(五)自然语言处理笔记——迁移学习
(五)自然语言处理笔记——迁移学习
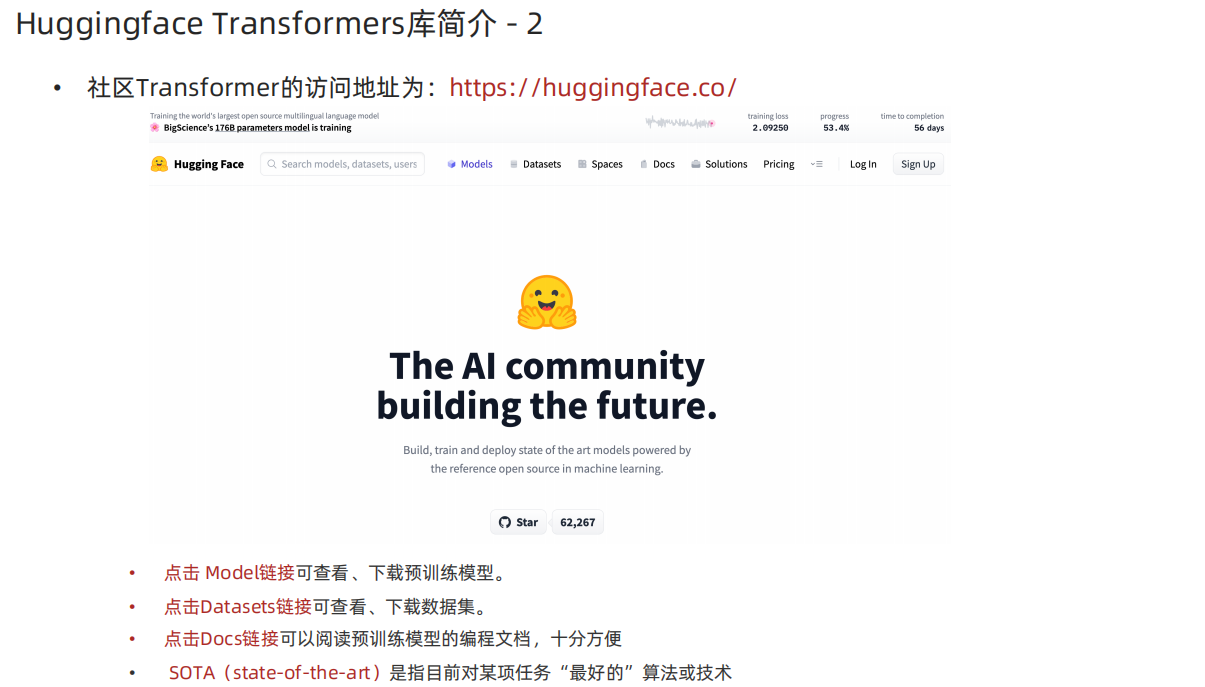
- 迁移学习
- Transformers
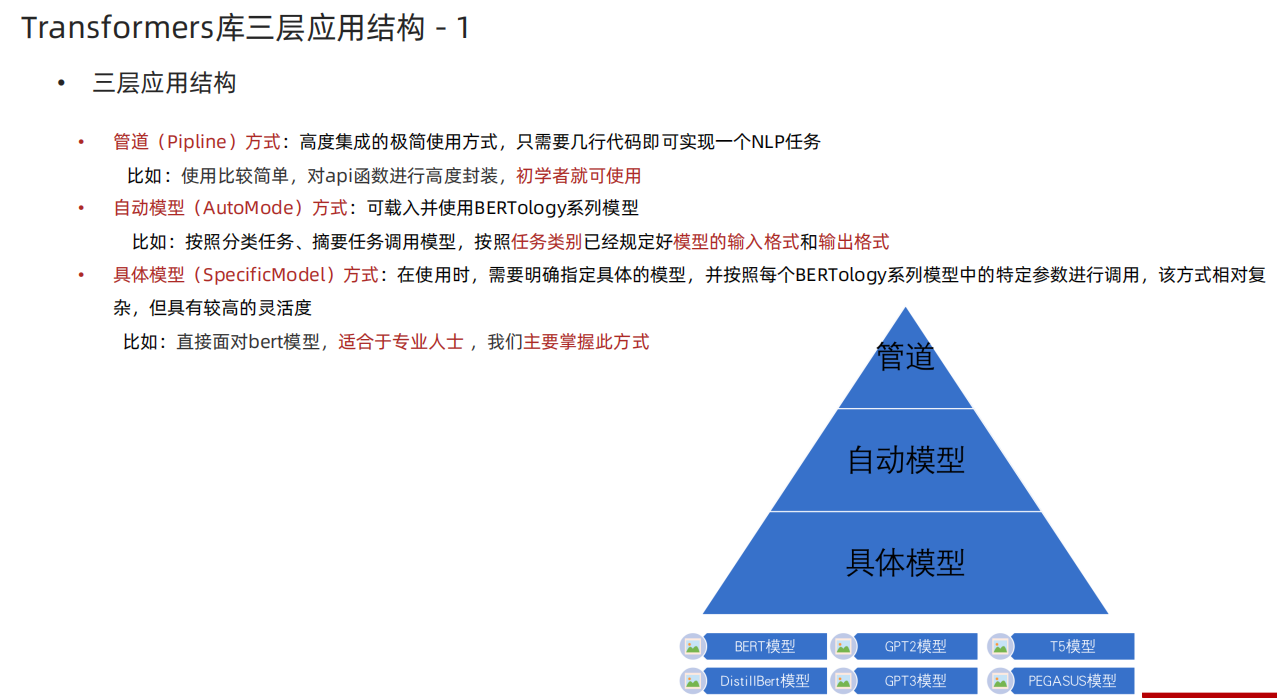
- pipeline—文本分类任务
- pipeline—特征提取任务
- pipeline—完形填空
- pipeline—阅读理解
- pipeline—命名实体的识别
- AutoModel——文本分类
- AutoModel——特征提取
- AutoModel——完形填空
- AutoModel——阅读理解
- AutoModel——文本摘要任务
- AutoModel——命名实体识别
- 直接使用Bert模型
迁移学习





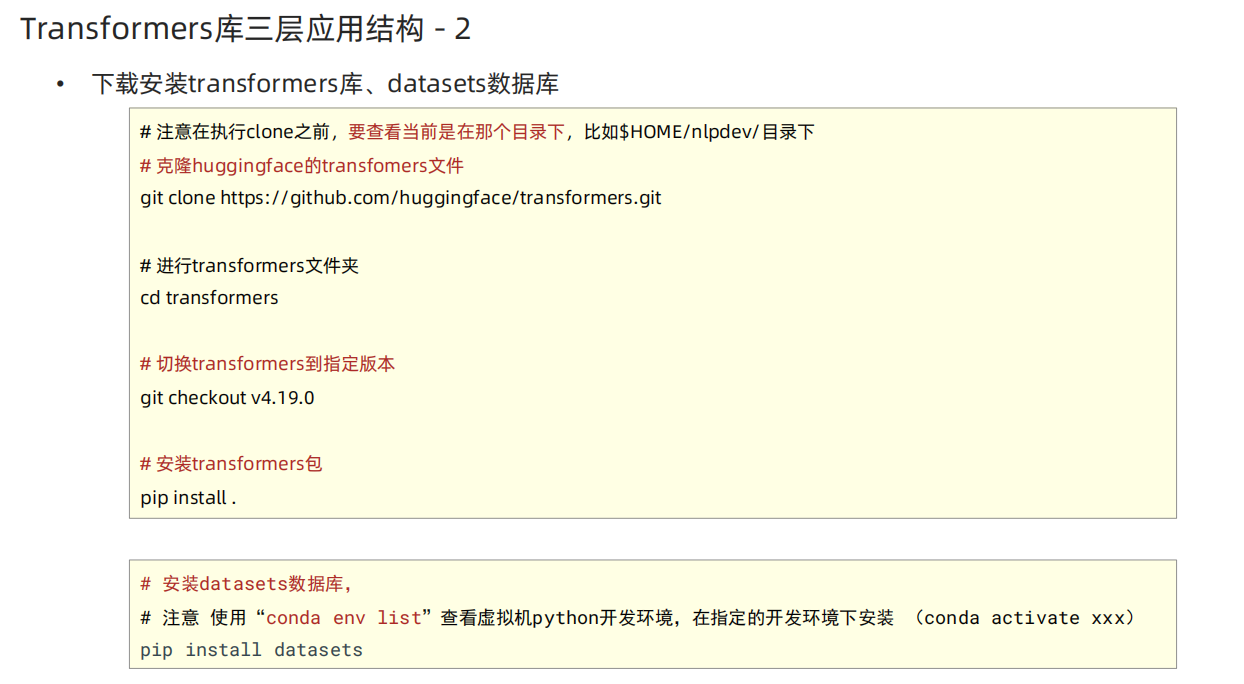
Transformers



pipeline—文本分类任务
pipeline—特征提取任务

pipeline—完形填空

pipeline—阅读理解

pipeline—命名实体的识别


import torch
from transformers import pipeline
import numpy as np# 学习目标
# 1 预训练模型的下载和使用
# 2 自然语言处理基本开发任务的识别
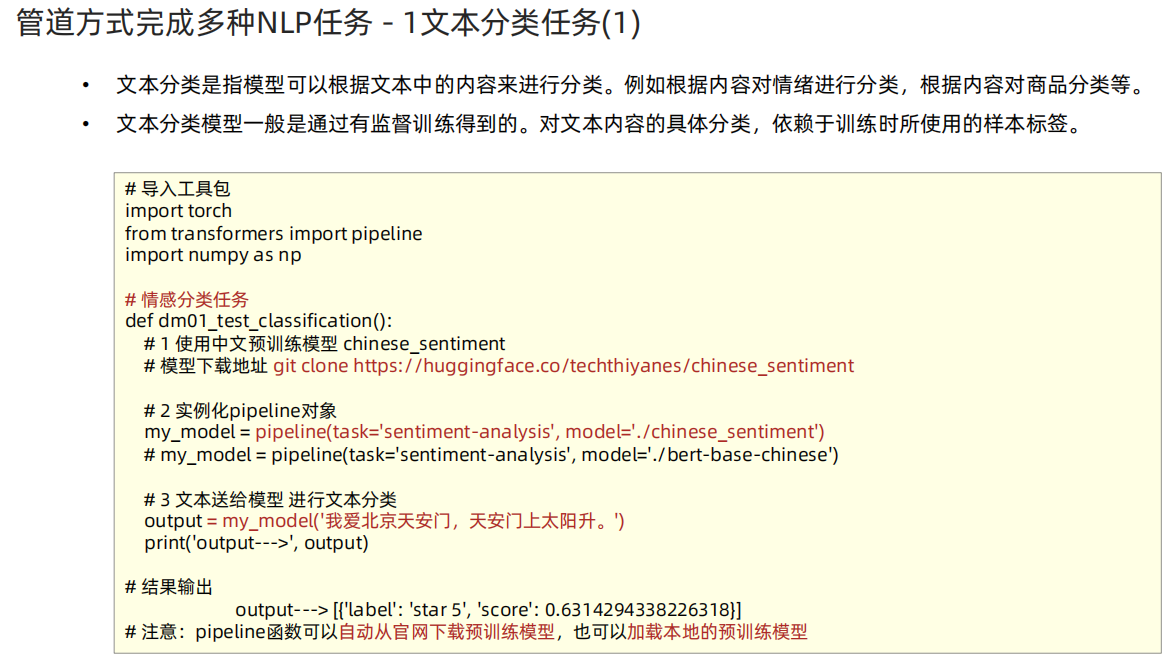
# 3 pipeline方式调用预训练模型# 情感分类任务 实现思路分析 dm_test_classification
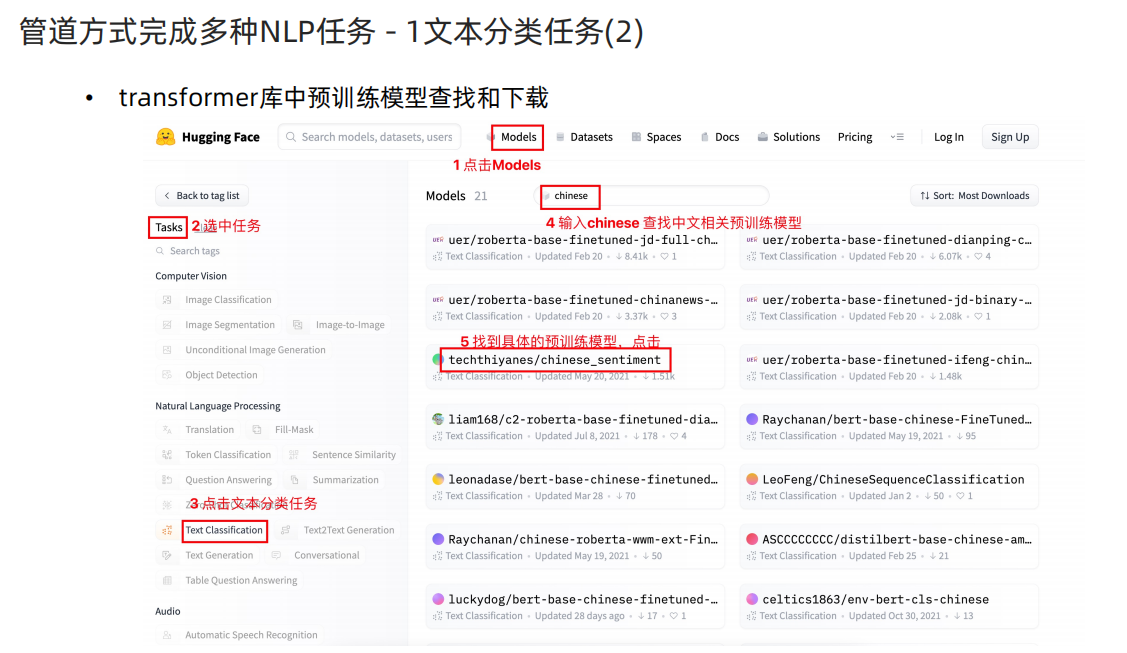
