EL表达式与JSTL标签库实战指南:从基础到OA系统改造
一、EL表达式
-
EL表达式是干什么用的?
-
Expression Language(表达式语言)
-
EL表达式可以代替JSP中的java代码,让JSP文件中的程序看起来更加整洁,美观。
-
JSP中夹杂着各种java代码,例如<% java代码 %>、<%=%>等,导致JSP文件很混乱,不好看,不好维护。所以才有了后期的EL表达式。
-
EL表达式可以算是JSP语法的一部分。EL表达式归属于JSP。
-
-
EL表达式出现在JSP中主要是:


-
-
从某个作用域中取数据,然后将其转换成字符串,然后将其输出到浏览器。这就是EL表达式的功效。三大功效:
-
第一功效:从某个域中取数据。
-
四个域:
-
pageContext
-
request
-
session
-
application
-
-
-
第二功效:将取出的数据转成字符串。
-
如果是一个java对象,也会自动调用java对象的toString方法将其转换成字符串。
-
-
第三功效:将字符串输出到浏览器。
-
和这个一样:<%= %>,将其输出到浏览器。
-
-
-
-
EL表达式很好用,基本的语法格式:
-
${表达式}
-
1.EL表达式的使用:


演示代码:
User类
package bean;
/**
* 符合javabean规范的一个java类。
*/
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private int age;
private Address addr;
public Address getAddr222() {
return addr;
}
public void setAddr(Address addr) {
this.addr = addr;
}
/*@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}*/
public User() {
}
public User(String username, String password, int age) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.age = age;
}
public String getUsername() {
System.out.println("getUsername()方法执行了");
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
System.out.println("getPassword()方法执行了");
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
// 或者getage()
// java程序员给方法起名的时候,建议驼峰。
public int getAge() {
System.out.println("getAge()方法执行了");
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/**
* 这个方法只是一个get方法而已。类中并没有声明email属性。
* 使用EL表达式可以获取Email吗?
* @return
*/
public String getEmail(){
return "dujubin@126.com";
}
}
Address类
package bean;
public class Address {
private String city;
private String street;
private String zipcode;
public Address() {
}
public Address(String city, String street, String zipcode) {
this.city = city;
this.street = street;
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getZipcode() {
return zipcode;
}
public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
}
7.jsp
<%@ page import="bean.User" %>
<%@ page import="bean.Address" %>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%
// 创建User对象
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("jackson");
user.setPassword("1234");
user.setAge(50);
// 创建地址Address对象
Address a = new Address();
a.setCity("北京");
a.setStreet("大兴区");
a.setZipcode("11111111");
user.setAddr(a);
// 将User对象存储到request域当中
request.setAttribute("userObj", user);
%>
<%--使用EL表达式,从request域当中,取出User对象,并将其输出到浏览器--%>
<%--1. EL表达式会自动从某个范围中取数据。2. 将其转成字符串。 3. 将其输出到浏览器。--%>
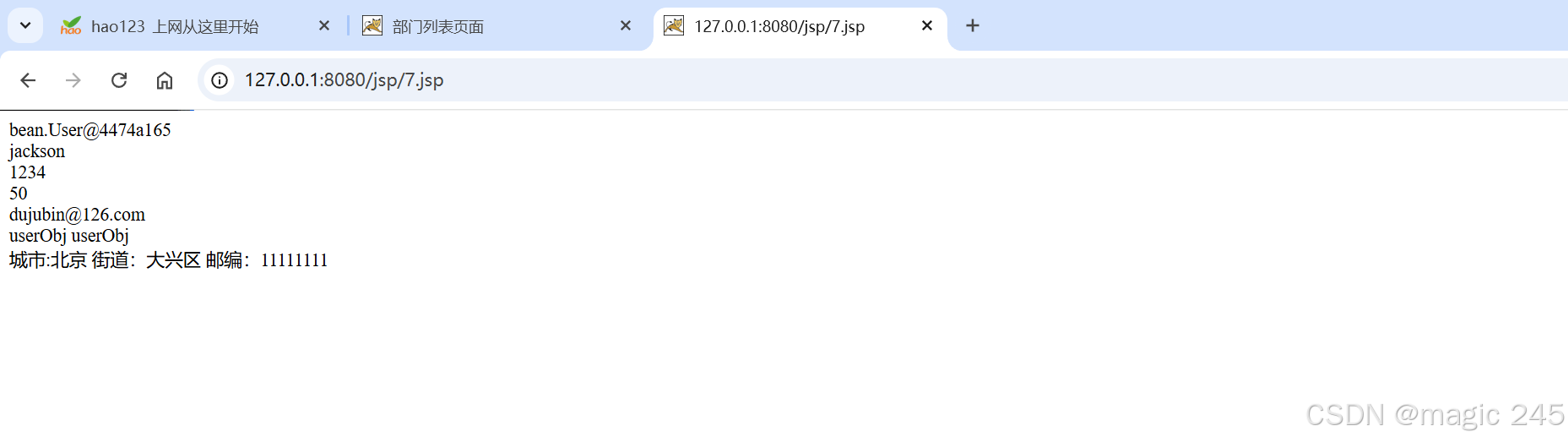
${userObj}
<br>
<%--你想输出的是user对象的username属性--%>
${userObj.username}
<br>
<%--输出password--%>
${userObj.password}
<br>
<%--输出年龄age--%>
${userObj.age}
<br>
<%--输出email--%>
${userObj.email}
<br>
<%--在EL表达式中不能添加双引号,如果添加了双引号,EL表达式就会将其当做普通的字符串输出到浏览器。--%>
${"userObj"}
userObj
<br>
<%--取出User对象是哪个城市的?--%>
城市:${userObj.addr222.city}
街道:${userObj.addr222.street}
邮编:${userObj.addr222.zipcode}

2.EL表达式优先从小范围中读取数据。
-
-
pageContext < request < session < application
-
-
EL表达式中有四个隐含的隐式的范围:
-
pageScope 对应的是 pageContext范围。
-
requestScope 对应的是 request范围。
-
sessionScope 对应的是 session范围。
-
applicationScope 对应的是 application范围。
-
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%
// 四个域都存储了数据,并且name相同。
session.setAttribute("data", "session");
request.setAttribute("data", "request");
pageContext.setAttribute("data", "pageContext");
application.setAttribute("data", "application");
%>
<%--在没有指定范围的前提下,EL表达式优先从小范围中取数据--%>
<%--pageContext < request < session < application --%>
${data}
<hr>
<%-- 在EL表达式中可以指定范围来读取数据--%>
<%--EL表达式有4个隐含的隐式的范围对象--%>
