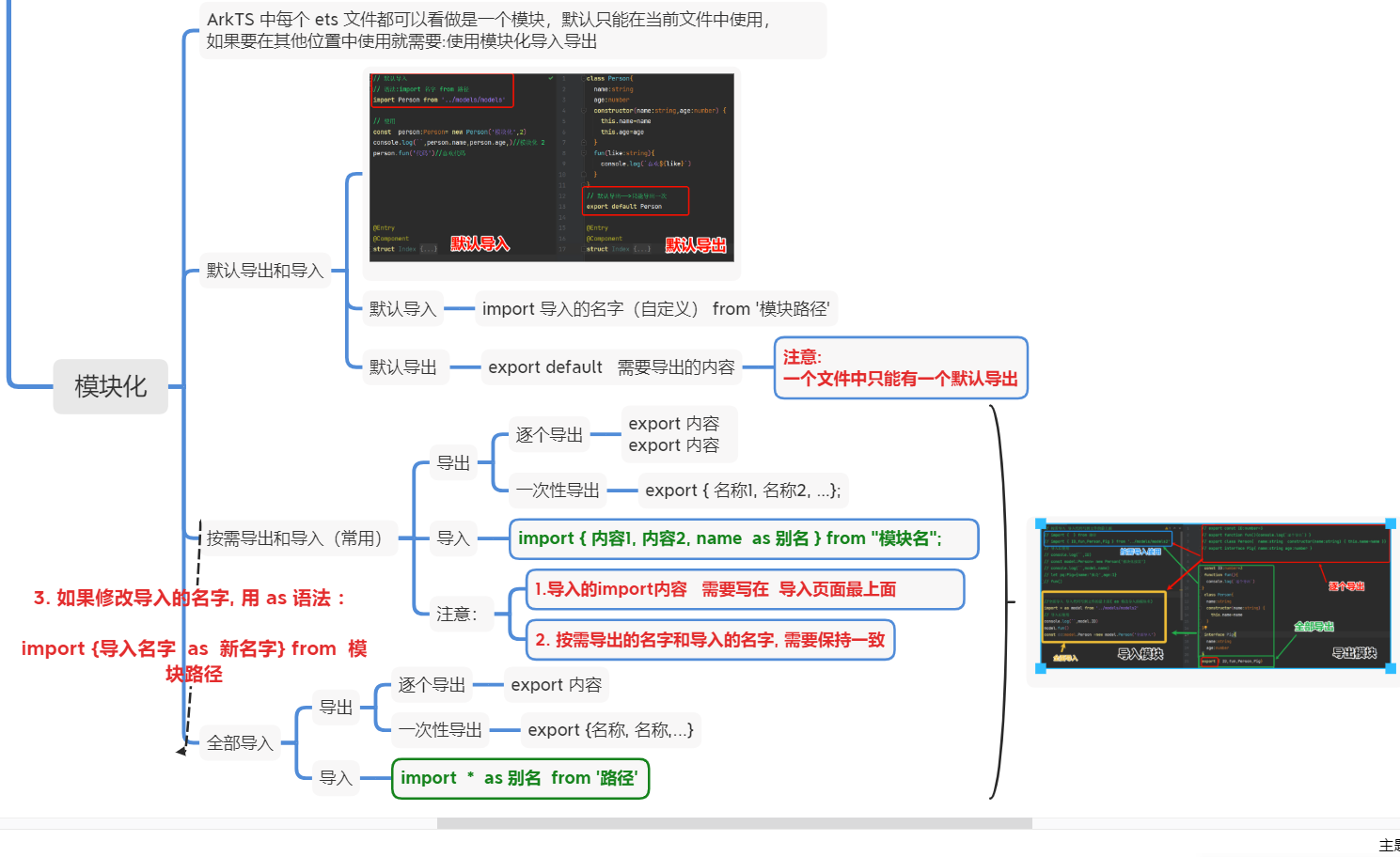
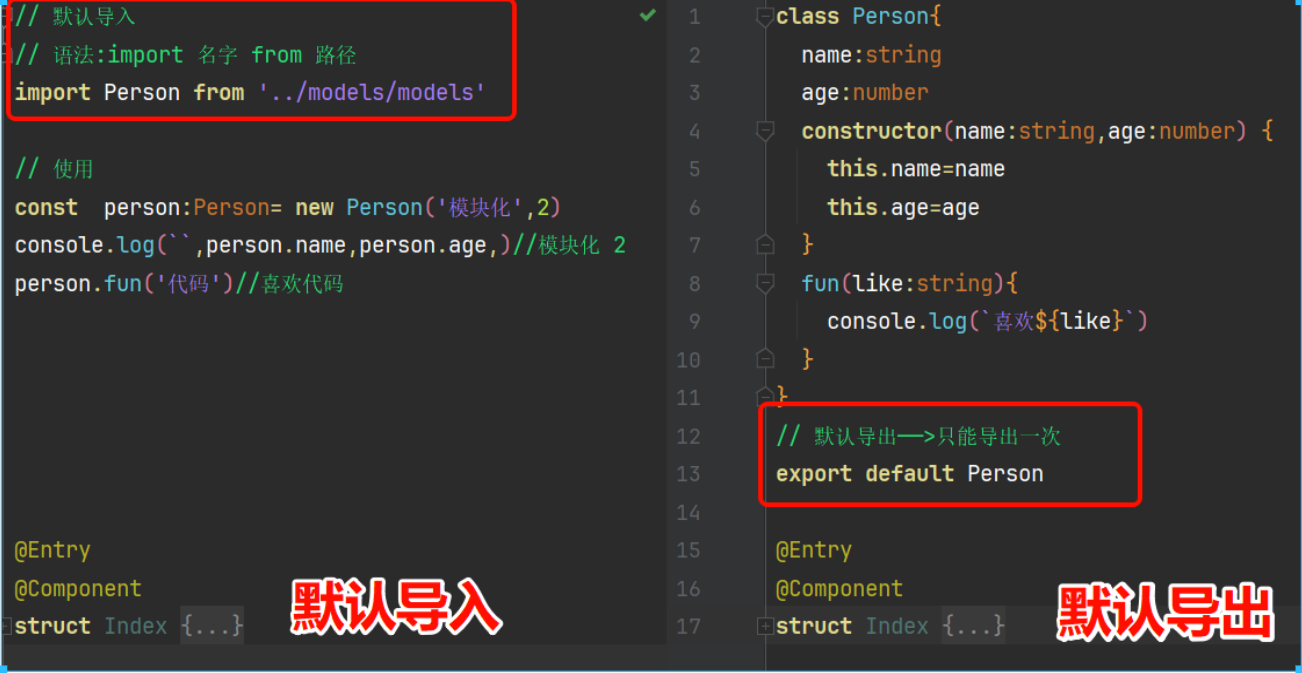
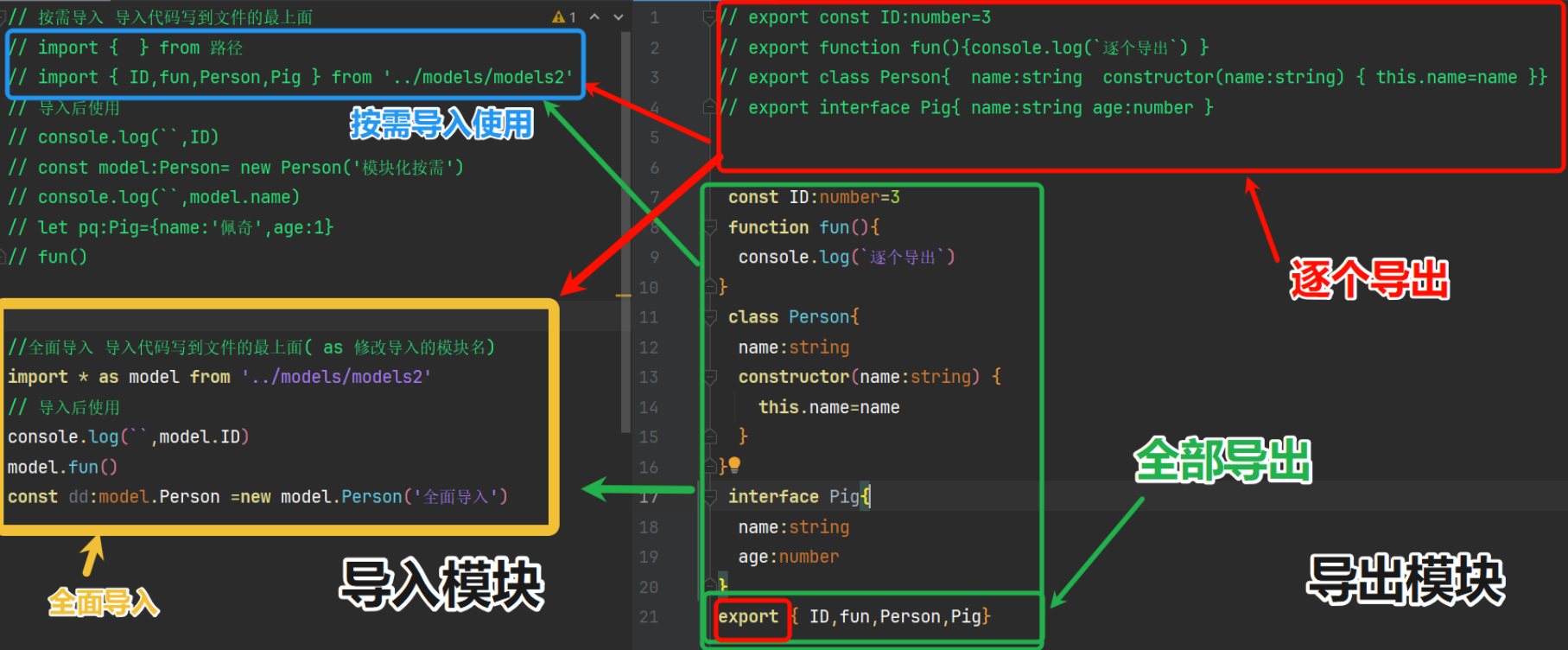
04 类型别名type + 检测数据类型(typeof+instanceof) + 空安全+剩余和展开(运算符 ...)简单类型和复杂类型 + 模块化
1、类型别名type
// 类型别名type
// type 别名=类型()
type IType=string|number//别名的定义
interface demo{name:string,age:IType//别名的使用url:ResourceStr//type ResourceStr = string | Resource
}2、检测数据类型
typeof 检测简单类型为主,instanceof 检测复杂类型为主
typeof检测数据类型
(以字符串的形式进行返回)
// typeof检测数据类型(以字符串的形式进行返回)
// 常规的返回值
console.log(`typeof01`,typeof 'ss')//string
console.log(`typeof`,typeof 12)//number
