Spring Boot 结合 CORS 解决前端跨域问题
Spring Boot 结合 CORS 解决前端跨域问题
1. 背景
在前后端分离的项目中,前端(例如 http://localhost:3000)调用后端接口(例如 http://localhost:8080)时,浏览器会因为 同源策略 限制而阻止请求,这就是所谓的 跨域问题。
同源策略要求:
- 协议(Protocol)
- 域名(Domain)
- 端口(Port)
三者必须完全一致,否则就会触发跨域。
跨域在前端调试、微服务接口调用、第三方 API 请求等场景中非常常见。为了让浏览器允许跨域访问,需要配置 CORS(跨域资源共享,Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)。
2. 什么是 CORS
CORS 是 W3C 定义的一种跨域访问标准,允许服务器在响应中添加特定的 HTTP 头,让浏览器判断是否允许跨域请求。核心是以下响应头:
| 响应头 | 作用 |
|---|---|
Access-Control-Allow-Origin | 允许访问的源(可以是具体域名或 *) |
Access-Control-Allow-Methods | 允许的 HTTP 方法(GET, POST, PUT, DELETE 等) |
Access-Control-Allow-Headers | 允许的自定义请求头 |
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials | 是否允许携带 Cookie |
Access-Control-Max-Age | 预检请求缓存时间(秒) |
3. Spring Boot 中解决跨域的常用方法
3.1 方法一:在 Controller 上使用 @CrossOrigin
Spring Boot 提供了 @CrossOrigin 注解,可以快速在类或方法级别开启 CORS。
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/user")
@CrossOrigin(origins = "http://localhost:3000") // 允许的前端地址
public class UserController {@GetMapping("/{id}")public String getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {return "用户ID: " + id;}
}
特点:
- 适合局部跨域控制。
- 不影响其他接口。
- 缺点是需要在每个 Controller 手动加注解,管理不便。
3.2 方法二:全局 CORS 配置(推荐)
如果你的接口都需要跨域访问,可以通过 WebMvcConfigurer 全局配置。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;@Configuration
public class GlobalCorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {registry.addMapping("/**") // 允许跨域的接口路径.allowedOriginPatterns("*") // 允许跨域的源(Spring Boot 2.4+ 推荐用 allowedOriginPatterns).allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "OPTIONS") // 允许的 HTTP 方法.allowedHeaders("*") // 允许的请求头.allowCredentials(true) // 是否允许携带 Cookie.maxAge(3600); // 预检请求缓存时间}
}
特点:
- 一次配置,所有接口生效。
- 方便统一管理。
- 生产环境建议改成精确匹配允许的域名,而不是
*。
3.3 方法三:使用 Filter 配置 CORS
通过自定义 CorsFilter 处理跨域请求,可以在 Spring Boot 启动时加载。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CorsFilter;@Configuration
public class CorsFilterConfig {@Beanpublic CorsFilter corsFilter() {CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();config.addAllowedOriginPattern("*");config.setAllowCredentials(true);config.addAllowedMethod("*");config.addAllowedHeader("*");config.setMaxAge(3600L);UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);return new CorsFilter(source);}
}
特点:
- 适用于需要跨越 Spring MVC、Spring Security 等多个层的情况。
- 能解决某些全局配置不生效的问题。
4. 配合 Spring Security 的特殊处理
如果项目使用了 Spring Security,默认会拦截 OPTIONS 预检请求,导致 CORS 配置不生效。这时需要额外在 Security 配置中开放 OPTIONS 请求。