<%--pageScope requestScope sessionScope applicationScope--%>
<%--以下是指定范围取数据。--%>
${pageScope.data}<br>
${requestScope.data}<br>
${sessionScope.data}<br>
${applicationScope.data}<br>
<%--在实际开发中,因为向某个域中存储数据的时候,name都是不同的。所以 xxxScope 都是可以省略的。--%>
3.EL表达式对null进行了预处理。如果是null,则向浏览器输出一个空字符串。
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%
request.setAttribute("username", "zhangsan");
%>
<%--取出数据并且输出到浏览器--%>
<%=request.getAttribute("username")%><br>
采用EL表达式:${username}
<br>
<%=request.getAttribute("usernam")%><br>
<%--EL表达式主要任务是做页面展示,要求最终页面展示上是友好的。--%>
<%--所以EL表达式对null进行了处理。如果是null,则在浏览器上显示空白。--%>
采用EL表达式:${usernam}
<hr>
<%--EL表达式表面上是这种写法,实际上运行的时候,还是要翻译生成java代码的。--%>
${usernam} 这个EL表达式等同于这一段java代码:<%=request.getAttribute("usernam") == null ? "" : request.getAttribute("usernam")%>
4.EL表达式取数据的时候有两种形式:
-
第一种:. (大部分使用这种方式)
-
第二种:[ ] (如果存储到域的时候,这个name中含有特殊字符,可以使用 [ ])
-
request.setAttribute("abc.def", "zhangsan");
-
${requestScope.abc.def} 这样是无法取值的。
-
应该这样:${requestScope["abc.def"]}
-
<%@ page import="bean.User" %>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%
// 创建user对象
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("zhangsan");
// 存储到request域当中。
request.setAttribute("fdsafdsafdsa", user);
// 向request域当中存储数据。
request.setAttribute("abc.def", "hello jsp el!!!");
%>
<%--使用EL表达式取出,并且输出到浏览器--%>
<%--从域当中取user--%>
${fdsafdsafdsa}<br>
<%--取user的username--%>
<%----%>
${fdsafdsafdsa.username}<br>
<%--取user的username,注意[]当中的需要添加 双引号--%>
<%--[] 里面的没有加双引号的话,会将其看做变量。如果是带双引号 "username",则去找user对象的username属性。--%>
${fdsafdsafdsa["username"]}<br>
<%--将数据取出并输出到浏览器--%>
${requestScope.abc.def}<br>
之前是空白滴:<br>
${requestScope["abc.def"]}
5.掌握使用EL表达式,怎么从Map集合中取数据:
-
${map.key}
-
掌握使用EL表达式,怎么从数组和List集合中取数据:
-
${数组[0]}
-
${数组[1]}
-
${list[0]}
-
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>EL表达式示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
// 创建一个Map集合
java.util.Map<String, String> map = new java.util.HashMap<>();
map.put("key1", "Map中的值1");
map.put("key2", "Map中的值2");
request.setAttribute("map", map);
// 创建一个数组
String[] array = {"数组元素1", "数组元素2"};
request.setAttribute("array", array);
// 创建一个List集合
java.util.List<String> list = new java.util.ArrayList<>();
list.add("List元素1");
list.add("List元素2");
request.setAttribute("list", list);
%>
<h2>从Map集合中取数据</h2>
<p>key1对应的值: ${map.key1}</p>
<p>key2对应的值: ${map.key2}</p>
<h2>从数组中取数据</h2>
<p>数组第一个元素: ${array[0]}</p>
<p>数组第二个元素: ${array[1]}</p>
<h2>从List集合中取数据</h2>
<p>List第一个元素: ${list[0]}</p>
<p>List第二个元素: ${list[1]}</p>
</body>
</html>
6.page指令当中,有一个属性,可以忽略EL表达式

<%--<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" isELIgnored="false" %>--%>
<%--<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>--%>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" isELIgnored="true" %>
<%
request.setAttribute("username", "zhangsan");
%>
<%-- isELIgnored="true" 表示忽略JSP中整个页面的所有EL表达式。如果想忽略其中某个,可以使用以下反斜杠。 --%>
\${username}
${username}
${username}
<%--<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" isELIgnored="false" %>--%>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%--<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" isELIgnored="true" %>--%>
<%
request.setAttribute("username", "zhangsan");
%>
<%-- isELIgnored="true" 表示忽略JSP中整个页面的所有EL表达式。如果想忽略其中某个,可以使用以下反斜杠。 --%>
\${username}
${username}
${username}
7.通过EL表达式获取应用的根:
1. JSP 内置对象
JSP 有九大内置对象,分别是
pageContext、request、session、application、response、out、config、page、exception。其中pageContext、request、session、application为四个域对象,pageContext是作用域最小的域对象,代表页面上下文。2.
