【算法题解答·六】栈队列堆
【算法题解答·六】栈队列堆
接上文【算法方法总结·六】栈队列堆的一些技巧和注意事项
栈队列堆相关题目如下:
232.用栈实现队列 简单
- 准备两个栈,一个负责入队的栈
A,一个负责出队的栈B - 出队和返回队列开头元素,都要先进行以下操作:如果
B为空,则A中的元素全部放到B中
class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stackIn;
Stack<Integer> stackOut;
public MyQueue() { // 初始化栈
stackIn = new Stack<>(); // 负责进队
stackOut = new Stack<>(); // 负责出队
}
public void push(int x) { // 入队
stackIn.push(x);
}
public int pop() { // 出队并返回元素
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.pop();
}
public int peek() { // 返回队列开头的元素
dumpstackIn();
return stackOut.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return stackIn.isEmpty() && stackOut.isEmpty();
}
// 如果stackOut为空,则stackIn中的元素全部放到stackOut中
public void dumpstackIn() {
if (!stackOut.isEmpty())
return;
while (!stackIn.isEmpty()) {
stackOut.push(stackIn.pop());
}
}
}
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 逆波兰表达式:是一种后缀表达式,所谓后缀就是指运算符写在后面。
- 平常使用的算式则是一种中缀表达式,如
(1+2)*(3+4)。 - 其逆波兰表达式为
((1 2+)(3 4+)*) - 适合用栈操作运算:遇到数字则入栈;遇到运算符则取出栈顶两个数字进行计算,并将结果压入栈中
class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
for (String s : tokens) {
if (s.equals("+")) { // 符号,取出两数进行运算,再压入栈中
deque.push(deque.pop() + deque.pop());
} else if (s.equals("-")) {
deque.push(-deque.pop() + deque.pop());
} else if (s.equals("*")) {
deque.push(deque.pop() * deque.pop());
} else if (s.equals("/")) {
int t1 = deque.pop();
int t2 = deque.pop();
deque.push(t2 / t1);
} else { // 数字入栈
deque.push(Integer.valueOf(s));
}
}
return deque.pop();
}
}
239. 滑动窗口最大值 困难

为什么队列用来存下标,是因为需要判断队首元素是否在窗口内
- 使用 由大到小的单调双端队列
- 把比当前元素小的弹出队尾;当前值加入队尾;判断队首元素是否有效;当窗口大于k时,开始记录最大值
class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
Deque<Integer> d = new LinkedList<>();
// 用双端队列存储下标(更方便)
int n = nums.length;
int[] res = new int[n - k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 维护单调性,保证从大到小,前面数小依次弹出
while (!d.isEmpty() && nums[i] >= nums[d.peekLast()]) {
d.pollLast();
}
// 添加当前值对应下标
d.offerLast(i);
// 判断队首元素是否有效,[i - k + 1, i]
if (d.peek() <= i - k) { // 不在范围内
d.poll();
}
// 当窗口长度为k时,保存记录
if (i + 1 >= k) {
res[i - k + 1] = nums[d.peek()];
}
}
return res;
}
}
347.前 K 个高频元素
-
- 要统计元素出现频率
HashMap
- 要统计元素出现频率
-
- 对频率排序
PriorityQueue 小根堆
- 对频率排序
-
- 找出前K个高频元素
class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
// 小根堆
PriorityQueue<int[]> p = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]);
int[] res = new int[k]; // 保存结果
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int n : nums) {
map.put(n, map.getOrDefault(n, 0) + 1);
}
