Java 字符串常量池 +反射,枚举和lambda表达式
文章目录
- 字符串常量池
- 反射
- 反射实例
- 获取class对象的三种方式
- 反射的使用实例
- 枚举
- 使用在switch语句中
- 枚举函数的使用
- Lambda表达式
- 变量捕获
- lambda表达式在集合当中的使用
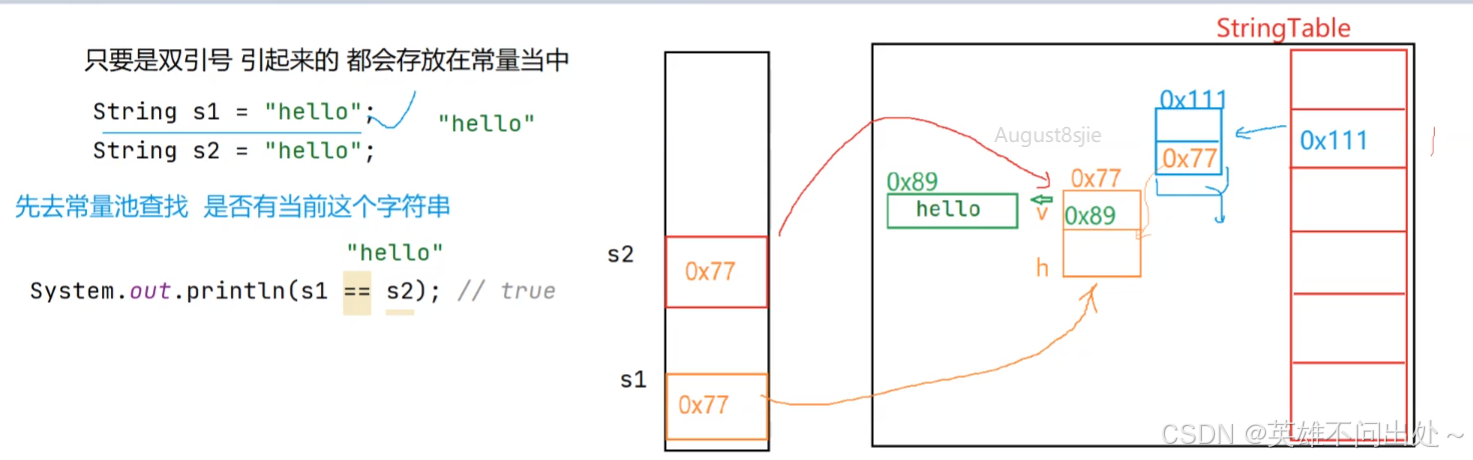
字符串常量池
- 用来存储是一个固定大小的HashTable
- 常量池在堆当中
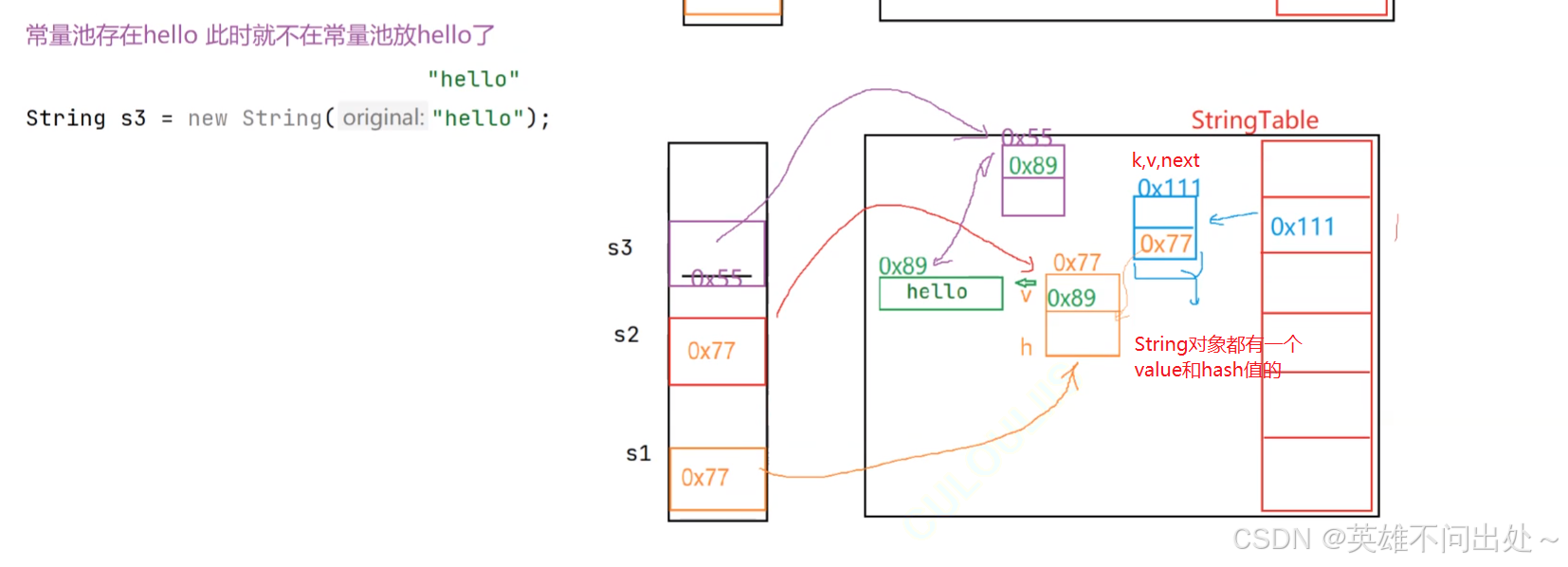
public static void main(String[] args) {String s1 = "hello";String s2 = "hello";String s3 = new String("hello");String s4 = new String("hello");System.out.println(s1 == s2);// trueSystem.out.println(s1 == s3);// falseSystem.out.println(s3 == s4);// false}
- 每次用双引号的时候都会去常量池中检查一遍是否存在字符串
- 如果常量池中有这个字符串,就不会生成直接引用,没有就会新建一个字符串
- 双引号引起的才会放入到常量池当中
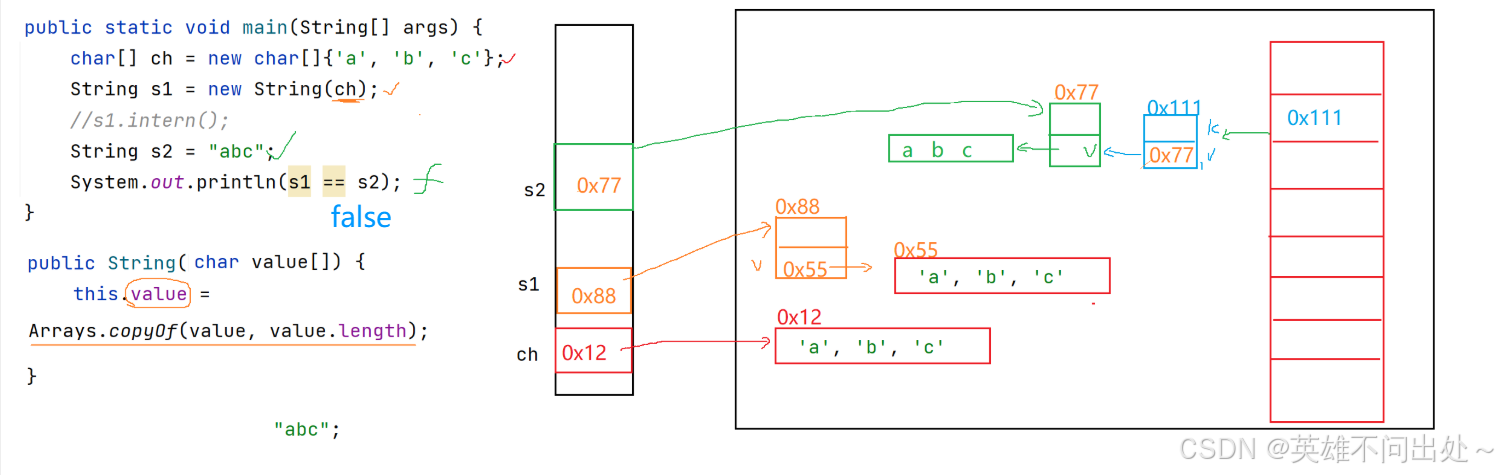
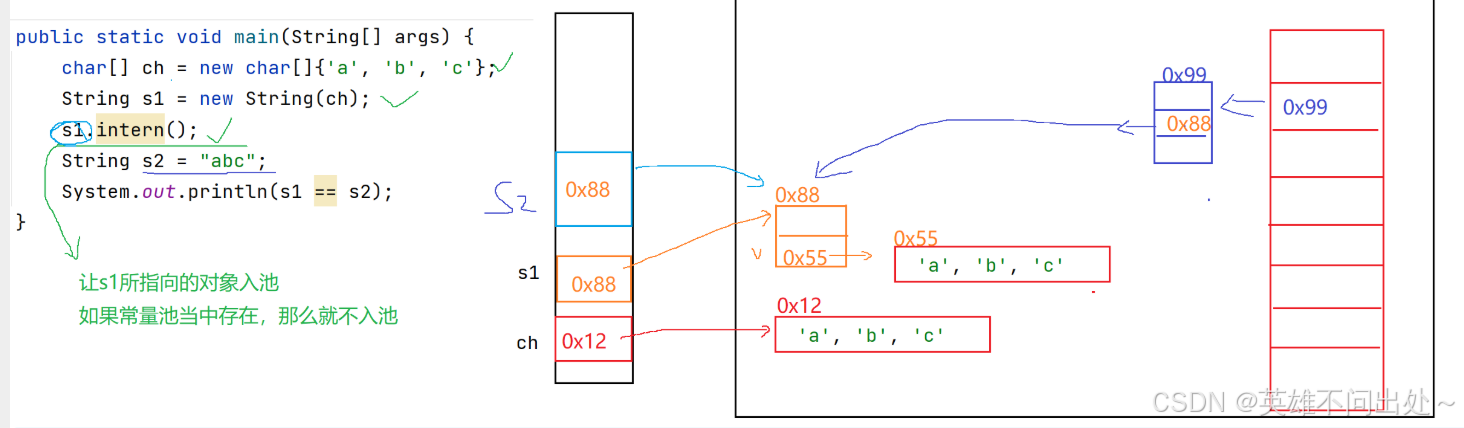
public static void main(String[] args) {char[] ch = new char[]{'a','b','c'};String s1 = new String(ch);// s1.intern();// 让s1所指的对象入池,如果在常量池中存在就不入池String s2 = "abc";System.out.println(s1 == s2);// false 有s1.intern()就是true}
反射
- 反射:在运行状态中,对于任何一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法
反射实例
获取class对象的三种方式
- 使用 Class.forName(“类的全路径名”); 静态方法。
前提:已明确类的全路径名。 - 使用 .class 方法。
说明:仅适合在编译前就已经明确要操作的 Class - 第三种,使用类对象的 getClass() 方法
public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> c1 = null;try {c1 = Class.forName("Demo1.Student");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}Class<?> c2 = Student.class;Student student = new Student();Class<?> c3 = student.getClass();// Class 对象只有一个System.out.println(c1 == c2);// trueSystem.out.println(c2 == c3);// true}
