【C++】模版(初阶)
目录
一. 函数模版
1. 格式 原理
2. 函数模版的实例化
二. 类模板
void Swap(int& left, int& right)
{int temp = left;left = right;right = temp;
}void Swap(double& left, double& right)
{double temp = left;left = right;right = temp;
}void Swap(char& left, char& right)
{char temp = left;left = right;right = temp;
}使用函数重载太麻烦
模具,填充不同类型,生成具体类型的代码
泛型编程:编写与类型无关的通用代码,是代码复用的一种手段。模板是泛型编程的基础
一. 函数模版
1. 格式 原理
template<typename T1, typename T2, ......, typename Tn>
返回类型 函数名(参数列表)
{ }
typename是用来定义模板参数关键字,也可以使用class,不能使用struct
模板参数作用范围:紧跟的 { }
template<typename T> // 模板参数 -- 类型
void Swap(T& left, T& right)
{T temp = left;left = right;right = temp;
}template<typename T1, typename T2>
T1 Func (const T1& x, const T2& y)
{cout << x << " " << y << endl;return x;
}int main()
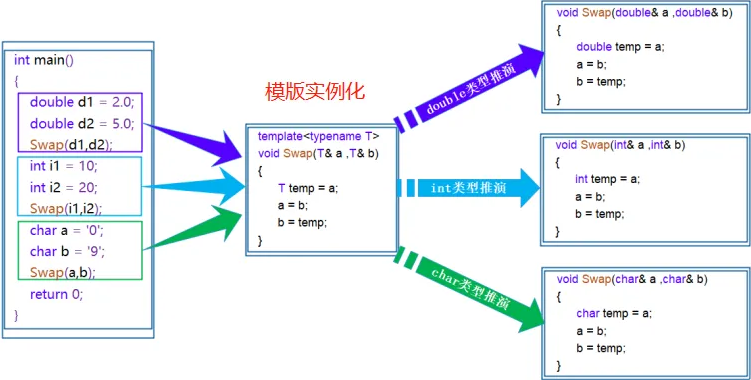
{int a = 0, b = 1;double c = 1.1, d = 2.2;Swap(a, b);Swap(c, d);// Date d1(1949, 10, 1), d2(2015, 7, 3);Func(1, 2);Func(1, 2.2);return 0;
}调用的是模版实例化出的函数(模板就是将本来应该我们做的重复的事情交给了编译器 )
C++库里面有。不需要写Swap,也不用写模版。直接使用

int main()
{int a = 0, b = 1;double c = 1.1, d = 2.2;swap(a, b);swap(c, d);// Date d1(1949, 10, 1), d2(2015, 7, 3);return 0;
}2. 函数模版的实例化
隐式实例化:让编译器根据实参 推演模板参数的实际类型
显示实例化:在函数名后的<>中 指定模板参数的实际类型
template<typename T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{return left + right;
}template<typename T>
T* Alloc(int n)
{return new T[n];
}int main()
{ int a1 = 10, a2 = 20;double d1 = 10.1, d2 = 20.2;cout << Add(a1, a2) << endl;cout << Add(d1, d2) << endl;// cout << Add(a1, d1) << endl; 报错:编译器无法确定T的类型// 解决方案1:用户自己强制转换cout << Add(a1, (int)d1) << endl;cout << Add((double)a1, d1) << endl;// 解决方案2:显示实例化cout << Add<int>(a1, d1) << endl;cout << Add<double>(a1, d1) << endl;// 有些函数无法自动推,只能显示实例化double* p1 = Alloc<double>(10);return 0;
}类型转换会产生临时变量(常性)。Add(a1, (int)d1) 这里不是把 d1 传给 right,所以 Add 要加 const
二. 类模板
template<class T1, class T2, ..., class Tn>
class 类模板名
{
// 类内成员定义
};
普通类,类名和类型是一样
类模板,类名和类型不一样
类名:Stack
类型:Stack<T>
构造函数不一定用T这个参数,所以类模板都无法通过推演实例化,类都是显示实例化
template<class T>
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int capacity = 4){_a = new T[capacity];_capacity = capacity;_size = 0;}void Push(const T& Date){// CheckCapacity();_a[_size] = Date;_size++;}~Stack(){if (_a){free(_a);_a = nullptr;_capacity = 0;_size = 0;}}private:T* _a;int _capacity;int _size;
};int main()
{Stack<int> s1; // intStack<double> s2; // doubleStack<char> s3; // char// Stack<int, double>s4; 多个模板参数return 0;
}类模板的声明和定义分离是别致的
类模板的声明和定义最好不要分离到 2个文件,会报错(后面讲)
template<class T>
class Stack
{
public:Stack(int capacity = 4);void Push(const T& Date);~Stack(){if (_a){free(_a);_a = nullptr;_capacity = 0;_size = 0;}}private:T* _a;int _capacity;int _size;
};template<class T>
Stack<T>::Stack(int capacity)
{_a = new T[capacity];_capacity = capacity;_size = 0;
}template<class T>
void Stack<T>::Push(const T& data)
{// CheckCapacity();_a[_size] = data;_size++;
}本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章
