从零搭建Cloud Alibaba (下) Sentinel篇
1.Sentinel控制台的安装
下载地址:
Releases · alibaba/Sentinelx
下载后是一个jar包
进入目录
CMD命令
java -jar "sentinel-dashboard-1.8.8 .jar"
如果发生了端口冲突则使用以下命令启动 修改端口号为8090
java -Dserver.port=8090 -jar "sentinel-dashboard-1.8.8 .jar"
启动成功:
访问控制台
Sentinel Dashboard

账号密码默认都是sentinel
进入首页:
此时控制台已经安装完成
2.整合微服务
sentinel 的 starter 依赖:
将此sentinel依赖引入项目中
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId></dependency>yml配置:
spring:cloud:sentinel:transport:# 添加sentinel的控制台地址dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8090如果是mvc的接口无需 @SentinelResource. 如果是业务方法, 需要 @SentinelResource
@SentinelResource("hello")public String hello() {return "Hello Sentinel";}@SentinelResource 注解用来标识资源是否被限流、降级。上述例子上该注解的属性 hello 表示资源名。 @SentinelResource 还提供了其它额外的属性如 blockHandler,blockHandlerClass,fallback 用于表示限流或降级的操作,更多内容可以参考 Sentinel 注解支持。
启用feign对sentinel的支持:
#启用feign对sentinel的支持
feign:sentinel:enabled: true # 启用 Sentinel 对 Feign 的支持此时我们只需要访问集成服务中的任意一个路径就能在sentinel中查看到
2.1 sentinel限流(blockHandler) 讲解
2.1.1没有使用@SentinelResource注解(使用默认限流响应)
创建一个类用于测试限流
