JUC之CompletableFuture【中】
文章目录
- 四、CompletableFuture基本使用
- 4.1 默认线程池、无返回值
- 4.2 默认线程池、有返回值
- 4.3 自定义线程池、有返回值
- 4.4 CompletableFuture 获取结果
- 五、对结果进行处理
- 5.1 方法说明
- 5.2 示例
- 5.3 thenApply vs thenApplyAsync
- 5.3.1 核心区别: 执行线程不同
- 5.3.2 thenApply: 同步执行(使用前序任务线程或者当前线程)
- 5.3.3 thenApplyAsync: 【异步执行: 使用新线程】
- 5.3.4 关键差异总结
- 5.3.5 典型应用场景
- 六、对计算结果进行消费
- 6.1 thenRun相关方法
- 6.2 thenAccept类型的方法
- 6.3 thenApply
- 七、theAcceptBoth
- 7.1 基本概念
- 7.2 方法签名
- 7.3 关键特性与行为
- 7.4 应用场景
- 7.5 一些示例
- 7.5.1 thenAcceptBothAsync
- 7.5.2 thenAcceptBoth
- 八、acceptEither
- 8.1 示例
- 8.2 thenAcceptBoth和acceptEither区别
- 九、thenCombine 合并操作
- 9.1 概述
- 9.2 示例一
- 9.3 示例二
- 十、anyOf
- 10.1 概述
- 10.2 示例
- 十一、allOf方法
四、CompletableFuture基本使用
4.1 默认线程池、无返回值
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
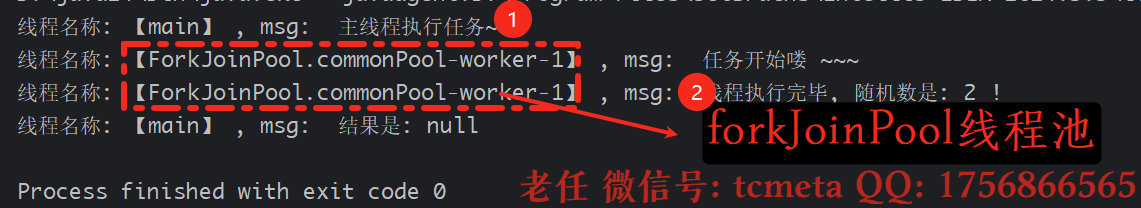
public class CompletionStageDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 任务开始喽 ~~~");int n = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(4000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 线程执行完毕, 随机数是: " + n + " !");});System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 主线程执行任务~~");Void result = completableFuture.get();System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 结果是: " + result);}
}
获取对象方式:
- 没有传入自己定义的线程池,那么使用的就是默认线程池,即:
ForkJoinPool, 通过打印线池的名称也可以证明这一点:
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {return asyncRunStage(ASYNC_POOL, runnable);
}private static final Executor ASYNC_POOL = USE_COMMON_POOL ?ForkJoinPool.commonPool() : new ThreadPerTaskExecutor();
4.2 默认线程池、有返回值
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// 默认线程池、有返回值CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 王麻子要装逼了~~~~ ");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}int n = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 线程执行完毕, 随机数是: " + n + " !");return n;}).whenComplete((n, e) -> {// 如果产生异常, 则直接对其进行操作即可if(e == null) {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), "whenComplete 线程执行完毕, 随机数是: " + n + " !");}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();return -1;});System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 主线程, 开始执行任务~~~");}
}
程序解析:
- 处理返回值姿势
// 参数 T, 表示,执行完任务,返回的结果.
