nest学习(5)
前端监控 RabbitMQ
前端监控系统是采集 用户端的异常,性能,业务埋点等数据上班,在服务端坐存储,并支持可视化分析的平台。
用户量大,采集的数据可能会比较多,服务端并发压力也会上升,要是直接存入数据库,数据库服务可能会崩掉。

要怎么保证面对大量并发请求的时候,服务不崩呢?
答案就是消息队列,比如常用的RabbitMQ

第一个web服务接受请求,将消息存入RabbiMQ,然后另一个web服务从MQ中取出消息存入数据库。
MQ的并发量比数据库高很多。

10w的消息进来,每次只取1k条数据来消费,这就是MQ的流量削峰功能。
而且可以多加几个web服务来同时消费MQ的消息

用docker跑一个MQ服务

import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
await channel.assertQueue('aaa');
await channel.sendToQueue('aaa',Buffer.from('hello'))
amqplib是rabbitmq的node客户端,上面代码链接了mq服务,
创建了一个aaa的队列,并向队列中发送了一个消息。
在管理界面就可以看到这个消息了

然后来消费他
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
const { queue } = await channel.assertQueue('aaa');
channel.consume(queue, msg => {
console.log(msg.content.toString())
}, { noAck: true });
assertQueue 是如果没有就创建队列,有的话就直接返回。
打印出就是hello。
模拟一下流量削峰功能。
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
await channel.assertQueue('aaa', {durable: false});
let i = 1;
setInterval(async () => {
const msg = 'hello' + i;
console.log('发送消息:', msg);
await channel.sendToQueue('aaa',Buffer.from(msg))
i++;
}, 500);
没0.5s向aaa队列发送消息。
然后
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
const { queue } = await channel.assertQueue('aaa');
channel.prefetch(3);
const currentTask = [];
channel.consume(queue, msg => {
currentTask.push(msg);
console.log('收到消息:', msg.content.toString());
}, { noAck: false });
setInterval(() => {
const curMsg = currentTask.pop();
channel.ack(curMsg);
}, 1000);
消费者每1s处理一条消息。
每条消息消费者要确认之后才会在MQ里删除,noACK为false表示不自动确认。
上述把收到的消息放入数组中,一秒确认一次。
prefetch为3表示最多并发处理3条。


生产者每0.5s网往队列发送一条消息,而消费者一开始取出三条,然后每处理完一条取一条,保证最多并发处理3条。这就是流量削峰的功能。
不同服务之间的速度差异可以通过MQ缓冲。

Connection是连接,但不会每用一次 rabbitmq 就创建一个单独的 Connection,而是在一个 Connection 里做一下划分,叫做 Channel,每个 Channel 做自己的事情。
Queue 就是两端存取消息的地方了。
整个接收消息和转发消息的服务就叫做 Broker。
Exchange,我们前面的例子没有用到,这个是把消息放到不同的队列里用的,叫做交换机。
前面的例子,生产者和消费者都是一对一的情况,指定从哪个队列读取数据,那如果是一对多场景呢?
不能一个一个调用sendQueue发消息,而是需要一个Exchange,来帮我们把消息按照规则放入不同的queue工作。
Exchange一共有四种
- fanout:把消息放到这个交换机的所有 Queue
- direct:把消息放到交换机的指定 key 的队列
- topic:把消息放到交换机的指定 key 的队列,支持模糊匹配
- headers:把消息放到交换机的满足某些 header 的队列
direct
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
await channel.assertExchange('direct-test-exchange', 'direct');
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange', 'aaa', Buffer.from('hello1'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange', 'bbb', Buffer.from('hello2'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange', 'ccc', Buffer.from('hello3'));
这里i我们创建一个exchange,然后调用publish往这个exchange发送消息。第二个参数是rouing kye,也就是消息路由到哪个队列。

包括 exchange 下的两个 queue 以及各自的 routing key。
然后创建两个消费者
1
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
const { queue } = await channel.assertQueue('queue1');
await channel.bindQueue(queue, 'direct-test-exchange', 'aaa');
channel.consume(queue, msg => {
console.log(msg.content.toString())
}, { noAck: true });
2
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
const { queue } = await channel.assertQueue('queue2');
await channel.bindQueue(queue, 'direct-test-exchange', 'bbb');
channel.consume(queue, msg => {
console.log(msg.content.toString())
}, { noAck: true });
通过bindQueue绑定到交换机上,然后指定路由key分别是aaa和bbb然后执行

