GeoTools 基础概念解析
1. 要素结构(schema)
(1)获取数据项或者表名称
先来看看数据名称,从数据存储对象方法getTypeNames()中可以获取数据项名称。如下方数据路径指向文件省.shp,typeName输出值即为“省”
// 省级行政区路径
String provinceLocation = "E:\data\基础数据\行政区\省级行政区\省级行政区\省.shp";// 数据项名称
String typeName = dataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
System.out.println("数据名称:"+typeName);
// 数据名称:省
当将矢量数据导入空间数据库时,从数据存储对象中获取到数据项名称,如果不做修改,该名称即成为数据库表名称。
:::block-1
// Get the name of the new Shapefile, which will be used to open the FeatureWriterString createdName = dataStore.getTypeNames()[0];
:::
(2)获取属性结构
了解了数据项名称,再来看一个GeoJSON格式的地理对象。要素Feature数据结构包括type属性"Feature"、几何对象属性"geometry"以及"properties"属性信息。
{"type": "Feature","geometry": {"type": "Point","coordinates": [125.6, 10.1]},"properties": {"name": "Dinagat Islands"}
}
GeoTools要素数据结构与GeoJSON地理对象类似,其用schema描述要素数据结构,可以通过getSchema()方法获取。
SimpleFeatureType schema = featureSource.getSchema();
System.out.println("数据结构: " + schema);
// 数据结构: SimpleFeatureTypeImpl 省 identified extends polygonFeature(the_geom:MultiPolygon,LAYER:String,Name:String,Kind:Integer,AdminCode:Integer)
在schema中存储数据字段及其类型,相当于数据库中的表结构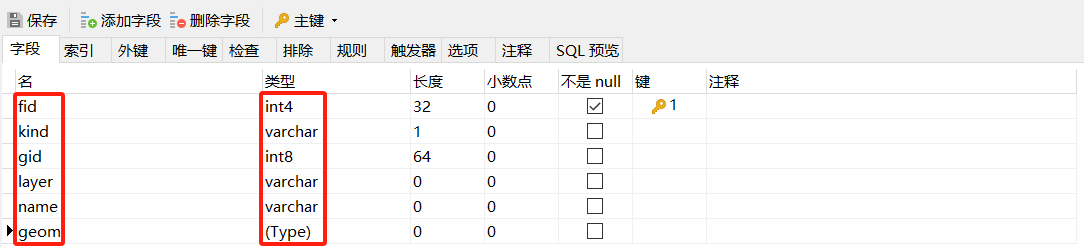
getAttributeDescriptors()方法可以获取所有属性对象,使用属性描述器AttributeDescriptor遍历属性字段,包括几何和属性信息。
for (AttributeDescriptor descriptor : schema.getAttributeDescriptors()) {System.out.println("属性字段~~~~"+descriptor.getLocalName() + ":" + descriptor.getType().getBinding().getSimpleName());
}
在将数据导入PostGIS空间数据库时,使用默认设置,即未新增或者修改字段的情况下,输出结果与数据库字段以及类型应该能够相互对应(此处与上图数据库字段fid、geom未能对应是因为fid是导入数据库时的新增字段,而geom几何字段默认情况下是the_geom。)。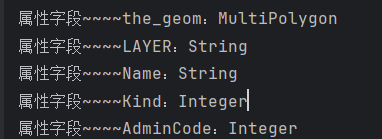
也可以单独获取几何属性。System.out.println("几何字段: " + schema.getGeometryDescriptor().getLocalName());将会输出“几何字段: the_geom”
(3)获取坐标系统
坐标系统可以通过getCoordinateReferenceSystem方法获取。
// 坐标系统
CoordinateReferenceSystem crs = schema.getCoordinateReferenceSystem();
System.out.println("坐标系统:" + crs);
以下输出结果地理坐标系WGS84。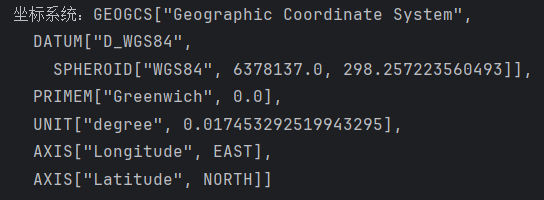
2. 获取要素集合
GeoTools中获取要素集合的大致路径如下
File(Database)->DataStoreFactory->featureSource->featureCollection
首先需要一个数据源,要么是文件,要么是数据库;然后将数据源交给数据存储工厂加工;经过加工之后出厂要素源对象;最后从要素源对象中获取到要素集合。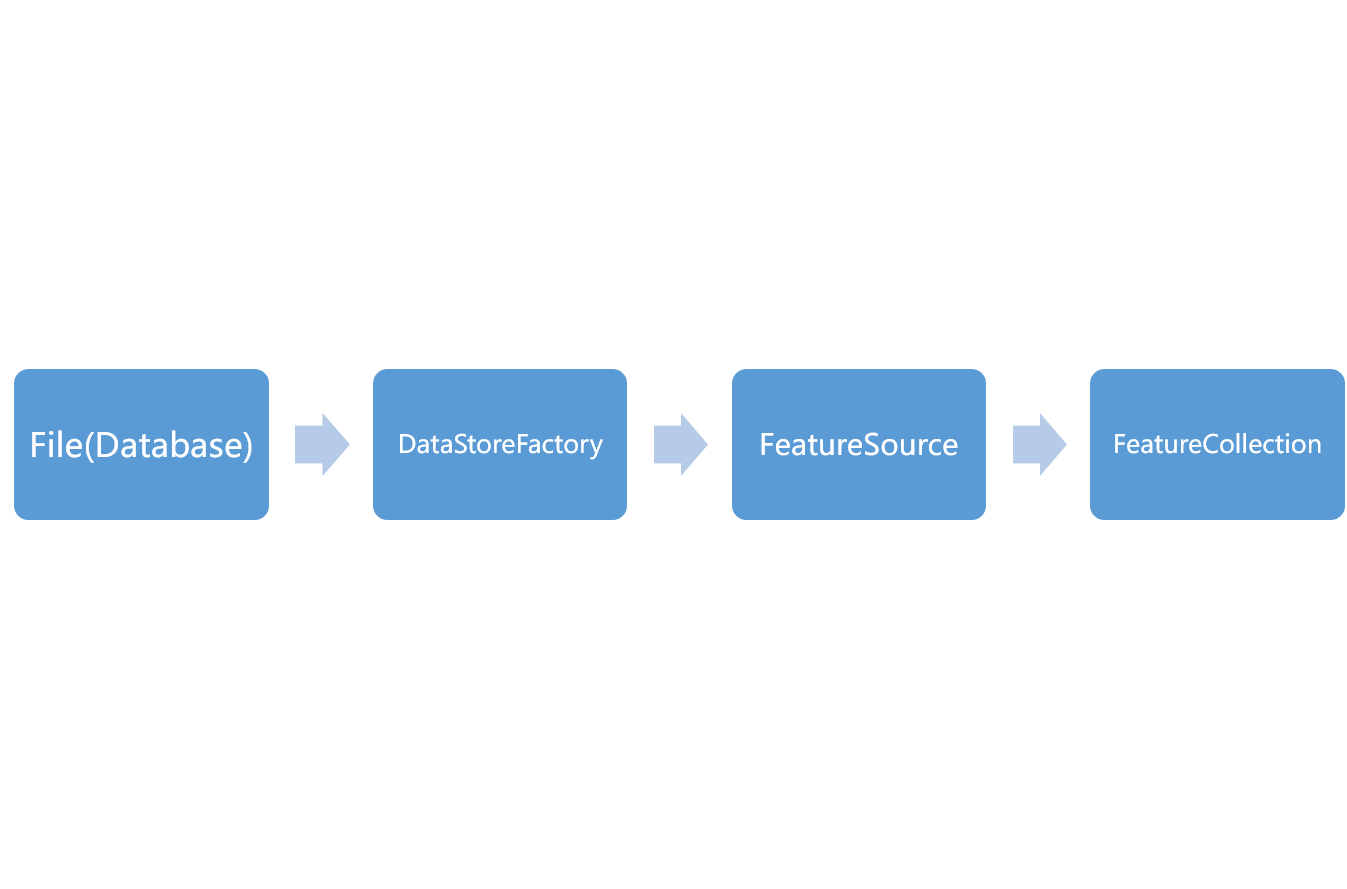
