Flink Stream API 源码走读 - 总结
Flink Stream API 源码走读 - 总结
概述
本文档详细分析Flink数据流处理的完整流程,从API调用到Transformation构建,再到最终的执行图生成。通过源码分析,深入理解Flink如何将用户的流式API调用转换为可执行的数据流图。
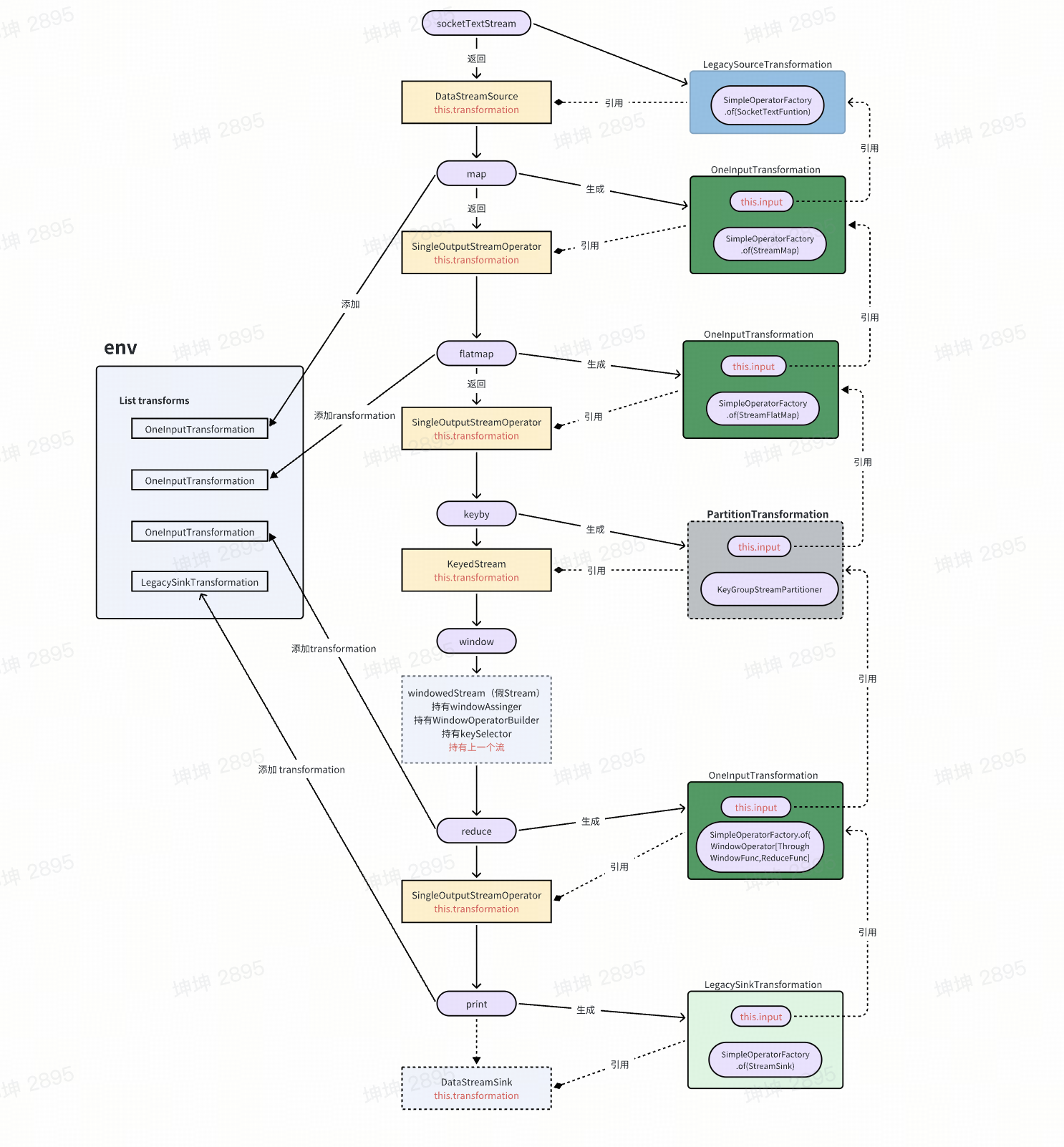
1. Source阶段:数据源的创建
1.1 API调用
// 用户代码
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStreamSource<String> source = env.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999);
1.2 内部处理流程
当调用env.socketTextStream()时,Flink内部会:
-
创建SourceFunction:
- 创建
SocketTextStreamFunction实例 - 封装Socket连接逻辑和数据读取逻辑
- 创建
-
生成LegacySourceTransformation:
// 源码位置:LegacySourceTransformation.java public class LegacySourceTransformation<T> extends PhysicalTransformation<T> {private final StreamOperatorFactory<T> operatorFactory;// ... }- 包含具体的运算逻辑(SocketTextStreamFunction)
- 通过
SimpleOperatorFactory.of(operator)包装成算子工厂 - 这是一个物理Transformation,包含实际的计算逻辑
-
返回DataStreamSource:
// DataStreamSource继承自SingleOutputStreamOperator public class DataStreamSource<T> extends SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> {// this.transformation 引用上面创建的LegacySourceTransformation }
2. Map阶段:数据转换操作
2.1 API调用
// 用户代码
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> mapped = source.map(new MapFunction<String, String>() {@Overridepublic String map(String value) throws Exception {return value.toUpperCase();}
});
2.2 内部处理流程
当调用map()方法时:
-
类型推断:
// DataStream.java 第588行 public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> map(MapFunction<T, R> mapper) {TypeInformation<R> outType = TypeExtractor.getMapReturnTypes(clean(mapper), getType(), Utils.getCallLocationName(), true);return map(mapper, outType); } -
创建StreamMap算子:
// DataStream.java 第631行 return transform("Map", outputType, new StreamMap<>(clean(mapper))); -
生成OneInputTransformation:
// DataStream.doTransform() 方法 OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform = new OneInputTransformation<>(this.transformation, // 引用上一个transformation(LegacySourceTransformation)operatorName, // "Map"operatorFactory, // SimpleOperatorFactory.of(StreamMap)outTypeInfo, // 输出类型信息environment.getParallelism(),false ); -
添加到执行环境:
// 将物理transformation添加到transformations列表 getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform); -
返回新的DataStream:
SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> returnStream =new SingleOutputStreamOperator(environment, resultTransform);