SentinelRatilimitConteroller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller")
public class SentinelRatilimitConteroller {/*** 测试sentinel限流 (没有添加@)* @return*/@GetMapping("/testSentinelRatilimitA")public String testSentinelRatilimitA() {return "没有达到限流的规则 --- 正常访问";}}此时我们启动服务 访问地址
localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitA
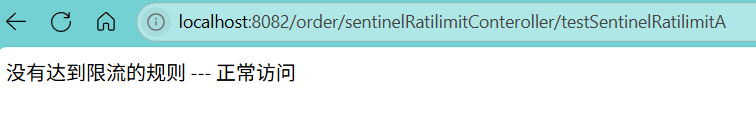
能够正常访问
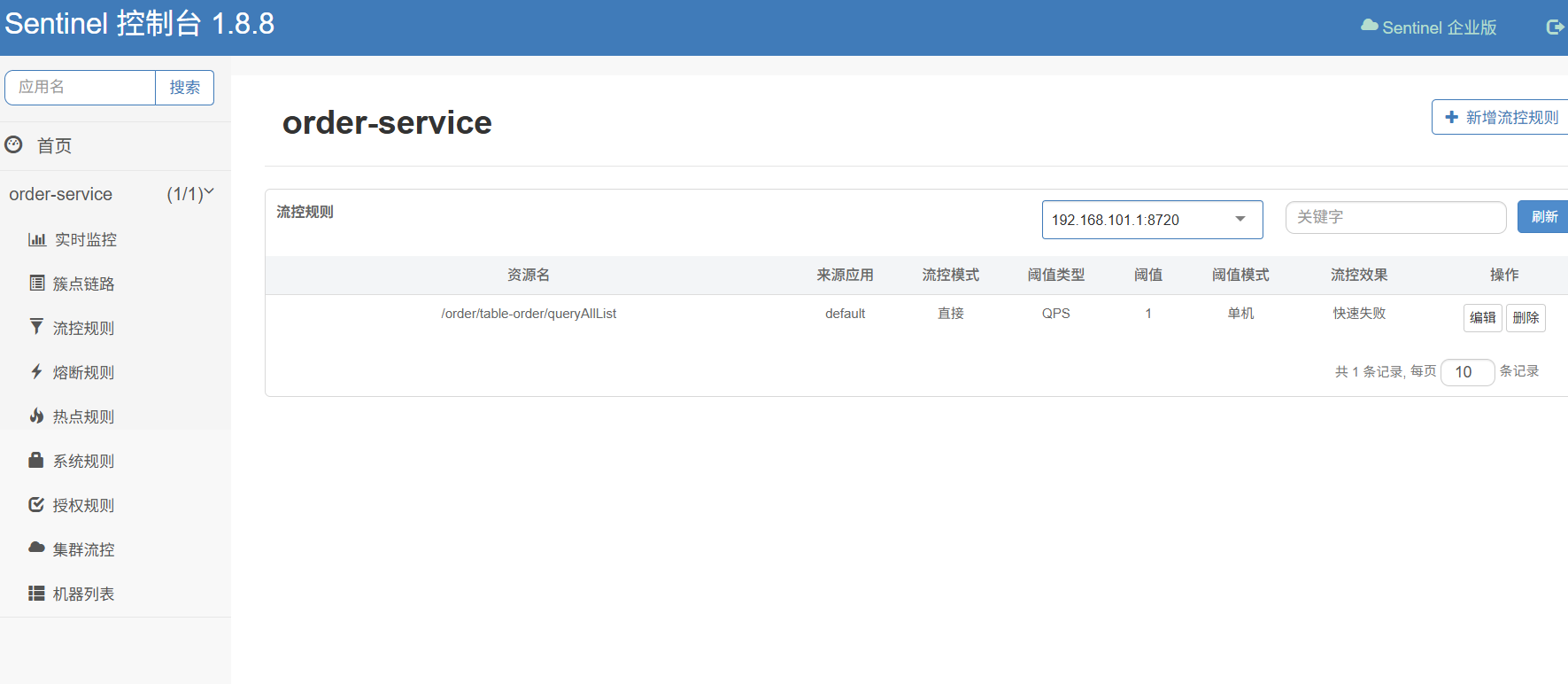
进入sentinel的控制台,给当前路径添加限流规则
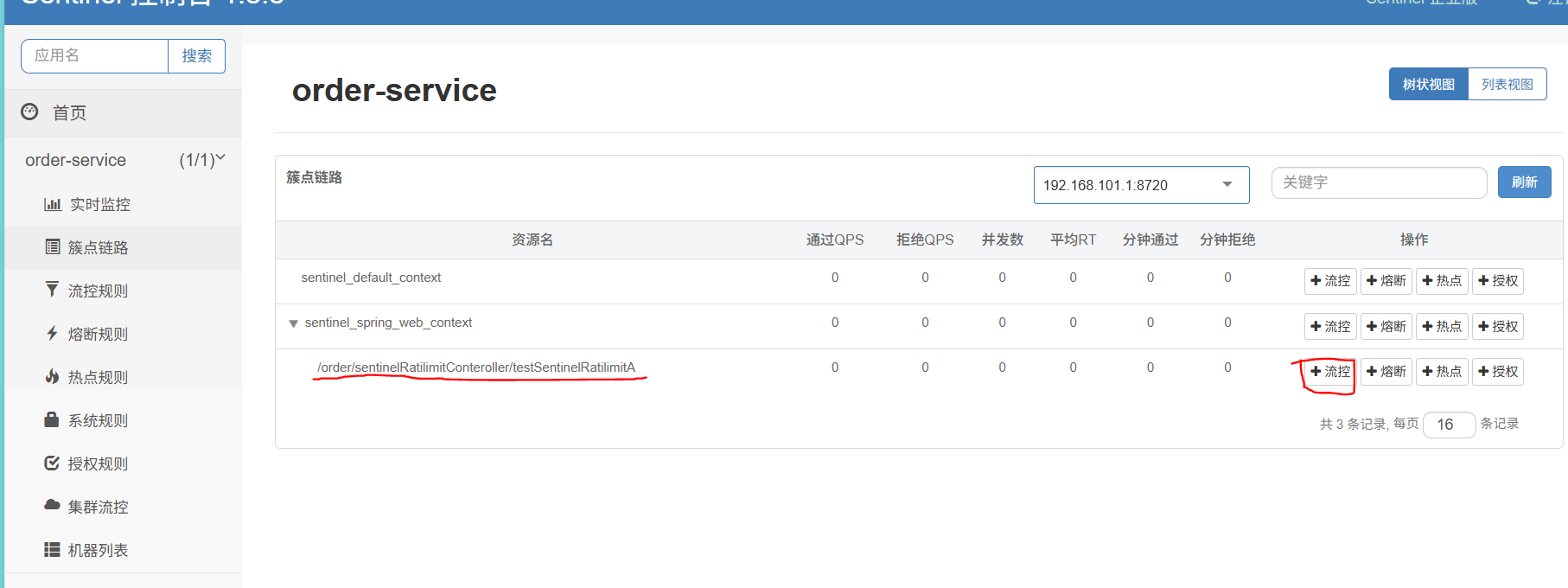
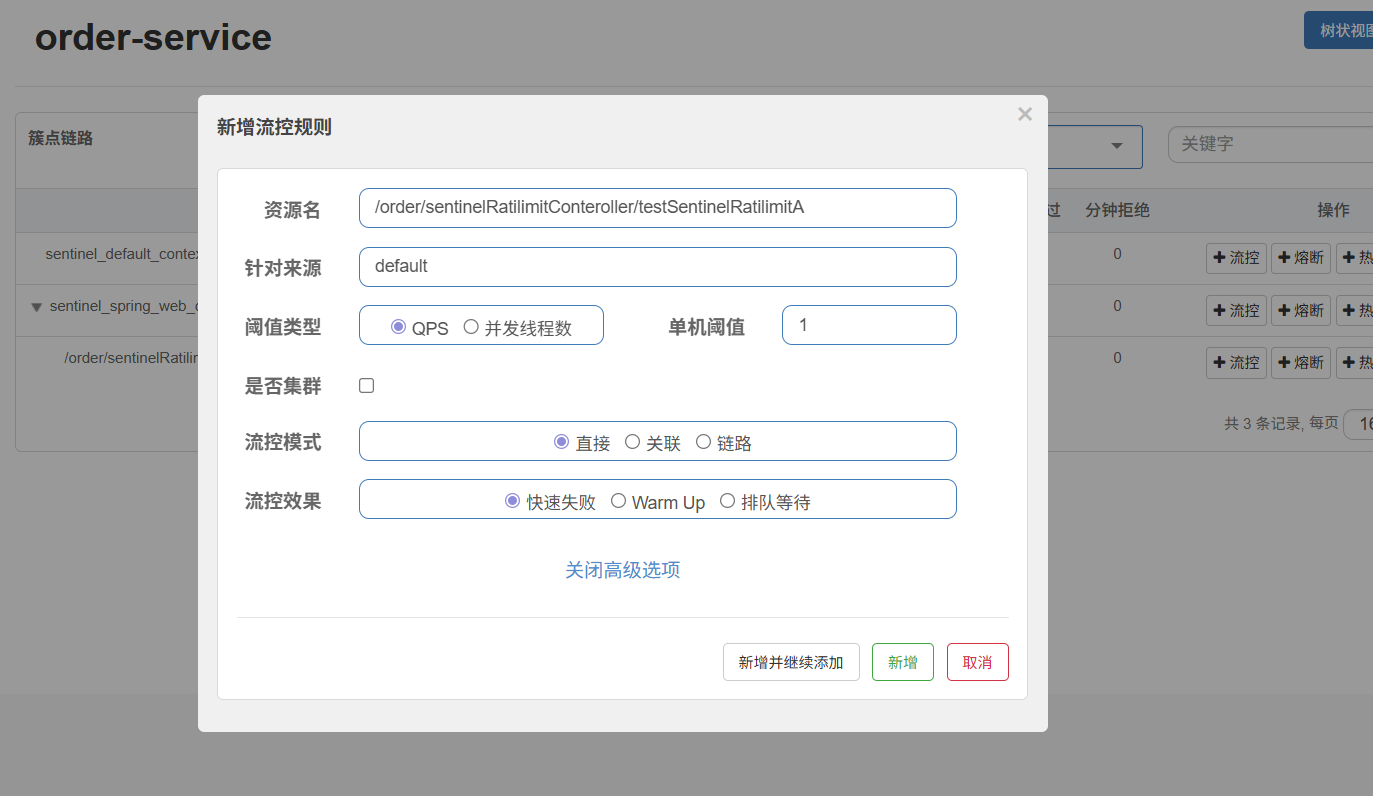
当QPS超过1时的请求会快速失败返回默认的失败响应
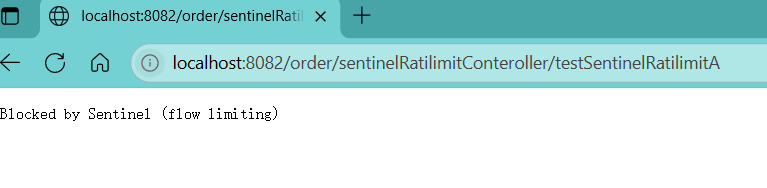
此时限流返回到响应为默认的响应
2.1.2使用@SentinelResource注解自定义限流响应
写法1:
在controller中添加以下代码
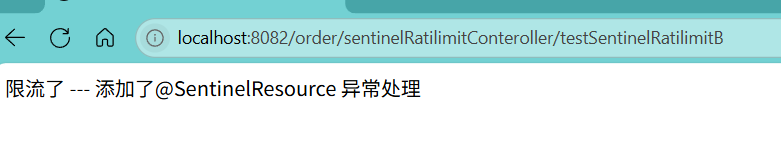
/*** 测试sentinel限流 (添加了@SentinelResource)* @SentinelResource value 为 限流规则的资源名称 blockHandler 为限流规则的异常处理方法*/@GetMapping("/testSentinelRatilimitB")@SentinelResource(value = "testSentinelRatilimitB",blockHandler = "testSentinelRatilimitBHandleException")public String testSentinelRatilimitB() {return "没有达到限流的规则 --- 添加了@SentinelResource 正常访问";}/***作为(testSentinelRatilimitB)的限流异常返回方法*/public String testSentinelRatilimitBHandleException(BlockException e) {return "限流了 --- 添加了@SentinelResource 异常处理";}