pageContext的使用
pageContext.getRequest()方法可以获取request对象,但在 JSP 中可以直接使用内置对象request。pageContext可用于获取其他内置对象和属性,是一个功能强大的上下文对象。3. EL 表达式隐式对象
- EL 表达式中没有
request这个隐式对象,requestScope仅代表 “请求范围”,不等同于request对象。- EL 表达式中有隐式对象
pageContext,它和 JSP 中的九大内置对象pageContext是同一个对象。4. 获取应用根路径
- 在 JSP 中可以通过
((HttpServletRequest)pageContext.getRequest()).getContextPath()获取应用的根路径。- 在 EL 表达式中可以使用
${pageContext.request.contextPath}来获取应用的根路径。
-
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<%@ page import="jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>JSP 和 EL 表达式获取应用根路径示例</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>使用 JSP 代码获取应用根路径</h2>
<p>应用根路径 (JSP 代码): <%=((HttpServletRequest)pageContext.getRequest()).getContextPath() %></p>
<h2>使用 EL 表达式获取应用根路径</h2>
<p>应用根路径 (EL 表达式): ${pageContext.request.contextPath}</p>
</body>
</html>
- 在 JSP 代码部分,通过
((HttpServletRequest)pageContext.getRequest()).getContextPath()获取应用的根路径并输出。 - 在 EL 表达式部分,使用
${pageContext.request.contextPath}获取应用的根路径并输出。
8.EL表达式中其他的隐式对象:
⑴. EL 表达式隐含对象概述
EL(Expression Language)表达式提供了多个隐含对象,这些对象可以简化 JSP 页面中对数据的访问,主要有 pageContext、param、paramValues、initParam 等。
⑵. 各隐含对象的作用
pageContext
- 它代表 JSP 的页面上下文,可用于获取其他 JSP 内置对象和属性。例如,通过
pageContext.request.contextPath可以获取应用的根路径。
param
- 用于获取请求参数的单个值。当请求中存在同名参数时,
param只会获取该参数一维数组中的第一个元素。
param 获取的参数来源
param隐式对象用于获取请求参数,具体包括:
URL 中的查询参数(GET 请求):例如 http://localhost:8080/page.jsp?username=lisi 中的 username=lisi。
表单提交的参数(POST 请求):例如表单中 <input type="text" name="password"> 的值。
HTTP 请求头中的参数(较少见,需特殊处理)。
应用场景
param常用于以下场景:
用户登录:获取用户名和密码。
搜索功能:获取用户输入的关键词。
分页参数:获取当前页码或每页显示数量。
动态页面参数:通过 URL 传递 ID(如 http://localhost:8080/article.jsp?id=123)。
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
用户名(JSP):<%=request.getParameter("username")%><br>
用户名(EL):${param.username}
</body>
</html>paramValues
- 用于获取请求参数的所有值,返回一个数组。可以通过索引访问数组中的具体元素。
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<%--假设用户提交的数据:http://localhost:8080/jsp/test.jsp?aihao=smoke&aihao=drink&aihao=tangtou--%>
<%--以上提交的数据显然是采用checkbox进行提交的。同一组的checkbox的name是一样的。--%>
<%--param 获取的是请求参数一维数组当中的第一个元素。--%>
爱好:${param.aihao} <br>
爱好:<%=request.getParameter("aihao")%> <br>
一维数组:${paramValues.aihao}<br>
一维数组:<%=request.getParameterValues("aihao")%><br>
<%--获取数组当中的元素:[下标]--%>
爱好:${paramValues.aihao[0]}、${paramValues.aihao[1]}、${paramValues.aihao[2]} <br>
</body>
</html>
initParam
- 用于获取在
web.xml中配置的应用初始化参数。这些参数是应用级别的,可通过ServletContext(在 JSP 中对应的是application内置对象)获取。
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
每页显示记录数(JSP):<%=application.getInitParameter("pageSize")%><br>
每页显示记录数(EL):${initParam.pageSize}<br>
页码(JSP):<%=application.getInitParameter("pageNum")%><br>
页码(EL):${initParam.pageNum}
<br>
<br>
<br>
<%--EL表达式中的隐含对象:initParam--%>
<%--ServletContext是Servlet上下文对象,对应的JSP九大内置对象之一是:application --%>
<%
String a = application.getInitParameter("pageSize");
String b = application.getInitParameter("pageNum");
%>
每页显示的记录条数:<%=a%> <br>
页码:<%=b%> <br>
每页显示的记录条数:<%=application.getInitParameter("pageSize")%> <br>
页码:<%=application.getInitParameter("pageNum")%> <br>
每页显示的记录条数:${initParam.pageSize} <br>
页码:${initParam.pageNum} <br>
</body>
</html>
⑶. 与 JSP 内置对象的对比
- JSP 有九大内置对象,如
request、application等。在获取请求参数和应用初始化参数时,既可以使用 JSP 内置对象的方法,也可以使用 EL 表达式的隐含对象,EL 表达式的使用更加简洁。
9.EL表达式的运算符
⑴. 算术运算符
在 EL 表达式中,算术运算符有 +、-、*、/、%。其中 + 只能进行求和运算,不能用于字符串拼接。当 + 两边的数据不是数字时,会尝试将其转换为数字,如果转换失败则会抛出 NumberFormatException。
⑵. 关系运算符
关系运算符包括 ==、!=、>、>=、<、<=,也可以使用 eq 替代 ==。在 EL 表达式中,== 和 != 会调用对象的 equals 方法来比较对象的值是否相等,而不是比较对象的引用。
⑶. 逻辑运算符
逻辑运算符有 !(取反)、&&(逻辑与)、||(逻辑或),也可以使用 not 替代 !,and 替代 &&,or 替代 ||。使用时需要注意逻辑优先级,必要时使用括号来明确运算顺序。
⑷ 条件运算符
条件运算符为 ? :,其语法为 条件表达式 ? 表达式1 : 表达式2。如果条件表达式为 true,则返回表达式 1 的值;否则返回表达式 2 的值。
⑸ 取值运算符
取值运算符有 [] 和 .。[] 通常用于访问数组、列表或映射中的元素,. 用于访问对象的属性或方法。
⑹ empty 运算符
empty 运算符用于判断一个值是否为空,运算结果是 boolean 类型。如果值为空,则结果为 true;否则为 false。可以使用 ! 或 not 对 empty 运算符的结果取反。
二、JSTL标签库
1.什么是JSTL标签库?
-
Java Standard Tag Lib(Java标准的标签库)
-
JSTL标签库通常结合EL表达式一起使用。目的是让JSP中的java代码消失。
-
标签是写在JSP当中的,但实际上最终还是要执行对应的java程序。(java程序在jar包当中。)
2.使用JSTL标签库的步骤:
-
第一步:引入JSTL标签库对应的jar包。
-
tomcat10之后引入的jar包是:
-
jakarta.servlet.jsp.jstl-2.0.0.jar
-
jakarta.servlet.jsp.jstl-api-2.0.0.jar
-
-
在IDEA当中怎么引入?
-
在WEB-INF下新建lib目录,然后将jar包拷贝到lib当中。然后将其“Add Lib...”
