MySQL查询语句(会持续更新)
MySQL查询语句目录
- 一、单表查询
- 1. 直接查询
- 2. 重命名:as
- 2.1 给字段重命名
- 2.2 给表名重命名
- 3. 去重查询
- 4. 条件查询:where子语句
- 4.1 逻辑运算符查询
- 4.2 算术运算符查询
- 4.3 范围查询:between…and…介于两者之间
- 4.4 in和not in运算符查询
- 4.5 模糊查询:like _ %
- 4.6 判断是否为空查询:is null/is not null
- 5. 排序查询:order by子语句
- 6. 限制查询/分页查询:limit子语句
- 限制查询
- 分页查询
- 7. 随机查询
- 8.2 最大值函数:max()
- 8.3 最小值:min()
- 8.4 平均值:avg()
- 8.5 记录数量:count()
- 9. 分组函数:group by
- 9.1 简单分组查询
- 9.2 having
- 二、多表查询
- 1. 多表查询三种关系
- 一对一
- 一对多
- 多对多
- 2. 多表简单查询
- 3. 连表查询
- 3.1 内连接:join…on…
- 3.2 外连接之左连接:left join…on…
- 3.3 外连接之右连接:right join…on…
一、单表查询
1. 直接查询
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名;
# 举例1: 从 student 表中查询 name 与 age
select name, age from student;
# 举例2: 查询student表中的所有记录
select * from student;
# 举例3: 查询student表和teacher表中的所有记录
select student.*,teacher.* from student,teacher;
2. 重命名:as
表名重命名和字段重命名可以一起使用。
2.1 给字段重命名
# 语法:select 字段 as 别名 from 表名;(as可省略)
# 举例: 从 student 表中查询 name 与 age
select name as myname, age as myage from student;
2.2 给表名重命名
单表一般不重命名,多表一般会重命名。
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 as 别名;(as可省略)
# 举例: 从 student 表中查询 name 与 age
select name, age from student as s;
3. 去重查询
# DISTINCT 用于从表中获取不重复的数据
# 语法:select distinct 字段 from 表名;
# 举例:查询 student 表中所有的不同年龄
select distinct age from student;
4. 条件查询:where子语句
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 条件;
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 age = 15 的 name
select name from student where age = 15;
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 name = '小明' 的 所有记录
# 字符串加引号
select * from student where name = '小明';
4.1 逻辑运算符查询
# 语法:and(并且), or(或), not(非)
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 class = 1 并且 sex = '女' 并且 age = 20 的所有记录
# and 所有条件都要满足
select * from student where clasas= 1 and sex = '女' and age = 20;
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 age = 15 或 sex = 'man' 的所有记录
# or 多个条件只要满足一个就行
select * from student where age = 15 or sex = 'man';
4.2 算术运算符查询
# 语法:>(大于), <(小于), =(等于), !=(不等于), <>(不等于), >=(大于等于), <=(小于等于)
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 age < 15 的所有记录
select * from student where age < 15;
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 age <= 15 并且 age >= 25 的所有记录
select * from student where age < 15 and age >= 25;
4.3 范围查询:between…and…介于两者之间
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 between 起始值 and 结束值;