* @SentinelResource value 为 限流规则的资源名称 blockHandler 为限流规则的异常处理方法
使得方法testSentinelRatilimitB 触发限流时 返回 testSentinelRatilimitBHandleException方法
正常访问:localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitB
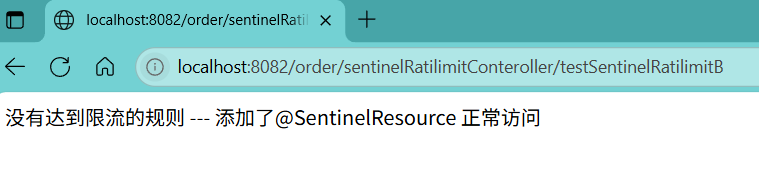
添加限流规则:
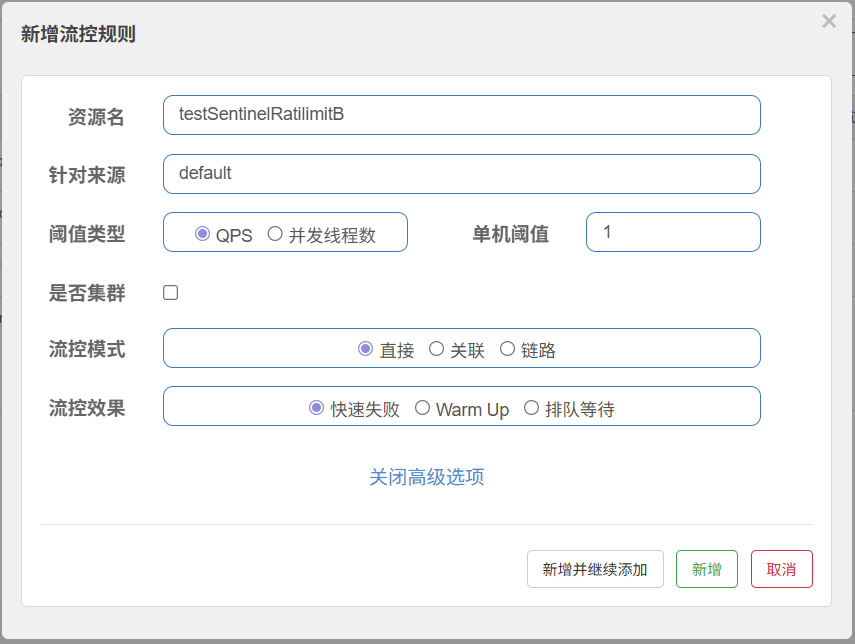
快速访问:
执行了自定义限流处理
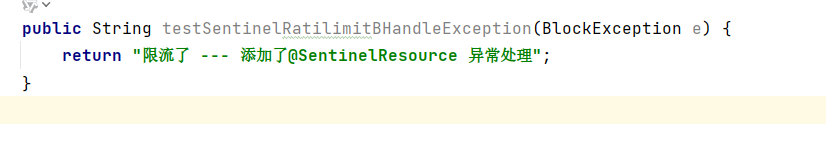
对应关系图
写法2:(推荐)
如果需要独立设置一个 限流类还可以这样写
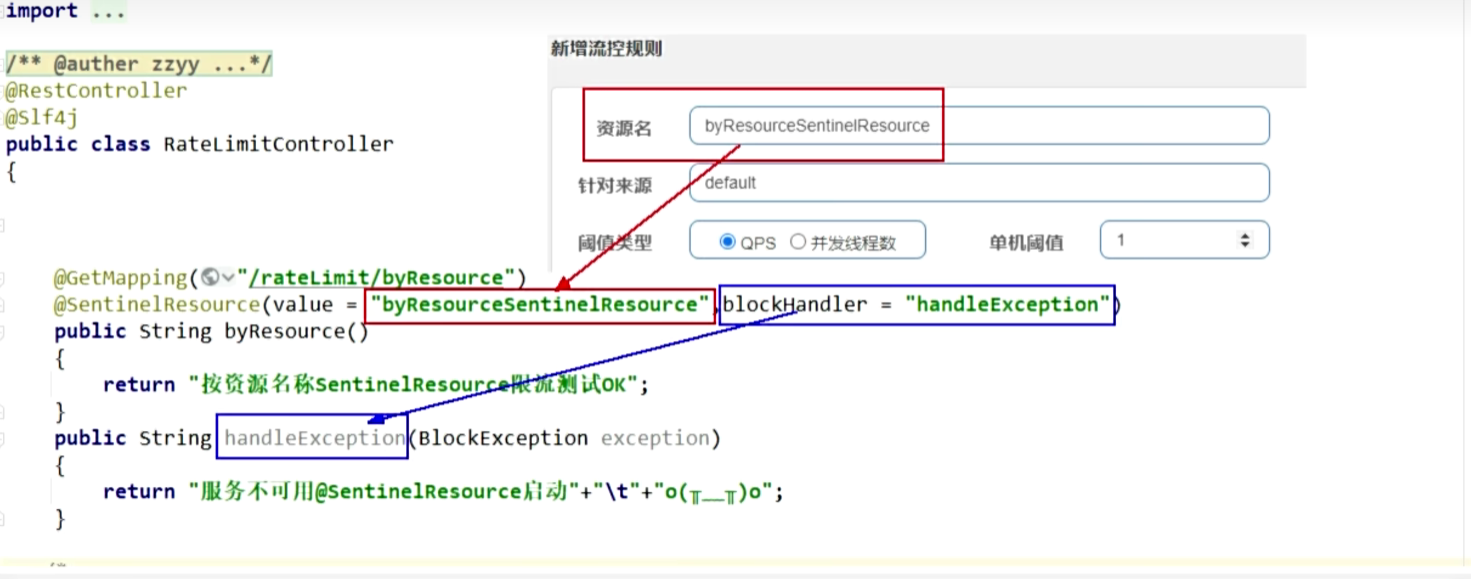
添加一个新的controller
指定了blockHandler类中的指定方法作为限流处理
@GetMapping("/testSentinelRatilimitC")@SentinelResource(value = "testSentinelRatilimitC",blockHandlerClass = OrderBlockHandler.class,// 限流异常返回方法所在类blockHandler = "testSentinelRatilimitC") //指定限流异常返回方法public String testSentinelRatilimitC() {return "没有达到限流的规则 --- 添加了@SentinelResource 默认异常处理";}
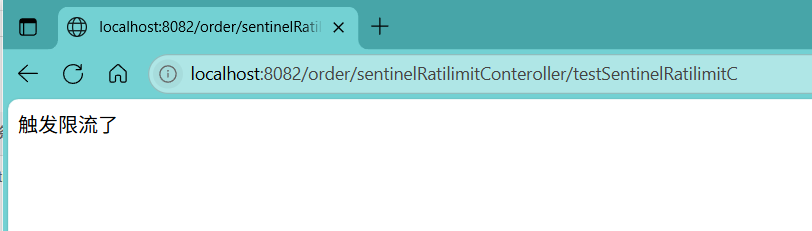
访问localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitC
为他编写一个类 和方法 (方法必须被 pblic static 修饰)
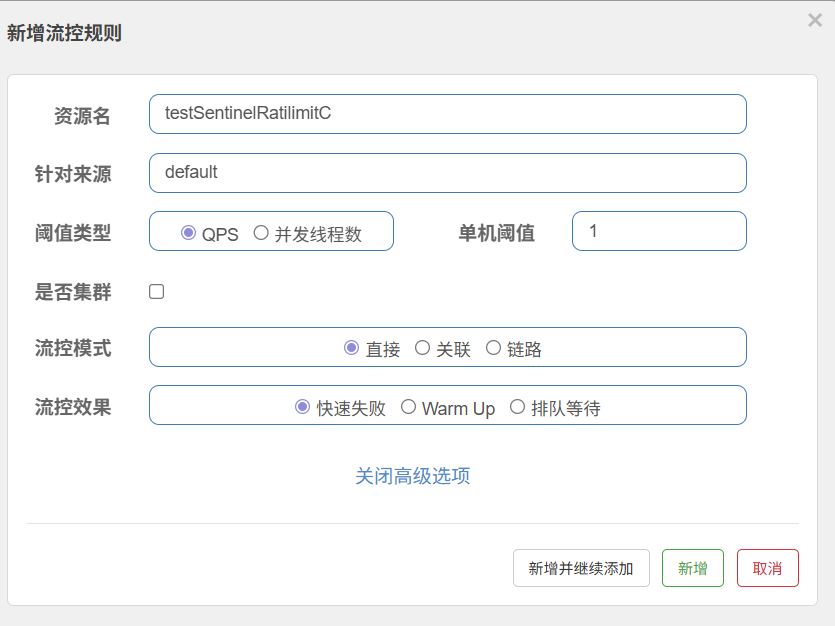