3. FlatMap阶段:扁平化映射操作
3.1 API调用
// 用户代码
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> flatMapped = mapped.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, String>() {@Overridepublic void flatMap(String value, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {String[] words = value.split(" ");for (String word : words) {out.collect(word);}}
});
3.2 内部处理流程
FlatMap操作的处理流程与Map类似:
- 创建StreamFlatMap算子:包装用户的FlatMapFunction
- 生成OneInputTransformation:引用上一个Map的transformation
- 添加到transformations列表:这是物理transformation
- 返回新的SingleOutputStreamOperator
4. KeyBy阶段:数据分组操作
4.1 API调用
// 用户代码
KeyedStream<String, String> keyed = flatMapped.keyBy(value -> value);
4.2 内部处理流程
KeyBy操作比较特殊:
-
生成PartitionTransformation:
// 源码位置:PartitionTransformation.java public class PartitionTransformation<T> extends Transformation<T> {private final Transformation<T> input; // 引用上一个transformationprivate final StreamPartitioner<T> partitioner; // 分区器,不是算子工厂 } -
关键特点:
- 这是一个虚拟transformation,不包含实际的计算逻辑
- 持有的是
KeyGroupStreamPartitioner分区器,而不是算子工厂 - 不会添加到transformations列表中
- 用于指导数据在网络中的分发策略
-
返回KeyedStream:
public class KeyedStream<T, KEY> extends DataStream<T> {// 继承自DataStream,但提供了按键分组后的特殊API }
5. Window阶段:窗口操作
5.1 API调用
// 用户代码
WindowedStream<String, String, TimeWindow> windowed =keyed.timeWindow(Time.seconds(5));
5.2 内部处理流程
Window操作创建了一个特殊的中间对象:
-
创建WindowedStream:
// 源码位置:WindowedStream.java 第79行 public WindowedStream(KeyedStream<T, K> input, WindowAssigner<? super T, W> windowAssigner) {this.input = input; // 保持对上游KeyedStream的引用this.builder = new WindowOperatorBuilder<>(windowAssigner, // 窗口分配器windowAssigner.getDefaultTrigger(input.getExecutionEnvironment()), // 触发器input.getExecutionConfig(), // 执行配置input.getType(), // 输入类型input.getKeySelector(), // Key选择器input.getKeyType() // Key类型); } -
WindowedStream特点:
- 不是真正的DataStream,只是一个工具类/API容器
- 不能调用map、flatMap等通用流操作
- 只能调用窗口相关的API:reduce、apply、process等
- 持有WindowOperatorBuilder,用于后续构建窗口算子
6. Reduce阶段:窗口聚合操作
6.1 API调用
// 用户代码
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> result = windowed.reduce(new ReduceFunction<String>() {@Overridepublic String reduce(String value1, String value2) throws Exception {return value1 + "," + value2;}
});
