLI means you would have to go to the kitchen (OS) and cook your desired food. In this example, Shell would help you cook your desired dish by giving you some recipe suggestions. Using CLI to perform operations in a Linux system gives you more power and control while carrying out the tasks.
假设你在一家餐厅里,有两种选择。第一种选择是从菜单上点菜,服务员会为你服务。第二种选择是自己在厨房里烹饪你想要的菜肴。对于 Linux 系统来说,这里的厨房就是操作系统,使用操作系统的 GUI 就像从菜单上点菜一样,服务员会为你服务。然而,使用 CLI 意味着你必须去厨房 (OS) 烹饪你想要的菜肴。在这个例子中,Shell 会通过给你一些食谱建议来帮助你烹饪你想要的菜肴。在 Linux 系统中使用 CLI 执行操作可以让你在执行任务时拥有更多的权力和控制权。
You may have seen hacking scenes in movies that show cool terminals with many commands getting executed. This is because most Linux users prefer to perform operations by writing commands on the CLI using shells instead of using the GUI. This room will teach us how to interact with a Linux shell. We will also explore different shells available in Linux and write some shell scripts in the end.
你可能在电影中看到过黑客攻击场景,展示了许多命令被执行的酷炫终端。这是因为大多数 Linux 用户更喜欢使用 shell 在 CLI 上编写命令来执行操作,而不是使用 GUI。这个房间将教导我们如何与 Linux shell 交互。我们还将探索 Linux 中可用的不同 shell, 并在最后编写一些 shell 脚本。
Learning Objectives学习目标
- Learn interaction with Linux shell学习与 Linux shell 的交互
- Use basic shell commands使用基本的 shell 命令
- Explore the types of Linux shells available
探索可用的 Linux shell 类型 - Write some shell scripts编写一些 shell 脚本
Room Prerequisites房间前提条件
- LinuxFundamentals moduleLinux 基础模块
问题
答案
Task2 How To Interact With a Shell? 如何与 shell 交互?
图片版
文字版
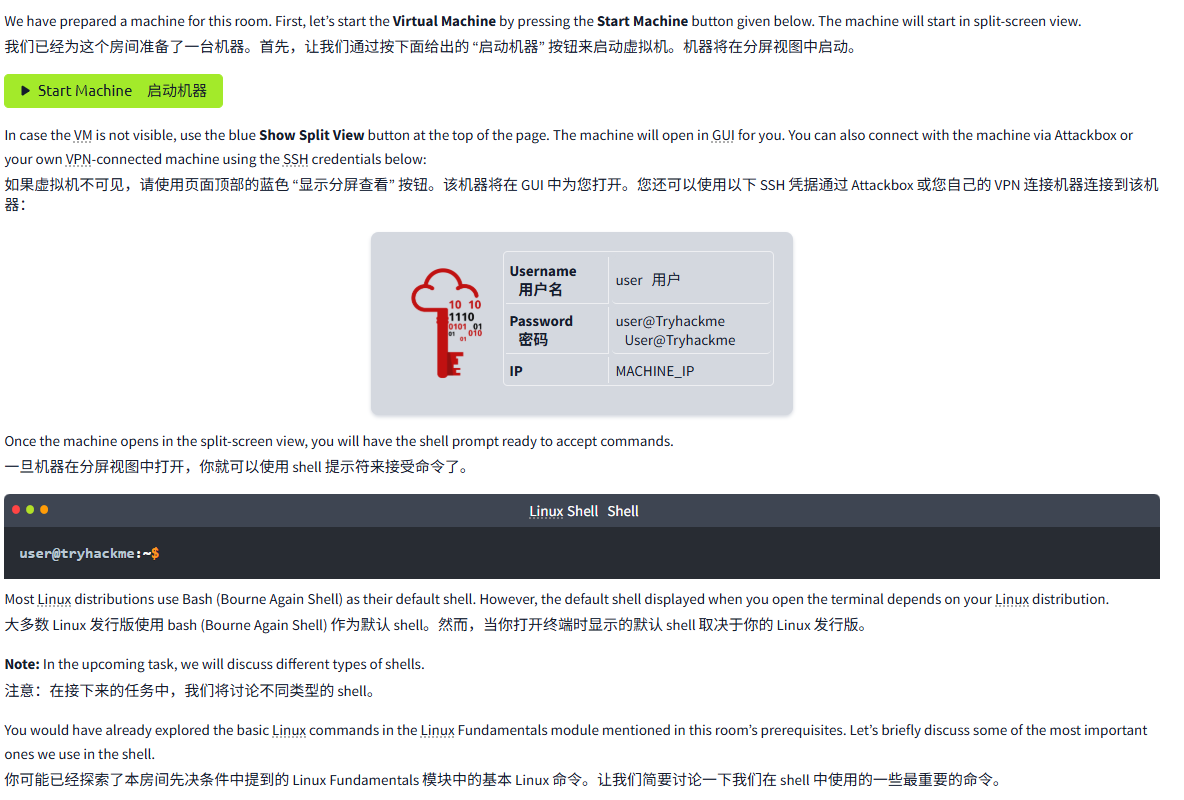
We have prepared a machine for this room. First, let’s start the Virtual Machine by pressing the Start Machine button given below. The machine will start in split-screen view.
我们已经为这个房间准备了一台机器。首先,让我们通过按下面给出的 “启动机器” 按钮来启动虚拟机。机器将在分屏视图中启动。
Start Machine启动机器
In case the VM is not visible, use the blue Show Split View button at the top of the page. The machine will open in GUI for you. You can also connect with the machine via Attackbox or your own VPN-connected machine using the SSH credentials below:
如果虚拟机不可见,请使用页面顶部的蓝色 “显示分屏查看” 按钮。该机器将在 GUI 中为您打开。您还可以使用以下 SSH 凭据通过 Attackbox 或您自己的 VPN 连接机器连接到该机器:

| Username 用户名 | user用户 |
| Password 密码 | user@TryhackmeUser@Tryhackme |
| IP | MACHINE_IP |
Once the machine opens in the split-screen view, you will have the shell prompt ready to accept commands.
一旦机器在分屏视图中打开,你就可以使用 shell 提示符来接受命令了。
LinuxShellShell
user@tryhackme:~$Most Linux distributions use Bash (Bourne Again Shell) as their default shell. However, the default shell displayed when you open the terminal depends on your Linux distribution.
大多数 Linux 发行版使用 bash (Bourne Again Shell) 作为默认 shell。然而,当你打开终端时显示的默认 shell 取决于你的 Linux 发行版。
Note: In the upcoming task, we will discuss different types of shells.
注意:在接下来的任务中,我们将讨论不同类型的 shell。
You would have already explored the basic Linux commands in the Linux Fundamentals module mentioned in this room’s prerequisites. Let’s briefly discuss some of the most important ones we use in the shell.