# between…and… 取得是连续一段(包含端点,闭区间)
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 age>=15 并且 age<=20 之间的记录
select * from student where age between 15 and 20;
4.4 in和not in运算符查询
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 in(列表)//或 not in(列表); in 表示在这个范围里,not in 表示不在这个范围里
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 id 为 (2, 5, 7) 之间的所有记录
方法一:使用or select * from student where id = 2 or id = 5 or id = 7;
方法二:使用in select * from student where id in(2, 5, 7);
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 age 不为 (15, 18, 21) 之间的所有记录
select * from student where age not in (15, 18, 21);
4.5 模糊查询:like _ %
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 like '%数据%';
# like:占位符 _:表示任意一个字符,有且必须有一个字符 %:表示任意字符,可以有多个
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 name 中含有 '张' 字的所有记录
select * from student where name like '%张%';
+---+------+-----+-----+
|id | name | age | sex |
+---+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张华 | 24 | 16 |
| 2 | 张建华| 19 | 17 |
| 3 | 小张 | 20 | 18 |
| 4 | 张三 | 21 | 18 |
| 5 | 小张玉| 15 | 30 |
+---+------+-----+-----+
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 name 中姓 '张' 的所有记录
select * from student where name like '张%';
+---+------+-----+-----+
|id | name | age | sex |
+---+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张华 | 24 | 16 |
| 2 | 张建华| 19 | 17 |
| 4 | 张三 | 21 | 18 |
+---+------+-----+-----+
# 举例3:从 student 表中查询 name 中 '张' 在 第二位置 的所有记录
select * from student1 where name like '_张%';
+---+------+-----+-----+
|id | name | age | sex |
+---+------+-----------+
| 3 | 小张 | 20 | 18 |
| 5 | 小张玉| 15 | 30 |
+---+------+-----+-----+
# 举例4:从 student 表中查询 name 中姓 '张' 且 是三个字 的所有记录
select * from student1 where name like '张__';
+---+------+-----+-----+
|id | name | age | sex |
+---+------+-----------+
| 2 | 张建华| 19 | 17 |
+---+------+-----+-----+
4.6 判断是否为空查询:is null/is not null
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 where 字段 is null(not null);
# null(为空) not (非空) 判断是否为空要用is
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 age 未填写(为空)的所有记录
select * from student where age is null;
+---+------+-----+-----+
|id | name | age | sex |
+---+------+-----------+
| 2 | 张建华| null| 17 |
+---+------+-----+-----+
优先级
优先级由高到低的顺序为:小括号>not>算术运算符>逻辑运算符
and比or先运算,如果同时出现,想先算or,可结合()使用
5. 排序查询:order by子语句
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 order by 字段 排序方式(升序 asc(可省)|降序 desc);
