JUC之CompletableFuture【下】
文章目录
- 十二、异步并行处理【提高效率】
- 12.1 电商商品详情页聚合多维度信息
- 12.1.1 业务流程展示
- 12.1.2 业务时序图
- 12.1.3 测试代码
- 12.2 多数据源聚合
- 12.2.1 业务流程图
- 12.2.2 数据聚合业务时序图
- 12.2.3 测试示例
- 十三、降级与熔断
- 13.1 时序图
- 13.2 参考代码
- 十四、并行搜索
- 14.1 业务时序图
- 14.2 参考代码
- 十五、异步任务链与状态更新
- 15.1 业务时序图
- 15.2 参考代码
- 十六、**电商平台订单创建与处理系统**
- 16.1 业务模型
- 16.2 系统流程图
- 16.3 模块划分
- 16.4 参考代码
- 16.5 关键点总结
十二、异步并行处理【提高效率】
12.1 电商商品详情页聚合多维度信息
- 需要同时调用多个独立服务,最后聚合结果(如电商商品详情页聚合多维度信息)
12.1.1 业务流程展示
12.1.2 业务时序图
12.1.3 测试代码
package cn.tcmeta.usecompletablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;// 商品服务模拟
class ProductService {// 获取商品基本信息public String getProductInfo(Long productId) {simulateDelay(100); // 模拟网络延迟return "商品ID: " + productId + ", 名称: 智能手机, 价格: 3999元";}// 获取商品库存public Integer getStock(Long productId) {simulateDelay(150);return 156;}// 获取商品评价public String getReviews(Long productId) {simulateDelay(200);return "好评率: 98%, 共2000条评价";}private void simulateDelay(int millis) {try { Thread.sleep(millis); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); }}
}public class ProductDetailExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ProductService service = new ProductService();Long productId = 1001L;long start = System.currentTimeMillis();// 异步()表示使用 ForkJoinPool.commonPool()CompletableFuture<String> productInfoFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> service.getProductInfo(productId));CompletableFuture<Integer> stockFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> service.getStock(productId));CompletableFuture<String> reviewsFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> service.getReviews(productId));// 等待所有任务完成并聚合结果CompletableFuture<Void> allDone = CompletableFuture.allOf(productInfoFuture, stockFuture, reviewsFuture);// 处理结果allDone.thenRun(() -> {try {String productInfo = productInfoFuture.get();Integer stock = stockFuture.get();String reviews = reviewsFuture.get();System.out.println("商品详情:\n" + productInfo + "\n库存: " + stock + "\n评价: " + reviews);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}).get(); // 等待最终处理完成System.out.println("总耗时: " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "ms");// 并行执行,总耗时接近最长的任务(200ms),而非串行的450ms}
}
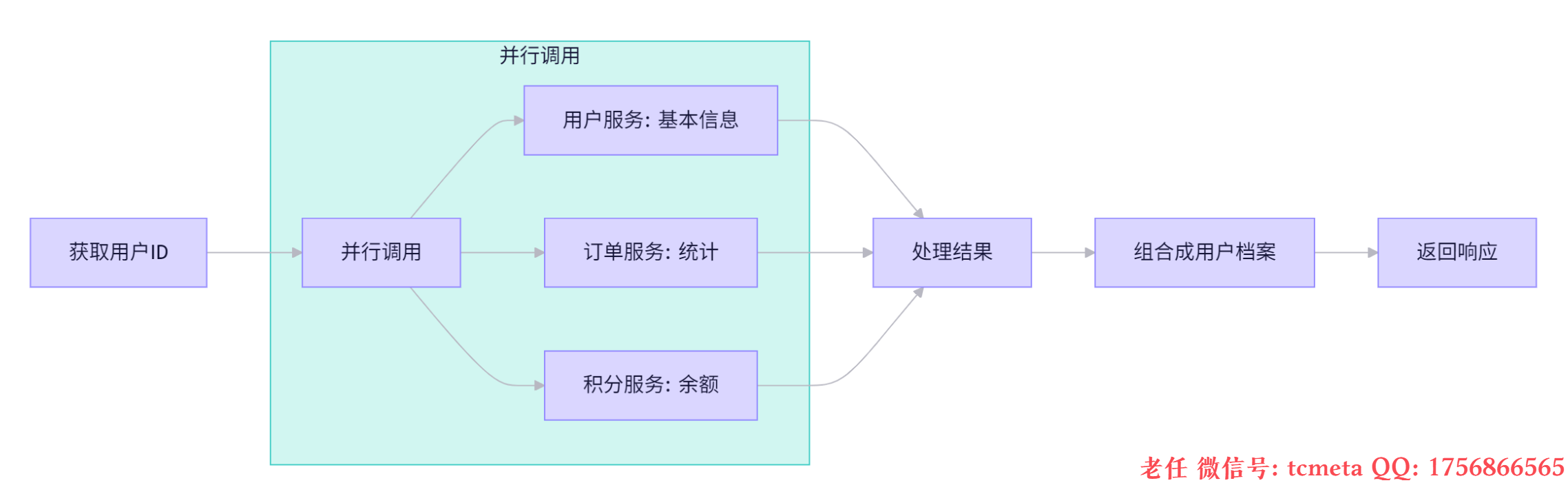
12.2 多数据源聚合
该示例12.1中的基本类似,都是通过CompletableFuture进行并发处理.