反射的使用实例
package Demo1;import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class ReflectClassDemo {// 在类外进行反射,获取Student对象中的私有成员和方法public static void reflectNewInstance(){// 创建一个Class对象Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("Demo1.Student");// 得到Class类的实例// 获取类的实例擦成了Object类,向下转型Student student = (Student)classStudent.newInstance();System.out.println(student);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}// 反射私有的构造方法public static void reflectPrivateConstructor(){Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("Demo1.Student");// 获取构造方法Constructor<?> constructor = classStudent.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);// 如果是私有的构造方法确定要修改,要设置为trueconstructor.setAccessible(true);// 利用构造方法构造对象Student student = (Student)constructor.newInstance("xiaoming",15);System.out.println(student);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}// 获取私有字段public static void reflectPrivateField(){Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("Demo1.Student");// 获取字段Field filed = classStudent.getDeclaredField("name");filed.setAccessible(true);// 获取对象Student student = (Student)classStudent.newInstance();// 修改该对象的字段filed.set(student,"caocao");System.out.println(student);} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}// 获取私有的方法public static void reflectPrivateMethod(){Class<?> classStudent = null;try {classStudent = Class.forName("Demo1.Student");// 获取私有的方法对象Method method = classStudent.getDeclaredMethod("function",String.class);// 设置为true可以调用私有方法method.setAccessible(true);// 获取student对象Student student = (Student) classStudent.newInstance();// 调用私有的方法method.invoke(student,"我是一个反射的参数");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InstantiationException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}public static void main(String[] args) {// reflectNewInstance();// reflectPrivateConstructor();// reflectPrivateField();reflectPrivateMethod();}
}
枚举
使用在switch语句中
public enum TestEnum {RED,GREEN,BLACK;
// 使用在switch语句public static void main1(String[] args) {TestEnum color = RED;switch (color){case GREEN:System.out.println("GREEN");break;case RED:System.out.println("RED");break;case BLACK:System.out.println("BLACK");break;default:System.out.println("error");break;}}
}
枚举函数的使用
- values() 方法是编译器生成的
- values() 方法是枚举类型的隐式方法
在 Java 中,所有枚举类型(enum)都会自动生成一个 values() 静态方法,它返回该枚举的所有实例(常量)组成的数组。
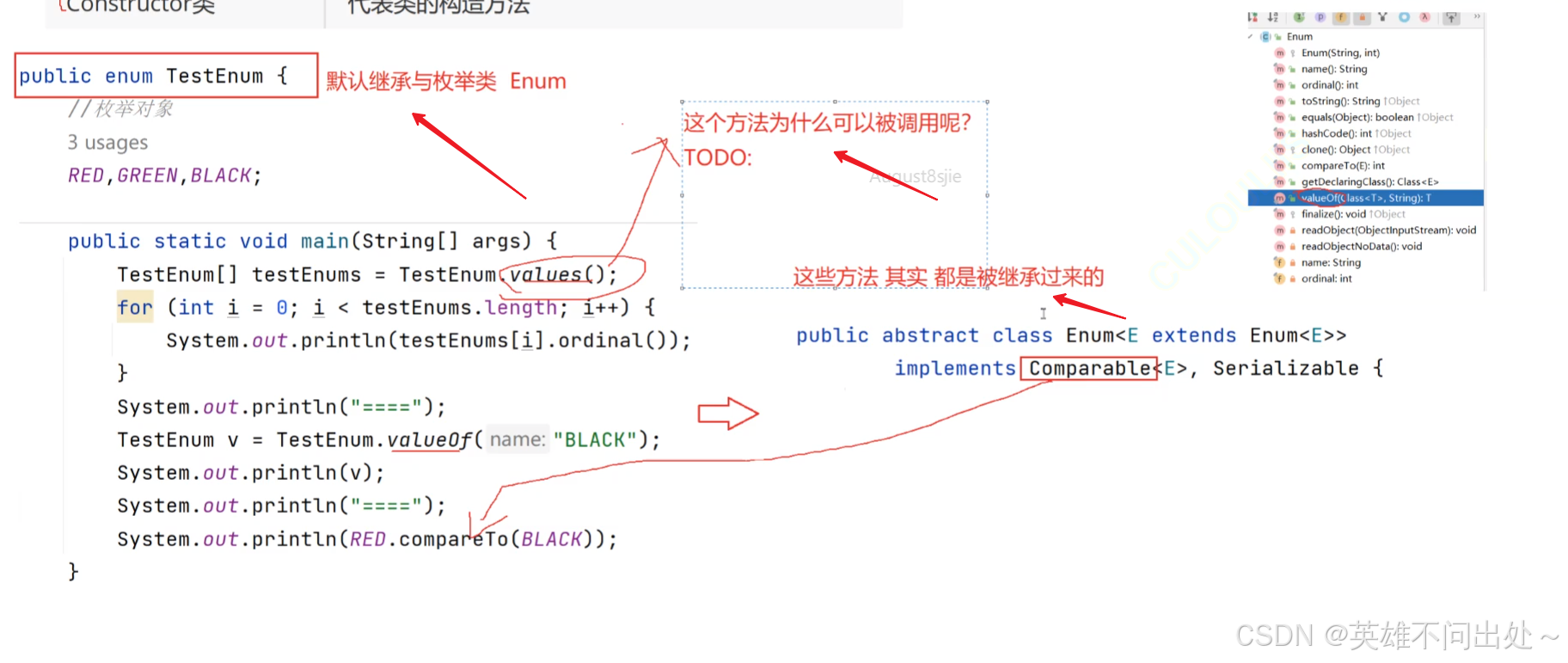
public enum TestEnum {RED,GREEN,BLACK;public static void main(String[] args) {// 以数组形式返回枚举类型的所有成员TestEnum[] testEnums = TestEnum.values();for(int i = 0;i < testEnums.length;i++){// 获取枚举成员的索引位置System.out.println(testEnums[i].ordinal());}System.out.println("===");// 将普通字符串转化为枚举实例TestEnum v = TestEnum.valueOf("BLACK");System.out.println(v);System.out.println("===");// 比较他们在定义时的顺序System.out.println(RED.compareTo(BLACK));// -2}
