【拓扑排序 最短路】P2149 [SDOI2009] Elaxia的路线|省选-
本文涉及知识点
C++图论 拓扑序 最短路
P2149 [SDOI2009] Elaxia的路线
题目描述
最近,Elaxia 和 w** 的关系特别好,他们很想整天在一起,但是大学的学习太紧张了,他们必须合理地安排两个人在一起的时间。
Elaxia 和 w** 每天都要奔波于宿舍和实验室之间,他们 希望在节约时间的前提下,一起走的时间尽可能的长。
现在已知的是 Elaxia 和 w** 所在的宿舍和实验室的编号以及学校的地图:
地图上有 nnn 个路口,mmm 条路,经过每条路都需要一定的时间。 具体地说,就是要求无向图中,两对点间最短路的最长公共路径。
输入格式
第一行两个正整数 n,mn,mn,m,表示点数和边数。
第二行四个正整数 x1,y1,x2,y2x_1,y_1,x_2,y_2x1,y1,x2,y2,分别表示 Elaxia 的宿舍和实验室及 w** 的宿舍和实验室的标号。
接下来 mmm 行,每行三个整数 u,v,wu,v,wu,v,w,表示 u,vu,vu,v之间有一条边,需要 www 的时间经过。
输出格式
一行一个整数表示答案。(即最长公共路径的长度)
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
9 10
1 6 7 8
1 2 1
2 5 2
2 3 3
3 4 2
3 9 5
4 5 3
4 6 4
4 7 2
5 8 1
7 9 1
输出 #1
3
说明/提示
【数据范围】
对于 30%30\%30% 的数据,1≤n≤1001\le n \le 1001≤n≤100;
对于 60%60\%60% 的数据,1≤n≤10001\le n \le 10001≤n≤1000;
对于 100%100\%100% 的数据,1≤n≤15001\le n \le 15001≤n≤1500,1≤m≤3×1051 \leq m \leq 3 \times 10^51≤m≤3×105,1≤w≤1041\le w \le 10^41≤w≤104,输入数据保证没有重边和自环。
最短路 拓扑排序
令x1到y1的最短距离是X。如果u→vu \rightarrow vu→v在x1→x2x1 \rightarrow x2x1→x2的任意最短路上(条件一),则有向图G1增加边u→vu \rightarrow vu→v。
条件一 ⟺\iff⟺ x1到u最大距离+w+x2到v的最短距离==Xx1到u最大距离+w+x2到v的最短距离==Xx1到u最大距离+w+x2到v的最短距离==X。
枚举所有边的,判断u→v和v→uu \rightarrow v和v \rightarrow uu→v和v→u是否在G1上。
同理,x2到y2的最短路的任意边形成G2。
G1和G2的共同边形成G3。
性质一:G1 任意两点u、v,任意u到v的路径边权和相等。
任意u到v的路径中间的点,出度为1,由于没有分叉。任意最短路都是经过整个路径,x1→u,r→v,v→y1x1 \rightarrow u,r \rightarrow v,v \rightarrow y1x1→u,r→v,v→y1,都选取最短的才是最短路。
由于边权相等,故只保留一条uv路径,其它删除。持续迭代。
性质二:G1不会存在环。性质一迭代结束时,除x2外,出度都为1。x2出度为0,故不会再环上。出度1的图,环上的点无法离开环。
性质三:G3任意u、v,如果u和x1,x2都连通,v和y1,y2都连通,则u→vu \rightarrow vu→v一定是最短路的公共部分。
实现
由于n×n<M×logMn \times n < M \times logMn×n<M×logM,故用朴素迪氏最短路,求x1,x2,y1,y2x1,x2,y1,y2x1,x2,y1,y2到各点距离。
通过u、v枚举各边,看u→vu \rightarrow vu→v和v→uv \rightarrow uv→u是否在G3上。
在G3上求x1,y1,x2,y2x1,y1,x2,y2x1,y1,x2,y2到各点距离。
按拓扑序处理各点cur,通过child枚举cur的孩子。如果child不能到达y1或y2忽略。 否则 MaxSelf(dp[cur],dp[child]+w)
dp的最大值便是答案。
下图是借用洛谷的:
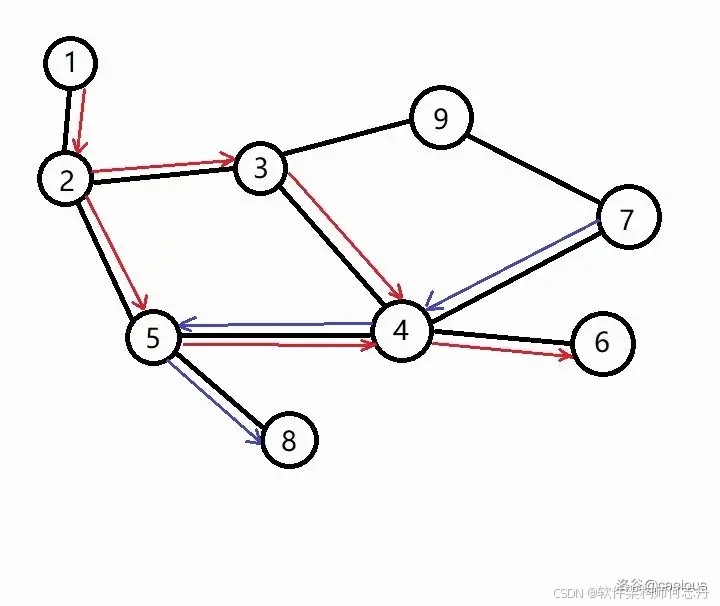
代码
核心代码
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<queue>
#include <stack>
#include<iomanip>
#include<numeric>
#include <math.h>
#include <climits>
#include<assert.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<list>#include <bitset>
using namespace std;template<class T1, class T2>
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, pair<T1, T2>& pr) {in >> pr.first >> pr.second;return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4,class T5 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4,T5>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t) >> get<4>(t);return in;
}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4, class T5,class T6 >