console.log(`typeof`,typeof true)//boolean
console.log(`typeof`,typeof undefined)//undefined
function fun(){}
console.log(`typeof`,typeof fun)//function
console.log(`------------------------------`,)
// 特殊场景的返回值
interface demo{name:string}
const obj:demo={ name:'' }
console.log(`typeof`,typeof NaN)//number //NaN not a number
console.log(`typeof`,typeof null)//object
console.log(`typeof`,typeof [])//object
console.log(`typeof`,typeof obj)//object
console.log(`typeof`,typeof typeof obj)//stringinstanceof-检测数据类型
//继承
class Father{name:stringage:numberconstructor(name:string,age:number) {this.name=namethis.age=age}fatherFun(){console.log(`父类的方法`)}
}
// 定义子类继承父类的属性和方法
class Son extends Father{hobby:stringconstructor(name:string,age:number,hobby:string) {super(name,age)///调用父类的构造函数 并传递实参(写在子类属性的前面)this.hobby=hobby}sonFun(){console.log(`子类的方法`)}
}
const my:Son= new Son('朱',18,'学习鸿蒙')
const YY:Son= new Son('杨洋',20,'唱歌')
const dd:Son= new Son('小李',18,'上学')
// instanceof----检测数据类型
//例如:检测实例化对象是不是属于这个类 实力化对象名 instanceof 类名
console.log(``,my instanceof Father)
console.log(``,YY instanceof Son)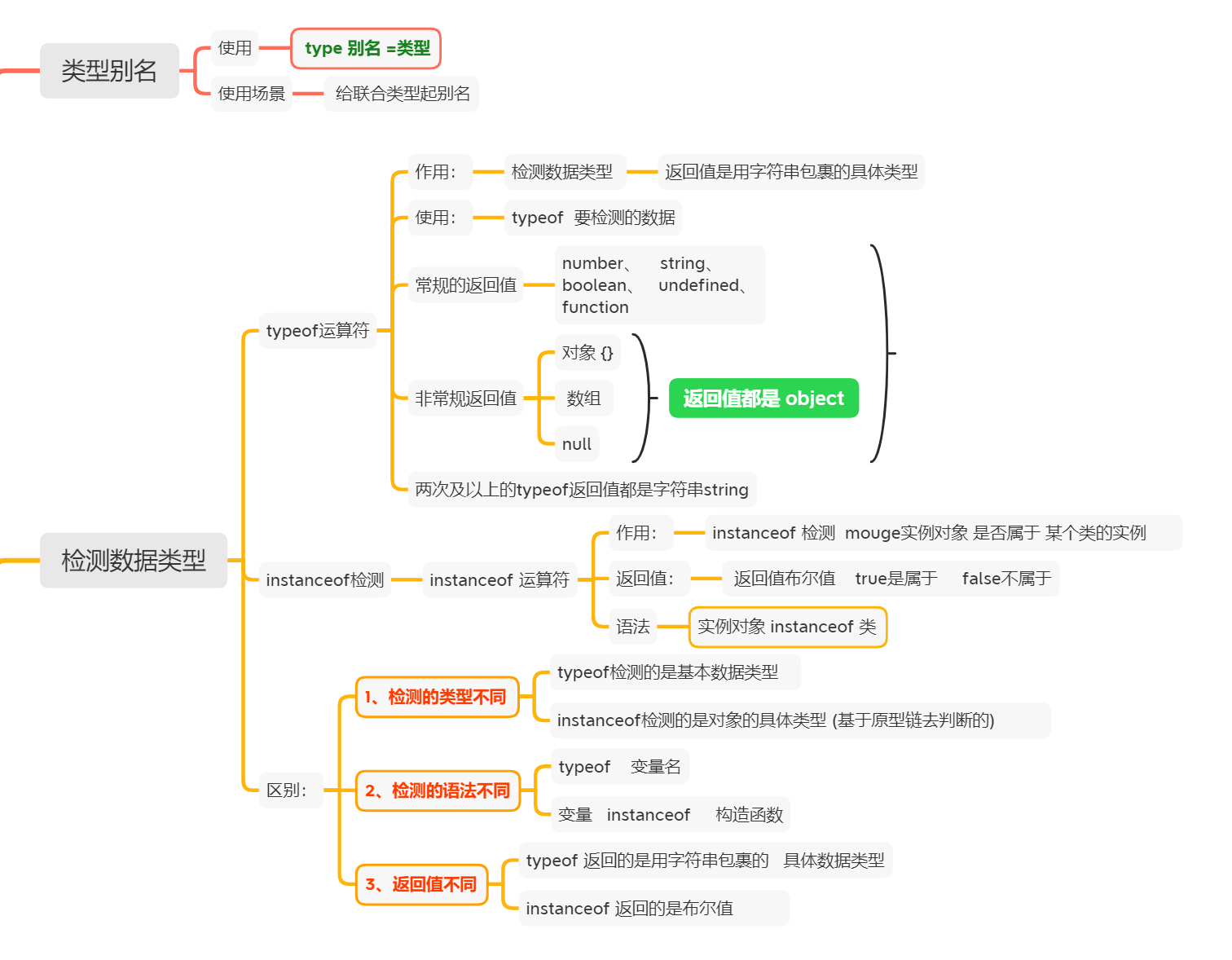
3、空安全
空安全: 写代码的过程当中,有可能接收到null,一旦接受null程序会出错,这时需要处理错误
1,联合类型+判断
2,非空断言运算符 !
3,空值合并运算符 ??
含义:?? 左侧如果不是null 直接返回左侧的值 如果左侧是null 直接返回右侧的值
类比逻辑中断 | | 一样的用法
4,可选链?

// 空安全——>处理空值,保证程序正常运行
//1.联合 + 判断
//2.非空断言运算符 !
//3.合并运算符 ?? ( 类似逻辑中断 || )
// 可选链操作符 ?let num: number | null = null
// num=num+1 //出错,(可能为null)
// ---------解决----------
// 1、联合 + 判断
if (num !== null) {// 运算num = num + 1
}
// 2.非空断言运算符 !(主观告诉它,你不可能为空)
num = num! + 1// 3.合并运算符 ?? ( 类似逻辑中断 || )
// 4.可选链操作符 ?
function sum(x: number, y?: number) {// let xy:number=y||0let xy: number = y ?? 0let res: number = x + xy
}
4、剩余和展开(运算符 ...)