}
- 枚举的构造方法默认是私有的
public enum TestEnum {RED(1,"红色"),GREEN(2,"绿色"),BLACK(3,"蓝色");public int ordinal;public String color;private TestEnum(int ordinal,String color){this.ordinal = ordinal;this.color = color;}
}
- 枚举不能被继承,因为它的构造方法是私有的,要被继承需要重写父类的构造方法

5. 枚举对象非常安全,就算通过反射也不能创建一个枚举对象的
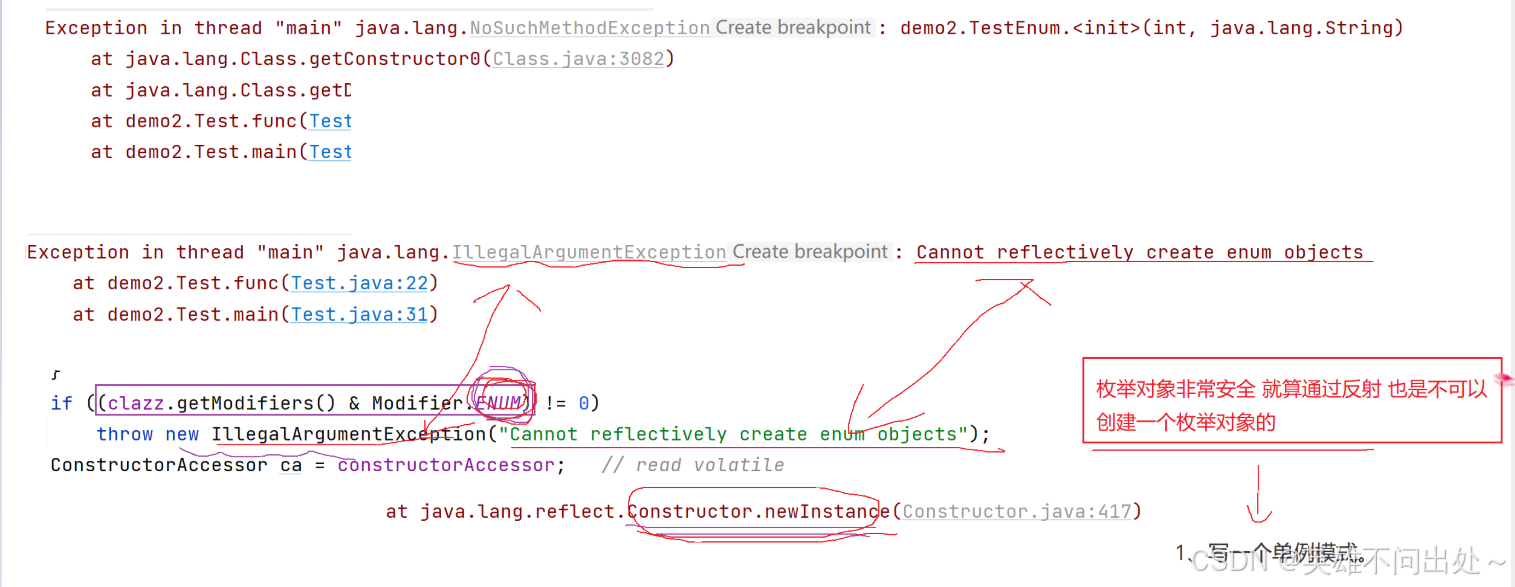
6. 枚举不能通过反射直接实例化,不能通过反射调用枚举的构造方法
枚举的构造方法默认是 private,即使你不写 private,编译器也会自动加上。
枚举的实例必须在枚举内部显式定义
package Demo2;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;public class ReflectClassTestEnum {public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException,InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException,InvocationTargetException {// 获取Class类Class<?> classTestEnum = Class.forName("Demo2.TestEnum");// 获取枚举类的对象Constructor<?> constructor = classTestEnum.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int.class, String.class);constructor.setAccessible(true);TestEnum testEnum = (TestEnum) constructor.newInstance("黑色",2,1,"白色");System.out.println(testEnum);}
}
Lambda表达式
- 函数式接口:一个接口只有一个抽象方法
实例
package Demo3;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;//无返回值无参数
// @FunctionalInterface表明着是一个函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
interface NoparameterNoReturn{// 只能有一个抽象方法void test();
}//无返回值一个参数
@FunctionalInterface
interface OneParameterNoReturn {