业务模型: 一个用户信息聚合服务。需要从多个独立的微服务(用户基本信息、订单统计、积分信息)获取数据,并将它们聚合到一个 UserProfile 对象中返回。任何一个服务超时或失败,应返回已有信息或降级信息,避免“雪崩”。
12.2.1 业务流程图
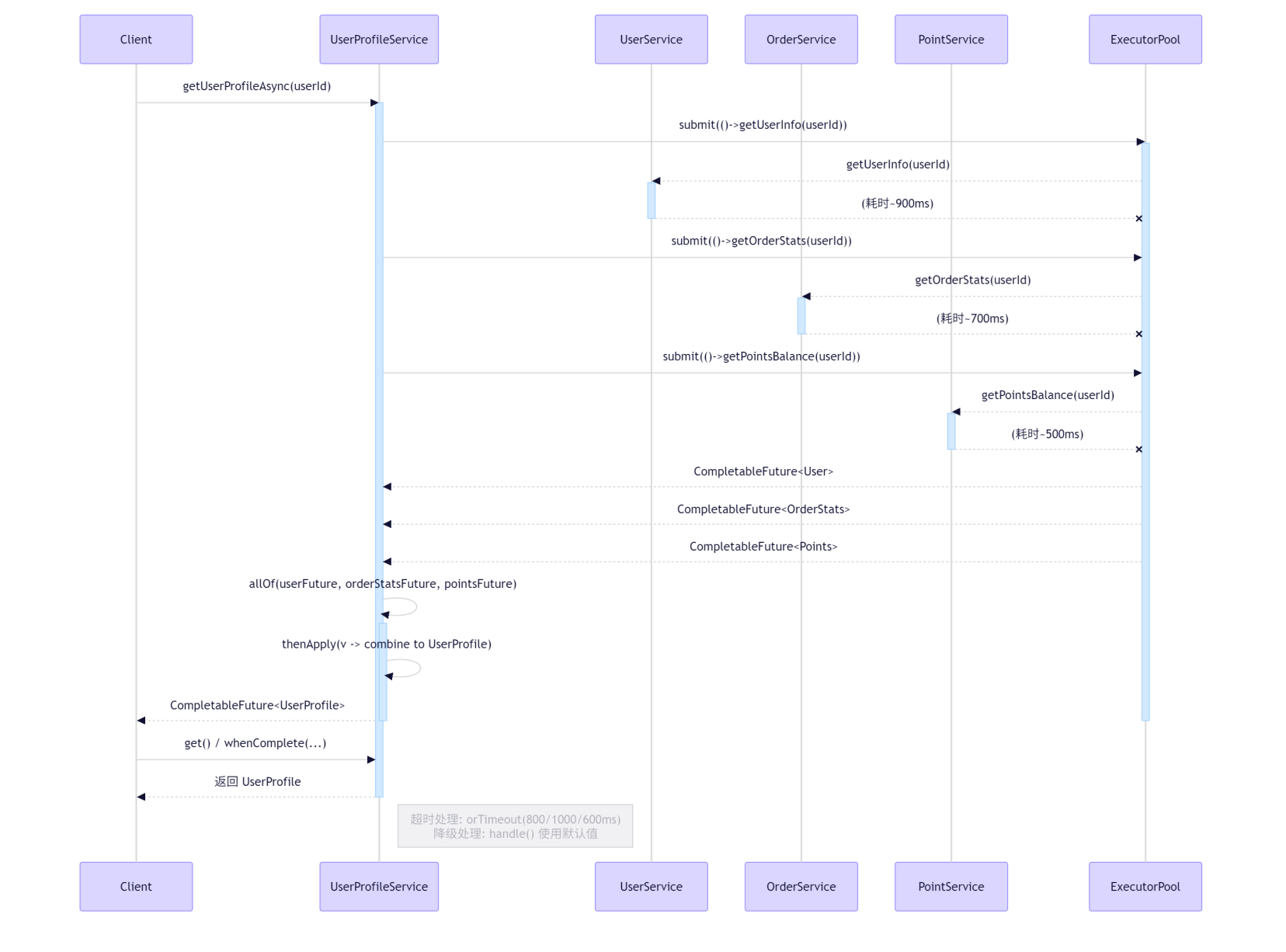
12.2.2 数据聚合业务时序图
12.2.3 测试示例
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
import java.util.function.Supplier;/*** 场景1: 多数据源聚合 (用户档案服务)* 展示并行调用、超时控制、降级策略*/
public class UserProfileService {private final UserService userService = new UserService();private final OrderService orderService = new OrderService();private final PointService pointService = new PointService();private final ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5, r -> new Thread(r, "UserProfile-Thread-"));// 模拟的默认/降级值private static final User DEFAULT_USER = new User("Unknown", "unknown@email.com");private static final OrderStats DEFAULT_STATS = new OrderStats(0, 0.0);private static final Points DEFAULT_POINTS = new Points(0);public CompletableFuture<UserProfile> getUserProfileAsync(String userId) {System.out.println("开始获取用户档案: " + userId);// 1. 为每个服务调用设置超时 (使用 orTimeout 或 completeOnTimeout)CompletableFuture<User> userFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> userService.getUserInfo(userId), executor).orTimeout(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) // 超时后抛出TimeoutException.handle((user, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("获取用户基本信息失败: " + ex.getMessage());return DEFAULT_USER; // 降级}return user;});CompletableFuture<OrderStats> orderStatsFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> orderService.getOrderStats(userId), executor).orTimeout(1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS).handle((stats, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("获取订单统计失败: " + ex.getMessage());return DEFAULT_STATS;}return stats;});CompletableFuture<Points> pointsFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> pointService.getPointsBalance(userId), executor).orTimeout(600, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS).handle((points, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("获取积分余额失败: " + ex.getMessage());return DEFAULT_POINTS;}return points;});// 2. 使用 allOf 等待所有调用完成 (无论成功或失败/超时)CompletableFuture<Void> allDone = CompletableFuture.allOf(userFuture, orderStatsFuture, pointsFuture);// 3. 组合结果return allDone.thenApply(v -> {User user = userFuture.getNow(DEFAULT_USER);OrderStats stats = orderStatsFuture.getNow(DEFAULT_STATS);Points points = pointsFuture.getNow(DEFAULT_POINTS);return new UserProfile(userId, user, stats, points);});}// --- 模拟的服务 ---static class UserService {public User getUserInfo(String userId) {return new User("Alice", "alice@email.com");}}static class OrderService {public OrderStats getOrderStats(String userId) {try { Thread.sleep(700); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}return new OrderStats(15, 2345.67);}}static class PointService {public Points getPointsBalance(String userId) {try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}return new Points(888);}}// --- 数据模型 ---static class User {private final String name;private final String email;public User(String name, String email) { this.name = name; this.email = email; }@Override public String toString() { return "User{name='" + name + "', email='" + email + "'}"; }}static class OrderStats {private final int orderCount;private final double totalAmount;public OrderStats(int orderCount, double totalAmount) { this.orderCount = orderCount; this.totalAmount = totalAmount; }@Override public String toString() { return "OrderStats{count=" + orderCount + ", total=" + totalAmount + "}"; }}static class Points {private final int balance;public Points(int balance) { this.balance = balance; }@Override public String toString() { return "Points{balance=" + balance + "}"; }}static class UserProfile {private final String userId;private final User user;private