Leetcode 最小生成树系列(1)
1135. 最低成本联通所有城市
想象一下你是个城市基建规划者,地图上有 nnn 座城市,它们按以 111 到 nnn 的次序编号。
给你整数 nnn 和一个数组 conectionsconectionsconections,其中 connections[i]=[xi,yi,costi]connections[i] = [x_{i}, y_{i}, cost_{i}]connections[i]=[xi,yi,costi] 表示将城市 xix_{i}xi 和城市 yiy{i}yi 连接所要的 costicost_{i}costi(连接是双向的)。
返回连接所有城市的最低成本,每对城市之间至少有一条路径。如果无法连接所有 nnn 个城市,返回 −1-1−1.
该 最小成本 应该是所用全部连接成本的总和。
示例 1:
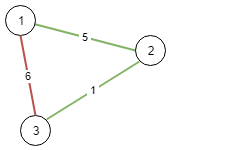
输入: n = 3, conections = [[1,2,5],[1,3,6],[2,3,1]]
输出: 6
解释: 选出任意 2 条边都可以连接所有城市,我们从中选取成本最小的 2 条。
示例 2:
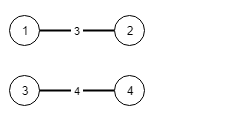
输入: n = 4, conections = [[1,2,3],[3,4,4]]
输出: -1
解释: 即使连通所有的边,也无法连接所有城市。
提示:
1<=n<=1041 <= n <= 1041<=n<=104
1<=connections.length<=1041 <= connections.length <= 1041<=connections.length<=104
connections[i].length==3connections[i].length == 3connections[i].length==3
1<=xi,yi<=n1 <= xi, yi <= n1<=xi,yi<=n
xi!=yixi != yixi!=yi
0<=costi<=1050 <= costi <= 1050<=costi<=105
题解:
从全局上看,这个题的核心就是——用最小的代价让所有节点(城市)互相连通。在图论里,这就是「最小生成树」(Minimum Spanning Tree, MST)问题。
🧩 核心思想可以浓缩为两句话:
- 只选能连通新城市的边:不断用代价最小、能增加图连通性的那条边扩展已有的网络。
- 避免形成回路:一旦出现闭环,就说明那条边是多余的,会浪费成本。
以 Kruskal 为例的思路
-
按边权从小到大排序 最便宜的连接优先考虑。
-
并查集判连通 每次加入一条边,只有当它连接了两个尚不在同一连通分量的城市时才真正采用。
-
重复直到形成 n−1 条边 此时正好连接了全部 n 个城市且无环,成本最小。
代码实现
import java.util.*;public class MSTConnector {// 并查集(Disjoint Set Union,支持路径压缩和按大小合并)static class DSU {int[] parent; // parent[i] 表示节点 i 的父节点int[] size; // size[i] 表示以 i 为根的集合大小// 构造函数:初始化 n 个独立的集合DSU(int n) {parent = new int[n];size = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {parent[i] = i; // 每个节点的父节点初始化为自己size[i] = 1; // 每个集合大小初始为 1}}// 查找 x 所在集合的根节点(路径压缩)int find(int x) {while (x != parent[x]) {parent[x] = parent[parent[x]]; // 压缩路径,加快后续查询x = parent[x];}return x;}// 合并 a 和 b 所在的集合(按集合大小合并)boolean union(int a, int b) {int ra = find(a), rb = find(b);if (ra == rb) return false; // 已在同一集合,不合并if (size[ra] < size[rb]) {int t = ra; ra = rb; rb = t; // 保证 ra 的集合较大}parent[rb] = ra; // 将较小集合合并到较大集合size[ra] += size[rb];return true;}}/*** Kruskal 算法求最小生成树的总成本* @param n 城市数量* @param connections 每条连接 [城市1, 城市2, 成本]* @return 最小总成本;若无法连通所有城市返回 -1*/public static int minimumCostKruskal(int n, int[][] connections) {if (n <= 1) return 0; // 没有城市或只有一个城市,不需要连接// 将边转成 [cost, u, v] 格式,并忽略自环List<int[]> edges = new ArrayList<>();for (int[] e : connections) {int x = e[0], y = e[1], c = e[2];if (x == y) continue; // 忽略自环edges.add(new int[]{c, x - 1, y - 1}); // 转换为 0-based 索引}// 按照成本升序排序edges.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));DSU dsu = new DSU(n); // 初始化并查集long total = 0; // 累加总成本int used = 0; // 已选用的边数量// 遍历所有边,贪心选择能连通两个不同集合的最小边for (int[] e : edges) {int c = e[0], u = e[1], v = e[2];if (dsu.union(u, v)) { // 如果连接了两个不同集合total += c;used++;if (used == n - 1) return (int) total; // 已构成生成树}}return -1; // 遍历完仍未连通所有城市}public static void main(String[] args) {int n = 4;int[][] connections = {{1, 2, 3},{2, 3, 4},{3, 4, 5},{1, 4, 10},{2, 4, 6}};// Kruskal 输出System.out.println(minimumCostKruskal(n, connections)); // 输出 12// Prim 输出System.out.println(minimumCostPrim(n, connections)); // 输出 12}/*** Prim 算法求最小生成树的总成本* @param n 城市数量* @param connections 每条连接 [城市1, 城市2, 成本]* @return 最小总成本;若无法连通所有城市返回 -1*/public static int minimumCostPrim(int n, int[][] connections) {if (n <= 1) return 0;// 构建邻接表,每个元素是 (cost, 目标城市)List<int[]>[] adj = new ArrayList[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();// 添加无向边for (int[] e : connections) {int x = e[0], y = e[1], c = e[2];if (x == y) continue; // 忽略自环int u = x - 1, v = y - 1;adj[u].add(new int[]{c, v});adj[v].add(new int[]{c, u});}boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; // 标记已加入生成树的城市PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));long total = 0; // 累加总成本int count = 1; // 已访问城市数// 从 0 号城市出发,将它的所有边加入最小堆visited[0] = true;for (int[] edge : adj[0]) pq.offer(edge);// 不断从堆中取最小边扩展while (!pq.isEmpty() && count < n) {int[] top = pq.poll();int c = top[0], v = top[1];if (visited[v]) continue; // 城市已访问,跳过visited[v] = true;count++;total += c;for (int[] edge : adj[v]) pq.offer(edge); // 加入新城市的边}return count == n ? (int) total : -1; // 判断是否连通}
}
运行结果