void test(int a);
}//无返回值多个参数
@FunctionalInterface
interface MoreParameterNoReturn {
void test(int a,int b);
}//有返回值无参数
@FunctionalInterface
interface NoParameterReturn {
int test();
}//有返回值一个参数
@FunctionalInterface
interface OneParameterReturn {
int test(int a);
}//有返回值多参数
@FunctionalInterface
interface MoreParameterReturn {
int test(int a,int b);
}public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {// 有返回值// 无参数// NoParameterReturn noParameterReturn = ()->{return 10;};NoParameterReturn noParameterReturn = ()->10;System.out.println(noParameterReturn.test());// 一个参数// OneParameterReturn oneParameterReturn = (a)->{return a;};OneParameterReturn oneParameterReturn = a-> 20;System.out.println(oneParameterReturn.test(10));// 两个参数MoreParameterReturn moreParameterReturn = (int a,int b)->{return a + b;};System.out.println(moreParameterReturn.test(10,20));}public static void main2(String[] args) {// lambda表达式 无参数// 无返回值NoparameterNoReturn noparameterNoReturn = ()-> System.out.println("重写了test1()方法");noparameterNoReturn.test();// 1个参数OneParameterNoReturn oneParameterNoReturn = (a)->{System.out.println("oneParameterNoReturn " + a);};oneParameterNoReturn.test(10);/*OneParameterNoReturn oneParameterNoReturn = a->System.out.println("oneParameterNoReturn " + a);*/// 可以省略类型MoreParameterNoReturn moreParameterNoReturn = (int a,int b)->{System.out.println(a+b);};moreParameterNoReturn.test(1,2);}public