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4, T5,T6>& t) {in >> get<0>(t) >> get<1>(t) >> get<2>(t) >> get<3>(t) >> get<4>(t) >>get<5>(t);return in;
}template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read() {int n;cin >> n;vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> ret[i];}return ret;
}
template<class T = int>
vector<T> ReadNotNum() {vector<T> ret;T tmp;while (cin >> tmp) {ret.emplace_back(tmp);if ('\n' == cin.get()) { break; }}return ret;
}template<class T = int>
vector<T> Read(int n) {vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {cin >> ret[i];}return ret;
}template<int N = 1'000'000>
class COutBuff
{
public:COutBuff() {m_p = puffer;}template<class T>void write(T x) {int num[28], sp = 0;if (x < 0)*m_p++ = '-', x = -x;if (!x)*m_p++ = 48;while (x)num[++sp] = x % 10, x /= 10;while (sp)*m_p++ = num[sp--] + 48;AuotToFile();}void writestr(const char* sz) {strcpy(m_p, sz);m_p += strlen(sz);AuotToFile();}inline void write(char ch){*m_p++ = ch;AuotToFile();}inline void ToFile() {fwrite(puffer, 1, m_p - puffer, stdout);m_p = puffer;}~COutBuff() {ToFile();}
private:inline void AuotToFile() {if (m_p - puffer > N - 100) {ToFile();}}char puffer[N], * m_p;
};template<int N = 1'000'000>
class CInBuff
{
public:inline CInBuff() {}inline CInBuff<N>& operator>>(char& ch) {FileToBuf();ch = *S++;return *this;}inline CInBuff<N>& operator>>(int& val) {FileToBuf();int x(0), f(0);while (!isdigit(*S))f |= (*S++ == '-');while (isdigit(*S))x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (*S++ ^ 48);val = f ? -x : x; S++;//忽略空格换行 return *this;}inline CInBuff& operator>>(long long& val) {FileToBuf();long long x(0); int f(0);while (!isdigit(*S))f |= (*S++ == '-');while (isdigit(*S))x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (*S++ ^ 48);val = f ? -x : x; S++;//忽略空格换行return *this;}template<class T1, class T2>inline CInBuff& operator>>(pair<T1, T2>& val) {*this >> val.first >> val.second;return *this;}template<class T1, class T2, class T3>inline CInBuff& operator>>(tuple<T1, T2, T3>& val) {*this >> get<0>(val) >> get<1>(val) >> get<2>(val);return *this;}template<class T1, class T2, class T3, class T4>inline CInBuff& operator>>(tuple<T1, T2, T3, T4>& val) {*this >> get<0>(val) >> get<1>(val) >> get<2>(val) >> get<3>(val);return *this;}template<class T = int>inline CInBuff& operator>>(vector<T>& val) {int n;*this >> n;val.resize(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {*this >> val[i];}return *this;}template<class T = int>vector<T> Read(int n) {vector<T> ret(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {*this >> ret[i];}return ret;}template<class T = int>vector<T> Read() {vector<T> ret;*this >> ret;return ret;}
