【日常问题解决方案】VS2022不小心解决方案资源管理器把关掉了怎么办

🔥个人主页:艾莉丝努力练剑
❄专栏传送门:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、C语言刷题12天IO强训、LeetCode代码强化刷题、C/C++干货分享&学习过程记录
🍉学习方向:C/C++方向
⭐️人生格言:为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平
目录
正文
一、翻车现场还原
二、解决方案
结尾
正文
我们在使用VS2022的时候一不小心把解决方案资源管理器关掉了或者解决方案资源管理器不见了,怎么办呢?我们可以按下面的步骤来找回【解决方案资源管理器】。
博主一般习惯把它拉到右边,这样看起来比较顺眼,也可以拉到最左边,看个人习惯。
一、翻车现场还原
铸币主包有好几次一不小心把【解决方案资源管理器】给叉掉了,就像下面这样——
找不到了!没关系!我们按下面的步骤来就能找回来了。
二、解决方案
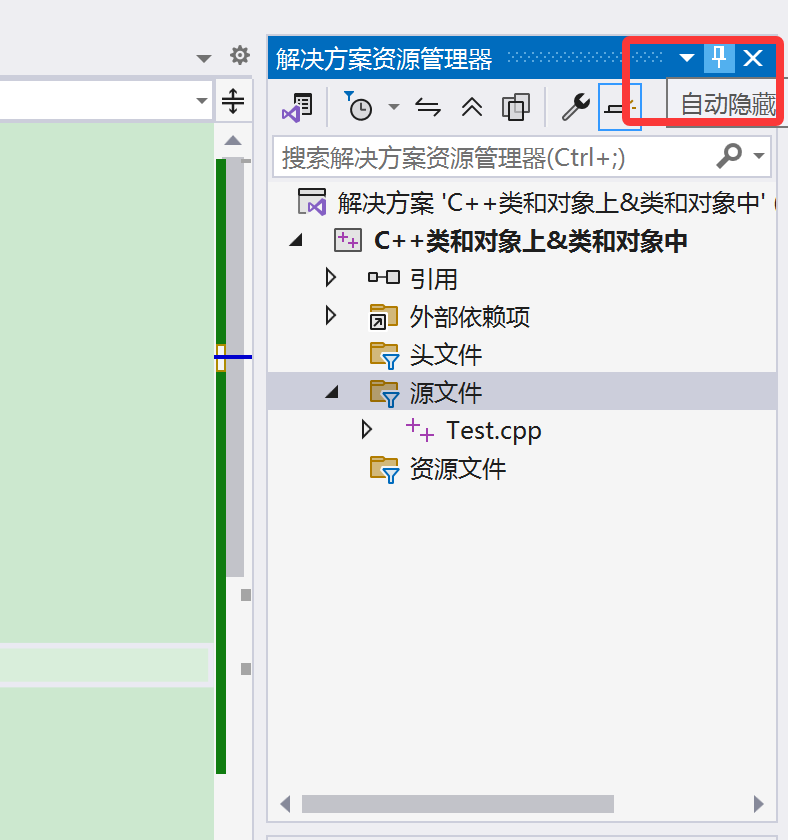
我们点击【视图】——
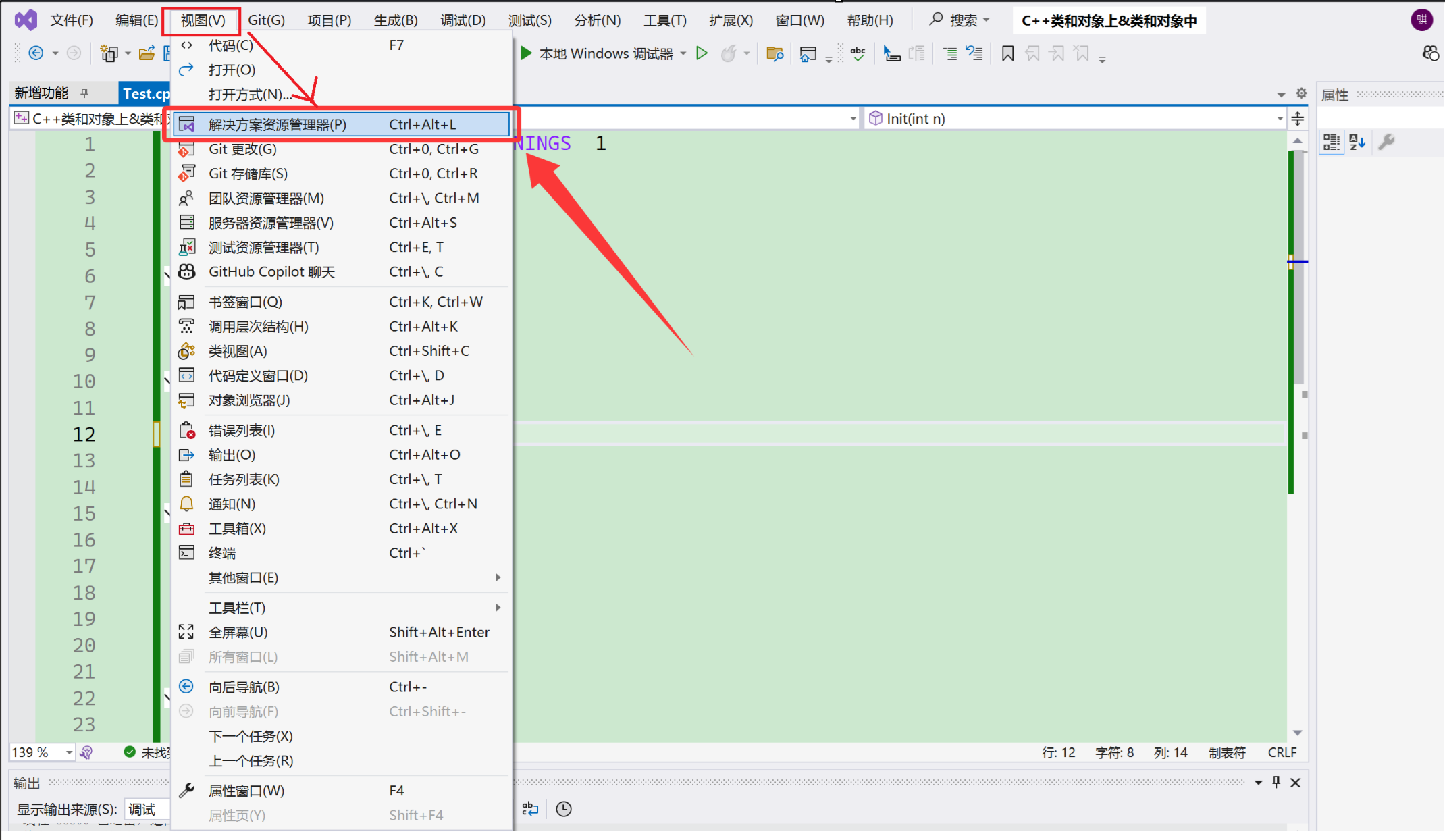
找到【解决方案资源管理器(P)】,这里我们看到有快捷键:Ctrl + Alt + L。
这样我们就找回解决方案资源管理器了。
我们也可以把【解决方案资源管理器】隐藏起来——
结尾
结语:本文内容到这里就结束了,希望对大家有所帮助!