static void main1(String[] args) {// 匿名内部类NoparameterNoReturn noparameterNoReturn = new NoparameterNoReturn() {@Overridepublic void test() {System.out.println("重写了test1()方法");}};noparameterNoReturn.test();PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return 0;}});PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue1 = new PriorityQueue<>((o1,o2)->{return o1 - o2;});}
}
变量捕获
- 变量捕获:要么是常量,要么是没有被修改过的变量
匿名内部类

lambda表达式
lambda表达式在集合当中的使用
- 打印,ArrayList的forEach方法
public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add("hello");list.add("world");list.add("queue");list.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(String s) {System.out.println(s);}});list.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));}
- sort方法
/*list.sort(new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {return o1.compareTo(o2);}});*/list.sort((o1,o2)->o1.compareTo(o2));list.forEach(s-> System.out.println(s));
- map方法
public static void main(String[] args) {HashMap<Integer,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();hashMap.put(1,"a");hashMap.put(2,"b");hashMap.put(3,"c");/*hashMap.forEach(new BiConsumer<Integer, String>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Integer integer, String s) {System.out.println("Integer:"+ integer + " String:" + s);}});*/hashMap.forEach((a,b)-> System.out.println("Integer:"+ a + " String:" + b));}
- lambda表达式可读性比较差,不可调试,但是比较简洁
