从零开始实现Qwen3(Dense架构)
文章目录
- 从零开始实现Qwen3(Dense)
- 简介
- Qwen3架构
- 参考
- 结构
- RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
- RMSNorm介绍
- 数学公式
- 代码实现
- Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE)
- RoPE介绍
- RoPE的数学公式
- 代码实现
- Grouped Query Attention (GQA)
- GQA介绍
- 数学公式
- 代码实现
- FFN层
- SwiGLU介绍
- 数学公式
- 代码实现
- Transformer Block
- Transformer Block介绍
- 数学表达
- 代码实现
- Qwen3-0.6B 完整模型
- 模型架构
- 代码实现
- 文本生成+推理
- 文本生成
- Tokenizer实现
- 内存优化
- 整体代码
从零开始实现Qwen3(Dense)
简介
- 实现一个Qwen3-Dense架构,重点讲一下Dencoder部分的结构,剩下的文本生成和推理就一笔带过
Qwen3架构
-
我们结合Qwen3-0.6B的config文件
{"architectures": ["Qwen3ForCausalLM"],"attention_bias": false,"attention_dropout": 0.0,"bos_token_id": 151643,"eos_token_id": 151645,"head_dim": 128,"hidden_act": "silu","hidden_size": 1024,"initializer_range": 0.02,"intermediate_size": 3072,"max_position_embeddings": 40960,"max_window_layers": 28,"model_type": "qwen3","num_attention_heads": 16,"num_hidden_layers": 28,"num_key_value_heads": 8,"rms_norm_eps": 1e-06,"rope_scaling": null,"rope_theta": 1000000,"sliding_window": null,"tie_word_embeddings": true,"torch_dtype": "bfloat16","transformers_version": "4.51.0","use_cache": true,"use_sliding_window": false,"vocab_size": 1以及下面的图
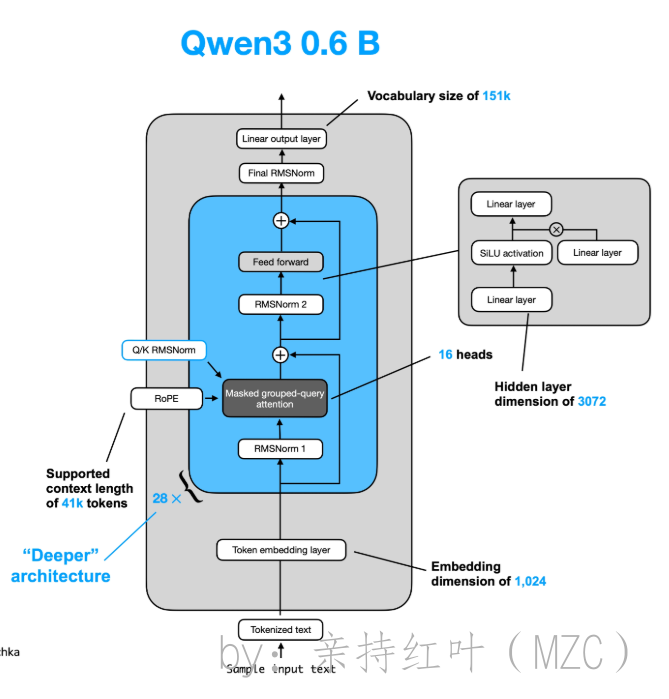
先来简单的看一下Qwen3系列的整体架构(其他dense模型仅仅是参数不同,但是整体架构一致)
- 词汇表大小: 151936
- 训练的上下文长度: 40960
- FFN层的激活函数:SwiGLU (Swish/SiLU + GLU)
- FFN层隐藏层维度:3072
- 使用ROPE边骂
- 使用Pre-Norm,且Normalization函数为RMSNorm
- 使用Q/K Norm,即在RoPE之前对Q和K使用RMSNorm
- 使用GQA, q共16个头,G=8
其他的没啥好说的了,使用pydantic定义一个config的数据模型,后续代码中出现的cfg即是这个数据模型的实例化
import torch from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldclass Qwen3Config(BaseModel):"""Pydantic model for Qwen3 configuration"""model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}vocab_size: int = Field(..., description="词汇表大小")context_length: int = Field(..., description="用于训练模型的上下文长度")emb_dim: int = Field(..., description="Embedding 维度")n_heads: int = Field(..., description="注意力头的数量")n_layers: int = Field(..., description="层数")hidden_dim: int = Field(..., description="FeedForward 层中中间维度的大小(隐藏层大小)")head_dim: int = Field(..., description="GQA 中每个注意力头的维度大小")qk_norm: bool = Field(..., description="是否在 GQA 中对key和value进行归一化")n_kv_groups: int = Field(..., description="用于分组查询注意力的 KV 组数")rope_base: float = Field(..., description="RoPE 中‘theta’的基数值")dtype: torch.dtype = Field(..., description="较低精度的数据类型,用于降低显存占用")QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936, # Vocabulary size"context_length": 40_960, # Context length that was used to train the model"emb_dim": 1024, # Embedding dimension"n_heads": 16, # Number of attention heads"n_layers": 28, # Number of layers"hidden_dim": 3072, # Size of the intermediate dimension in FeedForward"head_dim": 128, # Size of the heads in GQA"qk_norm": True, # Whether to normalize queries and values in GQA"n_kv_groups": 8, # Key-Value groups for grouped-query attention"rope_base": 1_000_000.0, # The base in RoPE's "theta""dtype": torch.bfloat16, # Lower-precision dtype to reduce memory usage}cfg = Qwen3Config(**QWEN3_CONFIG)
参考
-
参考代码:
https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/blob/main/ch05/11_qwen3/standalone-qwen3.ipynb
-
Qwen3: Think Deeper, Act Faster
https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwen3/
-
Qwen3 Technical Report Qwen3 技术报告
https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.09388
结构
RMSNorm(Root Mean Square Layer Normalization)
RMSNorm介绍
-
transformer-RMSNorm
-
RMSNorm通过对神经元输出的均方根值进行缩放,在保持训练稳定性的同时降低计算复杂度。与LayerNorm相比,RMSNorm移除了均值中心化操作,仅通过均方根值进行缩放,减少了约30%的计算量。
在Qwen3中,RMSNorm被广泛应用于每个Transformer层的归一化操作,包括注意力层前后和前馈网络前后的归一化。该方法通过单一缩放参数调整特征幅度,避免对输入进行平移操作,特别适合大规模模型训练。
数学公式
-
RMSNorm对输入张量最后一个维度进行均方根标准化:
RMS(x)=1emb_dim∑i=1emb_dimxi2out=γ⋅xRMS(x)2+ϵ+β\text{RMS}(x) = \sqrt{\frac{1}{emb\_{dim}}\sum_{i=1}^{emb\_{dim}}x_i^2} \\ \text{out} = \gamma \cdot \frac{x}{\sqrt{\text{RMS}(x)^2 + \epsilon}} + \beta RMS(x)=emb_dim1i=1∑emb_dimxi2out=γ⋅RMS(x)2+ϵx+β
其中:- γ∈Remb_dim\gamma \in \mathbb{R}^{emb\_{dim}}γ∈Remb_dim:可学习缩放参数(初始化为1)
- β\betaβ: 科学系平移参数(初始化为0)
- ϵ\epsilonϵ:数值稳定系数(默认1e-6)
emb_dimemb\_dimemb_dim 为特征维度。
代码实现
-
Qwen3中的RMSNorm实现
class RMSNorm(nn.Module):def __init__(self, emb_dim, eps=1e-6, bias=False, qwen3_compatible=False):super().__init__()self.eps = epsself.qwen3_compatible = qwen3_compatibleself.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(emb_dim)) # gammaself.shift = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(emb_dim)) if bias else None # betadef forward(self, x):input_dtype = x.dtypeif self.qwen3_compatible:x = x.to(torch.float32)variance = x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)norm_x = x * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.eps)norm_x = norm_x * self.scaleif self.shift is not None:norm_x = norm_x + self.shiftreturn norm_x.to(input_dtype)
Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE)
RoPE介绍
-
transformer-旋转位置编码RoPE
-
旋转位置编码(Rotary Position Embedding, RoPE)是Qwen3模型中使用的位置编码方法,通过对查询和键向量进行旋转变换来注入位置信息。与传统的绝对位置编码不同,RoPE能够更好地处理相对位置关系,并且对序列长度具有更好的外推能力。
在Qwen3中,RoPE被应用于每个注意力头的查询和键向量,通过预计算的正弦和余弦值对向量进行旋转变换,使得模型能够感知token之间的相对位置关系。
RoPE的数学公式
-
RoPE通过复数域的旋转操作实现位置编码:
对于位置为mmm的向量x\mathbf{x}x,RoPE变换定义为:
