池式结构之连接池
一、初识MySQL连接池
问:什么是数据库连接池?
答:维持管理一定数量连接的池式结构。
问:他解决了什么问题?
答:复用资源,而且提升了MySQl并发处理sql的能力。因为一次性建立多个连接,在MySQL内部也会创建多个线程对应多个连接,相比较一个连接的一个线程,并发度更高。
问:同步连接池和异步连接池的区别?
答:同步连接池:当服务端核心业务线程发起MySQL用户请求,该线程被阻塞。遍历同步连接池所有连接找到未加锁的连接,给他加锁然后执行SQL。收到答案后,解锁改连接并且返回结果,唤醒线程。应用场景:服务器刚刚启动,还未对外提供连接的时候,利用同步连接池初始化资源。
异步连接池:解决核 心业务线程阻塞问题,需要先实现一个线程池。阻塞的将是线程池线程,而非核心业务线程。线程池线程接收到返回结果后,通过future和promise机制将返回值给到核心业务线程。
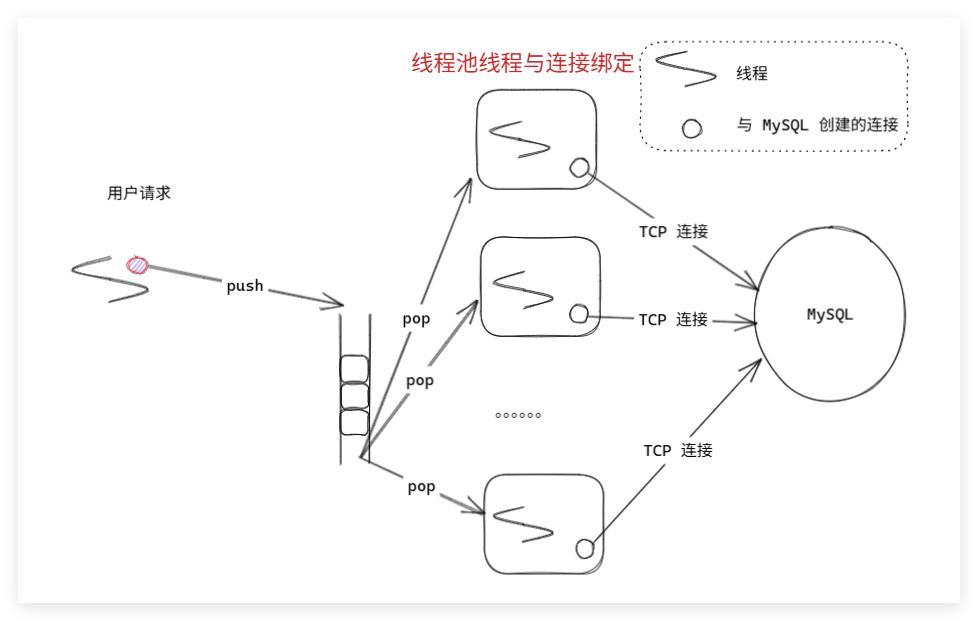
问:MySQL官方提供的 c/c++驱动(接口库)需要实现哪些内容?(方便服务器发送用户请求)
答:connect、recv、send、read、write等(都是阻塞IO的实现方法),并且需要实现一个mysql协议(确定如何解决粘包问题,数据包首部加长度或者用特殊字符分隔包)。
二、代码思路
0.对于传入的数据库名称“db1”创建一个唯一的连接池对象,并且通过map对映。初始化连接池(创建任务队列对象,创建pool_size个MySQLConn连接对象,并且创建MySQLWorker对象和连接对象绑定,启动工作线程等待阻塞队列),通过连接对象的Open()建立物理连接。
- 用户通过MySQLConnPool::Query发起查询sql
- sql的操作对象SQLOperation被创建,通过GetFuture(),使操作对象关联一个future后,把该操作对象放入BlockingQueue
MySQLWorker工作对象从队列获取操作对象,通过线程绑定的连接,执行sql并且将结果存入promise,通过
promise.set_value()将结果传递给关联的future- AsyncProcessor通过future_wait_for发现future已就绪,调用用户代码层传入的回调函数处理结果。
双重等待:
小范围:工作对象在等操作对象被创建。创建后工作对象执行SQL,拿到promise值,传给future.