// Throwable, 表示执行任务的时候,有异常产生,抛出的异常;
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}// BiFunction
void accept(T t, U u);
- 异常处理方法
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn) {return uniExceptionallyStage(fn);
}R apply(T t);
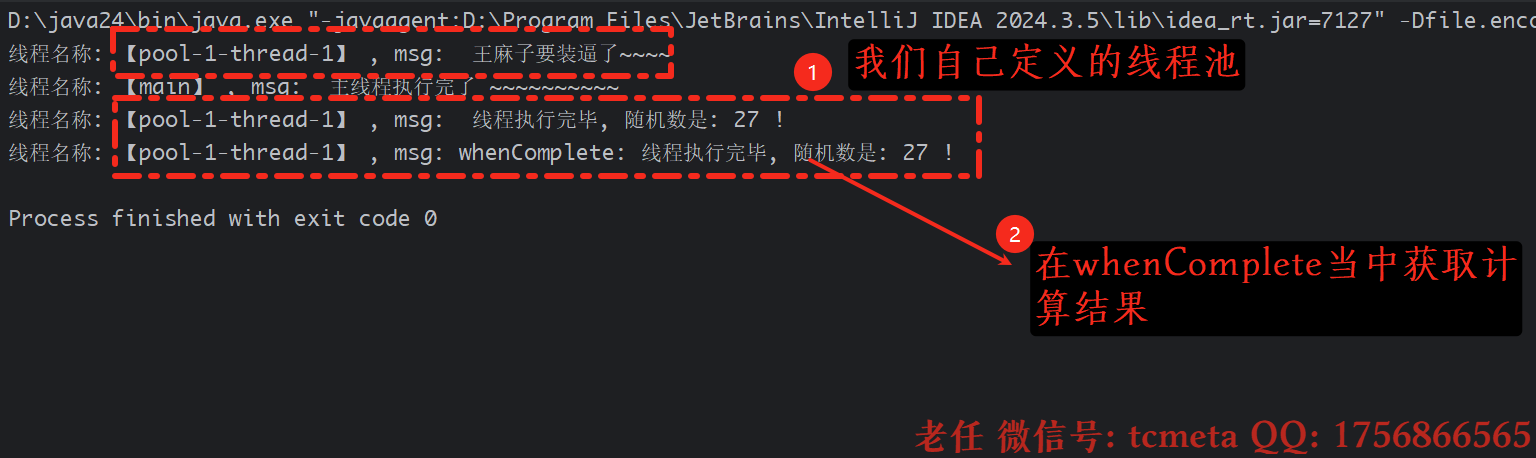
问题总结: 使用有默认线程池,想要将计算结果返回,但是ForkJoinPool线程池由于主线程退出了也会自动退出,所以无法通过whenComplete获取返回值
4.3 自定义线程池、有返回值
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 定义一个线程池ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 王麻子要装逼了~~~~ ");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(5000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}int n = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 线程执行完毕, 随机数是: " + n + " !");return n;}, executorService).whenComplete((n, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), "whenComplete: 线程执行完毕, 随机数是: " + n + " !");}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();return -1;});System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 主线程执行完了 ~~~~~~~~~~ ");executorService.shutdown();}
}
4.4 CompletableFuture 获取结果
| 方法名称 | 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| get | 无 | 等待拿到计算结果,会抛出异常 |
| get(long timeout,TimeUnit t) | Long, 等待时间, TimeUnit, 时间单位 | 在指定的时间内,获取结果,会抛出异常 |
| getNow(T valueIfAbsent) | valueIfAbsent, 如果计算未完成,则返回的值「缺省值」 | 如果完成则返回结果值(或抛出任何遇到的异常),否则返回给定的 valueIfAbsent。 |
| join | 无 | 获取计算结果 |
| complete | T value | 如果尚未完成,则将get()和相关方法返回的值设置为给定值。 参数:value – 结果值 |
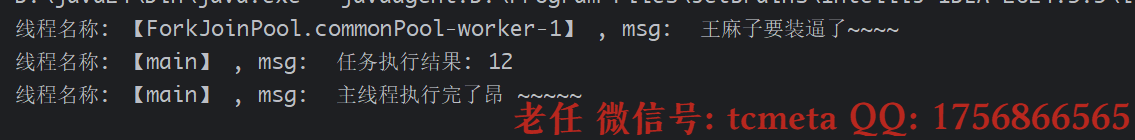
1. get方式获取结果
get阻塞的方式获取执行结果
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo03 {public static void main(String[] args) {CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 王麻子要装逼了~~~~ ");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(3000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);});// !. 使用【get】方式获取结果try {Integer result = completableFuture.get();System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 任务执行结果: " + result);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 主线程执行完了昂 ~~~~~");}
}
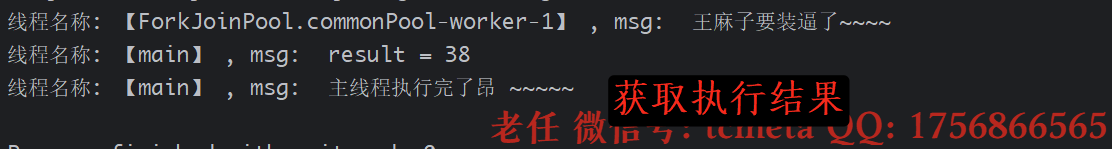
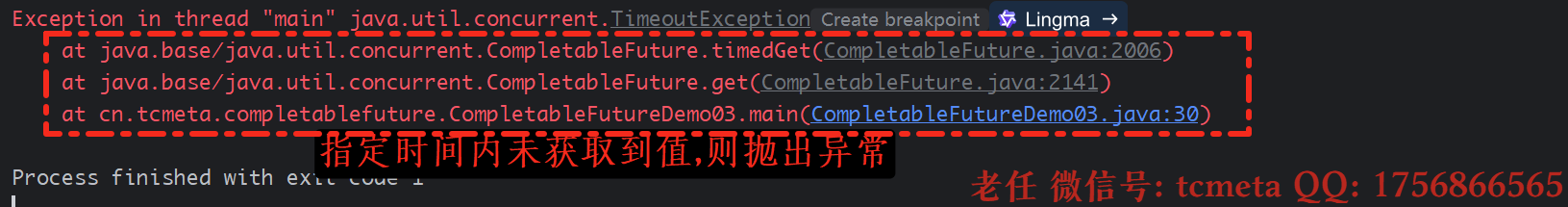
2. get指定获取结果的等待时间
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo03 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException, TimeoutException {CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 王麻子要装逼了~~~~ ");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(3000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100);});// !. 使用【get】方式获取结果// 2. 使用【get】指定等待时间方式获取结果Integer result = completableFuture.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " result = " + result);System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 主线程执行完了昂 ~~~~~");}