final OrderStats orderStats;private final Points points;public UserProfile(String userId, User user, OrderStats orderStats, Points points) {this.userId = userId; this.user = user; this.orderStats = orderStats; this.points = points;}@Override public String toString() {return "UserProfile{" +"userId='" + userId + '\'' +", user=" + user +", orderStats=" + orderStats +", points=" + points +'}';}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {UserProfileService service = new UserProfileService();// 演示聚合CompletableFuture<UserProfile> profileFuture = service.getUserProfileAsync("user123");UserProfile profile = profileFuture.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 总超时System.out.println("用户档案: " + profile);service.executor.shutdown();}
}

十三、降级与熔断
业务模型: 调用一个不稳定的外部服务(如天气API)。如果调用失败或超时,则返回缓存的旧数据或默认值。这体现了“优雅降级”思想。
13.1 时序图
13.2 参考代码
package cn.tcmeta.usecompletablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;/*** laoren* 当主服务失败时,使用缓存或默认值*/
public class WeatherServiceWithFallback {private final ExternalWeatherApi weatherApi = new ExternalWeatherApi();private final AtomicReference<String> cachedWeather = new AtomicReference<>("Sunny (Cached)");public CompletableFuture<String> getCurrentWeatherAsync(String city) {System.out.println("获取城市天气: " + city);// 1. 主调用: 调用外部APICompletableFuture<String> primaryCall = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> weatherApi.fetchWeather(city)).orTimeout(2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); // 2秒超时// 2. 降级调用: 获取缓存数据CompletableFuture<String> fallbackCall = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {String cached = cachedWeather.get();System.out.println("使用缓存天气: " + cached);return cached;});// 3. 使用 applyToEither: 返回最先完成的那个 (主调用成功则用主结果,否则用降级结果)return primaryCall.applyToEither(fallbackCall,result -> {System.out.println("采用结果: " + result);return result;}).exceptionally(ex -> {// 如果 applyToEither 内部也异常 (理论上 primaryCall 超时不会到这里,因为 fallbackCall 会完成)System.err.println("获取天气时发生未预期异常: " + ex.getMessage());return "Unknown";});}// --- 模拟的外部API ---static class ExternalWeatherApi {private int callCount = 0;public String fetchWeather(String city) {callCount++;try {Thread.sleep(2500); // 模拟慢响应,超过2秒超时} catch (InterruptedException e) {}// 模拟50%失败率if (callCount % 2 == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("API暂时不可用");}return "Rainy in " + city;}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {WeatherServiceWithFallback service = new WeatherServiceWithFallback();// 第一次调用 (可能超时,用缓存)CompletableFuture<String> weather1 = service.getCurrentWeatherAsync("Beijing");System.out.println("天气1: " + weather1.get());// 第二次调用 (可能成功,也可能失败用缓存)CompletableFuture<String> weather2 = service.getCurrentWeatherAsync("Shanghai");System.out.println("天气2: " + weather2.get());}
}
十四、并行搜索
业务模型: 在多个搜索引擎或数据源中并行搜索同一关键词,返回最先返回结果的那个。这可以显著降低用户感知的延迟。
14.1 业务时序图
14.2 参考代码
package cn.tcmeta.usecompletablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** laoren* 场景3: 并行搜索* 在多个来源中搜索,返回最快的那个结果*/
public class ParallelSearchService {private final SearchEngine engineA = new SearchEngine("FastEngine", 800);private final SearchEngine engineB = new SearchEngine("SlowEngine", 1200);private final SearchEngine engineC = new SearchEngine("UnreliableEngine", 1500);private final ExecutorService executor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, r -> new Thread(r, "Search-Thread-"));public CompletableFuture<SearchResult> searchAsync(String query) {System.out.println("开始并行搜索: '" + query + "'");// 1. 启动三个并行搜索任务CompletableFuture<SearchResult> searchA = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> engineA.search(query), executor);CompletableFuture<SearchResult> searchB = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> engineB.search(query), executor);CompletableFuture<SearchResult> searchC = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> engineC.search(query), executor);// 2. 