算法第五十一天:图论part02(第十一章)
1.岛屿数量
99. 岛屿数量
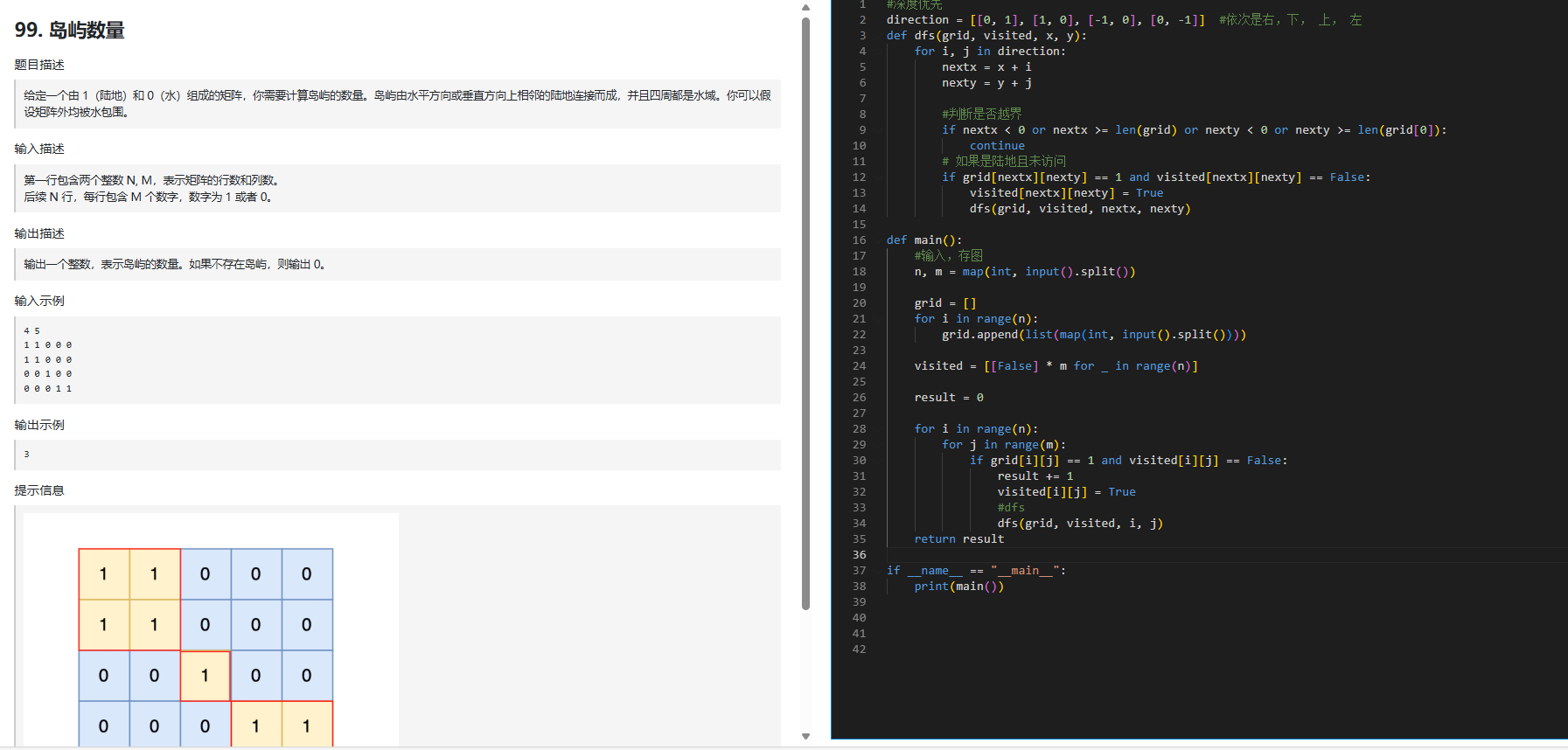
🌟 思路总结 — DFS 版
1️⃣ 问题本质
给定一个二维矩阵
grid,1 表示陆地,0 表示水统计岛屿数量,每个岛屿由上下左右相邻的陆地组成
本质是 在二维网格中找连通块 的问题。
2️⃣ 核心思路
遍历矩阵
对每个格子
(i,j):
如果是陆地 (
grid[i][j] == 1) 且未访问过
→ 说明发现一个新岛屿,岛屿计数 +1DFS 扩展岛屿
从新发现的陆地出发,深度优先递归访问上下左右相邻的陆地
每访问一个陆地就标记为已访问
visited[i][j] = True递归结束后,这块岛屿的所有陆地都被标记,避免重复计数
返回岛屿数量
遍历完矩阵后,岛屿计数就是答案
3️⃣ 核心技巧
方向数组:
direction = [[0,1],[1,0],[0,-1],[-1,0]] # 右、下、左、上
遍历邻居时统一处理
next_x = x + dx,next_y = y + dy
访问标记:
用
visited二维布尔数组标记已访问的陆地DFS 或 BFS 入队/递归时立即标记,防止重复访问
越界判断:
if nextx < 0 or nextx >= n or nexty < 0 or nexty >= m: continue
避免访问矩阵外的元素
#深度优先
direction = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]] #依次是右,下, 上, 左
def dfs(grid, visited, x, y):for i, j in direction:nextx = x + inexty = y + j#判断是否越界if nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(grid) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(grid[0]):continue# 如果是陆地且未访问if grid[nextx][nexty] == 1 and visited[nextx][nexty] == False:visited[nextx][nexty] = Truedfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)def main():#输入,存图n, m = map(int, input().split())grid = []for i in range(n):grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]result = 0for i in range(n):for j in range(m):if grid[i][j] == 1 and visited[i][j] == False:result += 1visited[i][j] = True#dfsdfs(grid, visited, i, j)return resultif __name__ == "__main__":print(main())2.广度优先搜索的理论基础
