零基础 “入坑” Java--- 十五、字符串String
文章目录
- 常用方法
- 1.字符串构造
- 2.String对象的比较
- 3.字符串查找
- 4.字符串转换
- 5.字符串替换
- 6.字符串拆分
- 7.字符串截取及trim操作
String这个类型我们并不陌生,在之前的学习中我们经常使用String来定义字符串,但是String的功能可不仅仅是定义字符串这么简单。本章节我们就来学习有关String的知识。
常用方法
1.字符串构造
String类中提供的构造方法很多,常用的有以下三种:
public static void main(String[] args) {//使用字符串直接构造String s1 = "hello";System.out.println(s1);//通过new关键字进行构造String s2 = new String("world");System.out.println(s2);//使用字符数组进行构造char[] array = new char[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'};String s3 = new String(array);System.out.println(s3);}
String是引用类型,其内部存储的并不是字符串本身。
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello";System.out.println(str);//方式一System.out.println(str.length());//方式二System.out.println("hello".length());System.out.println(str.isEmpty()); //判断元素是否为空:String str = "";String str2 = null; //指向为空System.out.println(str2.isEmpty()); //error}
我们可以通过 “.length()” 方法计算字符串的长度;通过 “.isEmpty()” 方法判断字符串中是否存在元素。
注意:“.isEmpty()” 方法用来判断字符串中是否有元素;而当一个字符串为null时,表示此字符串的指向为空,即不指向任何对象,此时调用方法会出现空指针异常的情况。注意区分 元素内容为空 和 指向为空。
2.String对象的比较
对于基本数据类型,使用 == 比较的是变量中存储的值是否相同:
public static void main(String[] args) {int a = 10;int b = 10;int c = 20;System.out.println(a == b);System.out.println(a == c);}
对于引用类型,使用 == 比较的是"地址"是否相同:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = new String("hello");String str2 = new String("hello");System.out.println(str1 == str2);System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));System.out.println("=======================");String str3 = "world";String str4 = "world";System.out.println(str3 == str4); //有关常量池知识,以后介绍}
我们通过new关键字构造str1,str2两个对象,因为都是通过new关键字构造的,虽然字符串中的内容相同,但所在的"地址"不同;在使用 == 进行比较时,比较的是"地址",因此结果为false;在Java中,String类重写了equals方法,因此可以通过equals方法对字符串中的内容进行比较。
但是当我们使用字符串直接构造时,此时使用 == 进行比较,结果却为true。这种情况涉及到有关常量池的知识,在这我们先特殊记忆一下。
使用".compareTo()"方法也可以比较String类型的大小。与equals不同的是,equals的返回值为boolean类型,而compareTo返回值为int类型。
字符串长度相同时,返回值为第一个不同字符的差值:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "abc";String str2 = "acc";System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); //-1:'b' - 'c'}
字符串长度不同时,若最短长度的内容均相同,返回值为长度的差值:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "abcaaa";String str2 = "abc";System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); //3:str1.length() - str2.length()}
字符串长度不同时,若最短长度的内容不同,返回值为第一个不同字符的差值:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "abc";String str2 = "acccc";System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2)); //-1:'b' - 'c'}