-
一定是要和mysql的数据库驱动一样,都是放在WEB-INF/lib目录下的。
-
什么时候需要将jar包放到WEB-INF/lib目录下?如果这个jar是tomcat服务器没有的。

-
-
maven就是将需要的工件放到WEB-INF/lib目录下
-
第二步:在JSP中引入要使用标签库。(使用taglib指令引入标签库。)
-
JSTL提供了很多种标签,你要引入哪个标签????重点掌握核心标签库。
-

第三步:在需要使用标签的位置使用即可。表面使用的是标签,底层实际上还是java程序。
3.JSTL标签的原理

源码解析:配置文件tld解析
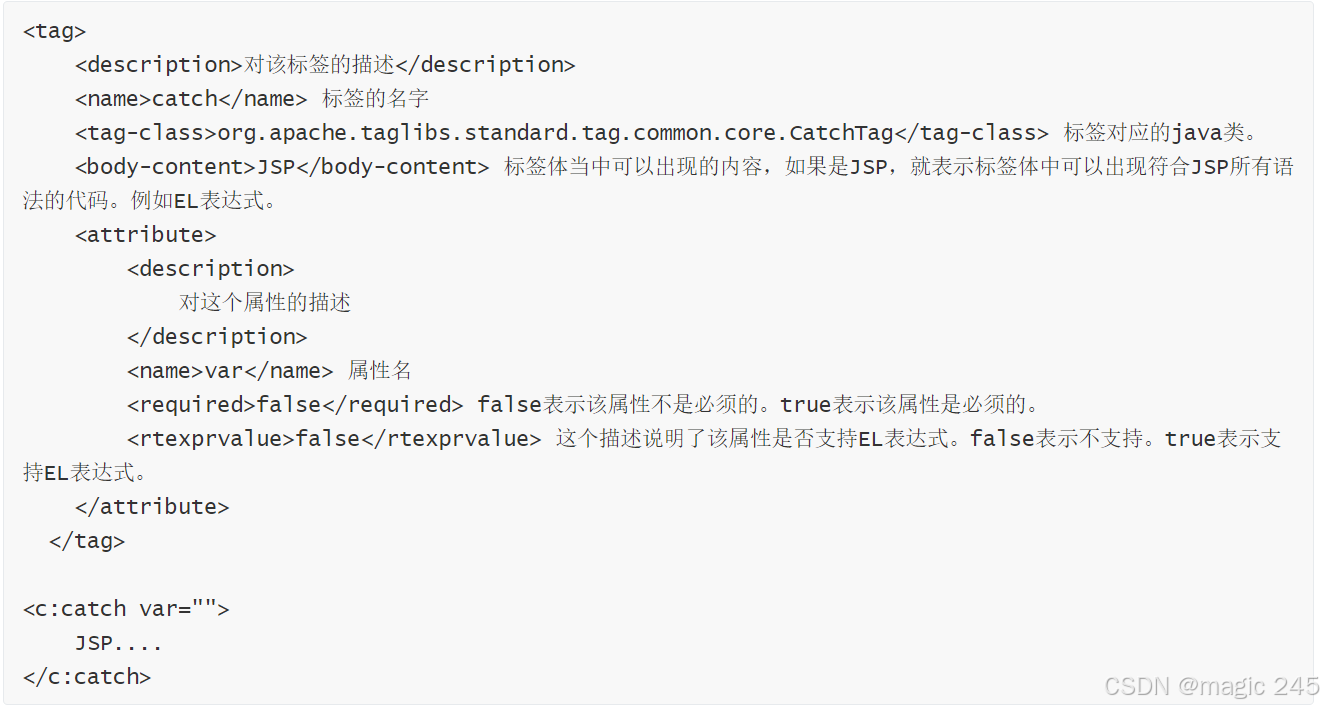
演示代码:
Student类
package bean;
import java.util.Objects;
public class Student {
private String id;
private String name;
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
System.out.println("equals方法执行了");
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
return Objects.equals(id, student.id) && Objects.equals(name, student.name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(id, name);
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(String id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
17.jsp
<%@ page import="bean.Student" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.List" %>
<%@ page import="java.util.ArrayList" %>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %>
<%--引入标签库。这里引入的是jstl的核心标签库。--%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%--格式化标签库,专门负责格式化操作的。--%>
<%--<%@taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt"%>--%>
<%--sql标签库--%>
<%--<%@taglib prefix="sql" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/sql" %>--%>
<%
// 创建List集合
List<Student> stuList = new ArrayList<>();
// 创建Student对象
Student s1 = new Student("110", "经常");
Student s2 = new Student("120", "救护车");
Student s3 = new Student("119", "消防车");
// 添加到List集合中
stuList.add(s1);
stuList.add(s2);
stuList.add(s3);
// 将list集合存储到request域当中
request.setAttribute("stuList", stuList);
%>
<%--需求:将List集合中的元素遍历。输出学生信息到浏览器--%>
<%--使用java代码--%>
<%
// 从域中获取List集合
List<Student> stus = (List<Student>)request.getAttribute("stuList");
// 编写for循环遍历list集合
for(Student stu : stus){
%>
id:<%=stu.getId()%>,name:<%=stu.getName()%><br>
<%
}
%>
<hr>
<%--使用core标签库中forEach标签。对List集合进行遍历--%>
<%--EL表达式只能从域中取数据。--%>
<%--var后面的名字是随意的。var属性代表的是集合中的每一个元素。--%>
<c:forEach items="${stuList}" var="s">
id:${s.id},name:${s.name} <br>
</c:forEach>

4.jstl中的核心标签库core当中有哪些常用的标签呢?
-
c:if
-
<c:if test="boolean类型,支持EL表达式"></c: if>
-
-
c:forEach
-
<c:forEach items="集合,支持EL表达式" var="集合中的元素" varStatus="元素状态对象"> ${元素状态对象.count} </c: forEach>
-
<c:forEach var="i" begin="1" end="10" step="2"> ${i} </c: forEach>
-
-
c:choose c:when c:otherwise

⑴.<c:if> 标签
- 功能:
<c:if>标签用于根据条件判断是否执行标签体内容,类似于 Java 中的if语句。 - 属性:
test:必填属性,其值为布尔类型,可以使用 EL 表达式。当test的值为true时,执行标签体内容;为false时,不执行。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>c:if 标签测试</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int num = 10;
request.setAttribute("number", num);
%>
<c:if test="${number > 5}">
<p>数字 ${number} 大于 5。</p>
</c:if>
</body>
</html>
⑵<c:choose>、<c:when> 和 <c:otherwise> 标签
- 功能:这三个标签组合使用,类似于 Java 中的
if - else if - else语句,用于进行多条件判断。 - 使用方式:
<c:choose>作为父标签,包裹<c:when>和<c:otherwise>标签。<c:when>标签可以有多个,每个<c:when>标签都有一个test属性,用于指定条件。当某个<c:when>的test条件为true时,执行该标签体内容,并且后续的<c:when>和<c:otherwise>标签不再执行。<c:otherwise>标签是可选的,当所有<c:when>的条件都为false时,执行<c:otherwise>标签体内容。
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>c:choose、c:when 和 c:otherwise 标签测试</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
int score = 85;
request.setAttribute("score", score);
%>
<c:choose>
<c:when test="${score >= 90}">
<p>成绩优秀!</p>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score >= 80}">
<p>成绩良好!</p>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${score >= 60}">
<p>成绩及格!</p>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<p>成绩不及格!</p>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
</html>
三、改造OA
-
使用什么技术改造呢?