public class OrderBlockHandler {// 必须是public static方法// 参数和返回类型要与原方法一致,最后加一个BlockException参数public static String testSentinelRatilimitC(BlockException ex) {return "触发限流了";}}设置限流规则
快速访问:
2.2异常处理(fallback)
为一个接口配置 @SentinelResource(value = "testSentinelRatilimitD",
fallback = "testSentinelRatilimitDfallback")
fallback属性表示当前方法遇到异常会调用指定的方法
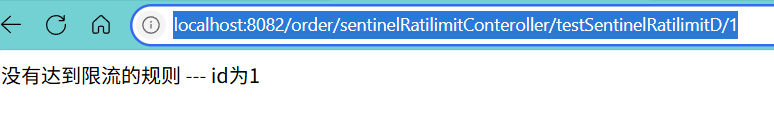
@GetMapping("/testSentinelRatilimitD/{id}")@SentinelResource(value = "testSentinelRatilimitD",blockHandler = "testSentinelRatilimitDBlockHandler",fallback = "testSentinelRatilimitDfallback")public String testSentinelRatilimitD(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {if (id == 0){throw new RuntimeException("id 不能为0");}return "没有达到限流的规则 --- id为"+ id;}//作为限流 处理public String testSentinelRatilimitDBlockHandler(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,BlockException e) {return "已触发限流 --- id为"+ id;}//作为 熔断 降级 异常处理public String testSentinelRatilimitDfallback(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,Throwable e) {return "触发率异常处理,传入id为:"+ id;}2.2.1测试限流