你可能已经探索了本房间先决条件中提到的 Linux Fundamentals 模块中的基本 Linux 命令。让我们简要讨论一下我们在 shell 中使用的一些最重要的命令。
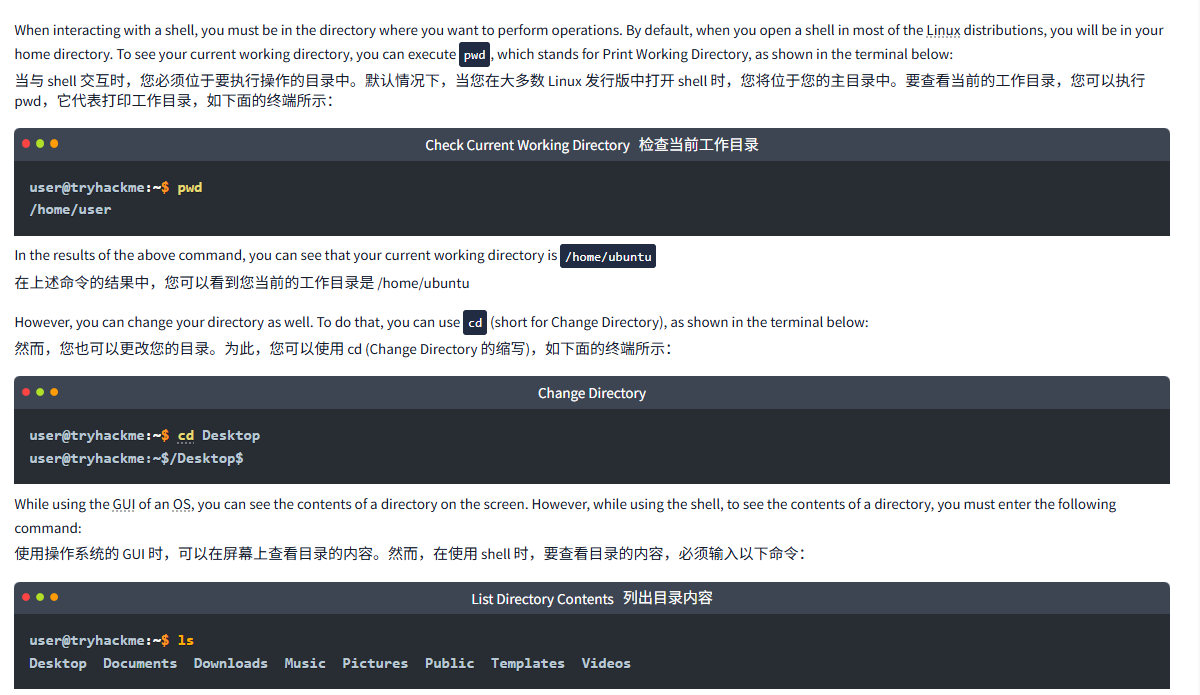
When interacting with a shell, you must be in the directory where you want to perform operations. By default, when you open a shell in most of the Linux distributions, you will be in your home directory. To see your current working directory, you can execute pwd, which stands for Print Working Directory, as shown in the terminal below:
当与 shell 交互时,您必须位于要执行操作的目录中。默认情况下,当您在大多数 Linux 发行版中打开 shell 时,您将位于您的主目录中。要查看当前的工作目录,您可以执行 pwd,它代表打印工作目录,如下面的终端所示:
Check Current Working Directory检查当前工作目录
user@tryhackme:~$ pwd
/home/userIn the results of the above command, you can see that your current working directory is /home/ubuntu
在上述命令的结果中,您可以看到您当前的工作目录是 /home/ubuntu
However, you can change your directory as well. To do that, you can use cd (short for Change Directory), as shown in the terminal below:
然而,您也可以更改您的目录。为此,您可以使用 cd (Change Directory 的缩写),如下面的终端所示:
Change Directory
user@tryhackme:~$ cd Desktop
user@tryhackme:~$/Desktop$While using the GUI of an OS, you can see the contents of a directory on the screen. However, while using the shell, to see the contents of a directory, you must enter the following command:
使用操作系统的 GUI 时,可以在屏幕上查看目录的内容。然而,在使用 shell 时,要查看目录的内容,必须输入以下命令:
List Directory Contents列出目录内容
user@tryhackme:~$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads Music Pictures Public Templates VideosIf you want to read the contents of a file, you can type the following command in your shell:
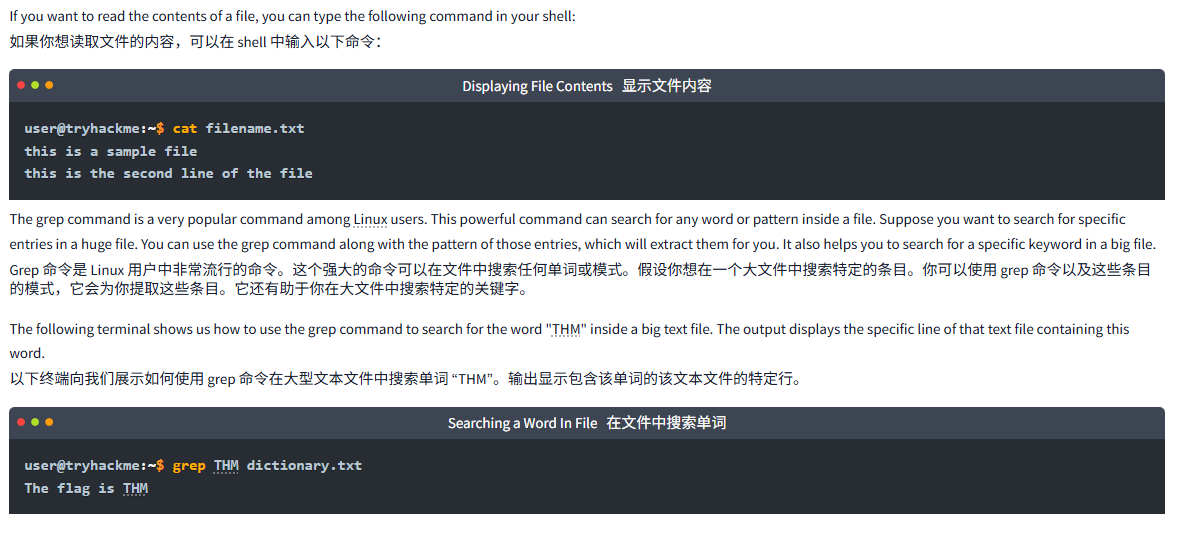
如果你想读取文件的内容,可以在 shell 中输入以下命令:
Displaying File Contents显示文件内容
user@tryhackme:~$ cat filename.txt
this is a sample file
this is the second line of the fileThe grep command is a very popular command among Linux users. This powerful command can search for any word or pattern inside a file. Suppose you want to search for specific entries in a huge file. You can use the grep command along with the pattern of those entries, which will extract them for you. It also helps you to search for a specific keyword in a big file.
Grep 命令是 Linux 用户中非常流行的命令。这个强大的命令可以在文件中搜索任何单词或模式。假设你想在一个大文件中搜索特定的条目。你可以使用 grep 命令以及这些条目的模式,它会为你提取这些条目。它还有助于你在大文件中搜索特定的关键字。
The following terminal shows us how to use the grep command to search for the word "THM" inside a big text file. The output displays the specific line of that text file containing this word.
以下终端向我们展示如何使用 grep 命令在大型文本文件中搜索单词 “THM”。输出显示包含该单词的该文本文件的特定行。
Searching a Word In File在文件中搜索单词
user@tryhackme:~$ grep THM dictionary.txt
The flag is THM问题
答案
Task3 Types of Linux Shells Linux Shell 的类型
图片版

文字版
Like the Command Prompt and PowerShell in Windows OS, Linux has different types of shells available, each with its own features and characteristics.
与 Windows 操作系统中的命令提示符和 PowerShell 类似,Linux 提供了不同类型的 shell, 每种 shell 都有自己的特性和特性。
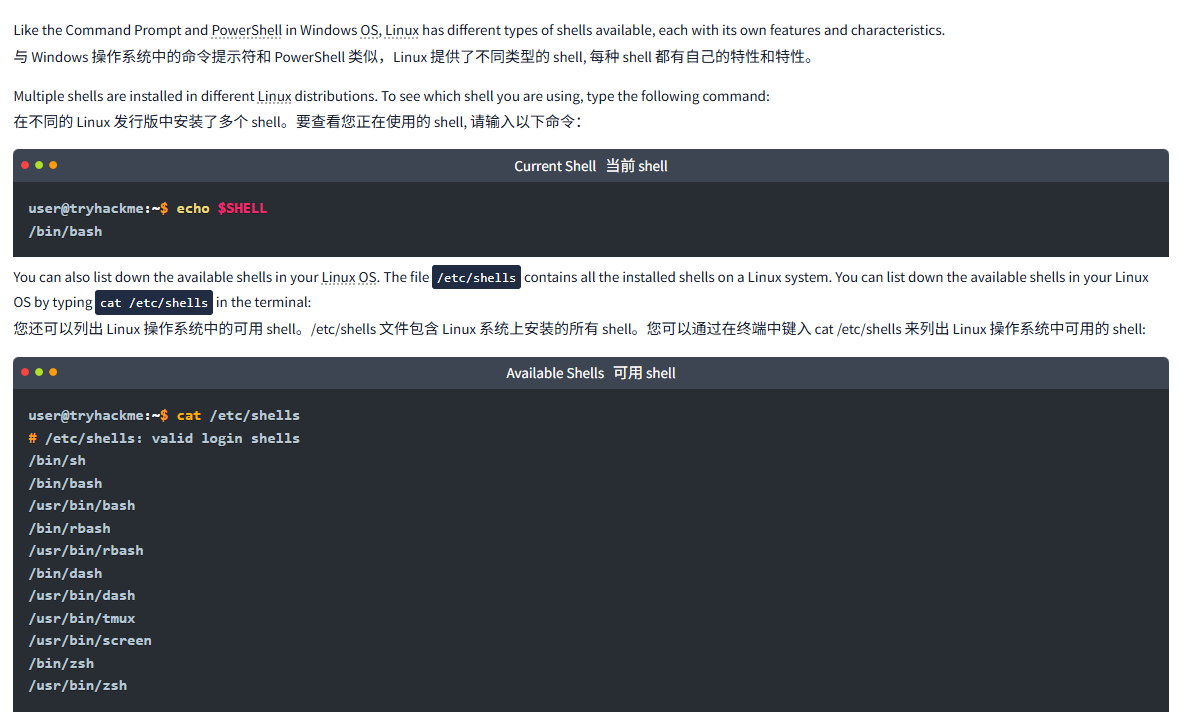
Multiple shells are installed in different Linux distributions. To see which shell you are using, type the following command:
在不同的 Linux 发行版中安装了多个 shell。要查看您正在使用的 shell, 请输入以下命令:
Current Shell当前 shell
user@tryhackme:~$ echo $SHELL
/bin/bashYou can also list down the available shells in your Linux OS. The file /etc/shells contains all the installed shells on a Linux system. You can list down the available shells in your Linux OS by typing cat /etc/shells in the terminal:
您还可以列出 Linux 操作系统中的可用 shell。/etc/shells 文件包含 Linux 系统上安装的所有 shell。您可以通过在终端中键入 cat /etc/shells 来列出 Linux 操作系统中可用的 shell:
Available Shells可用 shell
user@tryhackme:~$ cat /etc/shells
# /etc/shells: valid login shells
/bin/sh
/bin/bash
/usr/bin/bash
/bin/rbash
/usr/bin/rbash
/bin/dash
/usr/bin/dash
/usr/bin/tmux
/usr/bin/screen
/bin/zsh
/usr/bin/zshTo switch between these shells, you can type the shell name that is present on your OS, and it will open for you, as can be seen below:
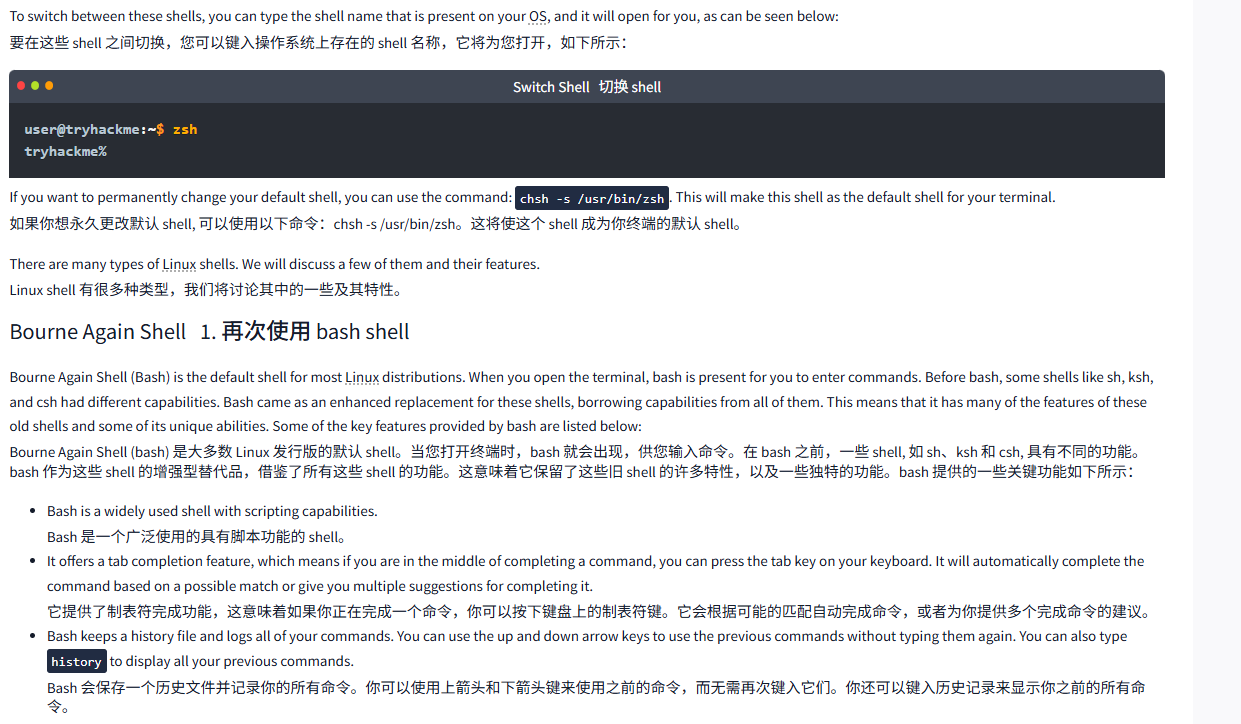
要在这些 shell 之间切换,您可以键入操作系统上存在的 shell 名称,它将为您打开,如下所示:
Switch Shell切换 shell
user@tryhackme:~$ zsh
tryhackme%If you want to permanently change your default shell, you can use the command: chsh -s /usr/bin/zsh. This will make this shell as the default shell for your terminal.
如果你想永久更改默认 shell, 可以使用以下命令:chsh -s /usr/bin/zsh。这将使这个 shell 成为你终端的默认 shell。
There are many types of Linux shells. We will discuss a few of them and their features.
Linux shell 有很多种类型,我们将讨论其中的一些及其特性。
Bourne Again Shell1. 再次使用 bash shell
Bourne Again Shell (Bash) is the default shell for most Linux distributions. When you open the terminal, bash is present for you to enter commands. Before bash, some shells like sh, ksh, and csh had different capabilities. Bash came as an enhanced replacement for these shells, borrowing capabilities from all of them. This means that it has many of the features of these old shells and some of its unique abilities. Some of the key features provided by bash are listed below:
Bourne Again Shell (bash) 是大多数 Linux 发行版的默认 shell。当您打开终端时,bash 就会出现,供您输入命令。在 bash 之前,一些 shell, 如 sh、ksh 和 csh, 具有不同的功能。bash 作为这些 shell 的增强型替代品,借鉴了所有这些 shell 的功能。这意味着它保留了这些旧 shell 的许多特性,以及一些独特的功能。bash 提供的一些关键功能如下所示:
- Bash is a widely used shell with scripting capabilities.
Bash 是一个广泛使用的具有脚本功能的 shell。 - It offers a tab completion feature, which means if you are in the middle of completing a command, you can press the tab key on your keyboard. It will automatically complete the command based on a possible match or give you multiple suggestions for completing it.
它提供了制表符完成功能,这意味着如果你正在完成一个命令,你可以按下键盘上的制表符键。它会根据可能的匹配自动完成命令,或者为你提供多个完成命令的建议。 - Bash keeps a history file and logs all of your commands. You can use the up and down arrow keys to use the previous commands without typing them again. You can also type
historyto display all your previous commands.
Bash 会保存一个历史文件并记录你的所有命令。你可以使用上箭头和下箭头键来使用之前的命令,而无需再次键入它们。你还可以键入历史记录来显示你之前的所有命令。
Friendly Interactive Shell1. fish 友好的交互式 shell
Friendly Interactive Shell (Fish) is also not default in most Linux distributions. As its name suggests, it focuses more on user-friendliness than other shells. Some of the key features provided by fish are listed below:
在大多数 Linux 发行版中,Friendly Interactive Shell (Fish) 也不是默认设置。正如其名字所示,它比其他 shell 更注重用户友好性。Fish 提供的一些关键功能如下:
- It offers a very simple syntax, which is feasible for beginner users.
它提供了一个非常简单的语法,对于初学者来说是可行的。 - Unlike bash, it has auto spell correction for the commands you write.
与 bash 不同,它为你编写的命令提供了自动拼写纠正功能。 - You can customize the command prompt with some cool themes using fish.
你可以使用 fish 来自定义命令提示符,并添加一些酷炫的主题。 - The syntax highlighting feature of fish colors different parts of a command based on their roles, which can improve the readability of commands. It also helps us to spot errors with their unique colors.
鱼类的语法突显功能根据其角色为命令的不同部分着色,这可以提高命令的可读性。它还有助于我们通过其独特的颜色发现错误。 - Fish also provides scripting, tab completion, and command history functionality like the shells mentioned in this task.
Fish 还提供脚本编写、选项卡完成和命令历史记录功能,如本任务中提到的 shell。
Z Shell
Z Shell (Zsh) is not installed by default in most Linux distributions. It is considered a modern shell that combines the functionalities of some previous shells. Some of the key features provided by zsh are listed below:
Z Shell (Zsh) 在大多数 Linux 发行版中默认不安装。它被认为是一个现代 shell, 结合了一些先前 shell 的功能。以下是 zsh 提供的一些关键功能:
- Zsh provides advanced tab completion and is also capable of writing scripts.
Zsh 提供高级选项卡完成功能,并且还能够编写脚本。 - Just like fish, it also provides auto spell correction for the commands.
就像 fish 一样,它还为命令提供自动拼写纠正功能。 - It offers extensive customization that may make it slower than other shells.
它提供了广泛的定制,这可能会使它比其他 shell 更慢。 - It also provides tab completion, command history functionality, and several other features.