当我们想忽略大小写进行比较时,就可以使用"compareToIgnoreCase"方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str1 = "ABC";String str2 = "abc";System.out.println(str1.compareToIgnoreCase(str2)); //字符串内容相同:0}
3.字符串查找
String类型提供了非常多的查找方式:
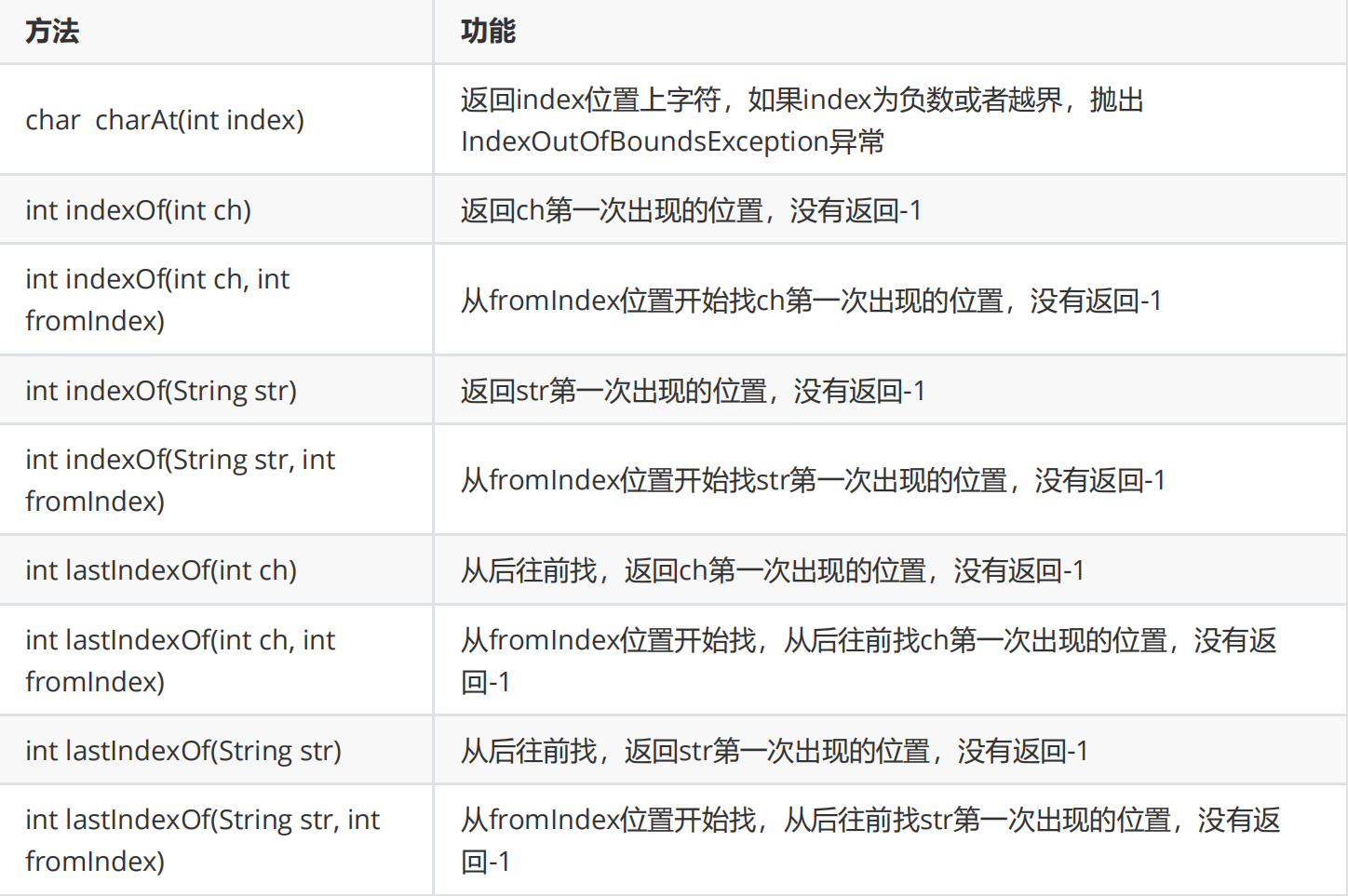
方法使用示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "abcdefabcdef";//charAt返回值类型为char,返回的是下标位置的值;不要越界,越界报错char ch = str.charAt(3);System.out.println(ch); //d//indexOf:返回值为int,返回第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1int x = str.indexOf('d');System.out.println(x); //3//indexOf:返回值为int,返回第一个字符 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1int y = str.indexOf("cd");System.out.println(y); //2//indexOf:返回值为int,从fromIndex下标开始寻找,没有返回-1int z = str.indexOf('d', 6);System.out.println(z); //9//indexOf:返回值为int,从fromIndex下标开始寻找,返回第一个字符 第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1int i = str.indexOf("cd", 6);System.out.println(i); //8System.out.println("==========================");String str2 = "ababcabcdabcde";//lastIndexOf:返回值为int,从后往前找第一次出现的位置,返回下标,没有返回-1int a = str2.lastIndexOf('d');System.out.println(a); //12//lastIndexOf:返回值为int,从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找第一次出现的位置,返回下标,没有返回-1int c = str2.lastIndexOf('d', 10);System.out.println(c); //8//lastIndexOf:返回值为int,从后往前找 第一个字符 第一次出现的位置,返回下标,没有返回-1int b = str2.lastIndexOf("cd");System.out.println(b); //11//lastIndexOf:返回值为int,从fromIndex位置开始,从后往前找 第一个字符 第一次出现的位置,返回下标,没有返回-1int d = str2.lastIndexOf("cd", 10);System.out.println(d); //7}
4.字符串转换
可以使用valueOf将数值转换为字符串;也可以通过"Integer.parseInt"等,将字符串转换为数值:
class Student {public String name;public int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}
}public static void main(String[] args) {//数字转字符串String s1 = String.valueOf(66);String s2 = String.valueOf(66.6);String s3 = String.valueOf(true);String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student("小王", 20)); //调用的为Object的toString,打印"地址"System.out.println(s1);System.out.println(s2);System.out.println(s3);System.out.println(s4);//字符串转数字int a = Integer.parseInt("66");double b = Double.parseDouble("66.66");System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);}
使用toUpperCase将小写字母转换为大写字母,toLowerCase将大写字母转换为小写字母,这两种方法只针对字母进行操作:
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "AbCdEFg";//大小写转换System.out.println(s.toUpperCase()); //ABCDEFGSystem.out.println(s.toLowerCase()); //abcdefg}
注意:转换之后,生成了一个新的字符串,并没有在原有字符串上进行改变。
字符串和字符数组之间也可以相互转换;此外,还可以对字符串进行格式化输出:
public static void main(String[] args) {//字符串转数组String s = "hello";char[] array = s.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}System.out.println();//数组转字符串String s1 = new String(array);System.out.println(s1);//格式化输出String s2 = String.format("%d/%d/%d", 1999, 9, 9);System.out.println(s2);}
5.字符串替换
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "ababcabcdabcde";//替换操作,字符串替换字符串,并不会在原有字符串上进行改动,生成新的字符串String s1 = s.replace("ab", "=");System.out.println(s1);//字符替换字符String s2 = s.replace('a', 'o');System.out.println(s2);//只替换第一次出现的位置String s3 = s.replaceFirst("ab", "o");System.out.println(s3);//替换全部String s4 = s.replaceAll("ab", "xy");System.out.println(s4);}
由于字符串是不可变对象,在进行替换操作时,并不会在当前字符串上进行修改,而是生成一个新的字符串。
6.字符串拆分
当我们想将一个字符串拆分为几段时,String中也提供了很多方法:
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "woshi tiancai";//需要用数组接收返回值String[] str = s.split(" ");for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {System.out.println(str[i]);}//自己决定分割几段(做不到平均分割,从前往后,割到段数就停止)String s1 = "hello woshi tiancai";String[] str1 = s1.split(" ", 2);for (int i = 0; i < str1.length; i++) {System.out.println(str1[i]);}//特殊符号需要使用转义字符(\\)String s2 = "1999/09/09";String[] str2 = s2.split("\\/");for (int i = 0; i < str2.length; i++) {System.out.println(str2[i]);}//多个分隔符,使用|进行连接System.out.println("====================");String s3 = "hello 1999/09/09";String[] str3 = s3.split(" |\\/");for (int i = 0; i < str3.length; i++) {System.out.println(str3[i]);}System.out.println("====================");//多次分割String s4 = "hello world&hello java";String[] str4 = s4.split("&");for (int i = 0; i < str4.length; i++) {System.out.println(str4[i]);String[] ss = str4[i].split(" ");for (int j = 0; j < ss.length; j++) {System.out.println(ss[j]);}}}
7.字符串截取及trim操作
使用substring方法可以对字符串进行截取操作,获取我们想要的 字符串中指定的内容;使用trim方法可以去掉字符串两边的空格,保留字符与字符之间的空格:
public static void main(String[] args) {String s = "abcdef";//如果参数为0,则返回原数组,若参数为其他,则返回新数组String str = s.substring(1);System.out.println(str);String str2 = s.substring(1, 4);//[1, 4) 左闭右开区间System.out.println(str2);System.out.println("====================");String ss = " abc 666 ";System.out.println(ss);//去掉字符串两边空格String ss1 = ss.trim();System.out.println(ss1);}
当substring有两个参数时,需要注意截取的范围是左闭右开区间。
未完待续…