// 获取文件数据源
File file = new File(provinceLocation);// 送到文件工厂进行加工,
FileDataStore dataStore = FileDataStoreFinder.getDataStore(file);// 加工之后出厂要素源
SimpleFeatureSource featureSource = dataStore.getFeatureSource(typeName);// 获取要素集合
SimpleFeatureCollection featureCollection = featureSource.getFeatures();
下图所示GeoTools与JDBC概念对应关系可能有助于加强理解。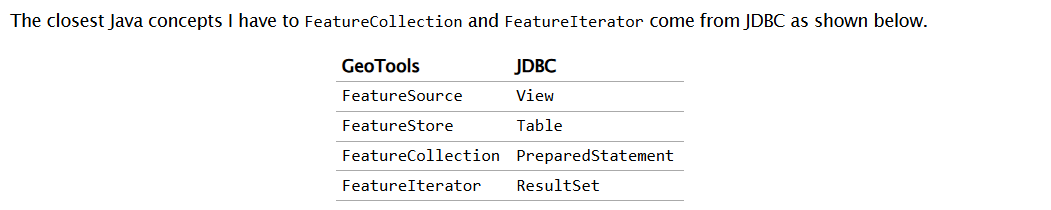
3. 创建要素
(1)创建数据结构
创建数据结构有两种方式,对于简单数据类型,可以直接使用DataUtilities工具类方法createType进行创建。
// 创建要素结构
final SimpleFeatureType TYPE = DataUtilities.createType("county","the_geom:Point:srid=4326,"+"name:String"
);
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(TYPE);
也可以将其封装为一个方法,将要素类型返回。使用此种方式首先要确定数据项名称和数据坐标系,具有更大的灵活性如限制字段长度等。
// 构造要素结构
private static SimpleFeatureType createFeatureType(String schema) {SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder builder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();builder.setName(schema);builder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); // 坐标系统// 按顺序添加字段builder.add("the_geom", Point.class);builder.length(15).add("name", String.class); // 限制字符串长度// 构造要素类型return builder.buildFeatureType();
}
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder("county");
有的数据字段很多,如果要进行数据格式转换或者将矢量数据导入空间数据库时,如果每一个字段都手动添加就会稍显麻烦。此时可以通过获取源数据属性结构,通过遍历schema,然后添加属性字段即可。
// 获取要素schema,也就是要素数据结构
SimpleFeatureType schema = featureCollection.getSchema();// 要素特征构建器
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder simpleFeatureTypeBuilder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.setName("Country"); // 定义名称
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); // 定义坐标系// 添加几何属性
simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add("the_geom",schema.getGeometryDescriptor().getType().getBinding());// 添加非几何属性字段
schema.getAttributeDescriptors().forEach(descriptor -> {if(!descriptor.getType().getBinding().isAssignableFrom(Geometry.class)){simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.add(descriptor);}
});
// 要素类型
SimpleFeatureType SHAPE_TYPE = simpleFeatureTypeBuilder.buildFeatureType();// 创建FeatureBuilder