private:inline void FileToBuf() {const int canRead = m_iWritePos - (S - buffer);if (canRead >= 100) { return; }if (m_bFinish) { return; }for (int i = 0; i < canRead; i++){buffer[i] = S[i];//memcpy出错 }m_iWritePos = canRead;buffer[m_iWritePos] = 0;S = buffer;int readCnt = fread(buffer + m_iWritePos, 1, N - m_iWritePos, stdin);if (readCnt <= 0) { m_bFinish = true; return; }m_iWritePos += readCnt;buffer[m_iWritePos] = 0;S = buffer;}int m_iWritePos = 0; bool m_bFinish = false;char buffer[N + 10], * S = buffer;
};class CDGTopSort
{
public:template <class T = vector<int> >CDGTopSort(const vector<T>& vNeiBo) :m_vDeg(vNeiBo.size()), m_neiBo(vNeiBo) {const int N = vNeiBo.size();m_backNeiBo.resize(N);for (int cur = 0; cur < N; cur++){m_vDeg[cur] = vNeiBo[cur].size();for (const auto& next : vNeiBo[cur]){m_backNeiBo[next].emplace_back(cur);}}}void Init() {auto Add = [&](int i) {if (0 != m_vDeg[i]) { return; }m_que.emplace(i);};for (int i = 0; i < m_vDeg.size(); i++){Add(i);}while (m_que.size()){const int cur = m_que.front(); m_que.pop();if (!OnDo(cur)) { continue; }for (const auto& next : m_backNeiBo[cur]){m_vDeg[next]--;Add(next);}};}queue<int> m_que;vector<int> m_vDeg;vector<int> m_vSort;
protected:const vector<vector<int>>& m_neiBo;vector<vector<int>> m_backNeiBo;virtual bool OnDo(int cur) {m_vSort.emplace_back(cur);return true;};
};class CN2Dis
{
public:CN2Dis(int iSize) :m_iSize(iSize), DIS(m_vDis), PRE(m_vPre){}void Cal(int start, const vector<vector<pair<int, int>>>& vNeiB){m_vDis.assign(m_iSize, -1);m_vPre.assign(m_iSize, -1);vector<bool> vDo(m_iSize);//点是否已处理auto AddNode = [&](int iNode){//const int iPreNode = m_vPre[iNode];long long llPreDis = m_vDis[iNode];vDo[iNode] = true;for (const auto& it : vNeiB[iNode]){if (vDo[it.first]){continue;}if ((-1 == m_vDis[it.first]) || (it.second + llPreDis < m_vDis[it.first])){m_vDis[it.first] = it.second + llPreDis;m_vPre[it.first] = iNode;}}long long llMinDis = LLONG_MAX;int iMinIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < m_vDis.size(); i++){if (vDo[i]){continue;}if (-1 == m_vDis[i]){continue;}if (m_vDis[i] < llMinDis){iMinIndex = i;llMinDis = m_vDis[i];}}return (LLONG_MAX == llMinDis) ? -1 : iMinIndex;};int next = start;m_vDis[start] = 0;while (-1 != (next = AddNode(next)));}void Cal(int start, const vector<vector<int>>& mat){m_vDis.assign(m_iSize, LLONG_MAX);m_vPre.assign(m_iSize, -1);vector<bool> vDo(m_iSize);//点是否已处理auto AddNode = [&](int iNode){long long llPreDis = m_vDis[iNode];vDo[iNode] = true;for (int i = 0; i < m_iSize; i++){if (vDo[i]){continue;}const long long llCurDis = mat[iNode][i];if (llCurDis <= 