使用 anyOf: 返回最先完成的 CompletableFuture// 注意: anyOf 返回 CompletableFuture<Object>,需要转换return CompletableFuture.anyOf(searchA, searchB, searchC).thenApply(result -> {System.out.println("采用最快结果");return (SearchResult) result; // 转换类型}).exceptionally(ex -> {System.err.println("所有搜索均失败: " + ex.getMessage());return new SearchResult("No results found", 0);});}// --- 模拟的搜索引擎 ---static class SearchEngine {private final String name;private final long delayMs;public SearchEngine(String name, long delayMs) {this.name = name;this.delayMs = delayMs;}public SearchResult search(String query) {try {Thread.sleep(delayMs);// 模拟部分引擎失败if ("UnreliableEngine".equals(name) && Math.random() < 0.5) {throw new RuntimeException("Engine down");}return new SearchResult("Result from " + name + " for '" + query + "'", 10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {Thread.currentThread().interrupt();return new SearchResult("Interrupted", 0);}}}static class SearchResult {private final String title;private final int count;public SearchResult(String title, int count) {this.title = title;this.count = count;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "SearchResult{title='" + title + "', count=" + count + "}";}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ParallelSearchService service = new ParallelSearchService();CompletableFuture<SearchResult> result = service.searchAsync("Java CompletableFuture");System.out.println("搜索结果: " + result.get(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS));service.executor.shutdown();}
}
十五、异步任务链与状态更新
业务模型: 一个复杂的业务流程,如“内容发布”。需要按顺序执行多个异步步骤,并在每个步骤完成后更新数据库中的任务状态。
15.1 业务时序图
15.2 参考代码
package cn.tcmeta.usecompletablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;/*** 场景4: 异步任务链与状态更新* 模拟内容发布流程*/
public class ContentPublishService {private final ExecutorService executor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3, r -> new Thread(r, "Publish-Thread-"));private final TaskStatusService statusService = new TaskStatusService();public CompletableFuture<Boolean> publishContentAsync(String contentId, String content) {String taskId = "PUB-" + contentId;System.out.println("开始发布内容: " + contentId);return CompletableFuture// 1. 步骤1: 内容审核.runAsync(() -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "审核中");try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}boolean approved = Math.random() > 0.2; // 80%通过率if (!approved) {throw new RuntimeException("内容审核未通过");}statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "审核通过");System.out.println("内容审核通过: " + contentId);}, executor)// 2. 步骤2: 生成缩略图 (依赖审核通过).thenRunAsync(() -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "生成缩略图");try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("缩略图生成完成: " + contentId);}, executor)// 3. 步骤3: 发布到主站 (依赖缩略图).thenRunAsync(() -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "发布到主站");try { Thread.sleep(400); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("内容已发布到主站: " + contentId);}, executor)// 4. 步骤4: 同步到CDN (依赖主站发布).thenRunAsync(() -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "同步到CDN");try { Thread.sleep(600); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("内容已同步到CDN: " + contentId);}, executor)// 5. 成功处理.thenApply(v -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "发布成功");System.out.println("内容发布流程完成: " + contentId);return true;})// 6. 异常处理 (降级或补偿).exceptionally(ex -> {statusService.updateStatus(taskId, "发布失败: " + ex.getMessage());System.err.println("内容发布失败: " + contentId + ", 原因: " + ex.getMessage());// 这里可以触发补偿任务,如清理临时文件return false;})// 7. 