访问地址:localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitD/1
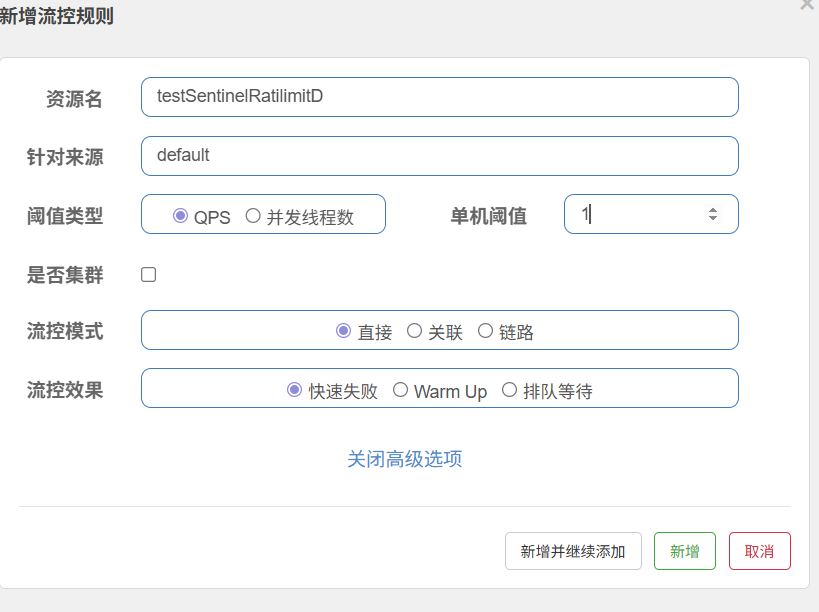
为他设置限流规则:
多次访问: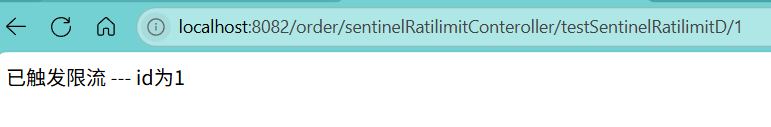
触发限流规则,走了BlockHandler 所配置的方法
2.2.2测试异常
访问
http://localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitD/0
传入id值为0,我们设置id为0时会抛出异常,看看是否会走fallback所配置的方法
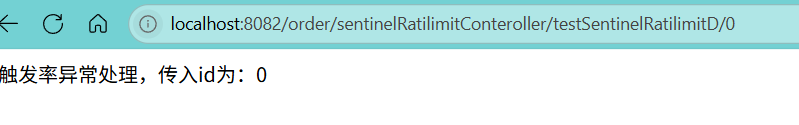
成功触发fallback
3.热点参数限流
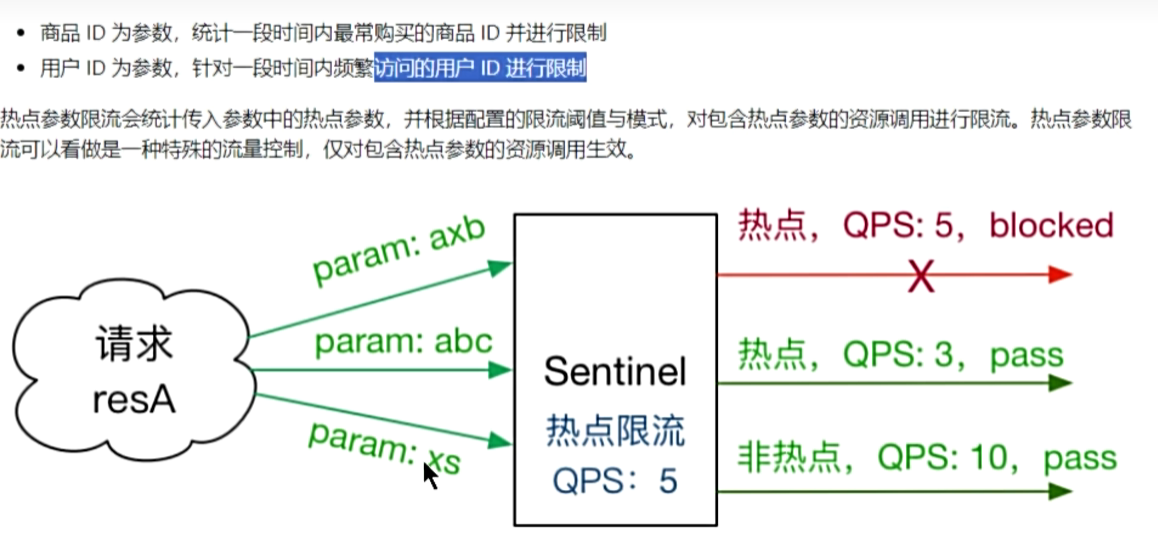
在我们比如商城服务中的商品流量是不均匀的,我们可能要对同一个接口的不同参数进行限流
例如
在查询某个商品信息时,同样根据商品id进行查询商品,商品ID: 1:华为 2:小米 3:苹果
查询接口
queryPhone(int id);
传入id为1的量较大,那么我们就需要对id为1的商品进行限流,如图:
写一个方法:
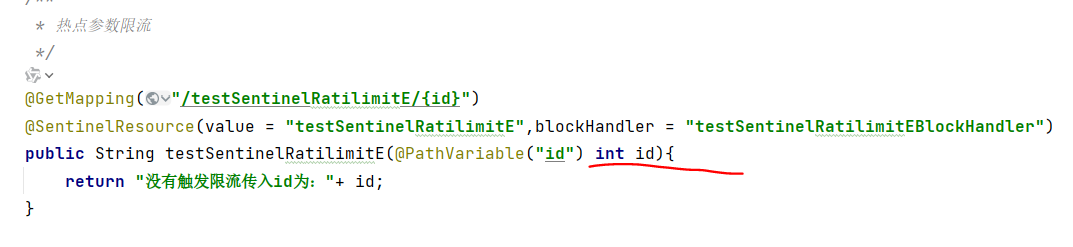
/*** 热点参数限流*/@GetMapping("/testSentinelRatilimitE/{id}")@SentinelResource(value = "testSentinelRatilimitE",blockHandler = "testSentinelRatilimitEBlockHandler")public String testSentinelRatilimitE(@PathVariable("id") int id){return "没有触发限流传入id为:"+ id;}/*** 热点参数限流处理*/public String testSentinelRatilimitEBlockHandler(int id,BlockException ex){return "触发限流处理,传入id为:"+ id;}访问 :localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitE/0
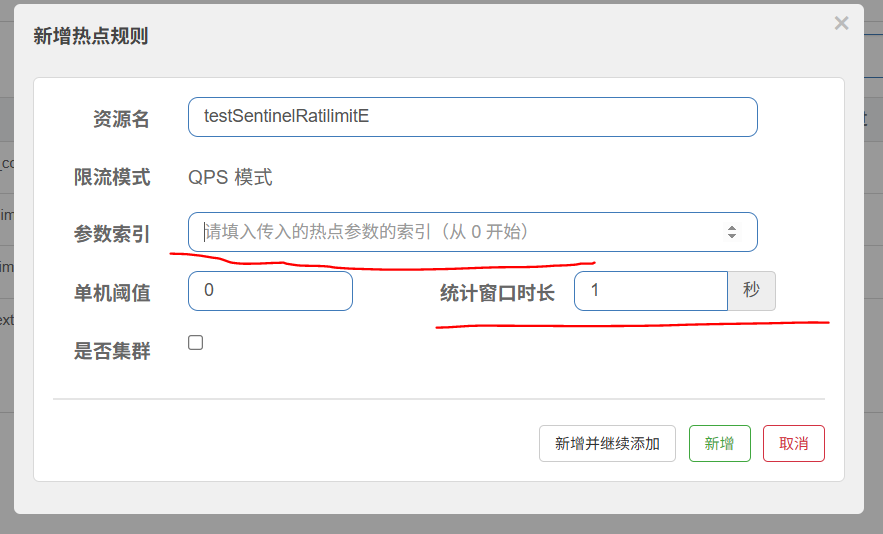