分别读取到了。
topic支持key模糊匹配
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
await channel.assertExchange('direct-test-exchange2', 'topic');
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange2', 'aaa.1', Buffer.from('hello1'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange2', 'aaa.2', Buffer.from('hello2'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange2', 'bbb.1', Buffer.from('hello3'));
消费者可以通过
import * as amqp from 'amqplib'
const connect = await amqp.connect(`amqp://localhost:5672`);
const channel = await connect.createChannel();
await channel.assertExchange('direct-test-exchange2', 'topic');
const { queue } = await channel.assertQueue('queue1');
await channel.bindQueue(queue, 'direct-test-exchange2', 'aaa.*');
channel.consume(queue, msg => {
console.log(msg.content.toString())
}, { noAck: true });
aaa.*来匹配所有的aaa的routing key。
fanout
往所有的queue中发送消息,指定了key也没用
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange3', '', Buffer.from('hello1'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange3', '', Buffer.from('hello2'));
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange3', '', Buffer.from('hello3'));
headers
不是根据routing key来制定,而是通过headers
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange4', '', Buffer.from('hello1'), {
headers: {
name: 'guang'
}
});
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange4', '', Buffer.from('hello2'), {
headers: {
name: 'guang'
}
});
channel.publish('direct-test-exchange4', '', Buffer.from('hello3'), {
headers: {
name: 'dong'
}
});
消费
await channel.bindQueue(queue, 'direct-test-exchange4', '', {
name: 'guang'
});
也是指定header。
小结
rabbimq解决了什么问题
- 流量削峰,把大流量的消息放到mq,按照一定流量上限慢慢消费。虽然慢点,但不会崩溃
- 应用解耦,应用之间不再直接依赖,某个应用挂掉了,也可以再恢复后继续从mq中消费消息。
前端监控系统的后端服务,就很适合使用 mq 来做流量削峰。
当一对多的时候,还要加一个 Exchange 交换机来根据不同的规则转发消息:
- direct 交换机:根据 routing key 转发消息到队列
- topic 交换机:根据 routing key 转发消息到队列,支持模糊匹配
- headers 交换机:根据 headers 转发消息到队列
- fanout 交换机:广播消息到交换机下的所有队列
消费者可以通过prefetch设置并发上线,保证不会并发过高而崩溃。
基于Redis实现关注关系。
在抖音,知乎,掘金等平台,可以关注其他用户,也可以被其他用户关注,如果彼此关注,就会标出互相关注。
这些一般是用redis的Set实现的。
Set是集合,有很多命令
SADD:添加元素
SMEMBERS:查看所有元素
SISMEMBER:某个 key 是否在集合中
SCARD:集合中某个 key 的元素数量
SMOVE:移动元素从一个集合到另一个集合
SDIFF:两个集合的差集
SINTER:两个集合的交集
SUNION:两个集合的并集
SINTERSTORE:两个集合的交集,存入新集合
SUNIONSTORE:两个集合的并集,存入新集合
SDIFFSTORE:两个集合的差集,存入新集合
关注关系的redis实现思路
张三的userId是1,然后用一个set集合存储他的关注者,followers:1。再用一个集合存储他关注的人:following:1
那么相互关注就是两个集合的交警结果,存入心集合,比如follow-each-other:1
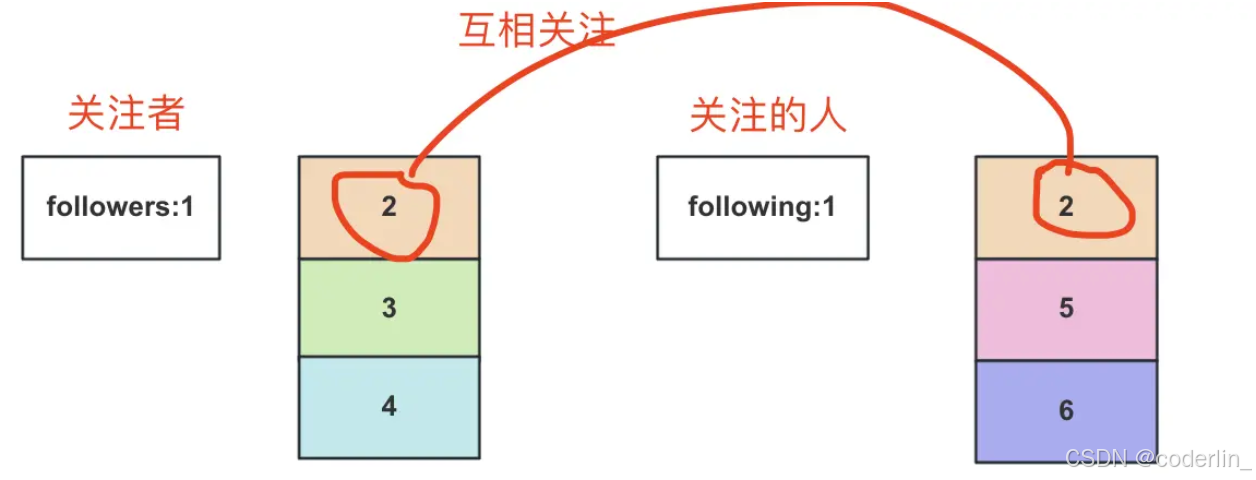
返回关注者或者关注的人的时候,用SISMEMBER判断用户是否在交集之中,是的话,就返回特殊标识,标记互相关注。
代码实现
创建Redis Module
import { Global, Module } from '@nestjs/common';
import { createClient } from 'redis';
import { RedisService } from './redis.service';
@Global()
@Module({
providers: [
RedisService,
{
provide: 'REDIS_CLIENT',
async useFactory() {
const client = createClient({
socket: {
host: 'localhost',
port: 6379
}
});
await client.connect();
return client;
}
}
],
exports: [RedisService]
})
import { Inject, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { RedisClientType } from 'redis';