f(x,m)=RΘ,mxf(\mathbf{x}, m) = \mathbf{R}_{\Theta, m} \mathbf{x} f(x,m)=RΘ,mx其中旋转矩阵RΘ,m\mathbf{R}_{\Theta, m}RΘ,m的计算公式为:
RΘ,m=(cos(mθ0)−sin(mθ0)00⋯sin(mθ0)cos(mθ0)00⋯00cos(mθ1)−sin(mθ1)⋯00sin(mθ1)cos(mθ1)⋯⋮⋮⋮⋮⋱)\mathbf{R}_{\Theta, m} = \begin{pmatrix} \cos(m\theta_0) & -\sin(m\theta_0) & 0 & 0 & \cdots \\ \sin(m\theta_0) & \cos(m\theta_0) & 0 & 0 & \cdots \\ 0 & 0 & \cos(m\theta_1) & -\sin(m\theta_1) & \cdots \\ 0 & 0 & \sin(m\theta_1) & \cos(m\theta_1) & \cdots \\ \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \vdots & \ddots \end{pmatrix} RΘ,m=cos(mθ0)sin(mθ0)00⋮−sin(mθ0)cos(mθ0)00⋮00cos(mθ1)sin(mθ1)⋮00−sin(mθ1)cos(mθ1)⋮⋯⋯⋯⋯⋱其中θi=base−2i/d\theta_i = \text{base}^{-2i/d}θi=base−2i/d,在Qwen3中base=1,000,000。
代码实现
-
RoPE参数计算函数
def compute_rope_params(head_dim, theta_base=10_000, context_length=4096, dtype=torch.float32):assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Embedding dimension must be even"# 计算逆频率inv_freq = 1.0 / (theta_base ** (torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2, dtype=dtype)[: (head_dim // 2)].float() / head_dim))# 生成位置索引positions = torch.arange(context_length, dtype=dtype)# 计算角度angles = positions[:, None] * inv_freq[None, :] # Shape: (context_length, head_dim // 2)# 扩展角度以匹配head_dimangles = torch.cat([angles, angles], dim=1) # Shape: (context_length, head_dim)# 预计算正弦和余弦cos = torch.cos(angles)sin = torch.sin(angles)return cos, sin -
RoPE应用函数
def apply_rope(x, cos, sin):# x: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim)batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim = x.shapeassert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Head dimension must be even"# 将x分为前半部分和后半部分x1 = x[..., : head_dim // 2] # 前半部分x2 = x[..., head_dim // 2:] # 后半部分# 调整sin和cos的形状cos = cos[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # Shape: (1, 1, seq_len, head_dim)sin = sin[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)# 应用旋转变换rotated = torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)x_rotated = (x * cos) + (rotated * sin)return x_rotated.to(dtype=x.dtype)
Grouped Query Attention (GQA)
GQA介绍
-
MHA、MQA、GQA:大模型注意力机制的演进
-
分组查询注意力(Grouped Query Attention, GQA)是Qwen3模型中使用的高效注意力机制。GQA通过减少键值对(Key-Value)的数量来降低内存使用和计算复杂度,同时保持与多头注意力相近的性能。
在传统的多头注意力中,每个头都有独立的查询、键、值投影。而在GQA中,多个查询头共享同一组键值对,通过分组的方式实现计算效率的提升。Qwen3-0.6B使用8个KV组来支持16个注意力头。
数学公式
-
GQA的计算过程可以表示为:
GQA(X)=Concat(head1,head2,...,headh)WO\text{GQA}(X) = \text{Concat}(\text{head}_1, \text{head}_2, ..., \text{head}_h) W^O GQA(X)=Concat(head1,head2,...,headh)WO
其中每个头的计算为:
headi=Attention(XWiQ,XW⌊i/g⌋K,XW⌊i/g⌋V)\text{head}_i = \text{Attention}(XW_i^Q, XW_{\lfloor i/g \rfloor}^K, XW_{\lfloor i/g \rfloor}^V) headi=Attention(XWiQ,XW⌊i/g⌋K,XW⌊i/g⌋V)关键参数:
- hhh:查询头的总数
- ggg:每组的大小(group_size = num_heads / num_kv_groups)
- ⌊i/g⌋\lfloor i/g \rfloor⌊i/g⌋:第i个查询头对应的KV组索引
代码实现
-
Qwen3中的GQA实现
class GroupQueryAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self, d_in, num_heads, num_kv_groups, head_dim=None, qk_norm=False, dtype=None):super().__init__()assert num_heads % num_kv_groups == 0, "num_heads must be divisible by num_kv_groups"self.num_heads = num_headsself.num_kv_groups = num_kv_groupsself.group_size = num_heads // num_kv_groupsif head_dim is None:assert d_in % num_heads == 0, "d_in must be divisible by num_heads if head_dim is not set"head_dim = d_in // num_headsself.head_dim = head_dimself.d_out = num_heads * head_dim# 查询投影:每个头都有独立的查询投影self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, self.d_out, bias=False, dtype=dtype)# 键值投影:多个头共享键值投影self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.d_out, d_in, bias=False, dtype=dtype)# 可选的QK归一化if qk_norm:self.q_norm = RMSNorm(head_dim, eps=1e-6)self.k_norm = RMSNorm(head_dim, eps=1e-6)else:self.q_norm = self.k_norm = Nonedef forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):b, num_tokens, _ = x.shape# 应用投影queries = self.W_query(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_heads * head_dim]keys = self.W_key(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim]values = self.W_value(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim]# 重塑张量queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)# 可选的QK归一化if self.q_norm:queries = self.q_norm(queries)if self.k_norm:keys = self.k_norm(keys)# 应用RoPE位置编码queries = apply_rope(queries, cos, sin)keys = apply_rope(keys, cos, sin)# 扩展K和V以匹配查询头的数量keys = keys.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)values = values.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)# 计算注意力attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3)attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(mask, -torch.inf)attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / self.head_dim ** 0.5, dim=-1)context = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2).reshape(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)return self.out_proj(context) -
关键特性解析
特性 说明 Qwen3-0.6B配置 num_heads 查询头数量 16 num_kv_groups 键值组数量 8 group_size 每组大小 2 head_dim 每个头的维度 128 qk_norm QK归一化 True -
维度变化流程