参数索引: 写0时则为接口中的第一个参数
索引为0
统计窗口:表示*秒内统计的量
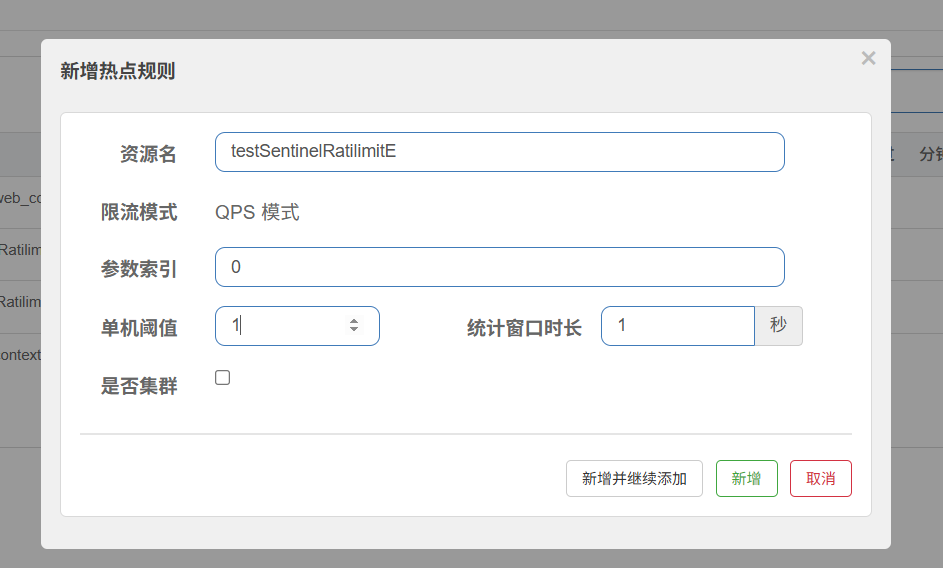
表示这个接口 带上参数ID时 QPS达到1开始限流
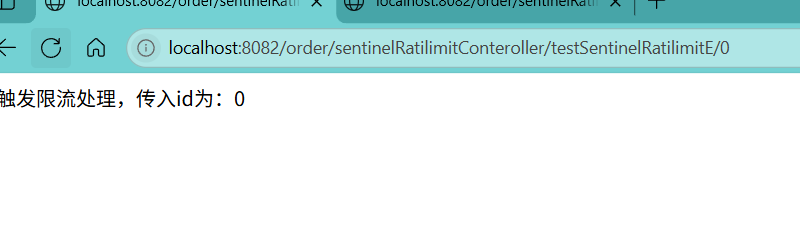
访问接口:localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitE/0
触发了限流
参数例外项:
例如当我们传入id为1时,我们的限流规则变成QPS为3才进行限流
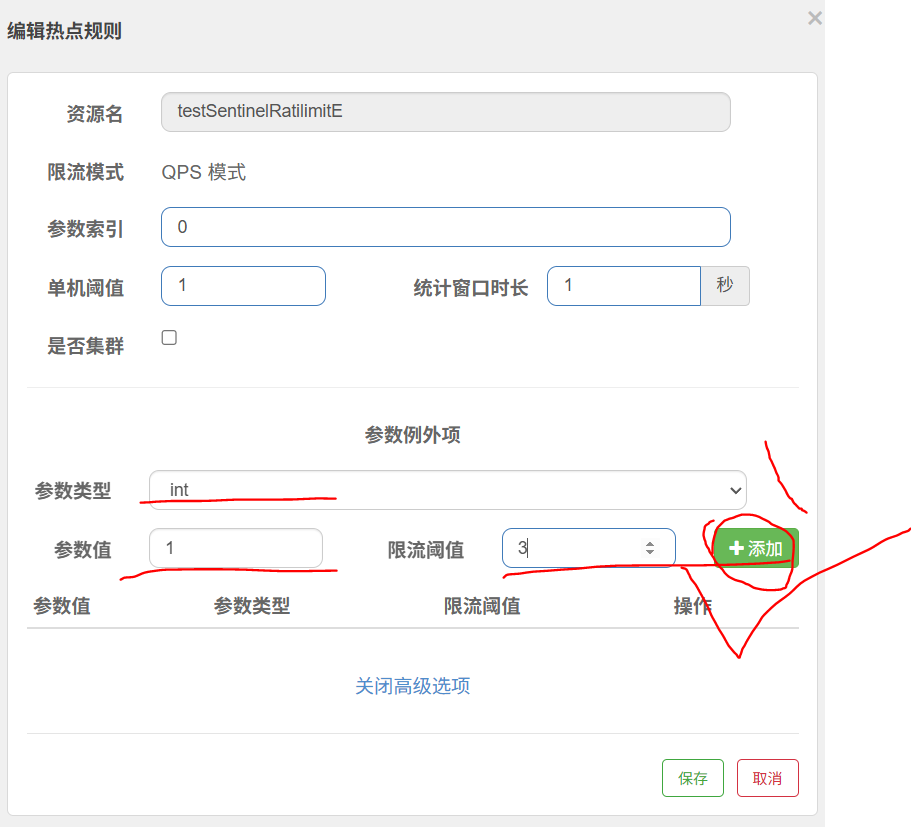
上面的参数表示,当带参数索引为0时,限流QPS为1 ,参数例外项:当参数索引0 传入值为1 时,限流阈值QPS提升为3才限流
务必要点击添加按钮
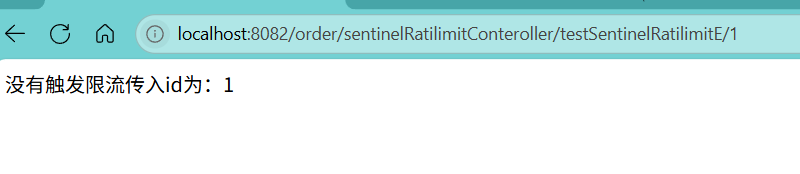
测试发现id等于1时 ,只有QPS达到3才会触发限流
4.sentinel规则持久化(不会因为微服务重启丢失配置)
我们服务配置完成后,我们的微服务重启会导致我们这个服务的所有的配置丢失,不可能每重启一次我们就重新配置一次限流规则,所以需要持久化,持久化到哪里呢? 我们会选择持久化到配置中心 nacos中
在服务中引入新的Maven坐标
<!--sentinel持久化--> <dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId><artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId> </dependency>
修改yml配置
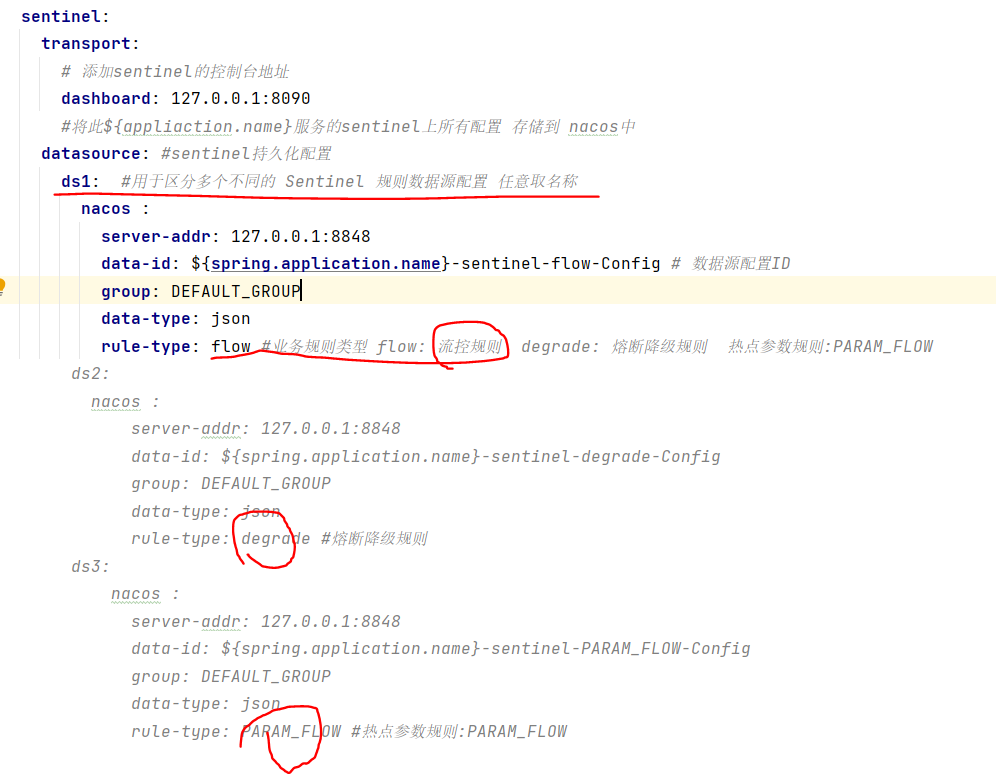
配置ds1 ds2 ds3 分别代表(流控规则)(熔断降级规则) (热点参数规则)的持久化配置
我们以流控规则作为演示
打开nacos创建对应的配置文件
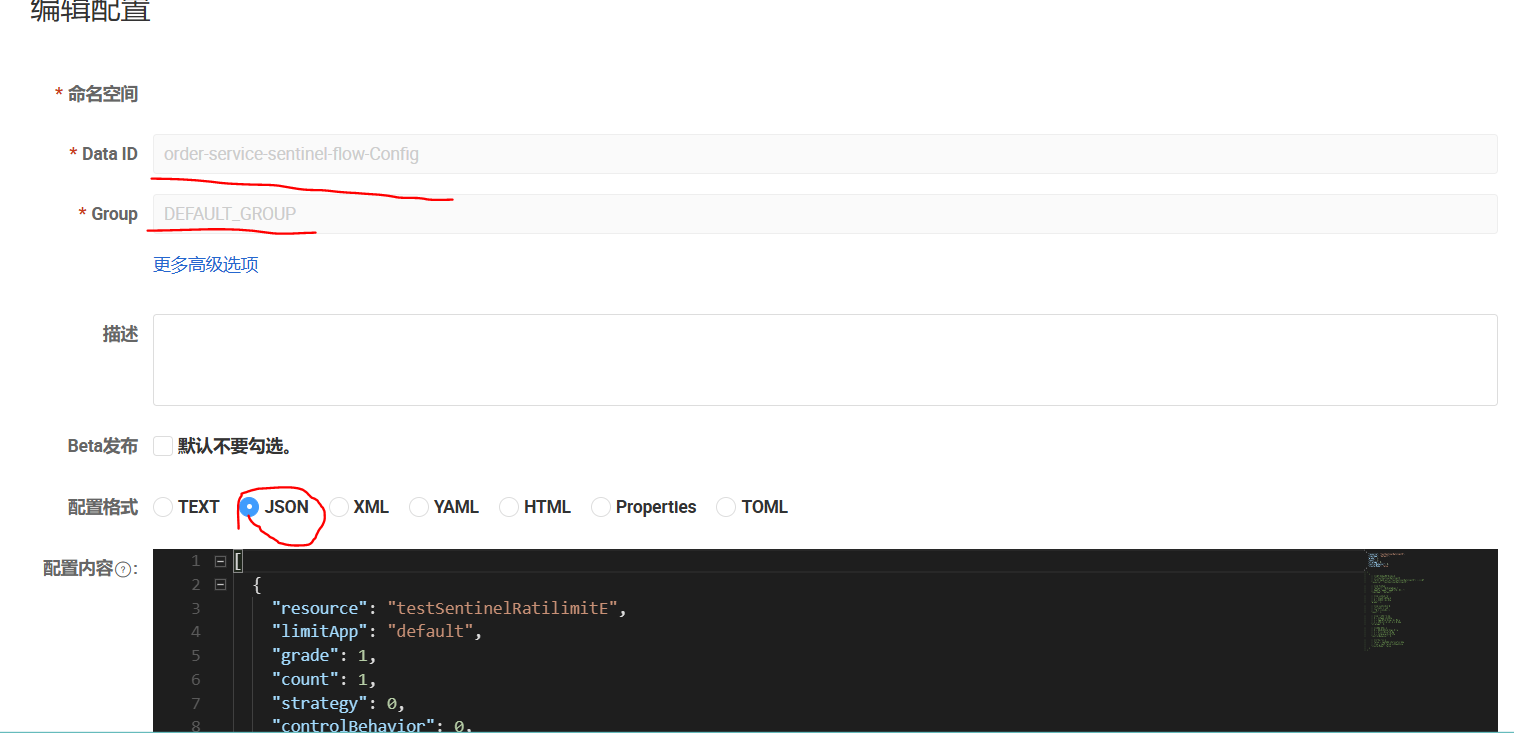
内容:
[{"resource": "testSentinelRatilimitE","limitApp": "default","grade": 1,"count": 1,"strategy": 0,"controlBehavior": 0,"clusterMode": false}
]
// [
// {
// // 🔹【资源名称】你想保护的是哪个接口或功能?