它还提供选项卡完成、命令历史记录功能和其他一些功能。
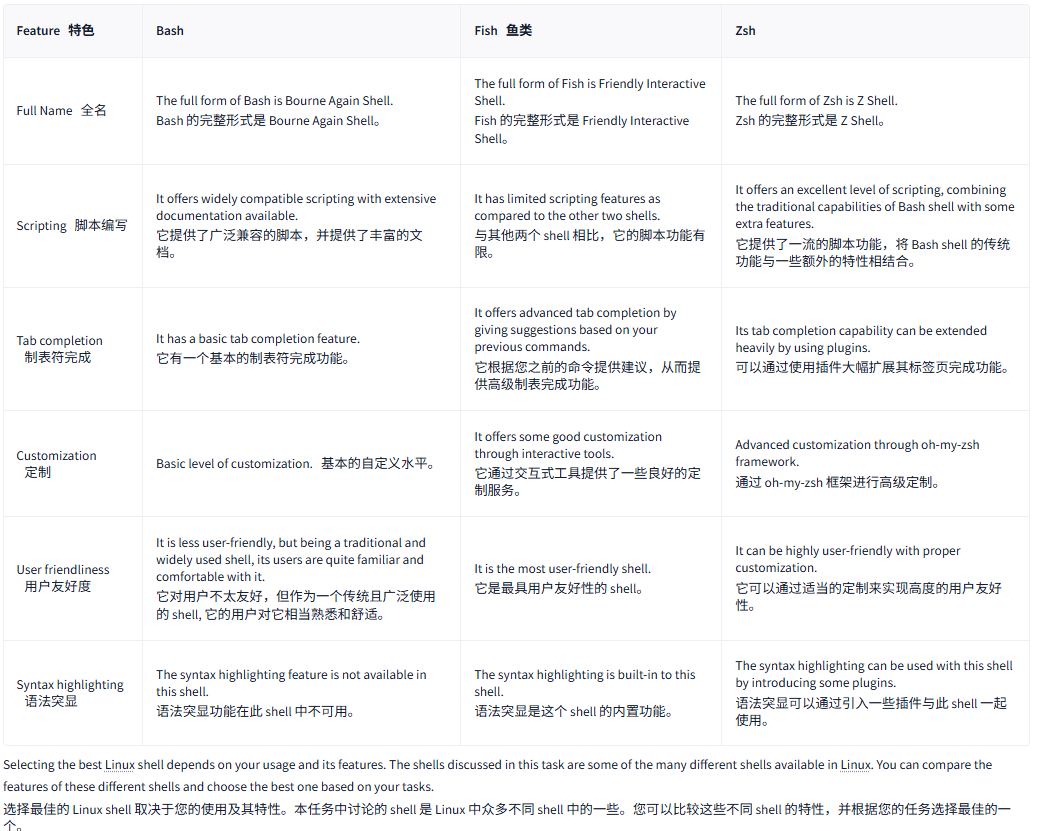
| Feature特色 | Bash | Fish鱼类 | Zsh |
| Full Name全名 | The full form of Bash is Bourne Again Shell. | The full form of Fish is Friendly Interactive Shell. | The full form of Zsh is Z Shell. |
| Scripting脚本编写 | It offers widely compatible scripting with extensive documentation available. | It has limited scripting features as compared to the other two shells. | It offers an excellent level of scripting, combining the traditional capabilities of Bash shell with some extra features. |
| Tab completion制表符完成 | It has a basic tab completion feature. | It offers advanced tab completion by giving suggestions based on your previous commands. | Its tab completion capability can be extended heavily by using plugins. |
| Customization定制 | Basic level of customization.基本的自定义水平。 | It offers some good customization through interactive tools. | Advanced customization through oh-my-zsh framework. |
| User friendliness用户友好度 | It is less user-friendly, but being a traditional and widely used shell, its users are quite familiar and comfortable with it. | It is the most user-friendly shell. | It can be highly user-friendly with proper customization. |
| Syntax highlighting语法突显 | The syntax highlighting feature is not available in this shell. | The syntax highlighting is built-in to this shell. | The syntax highlighting can be used with this shell by introducing some plugins. |
Selecting the best Linux shell depends on your usage and its features. The shells discussed in this task are some of the many different shells available in Linux. You can compare the features of these different shells and choose the best one based on your tasks.
选择最佳的 Linux shell 取决于您的使用及其特性。本任务中讨论的 shell 是 Linux 中众多不同 shell 中的一些。您可以比较这些不同 shell 的特性,并根据您的任务选择最佳的一个。
问题
答案
Task4 Shell Scripting and Components Shell 脚本和组件
图片版

文字版
A shell script is nothing but a set of commands. Suppose a repetitive task requires you to enter multiple commands using a shell. Instead of entering them one after one on every repetition of that task, which may take more of your time, you can combine them into a script. To execute all those commands, you will only execute the script, and all the commands will be executed. All the shells mentioned in the previous tasks have scripting capabilities. Scripting helps us to automate tasks. Before learning how to write a script, we need to know that even though Linux shells have scripting capabilities, this does not mean that you can only make a script using a shell. Scripting can be done in various programming languages as well. However, the scope of this room is to cover scripting using a shell.
Shell 脚本不过是一组命令。假设一个重复的任务需要你使用 shell 输入多个命令。与其在任务的每次重复中逐一输入这些命令 (这可能会占用更多时间), 不如将它们组合成一个脚本。要执行所有这些命令,你只需要执行脚本,所有命令都会被执行。前面任务中提到的所有 shell 都具有脚本功能。脚本有助于我们自动化任务。在学习如何编写脚本之前,我们需要知道,即使 Linux shell 具有脚本功能,这并不意味着你只能使用 shell 编写脚本。脚本编写也可以用各种编程语言进行。然而,本房间的范围是介绍如何使用 shell 编写脚本。
The first step is to open the terminal and select a shell. Let’s go with the bash shell, the default, and widely used shell in most distributions.
第一步是打开终端并选择一个 shell。让我们先来看看 bash shell, 它是大多数发行版中默认且广泛使用的 shell。
Unlike the other commands we type in the shell, we first need to create a file using any text editor for the script. The file must be named with an extension .sh, the default extension for bash scripts. The following terminal shows the script file creation:
与我们在 shell 中输入的其他命令不同,我们首先需要使用脚本的任何文本编辑器创建一个文件。文件必须以.sh 扩展名命名,这是 bash 脚本的默认扩展名。以下终端显示了脚本文件的创建过程:
Create Script File创建脚本文件
user@tryhackme:~$ nano first_script.shEvery script should start from shebang. Shebang is a combination of some characters that are added at the beginning of a script, starting with #! followed by the name of the interpreter to use while executing the script. As we are writing our script in bash, let’s define it as the interpreter in the shebang.
每个脚本都应该从 shebang 开始。Shebang 是在脚本开头添加的一些字符的组合,以 #! 开头,后面跟着执行脚本时要使用的解释器名称。由于我们是用 bash 编写脚本,让我们将其定义为 shebang 中的解释器。
first_script.shFirst_script.sh
#!/bin/bashWe are all set to write our first script now. There are some fundamental building blocks of a script that together make an efficient script. Let’s learn and utilize these script constructs to write one script ourselves.
我们现在都已经准备好写我们的第一个脚本了。脚本有一些基本的构成要素,它们共同构成了一个高效的脚本。让我们学习并利用这些脚本结构来自己写一个脚本。
Variables变量
A variable stores a value inside it. Suppose you need to use some complex values, like a URL, a file path, etc., several times in your script. Instead of memorizing and writing them repeatedly, you can store them in a variable and use the variable name wherever you need it.
变量在其中存储一个值。假设你需要在脚本中多次使用一些复杂的值,如 URL、文件路径等。你可以将它们存储在一个变量中,并在需要时使用变量名称,而不是反复记忆和写入它们。
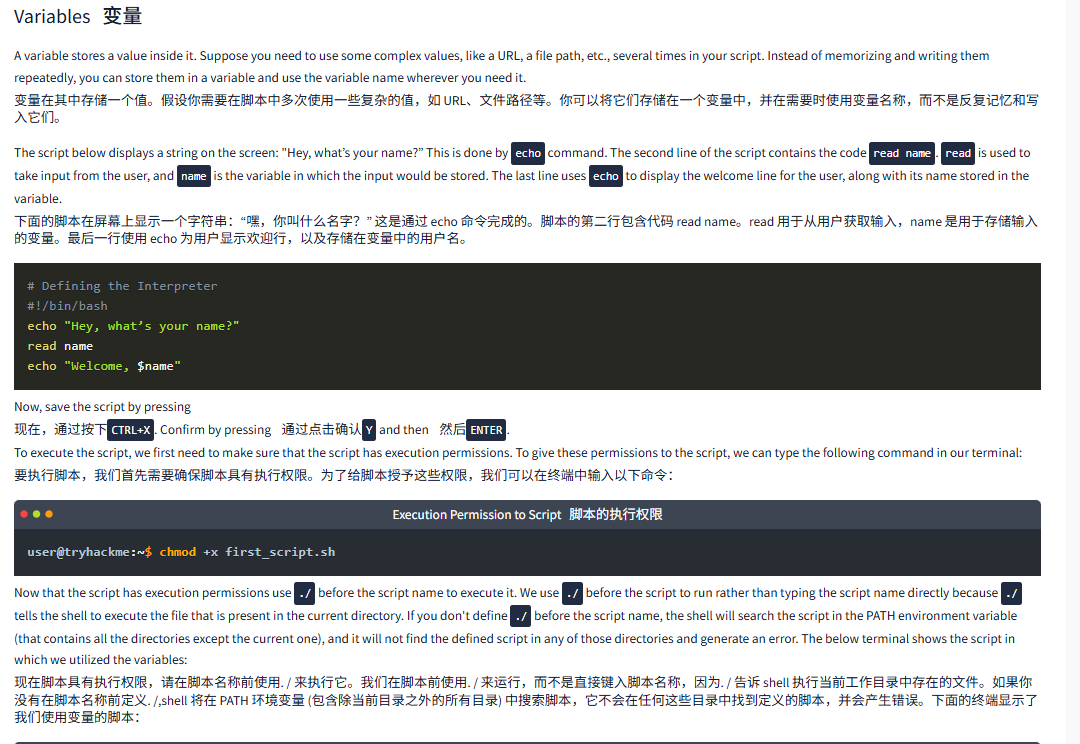
The script below displays a string on the screen: "Hey, what’s your name?” This is done by echo command. The second line of the script contains the code read name. read is used to take input from the user, and name is the variable in which the input would be stored. The last line uses echo to display the welcome line for the user, along with its name stored in the variable.