操作步骤 张量形状变化示例 输入数据 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 查询投影 [batch_size, seq_len, num_heads * head_dim] 键值投影 [batch_size, seq_len, num_kv_groups * head_dim] 重塑查询 [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim] 重塑键值 [batch_size, num_kv_groups, seq_len, head_dim] 扩展键值 [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim] 注意力计算 [batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim] 输出投影 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim]
FFN层
SwiGLU介绍
-
GLU 变种:ReGLU 、 GEGLU 、 SwiGLU
-
SwiGLU(Swish-Gated Linear Unit)是Qwen3模型中使用的激活函数,结合了Swish激活函数和门控机制。SwiGLU通过两个并行的线性变换和门控机制,提供了比传统ReLU更好的表达能力和梯度流动特性。
在Qwen3的前馈网络中,SwiGLU替代了传统的ReLU激活函数,通过门控机制选择性地激活神经元,提高了模型的非线性建模能力。该激活函数在大规模语言模型中表现出色,能够更好地处理复杂的语言模式。
数学公式
-
SwiGLU的计算公式为:
SwiGLU(x)=Swish(xW1+b1)⊙(xW2+b2)\text{SwiGLU}(x) = \text{Swish}(xW_1 + b_1) \odot (xW_2 + b_2) SwiGLU(x)=Swish(xW1+b1)⊙(xW2+b2)
其中:
- Swish(x)=x⋅σ(βx)=x⋅sigmoid(βx)\text{Swish}(x) = x \cdot \sigma(\beta x) = x \cdot \text{sigmoid}(\beta x)Swish(x)=x⋅σ(βx)=x⋅sigmoid(βx)
- 当β=1\beta = 1β=1时,Swish(x)=x⋅sigmoid(x)=SiLU(x)\text{Swish}(x) = x \cdot \text{sigmoid}(x) = \text{SiLU}(x)Swish(x)=x⋅sigmoid(x)=SiLU(x)
- ⊙\odot⊙ 表示逐元素乘法(Hadamard积)
- W1,W2W_1, W_2W1,W2 是两个独立的权重矩阵
- b1,b2b_1, b_2b1,b2 是偏置项(在Qwen3中通常省略)
完整的前馈网络公式:
FFN(x)=SwiGLU(x)W3=(SiLU(xW1)⊙xW2)W3\text{FFN}(x) = \text{SwiGLU}(x) W_3 = (\text{SiLU}(xW_1) \odot xW_2) W_3 FFN(x)=SwiGLU(x)W3=(SiLU(xW1)⊙xW2)W3
代码实现
-
Qwen3中的SwiGLU前馈网络实现
class FeedForward(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()# 两个并行的线性层用于门控机制self.fc1 = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.hidden_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.hidden_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)# 输出投影层self.fc3 = nn.Linear(cfg.hidden_dim, cfg.emb_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)def forward(self, x):"""SwiGLU激活函数"""# 第一个分支:应用SiLU激活x_fc1 = self.fc1(x)# 第二个分支:线性变换x_fc2 = self.fc2(x)# 门控机制:SiLU(x_fc1) * x_fc2x = F.silu(x_fc1) * x_fc2# 输出投影return self.fc3(x) -
相关解释
-
网络结构特点:- 双分支设计: fc1和fc2形成两个并行分支
- 门控机制: 通过逐元素乘法实现选择性激活
- 无偏置: 所有线性层都不使用偏置项,简化计算
-
激活函数选择:- SiLU: SiLU(x)=x⋅sigmoid(x)\text{SiLU}(x) = x \cdot \text{sigmoid}(x)SiLU(x)=x⋅sigmoid(x)
- 平滑性: 相比ReLU,SiLU在整个定义域内可微
- 门控效应: 通过sigmoid函数实现软门控
-
-
维度变化流程
操作步骤 张量形状变化示例 Qwen3-0.6B配置 输入数据 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] [4, 100, 1024] fc1分支 [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim] [4, 100, 3072] fc2分支 [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim] [4, 100, 3072] SiLU激活 [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim] [4, 100, 3072] 门控乘法 [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_dim] [4, 100, 3072] fc3输出 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] [4, 100, 1024]
Transformer Block
- 后续注意,实际现在llm基本都是Decoder-only,所以后面的Transformer Block一律默认为Decoder Block
Transformer Block介绍
-
Qwen3的Transformer Block是模型的核心构建单元,每个Block包含一个分组查询注意力层和一个SwiGLU前馈网络层。与标准Transformer不同,Qwen3采用了Pre-Norm结构,即在每个子层之前应用RMSNorm,这种设计有助于训练稳定性和梯度流动。
每个Transformer Block通过残差连接将输入与子层输出相加,形成深度网络中的信息高速公路。Qwen3-0.6B模型包含28个这样的Transformer Block,通过层层堆叠实现复杂的语言理解和生成能力。
数学表达
-
Transformer Block的计算过程可以表示为:
注意力子层:
Attn_Out=x+GQA(RMSNorm(x),mask,cos,sin)\text{Attn\_Out} = x + \text{GQA}(\text{RMSNorm}(x), \text{mask}, \cos, \sin) Attn_Out=x+GQA(RMSNorm(x),mask,cos,sin)前馈子层:
Block_Out=Attn_Out+SwiGLU(RMSNorm(Attn_Out))\text{Block\_Out} = \text{Attn\_Out} + \text{SwiGLU}(\text{RMSNorm}(\text{Attn\_Out})) Block_Out=Attn_Out+SwiGLU(RMSNorm(Attn_Out))其中:
- xxx 是输入张量
- GQA\text{GQA}GQA 是分组查询注意力
- SwiGLU\text{SwiGLU}SwiGLU 是使用SwiGLU的FFN层
- RMSNorm\text{RMSNorm}RMSNorm 是均方根归一化
- cos,sin\cos, \sincos,sin 是RoPE位置编码参数
代码实现
-
Qwen3中的Transformer Block实现
class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()# 分组查询注意力层self.att = GroupQueryAttention(d_in=cfg.emb_dim,num_heads=cfg.n_heads,head_dim=cfg.head_dim,num_kv_groups=cfg.n_kv_groups,qk_norm=cfg.qk_norm,dtype=cfg.dtype)# SwiGLU前馈网络self.ff = FeedForward(cfg)# 两个RMSNorm层self.norm1 = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim, eps=1e-6)self.norm2 = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim, eps=1e-6)def forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):# 注意力子层(Pre-Norm结构)shortcut = xx = self.norm1(x)x = self.att(x, mask, cos, sin)x = x + shortcut # 残差连接# 前馈子层(Pre-Norm结构)shortcut = xx = self.norm2(x)x = self.ff(x)x = x + shortcut # 残差连接return x -
关键设计特点
-
Pre-Norm结构:- 在每个子层之前应用归一化,而不是之后
- 有助于训练稳定性,特别是在深层网络中
- 减少梯度消失问题
-
残差连接:- 每个子层都有直接的跳跃连接
- 保证信息流动和梯度传播
- 使得深层网络训练成为可能
-
-
维度变化流程
操作步骤 张量形状变化示例 输入数据 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 注意力归一化 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 分组查询注意力 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 第一次残差连接 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 前馈归一化 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] SwiGLU前馈 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim] 第二次残差连接 [batch_size, seq_len, emb_dim]
Qwen3-0.6B 完整模型
模型架构
-
Qwen3的完整架构包含以下组件:
- 词嵌入层(Token Embedding):将输入token映射为高维向量
- 多层Transformer Block:核心的特征提取和变换层
- 最终归一化层(Final Norm):输出前的最后一次归一化
- 输出投影层(Output Head):将隐藏状态映射到词汇表空间
模型支持因果语言建模,通过上三角掩码确保生成过程中不会看到未来信息。
代码实现
-
Qwen3完整模型实现
