详解flink java基础(二)
文章目录
- 1.flink 特点
- 2.flink的应用场景
- 3. flink流式处理架构
- 4.flink分层API
- 5.flink环境准备
- 6.flink job 生命周期
- 7.flink 核心执行步骤
- 8.flink 序列化与反序列
- 9.flink数据转换
- 10.flink datasink
- 11.flink创建分支数据流
- 12 .flink windowing & Watermarks
- 13.flink keyed state
1.flink 特点
- 流批统一
- 性能卓越 (高吞吐,低延迟)
- 规模计算(支持水平扩展架构、支持超大状态与增量检查点机制)
- 生态兼容 (支持与Yarn集成、支持与k8s集成、支持单机模式运行)
- 高容错(故障自动重试、一致性检查点、保证故障场景下精确一次的状态一致性)
- 结果的准确性(flink提供了事件时间(event-time)和处理时间(processing-time)语义).对于乱序事件流、事件时间语义提供一致且准确的结果
- 精确一次(exactly-once)的状态一致性保证
- 可以连接到常用存储系统,eg:kafka,hive,jdbc,hdfs,redis等
- 高可用(本身高可用的设置,加上与k8s,Yarn和mesos的集成,再加上从故障中快速恢复和动态扩展任务的能力)
Flink核心目标是:数据流上的有状态计算(stateful computations over data streams)
Flink是一个框架和分布式处理引擎,用于对无界和有界数据流进行有状态计算
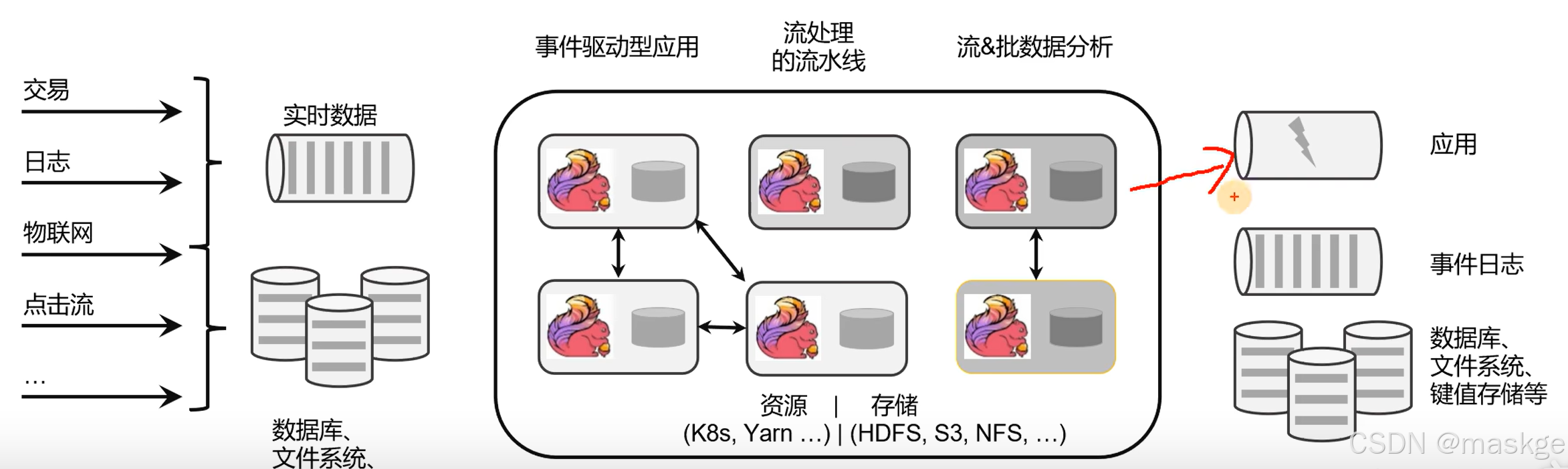
有界流与无界流
- 无界数据流:有定义流的开始,但没定义流的结束;无界流的数据必须持续处理
- 有界数据流(批处理):有定义流的开始,也有定义流的结束;有界流所有数据可以被排序;
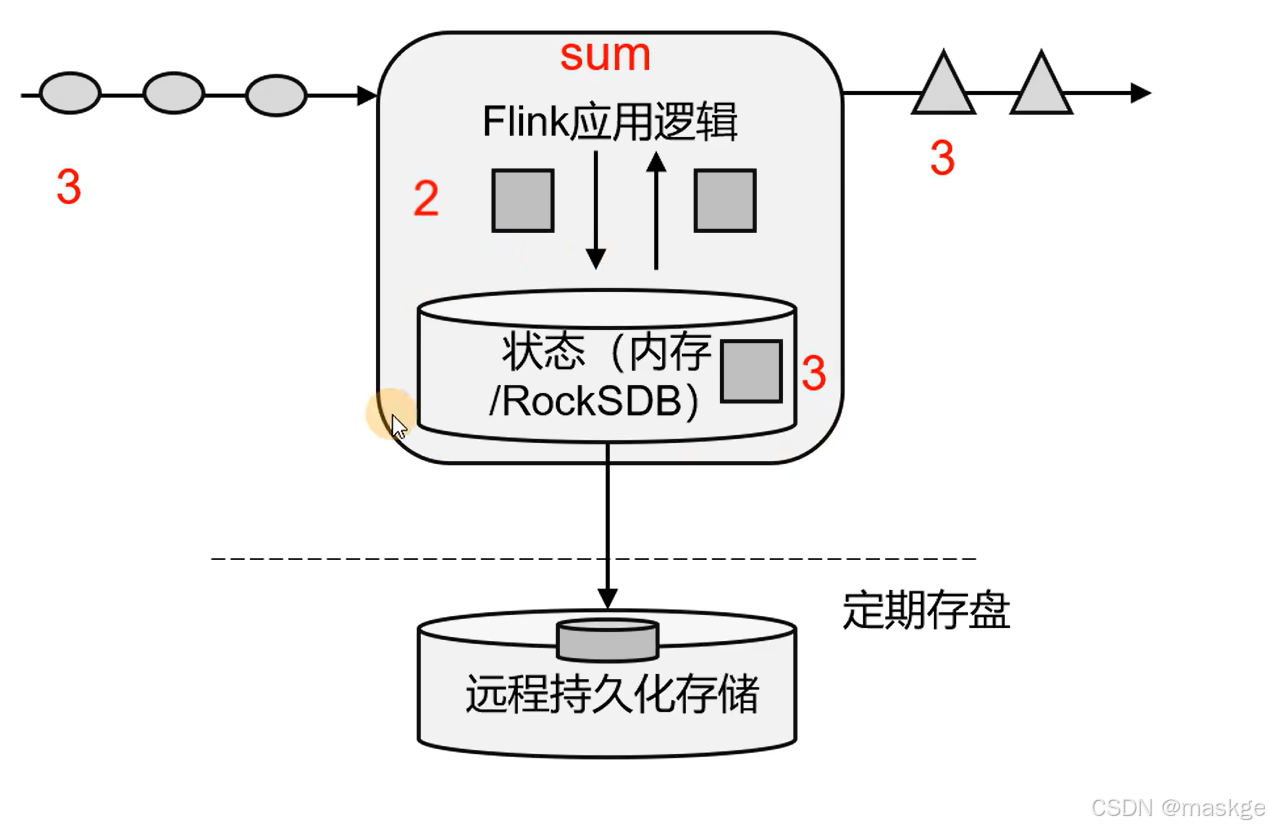
有状态流处理
- 把流处理需要的额外数据保存在一个"状态",然后针对这条数据进行处理,并且更新状态.
- 状态在内存中:优点,速度快;缺点,可靠性差
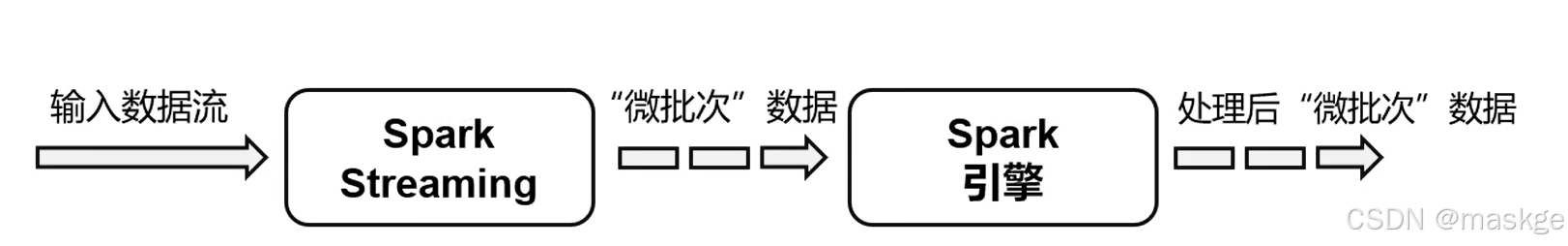
Flink VS SparkStreaming区别
Spark以批处理为根本
- Spark数据模型:Spark采用RDD模型,Spark Streaming的DStream实际上也是一组小批数据RDD的集合
- Spark运行时架构:Spark是批计算,将DAG划分为不同的stage,一个完成后才可以计算下一个
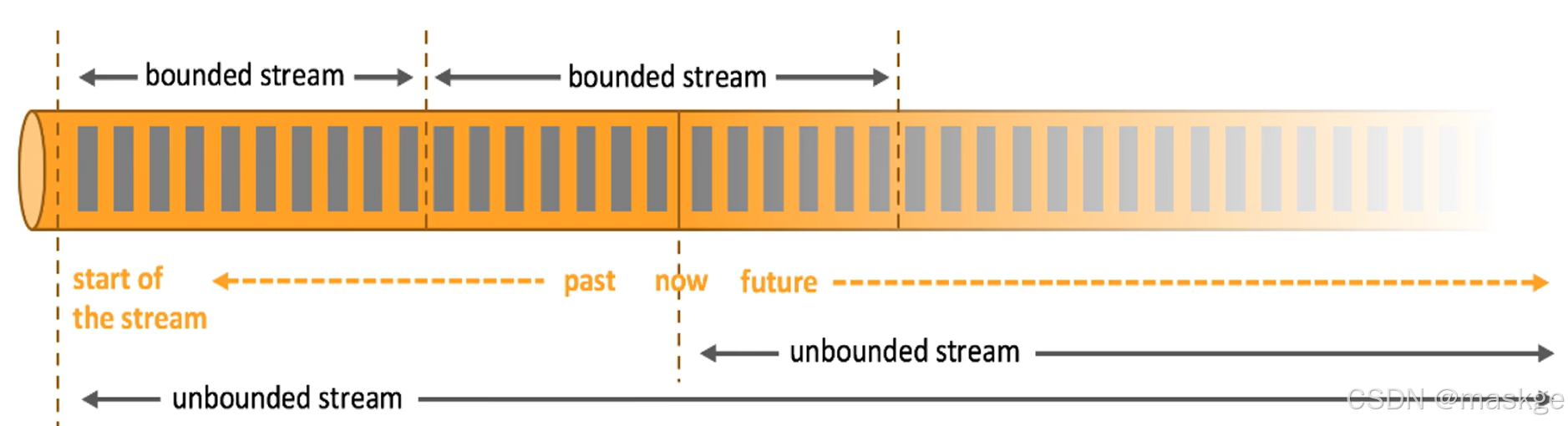
Flink以流处理为根本
- Flink数据模型:flink基本数据模型是数据流,以及事件(Event)序列
- Flink运行时架构:flink是标准的流执行模式,一个事件在一个节点处理完后可以直接发往下一个节点进行处理
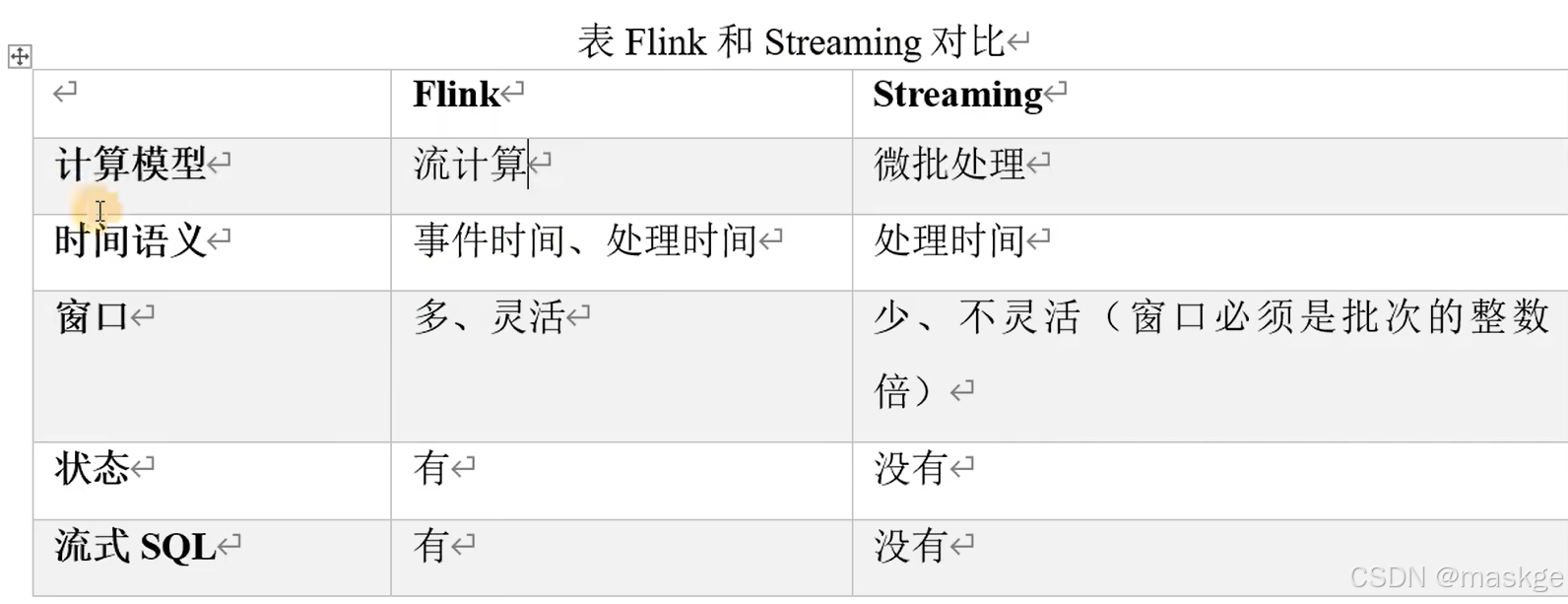
2.flink的应用场景
- 电商和市场营销 (eg:实时数据报表,广告投放、实时推荐)
- 物联网(LOT) (eg:传感器实时数据采集和显示,实时报警、交通运输业)
- 物流配送和服务业 (eg:订单状态实时更新、通知信息推送)
- 银行和金融业 (eg:实时结算和通知推送、实时检测异常行为)
3. flink流式处理架构
传统数据处理架构