下面的脚本在屏幕上显示一个字符串:“嘿,你叫什么名字?” 这是通过 echo 命令完成的。脚本的第二行包含代码 read name。read 用于从用户获取输入,name 是用于存储输入的变量。最后一行使用 echo 为用户显示欢迎行,以及存储在变量中的用户名。
# Defining the Interpreter
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hey, what’s your name?"
read name
echo "Welcome, $name"Now, save the script by pressing
现在,通过按下CTRL+X. Confirm by pressing 通过点击确认Y and then 然后ENTER.
To execute the script, we first need to make sure that the script has execution permissions. To give these permissions to the script, we can type the following command in our terminal:
要执行脚本,我们首先需要确保脚本具有执行权限。为了给脚本授予这些权限,我们可以在终端中输入以下命令:
Execution Permission to Script脚本的执行权限
user@tryhackme:~$ chmod +x first_script.shNow that the script has execution permissions use ./ before the script name to execute it. We use ./ before the script to run rather than typing the script name directly because ./ tells the shell to execute the file that is present in the current directory. If you don't define ./ before the script name, the shell will search the script in the PATH environment variable (that contains all the directories except the current one), and it will not find the defined script in any of those directories and generate an error. The below terminal shows the script in which we utilized the variables:
现在脚本具有执行权限,请在脚本名称前使用. / 来执行它。我们在脚本前使用. / 来运行,而不是直接键入脚本名称,因为. / 告诉 shell 执行当前工作目录中存在的文件。如果你没有在脚本名称前定义. /,shell 将在 PATH 环境变量 (包含除当前目录之外的所有目录) 中搜索脚本,它不会在任何这些目录中找到定义的脚本,并会产生错误。下面的终端显示了我们使用变量的脚本:
Script Execution脚本执行
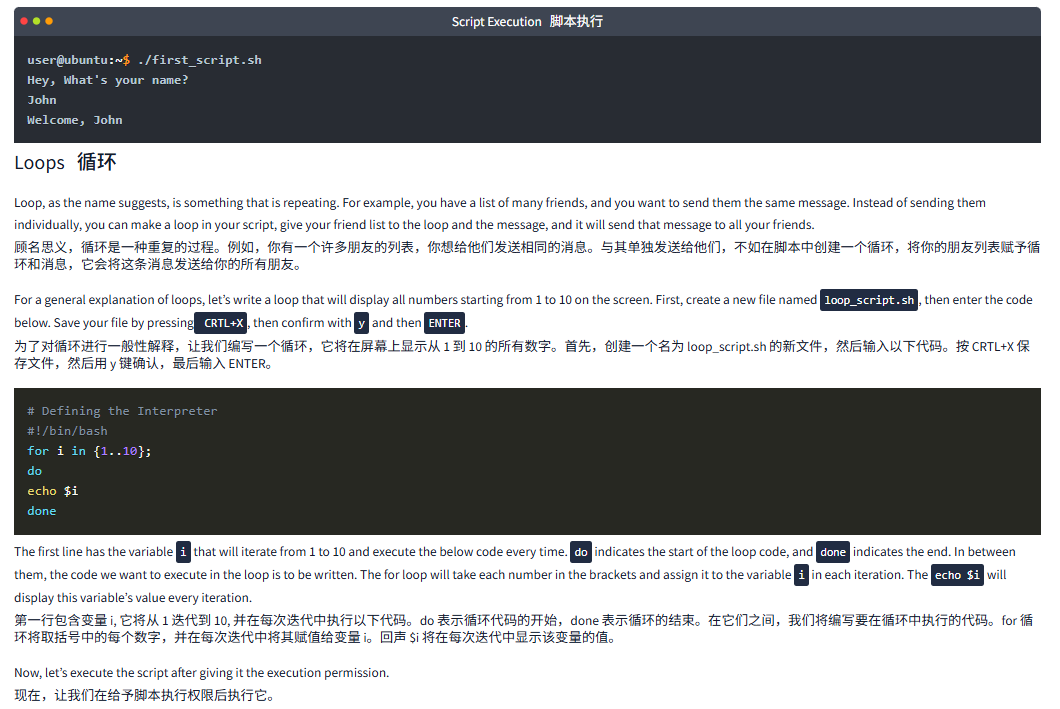
user@ubuntu:~$ ./first_script.sh
Hey, What's your name?
John
Welcome, JohnLoops循环
Loop, as the name suggests, is something that is repeating. For example, you have a list of many friends, and you want to send them the same message. Instead of sending them individually, you can make a loop in your script, give your friend list to the loop and the message, and it will send that message to all your friends.
顾名思义,循环是一种重复的过程。例如,你有一个许多朋友的列表,你想给他们发送相同的消息。与其单独发送给他们,不如在脚本中创建一个循环,将你的朋友列表赋予循环和消息,它会将这条消息发送给你的所有朋友。
For a general explanation of loops, let’s write a loop that will display all numbers starting from 1 to 10 on the screen. First, create a new file named loop_script.sh, then enter the code below. Save your file by pressing CRTL+X, then confirm with y and then ENTER.
为了对循环进行一般性解释,让我们编写一个循环,它将在屏幕上显示从 1 到 10 的所有数字。首先,创建一个名为 loop_script.sh 的新文件,然后输入以下代码。按 CRTL+X 保存文件,然后用 y 键确认,最后输入 ENTER。
# Defining the Interpreter
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..10};
do
echo $i
doneThe first line has the variable i that will iterate from 1 to 10 and execute the below code every time. do indicates the start of the loop code, and done indicates the end. In between them, the code we want to execute in the loop is to be written. The for loop will take each number in the brackets and assign it to the variable i in each iteration. The echo $i will display this variable’s value every iteration.
第一行包含变量 i, 它将从 1 迭代到 10, 并在每次迭代中执行以下代码。do 表示循环代码的开始,done 表示循环的结束。在它们之间,我们将编写要在循环中执行的代码。for 循环将取括号中的每个数字,并在每次迭代中将其赋值给变量 i。回声 $i 将在每次迭代中显示该变量的值。
Now, let’s execute the script after giving it the execution permission.
现在,让我们在给予脚本执行权限后执行它。
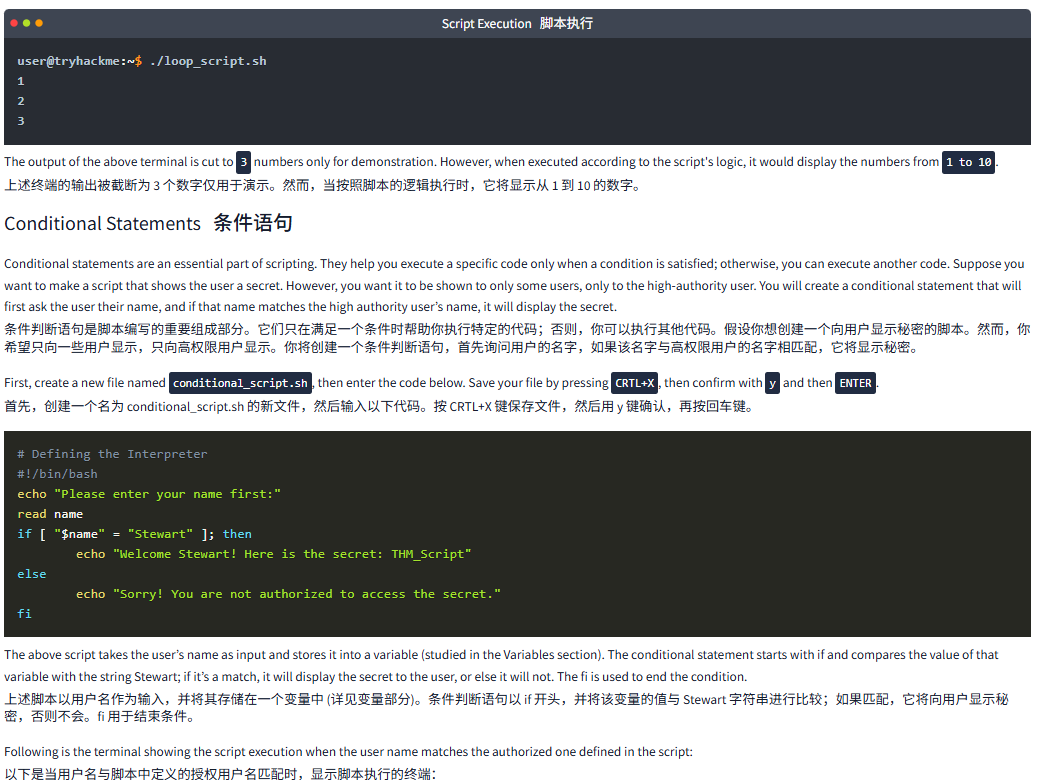
Script Execution脚本执行
user@tryhackme:~$ ./loop_script.sh
1
2
3The output of the above terminal is cut to 3 numbers only for demonstration. However, when executed according to the script's logic, it would display the numbers from 1 to 10.