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询所有记录并按照 age 升序排序
select * from student order by age asc;
# 进阶 select 字段 from 表名 order by 字段 排序方式,字段 排序方式;(当第一个字段相同时,按第二个字段排序顺序来)
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询所有记录并按照 age 升序,当 age 相同时,按score降序排序
select * from student order by age asc,score desc;
如果where子语句和order by子语句同时出现
where子语句在前,先进行查找
order by子语句在后,在进行排序# 举例:从 student 表中查询 sex = '男' 并且 age 降序排序 的 所有记录 select * from student where sex = '男' order by age desc;
6. 限制查询/分页查询:limit子语句
限制查询
# linit a,b a:表示其实索引值 b:限制查询的个数
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 limit a,b;
# 举例:查询 student 表从第一行开始,往后查询5条数据包含第一条, 0 表示第一行记录,也是从 0 开始,和数值类似
select * from student where limit 0,5;
# or
select * from student where limit 5;
分页查询
# 语法1:select 字段 from 表名 limit a,b;
# 举例:查询 student 表从第一行开始,往后查询3条所有记录
select * from student where limit 0,3; # 分为第一页
select * from student where limit 3,3; # 分为第二页
select * from student where limit 6,3; # 分为第三页
# 根据上面可得规律: 页码:page 一页大小:pageSize
select * from student where limit (page-1)*pageSize,pageSize;
# 语法2:select 字段 from 表名 limit b offset a;
# 举例:查询 student 表从第一行开始,往后查询3条所有记录
select * from student where limit 3 offset 0; # 分为第一页
如果where子语句、order by子语句和limit子语句同时出现
where子语句在前,先进行查找
order by子语句在中,在进行排序
limit子语句在最后# 举例:查询 student 表中 class = 1 并且 age 为降序排序 的 前三条 所有记录 select * from student where class = 1 order by age desc limit 0,3;
7. 随机查询
# rand() 用于从表中随机获取记录
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 order by rand() limit 随机生成记录条数;
# 举例:从 student 表中随机显示两个学生记录
select * from student order by rand() limit 2;
rand() 出现在 order by 之后,limit 之前
8.2 最大值函数:max()
# 语法:select max(字段) from 表名;
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 age 的最大值
select max(age) from student;
8.3 最小值:min()
# 语法:select min(字段) from 表名;
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 age 的最小值
select min(age) from student;
8.4 平均值:avg()
# 语法:select avg(字段) from 表名;
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 age 的平均值
select avg(age) from student;
8.5 记录数量:count()
# 语法:select count(字段) from 表名; count(字段)不统计为null的记录
# 举例1:从 student 表中查询 age 的记录数量
select count(age) from student;
# 举例2:从 student 表中查询 总共有几条记录
select count(*) from student;
9. 分组函数:group by
9.1 简单分组查询
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 group by 字段 ;
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 每个班级 的 age平均值
