IO流-序列化流
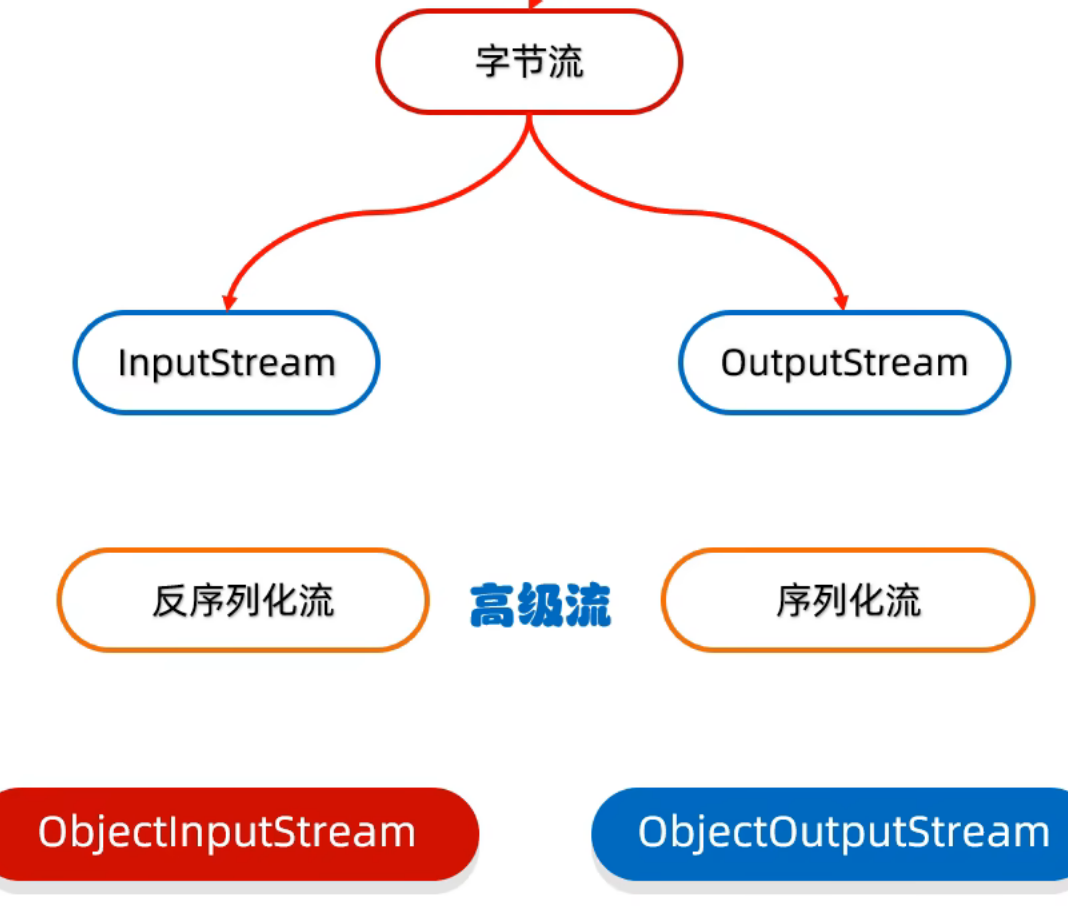
序列化流/对象操作输出流:
可以把Java中的对象写到本地文件中
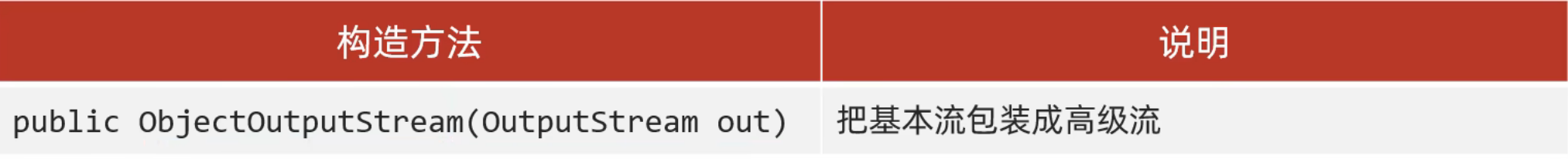
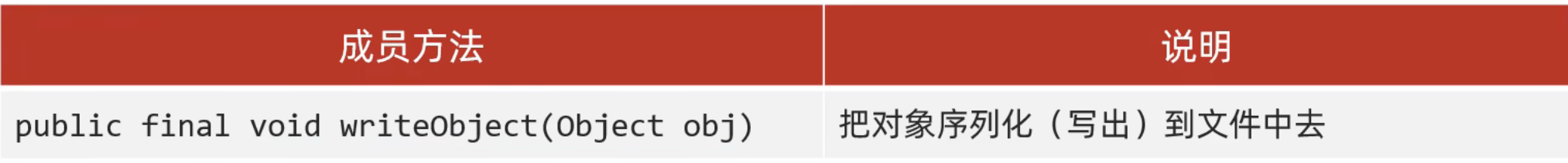
代码:
利用序列化流/对象操作输出流,把一个对象写到本地文件中
/*** Serializable接口里面是没有抽象方法的,标记性接口* 一旦实现这个接口,那么就表示当前的Student类可以被序列化*理解:* 一个物品的合格证**/public class Student implements Serializable {private String name;private int age;public Student(){}public Student(String name,int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public Student(String name) {this.name = name;}public Student(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
public class ObjectSreamDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {//1.创建对象Student student = new Student("张三",35);//2.创造序列化流ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));//3.写出数据oos.writeObject(student);//4.释放资源oos.close();}
}反序列化流/对象操作输入流:
可以把序列化到本地文件中的对象,读取到程序中来
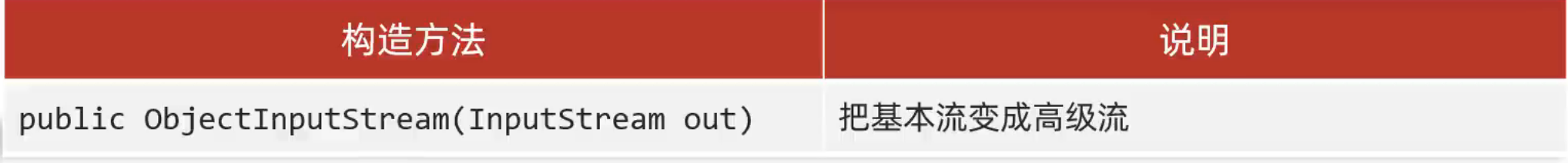
代码:
public class ObjectSreamDemo02 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {//1.创建反序列化流的对象ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));//2.读取数据Object o = ois.readObject();System.out.println(o);ois.close();}
}序列化流/反序列化流的细节汇总:
①使用序列化流将对象写到文件时,需要让Javabean类 实现Serializable接口。
否则,会出现NotSerializableException异常
②序列化流写到文件中的数据是不能修改的,一旦修改就无法再次读回来了
③序列化对象后,修改了Javabean类, 再次反序列化,会不会有问题?
会出问题,会抛出InvalidClassException异常
解决方案:给Javabean类 添加serialVersionUID (序列号、版本号)
④如果一个对象中的某个成员变量的值不想被序列化,又该如何实现呢?
解决方案:给该成员变量加transient关键字修饰,该关键字标记的成员变量不参与序列化过程
代码练习:
将多个自定义对象序列化到文件中,但是对象的个数不确定,反序列化如何读取?
public class Student implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 844768814497035445l;private String name;private int age;private String address;public Student(){}public Student(String name,int age,String address){this.name = name;this.age = age;this.address = address;}public Student(String name) {this.name = name;}public Student(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +", address='" + address + '\'' +'}';}
}
public class Test08 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Student s1 = new Student("zhangs",23,"南京");Student s2 = new Student("lishi",24,"重庆");Student s3 = new Student("wangwu",25,"上海");ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(s1);list.add(s2);list.add(s3);ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("a.txt"));oos.writeObject(list);/* oos.writeObject(s1);oos.writeObject(s2);oos.writeObject(s3);*/oos.close();}}
public class Test09 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));ArrayList<Student> list = (ArrayList<Student>) ois.readObject();for (Student student : list) {System.out.println(student);}/* Student s1 = (Student) ois.readObject();Student s2 = (Student) ois.readObject();Student s3 = (Student) ois.readObject();System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);*/ois.close();}
}