- 事务处理(OLTP)
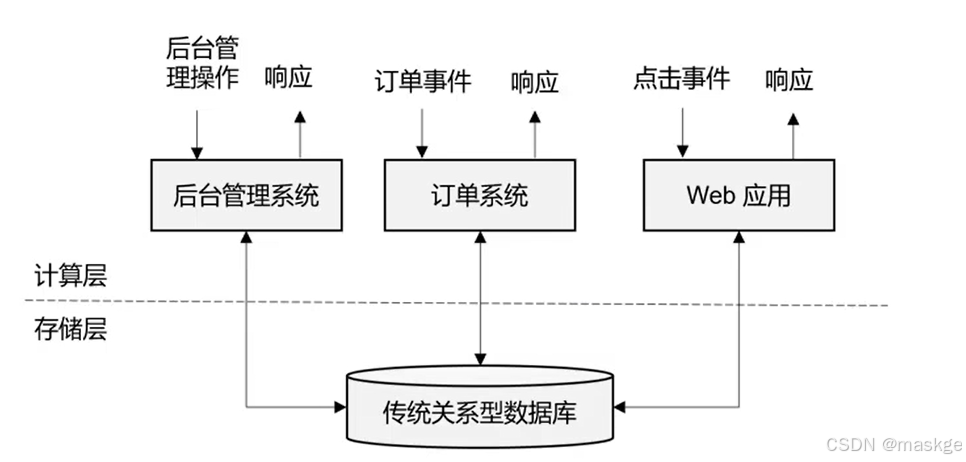
- 分析处理(OLAP)
有状态的流式处理
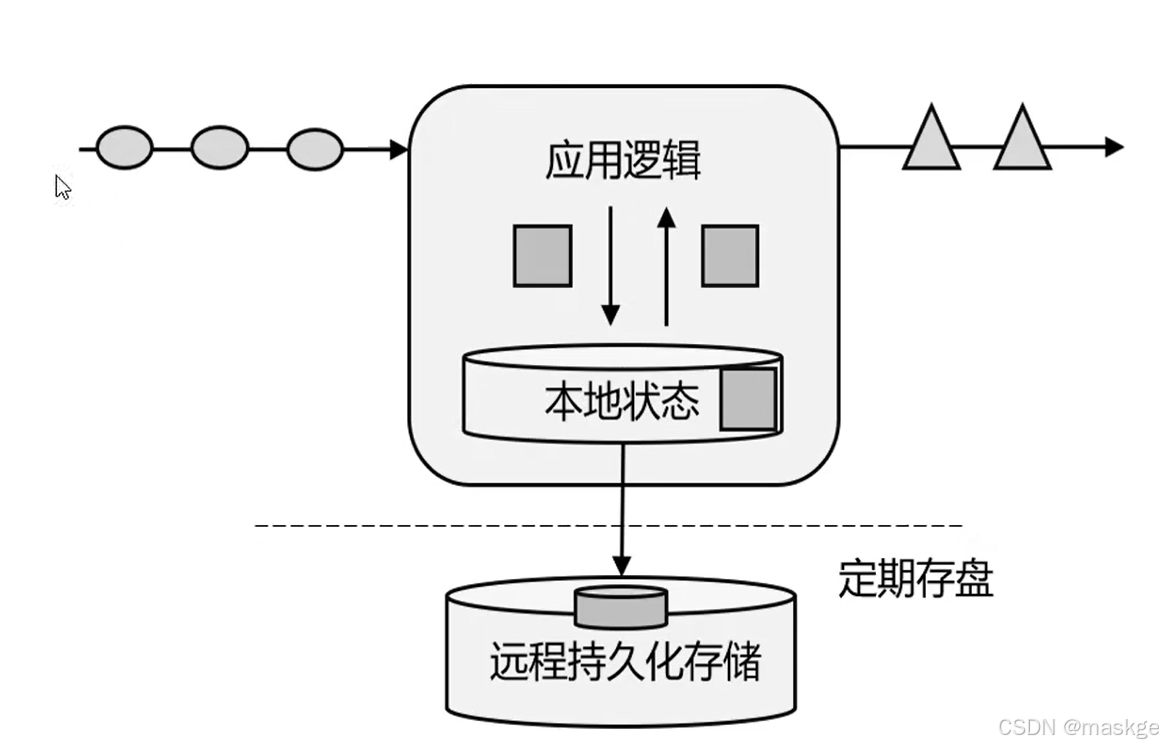
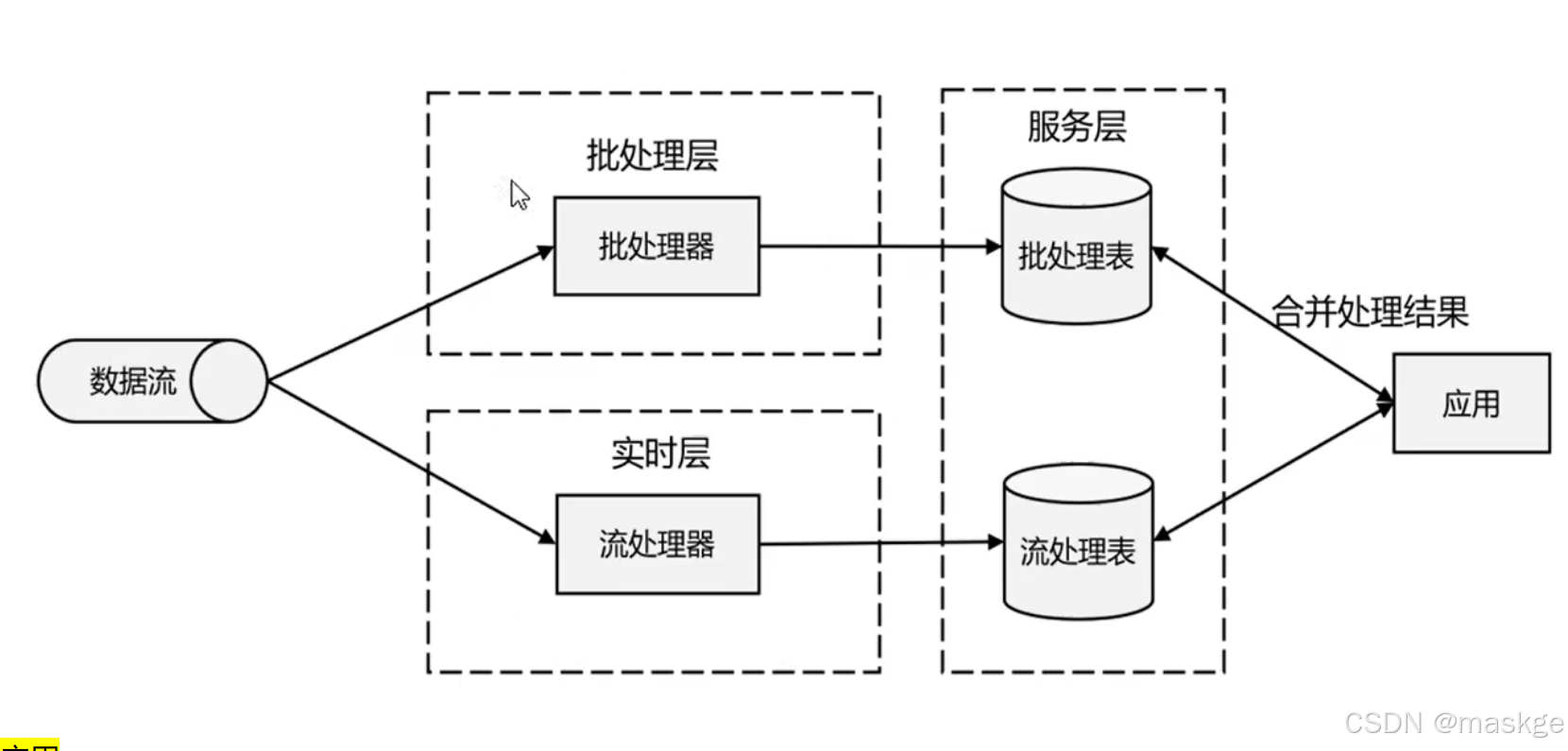
lambda架构
用两套系统,同时保证低延迟和结果准确
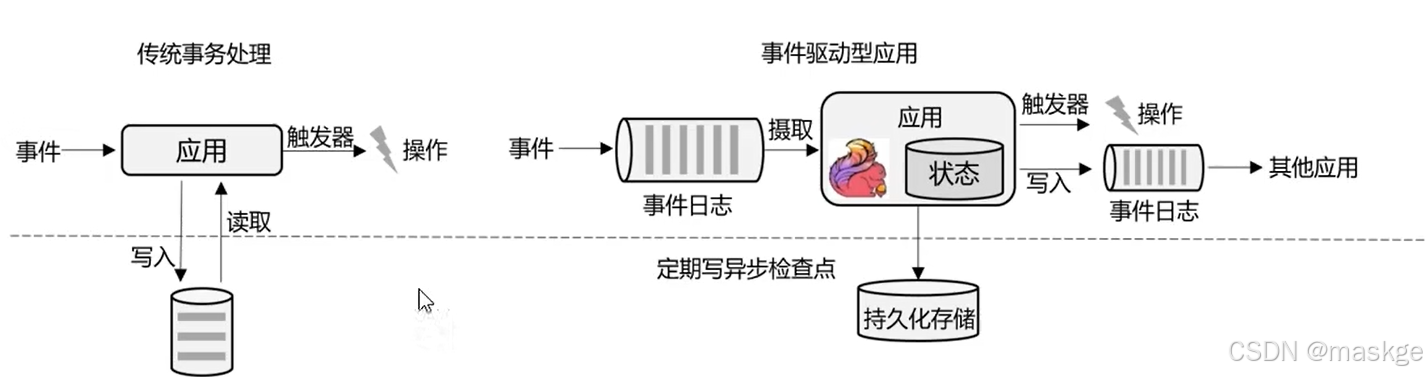
流处理的应用
-
事件驱动型应用
-
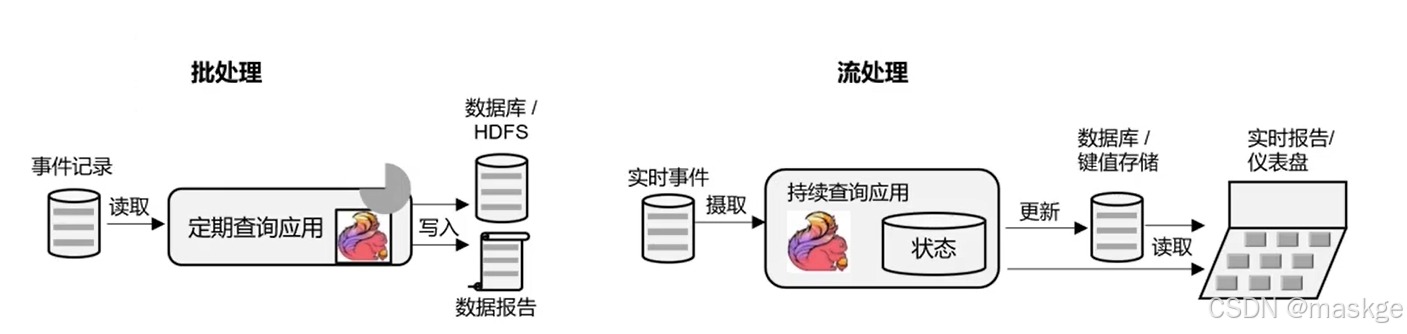
数据分析型应用
-
数据管道型应用
4.flink分层API
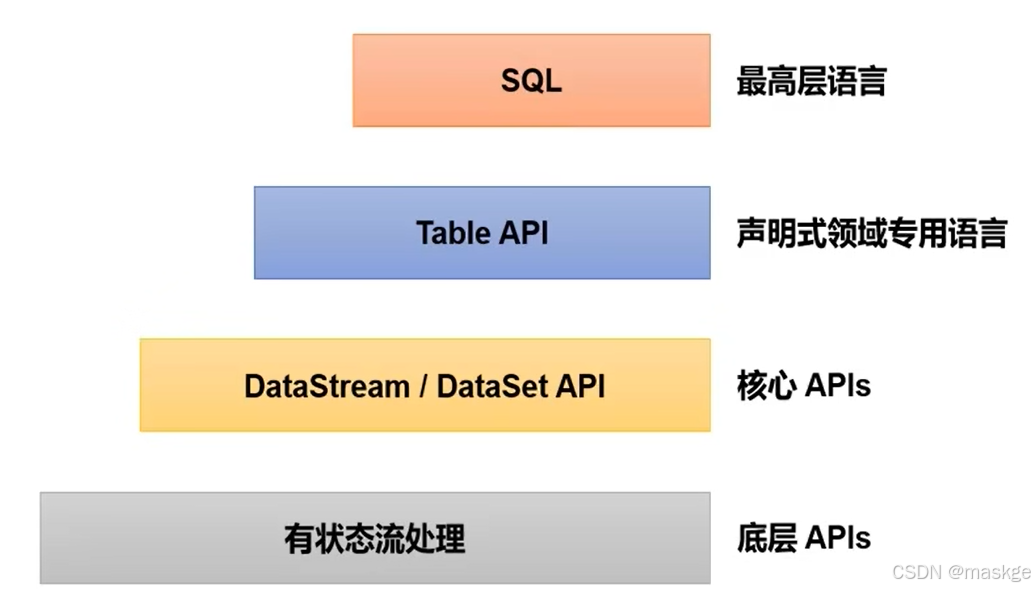
- 越顶层越抽象,表达含义越简明,使用越方便
- 越底层越具体,表达能力越丰富,使用越灵活

SQL这一层在语法与表达上与TableAPI类似,但是以SQL查询表达式的形式表现程序。SQL抽象与Table API交换密切,同时SQL查询可以直接在Table API定义的表上执行。
5.flink环境准备
-
ubuntu环境安装jdk17
下载oracle官方 jdk-17.0.12_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz
解压 sudo tar -zxvf jdk-17.0.12_linux-x64_bin.tar.gz配置环境变量:
打开文件: sudo vi /etc/profile,在文件末尾添加如下内容:
#jdk17 export JAVA_HOME_17=/usr/lib/jdk17/jdk-17.0.12#jdk8 export JAVA_HOME_8=/usr/lib/jdk1.8.0_461#设置当前环境jdk版本 export JAVA_HOME=$JAVA_HOME_8 export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH执行source /etc/profile刷新环境变量
执行 java -version验证jdk是否安装成功

-
安装flink
解压 flink安装包,给flink当前目录以及子目录授予执行权限
sudo chmod -R 777 *
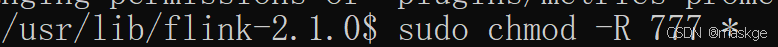
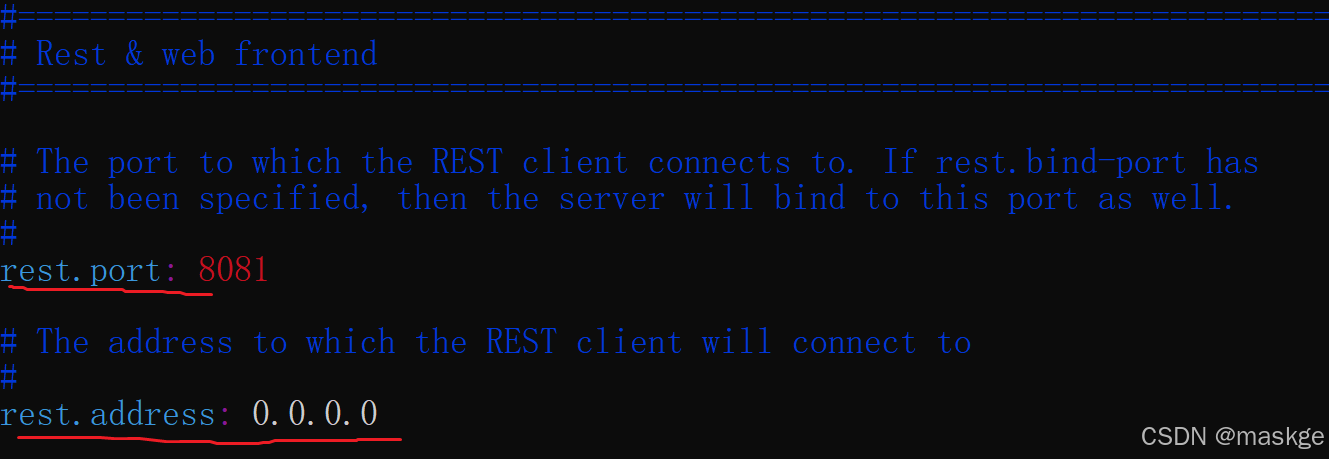
修改flink/conf中配置文件sudo vi conf.yaml如下内容:
执行如下命令启动:
./bin/start-cluster.sh
查看运行状态:
ps aux | grep flink
关闭防护墙
访问flink ui地址:
http://localhost:8081
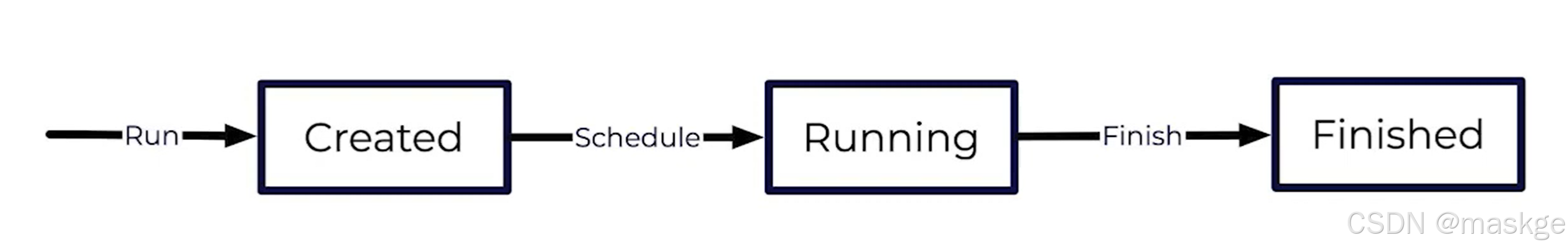
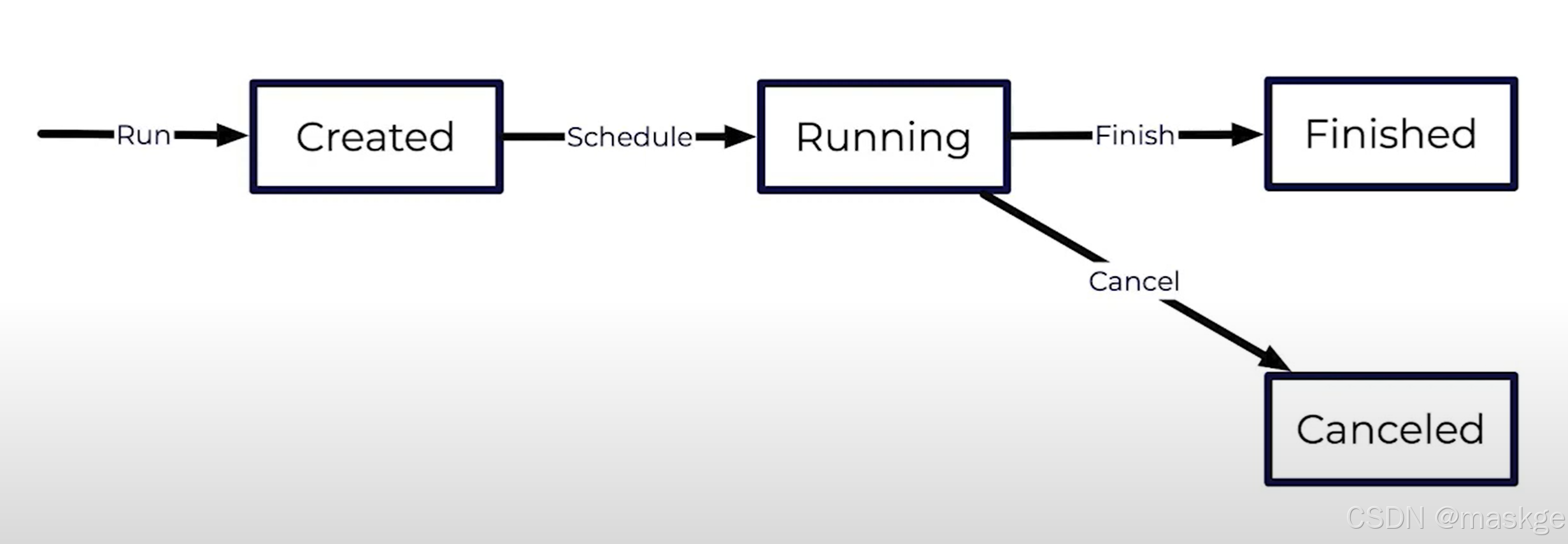
6.flink job 生命周期
-
Running a Job
-
Finishing a Job
-
Canceling a Job
-
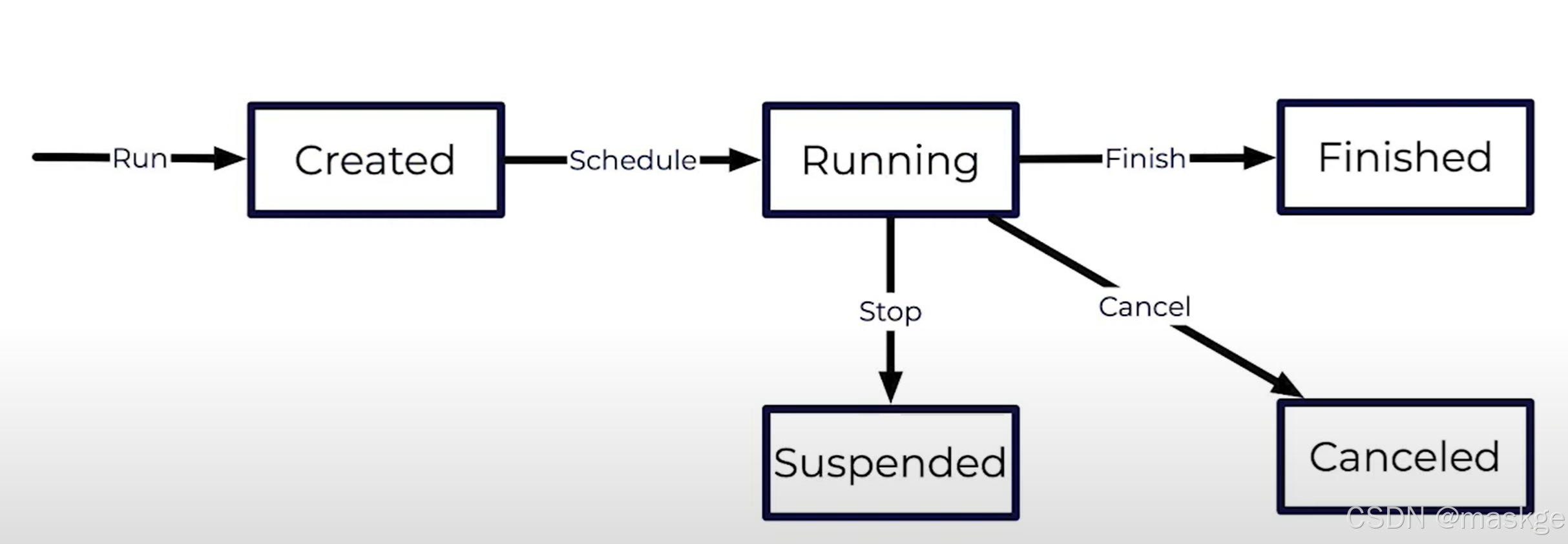
Stopping a Job
-
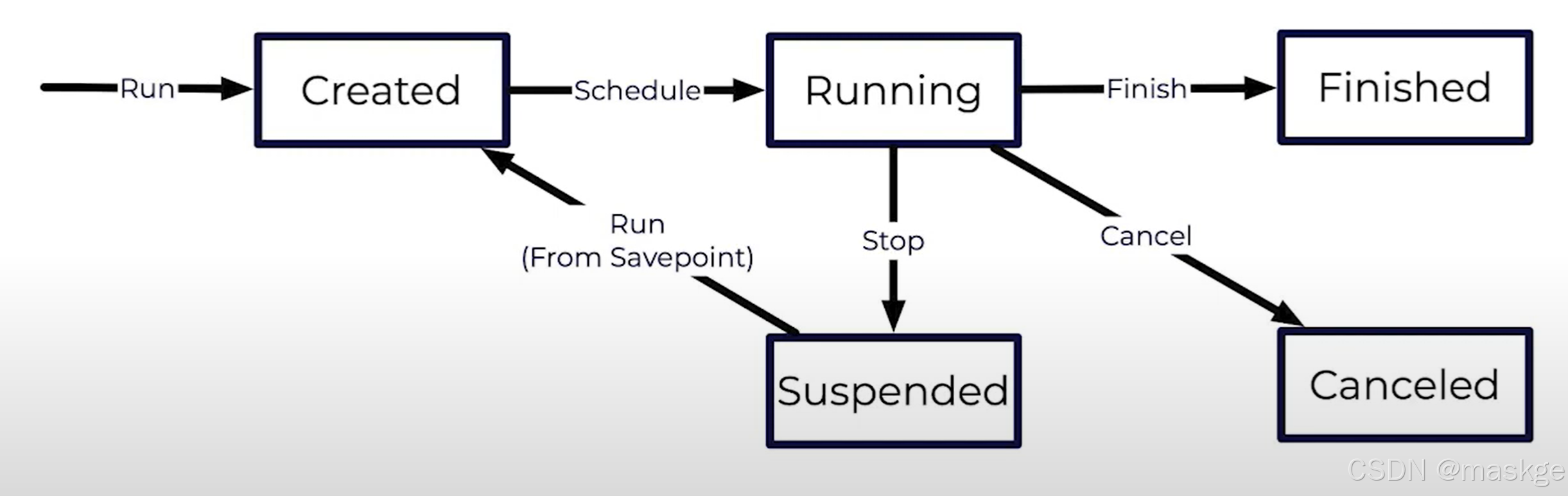
Resuming a Job
-
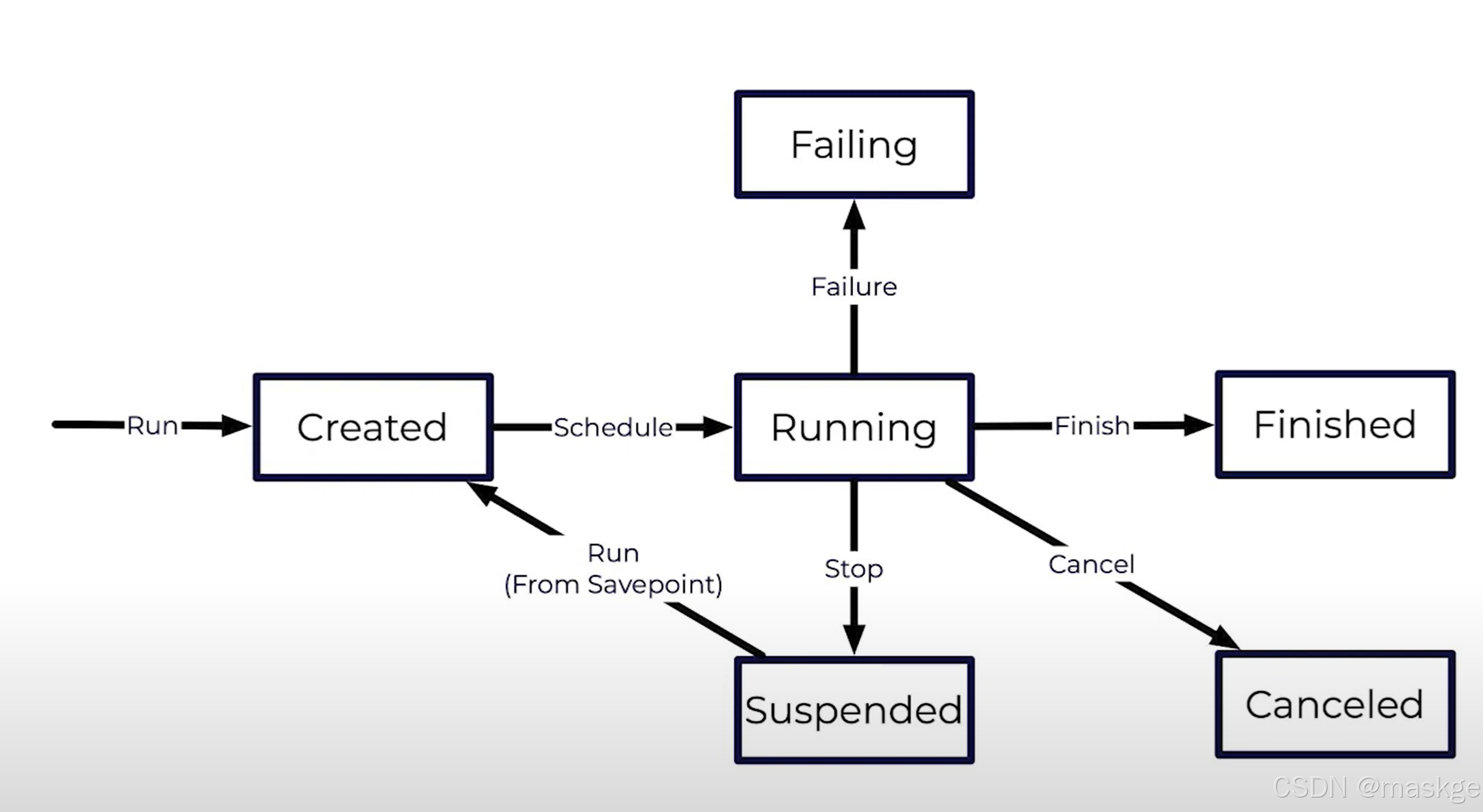