class Qwen3Model(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()# 主要模型参数self.tok_emb = nn.Embedding(cfg.vocab_size, cfg.emb_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype)self.trf_blocks = nn.ModuleList([TransformerBlock(cfg) for _ in range(cfg.n_layers)])self.final_norm = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim)self.out_head = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.vocab_size, bias=False, dtype=cfg.dtype)# 可重用的工具组件if cfg.head_dim is None:head_dim = cfg.emb_dim // cfg.n_headselse:head_dim = cfg.head_dimcos, sin = compute_rope_params(head_dim=head_dim,theta_base=cfg.rope_base,context_length=cfg.context_length)self.register_buffer("cos", cos, persistent=False)self.register_buffer("sin", sin, persistent=False)self.cfg = cfgdef forward(self, in_idx):# 前向传播tok_embeds = self.tok_emb(in_idx)x = tok_embedsnum_tokens = x.shape[1]# 创建因果掩码mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(num_tokens, num_tokens, device=x.device, dtype=torch.bool),diagonal=1)# 通过所有Transformer Blockfor block in self.trf_blocks:x = block(x, mask, self.cos, self.sin)# 最终归一化和输出投影x = self.final_norm(x)logits = self.out_head(x.to(self.cfg.dtype))return logits -
模型配置系统
def set_qwen3_config(choose_model="0.6B"):assert choose_model in ["0.6B", "1.7B", "4B", "8B", "14B", "32B"]if choose_model == "0.6B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 1024,"n_heads": 16,"n_layers": 28,"hidden_dim": 3072,"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}# ... 其他配置这里先不写,后续看整体代码,return Qwen3Config(**QWEN3_CONFIG) -
不同规模模型对比
模型规模 参数量 嵌入维度 注意力头 层数 隐藏维度 0.6B 0.6B 1024 16 28 3072 1.7B 1.7B 2048 16 28 6144 4B 4B 2560 32 36 9728 8B 8B 4096 32 36 12288 14B 14B 5120 40 40 17408 32B 32B 5120 64 64 25600 -
qwen3-0.6B加载后的模型print
model: Qwen3Model((tok_emb): Embedding(151936, 1024)(trf_blocks): ModuleList((0-27): 28 x TransformerBlock((W_query): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2048, bias=False)(W_key): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)(W_value): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)(out_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=False)(q_norm): RMSNorm()(k_norm): RMSNorm())(ff): FeedForward((fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=3072, bias=False)(fc2): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=3072, bias=False)(fc3): Linear(in_features=3072, out_features=1024, bias=False))(norm1): RMSNorm()(norm2): RMSNorm()))(final_norm): RMSNorm()(out_head): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=151936, bias=False) )
文本生成+推理
文本生成
-
基础的贪婪解码算法:
def generate_text_basic_stream(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):model.eval()with torch.no_grad():for _ in range(max_new_tokens):# 前向传播获取logitsout = model(token_ids)[:, -1] # 只取最后一个位置的输出# 贪婪解码:选择概率最高的tokennext_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)# 检查是否遇到结束tokenif (eos_token_id is not None and torch.all(next_token == eos_token_id)):breakyield next_token# 将新token添加到序列中token_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)
Tokenizer实现
-
Qwen3专用的Tokenizer实现
class Qwen3Tokenizer:_SPECIALS = ["<|endoftext|>", "<|im_start|>", "<|im_end|>","<|object_ref_start|>", "<|object_ref_end|>","<|box_start|>", "<|box_end|>","<|quad_start|>", "<|quad_end|>","<|vision_start|>", "<|vision_end|>","<|vision_pad|>", "<|image_pad|>", "<|video_pad|>",]_SPLIT_RE = re.compile(r"(<\|[^>]+?\|>)")def __init__(self, tokenizer_file_path="tokenizer.json", repo_id=None,apply_chat_template=True, add_generation_prompt=False, add_thinking=False):self.apply_chat_template = apply_chat_templateself.add_generation_prompt = add_generation_promptself.add_thinking = add_thinkingtok_file = Path(tokenizer_file_path)self._tok = Tokenizer.from_file(str(tok_file))self._special_to_id = {t: self._tok.token_to_id(t) for t in self._SPECIALS}self.pad_token_id = self._special_to_id.get("<|endoftext|>")self.eos_token_id = self.pad_token_iddef encode(self, text, chat_wrapped=None):if chat_wrapped is None:chat_wrapped = self.apply_chat_templateif chat_wrapped:text = self._wrap_chat(text)ids = []for part in filter(None, self._SPLIT_RE.split(text)):if part in self._special_to_id:ids.append(self._special_to_id[part])else:ids.extend(self._tok.encode(part).ids)return idsdef decode(self, ids):return self._tok.decode(ids, skip_special_tokens=False)def _wrap_chat(self, user_msg):s = f"<|im_start|>user\n{user_msg}<|im_end|>\n"if self.add_generation_prompt:s += "<|im_start|>assistant"if self.add_thinking:s += "\n"else:s += "\n<think>\n\n</think>\n\n"return s
内存优化
-
Qwen3模型采用了多种内存优化技术:
- 混合精度训练:使用bfloat16减少内存使用
- 分组查询注意力:减少KV缓存大小
- 权重共享:embedding层和输出层共享权重
def model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.float32):total_params = 0total_grads = 0for param in model.parameters():param_size = param.numel()total_params += param_sizeif param.requires_grad:total_grads += param_sizetotal_buffers = sum(buf.numel() for buf in model.buffers())element_size = torch.tensor(0, dtype=input_dtype).element_size()total_memory_bytes = (total_params + total_grads + total_buffers) * element_sizetotal_memory_gb = total_memory_bytes / (1024 ** 3)return total_memory_gb -
不同精度下的内存使用对比:
模型规模 float32 bfloat16 内存节省 0.6B 2.4 GB 1.2 GB 50% 1.7B 6.8 GB 3.4 GB 50% 4B 16.0 GB 8.0 GB 50% 8B 32.0 GB 16.0 GB 50%