最终清理 (无论成功失败).whenComplete((result, ex) -> {System.out.println("发布任务结束,结果: " + result);// 可以记录日志,触发监控等});}// --- 模拟的任务状态服务 ---static class TaskStatusService {public void updateStatus(String taskId, String status) {// 模拟更新数据库try { Thread.sleep(50); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("任务 [" + taskId + "] 状态更新: " + status);}}public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ContentPublishService service = new ContentPublishService();// 演示成功发布CompletableFuture<Boolean> result1 = service.publishContentAsync("C001", "Hello World!");System.out.println("发布结果1: " + result1.get());// 演示失败发布 (审核不通过)CompletableFuture<Boolean> result2 = service.publishContentAsync("C002", "Bad Content");System.out.println("发布结果2: " + result2.get());service.executor.shutdown();}
}
十六、电商平台订单创建与处理系统
16.1 业务模型
-
订单创建 (Order Creation):
- 接收用户创建订单请求。
- 需要并行执行多个校验和查询:
- 库存校验 (Inventory Check): 检查商品是否有足够库存。
- 用户信用校验 (User Credit Check): 检查用户信用额度是否足够。
- 优惠券校验 (Coupon Validation): 验证用户使用的优惠券是否有效且可用。
- 所有校验必须同时通过,订单才能创建。
- 创建订单记录。
- 扣减库存。
- 锁定用户信用额度。
- 标记优惠券为已使用。
- 发送订单创建成功通知(异步,失败不影响主流程)。
-
订单支付 (Order Payment):
-
用户发起支付。
-
调用第三方支付网关。
-
支付成功后:
- 更新订单状态为“已支付”。
- 触发发货流程(异步)。
- 发送支付成功通知。
-
-
订单发货 (Order Shipment):
-
支付成功后触发。
-
调用物流系统创建运单。
-
更新订单状态为“已发货”。
-
发送发货通知。
-
16.2 系统流程图
16.3 模块划分
- 用户交互模块:负责用户下单操作。
- 订单创建模块:负责生成订单信息。
- 库存检查模块:确保商品库存充足。
- 支付处理模块:处理用户的支付请求。
- 物流安排模块:安排商品的配送。
- 通知服务模块:向用户发送确认消息。
各个模块的时序图:
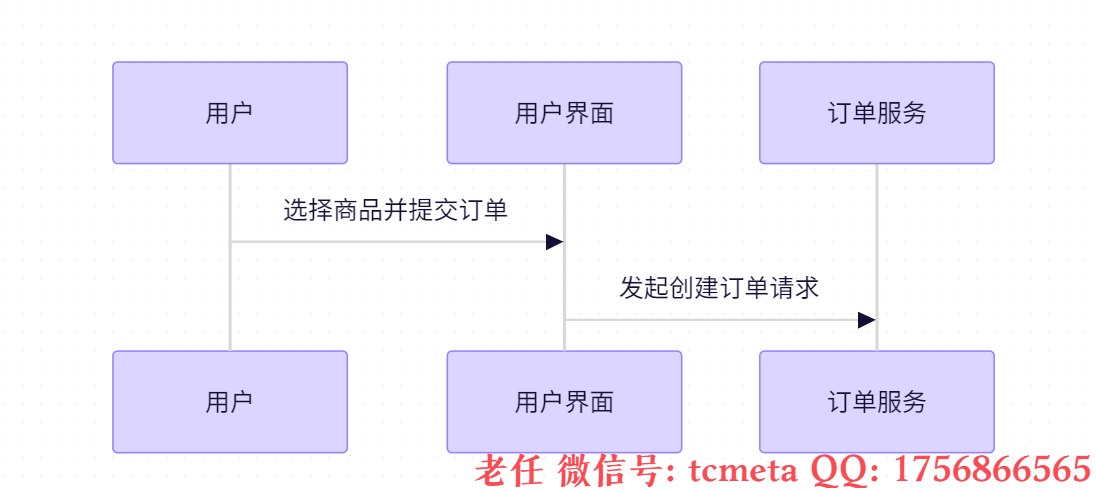
用户交互模块
订单创建模块
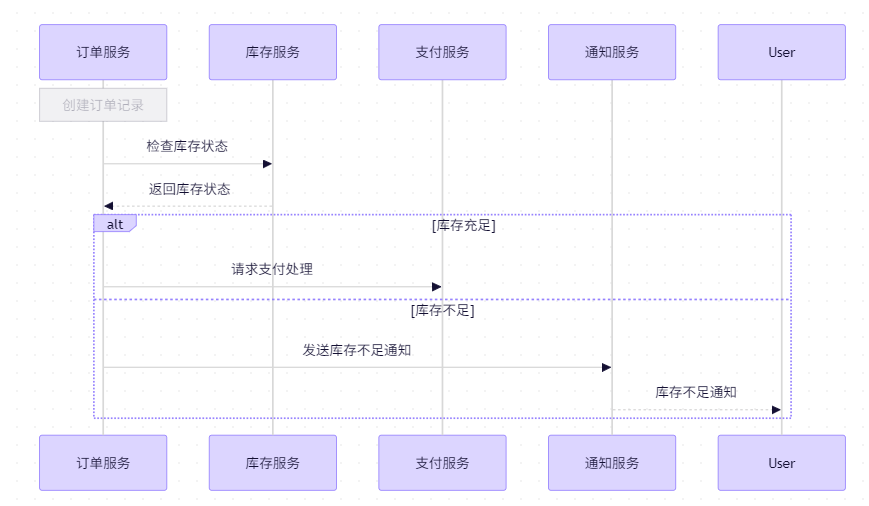
库存检查模块
支付处理模块
物流安排模块
通知服务模块
整个业务时序图
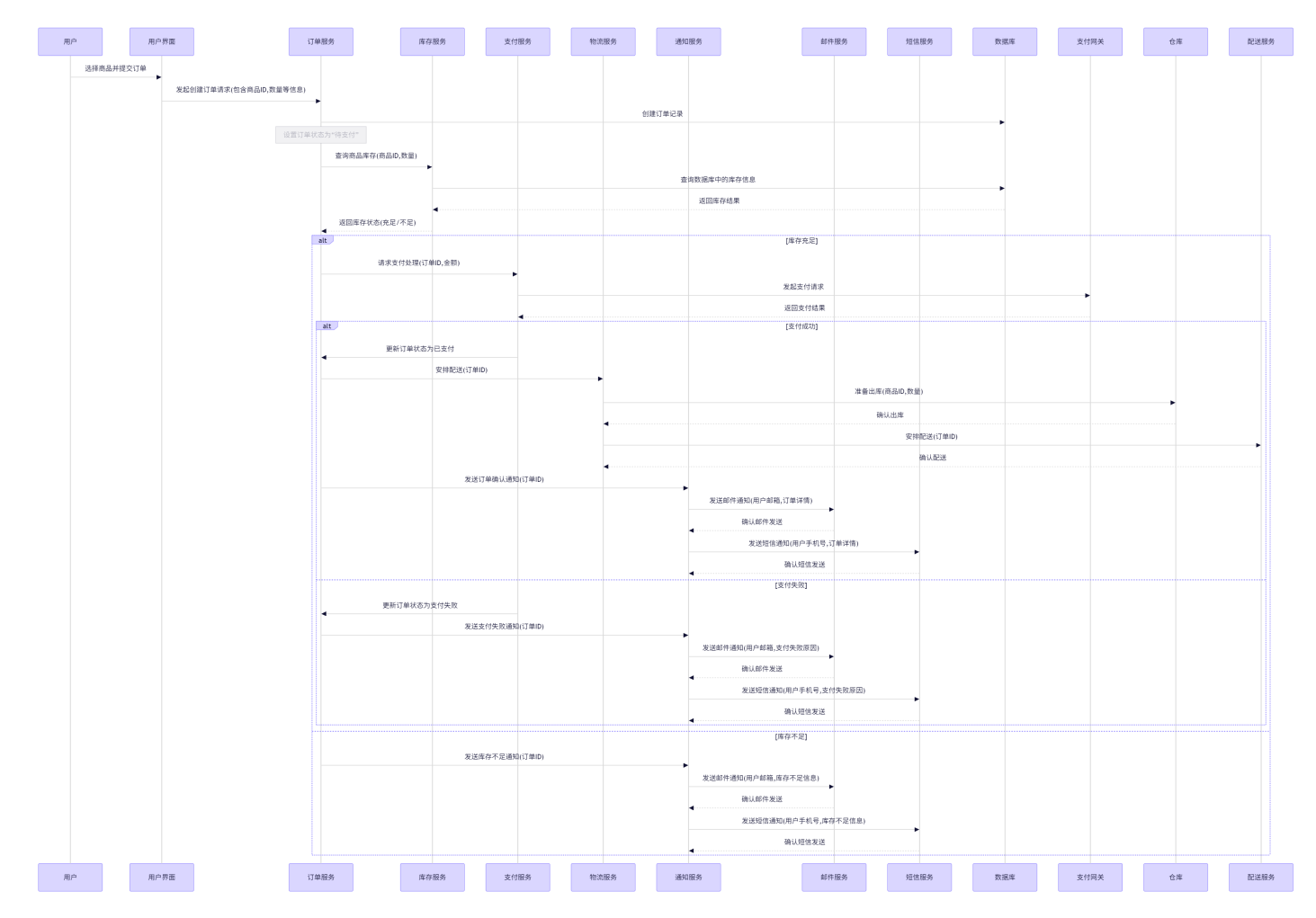
16.4 参考代码
package cn.tcmeta.usecompletablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;/*** 模拟电商平台订单系统* 展示 CompletableFuture 在实际业务中的综合应用*/
public class ECommerceOrderSystem {// 模拟的外部服务 (通常为 RPC 或 HTTP Client)private static final InventoryService inventoryService = new InventoryService();private static final UserService userService = new UserService();private static final CouponService couponService = new CouponService();private static final PaymentGateway paymentGateway = new PaymentGateway();private static final LogisticsService logisticsService = new LogisticsService();private static final NotificationService notificationService = new NotificationService();// 业务线程池 - 用于执行业务逻辑,避免阻塞ForkJoinPool.commonPoolprivate static final ExecutorService businessExecutor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10, r -> new Thread(r, "Business-Thread-"));// 通知线程池 - 用于发送通知等非关键路径操作private static final ExecutorService notificationExecutor =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2, r -> new Thread(r, "Notification-Thread-"));/*** 场景1: 创建订单 (核心业务 - 并行校验, 组合结果)** @param orderId 订单ID* @param userId 用户ID* @param productId 商品ID* @param quantity 数量* @param couponCode 优惠券码* @return CompletableFuture<Boolean> 订单创建是否成功*/public CompletableFuture<Boolean> createOrderAsync(String orderId,String userId,String productId,int quantity,String couponCode) {System.out.println("开始创建订单: " + orderId);// 1. 并行执行三个校验任务// 使用 supplyAsync 在 businessExecutor 中执行,避免阻塞主线程和 commonPoolCompletableFuture<Boolean> inventoryCheck = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> inventoryService.checkInventory(productId, quantity), businessExecutor).handle((result, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("库存校验异常: " + ex.getMessage());return false; // 校验失败}return result;});CompletableFuture<Boolean> creditCheck = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> userService.checkCredit(userId, quantity * 100), businessExecutor) // 假设单价100.handle((result, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("信用校验异常: " + ex.getMessage());return false;}return result;});CompletableFuture<Boolean> couponCheck = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> couponService.validateCoupon(couponCode, userId), businessExecutor).handle((result, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("优惠券校验异常: " + ex.getMessage());return false;}return result;});// 2. 