// // 这里是:testSentinelRatilimitE
// // 代码中要用 SphU.entry("testSentinelRatilimitE") 来标记这个资源
// "resource": "testSentinelRatilimitE",// // 🔹【限流对象】对谁限流?
// // "default" 表示:所有人都一样,一视同仁
// // 你也可以写成 "appA"、"appB",实现不同应用不同策略
// "limitApp": "default",// // 🔹【限流方式】按什么标准限流?
// // 1 = 按每秒请求数(QPS)来限
// // 0 = 按并发线程数来限(不常用)
// "grade": 1,// // 🔹【限流阈值】最多允许多少流量?
// // 这里是:每秒最多 1 个请求
// // 超过第 1 个就直接拒绝,不让进
// "count": 1,// // 🔹【限流策略】怎么判断要不要限?
// // 0 = 直接对自己限流(最简单常用)
// // 1 = 当另一个资源被限流时,我也跟着限(关联限流)
// // 2 = 只对某个调用链路限流(比如 A 调 B 才限)
// "strategy": 0,// // 🔹【触发限流后怎么办?】
// // 0 = 立刻拒绝,抛出“被限流”错误(快速失败)
// // 1 = 先预热,慢慢放行(适合突发流量)
// // 2 = 排队等待,一个一个处理(削峰填谷)
// "controlBehavior": 0,// // 🔹【是单机还是集群?】
// // false = 每台机器独立限流(单机模式,适合大多数场景)
// // true = 多台机器共享一个总限流值(需要额外配置集群)
// "clusterMode": false
// }
// ]!!!!非常非常难用,需要自己手动写json用于配置持久化,Sentinel控制台配置成为摆设,因为控制台上写的配置不会持久化,必须自己写!!!!
同样是阿里巴巴的产品 Nacos比sentinel好用太多了!
重启 当前服务
访问localhost:8082/order/sentinelRatilimitConteroller/testSentinelRatilimitE/1
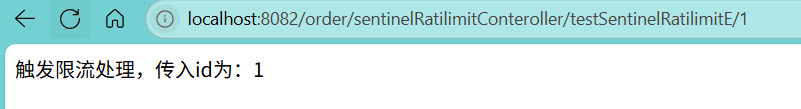
nacos 配置限流规则成功
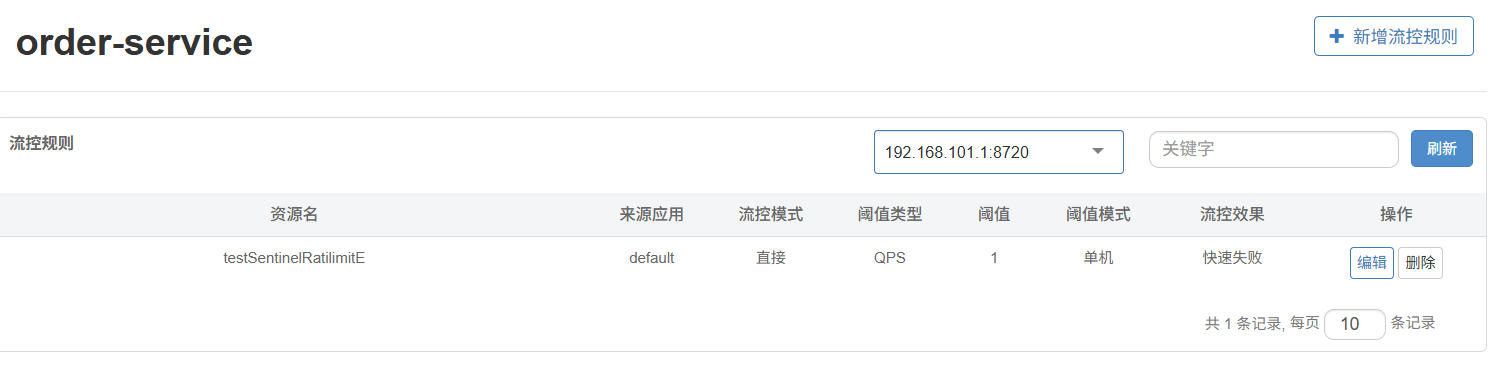
来到sentinel控制台查看限流规则
成功从nacos中读取限流规则
5.Sentinel集成OpenFeign实现fallback熔断降级
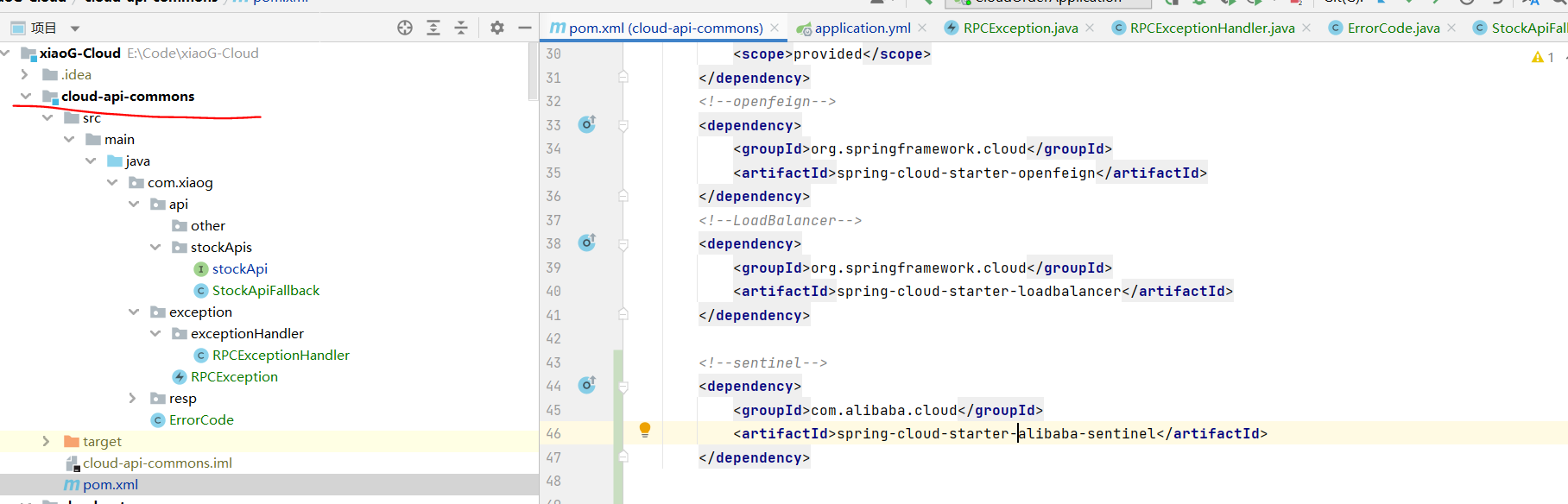
往公共API模块中引入sentinel maven 依赖
<!--sentinel--> <dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId> </dependency>
在api接口中添加fallbackFactory属性并创建对应的类
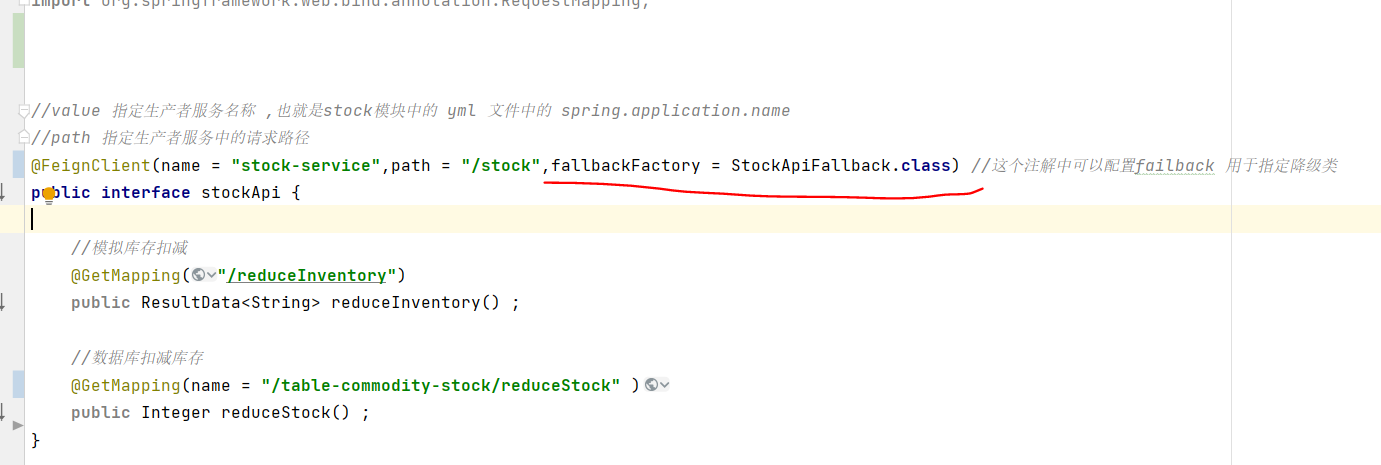