@Injectable()
export class RedisService {
@Inject('REDIS_CLIENT')
private redisClient: RedisClientType;
async sAdd(key: string, ...members: string[]) {
return this.redisClient.sAdd(key, members);
}
async sInterStore(newSetKey: string, set1: string, set2: string) {
return this.redisClient.sInterStore(newSetKey, [set1, set2]);
}
async sIsMember(key: string, member: string) {
return this.redisClient.sIsMember(key, member);
}
async sMember(key: string) {
return this.redisClient.sMembers(key);
}
async exists(key: string) {
const result = await this.redisClient.exists(key);
return result > 0
}
}
封装 SADD、SINTERSTORE、SISMEMBER、SMEMBER 命令,分别用来往集合中添加元素,求两个集合的交集创建新集合,判断元素是否在某个集合中、返回集合中的所有元素。
还有 EXISTS 用来判断某个 key 是否存在,返回 1 代表存在,返回 0 代表不存在。
然后
@Inject(RedisService)
redisService: RedisService;
// 传入userId,查询对应的User信息返回
async findUserByIds(userIds: string[] | number[]) {
let users = [];
for(let i = 0; i< userIds.length; i ++) {
const user = await this.entityManager.findOne(User, {
where: {
id: +userIds[i]
}
});
users.push(user);
}
return users;
}
// 获取集合关系
async getFollowRelationship(userId: number) {
// 判断该集合是否存在
const exists = await this.redisService.exists('followers:' + userId);
if(!exists) {
// 查处用户
const user = await this.entityManager.findOne(User, {
where: {
id: userId
},
relations: ['followers', 'following']
});
// 如果关注和被关注有一个为空,就不存在互相关注。
if(!user.followers.length || !user.following.length) {
return {
followers: user.followers,
following: user.following,
followEachOther: []
}
}
// 往followers集合添加所有关注他的人
await this.redisService.sAdd('followers:' + userId, ...user.followers.map(item => item.id.toString()));
// 往following结集合天啊急所有他关注的人
await this.redisService.sAdd('following:' + userId, ...user.following.map(item => item.id.toString()))
// 创建并集。
await this.redisService.sInterStore('follow-each-other:' + userId, 'followers:' + userId, 'following:' + userId);
// 获取所有交集中的人
const followEachOtherIds = await this.redisService.sMember('follow-each-other:' + userId);
// 获取所有交集中的人的信息
const followEachOtherUsers = await this.findUserByIds(followEachOtherIds);
// 返回,根据followEachOther即可判断是否是互相关注的人
return {
followers: user.followers,
following: user.following,
followEachOther: followEachOtherUsers
}
} else {
// 如果集合存在了,只需要拿出集合的用户id,然后获取对应的用户信息返回即可。
const followerIds = await this.redisService.sMember('followers:' + userId);
const followUsers = await this.findUserByIds(followerIds);
const followingIds = await this.redisService.sMember('following:' + userId);
const followingUsers = await this.findUserByIds(followingIds);
const followEachOtherIds = await this.redisService.sMember('follow-each-other:' + userId);
const followEachOtherUsers =await this.findUserByIds(followEachOtherIds);
return {
followers: followUsers,
following: followingUsers,
followEachOtherUsers: followEachOtherUsers
}
}
}
使用
@Get('follow-relationship')
async followRelationShip(@Query('id') id: string) {
if(!id) {
throw new BadRequestException('userId 不能为空');
}
return this.userService.getFollowRelationship(+id);
}