Failing Job
-
Restarting a Job
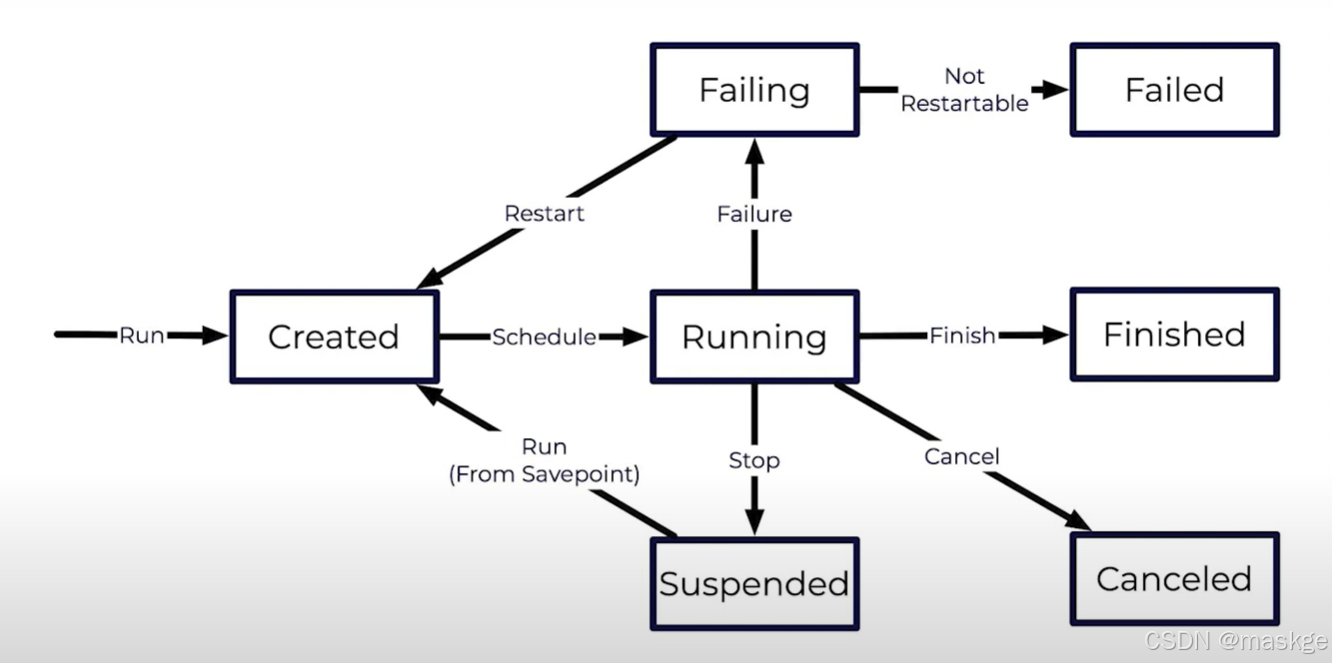
Recovery Strategies
- fixed-delay
- failure-rate
- exponential-delay
- job代码
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();env.fromElements(1,2,3,4,5).print();env.execute();
}
-
运行job
$ flink run $JAR_FILE$ flink run -c mypackage.MyClass $JAR_FILE$ flink run --detached $JAR_FILE -
取消job
$ flink cancel $JOB_ID -
停止job
$ flink stop --savepointPath $SAVEPOINT_FOLDER $JOB_ID -
resuming (唤醒) job
$ flink run --fromSavepoint $SAVEPOINT_FILE $JAR_FILE -
设置重启策略
env.setRestartStrategy(RestartStrategies.fixedDelayRestart(3, // number of restart attemptsTime.of(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) // delay ));
Run the job:
/bin/flink run target/travel-itinerary-0.1.jar
查看正在运行的所有job:
/flink*/bin/flink list
取消job:
bin/flink cancel <JobID>
当取消job的时候,看到异常:JobCancellationException,这是正常情况,可以忽略;
验证job是否取消成功,可以通过flink UI或者flink list名称查看
7.flink 核心执行步骤
1.flink datasource:
-
FromElements
DataStreamSource<Integer> stream = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); -
DataGeneratorSource
-
FileSource
FileSource<String> source=FileSource.forRecordStreamFormat(new TextLineInputFormat(),new Path("input/word.txt")).build(); -
KafaSource
Properties config=new Properties();config.setProperty("aa","11");KafkaSource<String> source=KafkaSource.<String>builder().setProperties(config).setTopics("topic1","topic2").setValueOnlyDeserializer(new SimpleStringSchema()).setBootstrapServers("localhost:9092").build();
2.flink创建流
