4.1vue3的setup()
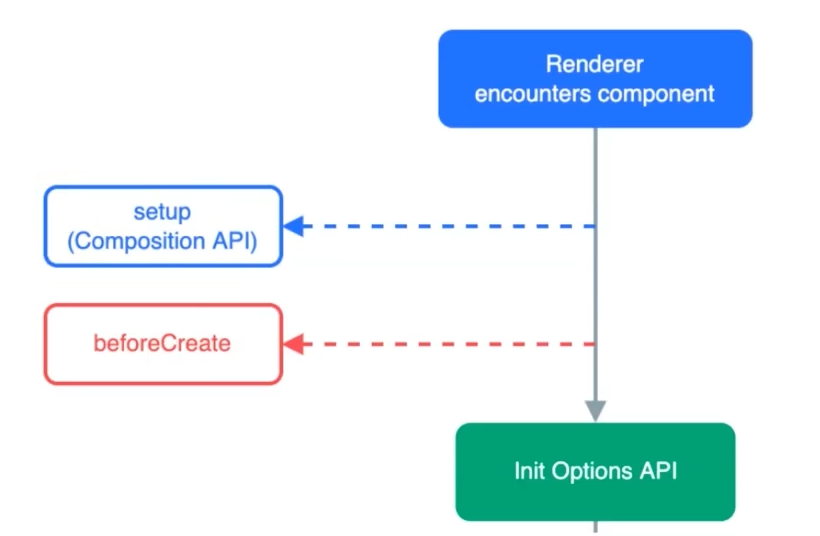
setup() 函数是 Vue 3 中引入的 Composition API 的核心入口,它为组件提供了更灵活、更强大的逻辑组织方式。
一、基本概念与执行时机
- 入口函数:
setup()是使用 Composition API 的起点。 - 执行时机:在组件实例被创建之前执行,早于
beforeCreate和created钩子。 this指向:在setup()内部,this为undefined,因为组件实例尚未创建。
二、基本使用
setup() 函数可以返回一个对象,该对象中的属性和方法将暴露给模板和其他选项式 API。
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'export default {setup() {const count = ref(0)const increment = () => {count.value++}// 返回的对象会暴露给模板return {count,increment}},mounted() {console.log(this.count) // 可以访问 setup 中返回的属性}
}
</script><template><div><p>{{ count }}</p> <!-- 模板中使用 ref 时自动解包,无需 .value --><button @click="increment">加1</button></div>
</template>三、setup() 的参数
setup() 接收两个参数:
props:包含组件所有 props 的响应式对象。注意:直接解构props会失去响应性,应使用toRefs()或toRef()来解构。import { toRefs, toRef } from 'vue'setup(props) {// ❌ 错误:解构后 title 失去响应性// const { title } = props// ✅ 正确:使用 toRefsconst { title } = toRefs(props)console.log(title.value) // 访问值需要 .value// ✅ 正确:使用 toRef (针对单个 prop)const titleRef = toRef(props, 'title')console.log(titleRef.value) }context:上下文对象,包含attrs、slots、emit和expose。这个对象是非响应式的,可以直接解构。setup(props, { attrs, slots, emit, expose }) {// attrs: 透传的非 prop 属性,相当于 $attrsconsole.log(attrs)// slots: 插槽内容,相当于 $slotsconsole.log(slots)// emit: 触发自定义事件,相当于 $emitemit('custom-event', payload)// expose: 暴露公共属性/方法给父组件通过 ref 访问expose({publicMethod() {// ...}}) }
四、定义响应式数据
主要使用 ref 和 reactive:
ref:- 用于定义基本类型数据(字符串、数字、布尔值等)。
- 也可以用于对象或数组,内部会自动调用
reactive转换。 - 在 JavaScript 中访问或修改值需要
.value,在模板中使用时会自动解包(无需.value)。
import { ref } from 'vue' const count = ref(0) count.value++ // 修改值reactive:- 用于定义对象或数组类型的响应式数据。
- 直接操作对象属性,无需
.value。
import { reactive } from 'vue' const user = reactive({ name: 'Alice', age: 25 }) user.age++ // 直接修改
五、定义方法
在 setup() 内部直接定义函数即可,然后将其返回。
setup() {const handleClick = () => {console.log('Button clicked!')}return {handleClick}
}六、计算属性 (computed)
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'setup() {const firstName = ref('John')const lastName = ref('Doe')// 简写:只有 getterconst fullName = computed(() => {return firstName.value + ' ' + lastName.value})// 完整写法:包含 getter 和 setterconst fullNameWritable = computed({get() {return firstName.value + '-' + lastName.value},set(newValue) {const [first, last] = newValue.split('-')firstName.value = firstlastName.value = last}})return {firstName,lastName,fullName,fullNameWritable}
}七、侦听器 (watch)