}public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException {long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);Object r;if ((r = result) == null)r = timedGet(nanos);return (T) reportGet(r, "get");
}
正确获取结果:
等待时间到了,则抛出异常:
3. join方式获取
join方式获取, 操作和get无参姿势一样,不同之处在于, 获取不到值的时候,不会抛出异常.很少使用;
- 使用频率不高
4. getNow方式获取
如果没有获取到值,则会使用给定的缺省信息;
较少使用;
5. complete方法获取, 指定缺省值,会打断正常任务的执行
public boolean complete(T value) {boolean triggered = completeValue(value);postComplete();return triggered;
}
五、对结果进行处理
5.1 方法说明
| 方名名称 | 参数说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| thenApply( Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) | 函数式接口 | 返回一个新的 CompletionStage,当此阶段正常完成时,将使用此阶段的结果作为所提供函数的参数来执行该阶段。此方法类似于Optional.map和Stream.map . 哪个阶段出现异常,处理中止,不走下个流程 |
| public CompletionStage handle (BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn); | 没有异常抛出 | 返回一个新的 CompletionStage,当此阶段正常或异常完成时,将使用此阶段的结果和异常作为所提供函数的参数来执行该阶段 |
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}
5.2 示例
- 使用
【thenApply】处理
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class CompletableFutureDemo06 {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, 100);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第一步");return 1000;}, executorService).thenApply(r1 -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第二步");return r1 + 1000;}).thenApply(r2 ->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第三步");return r2 + 1000;}).whenComplete((res, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 计算结果是: " + res);}}).exceptionally(e -> {e.printStackTrace();return -1;});executorService.shutdown();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 主线程执行完成了哦。。。。");}
}

- 使用
【thenApplyAsync】进行处理
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class CompletableFutureDemo07 {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, 100);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第一步");return 1000;}, executorService).thenApplyAsync(r1 -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第二步");return r1 + 1000;}, executorService).thenApplyAsync(r2 ->{System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 正计算第三步");return r2 + 1000;}, executorService).whenCompleteAsync((res, e) -> {if (e == null) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 计算结果是: " + res);}}, executorService).exceptionallyAsync(e -> {e.printStackTrace();return -1;}, executorService);executorService.shutdown();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 主线程执行完成了哦。。。。");}