StreamExecutionEnvironment env=StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();DataStream<String> stream=env.fromSource(source,//数据来源WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks(),"myFileSource" //数据来源名称);
3.打印流
stream.print();
4.执行流
//4.执行streamenv.execute("jobName");
8.flink 序列化与反序列
flink序列化分为内部序列化和外部序列化
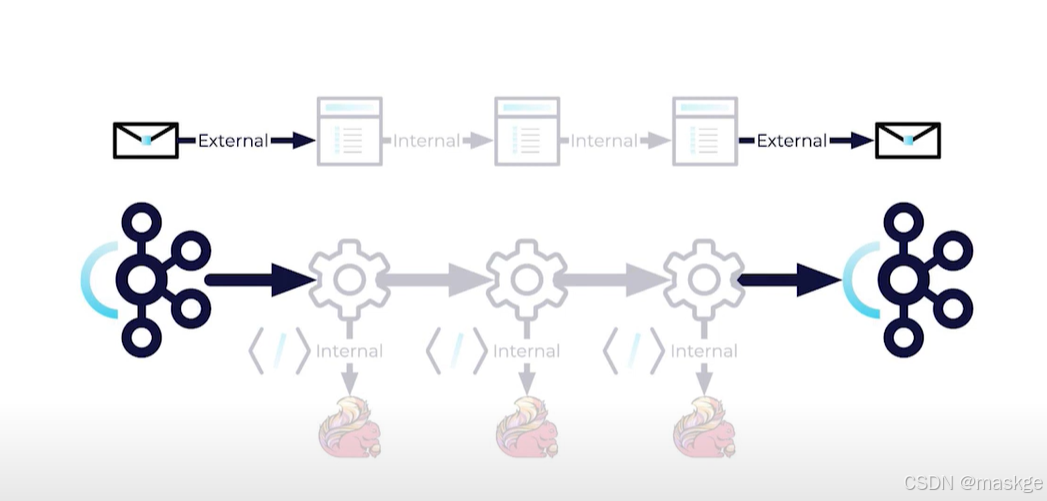
-
注册kryoType
env.getConfig().registerKryoType(MyCustomType.class);env.getConfig().disableGenericTypes(); -
JsonSerializationSchema 与JsonDeserializationSchema
//json反序列化JsonDeserializationSchema<MyCustomType>deserializer=new JsonDeserializationSchema<>(MyCustomType.class);//序列化JsonSerializationSchema<MyCustomType> serializer=new JsonSerializationSchema<>(()-> new ObjectMapper().registerModule(new JavaTimeModule()));<dependency><groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId><artifactId>flink-json</artifactId><version>1.17.2</version></dependency>
9.flink数据转换
-
ProcessFunction
- mapping elements
- flattening mapped elements
- filterElements
-
Process
stream.process(new MyProcessFunction()); -
Map
stream.map(input->new Output(input))DataStream<Double> doubles = integers.map(input -> Double.valueOf(input) / 2 ); -
FlatMap
stream.flatMap((collection,collector) -> {for(Input input: collection) {collector.collect(new Output(input));} });DataStream<Integer> letterCount = sentences.map(input -> input.split(" ")).flatMap((words, collector) -> {for (String word : words) {collector.collect(word.length());}}); -
Filter