-
Servlet + JSP + EL表达式 + JSTL标签。进行改造。
-
-
在前端HTML代码中,有一个标签,叫做base标签,这个标签可以设置整个网页的基础路径。
-
这是Java的语法,也不是JSP的语法。是HTML中的一个语法。HTML中的一个标签。通常出现在head标签中。
-
< base href="http://localhost:8080/oa/">
-
在当前页面中,凡是路径没有以“/”开始的,都会自动将base中的路径添加到这些路径之前。
-
< a href="ab/def"></ a>
-
等同于:< a href="http://localhost:8080/oa/ab/def"></ a>
-
-
需要注意:在JS代码中的路径,保险起见,最好不要依赖base标签。JS代码中的路径最好写上全路径。
-

四、Filter过滤器
-
当前的OA项目存在什么缺陷?
-
DeptServlet、EmpServlet、OrderServlet。每一个Servlet都是处理自己相关的业务。在这些Servlet执行之前都是需要判断用户是否登录了。如果用户登录了,可以继续操作,如果没有登录,需要用户登录。这段判断用户是否登录的代码是固定的,并且在每一个Servlet类当中都需要编写,显然代码没有得到重复利用。包括每一个Servlet都要解决中文乱码问题,也有公共的代码。这些代码目前都是重复编写,并没有达到复用。怎么解决这个问题?
-
可以使用Servlet规范中的Filter过滤器来解决这个问题。

-
-
-
Filter是什么,有什么用,执行原理是什么?
-
Filter是过滤器。
-
Filter可以在Servlet这个目标程序执行之前添加代码。也可以在目标Servlet执行之后添加代码。之前之后都可以添加过滤规则。
-
一般情况下,都是在过滤器当中编写公共代码。
-
1.一个过滤器怎么写呢?
-
第一步:编写一个Java类实现一个接口:jarkata.servlet.Filter。并且实现这个接口当中所有的方法。
-
init方法:在Filter对象第一次被创建之后调用,并且只调用一次。
-
doFilter方法:只要用户发送一次请求,则执行一次。发送N次请求,则执行N次。在这个方法中编写过滤规则。
-
destroy方法:在Filter对象被释放/销毁之前调用,并且只调用一次。
-
-
第二步:在web.xml文件中对Filter进行配置。这个配置和Servlet很像。

-
-
-
或者使用注解:@WebFilter({"*.do"})
-
-
-
注意:
-
Servlet对象默认情况下,在服务器启动的时候是不会新建对象的。
-
Filter对象默认情况下,在服务器启动的时候会新建对象。
-
Servlet是单例的。Filter也是单例的。(单实例。)
-
-
目标Servlet是否执行,取决于两个条件:
-
第一:在过滤器当中是否编写了:chain.doFilter(request, response); 代码。
-
第二:用户发送的请求路径是否和Servlet的请求路径一致。
-
-
chain.doFilter(request, response); 这行代码的作用:
-
执行下一个过滤器,如果下面没有过滤器了,执行最终的Servlet。
-
-
注意:Filter的优先级,天生的就比Servlet优先级高。
-
/a.do 对应一个Filter,也对应一个Servlet。那么一定是先执行Filter,然后再执行Servlet。
-
-
关于Filter的配置路径:
-
/a.do、/b.do、/dept/save。这些配置方式都是精确匹配。
-
/* 匹配所有路径。
-
*.do 后缀匹配。不要以 / 开始
-
/dept/* 前缀匹配。
-
-
在web.xml文件中进行配置的时候,Filter的执行顺序是什么?
-
依靠filter-mapping标签的配置位置,越靠上优先级越高。
-
-
过滤器的调用顺序,遵循栈数据结构。
-
使用@WebFilter的时候,Filter的执行顺序是怎样的呢?
-
执行顺序是:比较Filter这个类名。
-
比如:FilterA和FilterB,则先执行FilterA。
-
比如:Filter1和Filter2,则先执行Filter1.
-
-
Filter的生命周期?
-
和Servlet对象生命周期一致。
-
唯一的区别:Filter默认情况下,在服务器启动阶段就实例化。Servlet不会。
-
-
Filter过滤器这里有一个设计模式:
-
责任链设计模式。
-
过滤器最大的优点:
-
在程序编译阶段不会确定调用顺序。因为Filter的调用顺序是配置到web.xml文件中的,只要修改web.xml配置文件中filter-mapping的顺序就可以调整Filter的执行顺序。显然Filter的执行顺序是在程序运行阶段动态组合的。那么这种设计模式被称为责任链设计模式。
-
-
责任链设计模式最大的核心思想:
-
在程序运行阶段,动态的组合程序的调用顺序。
-
-
-
使用过滤器改造OA项目。
五、Listener监听器
1.什么是监听器?
-
监听器是Servlet规范中的一员。就像Filter一样。Filter也是Servlet规范中的一员。
-
在Servlet中,所有的监听器接口都是以“Listener”结尾。
2.监听器有什么用?
-
监听器实际上是Servlet规范留给我们javaweb程序员的特殊时机。
-
特殊的时刻如果想执行这段代码,你需要想到使用对应的监听器。
3.Servlet规范中提供了哪些监听器?
-
HttpSessionListener
-
HttpSessionAttributeListener
-
该监听器需要使用@WebListener注解进行标注。
-
该监听器监听的是什么?是session域中数据的变化。只要数据变化,则执行相应的方法。主要监测点在session域对象上。
-
-
HttpSessionBindingListener
-
该监听器不需要使用@WebListener进行标注。
-
假设User类实现了该监听器,那么User对象在被放入session的时候触发bind事件,User对象从session中删除的时候,触发unbind事件。
-
假设Customer类没有实现该监听器,那么Customer对象放入session或者从session删除的时候,不会触发bind和unbind事件。
-
-
HttpSessionIdListener
-
session的id发生改变的时候,监听器中的唯一一个方法就会被调用。
-
-
HttpSessionActivationListener
-
监听session对象的钝化和活化的。
-
钝化:session对象从内存存储到硬盘文件。
-
活化:从硬盘文件把session恢复到内存。
-
-
实现一个监听器的步骤:以ServletContextListener为例。
-
第一步:编写一个类实现ServletContextListener接口。并且实现里面的方法。
-
void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event)
-
-
第二步:在web.xml文件中对ServletContextListener进行配置,如下:
-
<listener> <listener-class>com.bjpowernode.javaweb.listener.MyServletContextListener</listener-class> </listener>
-
当然,第二步也可以不使用配置文件,也可以用注解,例如:@WebListener
-
-
-
注意:所有监听器中的方法都是不需要javaweb程序员调用的,由服务器来负责调用?什么时候被调用呢?