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> x : map.entrySet()) {
int[] tmp = new int[2];
tmp[0] = x.getKey(); // 元素
tmp[1] = x.getValue(); // 出现次数
p.offer(tmp); // (元素,出现次数)
if (p.size() > k) { // 弹出到只有k个元素,剩下的为最小的k个
p.poll();
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
res[i] = p.poll()[0];
}
return res;
}
}
20.有效的括号 简单
- 遇到左括号
( [ {,则让右括号) ] }入栈 - 遇到右括号
) ] },则和 栈顶元素 比较,相同则出栈,最后栈空 说明 有效
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Deque<Character> qu = new LinkedList<>(); // 栈
char[] ss = s.toCharArray();
for (char ch : ss) {
if (ch == '(') qu.push(')');
else if (ch == '[') qu.push(']');
else if (ch == '{') qu.push('}');
// 栈空 或 不等于
else if (qu.isEmpty() || qu.peek() != ch) {
return false;
} else {
qu.pop();
}
}
return qu.isEmpty();
}
}
155.最小栈
- 用一个 最小栈 来存储最小元素
class MinStack {
public Stack<Integer> stack;
public Stack<Integer> min_stack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
min_stack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
stack.push(val);
if(min_stack.isEmpty() || val<=min_stack.peek()){
min_stack.push(val);
}
}
public void pop() {
int x = stack.pop();
if(x==min_stack.peek()){
min_stack.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
return min_stack.peek();
}
}
394.字符串解码
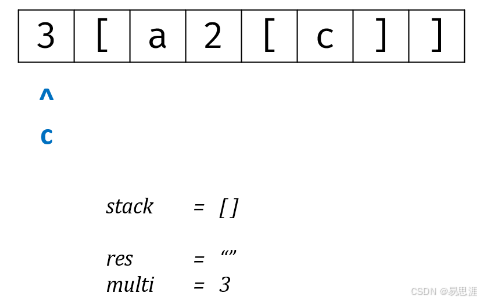
- 情况一:遍历到
[时,说明还不需要计算,乘积、字符串res均入栈 - 情况二:遍历到
]时,说明需要计算,乘积出栈,当前字符*乘积,拼接上字符串出栈 - 情况三:遍历到
0-9时,计算乘积为多少 - 情况四:遍历到
字母时,加入res字符串
class Solution {
public String decodeString(String s) {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
int multi = 0;
Deque<Integer> st_multi = new LinkedList<>(); //乘积栈
Deque<String> st_res = new LinkedList<>(); //字符栈
char[] ss = s.toCharArray();
for (char ch : ss) {
if (ch == '[') { //情况一:遍历到 [ 时,加入栈
st_multi.push(multi); // 乘积入栈
st_res.push(res.toString()); // 字符入栈
multi = 0; // 清0
res = new StringBuilder(); // 清0
} else if (ch == ']') { //情况二:遍历到 ] 时,出栈
StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder();
int cur_multi = st_multi.pop(); //乘积
for (int i = 0; i < cur_multi; i++) {
tmp.append(res);
}
res = new StringBuilder(st_res.pop() + tmp);
} else if (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') { //情况三:遍历到0-9时,计算
multi = multi * 10 + ch - '0';
} else { //情况四:遍历到字母时,res
res.append(ch);
}
}
return res.toString();
}
}
739.每日温度
- 遍历入栈,下一个要入栈的元素更大,则出栈
- 相当于是一个递减栈,即栈里只有递减元素
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Deque<Integer> qu = new LinkedList<>(); // 栈
int len = temperatures.length;
int[] ans = new int[len];
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 遍历入栈,下一个要入栈的元素更大,则出栈