stream.filter(input -> 7>9);DataStream<Integer> evenIntegers = integers.filter(input -> input % 2 == 0); -
keyBy
stream.keyBy(input -> input.getKey() ) -
KeyedProcessFunction
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators.Input; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators.Output; import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;/*** KeyedProcessFunction*/ public class MyKeyedProcessFunction extends KeyedProcessFunction<String, Input, Output> {@Overridepublic void processElement(Input input, KeyedProcessFunction<String, Input, Output>.Context ctx, Collector<Output> collector) throws Exception {String key=ctx.getCurrentKey();} } -
reduce
stream.keyBy(input -> input.key).reduce((s1, s2) -> s1.merge(s2));DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCountsByFirstLetter = itemIdsAndCounts.keyBy(tuple -> tuple.f0).reduce((l1, l2) -> new Tuple2(l1.f0, l1.f1 + l2.f1));
10.flink datasink
-
Serializers
KafkaRecordSerializationSchema<MyCustomType> serializerAA= KafkaRecordSerializationSchema.<MyCustomType>builder().setTopic("topic_name").setValueSerializationSchema(new JsonSerializationSchema<>()).build(); -
kafkaSink
KafkaSink<MyCustomType> sink=KafkaSink.<MyCustomType>builder().setKafkaProducerConfig(config).setRecordSerializer(serializerAA).setDeliveryGuarantee(DeliveryGuarantee.EXACTLY_ONCE).build(); -
使用sink
stream.sinkTo(sink).name("sink_name");
11.flink创建分支数据流
-
union:连接相同的数据流,成为一条流
DataStream<MyCustomType> stream1=null;DataStream<MyCustomType> stream2=null;DataStream<MyCustomType> union=stream1.union(stream2); -