import { ref, watch } from 'vue'setup() {const count = ref(0)// 侦听单个 refwatch(count, (newVal, oldVal) => {console.log(`count changed from ${oldVal} to ${newVal}`)})// 侦听多个源const firstName = ref('')const lastName = ref('')watch([firstName, lastName], ([newFirst, newLast], [oldFirst, oldLast]) => {console.log('Name changed!')})// 侦听 reactive 对象(注意:oldValue 可能不准确,deep 配置强制开启)const state = reactive({ count: 0, name: '' })watch(() => state.count, (newVal, oldVal) => {console.log(`state.count changed`)})// 立即执行watch(count,(newVal) => {console.log(newVal)},{ immediate: true })return { count, firstName, lastName, state }
}八、与选项式 API 的关系
- 兼容性:Vue 3 支持选项式 API (
data,methods,computed,watch)。 - 访问规则:
- 选项式 API (
data,methods等) 中可以访问setup()返回的属性和方法。 setup()中不能访问data、methods等选项式 API 定义的内容。
- 选项式 API (
- 优先级:如果
setup()和选项式 API 存在同名属性或方法,setup()中的定义优先。
九、<script setup> 语法糖
<script setup> 是 setup() 函数的语法糖,让代码更简洁。
- 特点:
- 无需显式定义
setup()函数和return。 - 在
<script setup>中定义的顶层变量、函数、导入的组件都会自动暴露给模板。 - 是单文件组件 (SFC) 中使用 Composition API 的推荐方式。
- 无需显式定义
<script setup>
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue'const count = ref(0)
const doubleCount = computed(() => count.value * 2)const increment = () => {count.value++
}// 导入的组件可直接在模板中使用
</script><template><div><p>{{ count }}</p><p>Double: {{ doubleCount }}</p><button @click="increment">+</button><ChildComponent /></div>
</template>十、在 Vue 3 的 <script setup> 语法糖中,访问 props 和 context(attrs, slots, emit)
访问 Props
1. 使用 defineProps() 宏
这是定义和访问 props 的标准方式。defineProps() 是一个编译时宏,不需要手动导入。
<script setup>
// 方式1: 使用对象类型声明 (推荐)
const props = defineProps({title: {type: String,required: true,default: 'Default Title'},count: {type: Number,default: 0}
})// 方式2: 使用运行时数组声明
// const props = defineProps(['title', 'count'])// 方式3: 使用类型声明 (TypeScript 推荐)
// defineProps<{
// title?: string
// count?: number
// }>()// 在 setup 脚本中使用 props
console.log(props.title)
console.log(props.count)// 注意:props 是响应式的,可以安全地解构(仅限读取)
// ❌ 错误:直接解构会失去响应性(在普通 setup() 中)
// const { title } = props // 不推荐// ✅ 正确:使用 toRefs 转换为 ref
import { toRefs } from 'vue'
const { title, count } = toRefs(props)// 或者,如果只是读取且不担心响应性丢失(比如在事件处理函数中)
// const title = props.title
</script>访问 Context (attrs, slots, emit)
1. 访问 attrs 和 slots
使用 useAttrs() 和 useSlots() 组合式 API 函数。
<script setup>
import { useAttrs, useSlots } from 'vue'const attrs = useAttrs()
const slots = useSlots()// 使用 attrs (相当于 $attrs)
console.log(attrs.id)
console.log(attrs.class)// 使用 slots (相当于 $slots)
// 通常在渲染函数中使用,模板中直接用 <slot> 标签
</script>2. 访问 emit (触发事件)
使用 defineEmits() 宏来声明和触发自定义事件。
<script setup>
// 方式1: 使用对象类型声明 (推荐)
const emit = defineEmits({'update:title': (newTitle) => typeof newTitle === 'string','custom-event': (payload) => payload !== undefined
})// 方式2: 使用运行时数组声明