创建
StockApiFallback.class
@Component
public class StockApiFallback implements FallbackFactory<stockApi> {@Overridepublic stockApi create(Throwable cause) {return new stockApi() {@Overridepublic ResultData<String> reduceInventory() {throw new RPCException("201","调用库存服务调用失败");}@Overridepublic Integer reduceStock() {throw new RPCException("201","调用库存服务调用失败");}};}}在fallback 的时候为了保证fallback后全局事务还能正常的回滚,fallback一般抛出自定义异常让事务回滚,并且全局异常处理器 处理整形后才返回给用户
自定义异常类:
@Data
public class RPCException extends RuntimeException{private String code;private String message;private Object data;public RPCException(String code,String message,Object data) {super(message);this.message = message;this.code = code;this.data =data ;}public RPCException(String code,String message) {super(message);this.message = message;this.code = code;}}自定义异常捕获
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class RPCExceptionHandler {// 拦截自定义业务异常@ExceptionHandler(RPCException.class)public ResultData handleBizException(RPCException e) {log.warn("远程调用异常: code={}, msg={}", e.getCode(), e.getMessage());return ResultData.fail(e.getCode(),"系统出现错误,请稍后再试"); // 通常返回 200,业务码区分}}
重点:!!!! 然后在调用者模块 配置文件中开启OpenFeign 支持Sentinel
feign:sentinel:enabled: true # 启用 Sentinel 对 Feign 的支持
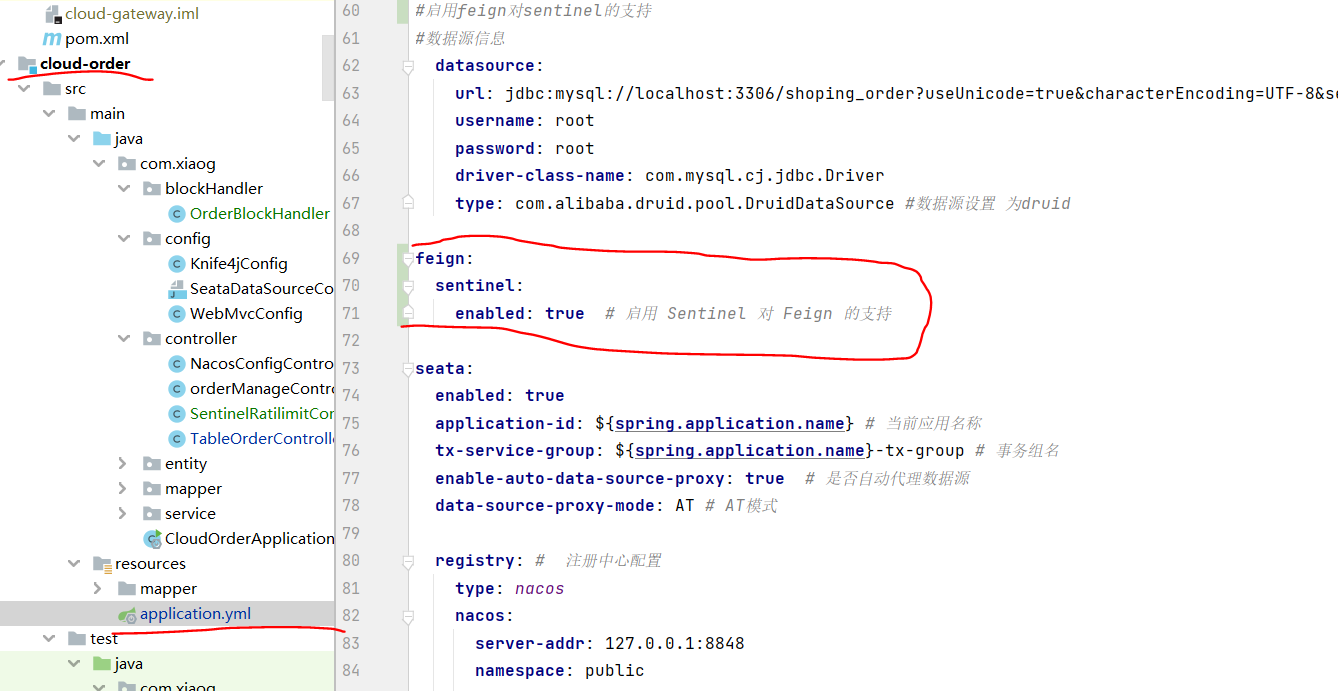
,然后重新启动 测试全局事务回滚是否正常
发现系统出现异常后,使用的是全局异常处理器返回的消息
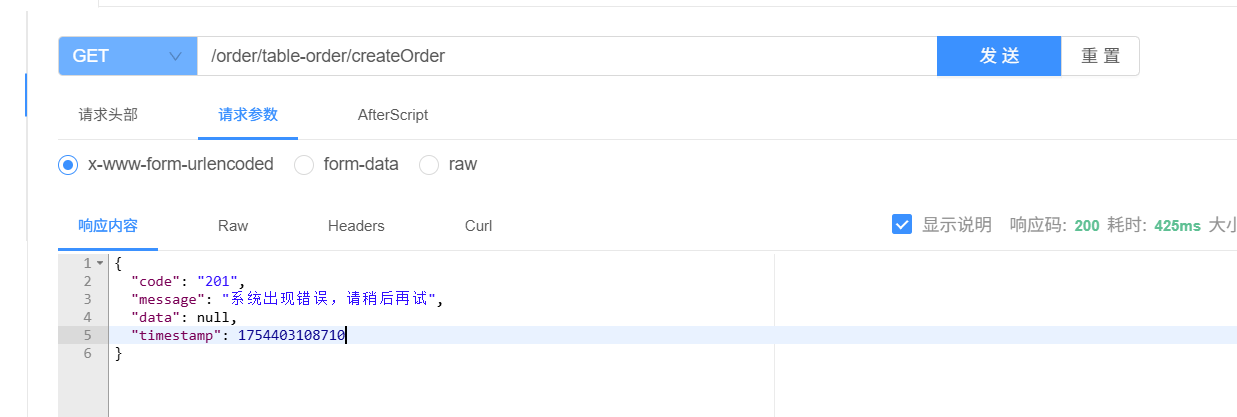
并且,事务全部正确回滚
任务完成