Connect:连接几种不相同的数据流,成为一条流
DataStream<MyCustomType> stream3=null;DataStream<String> stream4=null;ConnectedStreams<MyCustomType,String> connected=stream3.connect(stream4); -
CoProcessFunction
connected.process(new CoProcessFunction<MyCustomType, String, Output>() {@Overridepublic void processElement1(MyCustomType value, CoProcessFunction<MyCustomType, String, Output>.Context ctx, Collector<Output> out) throws Exception {}@Overridepublic void processElement2(String value, CoProcessFunction<MyCustomType, String, Output>.Context ctx, Collector<Output> out) throws Exception {}}); -
CoMapFunciton & CoFlatMapFunction
connected.map(new CoMapFunction<MyCustomType, String, Object>() {@Overridepublic Object map1(MyCustomType value) throws Exception {return null;}@Overridepublic Object map2(String value) throws Exception {return null;}});connected.flatMap(new CoFlatMapFunction<MyCustomType, String, Object>() {@Overridepublic void flatMap1(MyCustomType value, Collector<Object> out) throws Exception {}@Overridepublic void flatMap2(String value, Collector<Object> out) throws Exception {}});
无状态的简单操作使用map和union;有状态的操心使用CoProcessFunction
- 分隔流(spliting Streams)
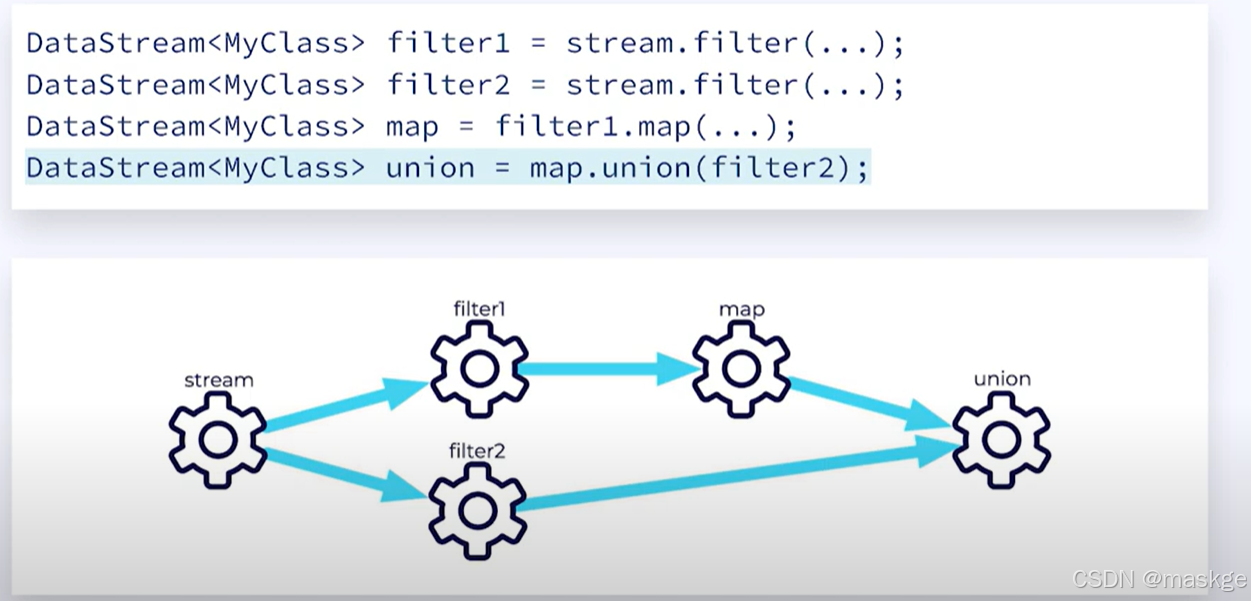
-
Side Outputs
-
side Output创建
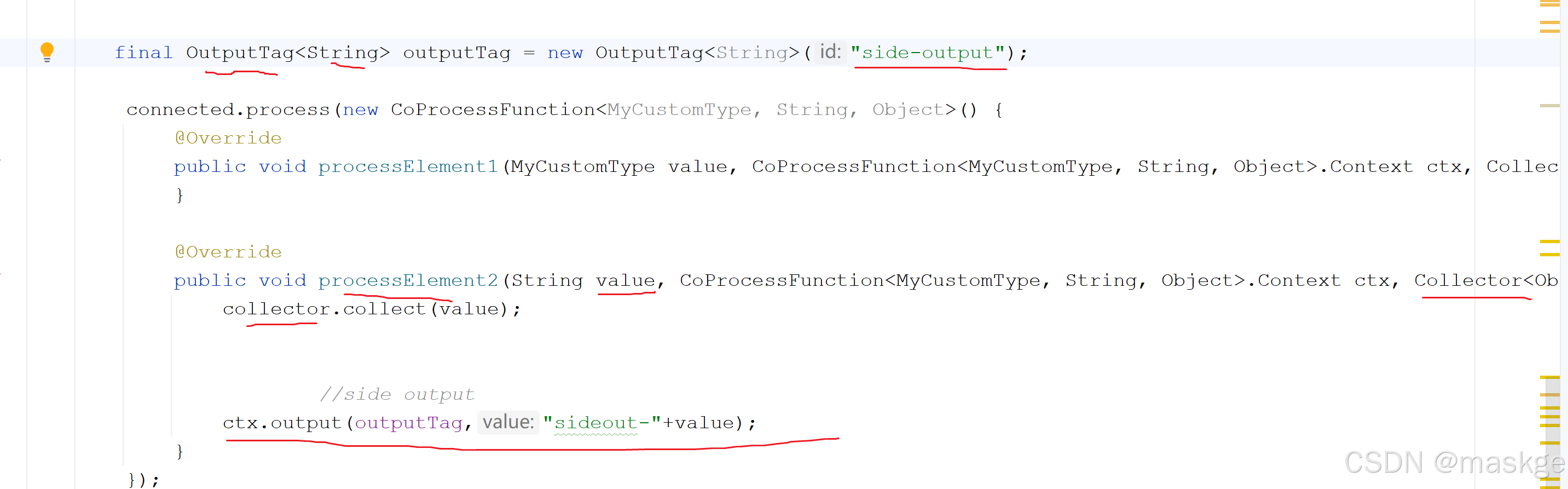
-
获取 side Output
//获取任何side output,通过outputTagSingleOutputStreamOperator<String> mainDataStream=null;DataStream<String> sideOutputStream=mainDataStream.getSideOutput(outputTag); -
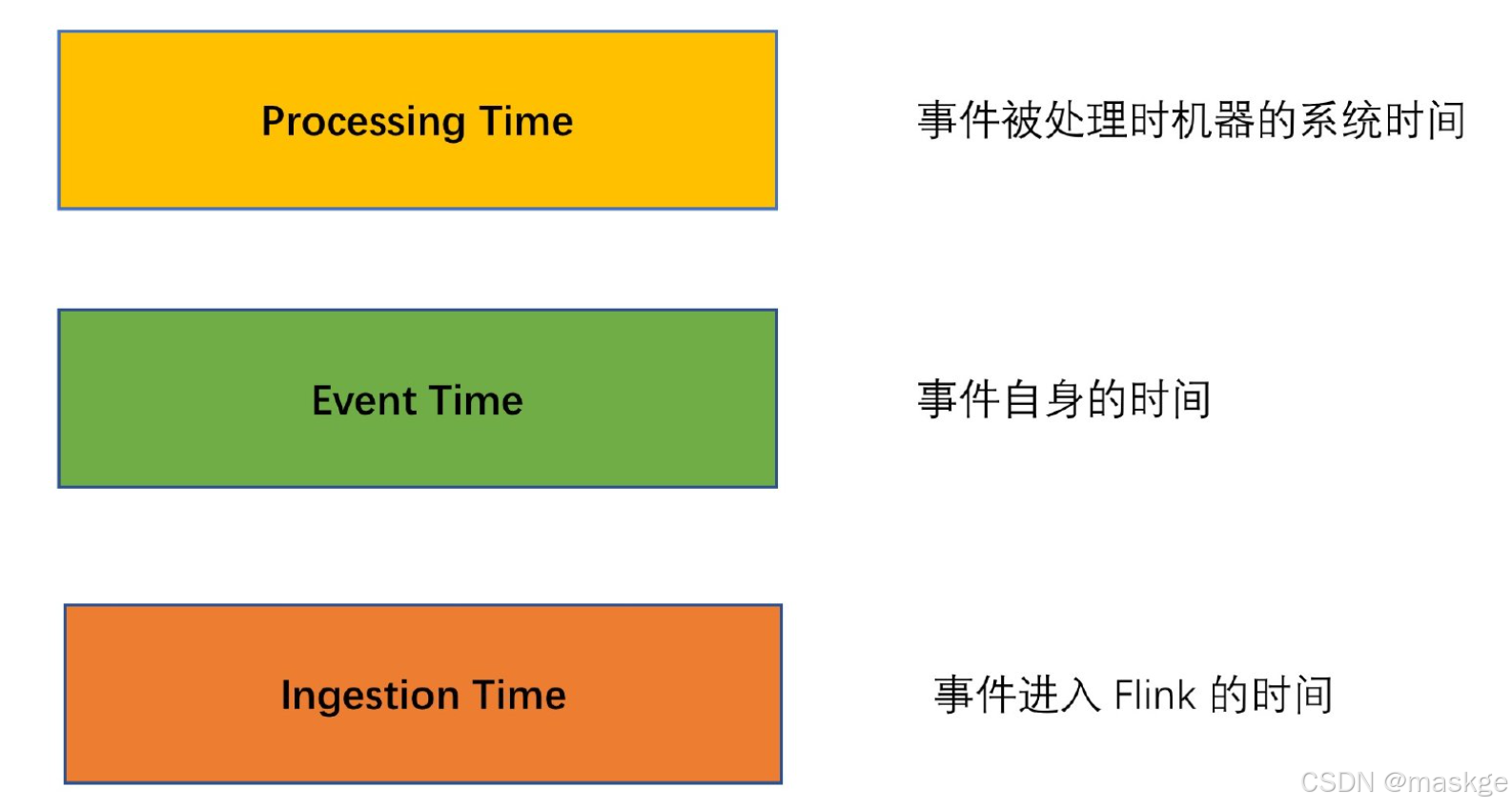
12 .flink windowing & Watermarks