select class,avg(age) from student group by class;
9.2 having
having是分完组之后的条件,如果想分组之前有条件使用where。
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名 group by 字段 having 条件;
# 举例:从 student 表中查询 1班 的 age平均值
select class,avg(age) from student group by class having class = 1;
如果where子语句、order by子语句和group by子语句同时出现
where子语句在前,先进行查找
group by子语句在中间,在分组查找
order by子语句在最后,最后进行排序# 举例:从 student 表中使用 group by 分组查询多个班级中 sex= '男' 并且为 一班的 age 的 升序排序 的记录 select age from student where sex = '男' group by class order by age asc;
二、多表查询
1. 多表查询三种关系
多表查询有:一对一、一对多、多对多这三种关系。
一对一
一个表的记录 只能对应 另一个表的 一条记录
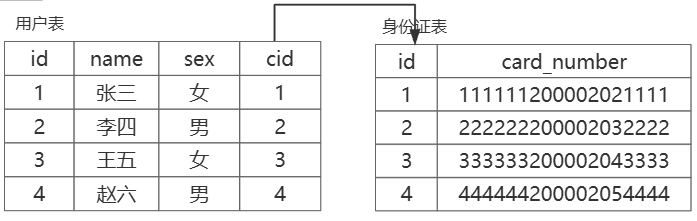
例如:用户表和身份证表(一个用户只能对应一个身份证号)
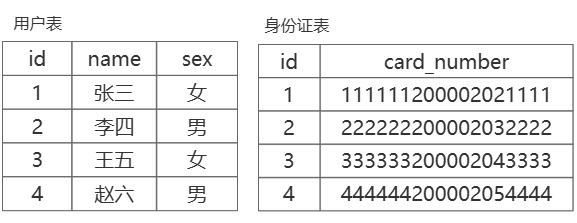
- 两个表可以合并为一个表(推荐⭐)
- 进行多表查询:设置外键,来自第二张表的关键标识
一对多
一个表的记录 可以对于 另一个表的 多条记录
例如:学生表和班级表(一个班级可以有多名学生,一个学生只能对应一个班级)
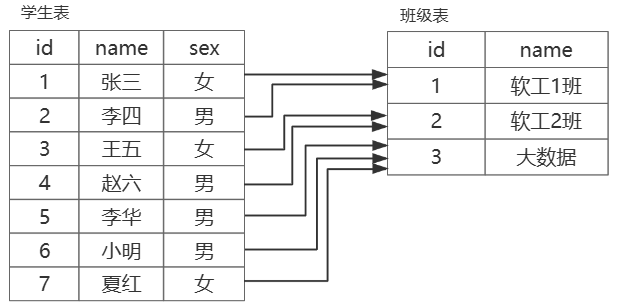
- 两个表可以合并为一个表(不推荐,数据冗余)
- 在数据少的乙方加外键(不推荐,数据冗余)
- 在数据多的一方加外键(推荐⭐)
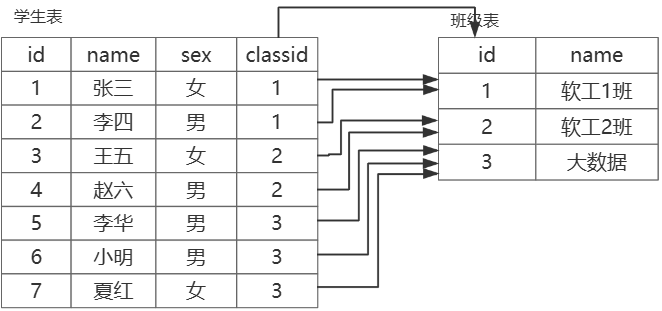
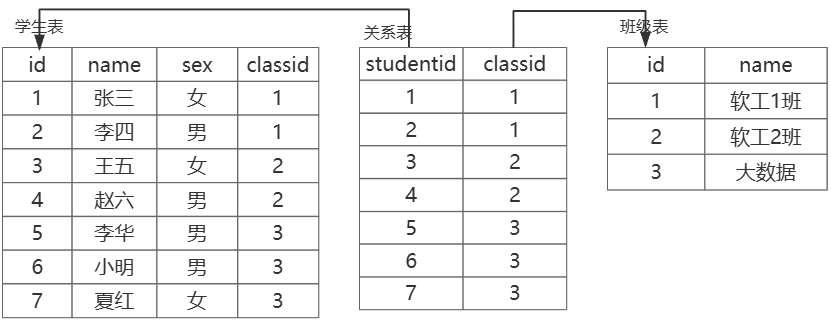
- 另加一个表存储两个表的关系(不推荐,查找效率不高)
多对多
一个表的记录 可以关联 另一个表的 多条记录,反之亦然
例如:学生表和课程表(一个学生可以选多门课,一门课可以有多个学生)
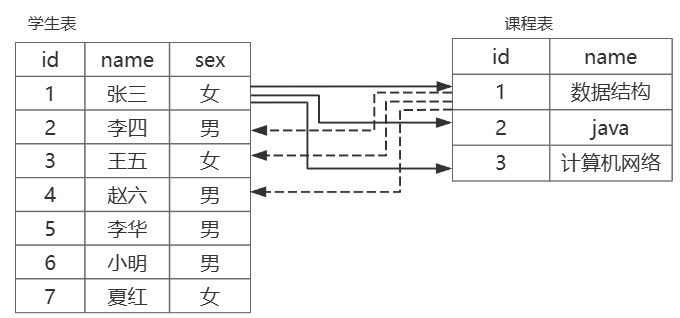
- 两个表可以合并为一个表(不推荐,数据冗余)
- 在任意一方表加外键(不推荐,数据冗余)
- 另加一个表存储两个表的关系,另加的表中还可以存储别的数据(推荐⭐)
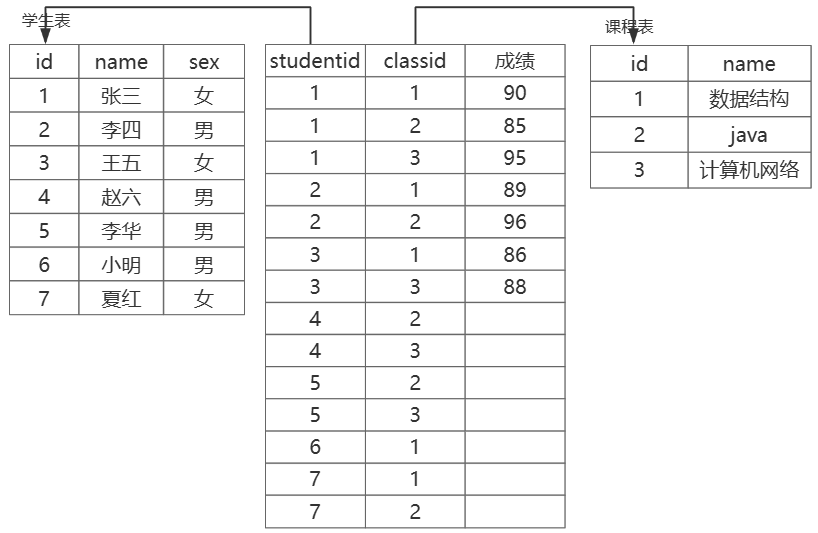
2. 多表简单查询
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名1, 表名2;
# 举例:查询 student 表 和 class 表的所有记录
select * from student, class;
与where连用:
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名1, 表名2 where 条件;
# 举例:查询 student 表外键 和 class 表 id 相等的所有记录
select * from student, class where student.classid = class.id;
# where条件中字段不冲突,可以不挂表名;如果字段冲突了,字段前挂表名
3. 连表查询
3.1 内连接:join…on…
- 将条件的关键词从
where改成了on
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名1 (inner)join 表名2 on 表名1.字段 = 表名2.字段; inner可省略
# 举例:查询 student 表外键classid 和 class 表 id 相等的所有记录
select * from student join class on student.classid = class.id;
3.2 外连接之左连接:left join…on…
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 表名1.字段 = 表名2.字段;
# 举例:以 student 表为主表,查询 student 表外键 classid 和 class 表 id 相等的所有记录
select * from student left join class on student.classid = class.id;
3.3 外连接之右连接:right join…on…
# 语法:select 字段 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 表名1.字段 = 表名2.字段;
# 举例:以 class 表为主表,查询 student 表外键 classid 和 class 表 id 相等的 student 表 id = 1 记录
select * from student right join class on student.classid = class.id where student.id = 1;