李四是互相关注的人。
Redis也可以看到这三个集合

有了新的关注者,就需要更新集合信息。
async follow(userId: number, userId2: number){
const user = await this.entityManager.findOne(User, {
where: {
id: userId
},
relations: ['followers', 'following']
});
const user2 = await this.entityManager.findOne(User, {
where: {
id: userId2
}
});
user.followers.push(user2);
await this.entityManager.save(User, user);
// 判断该集合是否存在
const exists = await this.redisService.exists('followers:' + userId);
if(exists) {
// 存在,更新followers中的信息
await this.redisService.sAdd('followers:' + userId, userId2.toString());
// 更新follow-each-other的信息
await this.redisService.sInterStore('follow-each-other:' + userId, 'followers:' + userId, 'following:' + userId);
}
// 判断userId2是否也有following
const exists2 = await this.redisService.exists('following:' + userId2);
if(exists2) {
//有的话,往user2的followinguser1
await this.redisService.sAdd('following:' + userId2, userId.toString());
// 更新user2的follow-each-other
await this.redisService.sInterStore('follow-each-other:' + userId2, 'followers:' + userId2, 'following:' + userId2);
}
}
这里user1和user2的集合都要查询更新下。
- 在 mysql 里用中间表来存储 user 和 user 的关系。
- 互相关注用redis的Set实现,把user的followers和following存储到集合中。
- 取出交集,放入一个新的集合,该集合就是互相关注的人
- 当有新的关注和取消关注的时候,除了更新数据库,也顺便更新下redis。
基于redis实现排行榜
生活中很多排行榜,比如微信步数,热搜等。如果用mysql做,加一个排序字段,这样效率很低,mysql的读写性能比redis低很多,而且排序依据可能只是一个临时数据,不需要存在数据库里。
一般涉及到排行榜,都使用Redis来做,因为他有一个专为排行榜准备的数据结构,有序集合ZSET。
涉及命令:
ZADD:往集合中添加成员
ZREM:从集合中删除成员
ZCARD:集合中的成员个数
ZSCORE:某个成员的分数
ZINCRBY:增加某个成员的分数
ZRANK:成员在集合中的排名
ZRANGE:打印某个范围内的成员
ZRANGESTORE:某个范围内的成员,放入新集合
ZCOUNT:集合中分数在某个返回的成员个数
ZDIFF:打印两个集合的差集
ZDIFFSTORE:两个集合的差集,放入新集合
ZINTER:打印两个集合的交集
ZINTERSTORE:两个集合的交集,放入新集合
ZINTERCARD:两个集合的交集的成员个数
ZUNION:打印两个集合的并集
ZUNIONSTORE:两个集合的并集,放回新集合
ZUNIONSTORE,并集然后放入新集合,此时相同key的分数会相加,月榜就是周榜的合并,年榜就是月榜的合并。
用nest实现类似排行榜功能。
新建RedisModule,上面有。
针对ZSet新建方法。
import { Inject, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import { RedisClientType } from 'redis';
@Injectable()
export class RedisService {
@Inject('REDIS_CLIENT')
private redisClient: RedisClientType;
// 打印集合成员
async zRankingList(key: string, start: number = 0, end: number = -1) {
const keys = await this.redisClient.zRange(key, start, end, {
REV: true
});
const rankingList = {};
for(let i = 0; i< keys.length; i++){
rankingList[keys[i]] = await this.zScore(key, keys[i]);
}
return rankingList;
}
async zAdd(key: string, members: Record<string, number>) {
const mems = [];
for(let key in members) {
mems.push({
value: key,
score: members[key]
});
}
return await this.redisClient.zAdd(key, mems);
}
// 查询某个成员分数
async zScore(key: string, member: string) {
return await this.redisClient.zScore(key, member);
}
async zRank(key: string, member: string) {
return await this.redisClient.zRank(key, member);
}
async zIncr(key: string, member: string, increment: number) {
return await this.redisClient.zIncrBy(key, increment, member)
}
async zUnion(newKey: string, keys: string[]) {
if(!keys.length) {
return []
};
if(keys.length === 1) {
return this.zRankingList(keys[0]);
}
await this.redisClient.zUnionStore(newKey, keys);
return this.zRankingList(newKey);
}
async keys(pattern: string) {
return this.redisClient.keys(pattern);
}
}
实现排行模块RankingSerice
import { RedisService } from './../redis/redis.service';
import { Inject, Injectable } from '@nestjs/common';
import * as dayjs from 'dayjs';
@Injectable()
export class RankingService {
@Inject(RedisService)
redisService: RedisService;
private getMonthKey() {
const dateStr = dayjs().format('YYYY-MM');
return `learning-ranking-month:${dateStr}`;
}
private getYearKey() {
const dateStr = dayjs().format('YYYY');
return `learning-ranking-year:${dateStr}`;
}
// 增加key
async join(name: string) {
await this.redisService.zAdd(this.getMonthKey(), { [name]: 0 });
}
// 增加 分数
async addLearnTime(name:string, time: number) {
await this.redisService.zIncr(this.getMonthKey(), name, time);
}
// 获取月榜前10
async getMonthRanking() {
return this.redisService.zRankingList(this.getMonthKey(), 0, 10);
}
// 获取年榜,先获取redis中的当年的所有月份,然后创建新的集合返回。
async getYearRanking() {
const dateStr = dayjs().format('YYYY');
const keys = await this.redisService.keys(`learning-ranking-month:${dateStr}-*`);
return this.redisService.zUnion(this.getYearKey(), keys);
}
}
月份的榜单就是 learning-ranking-mongth:2024-01、learning-ranking-mongth:2024-02 的格式
年份就是 learning-ranking-mongth:2023、learning-ranking-mongth:2024
年份的榜单是拿到用 learning-ranking-month:当前年份- 开头的所有 zset,也就是每个月,然后合并返回。
加一下controller
import { Controller, Get, Inject, Query } from '@nestjs/common';
import { RankingService } from './ranking.service';
@Controller('ranking')
export class RankingController {
@Inject(RankingService)
rankingService: RankingService;
// 加入成员
@Get('join')
async join(@Query('name') name: string) {
await this.rankingService.join(name);
return 'success';
}
// 增加时长
@Get('learn')
async addLearnTime(@Query('name') name:string, @Query('time') time: string) {
await this.rankingService.addLearnTime(name, parseFloat(time));
return 'success';
}
// 获取月份榜单
@Get('monthRanking')
async getMonthRanking() {
return this.rankingService.getMonthRanking();
}
// 获取年份榜单
@Get('yearRanking')
async getYearRanking() {
return this.rankingService.getYearRanking();
}
}
调用相关接口就行了
微服务实战项目-考试系统(问卷星)