// 栈非空,且栈顶温度<当前温度
while (!qu.isEmpty() && temperatures[qu.peek()] < temperatures[i]) {
int idx = qu.pop();
ans[idx] = i - idx;
}
qu.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
84.柱状图中最大的矩形 困难
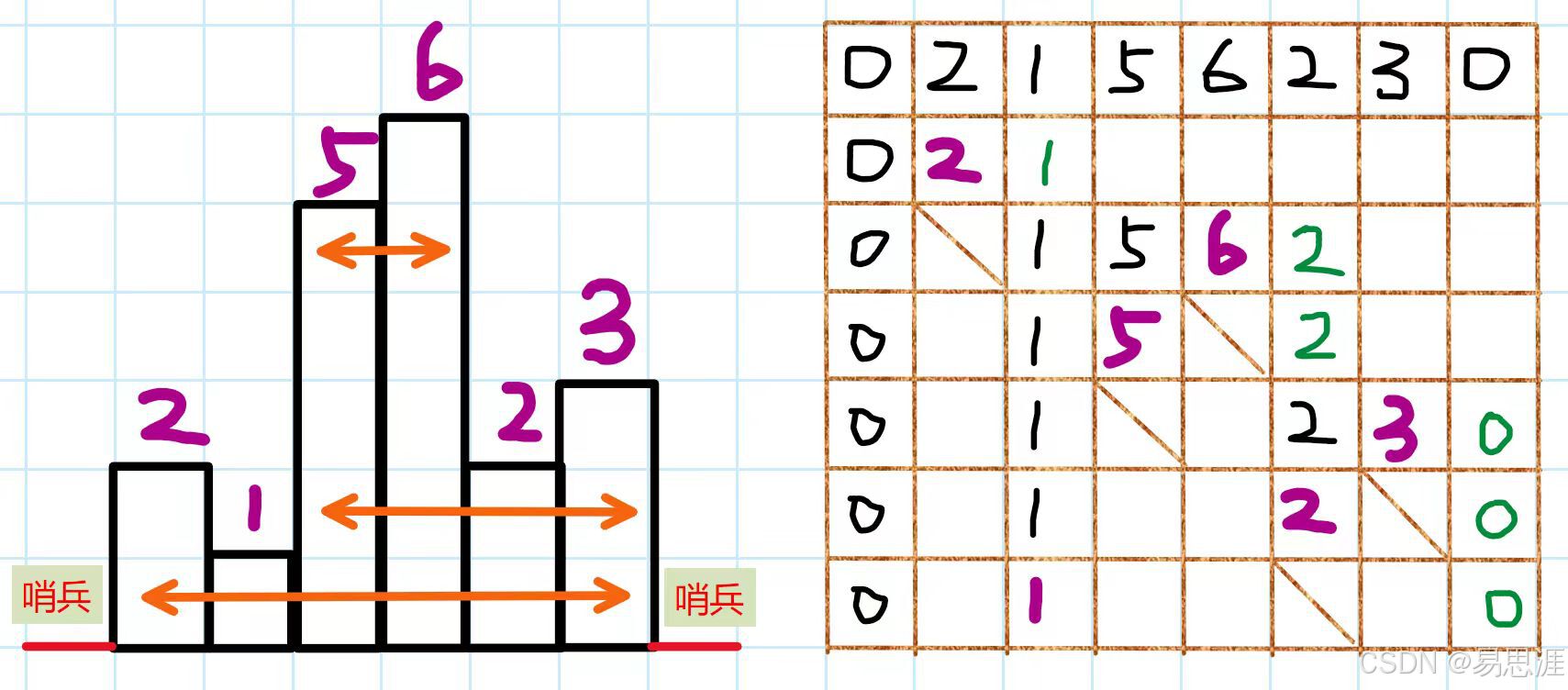
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int len = heights.length;
Deque<Integer> st = new LinkedList<>();
int res = 0;
// 两端各加一哨兵
int[] newHeight = new int[len + 2];
// 数组扩容
newHeight[0] = 0;
newHeight[len + 1] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
newHeight[i + 1] = heights[i];
}
heights = newHeight;
len = heights.length;
st.push(0);
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
// 有更大的,入栈
if (heights[i] >= heights[st.peek()]) {
st.push(i);
} else {
// 下一个准备入栈的元素 < 栈顶,开始计算并出栈
while (heights[i] < heights[st.peek()]) {
int mid = st.pop();
int left = st.peek();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
res = Math.max(res, h * w);
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
215.数组中的第k个最大元素
-
方法一:内置排序
Arrays.sort()时间复杂度O(n log n) -
方法二:快速排序 + 选择
class Solution {
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
List<Integer> numList = new ArrayList<>(); // 数组->链表
for (int num : nums) {
numList.add(num);
}
return quickSelect(numList, k); // 快速排序+选择
}
public int quickSelect(List<Integer> nums, int k) {
// 随机选择哨兵
Random rand = new Random();
int pivot = nums.get(rand.nextInt(nums.size()));
// 划分
List<Integer> big = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> equal = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> small = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (num > pivot)
big.add(num);
else if (num < pivot)
small.add(num);
else
equal.add(num);
}
// 第k大元素在big中,递归划分
if (k <= big.size()) {
return quickSelect(big, k);
}
// 第k大元素在small中,递归划分
if (nums.size() - small.size() < k) {
return quickSelect(small, k - nums.size() + small.size());
}
// 第k大元素在equal中,返回pivot
return pivot;
}
}
295.数据流的中位数 困难
A小根堆 用来保存 较大的一半B大根堆 用来保存 较小的一半
class MedianFinder {
Queue<Integer> A, B;
public MedianFinder() {
A = new PriorityQueue<>(); // 小根堆
B = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> (y - x)); // 大根堆
}
public void addNum(int num) {
if (A.size() != B.size()) { // 再添加后为偶数
A.add(num);
B.add(A.poll());
} else { // 再添加后为奇数
B.add(num);
A.add(B.poll());
}
}
public double findMedian() {
if (A.size() != B.size()) {
return A.peek();
} else {
return (A.peek() + B.peek()) / 2.0;
}
}
}
算法题解答系列
【算法题解答·一】二分法
【算法题解答·二】双指针法
【算法题解答·三】滑动窗口
【算法题解答·四】字符串操作
【算法题解答·五】链表操作