整体代码
-
整体代码如下
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # # @File : 1_qwen3_architecture.py.py # @Date : 2025/8/3 # @Author : mengzhichao # @Version : 1.0 # @Desc :import torch from torch import nn from torch.nn import functional as F from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldimport json import os from pathlib import Path from safetensors.torch import load_file from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download, snapshot_downloadimport re from tokenizers import Tokenizerclass Qwen3Config(BaseModel):"""Pydantic model for Qwen3 configuration"""model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}vocab_size: int = Field(..., description="词汇表大小")context_length: int = Field(..., description="用于训练模型的上下文长度")emb_dim: int = Field(..., description="Embedding 维度")n_heads: int = Field(..., description="注意力头的数量")n_layers: int = Field(..., description="层数")hidden_dim: int = Field(..., description="FeedForward 层中中间维度的大小(隐藏层大小)")head_dim: int = Field(..., description="GQA 中每个注意力头的维度大小")qk_norm: bool = Field(..., description="是否在 GQA 中对key和value进行归一化")n_kv_groups: int = Field(..., description="用于分组查询注意力的 KV 组数")rope_base: float = Field(..., description="RoPE 中‘theta’的基数值")dtype: torch.dtype = Field(..., description="较低精度的数据类型,用于降低显存占用")class FeedForward(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()self.fc1 = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.hidden_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.hidden_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(cfg.hidden_dim, cfg.emb_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype, bias=False)def forward(self, x):"""SwiGLU"""x_fc1 = self.fc1(x)x_fc2 = self.fc2(x)x = F.silu(x_fc1) * x_fc2return self.fc3(x)class RMSNorm(nn.Module):def __init__(self, emb_dim, eps=1e-6, bias=False, qwen3_compatible=False):super().__init__()self.eps = epsself.qwen3_compatible = qwen3_compatibleself.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(emb_dim)) # gammaself.shift = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(emb_dim)) if bias else None # betadef forward(self, x):input_dtype = x.dtypeif self.qwen3_compatible:x = x.to(torch.float32)variance = x.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)norm_x = x * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.eps)norm_x = norm_x * self.scaleif self.shift is not None:norm_x = norm_x + self.shiftreturn norm_x.to(input_dtype)def compute_rope_params(head_dim, theta_base=10_000, context_length=4096, dtype=torch.float32):assert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Embedding dimension must be even"# Compute the inverse frequenciesinv_freq = 1.0 / (theta_base ** (torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2, dtype=dtype)[: (head_dim // 2)].float() / head_dim))# Generate position indicespositions = torch.arange(context_length, dtype=dtype)# Compute the anglesangles = positions[:, None] * inv_freq[None, :] # Shape: (context_length, head_dim // 2)# Expand angles to match the head_dimangles = torch.cat([angles, angles], dim=1) # Shape: (context_length, head_dim)# Precompute sine and cosinecos = torch.cos(angles)sin = torch.sin(angles)return cos, sindef apply_rope(x, cos, sin):# x: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim)batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, head_dim = x.shapeassert head_dim % 2 == 0, "Head dimension must be even"# Split x into first half and second halfx1 = x[..., : head_dim // 2] # First halfx2 = x[..., head_dim // 2:] # Second half# Adjust sin and cos shapescos = cos[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0) # Shape: (1, 1, seq_len, head_dim)sin = sin[:seq_len, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)# Apply the rotary transformationrotated = torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)x_rotated = (x * cos) + (rotated * sin)# It's ok to use lower-precision after applying cos and sin rotationreturn x_rotated.to(dtype=x.dtype)class GroupQueryAttention(nn.Module):def __init__(self, d_in, num_heads, num_kv_groups, head_dim=None, qk_norm=False, dtype=None):super().__init__()assert num_heads % num_kv_groups == 0, "num_heads must be divisible by num_kv_groups"self.num_heads = num_headsself.num_kv_groups = num_kv_groupsself.group_size = num_heads // num_kv_groupsif head_dim is None:assert d_in % num_heads == 0, "d_in must be divisible by num_heads if head_dim is not set"head_dim = d_in // num_headsself.head_dim = head_dimself.d_out = num_heads * head_dimself.