使用 allOf 等待所有校验任务完成// allOf 返回 CompletableFuture<Void>,当所有任务完成时(无论成功或失败)即完成CompletableFuture<Void> allChecksDone = CompletableFuture.allOf(inventoryCheck, creditCheck, couponCheck);// 3. 当所有校验完成时,检查结果return allChecksDone.thenApply(v -> {try {// getNow 是安全的,因为 allOf 已经确保任务完成boolean invOk = inventoryCheck.getNow(false);boolean creditOk = creditCheck.getNow(false);boolean couponOk = couponCheck.getNow(false);System.out.printf("校验结果 - 库存: %b, 信用: %b, 优惠券: %b%n", invOk, creditOk, couponOk);// 所有校验必须通过if (invOk && creditOk && couponOk) {return true;} else {System.out.println("订单创建失败: 校验未通过");return false;}} catch (Exception e) {// 理论上不会到这里,因为用了 handleSystem.err.println("检查校验结果时出错: " + e.getMessage());return false;}}).thenCompose(success -> {// 4. 如果校验通过,继续创建订单 (thenCompose 用于链式异步操作)if (success) {System.out.println("所有校验通过,开始创建订单记录...");return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 模拟创建订单记录try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("订单记录创建成功: " + orderId);return true;}, businessExecutor)// 使用 thenCombine 组合后续操作 (扣减库存、锁定额度、标记优惠券).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {inventoryService.deductInventory(productId, quantity);System.out.println("库存已扣减");}, businessExecutor),(orderCreated, ignore) -> orderCreated // 忽略 runAsync 的 void 结果).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {userService.lockCredit(userId, quantity * 100);System.out.println("信用额度已锁定");}, businessExecutor),(prev, ignore) -> prev).thenCombine(CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {couponService.useCoupon(couponCode);System.out.println("优惠券已使用");}, businessExecutor),(prev, ignore) -> prev).handle((result, ex) -> {if (ex != null) {System.err.println("创建订单后续操作失败: " + ex.getMessage());// 这里应该有补偿机制 (如事务回滚、补偿任务),为简化省略return false;}return result;});} else {// 校验未通过,直接返回失败return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(false);}}).whenComplete((success, ex) -> {// 5. 最终处理: 发送通知 (使用独立线程池,失败不影响主流程)CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {try {if (ex != null) {notificationService.sendNotification(userId, "订单创建失败: " + ex.getMessage());System.out.println("已发送失败通知");} else if (success) {notificationService.sendNotification(userId, "订单创建成功! 订单号: " + orderId);System.out.println("已发送成功通知");}// 如果成功但后续操作失败,通知可能也需要发送,根据业务定} catch (Exception notificationEx) {System.err.println("发送通知失败,但订单创建成功: " + notificationEx.getMessage());// 通知失败通常记录日志,可能加入重试队列}}, notificationExecutor); // 使用独立线程池if (ex != null) {System.err.println("订单创建流程异常: " + ex.getMessage());} else {System.out.println("订单创建流程结束,结果: " + success);}});}/*** 场景2: 支付订单 (串行化操作, 异常处理)** @param orderId 订单ID* @param amount 支付金额* @return CompletableFuture<Boolean> 支付是否成功*/public CompletableFuture<Boolean> payOrderAsync(String orderId, double amount) {System.out.println("开始支付订单: " + orderId + ", 金额: " + amount);// 1. 调用支付网关 (异步)return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> paymentGateway.processPayment(orderId, amount), businessExecutor).handle((paymentResult, ex) -> {// 2. 处理支付结果或异常if (ex != null) {System.err.println("调用支付网关失败: " + ex.getMessage());return false;}if (!paymentResult) {System.out.println("支付网关返回失败");return false;}System.out.println("支付网关返回成功");return true;}).thenCompose(paymentSuccess -> {// 3. 如果支付成功,更新订单状态 (假设有一个订单服务)if (paymentSuccess) {return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(50);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("订单状态已更新为 '已支付': " + orderId);// 调用订单服务更新状态}, businessExecutor).thenApply(v -> true); // runAsync 返回 CompletableFuture<Void>, 转为 CompletableFuture<Boolean>} else {return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(false);}}).thenCompose(updateSuccess -> {// 4. 