大范围:回调对象在等future值。
三、代码实现
1.连接池对象
//MySQLConnPool.cpp#include "MySQLConnPool.h"
#include "MySQLConn.h"
#include "SQLOperation.h"
#include "QueryCallback.h"
#include <cppconn/resultset.h>
#include "BlockingQueue.h"std::unordered_map<std::string, MySQLConnPool *> MySQLConnPool::instances_;MySQLConnPool *MySQLConnPool::GetInstance(const std::string &db) {if (instances_.find(db) == instances_.end()) {instances_[db] = new MySQLConnPool(db);}return instances_[db];
}void MySQLConnPool::InitPool(const std::string &url, int pool_size) {task_queue_ = new BlockingQueue<SQLOperation *>();for (int i = 0; i < pool_size; ++i) {MySQLConn *conn = new MySQLConn(url, database_, *task_queue_);conn->Open();pool_.push_back(conn);}
}MySQLConnPool::~MySQLConnPool() {if (task_queue_)task_queue_->Cancel();for (auto conn : pool_) {delete conn;}if (task_queue_) {delete task_queue_;task_queue_ = nullptr;}pool_.clear();
}第二个参数是用户传入的回调函数 在future有值后执行
QueryCallback MySQLConnPool::Query(const std::string &sql, std::function<void(std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>)> &&cb) {SQLOperation *op = new SQLOperation(sql);auto future = op->GetFuture();task_queue_->Push(op);return QueryCallback(std::move(future), std::move(cb));
}
2.连接对象
//MySQLConn.cpp#include "MySQLConn.h"
#include "QueryCallback.h"
#include "MySQLWorker.h"
#include "BlockingQueue.h"#include <cppconn/driver.h>
#include <cppconn/connection.h>
#include <cppconn/exception.h>
#include <cppconn/statement.h>
#include <cppconn/resultset.h>#include <vector>
#include <string>// "tcp://127.0.0.1:3306;root;123456"
static std::vector<std::string_view>
Tokenize(std::string_view str, char sep, bool keepEmpty)
{//划分上面的指令
}MySQLConnInfo::MySQLConnInfo(const std::string &info, const std::string &db)
{auto tokens = Tokenize(info, ';', false);if (tokens.size() != 3)return;url.assign(tokens[0]);user.assign(tokens[1]);password.assign(tokens[2]);database.assign(db);
}MySQLConn::MySQLConn(const std::string &info, const std::string &db, BlockingQueue<SQLOperation *> &task_queue): info_(info, db)
{worker_ = new MySQLWorker(this, task_queue);//创建工作对象 并且和this指向的当前连接对象绑定worker_->Start();
}MySQLConn::~MySQLConn()
{if (worker_) {worker_->Stop();delete worker_;worker_ = nullptr;}if (conn_) {delete conn_;}
}int MySQLConn::Open()
{int err = 0;try {driver_ = get_driver_instance();conn_ = driver_->connect(info_.url, info_.user, info_.password);if (!conn_) {return -1;}conn_->setSchema(info_.database);} catch (sql::SQLException &e) {HandlerException(e);err = e.getErrorCode();}return err;
}void MySQLConn::Close()
{if (conn_) {conn_->close();delete conn_;conn_ = nullptr;}
}sql::ResultSet* MySQLConn::Query(const std::string &sql)
{//底层的执行try {sql::Statement *stmt = conn_->createStatement();//MYSQL原生的apireturn stmt->executeQuery(sql);} catch (sql::SQLException &e) {HandlerException(e);}return nullptr;
}void MySQLConn::HandlerException(sql::SQLException &e)
{if (e.getErrorCode() != 0){std::cerr << "# ERR: SQLException in " << __FILE__;std::cerr << "(" << __FUNCTION__ << ") on line " << __LINE__ << std::endl;std::cerr << "# ERR: " << e.what();std::cerr << " (MySQL error code: " << e.getErrorCode();std::cerr << ", SQLState: " << e.getSQLState() << " )" << std::endl;}
}3.工作对象
职责:拿到操作对象后,执行SQL,将结果存入promise
//MySQLWorker.cpp
#include "MySQLWorker.h"#include "BlockingQueue.h"
#include "SQLOperation.h"
#include "MySQLConn.h"MySQLWorker::MySQLWorker(MySQLConn *conn, BlockingQueue<SQLOperation *> &task_queue): conn_(conn), task_queue_(task_queue)
{
}MySQLWorker::~MySQLWorker()
{Stop();
}void MySQLWorker::Start()//start一次 创建一个线程
{worker_ = std::thread(&MySQLWorker::Worker, this);//this表示该线程可以执行工作对象所有函数 比如下面的Worker执行函数
}void MySQLWorker::Stop()
{if (worker_.joinable()) {worker_.join();}
}void MySQLWorker::Worker() {while (true) {SQLOperation *op = nullptr;if (!task_queue_.Pop(op)) {break;}op->Execute(conn_);delete op;}
}4.sql操作对象
//SQLOperation.cpp
#include "SQLOperation.h"
#include "MySQLConn.h"void SQLOperation::Execute(MySQLConn *conn)
{auto result = conn->Query(sql_); 走连接对象的底层的查询把promise的值传给futurepromise_.set_value(std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>(result));
}
5.回调管理对象
//AsyncProcessor.cpp#include "AsyncProcessor.h"
#include "QueryCallback.h"把用户调用query后生成的回调对象移动到管理对象内部的vertor中管理
void AsyncProcessor::AddQueryCallback(QueryCallback &&query_callback)
{pending_queries_.emplace_back(std::move(query_callback));
}检测vector集合中的回调对象是否有就绪的
void AsyncProcessor::InvokeIfReady()
{for (auto it = pending_queries_.begin(); it != pending_queries_.end();){if (it->InvokeIfReady())it = pending_queries_.erase(it);else++it;}
}6.回调对象
//QueryCallback.h
#pragma once#include <future>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <cppconn/resultset.h>namespace sql //MYSQL提供
{class ResultSet;
}class QueryCallback {
public:QueryCallback(std::future<std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>> &&future, std::function<void(std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>)> &&cb): future_(std::move(future)), cb_(std::move(cb)){}检测future值 判断是否就绪bool InvokeIfReady() {if (future_.wait_for(std::chrono::seconds(0)) == std::future_status::ready) {cb_(std::move(future_.get())); 执行用户回调return true;}return false;}
private:std::future<std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>> future_;std::function<void(std::unique_ptr<sql::ResultSet>)> cb_;
};