上述终端的输出被截断为 3 个数字只是为了演示。然而,当按照脚本的逻辑执行时,它将显示从 1 到 10 的数字。
Conditional Statements条件声明
Conditional statements are an essential part of scripting. They help you execute a specific code only when a condition is satisfied; otherwise, you can execute another code. Suppose you want to make a script that shows the user a secret. However, you want it to be shown to only some users, only to the high-authority user. You will create a conditional statement that will first ask the user their name, and if that name matches the high authority user’s name, it will display the secret.
条件判断语句是脚本编写的重要组成部分。它们只在满足一个条件时帮助你执行特定的代码;否则,你可以执行其他代码。假设你想创建一个向用户显示秘密的脚本。然而,你希望只向一些用户显示,只向高权限用户显示。你将创建一个条件判断语句,首先询问用户的名字,如果该名字与高权限用户的名字相匹配,它将显示秘密。
First, create a new file named conditional_script.sh, then enter the code below. Save your file by pressing CRTL+X, then confirm with y and then ENTER.
首先,创建一个名为 conditional_script.sh 的新文件,然后输入以下代码。按 CRTL+X 保存文件,然后用 y 和 ENTER 进行确认。
# Defining the Interpreter
#!/bin/bash
echo "Please enter your name first:"
read name
if [ "$name" = "Stewart" ]; thenecho "Welcome Stewart! Here is the secret: THM_Script"
elseecho "Sorry! You are not authorized to access the secret."
fiThe above script takes the user’s name as input and stores it into a variable (studied in the Variables section). The conditional statement starts with if and compares the value of that variable with the string Stewart; if it’s a match, it will display the secret to the user, or else it will not. The fi is used to end the condition.
上述脚本以用户名作为输入,并将其存储在一个变量中 (详见变量部分)。条件判断语句以 if 开头,并将该变量的值与 Stewart 字符串进行比较;如果匹配,它将向用户显示秘密,否则不会。fi 用于结束条件。
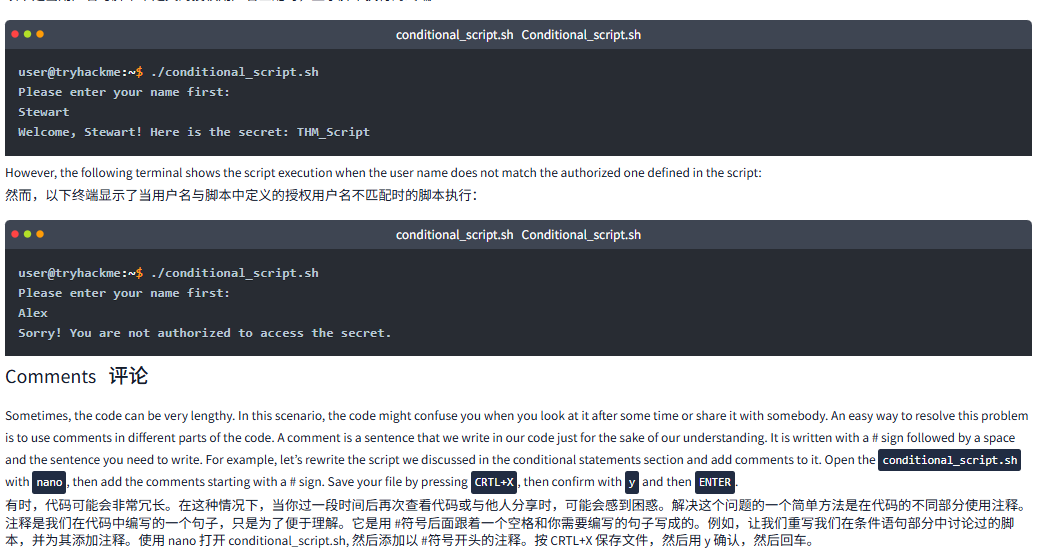
Following is the terminal showing the script execution when the user name matches the authorized one defined in the script:
以下是当用户名与 script 中定义的授权用户名匹配时显示 script 执行的终端:
conditional_script.sh
user@tryhackme:~$ ./conditional_script.sh
Please enter your name first:
Stewart
Welcome, Stewart! Here is the secret: THM_ScriptHowever, the following terminal shows the script execution when the user name does not match the authorized one defined in the script:
然而,以下终端显示了当用户名与脚本中定义的授权用户名不匹配时的脚本执行:
conditional_script.sh
user@tryhackme:~$ ./conditional_script.sh
Please enter your name first:
Alex
Sorry! You are not authorized to access the secret.Comments 注释
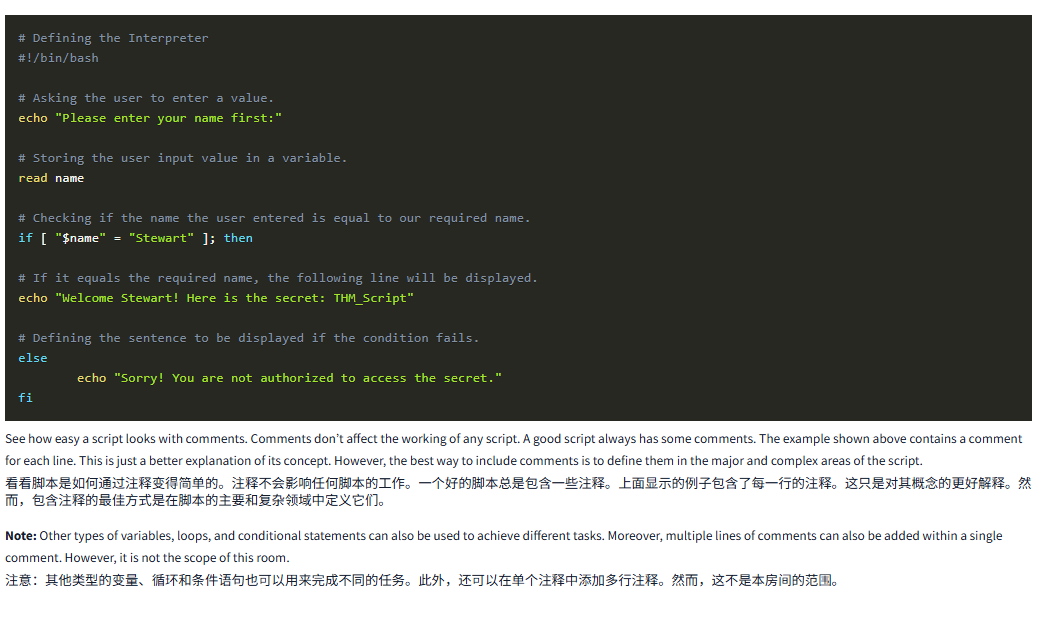
Sometimes, the code can be very lengthy. In this scenario, the code might confuse you when you look at it after some time or share it with somebody. An easy way to resolve this problem is to use comments in different parts of the code. A comment is a sentence that we write in our code just for the sake of our understanding. It is written with a # sign followed by a space and the sentence you need to write. For example, let’s rewrite the script we discussed in the conditional statements section and add comments to it. Open the conditional_script.sh with nano, then add the comments starting with a # sign. Save your file by pressing CRTL+X, then confirm with y and then ENTER.
有时,代码可能会非常冗长。在这种情况下,代码可能会让你在一段时间后查看或与他人分享时感到困惑。解决这个问题的一个简单方法是在代码的不同部分使用注释。注释是我们在代码中写的一个句子,只是为了让我们理解。它是用 #符号后面跟着一个空格和你需要写的句子写成的。例如,让我们重写我们在条件语句部分讨论过的脚本,并为其添加注释。使用 nano 打开 conditional_script.sh, 然后添加以 #符号开头的注释。按 CRTL+X 保存文件,然后用 y 确认,然后回车。
# Defining the Interpreter
#!/bin/bash# Asking the user to enter a value.
echo "Please enter your name first:"# Storing the user input value in a variable.
read name# Checking if the name the user entered is equal to our required name.
if [ "$name" = "Stewart" ]; then# If it equals the required name, the following line will be displayed.
echo "Welcome Stewart! Here is the secret: THM_Script"# Defining the sentence to be displayed if the condition fails.
elseecho "Sorry! You are not authorized to access the secret."
fiSee how easy a script looks with comments. Comments don’t affect the working of any script. A good script always has some comments. The example shown above contains a comment for each line. This is just a better explanation of its concept. However, the best way to include comments is to define them in the major and complex areas of the script.
看看脚本是如何通过注释变得简单的。注释不会影响任何脚本的工作。一个好的脚本总是包含一些注释。上面显示的例子包含了每一行的注释。这只是对其概念的更好解释。然而,包含注释的最佳方式是在脚本的主要和复杂领域中定义它们。
Note: Other types of variables, loops, and conditional statements can also be used to achieve different tasks. Moreover, multiple lines of comments can also be added within a single comment. However, it is not the scope of this room.
注意:其他类型的变量、循环和条件语句也可以用于实现不同的任务。此外,还可以在单个注释中添加多行注释。然而,这不是本房间的范围。
问题
答案
Task5 The Locker Script 储物柜脚本
图片版


文字版
In the previous task, we studied variables, loops, and conditional statements in shell scripting. Let’s use that knowledge to create a shell script that utilizes all these components.