SimpleFeatureBuilder featureBuilder = new SimpleFeatureBuilder(SHAPE_TYPE);
(2)添加字段数据
// 添加数据
featureBuilder.add(geometry);
featureBuilder.add(name);
SimpleFeature tarFeature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null);
在写入数据时,如果源数据属性字段很多,每次使用add方法添加,源数据结构类型改变时无法动态修改数据字段名称和数据类型,造成代码修改困难。此时可以使用set方法灵活添加属性字段以及字段类型。
// 复制几何属性
featureBuilder.set(SHAPE_TYPE.getGeometryDescriptor().getLocalName(), feature.getDefaultGeometry());// 复制非几何属性
SHAPE_TYPE.getAttributeDescriptors().forEach(descriptor -> {// 属性名称String name = descriptor.getLocalName();if(!descriptor.getType().getBinding().isAssignableFrom(Geometry.class)&& feature.getAttribute(name) != null){featureBuilder.set(name,feature.getAttribute(name));}
});
SimpleFeature targetFeature = featureBuilder.buildFeature(null);
4. 创建几何对象
GeoTools创建几何对象的过程也不复杂,可以使用WKTReader或者几何对象工厂GeometryFactory进行创建。使用Well-Known-Text (WKT)格式创建几何对象点数据。
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory(null);WKTReader reader = new WKTReader(geometryFactory);
Point point = (Point) reader.read("POINT (1 1)");
使用几何对象工厂GeometryFactory创建点数据。
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory(null);
Coordinate coord = new Coordinate(102.235800, 25.255800);
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint(coord);
5. 指定坐标系统
系统中使用的数据坐标系必须是明确的,所以在创建数据结构时就需要指定所使用的坐标系。
SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder builder = new SimpleFeatureTypeBuilder();
builder.setName(schema);
builder.setCRS(DefaultGeographicCRS.WGS84); // 坐标系统
在数据存储器也需要明确指定坐标系统。
// 创建要素结构, 应用定义好的Schema
dataStore.createSchema(SHAPE_TYPE);
dataStore.forceSchemaCRS(CRS.decode("EPSG:4326")); // 明确CRS
6. 数据模型
数据模型作为现实世界的抽象,是GeoTools实现从真实世界映射到地理对象的关键。在GeoTools中,使用要素对象来描述客观世界,具有地理实体对应关系。
详情请查看文章:GeoTools 数据模型
7. 工厂设计模式
工厂模式是软件开发的核心设计模式。GeoTools采用工厂设计模式思想,用于创建与客观世界相联系的地理实体对象或者其他关联对象。使得其在创建对象时,只需要专注于业务逻辑,而无需关心工厂实现。
详情请查看文章:GeoTools 工厂设计模式
OpenLayers示例数据下载,请回复关键字:ol数据
全国信息化工程师-GIS 应用水平考试资料,请回复关键字:GIS考试
【GIS之路】 已经接入了智能助手,欢迎关注,欢迎提问。
欢迎访问我的博客网站-长谈GIS:
http://shanhaitalk.com
都看到这了,不要忘记点赞、收藏 + 关注 哦 !
本号不定时更新有关 GIS开发 相关内容,欢迎关注 !