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, self.d_out, bias=False, dtype=dtype)self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, num_kv_groups * head_dim, bias=False, dtype=dtype)self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.d_out, d_in, bias=False, dtype=dtype)if qk_norm:self.q_norm = RMSNorm(head_dim, eps=1e-6)self.k_norm = RMSNorm(head_dim, eps=1e-6)else:self.q_norm = self.k_norm = Nonedef forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):b, num_tokens, _ = x.shape# Apply projectionsqueries = self.W_query(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_heads * head_dim]keys = self.W_key(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim]values = self.W_value(x) # [b, num_tokens, num_kv_groups * head_dim]# Reshapequeries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1,2) # [b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim]keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1,2) # [b, num_kv_groups,head_dim, num_tokens,head_dim]values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_kv_groups, self.head_dim).transpose(1,2) # [b, num_kv_groups,head_dim, num_tokens,head_dim]# Optional normalizationif self.q_norm:queries = self.q_norm(queries)if self.k_norm:keys = self.k_norm(keys)# Apply RoPEqueries = apply_rope(queries, cos, sin)keys = apply_rope(keys, cos, sin)# Expand K and V to match number of headskeys = keys.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)values = values.repeat_interleave(self.group_size, dim=1)# Attentionattn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3)attn_scores = attn_scores.masked_fill(mask, -torch.inf)attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / self.head_dim ** 0.5, dim=-1)context = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2).reshape(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)return self.out_proj(context)class TransformerBlock(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()self.att = GroupQueryAttention(d_in=cfg.emb_dim,num_heads=cfg.n_heads,head_dim=cfg.head_dim,num_kv_groups=cfg.n_kv_groups,qk_norm=cfg.qk_norm,dtype=cfg.dtype)self.ff = FeedForward(cfg)self.norm1 = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim, eps=1e-6)self.norm2 = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim, eps=1e-6)def forward(self, x, mask, cos, sin):# shortcut connection for attention blockshortcut = xx = self.norm1(x)x = self.att(x, mask, cos, sin) # Shape [batch_size,num_tokens,emb_size]x = x + shortcut# shortcut connection for feed-forward blockshortcut = xx = self.norm2(x)x = self.ff(x)x = x + shortcut # Add the original input backreturn xclass Qwen3Model(nn.Module):def __init__(self, cfg):super().__init__()# Main model parametersself.tok_emb = nn.Embedding(cfg.vocab_size, cfg.emb_dim, dtype=cfg.dtype)self.trf_blocks = nn.ModuleList(# ModuleList since Sequential can only accept one input, and we need `x, mask, cos, sin`[TransformerBlock(cfg) for _ in range(cfg.n_layers)])self.final_norm = RMSNorm(cfg.emb_dim)self.out_head = nn.Linear(cfg.emb_dim, cfg.vocab_size, bias=False, dtype=cfg.dtype)# Reusuable utilitiesif cfg.head_dim is None:head_dim = cfg.emb_dim // cfg.n_headselse:head_dim = cfg.head_dimcos, sin = compute_rope_params(head_dim=head_dim,theta_base=cfg.rope_base,context_length=cfg.context_length)self.register_buffer("cos", cos, persistent=False)self.register_buffer("sin", sin, persistent=False)self.cfg = cfgdef forward(self, in_idx):# Forward passtok_embeds = self.tok_emb(in_idx)x = tok_embedsnum_tokens = x.shape[1]mask = torch.triu(torch.ones(num_tokens, num_tokens, device=x.device, dtype=torch.bool),diagonal=1)for block in self.trf_blocks:x = block(x, mask, self.cos, self.sin)x = self.final_norm(x)logits = self.out_head(x.to(self.cfg.dtype))return logitsdef set_qwen3_config(choose_model="0.6B"):assert choose_model in ["0.6B", "1.7B", "4B", "8B", "14B","32B"], "model choose error, must be one of [0.6B, 1.7B, 4B, 8B, 14B, 32B]"CHOOSE_MODEL = choose_modelif CHOOSE_MODEL == "0.6B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936, # Vocabulary size"context_length": 40_960, # Context length that was used to train the model"emb_dim": 1024, # Embedding dimension"n_heads": 16, # Number of attention heads"n_layers": 28, # Number of layers"hidden_dim": 3072, # Size of the intermediate dimension in FeedForward"head_dim": 128, # Size of the heads in GQA"qk_norm": True, # Whether to normalize queries and values in GQA"n_kv_groups": 8, # Key-Value groups for grouped-query attention"rope_base": 1_000_000.0, # The base in RoPE's "theta""dtype": torch.bfloat16, # Lower-precision dtype to reduce memory usage}elif CHOOSE_MODEL == "1.7B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 2048, # 2x larger than above"n_heads": 16,"n_layers": 28,"hidden_dim": 6144, # 2x larger than above"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}elif CHOOSE_MODEL == "4B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 2560, # 25% larger than above"n_heads": 32, # 2x larger than above"n_layers": 36, # 29% larger than above"hidden_dim": 9728, # ~3x larger than above"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}elif CHOOSE_MODEL == "8B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 4096, # 60% larger than above"n_heads": 32,"n_layers": 36, # 26% larger than above"hidden_dim": 12288,"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}elif CHOOSE_MODEL == "14B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 5120, # 25% larger than above"n_heads": 40, # 25% larger than above"n_layers": 40, # 11% larger than above"hidden_dim": 17408, # 42% larger than above"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}elif CHOOSE_MODEL == "32B":QWEN3_CONFIG = {"vocab_size": 151_936,"context_length": 40_960,"emb_dim": 5120,"n_heads": 64, # 60% larger than above"n_layers": 64, # 60% larger than above"hidden_dim": 25600, # 47% larger than above"head_dim": 128,"qk_norm": True,"n_kv_groups": 8,"rope_base": 1_000_000.0,"dtype": torch.bfloat16,}else:raise ValueError(f"{CHOOSE_MODEL} is not supported.")return Qwen3Config(**QWEN3_CONFIG)def load_weights_into_qwen(model, param_config, params):def assign(left, right, tensor_name="unknown"):if left.shape != right.shape:raise ValueError(f"Shape mismatch in tensor '{tensor_name}'. Left: {left.shape}, Right: {right.shape}")return torch.nn.Parameter(right.clone().detach() if isinstance(right, torch.Tensor) else torch.tensor(right))model.tok_emb.weight = assign(model.tok_emb.