在上一个任务中,我们研究了 shell 脚本中的变量、循环和条件语句。让我们利用这些知识来创建一个利用所有这些组件的 shell 脚本。
Requirement要求
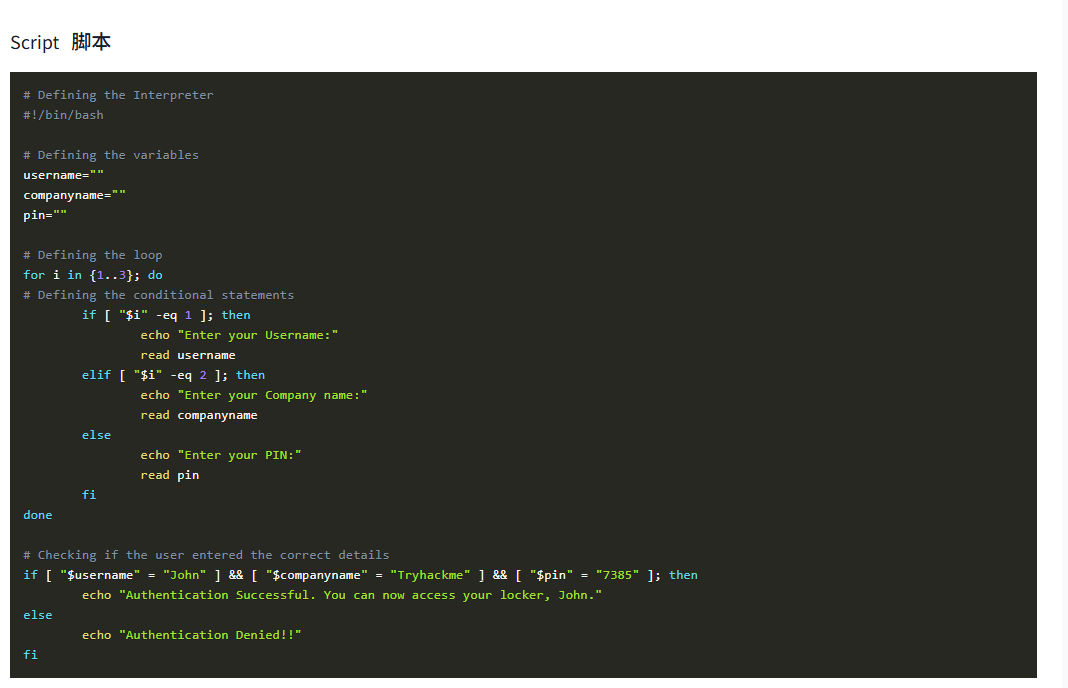
A user has a locker in a bank. To secure the locker, we have to have a script in place that verifies the user before opening it. When executed, the script should ask the user for their name, company name, and PIN. If the user enters the following details, they should be allowed to enter, or else they should be denied access.
用户在银行有一个储物柜。为了确保储物柜的安全,我们必须准备一个脚本,在打开储物柜之前验证用户的身份。执行时,脚本应询问用户的姓名、公司名称和 PIN 码。如果用户输入以下详细信息,应允许他们进入,否则应拒绝他们的访问。
- Username: John用户名:John
- Company name: Tryhackme公司名称:Tryhackme
- PIN: 7385PIN:7385

Script脚本
# Defining the Interpreter
#!/bin/bash # Defining the variables
username=""
companyname=""
pin=""# Defining the loop
for i in {1..3}; do
# Defining the conditional statementsif [ "$i" -eq 1 ]; thenecho "Enter your Username:"read usernameelif [ "$i" -eq 2 ]; thenecho "Enter your Company name:"read companynameelseecho "Enter your PIN:"read pinfi
done# Checking if the user entered the correct details
if [ "$username" = "John" ] && [ "$companyname" = "Tryhackme" ] && [ "$pin" = "7385" ]; thenecho "Authentication Successful. You can now access your locker, John."
elseecho "Authentication Denied!!"
fiScript Execution脚本执行
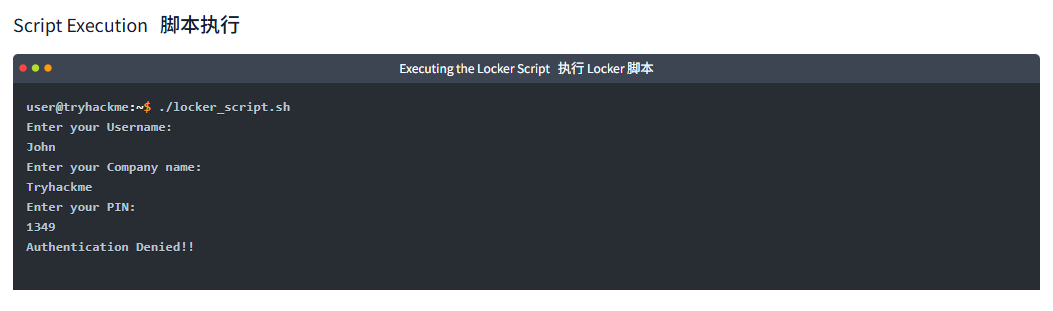
Executing the Locker Script执行 Locker 脚本
user@tryhackme:~$ ./locker_script.sh
Enter your Username:
John
Enter your Company name:
Tryhackme
Enter your PIN:
1349
Authentication Denied!!问题
答案
Task6 Practical Exercise 实践练习