p1.Flink windowing
-
windowAll:处理单个任务
stream.windowAll(timeWindow) -
window
stream.keyBy(record-> record.key).window(timeWindow); -
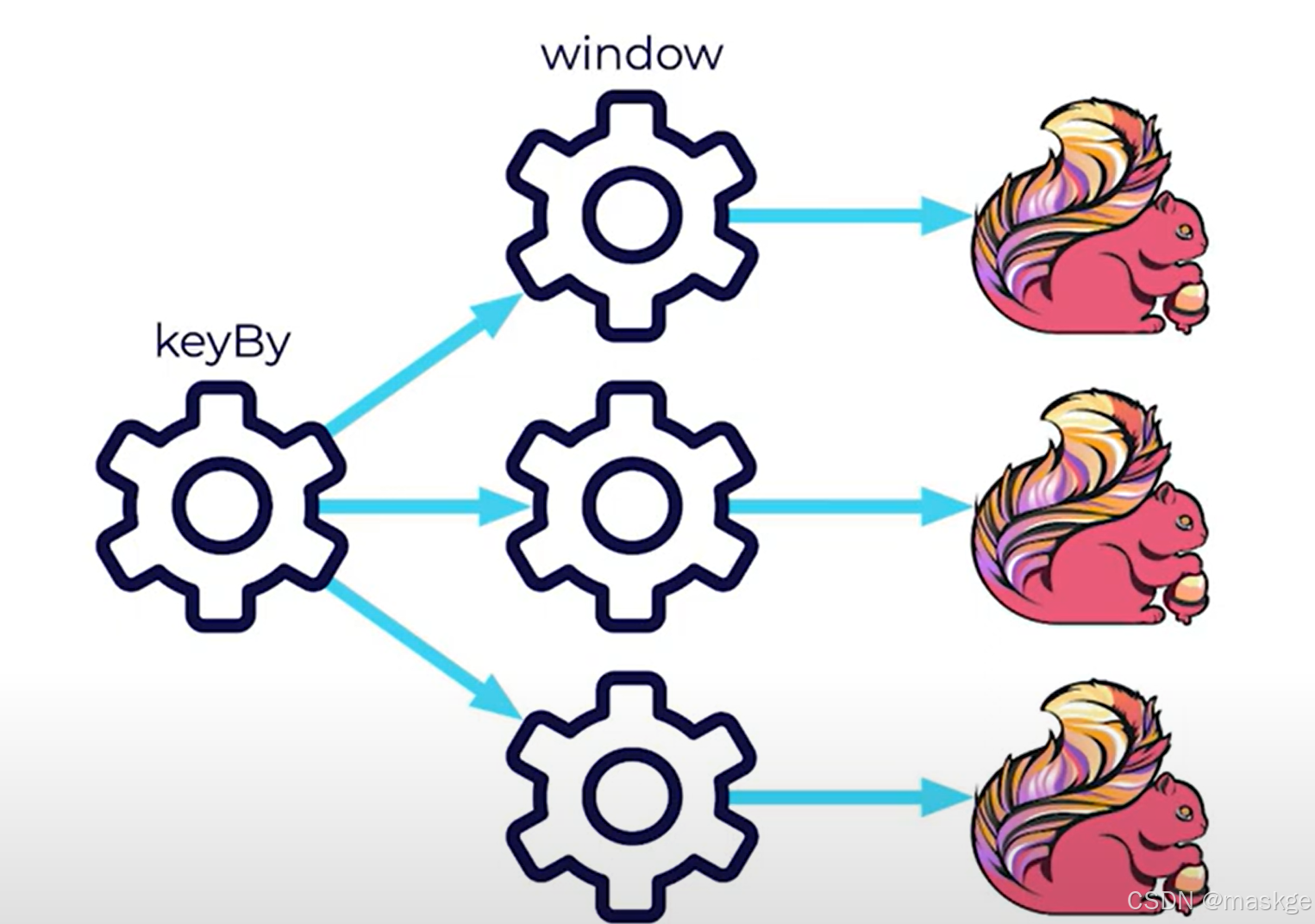
Parallelism:处理多个任务, keyBy是关键
-
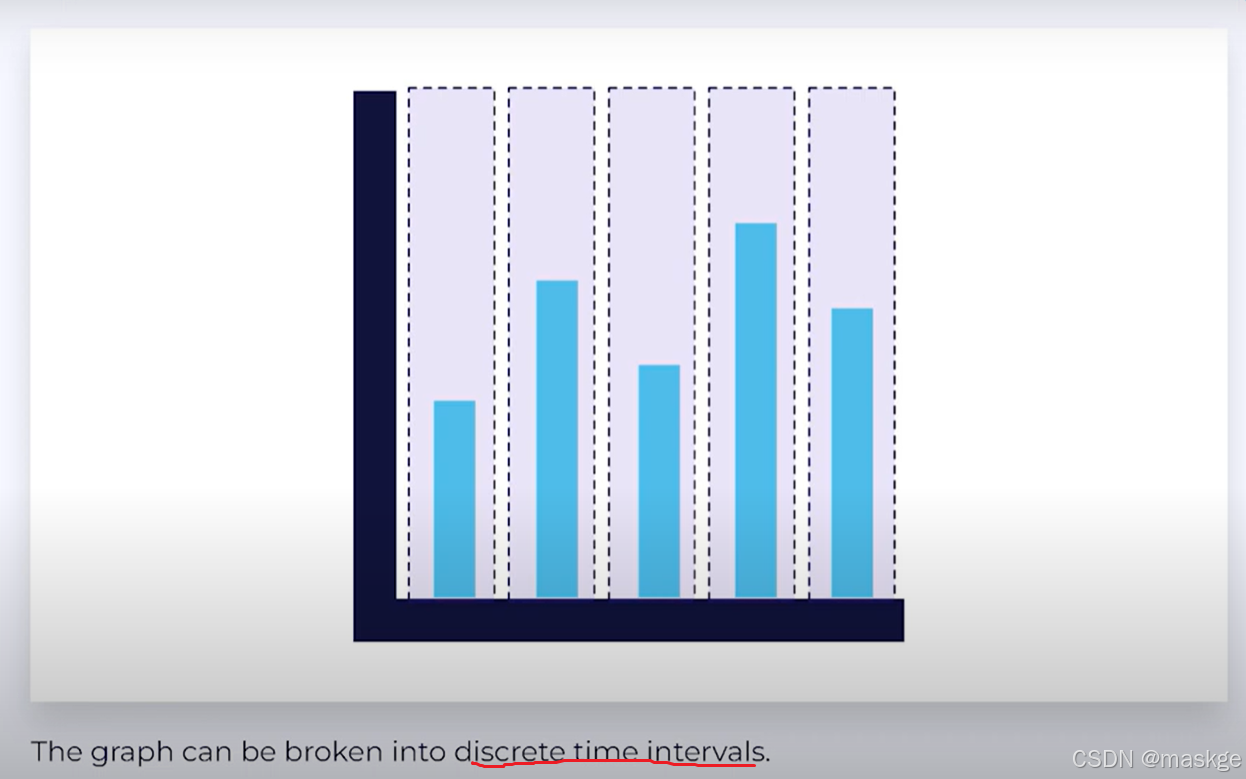
Tumbling Time Windows(滚动时间窗口):有固定的时间窗口
Tumbling Event Time Windows
//滚动事件时间窗口stream.keyBy(record->record).window(TumblingEventTimeWindows.of(org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time.seconds(5)));
- Sliding Time Windows :滑动时间窗口;窗口向前滑动,随着时间进行;多个滑动窗口有数据重叠
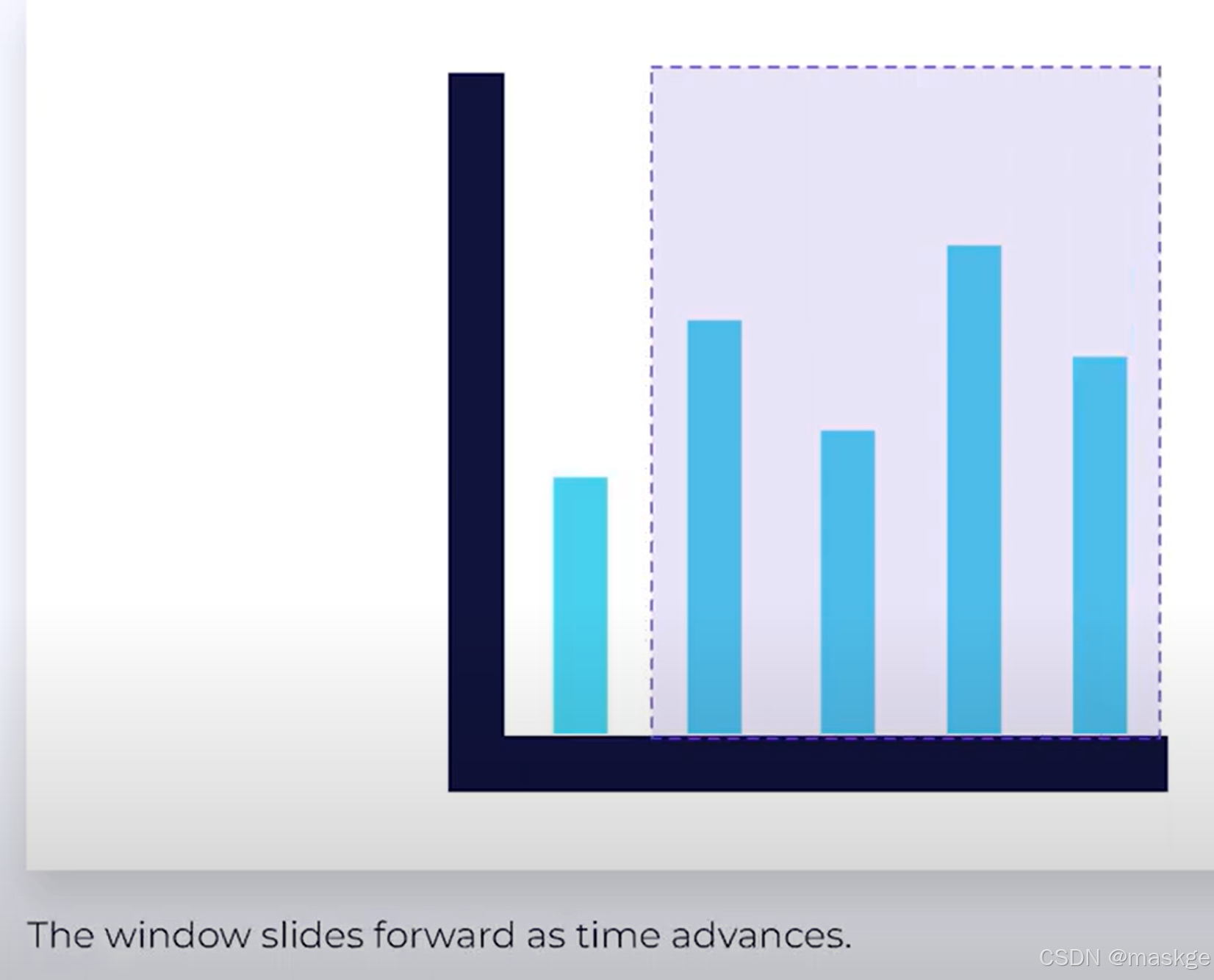
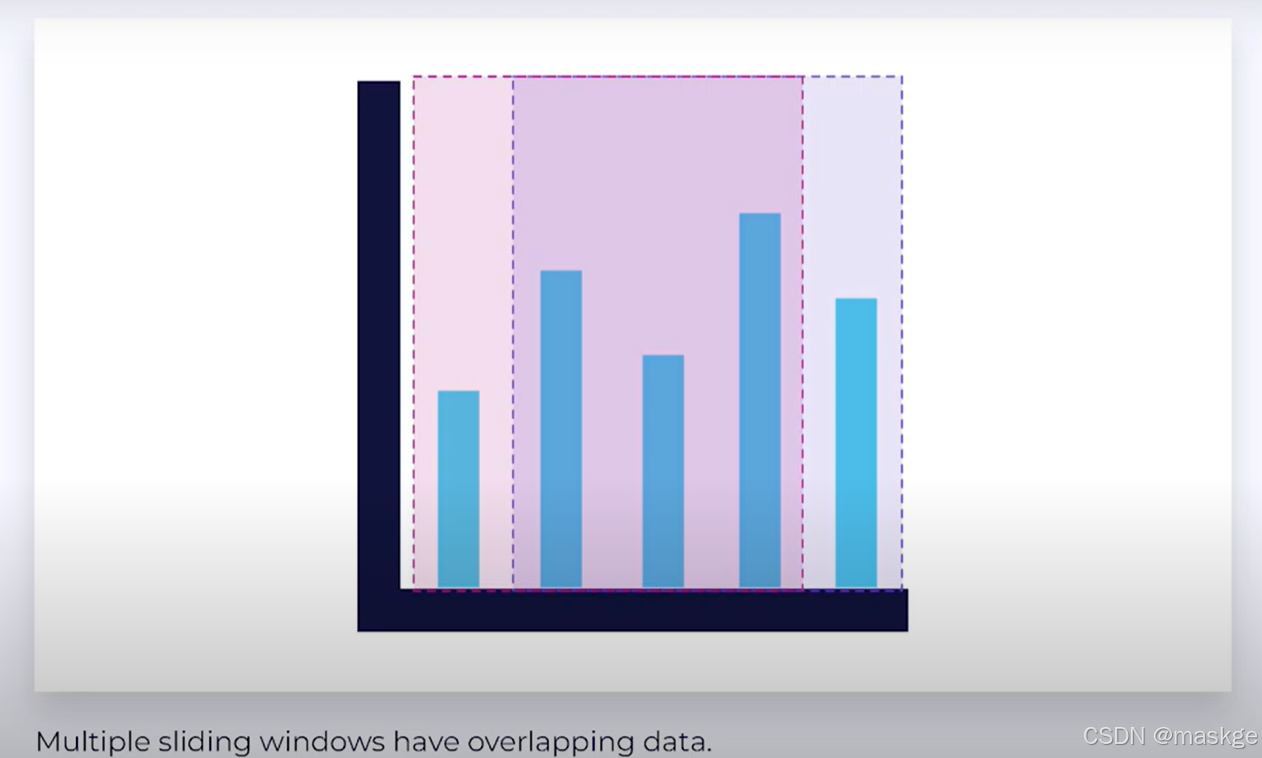
Sliding Event Time Windows
stream.keyBy(record->record.key).window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(windowSize,windowSlide))//滑动窗口stream.keyBy(record->record.key).window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time.seconds(10), org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time.seconds(5)));
- Session Time Windows:没有固定的时间窗口;session由窗口活动期决定;多个session有不同的会话时间
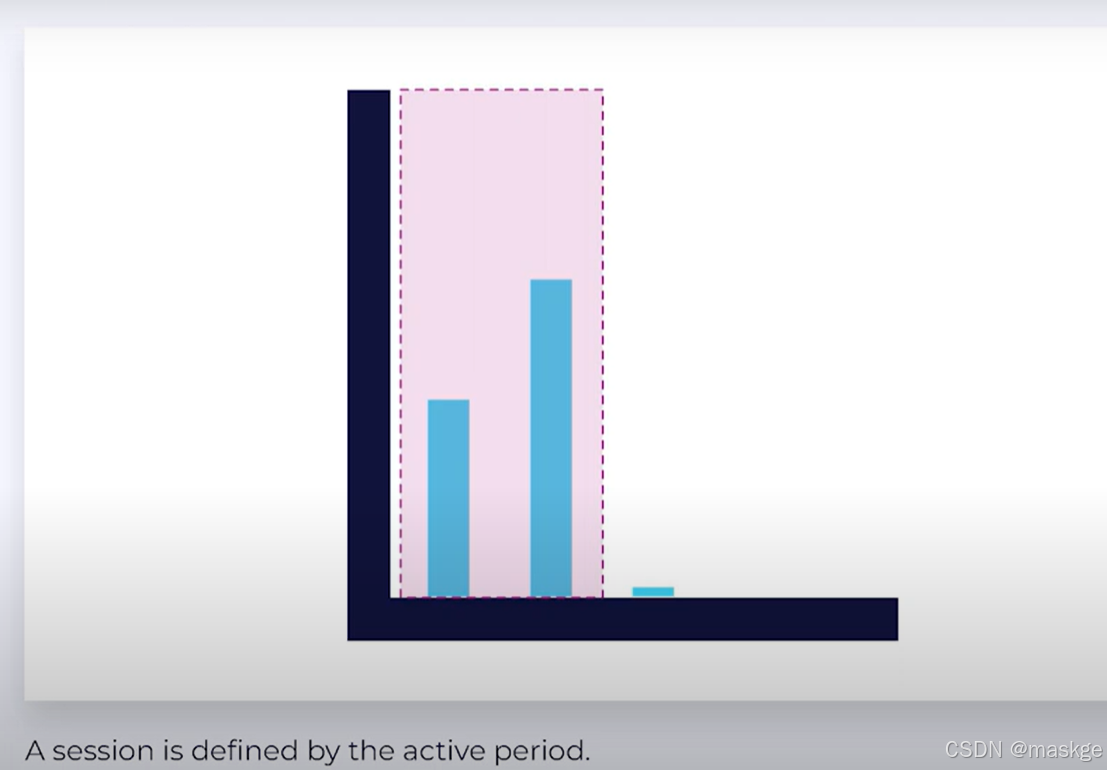
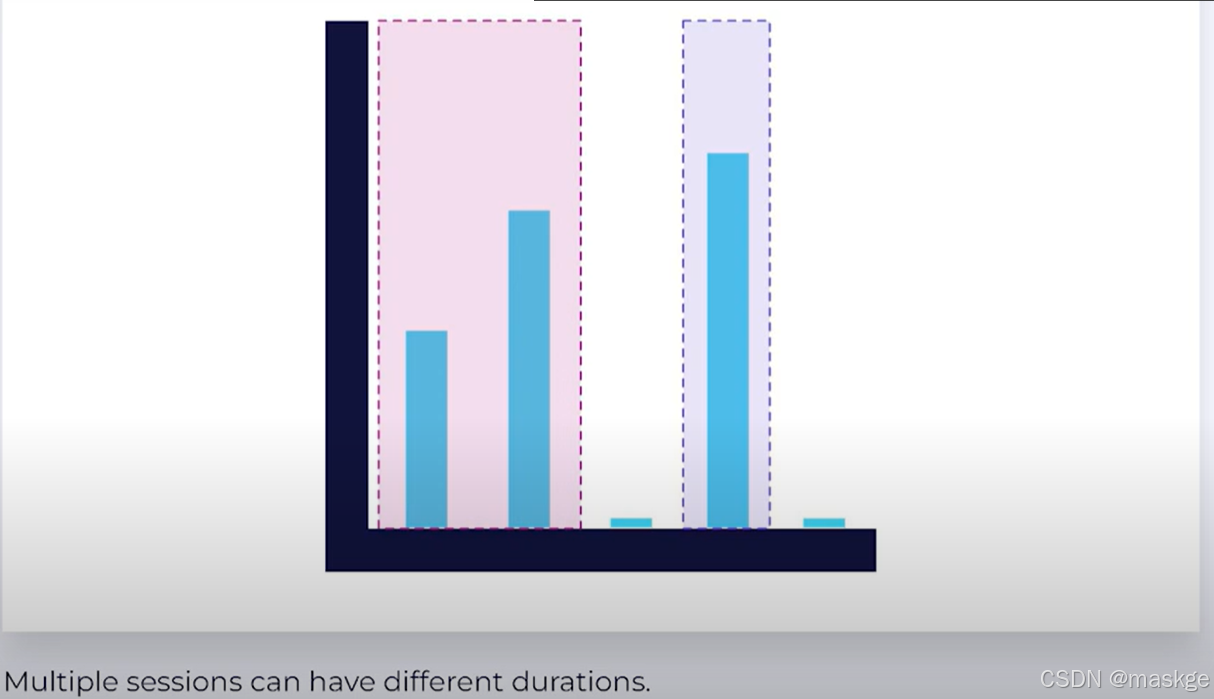
Session Event Time Windows
//会话窗口stream.keyBy(record->record.key).window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time.minutes(10)));//10分钟后关闭窗口
-
窗口操作
-
Window Join
stream1.join(stream4).where(elem1->elem1.getName()).equalTo(elem2->elem2).window(timeWindow).apply(new JoinFunction<MyCustomType, String, Object>() {@Overridepublic Object join(MyCustomType myCustomType, String s) throws Exception {return null;}});
p2. Watermarks:决定何种数据进入flink,类似一个时间戳timeStamp