展开运算符
let arr1:number[]=[1,2,3]
let arr2:number[]=[4,5,6]
// 将数组1和数组2合并到数组3
// 展开运算符... 变量名 作用:取出数组中的数据
let arr3:number[]=[...arr1,...arr2]
console.log(``,arr3)//1,2,3,4,5,6let arr4:number[]=[1,2,3]
let arr5:number[]=[4,5,6]//将数组5的数据存放到数组4中
arr4.push(...arr5)
console.log(``,arr4)//1,2,3,4,5,6
剩余参数
// 剩余参数.,是使用在函数中
// function 函数名(参数:类型,...参数名:类型口)
function fun(a:number,b:number,...other:number[]){let total= a+b//检测一下other是不是一个数组console.log(``,other instanceof Array)//truefor(let item of other){// for of 循环数组,item是数组的每一项total+=item}return total
}
console.log(`结果1`,fun(1,2))
console.log(`结果2`,fun(3,4,5,6))5.值类型和引用类型
简单类型和复杂类型
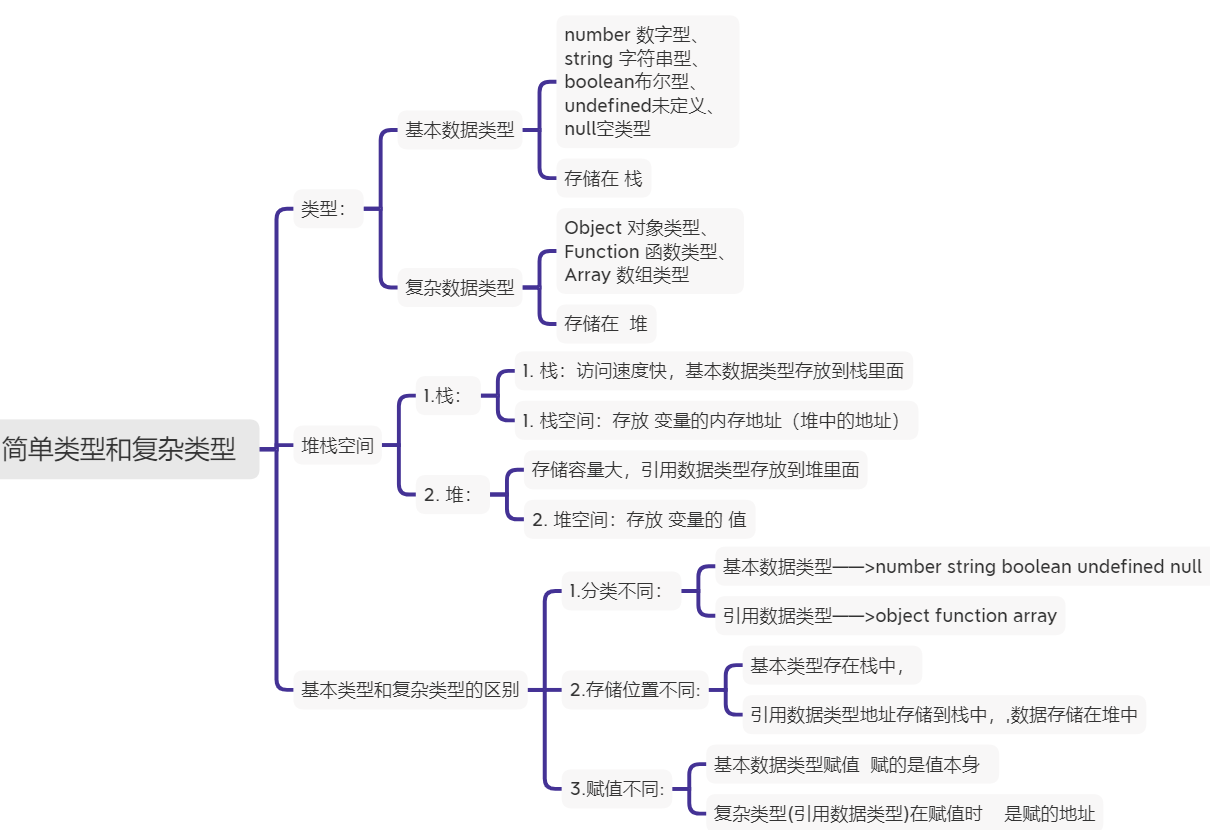
// 基本数据类型
let numA: number = 10
let numB: number = numA
numB++
console.log('numA:', numA) // ?
console.log('numB:', numB) // ?// 引用数据类型
class Person {name: string = ''constructor(name: string) {this.name = name}
}const p1: Person = new Person('jack')
const p2: Person = p1
// 修改 P2 是否会报错
p2.name = 'rose'console.log('p1.name:', p1.name) // rose
console.log('p2.name:', p2.name) // rose
// 值类型和引用数据类型的区别:
// 本数据类型(值类型/简单数据类型) 和引用数据类型(复杂数据类型)的区别
//1.分类:基本数据类型——>number string boolean undefined null
// 引用数据类型——>object function array
//2.存储:基本数据类型存储栈内存中 引用数据类型存储地址存储到栈中 数据存储到堆
//3.赋值:基本数据类型赋值是值本身 引用数据类型赋值是赋的地址
6、模块化