图片版

文字版
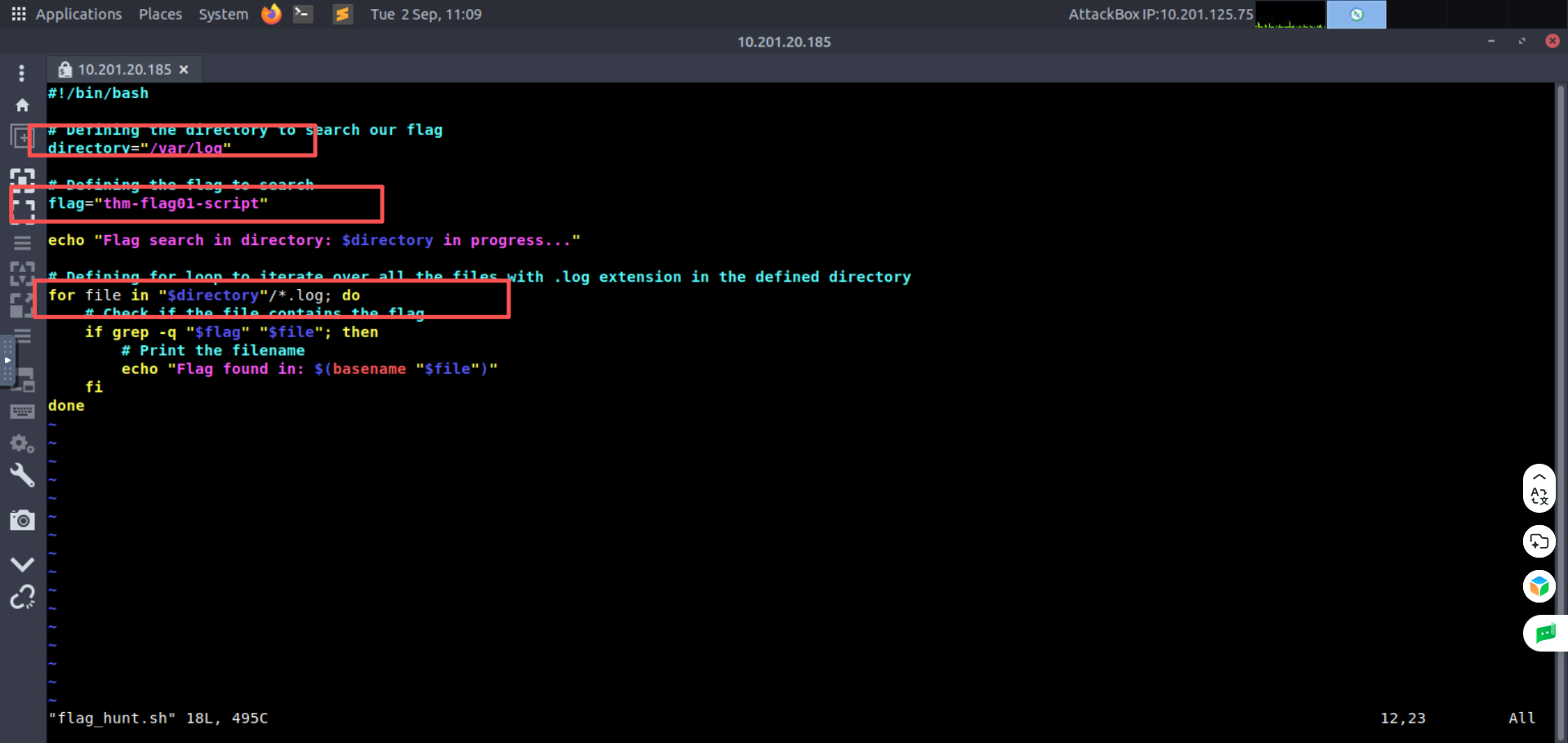
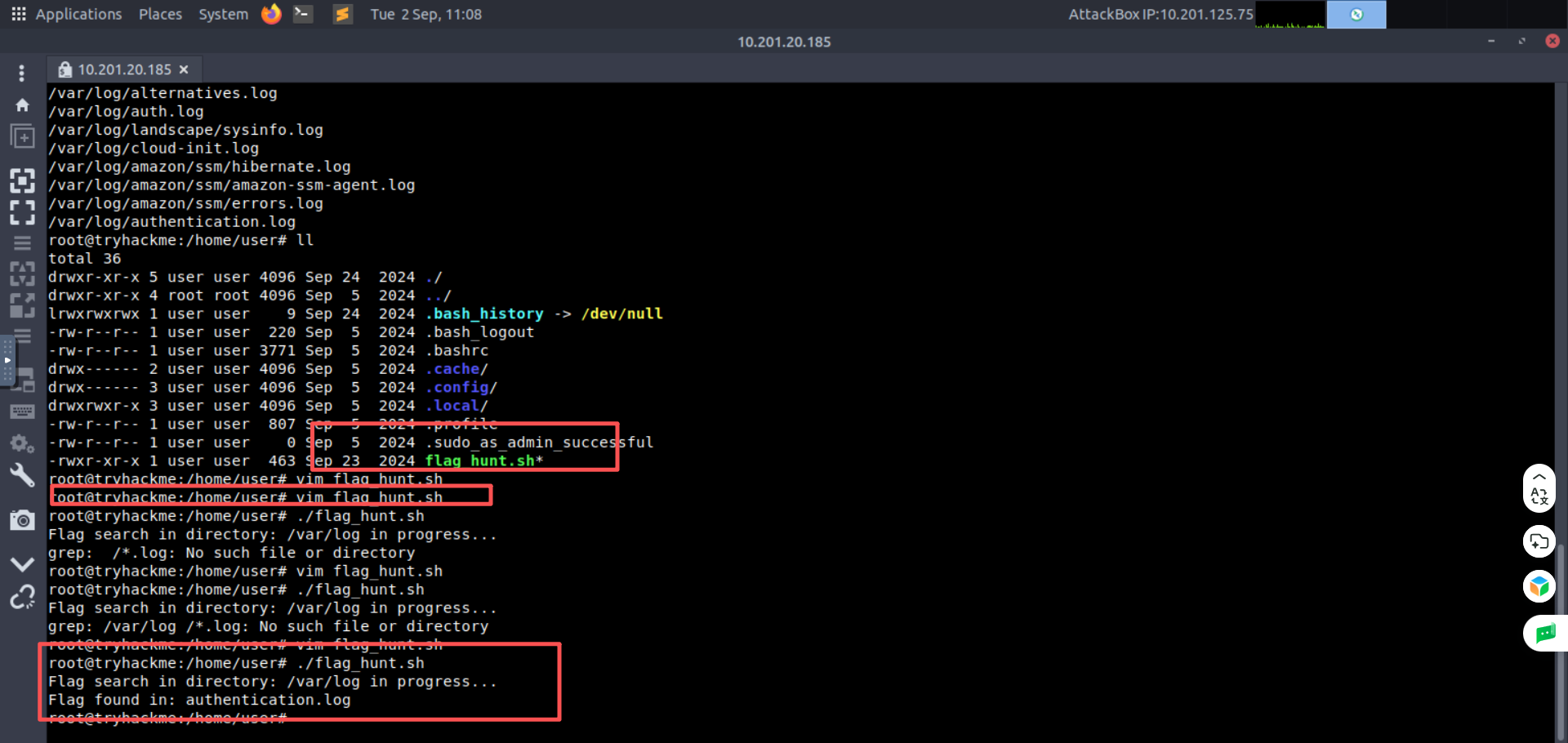
We have placed a script on the default user directory /home/user of the attached Ubuntu machine. This script searches for a specific keyword in all the files (with .log extension) in a specific directory.
我们在附加的 Ubuntu 计算机的默认用户目录 /home/user 中放置了一个脚本。该脚本在特定目录中的所有文件中搜索特定的关键字 (带有.log 扩展名)。
Note: Some changes are required inside the script file before you execute it. When you open the machine according to the instructions in task #2, you will be able to gain the session as a normal user. However, we recommend you to become the root user in order to search for the flag in all the files of the given directory. To become one, you only need to type the following command and enter the password of the user (The credentials are included in Task 2):
注意:在执行脚本文件之前,需要对其进行一些更改。当您按照任务 #2 中的说明打开机器时,您将能够以普通用户的身份获得会话。然而,我们建议您成为 root 用户,以便在给定目录的所有文件中搜索该标志。要成为 root 用户,您只需键入以下命令并输入用户的密码 (凭据包含在任务 #2 中):
Become Root User成为 root 用户
user@tryhackme:~$ sudo su
[sudo] password for user:
root@tryhackme:/home/user#You can make the changes in the script file by keeping in view the following details:
您可以通过查看以下详细信息来对脚本文件进行更改:
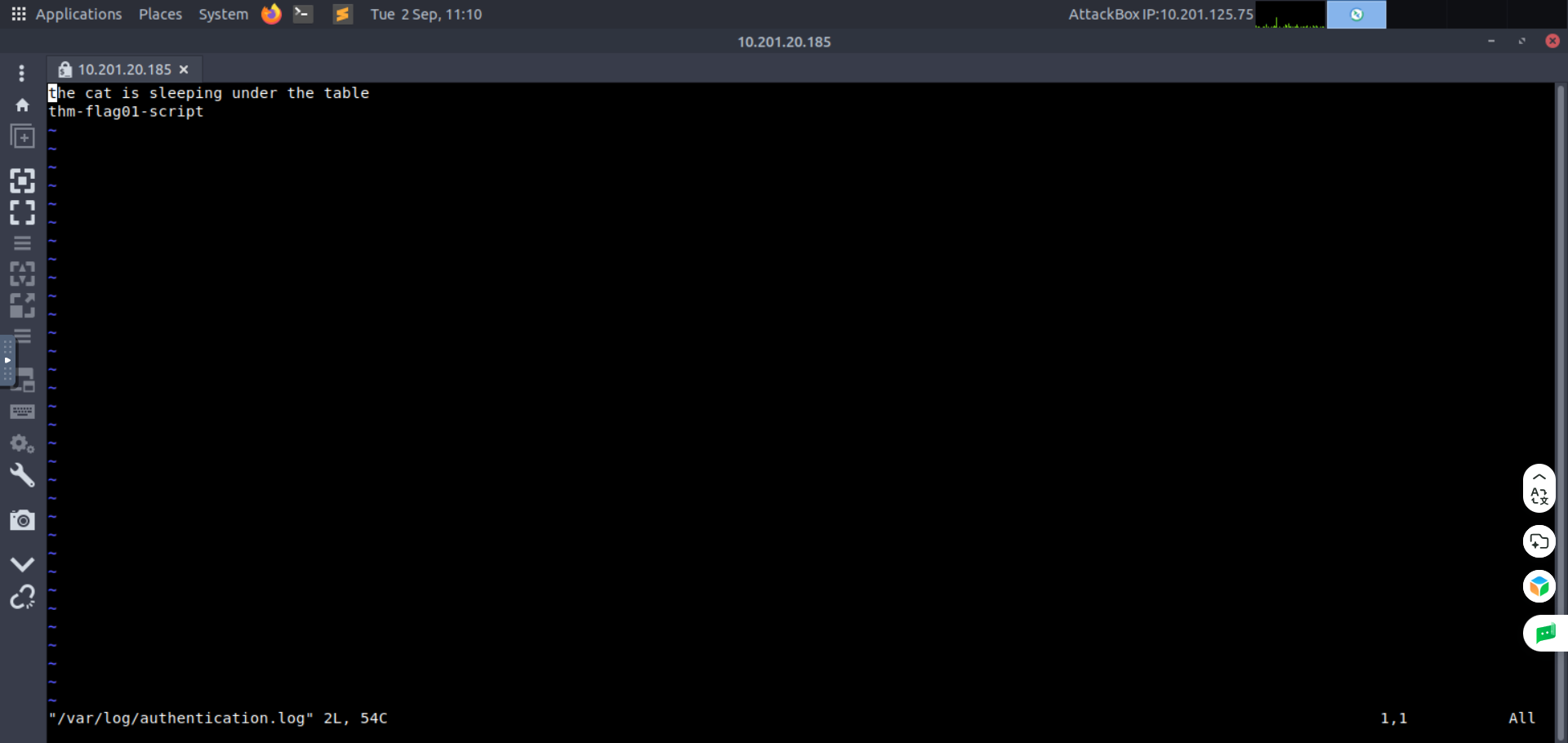
- Flag: thm-flag01-script标志:thm-flag01-script
- Directory: /var/log目录:/var/log
Hint: Look for empty double quotes " " inside the script file and fill them. Make sure not to leave any space between them.
提示:在 script 文件中寻找空的双引号 “” 并填充它们。确保它们之间不要留下任何空格。
问题
答案
Task7 Conclusion 结论