-
当某个特殊的事件发生(特殊的事件发生其实就是某个时机到了。)之后,被web服务器自动调用。
-
-
思考一个业务场景:
-
请编写一个功能,记录该网站实时的在线用户的个数。
-
我们可以通过服务器端有没有分配session对象,因为一个session代表了一个用户。有一个session就代表有一个用户。如果你采用这种逻辑去实现的话,session有多少个,在线用户就有多少个。这种方式的话:HttpSessionListener够用了。session对象只要新建,则count++,然后将count存储到ServletContext域当中,在页面展示在线人数即可。
-
业务发生改变了,只统计登录的用户的在线数量,这个该怎么办?
-
session.setAttribute("user", userObj);
-
用户登录的标志是什么?session中曾经存储过User类型的对象。那么这个时候可以让User类型的对象实现HttpSessionBindingListener监听器,只要User类型对象存储到session域中,则count++,然后将count++存储到ServletContext对象中。页面展示在线人数即可。
-
-
-
实现oa项目中当前登录在线的人数。
-
什么代表着用户登录了?
-
session.setAttribute("user", userObj); User类型的对象只要往session中存储过,表示有新用户登录。
-
-
什么代表着用户退出了?
-
session.removeAttribute("user"); User类型的对象从session域中移除了。
-
或者有可能是session销毁了。(session超时)
-
-
六、oa案例

1.Dept类
package oa.bean;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* 一个普通的java类,这个java类可以封装零散的数据。代表了一个部门对象。
*/
public class Dept {
private String deptno;
private String dname;
private String loc;
public Dept() {
}
public String getDeptno() {
return deptno;
}
public void setDeptno(String deptno) {
this.deptno = deptno;
}
public String getDname() {
return dname;
}
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
public String getLoc() {
return loc;
}
public void setLoc(String loc) {
this.loc = loc;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dept{" +
"deptno='" + deptno + '\'' +
", dname='" + dname + '\'' +
", loc='" + loc + '\'' +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Dept dept = (Dept) o;
return Objects.equals(deptno, dept.deptno) && Objects.equals(dname, dept.dname) && Objects.equals(loc, dept.loc);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(deptno, dname, loc);
}
}
2.User
package oa.bean;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletContext;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingEvent;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingListener;
public class User implements HttpSessionBindingListener {
@Override
public void valueBound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
// 用户登录了
// User类型的对象向session中存放了。
// 获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext application = event.getSession().getServletContext();
// 获取在线人数。
Object onlinecount = application.getAttribute("onlinecount");
if (onlinecount == null) {
application.setAttribute("onlinecount", 1);
} else {
int count = (Integer)onlinecount;
count++;
application.setAttribute("onlinecount", count);
}
}
@Override
public void valueUnbound(HttpSessionBindingEvent event) {
// 用户退出了
// User类型的对象从session域中删除了。
ServletContext application = event.getSession().getServletContext();
Integer onlinecount = (Integer)application.getAttribute("onlinecount");
onlinecount--;
application.setAttribute("onlinecount", onlinecount);
}
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
}
public User(String username, String password) {
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
3.DBUtil
package oa.utils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* JDBC的工具类
*/
public class DBUtil {
// 静态变量:在类加载时执行。
// 并且是有顺序的。自上而下的顺序。
// 属性资源文件绑定
private static ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("resources.jdbc");
// 根据属性配置文件key获取value
private static String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
private static String url = bundle.getString("url");
private static String user = bundle.getString("user");
private static String password = bundle.getString("password");
static {
// 注册驱动(注册驱动只需要注册一次,放在静态代码块当中。DBUtil类加载的时候执行。)
try {
// "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" 是连接数据库的驱动,不能写死。因为以后可能还会连接Oracle数据库。
// 如果连接oracle数据库的时候,还需要修改java代码,显然违背了OCP开闭原则。
// OCP开闭原则:对扩展开放,对修改关闭。(什么是符合OCP呢?在进行功能扩展的时候,不需要修改java源代码。)
//Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象
* @return conn 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 获取连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param conn 连接对象
* @param ps 数据库操作对象
* @param rs 结果集对象
*/
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement ps, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.DeptServlet
package oa.web.action;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import oa.bean.Dept;
import oa.utils.DBUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@WebServlet({"/dept/list", "/dept/detail", "/dept/delete", "/dept/save", "/dept/modify"})
public class DeptServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
/*// post请求乱码问题
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 响应中文乱码问题
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");*/
// 获取session(这个session是不需要新建的)
// 只是获取当前session,获取不到这返回null
/*HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if(session != null && session.getAttribute("username") != null){
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
if("/dept/list".equals(servletPath)){
doList(request, response);
}else if("/dept/detail".equals(servletPath)){
doDetail(request, response);
}else if("/dept/delete".equals(servletPath)){
doDel(request, response);
}else if("/dept/save".equals(servletPath)){
doSave(request, response);
}else if("/dept/modify".equals(servletPath)){
doModify(request, response);
}
}else{
// 跳转到登录页面
//response.sendRedirect("/oa/index.jsp");
//response.sendRedirect("/oa");
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp"); // 访问web站点的根即可,自动找到欢迎页面。
}*/
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
if("/dept/list".equals(servletPath)){
doList(request, response);
}else if("/dept/detail".equals(servletPath)){
doDetail(request, response);
}else if("/dept/delete".equals(servletPath)){
doDel(request, response);
}else if("/dept/save".equals(servletPath)){
doSave(request, response);
}else if("/dept/modify".equals(servletPath)){
doModify(request, response);
}
}
/**
* 保存部门信息
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void doSave(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取部门的信息
// 注意乱码问题(Tomcat10不会出现这个问题)
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String deptno = request.getParameter("deptno");
String dname = request.getParameter("dname");
String loc = request.getParameter("loc");
// 连接数据库执行insert语句
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into dept(deptno, dname, loc) values(?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, deptno);
ps.setString(2, dname);
ps.setString(3, loc);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
if (count == 1) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/dept/list");
}
}
/**
* 根据部门编号删除部门
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void doDel(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取部门编号
String deptno = request.getParameter("deptno");
// 连接数据库,删除部门
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from dept where deptno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, deptno);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
if (count == 1) {
// 删除成功
// 重定向到列表页面
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
response.sendRedirect(contextPath + "/dept/list");
}
}
/**
* 根据部门编号获取部门的信息。
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void doDetail(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建部门对象
Dept dept = new Dept();
// 获取部门编号
String dno = request.getParameter("dno");
// 根据部门编号获取部门信息,将部门信息封装成咖啡豆
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select dname, loc from dept where deptno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, dno);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 这个结果集当中只有一条数据,不需要while循环
if (rs.next()) {
String dname = rs.getString("dname");
String loc = rs.getString("loc");
// 封装对象(创建豆子)
dept.setDeptno(dno);
dept.setDname(dname);
dept.setLoc(loc);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
// 这个豆子只有一个,所以不需要袋子,只需要将这个咖啡豆放到request域当中即可。
request.setAttribute("dept", dept);
// 转发(不是重定向,因为要跳转到JSP做数据展示)
//request.getRequestDispatcher("/detail.jsp").forward(request, response);
/*String f = request.getParameter("f");
if ("m".equals(f)) {
// 转发到修改页面
request.getRequestDispatcher("/edit.jsp").forward(request, response);
} else if("d".equals(f)){
// 转发到详情页面
request.getRequestDispatcher("/detail.jsp").forward(request, response);