}

5.3 thenApply vs thenApplyAsync
在 CompletableFuture 中,thenApply 和 thenApplyAsync 都是用于对前一个任务的结果进行转换的方法,但它们的执行线程和时机有本质区别,这直接影响代码的并发行为。
5.3.1 核心区别: 执行线程不同
两者的功能相同(都是接收前一个任务的结果,通过函数转换为新结果),但执行转换操作的线程不同:
| 方法 | 执行线程 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
thenApply(Function) | 前一个任务的线程(如果前一个任务已完成,则用当前线程) | 转换逻辑简单、耗时短,无需额外线程 |
thenApplyAsync(Function) | 默认线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool ()) 或指定的自定义线程池 | 转换逻辑复杂、耗时长,需要异步执行不阻塞前序任务线程 |
5.3.2 thenApply: 同步执行(使用前序任务线程或者当前线程)
thenApply 的转换操作会复用前一个任务的执行线程。如果前一个任务已经完成,则直接在当前调用线程中执行。
- 情况一:前一个任务
supplyAsync已经完成 (Synchronous Callback Execution)- 如果
supplyAsync启动的任务在主线程执行到thenApply之前就已经完成了,那么CompletableFuture的状态已经是completed。 - 当你在主线程调用
thenApply时,系统会立即执行你传入的Function,因为没有“等待”的必要了。 - 结果:
thenApply的代码在主线程上同步执行。
- 如果
- 情况二:前一个任务
supplyAsync尚未完成 (Asynchronous Callback Execution)- 如果
supplyAsync启动的任务在主线程执行到thenApply时还未完成,那么CompletableFuture的状态是incomplete。 - 当你在主线程调用
thenApply时,系统只是将你的Function注册为一个待执行的回调。 - 当
supplyAsync内部的任务最终在ForkJoinPool的某个线程中完成时,该线程会立即触发所有已注册的回调(包括thenApply)。 - 结果:
thenApply的代码在ForkJoinPool的工作线程上执行。
- 如果
测试代码:
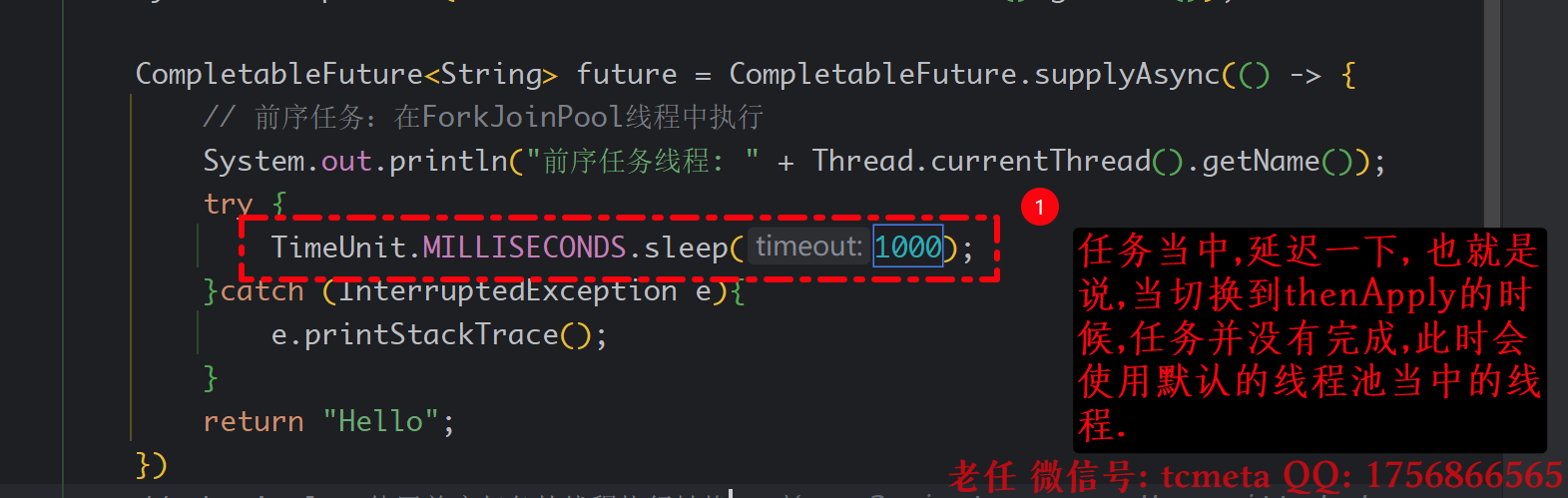
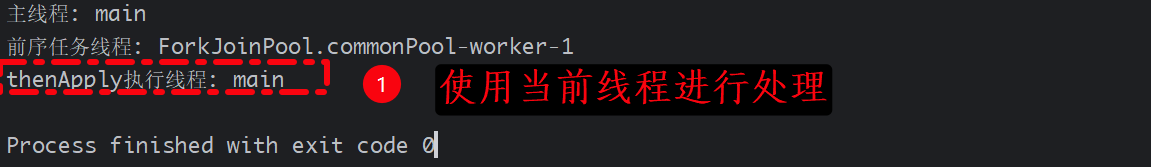
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ThenApplyDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("主线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 前序任务:在ForkJoinPool线程中执行System.out.println("前序任务线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return "Hello";})// thenApply:使用前序任务的线程执行转换.thenApply(s -> {System.out.println("thenApply执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());return s + " World";});future.join(); // 等待完成}
}
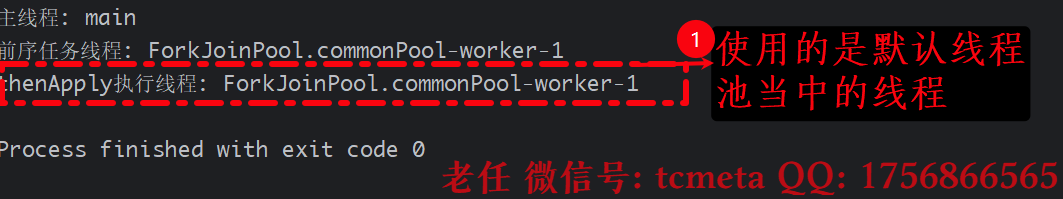
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class ThenApplyDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("主线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {// 前序任务:在ForkJoinPool线程中执行System.out.println("前序任务线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());// try {// TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);// }catch (InterruptedException e){// e.printStackTrace();// }return "Hello";})// thenApply:使用前序任务的线程执行转换.thenApply(s -> {System.out.println("thenApply执行线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());return s + " World";});future.join(); // 等待完成}
}
由于上一个任务已经执行完了, 所以此时再切换的时候,直接使用的是当前线程来执行.