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.cors().and().csrf().disable(); // 启用 CORS & 禁用 CSRFhttp.authorizeHttpRequests().anyRequest().permitAll();return http.build();}
}
关键点:
http.cors()会读取WebMvcConfigurer或CorsFilter中的配置。- 关闭 CSRF 主要是为了方便调试跨域(生产环境需根据业务需求启用)。
5. 常见问题排查
- 前端依旧报跨域
- 确认是浏览器报的 CORS 错误,而不是接口 404/500。
- 确认后端响应中包含
Access-Control-Allow-Origin。
- Cookie 不生效
- 后端
allowCredentials(true)。 - 前端请求设置
fetch或 Axios 的withCredentials: true。 - 注意:当
allowCredentials(true)时,Access-Control-Allow-Origin不能为*。
- 后端
- Spring Security 版本冲突
- Spring Boot 3.x 下要用
SecurityFilterChain而不是WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter(已废弃)。
- Spring Boot 3.x 下要用
6. 总结
- 局部跨域 →
@CrossOrigin - 全局跨域(推荐) →
WebMvcConfigurer - 复杂场景(如结合 Spring Security) →
CorsFilter+SecurityConfig - 生产环境建议精确配置
allowedOrigins,避免安全隐患。
✅ 最佳实践推荐
@Configuration
public class GlobalCorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {@Overridepublic void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {registry.addMapping("/**").allowedOrigins("https://yourdomain.com") // 精确指定.allowedMethods("GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE").allowedHeaders("*").allowCredentials(true).maxAge(3600);}
}
配合:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.cors().and().csrf().disable();return http.build();}
}
这样前端就可以愉快地调用后端接口而不会再被 CORS 卡住了。
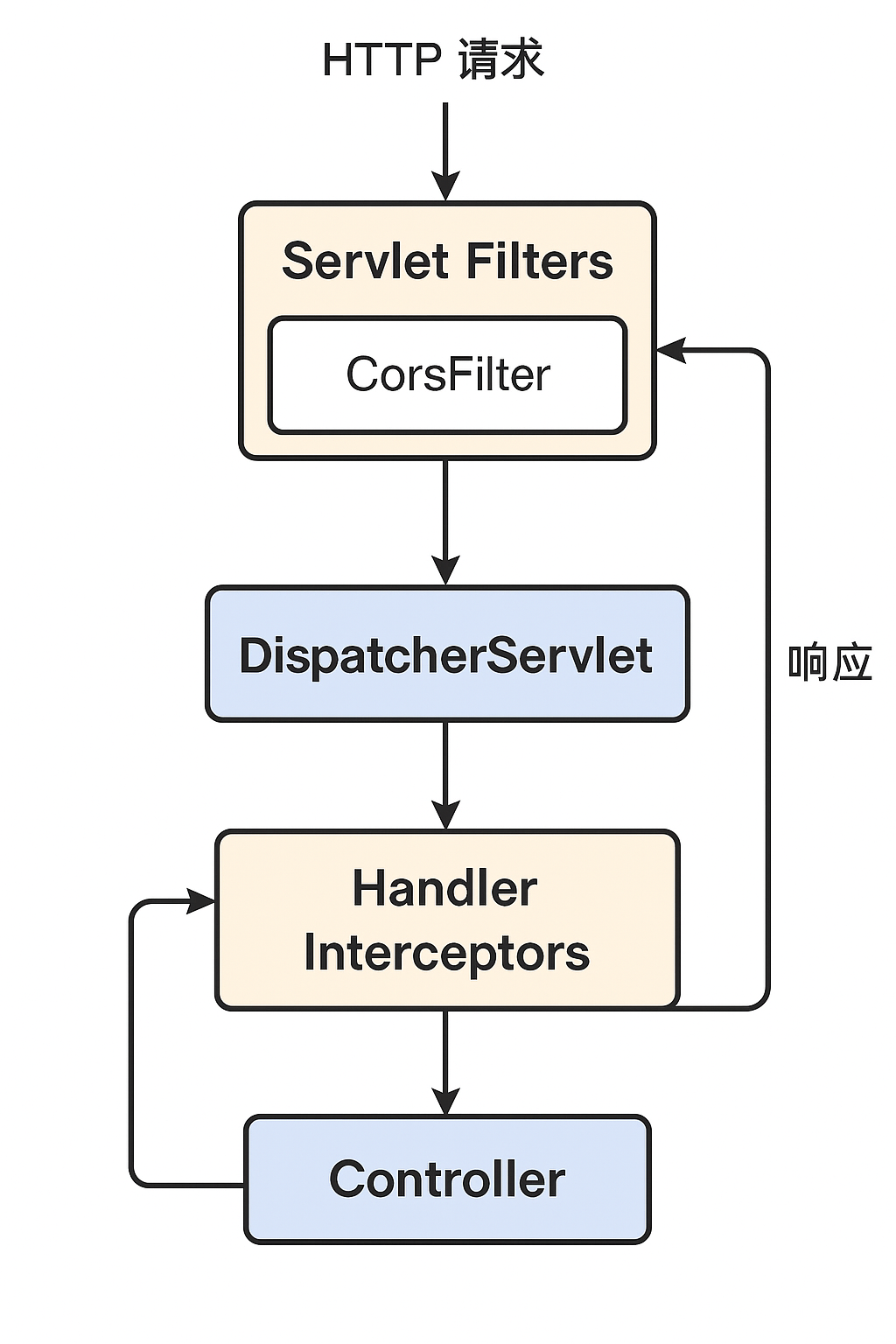
7.本质
CORS 在 Spring Boot 里的本质,其实并不是靠普通的 拦截器(HandlerInterceptor) 去做的,而是由 底层的 CORS 处理机制 在 Servlet Filter 层完成的。
7.1. 核心机制
在 Spring Web(Spring MVC)里,CORS 处理是通过 CorsProcessor 在请求进入 Controller 之前拦截,并根据配置动态添加 CORS 响应头。
整个流程分两种情况:
- 预检请求(OPTIONS)
- 浏览器先发一个 OPTIONS 请求,询问服务器是否允许该跨域。
- Spring 的 CORS 处理器判断后直接返回带有
Access-Control-Allow-*的响应,并终止后续调用,不进入 Controller。
- 实际请求(GET、POST…)
- 在进入 Controller 前,CORS 处理器检查请求来源和方法是否合法,如果允许,就在响应头里加上 CORS 相关字段。
7.2. Spring Boot 的执行链
当你用
@CrossOriginWebMvcConfigurer#addCorsMappings()- 或
CorsFilter
配置 CORS 后,Spring Boot 会:
- 注册一个
CorsFilter或HandlerMappingIntrospector内部的 CORS 拦截逻辑。 - 请求进入 Servlet 容器后,先走 Filter 链,Spring CORS 逻辑会最先判断跨域。
- 如果是 OPTIONS 预检且允许跨域,直接返回响应,不再走后续 Controller。
- 如果是实际请求,进入 Controller 处理业务逻辑,但响应会自动加上 CORS 头。
7.3. 为什么不用普通拦截器
- 普通的
HandlerInterceptor只能拦截已经匹配到 Handler 的请求,但 CORS 预检请求往往不需要进入业务 Controller。 - CORS 要尽早处理,最好在 Filter 层拦截,这样性能更好、逻辑更统一。
- Spring MVC 的 CORS 是在 DispatcherServlet 处理请求前就能处理的,而拦截器是在 HandlerAdapter 调用前才运行。
✅ 总结一句话:
Spring Boot 的 CORS 本质是通过 Servlet Filter 层的 CorsFilter + Spring MVC 的 CorsProcessor 在请求到达 Controller 前处理的,而不是靠普通的业务拦截器实现的。