nacos做注册配置中心,统一管理所有的配置,服务的注册地址。rabbitMq做消息队列,用于微服务之间的异步通信。
根据上述模块,拆分为四个微服务

数据库表

考试表跟用户表是多对一的关系,一个用户可以创建多个考试,但是一个考试只能由一个用户创建。
答卷表跟用户表示多对一关系。
答卷表跟考试表是多对一关系。
user
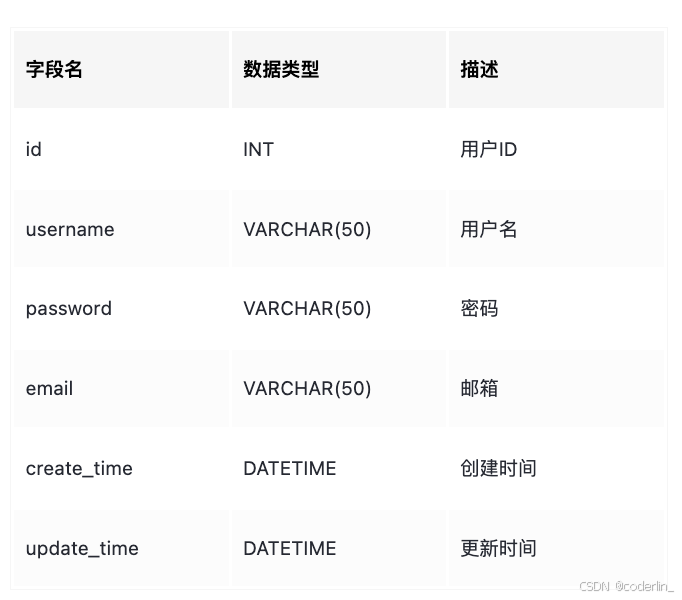
考试表

答卷表

然后是模块划分,分别为用户模块,
用户模块使用github登陆即可。
/user/login POST 用户登录,用户github跳转回来拿到token再继续拿用户信息保存到数据库。
试卷模块

答卷模块

分析模块