由于cpu性能不同,测试结果可能出现出入
5.3.3 thenApplyAsync: 【异步执行: 使用新线程】
- 方法签名
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn)
// 或者指定自定义的 Executor
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor)
- 无参版:使用 默认公共线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool ()) 的线程执行转换。
- 带
Executor参数版:使用 自定义线程池 的线程执行转换。
5.3.4 关键差异总结
- 线程复用
thenApply可能复用前序任务的线程,避免线程切换开销。thenApplyAsync一定会使用新线程(来自默认或自定义线程池),有额外的线程切换成本。
- 阻塞风险
thenApply如果转换逻辑耗时,会阻塞前序任务的线程(可能影响其他任务)。thenApplyAsync的转换逻辑在独立线程中执行,不会阻塞前序任务线程。
- 使用选择
- 简单转换(如字符串拼接、数值计算)用
thenApply,效率更高。 - 复杂转换(如数据库查询、网络请求)用
thenApplyAsync,避免阻塞。
- 简单转换(如字符串拼接、数值计算)用
| 特性 | thenApply | thenApplyAsync |
|---|---|---|
| 执行线程 | 通常与前一个任务完成的线程相同。 | 在ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 或指定的 Executor 的线程中执行。 |
| 是否异步 | 逻辑上是异步回调,但执行上下文与前一个任务共享。 | 强制异步执行,一定会切换到另一个线程。 |
| 线程切换开销 | 通常较低(无额外线程切换)。 | 有额外的线程切换开销。 |
| 阻塞性风险 | 如果前一个任务在主线程完成,且 thenApply 的函数很耗时,则会阻塞主线程。 | 不会阻塞前一个任务的完成线程(如主线程),因为执行被移交到其他线程。 |
| 灵活性 | 较低。 | 较高(可以指定自定义 Executor)。 |
5.3.5 典型应用场景
thenApply场景:轻量级转换,例如对查询结果做简单格式化(如s -> s.trim())。thenApplyAsync场景:重量级转换,例如将原始数据解析为复杂对象、调用另一个服务处理数据等。
六、对计算结果进行消费
| public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action); | 传入Runnable接口,对前后流程都没有影响 | 有出参,没有入参 |
|---|---|---|
| public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action); | 传入Consumer接口,消费数据,没有出参 | 没有出参 |
| public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn); | Function接口,有入参,有出参 | 有出参,有出参,可以拿到计算的返回值 |
6.1 thenRun相关方法
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {return uniRunStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor) {return uniRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
6.2 thenAccept类型的方法
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(null, action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action) {return uniAcceptStage(defaultExecutor(), action);
}public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor) {return uniAcceptStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
6.3 thenApply
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {return uniApplyStage(defaultExecutor(), fn);
}public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor) {return uniApplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), fn);
}
七、theAcceptBoth
thenAcceptBoth 是 CompletableFuture 提供的用于组合(Composing) 两个异步任务结果的强大工具。它允许你在两个 CompletableFuture 都成功完成时,执行一个操作来消费它们的结果,但这个操作本身不返回新的值(即返回 void)。
7.1 基本概念
- 目的:等待两个异步任务(
CompletableFuture)都完成,然后基于它们的结果执行一个副作用操作(如打印日志、更新 UI、写入数据库等),该操作不产生新的结果用于后续链式调用。 - 行为:
thenAcceptBoth会注册一个回调。当调用它的CompletableFuture和 作为参数传入的另一个CompletableFuture都成功完成时,这个回调就会被触发。 - 返回值:它返回一个新的
CompletableFuture<Void>。这个新的CompletableFuture代表了thenAcceptBoth本身所执行的操作的完成状态。当传入的函数执行完毕后,这个新的CompletableFuture也就完成了。它的泛型是Void,因为它不产生有意义的结果。
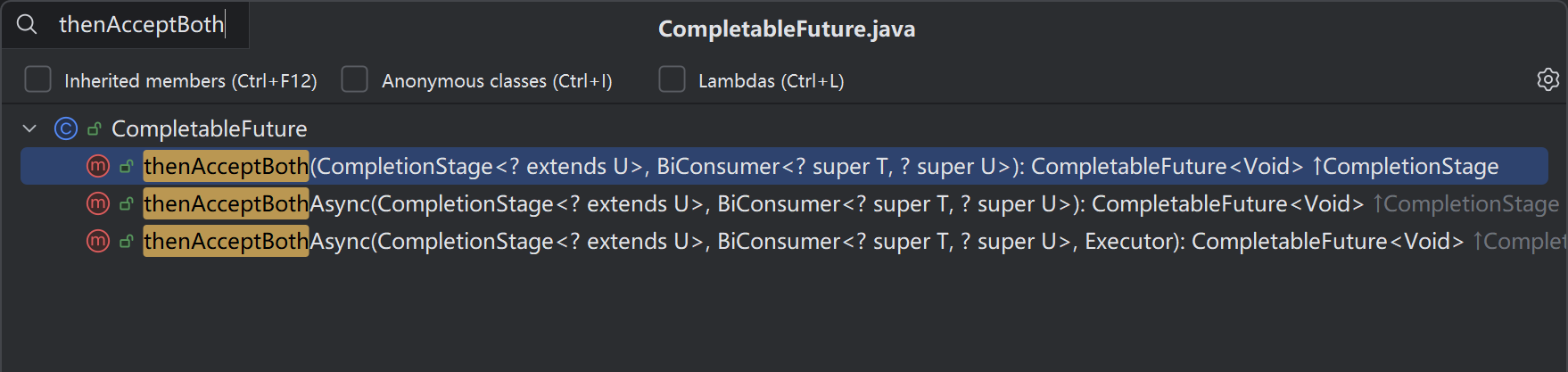
7.2 方法签名
CompletableFuture 类提供了两个重载版本的 thenAcceptBoth:
使用默认异步执行器 (ForkJoinPool.commonPool())
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action
)
-
``other
: 另一个需要等待完成的CompletionStage(通常是另一个CompletableFuture`)。 -