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"],"model.embed_tokens.weight")for l in range(param_config.n_layers):block = model.trf_blocks[l]att = block.att# Q, K, V projectionsatt.W_query.weight = assign(att.W_query.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_proj.weight")att.W_key.weight = assign(att.W_key.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_proj.weight")att.W_value.weight = assign(att.W_value.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.v_proj.weight")# Output projectionatt.out_proj.weight = assign(att.out_proj.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.o_proj.weight")# QK normsif hasattr(att, "q_norm") and att.q_norm is not None:att.q_norm.scale = assign(att.q_norm.scale,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_norm.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.q_norm.weight")if hasattr(att, "k_norm") and att.k_norm is not None:att.k_norm.scale = assign(att.k_norm.scale,params[f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_norm.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.self_attn.k_norm.weight")# Attention layernormblock.norm1.scale = assign(block.norm1.scale,params[f"model.layers.{l}.input_layernorm.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.input_layernorm.weight")# Feedforward weightsblock.ff.fc1.weight = assign(block.ff.fc1.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.gate_proj.weight")block.ff.fc2.weight = assign(block.ff.fc2.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.up_proj.weight")block.ff.fc3.weight = assign(block.ff.fc3.weight,params[f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.mlp.down_proj.weight")block.norm2.scale = assign(block.norm2.scale,params[f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight"],f"model.layers.{l}.post_attention_layernorm.weight")# Final normalization and output headmodel.final_norm.scale = assign(model.final_norm.scale, params["model.norm.weight"], "model.norm.weight")if "lm_head.weight" in params:model.out_head.weight = assign(model.out_head.weight, params["lm_head.weight"], "lm_head.weight")else:# Model uses weight tying, hence we reuse the embedding layer weights hereprint("Model uses weight tying.")model.out_head.weight = assign(model.out_head.weight, params["model.embed_tokens.weight"],"model.embed_tokens.weight")class Qwen3Tokenizer:_SPECIALS = ["<|endoftext|>","<|im_start|>", "<|im_end|>","<|object_ref_start|>", "<|object_ref_end|>","<|box_start|>", "<|box_end|>","<|quad_start|>", "<|quad_end|>","<|vision_start|>", "<|vision_end|>","<|vision_pad|>", "<|image_pad|>", "<|video_pad|>",]_SPLIT_RE = re.compile(r"(<\|[^>]+?\|>)")def __init__(self, tokenizer_file_path="tokenizer.json", repo_id=None,apply_chat_template=True, add_generation_prompt=False, add_thinking=False):self.apply_chat_template = apply_chat_templateself.add_generation_prompt = add_generation_promptself.add_thinking = add_thinkingtok_file = Path(tokenizer_file_path)self._tok = Tokenizer.from_file(str(tok_file))self._special_to_id = {t: self._tok.token_to_id(t) for t in self._SPECIALS}self.pad_token_id = self._special_to_id.get("<|endoftext|>")self.eos_token_id = self.pad_token_idif repo_id and "Base" not in repo_id:eos_token = "<|im_end|>"else:eos_token = "<|endoftext|>"if eos_token in self._special_to_id:self.eos_token_id = self._special_to_id[eos_token]def encode(self, text, chat_wrapped=None):if chat_wrapped is None:chat_wrapped = self.apply_chat_templatestripped = text.strip()if stripped in self._special_to_id and "\n" not in stripped:return [self._special_to_id[stripped]]if chat_wrapped:text = self._wrap_chat(text)ids = []for part in filter(None, self._SPLIT_RE.split(text)):if part in self._special_to_id:ids.append(self._special_to_id[part])else:ids.extend(self._tok.encode(part).ids)return idsdef decode(self, ids):return self._tok.decode(ids, skip_special_tokens=False)def _wrap_chat(self, user_msg):s = f"<|im_start|>user\n{user_msg}<|im_end|>\n"if self.add_generation_prompt:s += "<|im_start|>assistant"if self.add_thinking:s += "\n"else:s += "\n<think>\n\n</think>\n\n"return sdef generate_text_basic_stream(model, token_ids, max_new_tokens, eos_token_id=None):model.eval()with torch.no_grad():for _ in range(max_new_tokens):out = model(token_ids)[:, -1]next_token = torch.argmax(out, dim=-1, keepdim=True)if (eos_token_id is not Noneand torch.all(next_token == eos_token_id)):breakyield next_tokentoken_ids = torch.cat([token_ids, next_token], dim=1)def