步骤:先将起点加入队列, 标记为true, 取出当前节点,沿四个方向遍历判断是否访问过,未访问则加入队列,标记为true。直至队列为空则广搜结束
direction = [[0,1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]def bfs(grid, visited, x, y):que = deque()que.apppend(x, y)visited[x][y] == Truewhile que:curx, cury = que.popleft()for i, j in direction:nextx = curx + inexty = cury + jif nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(grid) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(grid[0]):continueif not visited[nextx][nexty]:que.append([nextx, nexty])visited[nextx][nexty] == 1
岛屿数量用广度搜索重做一遍:
from collections import dequedirection = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]] def bfs(grid, visited, x, y):queue = deque()queue.append([x, y])visited[x][y] = Truewhile queue:cur_x, cur_y = queue.popleft() #取出队首元素for i, j in direction:nextx = cur_x + inexty = cur_y + jif nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(grid) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(grid[0]):continueif not visited[nextx][nexty] and grid[nextx][nexty] == 1:visited[nextx][nexty] = Truequeue.append([nextx, nexty])def main():n, m = map(int, input().split())grid = []for i in range(n):grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]result = 0for i in range(n):for j in range(m):if grid[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:result += 1bfs(grid, visited, i, j)print(result)if __name__ == "__main__":main()