}*/
request.getRequestDispatcher("/" + request.getParameter("f") + ".jsp").forward(request, response);
}
/**
* 连接数据库,查询所有的部门信息,将部门信息收集好,然后跳转到JSP做页面展示。
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void doList(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 准备一个容器,用来专门存储部门
List<Dept> depts = new ArrayList<>();
// 连接数据库,查询所有的部门信息
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 获取连接
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
// 执行查询语句
String sql = "select deptno,dname,loc from dept";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 遍历结果集
while (rs.next()) {
// 从结果集中取出。
String deptno = rs.getString("deptno");
String dname = rs.getString("dname");
String loc = rs.getString("loc");
// 将以上的零散的数据封装成java对象。
Dept dept = new Dept();
dept.setDeptno(deptno);
dept.setDname(dname);
dept.setLoc(loc);
// 将部门对象放到list集合当中
depts.add(dept);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
// 将一个集合放到请求域当中
request.setAttribute("deptList", depts);
// 转发(不要重定向)
request.getRequestDispatcher("/list.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
/**
* 修改部门
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws IOException
*/
private void doModify(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 解决请求体的中文乱码问题。
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 获取表单中的数据
String deptno = request.getParameter("deptno");
String dname = request.getParameter("dname");
String loc = request.getParameter("loc");
// 连接数据库执行更新语句
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "update dept set dname = ?, loc = ? where deptno = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, dname);
ps.setString(2, loc);
ps.setString(3, deptno);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, null);
}
if (count == 1) {
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/dept/list");
}
}
}
5.EmpServlet
package oa.web.action;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 员工管理的。
* 员工管理的前提也是需要先登录。
*/
public class EmpServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
/*// post请求乱码问题
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 响应中文乱码问题
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");*/
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if(session != null && session.getAttribute("username") != null){
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
//...
}else{
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
}
}
}
6.OrderServlet
package oa.web.action;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 处理订单相关业务的类。
* 订单处理的前提还是需要先登录,才能处理订单。
*/
public class OrderServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
/*// post请求乱码问题
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
// 响应中文乱码问题
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");*/
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if(session != null && session.getAttribute("username") != null){
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
//...
}else{
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
}
}
}
7.UserServlet
package oa.web.action;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import oa.bean.User;
import oa.utils.DBUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
// Servlet负责业务的处理
// JSP负责页面的展示。
@WebServlet({"/user/login","/user/exit"})
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
if("/user/login".equals(servletPath)){
doLogin(request, response);
}else if("/user/exit".equals(servletPath)){
doExit(request, response);
}
}
protected void doExit(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取session对象,销毁session
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
// 从session域中删除user对象
session.removeAttribute("user");
// 手动销毁session对象。
session.invalidate();
// 销毁cookie(退出系统将所有的cookie全部销毁)
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
if (cookies != null) {
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
// 设置cookie的有效期为0,表示删除该cookie
cookie.setMaxAge(0);
// 设置一个下cookie的路径
cookie.setPath(request.getContextPath()); // 删除cookie的时候注意路径问题。
// 响应cookie给浏览器,浏览器端会将之前的cookie覆盖。
response.addCookie(cookie);
}
}
// 换一种方案
/*Cookie cookie1 = new Cookie("username","");
cookie1.setMaxAge(0);
cookie1.setPath(request.getContextPath());
Cookie cookie2 = new Cookie("password", "");
cookie2.setMaxAge(0);
cookie2.setPath(request.getContextPath());
response.addCookie(cookie1);
response.addCookie(cookie2);*/
// 跳转到登录页面
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath());
}
}
protected void doLogin(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
boolean success = false;
// 你要做一件什么事儿?验证用户名和密码是否正确。
// 获取用户名和密码
// 前端你是这样提交的:username=admin&password=123
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
// 连接数据库验证用户名和密码
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = ? and password = ?";
// 编译SQL
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给?传值
ps.setString(1, username);
ps.setString(2, password);
// 执行SQL
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 这个结果集当中最多只有一条数据。
if (rs.next()) { // 不需要while循环
// 登录成功
success = true;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
// 登录成功/失败
if (success) {
// 获取session对象(这里的要求是:必须获取到session,没有session也要新建一个session对象。)
HttpSession session = request.getSession(); // session对象一定不是null
//session.setAttribute("username", username);
User user = new User(username, password);
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 登录成功了,并且用户确实选择了“十天内免登录”功能。
String f = request.getParameter("f");
if("1".equals(f)){
// 创建Cookie对象存储登录名
Cookie cookie1 = new Cookie("username", username);
// 创建Cookie对象存储密码
Cookie cookie2 = new Cookie("password", password); // 真实情况下是加密的。
// 设置cookie的有效期为十天
cookie1.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 10);
cookie2.setMaxAge(60 * 60 * 24 * 10);
// 设置cookie的path(只要访问这个应用,浏览器就一定要携带这两个cookie)
cookie1.setPath(request.getContextPath());
cookie2.setPath(request.getContextPath());
// 响应cookie给浏览器
response.addCookie(cookie1);
response.addCookie(cookie2);
}
// 成功,跳转到用户列表页面
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/dept/list");
} else {
// 失败,跳转到失败页面
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/error.jsp");
}
}
}
8.WelcomeServlet
package oa.web.action;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import jakarta.servlet.http.*;
import oa.bean.User;
import oa.utils.DBUtil;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@WebServlet("/welcome")
public class WelcomeServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 获取cookie
// 这个Cookie[]数组可能是null,如果不是null,数组的长度一定是大于0的。
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
String username = null;
String password = null;
if (cookies != null) {
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
String name = cookie.getName();
if("username".equals(name)){
username = cookie.getValue();
}else if("password".equals(name)){
password = cookie.getValue();
}
}
}
// 要在这里使用username和password变量
if(username != null && password != null){
// 验证用户名和密码是否正确
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
boolean success = false;
try {
conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = ? and password = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,username);
ps.setString(2,password);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
// 登录成功
success = true;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
DBUtil.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
if (success) {
// 获取session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//session.setAttribute("username", username);
User user = new User(username, password);
session.setAttribute("user", user);
// 正确,表示登录成功
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/dept/list");
}else{
// 错误,表示登录失败
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
}
}else{
// 跳转到登录页面
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
}
}
}
9.LoginCheckFilter
package oa.web.filter;
import jakarta.servlet.*;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
public class LoginCheckFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse resp, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
/**
* 什么情况下不能拦截?