action: 一个 BiConsumer 函数式接口的实现。它接收两个参数:
- 第一个参数是调用 thenAcceptBoth 的这个 CompletableFuture 的结果 (T)。
- 第二个参数是 other 这个 CompletableFuture 的结果 (U)。
- BiConsumer 的 accept 方法返回 void,所以这个操作是消费性的,不返回新值。
- 执行线程:
action函数的执行线程是不确定的。它可能在this或other任一CompletableFuture完成的线程上执行(类似于thenApply的行为,取决于哪个任务后完成以及完成时的状态)。这通常发生在ForkJoinPool.commonPool()的线程中,但不保证。
指定自定义执行器 (Executor)
public <U> CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action,Executor executor
)
executor: 一个自定义的Executor,用于异步执行action函数。- 执行线程:
action函数总是被提交到你提供的executor所管理的线程池中执行。这提供了对执行线程的精确控制,避免阻塞关键线程(如主线程或 I/O 线程)。
7.3 关键特性与行为
- 等待两者完成:
thenAcceptBoth必须等到两个CompletableFuture都成功完成才会触发action。 - 短路行为 (Short-circuiting)
- 如果任何一个
CompletableFuture以异常结束(即completeExceptionally),那么thenAcceptBoth不会执行action函数。 - 返回的新的
CompletableFuture<Void>会继承那个异常状态。如果两个都异常,通常继承第一个遇到的异常。
- 如果任何一个
- 无返回值:与
thenCombine或thenApply不同,thenAcceptBoth不产生可用于后续thenApply或thenCompose的新值。它专注于执行有副作用的操作。 - 执行线程的不确定性:如前所述,基础版本的执行线程取决于任务完成的时机和线程。使用
thenAcceptBothAsyncwithExecutor可以消除这种不确定性。
7.4 应用场景
thenAcceptBoth 非常适合以下场景:
- 日志记录:当两个异步操作(如获取用户信息和获取订单信息)都完成后,记录一条日志。
- UI 更新:在 GUI 应用中,等待数据加载和视图准备都完成后,更新界面。
- 资源清理或通知:在两个异步任务(如文件上传和数据库记录更新)都成功后,发送通知或清理临时资源。
- 聚合状态:检查两个独立异步检查的结果(如健康检查、权限验证),然后根据两者结果执行一个操作(如标记服务状态)。
7.5 一些示例
7.5.1 thenAcceptBothAsync
public class CompletableFutureDemo08 {public static void main(String[] args) {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + "第一个任务执行了呃 ..... ");int n = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, 1000);return n;}, executorService);CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " 第二个任务哦");return "hello world";},executorService).thenAcceptBothAsync(completableFuture, (s1, v) -> { // 消费操作System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + " thenAcceptBoth");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + "s1 = " + s1);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + "v = " + v);}, executorService);executorService.shutdown();System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -- \t" + "主线程执行完任务了哦.");}
}

7.5.2 thenAcceptBoth
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
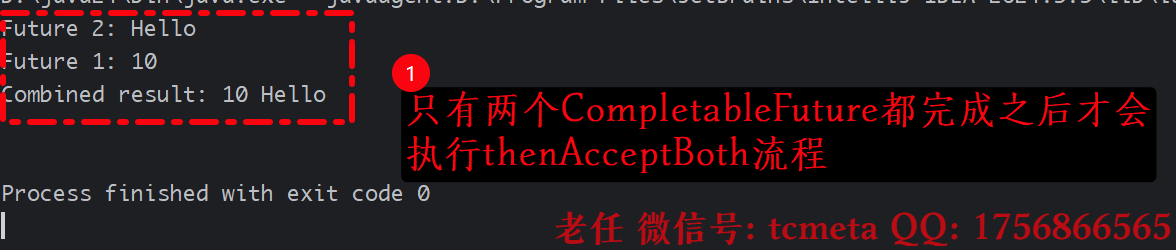
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class CompletableFutureExample {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 第一个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int result = 10;System.out.println("Future 1: " + result);try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);}catch (InterruptedException e){e.printStackTrace();}return result;});// 第二个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {String result = "Hello";System.out.println("Future 2: " + result);return result;});// 使用thenAcceptBoth处理两个CompletableFuture的结果future1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, (num, str) -> {System.out.println("Combined result: " + num + " " + str);});System.in.read();}
}
八、acceptEither
acceptEither是CompletableFuture类提供的一个方法,用于在两个CompletableFuture中任意一个完成后执行一个消费者操作。该方法接受两个参数:另一个CompletableFuture对象和一个Consumer函数接口,用于处理完成的CompletableFuture的结果。