3.岛屿的最大面积
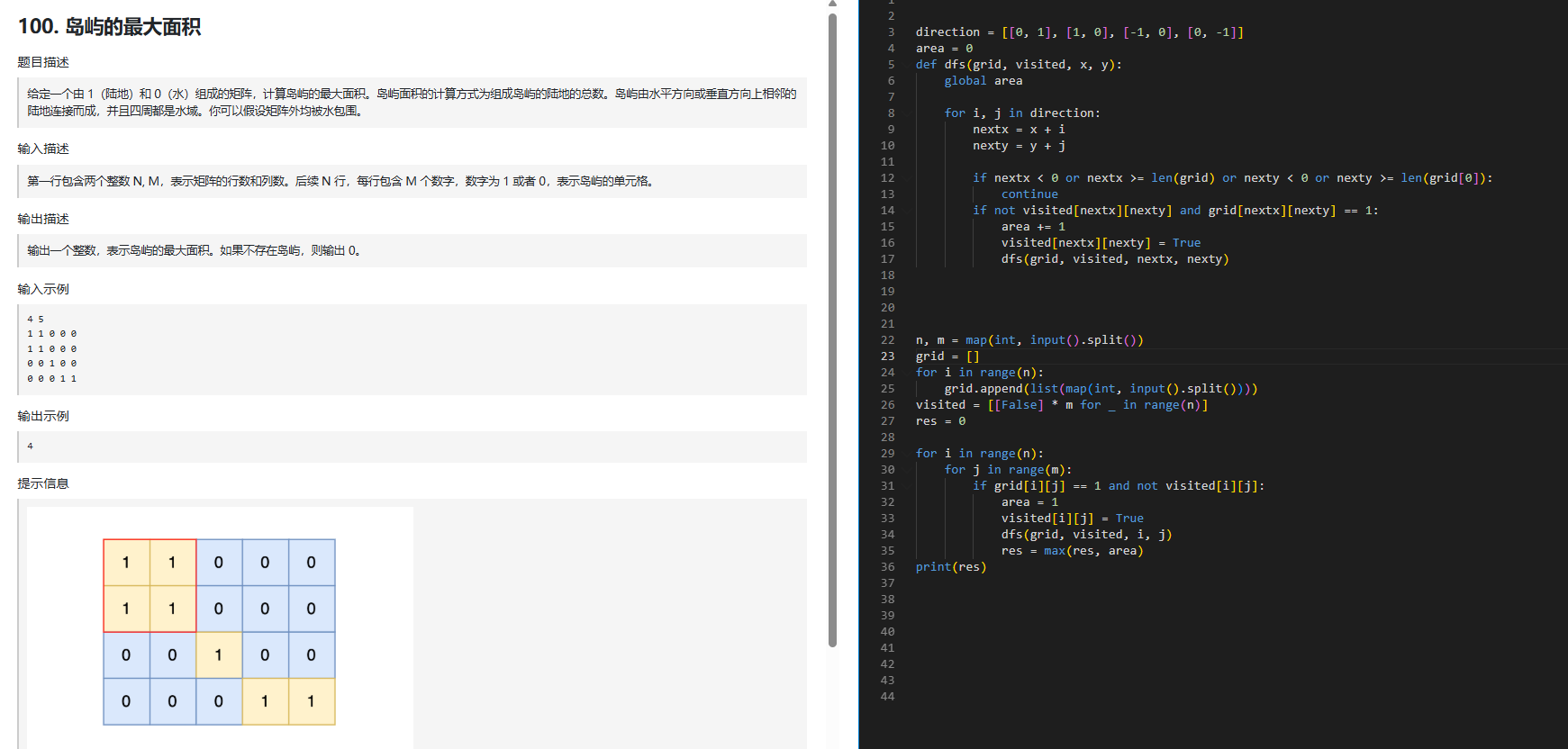
📝 代码功能
这是一个求最大岛屿面积的程序(不是岛屿数量)。
输入一个
n×m的矩阵grid,1表示陆地,0表示水。使用 DFS(深度优先搜索)遍历每一块岛屿,同时统计它的面积。
最终输出所有岛屿中的最大面积。
🔑 核心思路
方向数组
direction = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]用来表示四个相邻方向:右、下、上、左。
DFS 深度优先搜索
def dfs(grid, visited, x, y): global area for i, j in direction: nextx = x + i nexty = y + j ...
从一个陆地
(x, y)出发,递归探索它相邻的陆地;每发现一个新的陆地,就
area += 1;并且标记
visited[nextx][nexty] = True,避免重复访问。遍历矩阵
for i in range(n): for j in range(m): if grid[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]: area = 1 visited[i][j] = True dfs(grid, visited, i, j) res = max(res, area)
遍历整个矩阵;
每遇到一个未访问的陆地
(i, j),说明发现一块新岛屿;从这里开始 DFS,计算该岛屿面积;
更新最大面积
res。
direction = [[0, 1], [1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, -1]]
area = 0
def dfs(grid, visited, x, y):global areafor i, j in direction:nextx = x + inexty = y + jif nextx < 0 or nextx >= len(grid) or nexty < 0 or nexty >= len(grid[0]):continueif not visited[nextx][nexty] and grid[nextx][nexty] == 1:area += 1visited[nextx][nexty] = Truedfs(grid, visited, nextx, nexty)n, m = map(int, input().split())
grid = []
for i in range(n):grid.append(list(map(int, input().split())))
visited = [[False] * m for _ in range(n)]
res = 0for i in range(n):for j in range(m):if grid[i][j] == 1 and not visited[i][j]:area = 1visited[i][j] = Truedfs(grid, visited, i, j)res = max(res, area)
print(res)今日结束啦!!!