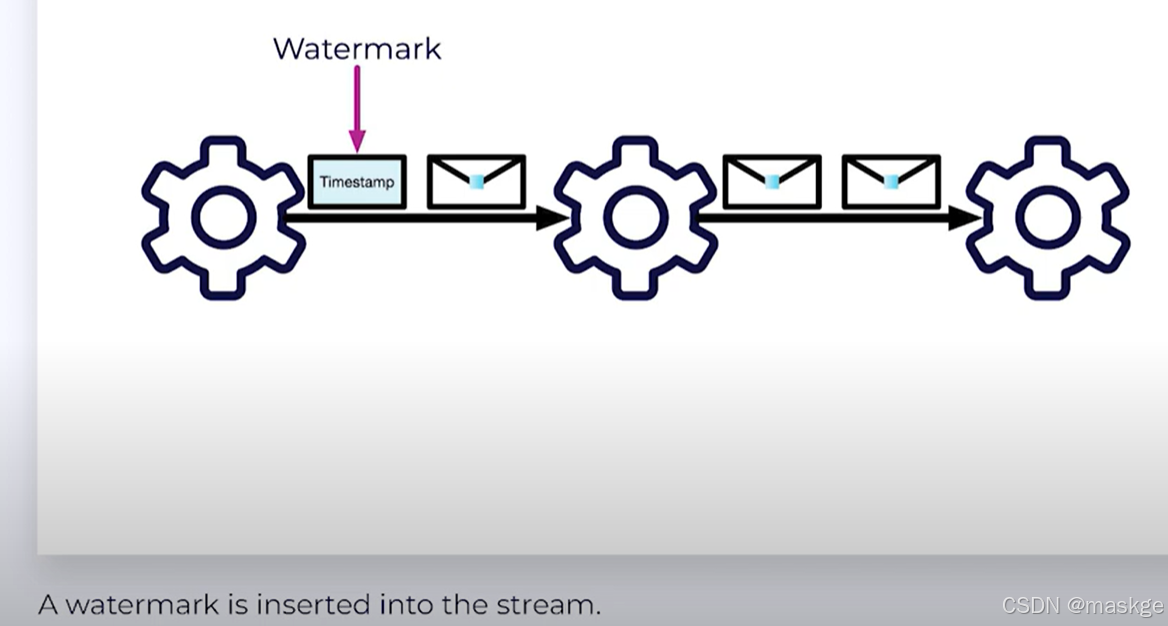
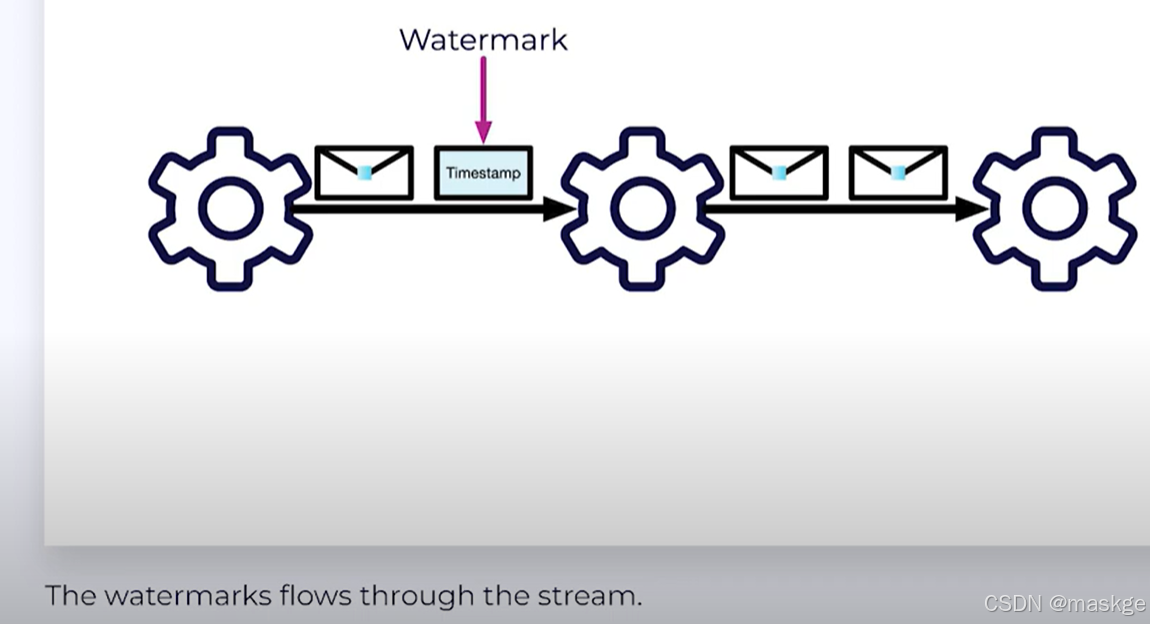
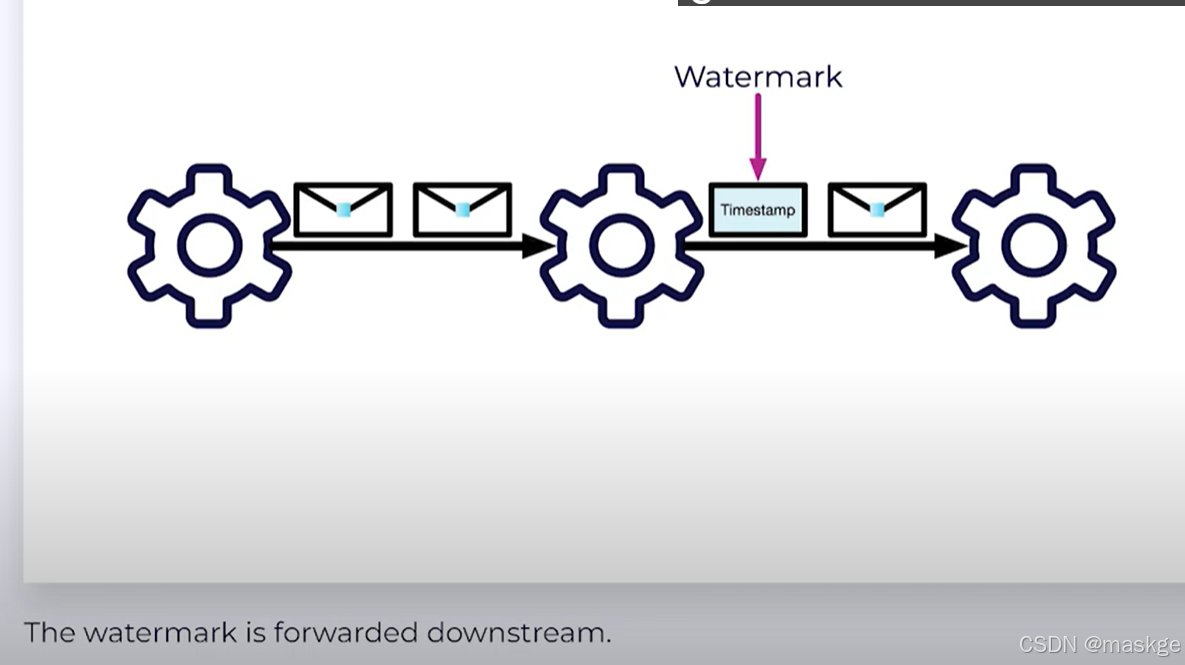
-
WatermarkStrategy
- noWatermarks
WatermarkStrategy watermarkStrategy=WatermarkStrategy.noWatermarks()
-
forMonotonousTimestamps:适合单线程处理消息
WatermarkStrategy watermarkStrategy=WatermarkStrategy.forMonotonousTimestamps(); -
forBoundedOutOfOrderness:处理无序消息
WatermarkStrategy watermarkStrategy=WatermarkStrategy.forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(10)); -
withTimestampAssigner:指定如何计算时间戳
-
withIdleness
WatermarkStrategy watermarkStrategy=WatermarkStrategy.forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(10)).withTimestampAssigner((event,timestamp)->timestamp).withIdleness(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
13.flink keyed state
-
Stateless Operations

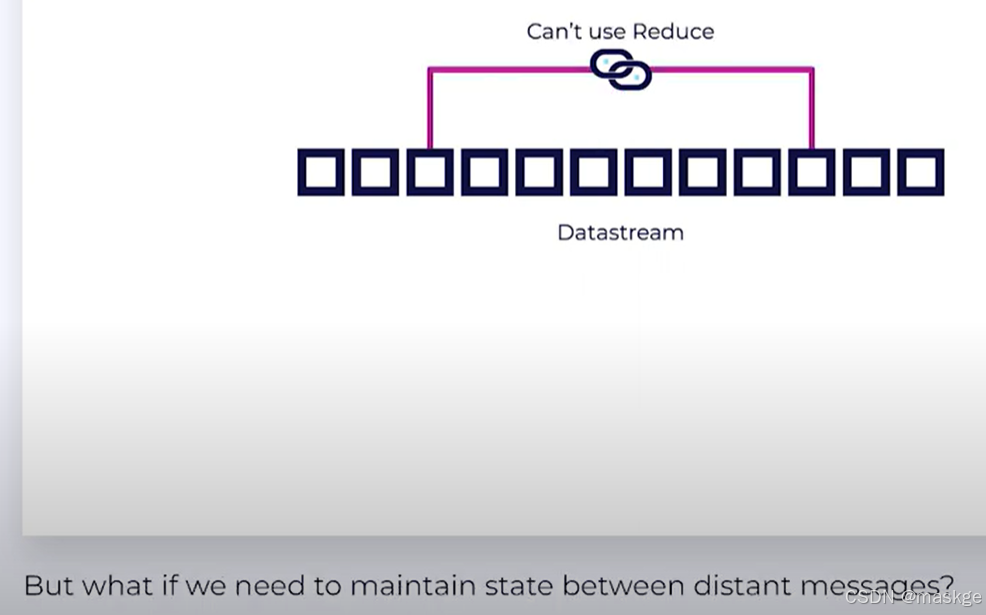
-
Fraud Detection(反欺诈)
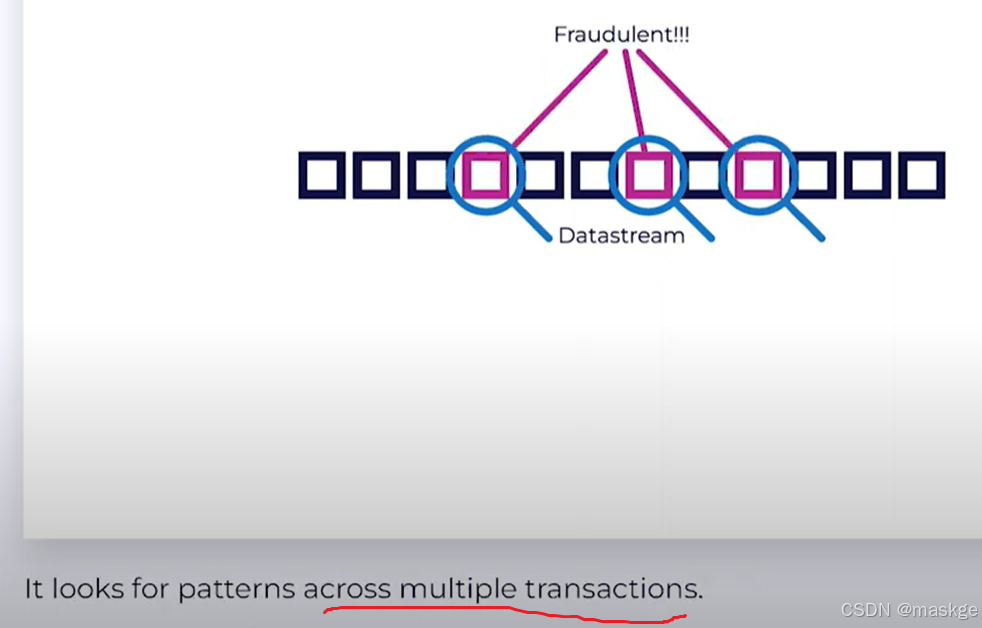
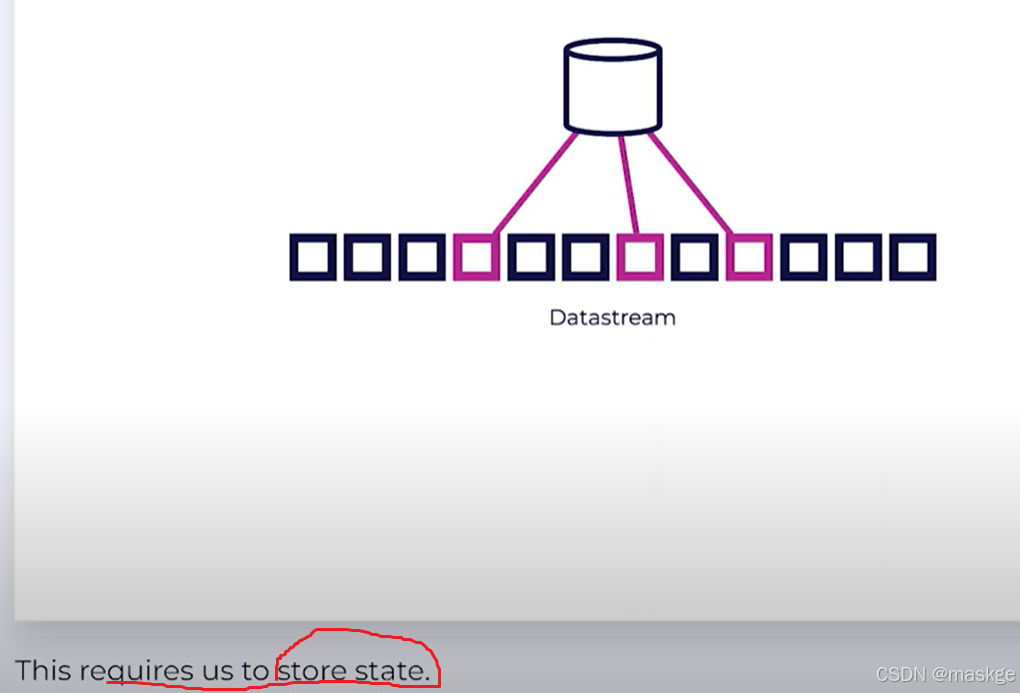
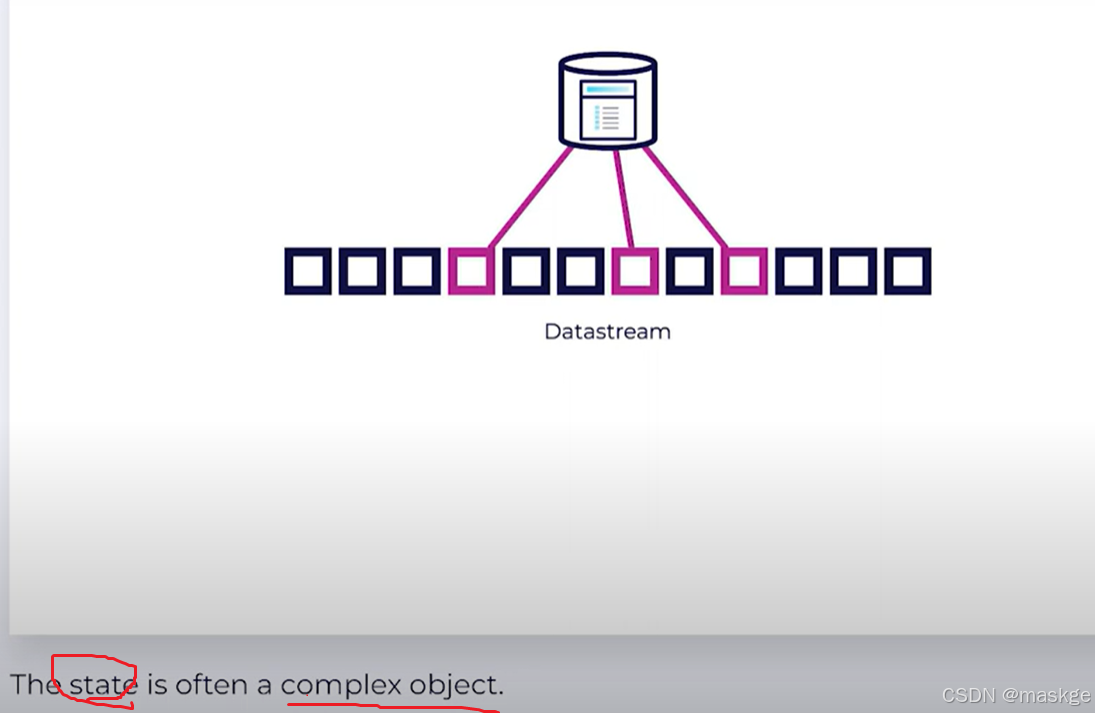
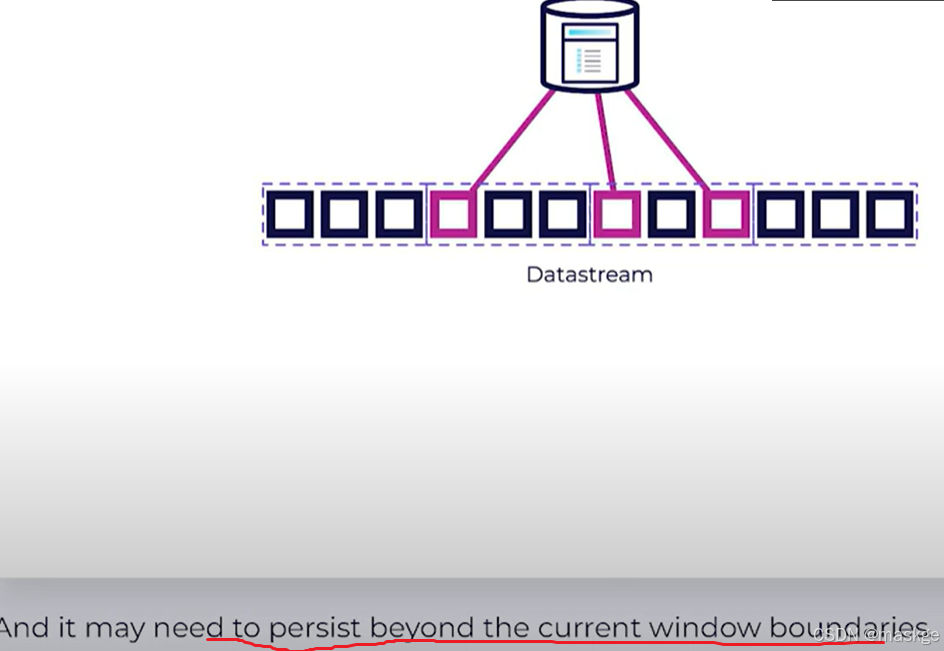
-
Key-Value Storage
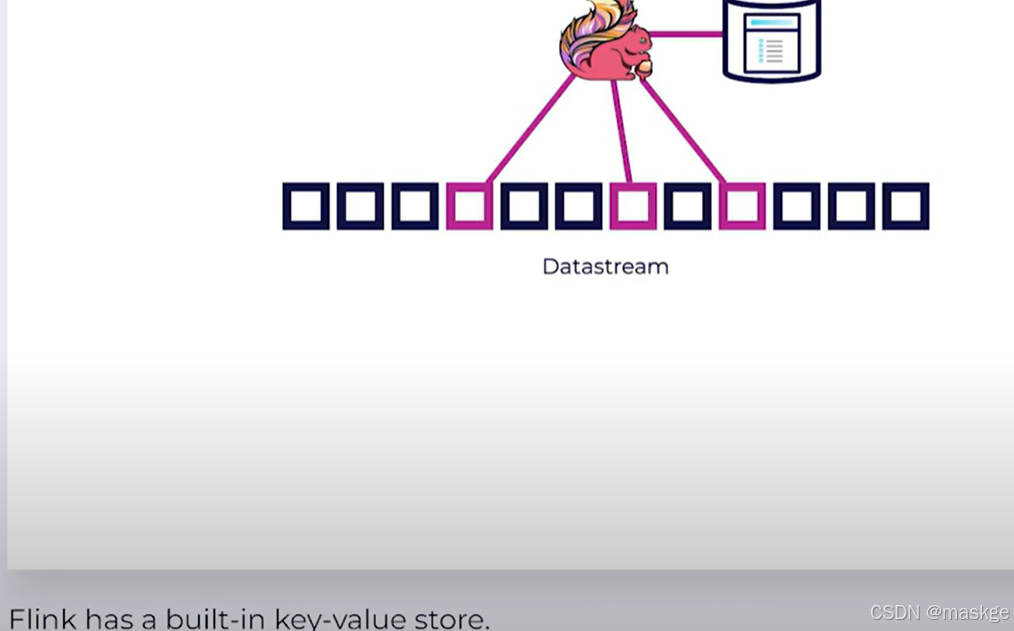
-
Keyed State

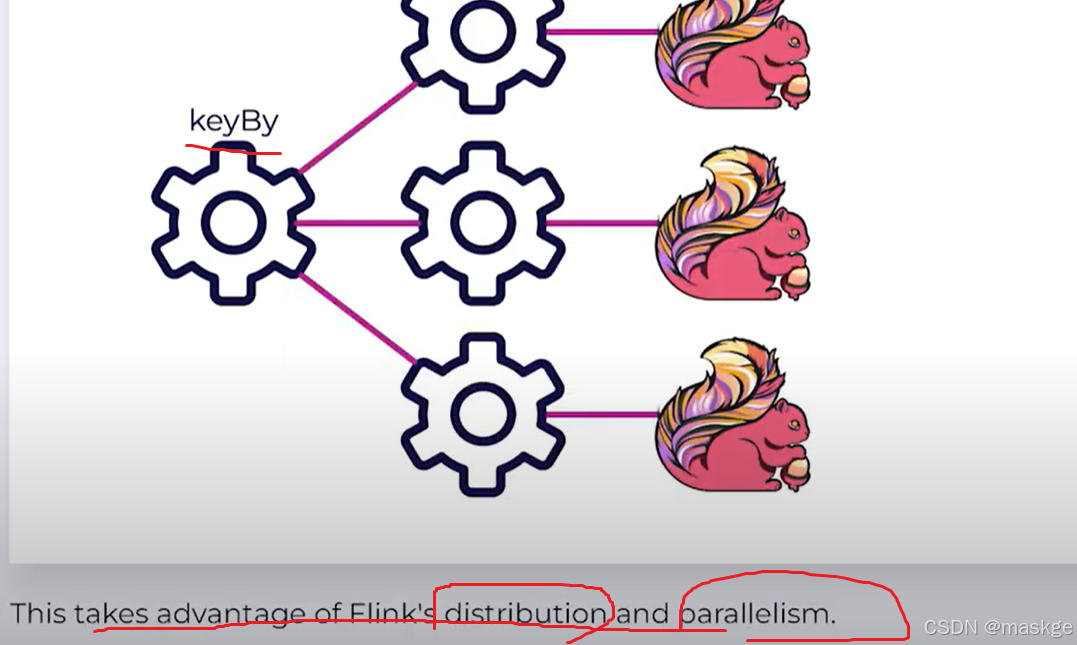
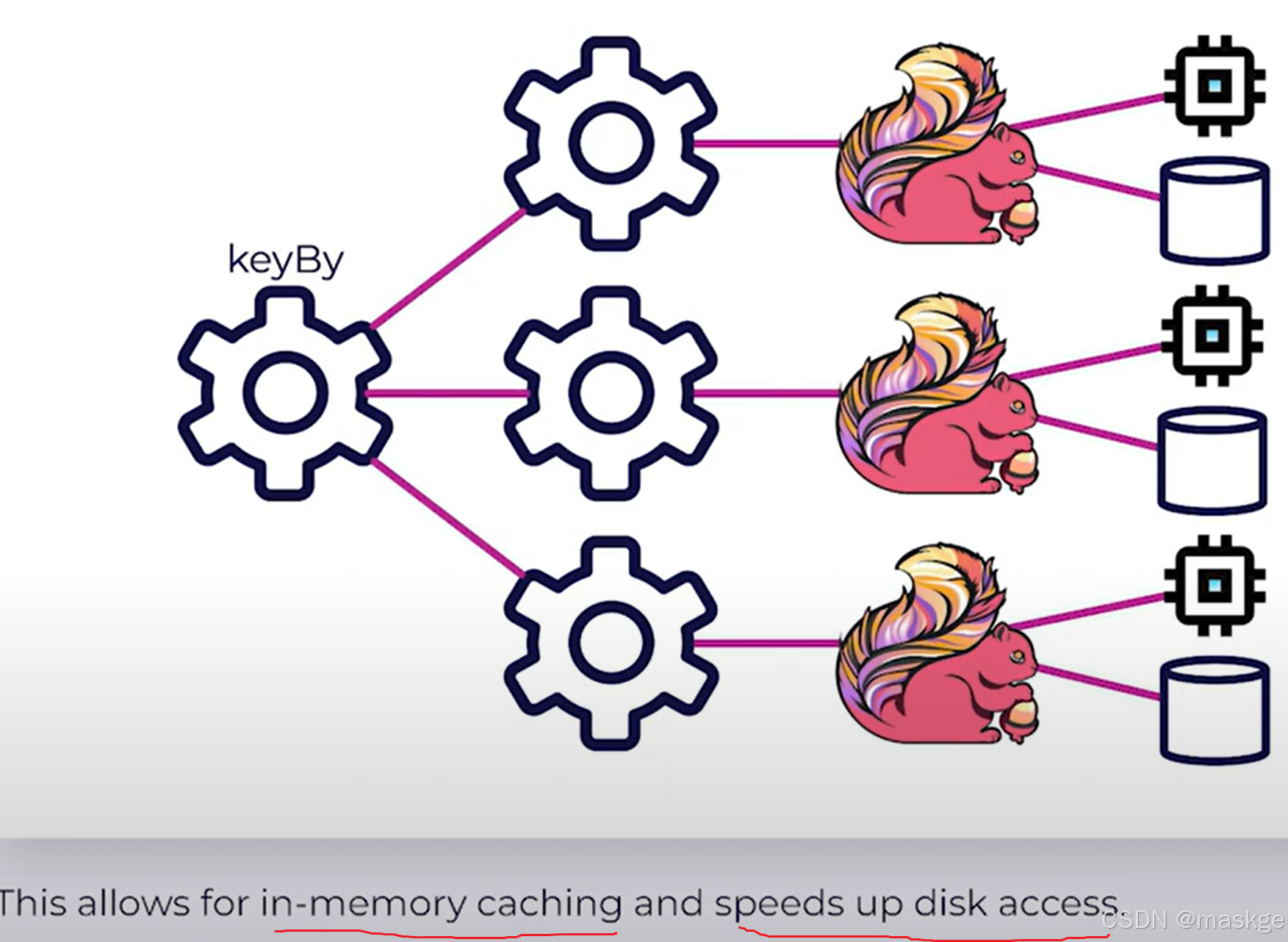
-
StateTypes:
1. ValueState: 对象状态 1. ListState:列表状态 1. MapState:map状态 1. ReducingState 1. AggregatingState
step1. Descriptors:状态描述符


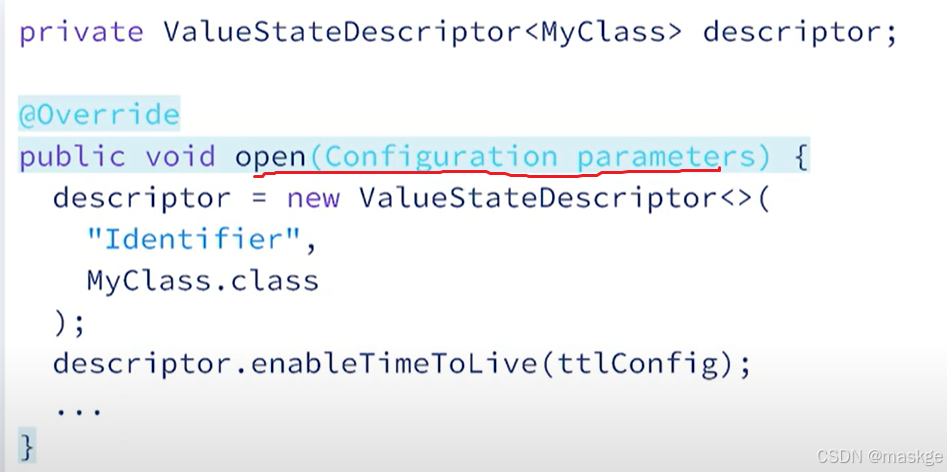
step2.Acessing State


step3. updating state

使用keyed state必须防止状态爆炸式增长,这些状态对象会占用磁盘和内存,特别是在处理全局状态而非窗口状态的时候;可以通过设置状态的生存时间减轻风险;使用全局状态的时候尽量保持对象较小,并且键空间有限