6.2 内部处理流程
这是窗口操作的核心实现:
-
构建WindowOperator:
// WindowedStream.java 第230行 OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator = builder.reduce(reduceFunction, function); -
WindowOperatorBuilder.reduce()方法:
- 创建
WindowOperator实例 - 将用户的
ReduceFunction和内部的PassThroughWindowFunction组合 - WindowOperator包含完整的窗口处理逻辑:
- 窗口分配(WindowAssigner)
- 窗口触发(Trigger)
- 数据聚合(ReduceFunction)
- 结果输出(WindowFunction)
- 创建
-
生成OneInputTransformation:
// WindowedStream.java 第233行 return input.transform(opName, resultType, operator).setDescription(opDescription);- 这是一个物理transformation
- 包含具体的窗口+聚合运算逻辑
- 会被添加到transformations列表中
-
返回SingleOutputStreamOperator:
- 又回到了正常的DataStream
- 可以继续进行其他流操作
7. Sink阶段:数据输出操作
7.1 API调用
// 用户代码
DataStreamSink<String> sink = result.print();
7.2 内部处理流程
Sink操作是数据流的终点:
-
创建PrintSinkFunction:
// 内部会创建PrintSinkFunction实例 // 包含将数据打印到控制台的逻辑 -
生成LegacySinkTransformation:
// 通过SimpleOperatorFactory.of()包装成算子工厂 // 创建LegacySinkTransformation实例 LegacySinkTransformation<T> sinkTransformation = new LegacySinkTransformation<>(input.getTransformation(), // 引用上一个transformationname, // "Sink: Print to Std. Out"operatorFactory, // SimpleOperatorFactory.of(StreamSink)parallelism ); -
添加到transformations列表:
- 这是一个物理transformation
- 包含具体的数据处理逻辑(打印到屏幕)
- 会被添加到环境的transformations列表中
-
返回DataStreamSink:
public class DataStreamSink<T> {private final Transformation<T> transformation;// 不是真正的流,只是一个封装工具类// 不能再调用map、flatMap等API// 只持有自己的transformation引用 }
8. Transformation链式结构分析
8.1 物理Transformation vs 虚拟Transformation
物理Transformation(会添加到transformations列表):
LegacySourceTransformation:包含Source算子逻辑OneInputTransformation:包含Map、FlatMap、Window等算子逻辑LegacySinkTransformation:包含Sink算子逻辑
虚拟Transformation(不会添加到transformations列表):
PartitionTransformation:只包含分区策略,用于指导数据分发
8.2 引用关系链
LegacySourceTransformation (Source)↑ input
OneInputTransformation (Map)↑ input
OneInputTransformation (FlatMap)↑ input
PartitionTransformation (KeyBy) [虚拟]↑ input
OneInputTransformation (Window+Reduce)↑ input
LegacySinkTransformation (Sink)
8.3 关键特点
-
Source Transformation:
- 没有input引用(数据流的起点)
- 包含数据源逻辑
-
中间Transformation:
- 都有input成员变量,引用上一个transformation
- 形成链式结构
-
Sink Transformation:
- 有input引用,但没有下游
- 数据流的终点
-
遍历能力:
- 通过最后一个transformation可以向上遍历整个链路
- 这是Flink构建执行图的基础
返回目录
Flink 源码系列 - 前言
