单片机外设(七)RTC时间获取
文章目录
- 一.RTC介绍
- 二.IMX6ull RTC介绍
- 1.SNVS_HP (high power domain)
- 2.SNVS_LP (low power domain)
- 3.SNVS interrupts and alarms
- 三. SNVS重点寄存器介绍
- 1.SNVS_HP Command(HPCOMR)
- 2.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP Control register (SNVS_HPCR/SNVS_LPCR)
- 3.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 状态寄存器(SNVS_HPSR/SNVS_LPSR)
- 4.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 实时计数器高字节寄存器(HPRTCMR/LPSRTCMR)
- 5.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 实时计数器低字节寄存器(SNVS_HPRTCLR/SNVS_LPSRTCLR)
- 6.SNVS_HP 时间报警高字节寄存器(SNVS_HPTAMR)
- 四.获取RTC时间
- 1.编程思路
- 2.日期时间与秒时间之间转换
- (1)daetime.h
- (2)datetime.c
- 3.代码
- 五.Alarm 中断
- 1. 编程思路
- RTC 闹钟功能操作步骤
- 2.代码
一.RTC介绍
实时时钟(Real Time Clock, RTC):可在系统断电时用备用电池工作,断电时备用电池能存储秒、分、小时、周、日、月、年时间数据,单元外接32.768 kHz晶振,有定时报警功能 。
二.IMX6ull RTC介绍
- 硬件功能:imx6ull芯片的Secure Non - Volatile Storage (SNVS)提供RTC功能 ,其低功耗(电池支持)部分含安全实时计数器、单调计数器、通用寄存器,由电池供电,芯片断电时电池保持SNVS_LP寄存器状态 。
- 专业术语:Secure Non - Volatile Storage (SNVS)(安全非易失性存储)、RTC(Real Time Clock,实时时钟 ) 、monotonic counter(单调计数器 ) 、SNVS_LP registers(SNVS低功耗寄存器 ) 。
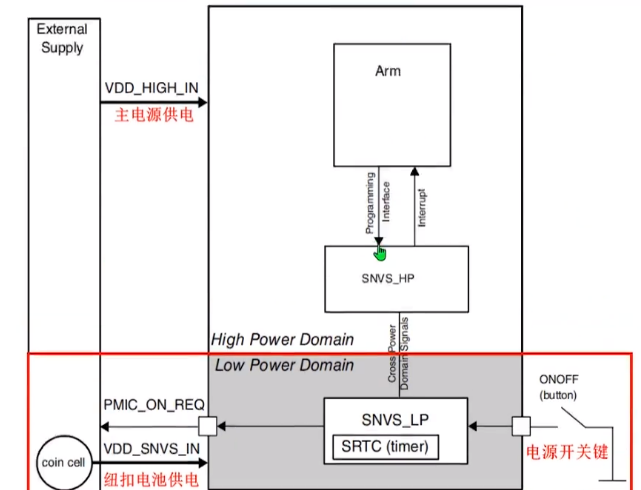
- SNVS_HP部分功能:实现启用系统通信和SNVS_LP部分分配配置的所有功能
- SNVS_LP部分功能:提供能够安全存储和保护敏感数据的硬件,其内部有SRTC(定时器 ),核心板为其提供32.768KHz时钟信号即可工作 。
1.SNVS_HP (high power domain)
- 功能单元:SNVS_HP分为IP总线接口、SNVS_LP接口、带报警功能的实时计数器、控制和状态寄存器这些功能单元 。
- 供电与接口:SNVS_HP位于芯片电源域,与芯片其余部分一同供电;是SNVS_LP和系统其余部分间的接口,访问SNVS_LP寄存器须经SNVS_HP且其需上电,通过寄存器访问权限策略决定是否允许访问特定寄存器 。
2.SNVS_LP (low power domain)
功能单元:SNVS_LP(低功耗域)的功能单元有非翻转单调计数器、通用寄存器、控制和状态寄存器 。
子系统与电源:SNVS_LP是数据存储子系统,用于存储和保护系统数据,不受主系统电源状态影响;处于始终上电域,为单独电源域,有自身电源 。
3.SNVS interrupts and alarms

- 时间报警寄存器功能:
- SNVS_HP非安全RTC有自身时间报警寄存器,应用程序可更新。
- 能生成中断提醒主机处理器,可从低功耗模式唤醒主机处理器;系统断电时无法唤醒整个系统(因报警也断电 )。
- 周期性中断功能:
- SNVS_HP非安全RTC含周期性中断,RTC选定位0 - 1或1 - 0转换时产生。
- 中断源依HP控制寄存器PI_FREQ字段,从HP RTC 16位中选,位选择定义中断频率 。
三. SNVS重点寄存器介绍
1.SNVS_HP Command(HPCOMR)