下面的代码是只是为了凑凑字数,大家直接忽略就好啦。
对比排序性能:测试代码的代码实现:
//测试排序的性能对比
void TestOP()
{srand(time(0));const int N = 100000;int* a1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a2 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a3 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a4 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a5 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a6 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);int* a7 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * N);for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i){a1[i] = rand();a2[i] = a1[i];a3[i] = a1[i];a4[i] = a1[i];a5[i] = a1[i];a6[i] = a1[i];a7[i] = a1[i];}//begin和end的时间差就是int begin1 = clock();InsertSort(a1, N);int end1 = clock();int begin2 = clock();ShellSort(a2, N);int end2 = clock();int begin3 = clock();SelectSort(a3, N);int end3 = clock();int begin4 = clock();HeapSort(a4, N);int end4 = clock();int begin5 = clock();QuickSort(a5, 0, N - 1);int end5 = clock();int begin6 = clock();MergeSort(a6, N);int end6 = clock();int begin7 = clock();BubbleSort(a7, N);int end7 = clock();printf("InsertSort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);printf("ShellSort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);printf("SelectSort:%d\n", end3 - begin3);printf("HeapSort:%d\n", end4 - begin4);printf("QuickSort:%d\n", end5 - begin5);printf("MergeSort:%d\n", end6 - begin6);printf("BubbleSort:%d\n", end7 - begin7);free(a1);free(a2);free(a3);free(a4);free(a5);free(a6);free(a7);
}非比较排序——计数排序的代码实现:
//非比较排序——计数排序
void CountSort(int* arr, int n)
{//找min maxint min = arr[0], max = arr[0];for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){if (arr[i] < min){min = arr[i];}if (arr[i] > max){max = arr[i];}}//确定count数组的大小 max-min+1int range = max - min + 1;int* count = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (range));if (count == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(1);}//对count初始化:calloc memsetmemset(count, 0, sizeof(int) * (range));for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){count[arr[i] - min]++;}//将count数组中的数据还原到原数组中int index = 0;for (int i = 0; i < range; i++){while (count[i]--){arr[index++] = i + min;}}
}动态顺序表代码实现:
SeqList.h:
#pragma once#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>//定义动态顺序表的结构
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{SLTDataType* arr; //存储数据int size; //有效数据个数int capacity; //空间大小
}SL;//typedef struct SeqList SL;void SLPrint(SL* ps);
void SLInit(SL* ps);
void SLDestroy(SL* ps);//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLTDataType x);//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLTDataType x);//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLTDataType x);//指定位置之前插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x);//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertAfter(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x);//删除pos(指定)位置的数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos);//修改
void SLModity(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x);SeqList.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"SeqList.h"void SLInit(SL* ps)
{ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{if (ps->arr)free(ps->arr);ps->arr = NULL;ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{if (ps->size == ps->capacity){int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;//增容SLTDataType* tmp = (SLTDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(SLTDataType));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}ps->arr = tmp;ps->capacity = newCapacity;}
}//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLTDataType x)
{assert(ps);//空间不够SLCheckCapacity(ps);//空间足够ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;
}//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLTDataType x)
{//温柔的处理方式//if (ps == NULL)//{// return;//}assert(ps != NULL); //等价于assert(ps)//空间不够SLCheckCapacity(ps);//数据整体向后挪动一位for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];}ps->arr[0] = x;ps->size++;
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{assert(ps && ps->size);ps->size--;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{assert(ps && ps->size);//数据整体向前挪动一位for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--;
}//查找
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLTDataType x)
{assert(ps);for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++){if (ps->arr[i] == x){//找到了return i;}}//未找到return -1;
}
//指定位置之前插入
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(ps);//0<= pos < ps->sizeassert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);//判断空间是否足够SLCheckCapacity(ps);//pos及之后数据向后挪动一位for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];}ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertAfter(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(ps);//0<= pos < ps->sizeassert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);//判断空间是否足够SLCheckCapacity(ps);ps->arr[pos] = x;ps->size++;
}//删除pos位置的数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{assert(ps);//pos:[0,ps->size)assert(pos >= 0 && pos < ps->size);//pos后面的数据向前挪动一位for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++){ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];}ps->size--;
}//修改
void SLModity(SL* ps, int pos, SLTDataType x)
{assert(pos < ps->size);ps->arr[pos] = x;
}test.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"SeqList.h"void test01()
{SL sl;SLInit(&sl);//具备了一个空的顺序表SLPushBack(&sl, 1);SLPushBack(&sl, 2);SLPushBack(&sl, 3);SLPushBack(&sl, 4);SLPrint(&sl);//SLPushFront(&sl, 1);//SLPushFront(&sl, 2);//2 1//SLPushFront(&sl, 3);//3 2 1//SLPushFront(&sl, 4);//4 3 2 1//SLPopBack(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//1 2 3//SLPopBack(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//1 2 //SLPopBack(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//1 //SLPopBack(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);////SLPopBack(&sl);////头删//SLPopFront(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLPopFront(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLPopFront(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLPopFront(&sl);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLPopFront(&sl);//测试查找int pos = SLFind(&sl, 3);//if (pos < 0)//{// printf("未找到!\n");//}//else // {// printf("找到了!\n");//}//SLInsert(&sl, pos, 100);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLInsert(&sl, pos, 200);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLInsert(&sl, pos, 300);//SLPrint(&sl);//SLInsert(&sl, pos, 400);//SLPrint(&sl);SLErase(&sl, pos);SLPrint(&sl);SLDestroy(&sl);
}int main()
{test01();return 0;
}