// const emit = defineEmits(['update:title', 'custom-event'])// 方式3: 使用类型声明 (TypeScript 推荐)
// defineEmits<{
// (e: 'update:title', newTitle: string): void
// (e: 'custom-event', payload: any): void
// }>()// 触发事件
const handleChangeTitle = () => {emit('update:title', 'New Title')
}const handleCustomEvent = () => {emit('custom-event', { message: 'Hello' })
}
</script><template><button @click="handleChangeTitle">Change Title</button><button @click="handleCustomEvent">Custom Event</button>
</template>访问 expose
使用 defineExpose() 宏来暴露组件内部的属性或方法,供父组件通过 ref 访问。
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'const count = ref(0)const increment = () => {count.value++
}const reset = () => {count.value = 0
}// 暴露给父组件
defineExpose({count, // 暴露 refincrement,reset
})
</script>父组件中使用:
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue'const childRef = ref()const callChildMethod = () => {childRef.value.increment() // 调用子组件暴露的方法
}
</script><template><ChildComponent ref="childRef" /><button @click="callChildMethod">Call Child Increment</button>
</template>完整示例
<script setup>
import { ref, toRefs, useAttrs, useSlots } from 'vue'// 1. 定义和使用 Props
const props = defineProps({title: String,modelValue: Number
})// 将 props 转换为 refs (保持响应性)
const { title, modelValue } = toRefs(props)// 2. 定义 Emits
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue', 'close'])// 3. 使用 useAttrs 和 useSlots
const attrs = useAttrs()
const slots = useSlots()// 4. 内部状态和方法
const localCount = ref(modelValue.value || 0)const increment = () => {localCount.value++emit('update:modelValue', localCount.value)
}const handleClose = () => {emit('close')
}// 5. 暴露给外部
defineExpose({localCount,increment
})
</script><template><div v-bind="attrs"> <!-- 透传 attrs --><h2>{{ title }}</h2><p>Count: {{ localCount }}</p><button @click="increment">+</button><button @click="handleClose">Close</button><!-- 使用插槽 --><slot name="header"></slot><slot></slot><slot name="footer"></slot></div>
</template>总结
| 目的 | 语法糖方式 |
|---|---|
| 定义 Props | const props = defineProps({...}) |
| 触发事件 | const emit = defineEmits([...]) |
| 暴露 API | defineExpose({...}) |
| 访问 attrs | const attrs = useAttrs() |
| 访问 slots | const slots = useSlots() |
<script setup> 语法糖通过 defineProps、defineEmits、defineExpose 这些编译时宏以及 useAttrs、useSlots 这些运行时函数,优雅地解决了 props 和 context 的访问问题,代码更加简洁直观。
重要注意事项
- 不要使用
async:setup()不能是async函数,因为其返回值必须是包含属性和方法的对象,而async函数返回的是Promise。 - 响应式原理:
ref:基于Object.defineProperty()(Vue 2) 或Proxy(Vue 3) 的get/set实现。reactive:基于Proxy实现,性能更好,支持深层响应式。
<script setup>优先:在单文件组件中,应优先使用<script setup>语法糖。
总而言之,setup() 函数为 Vue 3 带来了更灵活的逻辑组织方式,而 <script setup> 语法糖则极大地简化了其使用,是现代 Vue 开发的推荐实践。