model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.float32):total_params = 0total_grads = 0for param in model.parameters():# Calculate total number of elements per parameterparam_size = param.numel()total_params += param_size# Check if gradients are stored for this parameterif param.requires_grad:total_grads += param_size# Calculate buffer size (non-parameters that require memory)total_buffers = sum(buf.numel() for buf in model.buffers())# Size in bytes = (Number of elements) * (Size of each element in bytes)# We assume parameters and gradients are stored in the same type as input dtypeelement_size = torch.tensor(0, dtype=input_dtype).element_size()total_memory_bytes = (total_params + total_grads + total_buffers) * element_size# Convert bytes to gigabytestotal_memory_gb = total_memory_bytes / (1024 ** 3)return total_memory_gbif __name__ == "__main__":# loading modelUSE_REASONING_MODEL = Truechoose_model = "0.6B"qwen3_cfg = set_qwen3_config(choose_model)model = Qwen3Model(qwen3_cfg)print(f"model: \n{model}")model(torch.tensor([1, 2, 3]).unsqueeze(0))# calculate model sizetotal_params = sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters())print(f"Total number of parameters: {total_params:,}")# Account for weight tyingtotal_params_normalized = total_params - model.tok_emb.weight.numel()print(f"\nTotal number of unique parameters: {total_params_normalized:,}")print(f"float32 (PyTorch default): {model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.float32):.2f} GB")print(f"bfloat16: {model_memory_size(model, input_dtype=torch.bfloat16):.2f} GB")# set gpu device and load model to deviceif torch.cuda.is_available():device = torch.device("cuda")elif torch.backends.mps.is_available():device = torch.device("mps")else:device = torch.device("cpu")model.to(device)# download weightsif USE_REASONING_MODEL:repo_id = f"Qwen/Qwen3-{choose_model}"else:repo_id = f"Qwen/Qwen3-{choose_model}-Base"local_dir = Path(repo_id).parts[-1]if choose_model == "0.6B":weights_file = hf_hub_download(repo_id=repo_id,filename="model.safetensors",local_dir=local_dir,)tokenizer_file = hf_hub_download(repo_id=repo_id,filename="tokenizer.json",local_dir=local_dir,)weights_dict = load_file(weights_file)else:repo_dir = snapshot_download(repo_id=repo_id, local_dir=local_dir)index_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, "model.safetensors.index.json")with open(index_path, "r") as f:index = json.load(f)weights_dict = {}for filename in set(index["weight_map"].values()):shard_path = os.path.join(repo_dir, filename)shard = load_file(shard_path)weights_dict.update(shard)load_weights_into_qwen(model, qwen3_cfg, weights_dict)model.to(device)del weights_dict# download tokenizerif USE_REASONING_MODEL:tokenizer_file_path = f"Qwen3-{choose_model}/tokenizer.json"else:tokenizer_file_path = f"Qwen3-{choose_model}-Base/tokenizer.json"tokenizer = Qwen3Tokenizer(tokenizer_file_path=tokenizer_file_path,repo_id=repo_id,add_generation_prompt=USE_REASONING_MODEL,add_thinking=USE_REASONING_MODEL)# generate textprompt = "请给我简要的介绍下大模型."input_token_ids = tokenizer.encode(prompt)text = tokenizer.decode(input_token_ids)print(f'text: {text}')input_token_ids_tensor = torch.tensor(input_token_ids, device=device).unsqueeze(0)for token in generate_text_basic_stream(model=model,token_ids=input_token_ids_tensor,max_new_tokens=500,eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id):token_id = token.squeeze(0).tolist()print(tokenizer.decode(token_id),end="",flush=True) -
输出示例
model: Qwen3Model((tok_emb): Embedding(151936, 1024)(trf_blocks): ModuleList((0-27): 28 x TransformerBlock((att): GroupQueryAttention((W_query): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=2048, bias=False)(W_key): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)(W_value): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)(out_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=1024, bias=False)(q_norm): RMSNorm()(k_norm): RMSNorm())(ff): FeedForward((fc1): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=3072, bias=False)(fc2): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=3072, bias=False)(fc3): Linear(in_features=3072, out_features=1024, bias=False))(norm1): RMSNorm()(norm2): RMSNorm()))(final_norm): RMSNorm()(out_head): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=151936, bias=False) )Total number of parameters: 751,632,384Total number of unique parameters: 596,049,920float32 (PyTorch default): 5.64 GB bfloat16: 2.82 GBtext: <|im_start|>user 请给我简要的介绍下大模型.<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant<think> 好的,用户让我简要介绍大模型。首先,我需要确定用户的需求是什么。他们可能对大模型的基本概念、应用场景感兴趣,或者需要了解其特点和优势。用户可能没有太多背景 ,所以需要保持回答简洁明了。 接下来,我应该从几个关键点来组织信息:大模型的定义、核心特点、应用场景、优势和挑战。要确保每个部分都简短,避免冗长。同时,要使用用户容易理解的语言,避免专业术语过多。还要考虑用户可能的深层需求。他们可能想了解大模型的实际应用,或者是否需要进一步的细节。因此,在介绍时,可以提到一些实际例子,比如医疗、金融、教育等,这样用 户更容易理解。另外,要注意结构清晰,分点说明,这样用户一目了然。可能需要检查是否有遗漏的重要信息,比如数据来源、训练方法等,但保持简要。最后,确保回答友好,鼓励用户进一 步提问。 </think>大模型(Large Language Model,LLM)是一种基于深度学习的AI系统,能够理解和生成人类语言。它通过大量文本数据训练,具备理解、生成和推理能力,广泛应用于自然语 言处理(NLP)领域。核心特点包括但不限于:1. **语言理解**:理解上下文、语法和语义,支持多轮对话和复杂推理。 2. **生成能力**:生成文本、代码、摘要等,适用于写作、内容创作等场景。 3. **多模态处理**:支持文本、图像、音频等多种信息的交互。**优势**:高效处理复杂任务,提升效率;**挑战**:数据隐私、伦理问题、模型可解释性等仍需关注。