0){continue;}m_vDis[i] = min(m_vDis[i], m_vDis[iNode] + llCurDis);}long long llMinDis = LLONG_MAX;int iMinIndex = -1;for (int i = 0; i < m_iSize; i++){if (vDo[i]){continue;}if (m_vDis[i] < llMinDis){iMinIndex = i;llMinDis = m_vDis[i];}}if (LLONG_MAX == llMinDis){return -1;}m_vPre[iMinIndex] = iNode;return iMinIndex;};int next = start;m_vDis[start] = 0;while (-1 != (next = AddNode(next)));}const vector<long long>& DIS;const vector<int>& PRE;
private:const int m_iSize;vector<long long> m_vDis;//各点到起点的最短距离vector<int> m_vPre;//最短路径的前一点
};
class CNeiBo
{
public:static vector<vector<int>> Two(int n, const vector<pair<int, int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<int>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& [i1, i2] : edges){vNeiBo[i1 - iBase].emplace_back(i2 - iBase);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[i2 - iBase].emplace_back(i1 - iBase);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<int>> Two(int n, const vector<vector<int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<int>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& v : edges){vNeiBo[v[0] - iBase].emplace_back(v[1] - iBase);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v[1] - iBase].emplace_back(v[0] - iBase);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> Three(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& v : edges){vNeiBo[v[0] - iBase].emplace_back(v[1] - iBase, v[2]);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v[1] - iBase].emplace_back(v[0] - iBase, v[2]);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> Three(int n, const vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edges, bool bDirect, int iBase = 0){vector<vector<std::pair<int, int>>> vNeiBo(n);for (const auto& [u, v, w] : edges){vNeiBo[u - iBase].emplace_back(v - iBase, w);if (!bDirect){vNeiBo[v - iBase].emplace_back(u - iBase, w);}}return vNeiBo;}static vector<vector<int>> Mat(vector<vector<int>>& neiBoMat){vector<vector<int>> neiBo(neiBoMat.size());for (int i = 0; i < neiBoMat.size(); i++){for (int j = i + 1; j < neiBoMat.size(); j++){if (neiBoMat[i][j]){neiBo[i].emplace_back(j);neiBo[j].emplace_back(i);}}}return neiBo;}
};
class Solution {
public:int Ans(const int N, int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edge) {x1--, x2--, x3--, x4--;for (auto& [u, v, w] : edge) { u--, v--; };const int ans1 = Ans1(N, x1, x2, x3, x4, edge);//同向边const int ans2 = Ans1(N, x1, x2, x4, x3, edge);//反向边return max(ans1, ans2);}int Ans1(const int N, int x1, int x2, int x3, int x4, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edge) {auto neiBo = G3(N, x1, x2, x3, x4, edge);vector<vector<int>> neiBoT(N);for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {for (const auto& [v, w] : neiBo[i]) {neiBoT[i].emplace_back(v);}}CDGTopSort topSort(neiBoT);topSort.Init();vector<int> ans(N);for (const auto& cur : topSort.m_vSort) {for (const auto& [child, w] : neiBo[cur]) {ans[cur] = max(ans[cur], ans[child] + w);}}return *max_element(ans.begin(), ans.end());}vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> G3(const int N, const int x1, const int x2, const int x3, const int x4, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>& edge) {auto neiBo = CNeiBo::Three(N, edge, false);CN2Dis dis1(N), dis2(N), dis3(N), dis4(N);dis1.Cal(x1, neiBo);dis2.Cal(x2, neiBo);dis3.Cal(x3, neiBo);dis4.Cal(x4, neiBo);const int D1 = dis1.DIS[x2];const int D3 = dis3.DIS[x4];vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> ret(N);auto Add = [&](int u, int v, int w) {if (dis1.DIS[u] + w + dis2.DIS[v] > D1) { return; }if (dis3.DIS[u] + w + dis4.DIS[v] > D3) { return; }ret[u].emplace_back(v, w);};for (auto& [u, v, w] : edge){Add(u, v, w);Add(v, u, w);}return ret;}
};int main() {
#ifdef _DEBUGfreopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
#endif // DEBUGios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(nullptr); cout.tie(nullptr); int N, M,x1,x2,x3,x4;cin >> N >> M >> x1 >> x2 >> x3 >> x4;auto edge = Read<tuple<int, int, int>>(M);
#ifdef _DEBUGprintf("N=%d,x1=%d,x2=%d,x3=%d,x4=%d",N,x1,x2,x3,x4);Out(edge, ",edge=");//Out(que, ",que=");
#endif // DEBUGauto res = Solution().Ans(N,x1,x2,x3,x4, edge);cout << res << "\n";return 0;
}
单元测试
int N,x1,x2,x3,x4;vector<tuple<int, int, int>> edge;TEST_METHOD(TestMethod11){N = 9, x1 = 1, x2 = 6, x3 = 7, x4 = 8, edge = { {1,2,1},{2,5,2},{2,3,3},{3,4,2},{3,9,5},{4,5,3},{4
,6,4},{4,7,2},{5,8,1},{7,9,1} };auto res = Solution().Ans(N, x1, x2, x3, x4, edge);AssertEx(3, res);}TEST_METHOD(TestMethod12){N = 9, x1 = 1, x2 = 6, x3 = 8, x4 = 7, edge = { {1,2,1},{2,5,2},{2,3,3},{3,4,2},{3,9,5},{4,5,3},{4
,6,4},{4,7,2},{5,8,1},{7,9,1} };auto res = Solution().Ans(N, x1, x2, x3, x4, edge);AssertEx(3, res);}

扩展阅读
| 我想对大家说的话 |
|---|
| 工作中遇到的问题,可以按类别查阅鄙人的算法文章,请点击《算法与数据汇总》。 |
| 学习算法:按章节学习《喜缺全书算法册》,大量的题目和测试用例,打包下载。重视操作 |
| 有效学习:明确的目标 及时的反馈 拉伸区(难度合适) 专注 |
| 员工说:技术至上,老板不信;投资人的代表说:技术至上,老板会信。 |
| 闻缺陷则喜(喜缺)是一个美好的愿望,早发现问题,早修改问题,给老板节约钱。 |
| 子墨子言之:事无终始,无务多业。也就是我们常说的专业的人做专业的事。 |
| 如果程序是一条龙,那算法就是他的是睛 |
| 失败+反思=成功 成功+反思=成功 |
视频课程
先学简单的课程,请移步CSDN学院,听白银讲师(也就是鄙人)的讲解。
https://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/38771
如何你想快速形成战斗了,为老板分忧,请学习C#入职培训、C++入职培训等课程
https://edu.csdn.net/lecturer/6176
测试环境
操作系统:win7 开发环境: VS2019 C++17
或者 操作系统:win10 开发环境: VS2022 C++17
如无特殊说明,本算法用**C++**实现。