8.1 示例
public class CompletableFutureExample {public static void main(String[] args) {// 第一个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int result = 10;System.out.println("Future 1: " + result);return result;});// 第二个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int result = 20;System.out.println("Future 2: " + result);return result;});// 使用acceptEither处理两个CompletableFuture中任意一个的结果future1.acceptEither(future2, result -> {System.out.println("Accepted result: " + result);});}
}
acceptEither方法能够在任意一个CompletableFuture完成后执行对结果的处理操作。无论是future1还是future2中的结果先完成,都会触发acceptEither中的操作。

8.2 thenAcceptBoth和acceptEither区别
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| thenAcceptBoth | 两个Future【都完成】,才会触发thenAcceptBoth中的操作 |
| acceptEither | 两个Future有【一个】完成, 就会触发acceptEither中的操作 |
九、thenCombine 合并操作
9.1 概述
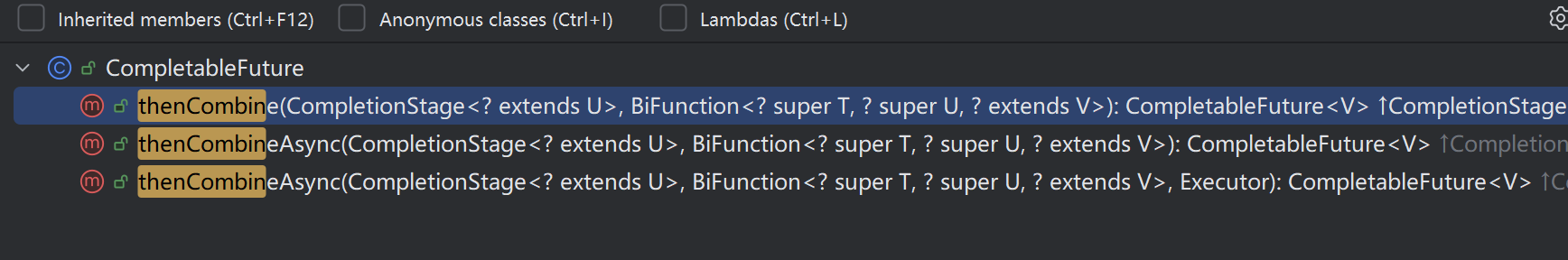
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
thenCombine是CompletableFuture类提供的一个方法,用于在两个CompletableFuture都完成后执行一个合并操作,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture来处理合并的结果。该方法接受两个参数:另一个CompletableFuture对象和一个BiFunction函数接口,用于合并处理两个CompletableFuture的结果并生成新的结果。
9.2 示例一
- 处理两个任务
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class ThenCombineDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 第一个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {int result = 10;System.out.println("Future 1: " + result);return result;});// 第二个CompletableFutureCompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {String result = "Hello";System.out.println("Future 2: " + result);return result;});// 使用thenCombine合并处理两个CompletableFuture的结果CompletableFuture<String> combinedFuture = future1.thenCombine(future2, (num, str) -> {String combinedResult = num + " " + str;System.out.println("Combined result: " + combinedResult);return combinedResult;});// 获取合并后的结果try {String result = combinedFuture.get();System.out.println("Final result: " + result);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
9.3 示例二
- 处理多个任务
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class CompletableFutureDemo09 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);CompletableFuture<String> c1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 第一个任务!");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "AAA";}, executorService);CompletableFuture<String> c2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 第二个任务!");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "BBB";}, executorService);CompletableFuture<String> c3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 第三个任务!");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "CCC";}, executorService);CompletableFuture<String> c4 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 第四个任务!");try {TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(6000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "DDD";}, executorService);CompletableFuture<String> cc = c4.thenCombineAsync(c3, (s1, s2) -> s1.concat(" - ").concat(s2), executorService).thenCombineAsync(c2, (s1, s2) -> s1.concat(" : ").concat(s2), executorService).thenCombineAsync(c1, (s1, s2) -> s1.concat(" # ").concat(s2), executorService);String result = cc.get();System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 最后结果: " + result);System.out.printf("线程名称: 【%s】 , msg: %s \n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), " 任务执行完成");executorService.shutdown();}