如果状态更新成功,触发发货流程if (updateSuccess) {System.out.println("准备触发发货流程...");// 发货是独立的异步流程,启动后立即返回,不等待其完成triggerShipmentAsync(orderId).exceptionally(ex -> {System.err.println("触发发货流程时发生异常,但支付已完成: " + ex.getMessage());return null; // 吞掉异常,不影响支付结果});return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(true);} else {return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(false);}});}/*** 触发发货流程 (独立的异步任务)** @param orderId 订单ID* @return CompletableFuture<Void> 发货流程的完成状态*/private CompletableFuture<Void> triggerShipmentAsync(String orderId) {System.out.println("触发发货流程: " + orderId);return CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.println("调用物流系统创建运单... " + orderId);boolean shipmentSuccess = logisticsService.createShipment(orderId, "LOGI001");if (shipmentSuccess) {System.out.println("运单创建成功,订单状态更新为 '已发货': " + orderId);// 更新订单状态notificationService.sendNotification("user123", "您的订单 " + orderId + " 已发货!");System.out.println("已发送发货通知");} else {System.err.println("运单创建失败: " + orderId);// 可能需要人工干预或重试机制}}, businessExecutor);}// 模拟的外部服务类static class InventoryService {private final AtomicInteger stock = new AtomicInteger(100); // 初始库存100public boolean checkInventory(String productId, int quantity) {try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}int currentStock = stock.get();boolean result = currentStock >= quantity;System.out.printf("库存校验 - 商品: %s, 需求: %d, 当前: %d, 通过: %b%n",productId, quantity, currentStock, result);return result;}public void deductInventory(String productId, int quantity) {try {Thread.sleep(150);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}stock.addAndGet(-quantity);System.out.printf("扣减库存 - 商品: %s, 数量: %d, 剩余: %d%n",productId, quantity, stock.get());}}static class UserService {private final AtomicInteger creditLimit = new AtomicInteger(5000); // 初始额度5000public boolean checkCredit(String userId, double amount) {try {Thread.sleep(180);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}int currentLimit = creditLimit.get();boolean result = currentLimit >= amount;System.out.printf("信用校验 - 用户: %s, 需求: %.2f, 当前: %d, 通过: %b%n",userId, amount, currentLimit, result);return result;}public void lockCredit(String userId, double amount) {try {Thread.sleep(120);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}creditLimit.addAndGet(-(int) amount);System.out.printf("锁定信用额度 - 用户: %s, 金额: %.2f, 剩余额度: %d%n",userId, amount, creditLimit.get());}}static class CouponService {private volatile boolean couponValid = true;public boolean validateCoupon(String code, String userId) {try {Thread.sleep(250);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}boolean result = "SAVE10".equals(code) && couponValid;System.out.printf("优惠券校验 - 码: %s, 用户: %s, 有效: %b, 通过: %b%n",code, userId, couponValid, result);return result;}public void useCoupon(String code) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}if ("SAVE10".equals(code)) {couponValid = false; // 标记为已使用}System.out.println("优惠券已标记为使用: " + code);}}static class PaymentGateway {// 模拟 90% 成功率private final AtomicInteger callCount = new AtomicInteger(0);public boolean processPayment(String orderId, double amount) {try {Thread.sleep(300);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}boolean success = callCount.incrementAndGet() % 10 != 0; // 每10次失败1次System.out.printf("支付网关处理 - 订单: %s, 金额: %.2f, 成功: %b%n",orderId, amount, success);return success;}}static class LogisticsService {public boolean createShipment(String orderId, String trackingNumber) {try {Thread.sleep(400);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}// 模拟 95% 成功率boolean success = Math.random() > 0.05;System.out.printf("物流系统创建运单 - 订单: %s, 运单号: %s, 成功: %b%n",orderId, trackingNumber, success);return success;}}static class NotificationService {public void sendNotification(String userId, String message) {try {Thread.sleep(80);} catch (InterruptedException e) {}System.out.printf("发送通知 - 用户: %s, 内容: %s%n", userId, message);// 实际中可能是调用短信、邮件、站内信服务}}// --- 主函数演示 ---public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ECommerceOrderSystem system = new ECommerceOrderSystem();// 演示1: 成功创建订单System.out.println("=== 演示1: 创建订单 (成功) ===");CompletableFuture<Boolean> createResult1 = system.createOrderAsync("ORD001", "user123", "PROD001", 2, "SAVE10");Boolean success1 = createResult1.get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 设置超时System.out.println("订单创建结果 (成功): " + success1);System.out.println("\n" + "=".repeat(50) + "\n");// 演示2: 支付订单 (模拟成功)System.out.println("=== 演示2: 支付订单 ===");CompletableFuture<Boolean> payResult = system.payOrderAsync("ORD001", 200.0);Boolean paySuccess = payResult.get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("支付结果: " + paySuccess);// 等待发货流程完成 (仅用于演示观察)Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println("\n" + "=".repeat(50) + "\n");// 演示3: 创建订单 (失败 - 优惠券无效)System.out.println("=== 演示3: 创建订单 (失败 - 优惠券无效) ===");// 先让之前的优惠券被使用system.createOrderAsync("ORD002", "user123", "PROD001", 1, "SAVE10").get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 再次使用同一优惠券CompletableFuture<Boolean> createResult2 = system.createOrderAsync("ORD003", "user123", "PROD001", 1, "SAVE10");Boolean success2 = createResult2.get(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.println("订单创建结果 (失败): " + success2);// 关闭线程池businessExecutor.shutdown();notificationExecutor.shutdown();// 等待线程池关闭if (!businessExecutor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {businessExecutor.shutdownNow();}if (!notificationExecutor.awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {notificationExecutor.shutdownNow();}System.out.println("\n演示结束。");}
}
相关日志输出:
=== 演示1: 创建订单 (成功) ===
开始创建订单: ORD001
信用校验 - 用户: user123, 需求: 200.00, 当前: 5000, 通过: true
库存校验 - 商品: PROD001, 需求: 2, 当前: 100, 通过: true
优惠券校验 - 码: SAVE10, 用户: user123, 有效: true, 通过: true
校验结果 - 库存: true, 信用: true, 优惠券: true
所有校验通过,开始创建订单记录...
订单记录创建成功: ORD001
优惠券已标记为使用: SAVE10
优惠券已使用
锁定信用额度 - 用户: user123, 金额: 200.00, 剩余额度: 4800
信用额度已锁定
扣减库存 - 商品: PROD001, 数量: 2, 剩余: 98
库存已扣减
订单创建流程结束,结果: true
订单创建结果 (成功): true===================================================== 演示2: 支付订单 ===
开始支付订单: ORD001, 金额: 200.0
发送通知 - 用户: user123, 内容: 订单创建成功! 订单号: ORD001
已发送成功通知
支付网关处理 - 订单: ORD001, 金额: 200.00, 成功: true
支付网关返回成功
订单状态已更新为 '已支付': ORD001
准备触发发货流程...
触发发货流程: ORD001
支付结果: true
调用物流系统创建运单... ORD001
物流系统创建运单 - 订单: ORD001, 运单号: LOGI001, 成功: true
运单创建成功,订单状态更新为 '已发货': ORD001
发送通知 - 用户: user123, 内容: 您的订单 ORD001 已发货!
已发送发货通知===================================================== 演示3: 创建订单 (失败 - 优惠券无效) ===
开始创建订单: ORD002
信用校验 - 用户: user123, 需求: 100.00, 当前: 4800, 通过: true
库存校验 - 商品: PROD001, 需求: 1, 当前: 98, 通过: true
优惠券校验 - 码: SAVE10, 用户: user123, 有效: false, 通过: false
校验结果 - 库存: true, 信用: true, 优惠券: false
订单创建失败: 校验未通过
订单创建流程结束,结果: false
开始创建订单: ORD003
信用校验 - 用户: user123, 需求: 100.00, 当前: 4800, 通过: true
库存校验 - 商品: PROD001, 需求: 1, 当前: 98, 通过: true
优惠券校验 - 码: SAVE10, 用户: user123, 有效: false, 通过: false
校验结果 - 库存: true, 信用: true, 优惠券: false
订单创建失败: 校验未通过
订单创建流程结束,结果: false
订单创建结果 (失败): false演示结束。
16.5 关键点总结
- 线程池管理: 永远不要依赖
ForkJoinPool.commonPool()执行耗时或阻塞的业务逻辑。创建独立的ExecutorService(businessExecutor) 来控制资源和避免相互影响。 - 并行化 (
allOf): 使用CompletableFuture.allOf()并行执行多个独立的、可以同时进行的任务(如校验),显著减少总耗时。 - 任务组合 (
thenCombine,thenCompose)thenCombine: 组合两个CompletableFuture的结果,通常用于并行任务后的聚合。thenCompose: 将一个CompletableFuture的结果作为输入,启动另一个异步任务,用于构建异步的“流水线”。
- 异常处理 (
handle,exceptionally,whenComplete)handle: 最常用,无论成功或失败都会执行,可用于转换结果或进行恢复。exceptionally: 仅在发生异常时执行,用于提供默认值或进行特定异常处理。whenComplete: 类似handle,但不改变结果,常用于资源清理或最终通知。
- 非关键路径异步化: 像发送通知这样的操作,即使失败也不应影响主业务流程(如订单创建)。使用独立的线程池(
notificationExecutor)并exceptionally吞掉异常或记录日志。 - 超时控制: 在
get()时使用带超时的版本 (get(timeout, unit)),防止无限期等待。 - 资源清理: 记得在程序结束时
shutdown()自定义的线程池。