2.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP Control register (SNVS_HPCR/SNVS_LPCR)

3.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 状态寄存器(SNVS_HPSR/SNVS_LPSR)

4.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 实时计数器高字节寄存器(HPRTCMR/LPSRTCMR)

5.SNVS_HP/SNVS_LP 实时计数器低字节寄存器(SNVS_HPRTCLR/SNVS_LPSRTCLR)

6.SNVS_HP 时间报警高字节寄存器(SNVS_HPTAMR)


四.获取RTC时间
1.编程思路
- 操作步骤类:
- 使能SNVS时钟
- 设置寄存器访问不受权限限制
- 停止RTC计数器,等待RTC计数器停止成功
- 设置日期
- 开启RTC计数器,等待RTC计数器开启成功
- 每隔1秒读取RTC数据,然后输出
2.日期时间与秒时间之间转换
(1)daetime.h
#ifndef _DATETIME_HEAD_H
#define _DATETIME_HEAD_H#include <stdint.h>#define SECONDS_IN_A_DAY (86400U)
#define SECONDS_IN_A_HOUR (3600U)
#define SECONDS_IN_A_MINUTE (60U)
#define DAYS_IN_A_YEAR (365U)
#define YEAR_RANGE_START (1970U)
#define YEAR_RANGE_END (2099U)typedef struct rtc_datetime
{uint16_t year; /*!< Range from 1970 to 2099. */uint8_t month; /*!< Range from 1 to 12. */uint8_t day; /*!< Range from 1 to 31 (depending on month). */uint8_t hour; /*!< Range from 0 to 23. */uint8_t minute; /*!< Range from 0 to 59. */uint8_t second; /*!< Range from 0 to 59. */
} rtc_datetime_t;extern uint32_t convert_datetime_to_seconds(const rtc_datetime_t *datetime);
extern void convert_seconds_to_datetime(uint32_t seconds, rtc_datetime_t *datetime);#endif /* _DATETIME_HEAD_H */
(2)datetime.c
#include "datetime.h"uint32_t convert_datetime_to_seconds(const rtc_datetime_t *datetime)
{/* Number of days from begin of the non Leap-year*/uint16_t monthDays[] = {0U, 31U, 59U, 90U, 120U, 151U, 181U, 212U, 243U, 273U, 304U, 334U};uint32_t seconds = 0;/* Compute number of days from 1970 till given year*/seconds = (datetime->year - 1970U) * DAYS_IN_A_YEAR;/* Add leap year number of days */seconds += ((datetime->year / 4) - (1970U / 4));/* Add number of days till given month*/seconds += monthDays[datetime->month];/* Add days in given month. We subtract the current day as it is * represented in the hours, minutes and seconds field*/seconds += (datetime->day - 1);/* For leap year if month less than or equal to February, decrement day counter*/if ((!(datetime->year & 3U)) && (datetime->month <= 2U)){seconds--;}seconds = (seconds * SECONDS_IN_A_DAY) + (datetime->hour * SECONDS_IN_A_HOUR) + (datetime->minute * SECONDS_IN_A_MINUTE) + datetime->second;return seconds;
}void convert_seconds_to_datetime(uint32_t seconds, rtc_datetime_t *datetime)
{uint32_t x;uint32_t secondsRemaining, days;uint16_t daysInYear;/* Table of days in a month for a non leap year. First entry in the table is not used,* valid months start from 1*/uint8_t daysPerMonth[] = {0U, 31U, 28U, 31U, 30U, 31U, 30U, 31U, 31U, 30U, 31U, 30U, 31U};/* Start with the seconds value that is passed in to be converted to * date time format*/secondsRemaining = seconds;/* Calculate the number of days, we add 1 for the current day which is represented in * the hours and seconds field*/days = secondsRemaining / SECONDS_IN_A_DAY + 1;/* Update seconds left*/secondsRemaining = secondsRemaining % SECONDS_IN_A_DAY;/* Calculate the datetime hour, minute and second fields */datetime->hour = secondsRemaining / SECONDS_IN_A_HOUR;secondsRemaining = secondsRemaining % SECONDS_IN_A_HOUR;datetime->minute = secondsRemaining / 60U;datetime->second = secondsRemaining % SECONDS_IN_A_MINUTE;/* Calculate year */daysInYear = DAYS_IN_A_YEAR;datetime->year = YEAR_RANGE_START;while (days > daysInYear){/* Decrease day count by a year and increment year by 1 */days -= daysInYear;datetime->year++;/* Adjust the number of days for a leap year */if (datetime->year & 3U){daysInYear = DAYS_IN_A_YEAR;}else{daysInYear = DAYS_IN_A_YEAR + 1;}}/* Adjust the days in February for a leap year */if (!(datetime->year & 3U)){daysPerMonth[2] = 29U;}for (x = 1U; x <= 12U; x++){if (days <= daysPerMonth[x]){datetime->month = x;break;}else{days -= daysPerMonth[x];}}datetime->day = days;return;
}
3.代码
#include "imx6ull.h"
#include "datetime.h"
void rtc_init(void)
{/*Enable Clock*/CCM_CCGR5 |= (0x3 << 18);/*NPSWA_EN [31] 1 Any software can accsee*/SNVS->HPCOMR |= (1 << 31);
}void rtc_stop(void)
{/*RTC_EN [0] 0b clear Enable*/SNVS->HPCR &= ~(1 << 0);while(SNVS->HPCR & (1 << 0)){}
}void rtc_start(void)
{/*RTC_EN [0] 1b Enable*/SNVS->HPCR |= (1 << 0);while((SNVS->HPCR & (1 << 0)) == 0){}
}void rtc_set_datetime(rtc_datetime_t *datetime)
{uint32_t seconds;rtc_stop();seconds = convert_datetime_to_seconds(datetime);SNVS->HPRTCMR = seconds >> 17;//[31:18][17:0]SNVS->HPRTCLR = seconds << 15;rtc_start();return;}void rtc_get_datetime(rtc_datetime_t *datetime)
{uint32_t tmp = 0;
uint32_t seconds = 0;do {tmp = seconds;seconds = (SNVS->HPRTCMR << 17) | (SNVS->HPRTCLR >> 15);
} while (seconds != tmp);convert_seconds_to_datetime(seconds, datetime);return;
}void rtc_test(void)
{rtc_datetime_t datetime;rtc_init();datetime.year = 2025;
datetime.month = 1;
datetime.day = 1;
datetime.hour = 21;
datetime.minute = 40;
datetime.second = 30;rtc_set_datetime(&datetime);while(1) {rtc_get_datetime(&datetime);uart_printf("%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d\r\n", datetime.year, datetime.month, datetime.day, datetime.hour, datetime.minute, datetime.second);gpt_delay_sec(1);
}return;
}五.Alarm 中断
1. 编程思路
RTC 闹钟功能操作步骤
-
注册 RTC 中断
需编写代码完成 RTC 中断的注册,使系统能响应 RTC 相关中断事件(如闹钟触发 )。 -
设置 RTC alarm 日期
- Disable RTC alarm:先禁用 RTC 闹钟,避免设置过程中误触发。
- 设置日期:配置闹钟触发的具体日期、时间等参数(如年、月、日、时、分、秒 )。
- Enable RTC alarm:启用 RTC 闹钟,使配置的闹钟参数生效,到指定时间触发中断。
-
中断处理函数逻辑
- 判断是否是 RTC alarm 中断:在中断处理函数中,通过检测中断标志等方式,识别是否由 RTC 闹钟触发中断。
- 输出提醒信息:若确认是 RTC alarm 中断,输出“闹钟时间到达”等提示信息(可通过串口、显示屏等方式输出 )。
- 清除中断标志:执行写 1 清 0 操作,清除 RTC alarm 中断标志,确保后续中断能正常触发。
2.代码
int rtc_interrupt_handler(int id)
{if(SNVS->HPSR & (1 << 0)){uart_printf("RTC Alarm\r\n");//clear interruptSNVS->HPSR |= (1 << 0);while(SNVS->HPSR & (1 << 0)){}}return 0;
}void rtc_set_alarm(rtc_datetime_t *datetime)
{int seconds;// 请求 RTC 中断:注册中断请求,绑定中断处理函数
request_irq(SNVS_Consolidated_IRQn, rtc_interrupt_handler);// 禁用闹钟:通过操作 HPCR 寄存器,等待禁用完成
SNVS->HPCR &= ~(1 << 1);
while (SNVS->HPCR & (1 << 1)) {// 等待寄存器位清除,确保闹钟已禁用
}// 设置闹钟时间:将 datetime 转换为秒数,拆分后写入寄存器
seconds = convert_datetime_to_seconds(datetime);
// 高 15 位写入 HPRTCMR([31:17] 存储秒数高段)
SNVS->HPRTCMR = seconds >> 17;
// 低 17 位写入 HPRTCLR([16:0] 存储秒数低段,通过左移 15 位对齐)
SNVS->HPRTCLR = seconds << 15;//Enable alarmSNVS->HPCR |= (1 << 1);while((SNVS->HPCR & (1 << 1)) == 0){}
}