}
十、anyOf
10.1 概述
要实现在多个相同的任务中,如果其中一个任务成功执行则取消另一个任务的执行,可以使用CompletableFuture的anyOf和cancel方法结合起来实现.
10.2 示例
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
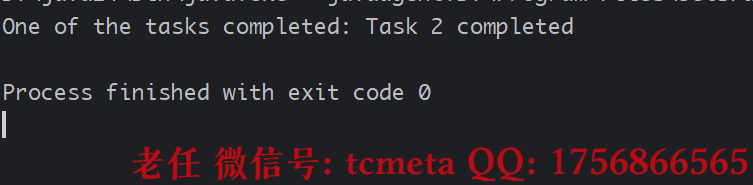
public class AnyOfDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建两个相同的任务CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 模拟任务执行Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "Task 1 completed";});CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 模拟任务执行Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "Task 2 completed";});// 使用anyOf方法等待任意一个任务完成CompletableFuture<Object> anyOfFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);// 如果其中一个任务成功执行,则取消另一个任务anyOfFuture.thenAccept(result -> {if (result.equals("Task 1 completed")) {future2.cancel(true);} else if (result.equals("Task 2 completed")) {future1.cancel(true);}System.out.println("One of the tasks completed: " + result);});// 等待任务执行完成try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
十一、allOf方法
要在CompletableFuture中实现并发执行多个任务,可以使用CompletableFuture.allOf方法。allOf方法接受一个CompletableFuture数组作为参数,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture,该新的CompletableFuture在所有输入的CompletableFuture都完成后完成。
package cn.tcmeta.completablefuture;import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;/*** @author: laoren* @version: 1.0.0*/
public class AllOfDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建多个任务CompletableFuture<String> task1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 模拟任务执行Thread.sleep(2000);return "Task 1 Completed";} catch (InterruptedException e) {return "Task 1 Cancelled";}});CompletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 模拟任务执行Thread.sleep(3000);return "Task 2 Completed";} catch (InterruptedException e) {return "Task 2 Cancelled";}});CompletableFuture<String> task3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try {// 模拟任务执行Thread.sleep(1500);return "Task 3 Completed";} catch (InterruptedException e) {return "Task 3 Cancelled";}});// 并发执行多个任务CompletableFuture<Void> allTasks = CompletableFuture.allOf(task1, task2, task3);try {// 等待所有任务完成allTasks.get();// 获取各个任务的结果String result1 = task1.get();String result2 = task2.get();String result3 = task3.get();// 输出任务结果System.out.println(result1);System.out.println(result2);System.out.println(result3);} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}
我们创建了三个任务task1、task2和task3,它们都会执行一段耗时的操作。我们使用CompletableFuture.allOf方法将这三个任务组合起来,并返回一个新的CompletableFuture。然后,我们通过调用get方法等待所有任务完成,并使用get方法获取各个任务的结果。
注意,allOf方法返回的CompletableFuture本身不包含结果,只是用于等待所有任务的完成。要获取各个任务的结果,还需要分别调用各个任务的get方法。