* 目前写的路径是:/* 表示所有的请求均拦截。
*
* 用户访问 index.jsp的时候不能拦截
* 用户已经登录了,这个需要放行,不能拦截。
* 用户要去登录,这个也不能拦截。
* WelcomeServlet也不能拦截。
*/
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) resp;
// 获取请求路径
String servletPath = request.getServletPath();
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
/*if("/index.jsp".equals(servletPath) || "/welcome".equals(servletPath) ||
"/user/login".equals(servletPath) || "/user/exit".equals(servletPath)
|| (session != null && session.getAttribute("username") != null)){*/
if("/index.jsp".equals(servletPath) || "/welcome".equals(servletPath) ||
"/user/login".equals(servletPath) || "/user/exit".equals(servletPath)
|| (session != null && session.getAttribute("user") != null)){
// 继续往下走
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}else{
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/index.jsp");
}
}
}

10.add.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>新增部门</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>欢迎${username},在线人数${onlinecount}人</h3>
<h1>新增部门</h1>
<hr >
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/dept/save" method="post">
部门编号<input type="text" name="deptno"/><br>
部门名称<input type="text" name="dname"/><br>
部门位置<input type="text" name="loc"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="保存"/><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
11.detail.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>部门详情</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>欢迎${username},在线人数${onlinecount}人</h3>
<h1>部门详情</h1>
<hr >
部门编号:${dept.deptno} <br>
部门名称:${dept.dname}<br>
部门位置:${dept.loc}<br>
<input type="button" value="后退" onclick="window.history.back()"/>
</body>
</html>
12.edit.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>修改部门</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3>欢迎${username},在线人数${onlinecount}人</h3>
<h1>修改部门</h1>
<hr >
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/dept/modify" method="post">
部门编号<input type="text" name="deptno" value="${dept.deptno}" readonly /><br>
部门名称<input type="text" name="dname" value="${dept.dname}"/><br>
部门位置<input type="text" name="loc" value="${dept.loc}"/><br>
<input type="submit" value="修改"/><br>
</form>
</body>
</html>
13.error.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>登录失败</title>
</head>
<body>
登录失败,请<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/index.jsp">重新登录</a>
</body>
</html>
14.index.jsp
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8"%>
<%--访问jsp的时候不生成session对象。--%>
<%@page session="false" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>欢迎使用OA系统</title>
</head>
<body>
<%-- 前端发送请求路径的时候,如果请求路径是绝对路径,要以 / 开始,加项目名。--%>
<%-- 以下这样写代码,oa项目名写死了。这种设计显然是不好的。--%>
<%--<a href="/oa/list.jsp">查看部门列表</a>--%>
<%--注意空格的问题。--%>
<%--<a href="<%=request.getContextPath() %>/list.jsp">查看部门列表</a>--%>
<%-- 执行一个Servlet,查询数据库,收集数据。--%>
<%--<a href="<%=request.getContextPath() %>/dept/list">查看部门列表</a>--%>
<%--<hr>--%>
<%--调用哪个对象的哪个方法,可以动态的获取一个应用的根路径。--%>
<%--<%=request.getContextPath() %>--%> <%-- out.print(request.getContextPath()); --%>
<h1>LOGIN PAGE</h1>
<hr>
<%--前端页面发送请求的时候,请求路径以“/”开始,带项目名。--%>
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/user/login" method="post">
username: <input type="text" name="username" ><br>
password: <input type="password" name="password"><br>
<input type="checkbox" name="f" value="1">十天内免登录<br>
<input type="submit" value="login">
</form>
</body>
</html>
15.list.jsp
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
<%@page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>部门列表页面</title>
<%--设置整个网页的基础路径是:http://localhost:8080/oa/ --%>
<%--<base href="http://localhost:8080/oa/">--%>
<base href="${pageContext.request.scheme}://${pageContext.request.serverName}:${pageContext.request.serverPort}${pageContext.request.contextPath}/">
</head>
<body>
<h3>欢迎${username},在线人数${onlinecount}人</h3>
<a href="user/exit">[退出系统]</a>
<script type="text/javascript">
function del(dno){
var ok = window.confirm("亲,删了不可恢复哦!");
if(ok){
/*注意html的base标签可能对JS代码不起作用。所以JS代码最好前面写上"/oa" */
document.location.href = "${pageContext.request.contextPath}/dept/delete?deptno=" + dno;
}
}
</script>
<h1 align="center">部门列表</h1>
<hr >
<table border="1px" align="center" width="50%">
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>部门编号</th>
<th>部门名称</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${deptList}" varStatus="deptStatus" var="dept">
<tr>
<td>${deptStatus.count}</td>
<td>${dept.deptno}</td>
<td>${dept.dname}</td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:void(0)" onclick="del(${dept.deptno})">删除</a>
<a href="dept/detail?f=edit&dno=${dept.deptno}">修改</a>
<a href="dept/detail?f=detail&dno=${dept.deptno}">详情</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
<hr >
<a href="add.jsp">新增部门</a>
</body>
</html>