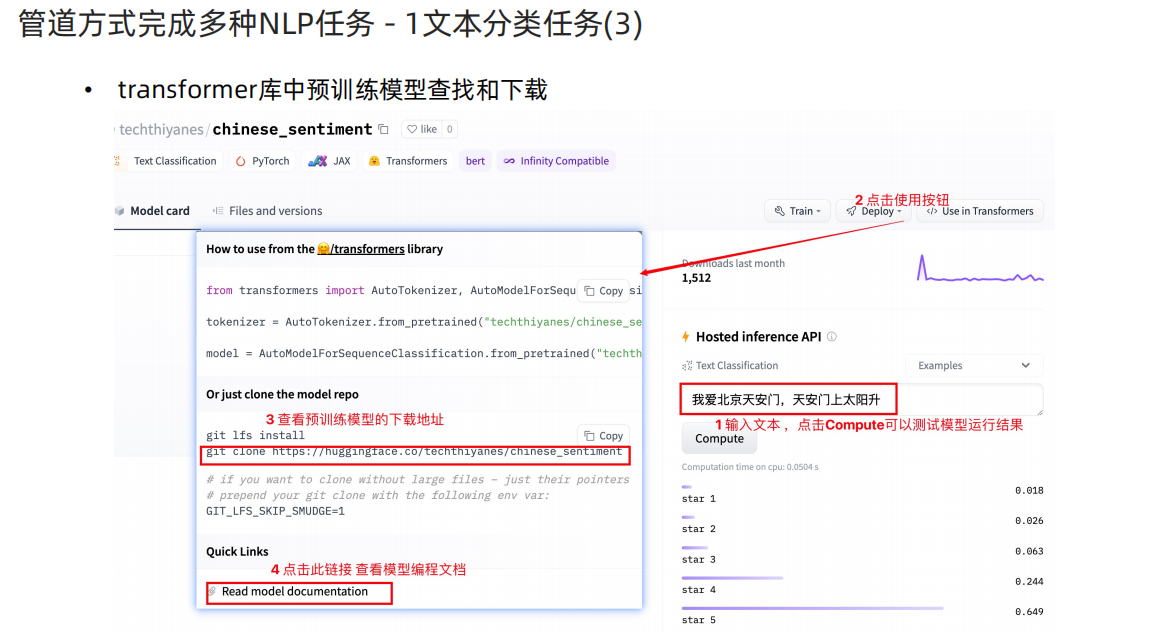
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 chinese_sentiment
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/techthiyanes/chinese_sentiment
# 2 实例化pipeline对象
# my_model = pipeline(task='', model='')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = my_model('xxxx')
def dm01_test_classification():# 1 使用中文预训练模型chinese_sentiment# 如果没有安装git需要: 在linux虚拟机上: git lfs install 注意: linux虚拟机上已经安装好了# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/techthiyanes/chinese_sentiment# 2 实例化pipeline对象# my_model = pipeline(task='sentiment-analysis', model='./bert-base-chinese')my_model = pipeline(task='sentiment-analysis', model='/home/data/project/customer_AAA/NLP/Heima/012_Transformers/bert_base_chinese')# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类output = my_model('我爱北京天安门,天安门上太阳升。')print('output--->', output)# 输出结果# output---> [{'label': 'star 5', 'score': 0.6314294338226318}]# 2 默认模型不支持中文分类# my_model = pipeline(task='sentiment-analysis')# output = my_model('我爱北京天安门,天安门上太阳升。')# print('output--->', output)# No model was supplied, defaulted to distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english# (https://huggingface.co/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english)# 特征提取任务 实现思路分析 dm_test_feature_extraction():
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 bert-base-chinese
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/bert-base-chinese
# 2 实例化pipeline对象
# my_model = pipeline(task='', model='')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = my_model('xxxx')
def dm02_test_feature_extraction():# 1 下载中文预训练模型 git clone https://huggingface.co/bert-base-chinese# 2 实例化pipeline对象 返回模型对象my_model = pipeline(task='feature-extraction', model='/home/data/project/customer_AAA/NLP/Heima/012_Transformers/bert_base_chinese')# 3 给模型送数据 提取语句特征output = my_model('人生该如何起头')print('output--->', type(output), np.array(output).shape)# 输出结果:# [CLS] 人 生 该 如 何 起 头 [SEP]# (1, 9, 768)# output---> <class 'list'> (1, 9, 768)# 注意1:bert基于字的。# 注意2:bert的词典的大小# 注意3:带头任务-分类、阅读理解、完型填空 不带头任务-特征抽取# 完形填空任务 实现思路分析 dm03_test_fill_mask():
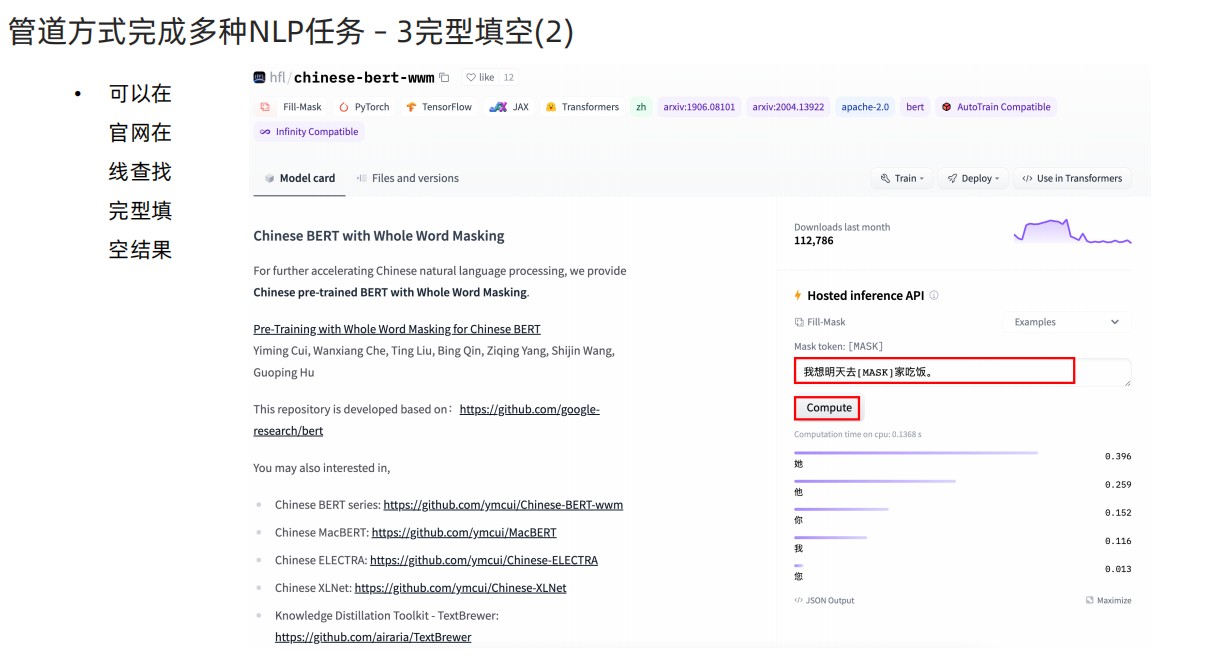
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 chinese-bert-wwm
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/hfl/chinese-bert-wwm 全词模型
# 2 实例化pipeline对象
# my_model = pipeline(task='', model='')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = my_model('xxxx')
def dm03_test_fill_mask():# 1 下载预训练模型 全词模型 git clone https://huggingface.co/hfl/chinese-bert-wwmpath = '/home/data/project/customer_AAA/NLP/Heima/012_Transformers/bert_base_chinese'# 2 实例化pipeline对象 返回一个模型my_model = pipeline(task='fill-mask', model=path)# 3 给模型送数据 做预测input = '我想明天去[MASK]家吃饭。'output = my_model(input)# 4 输出预测结果print('output--->', output)# 输出结果# output---># [{'score': 0.34331339597702026, 'token': 1961, 'token_str': '她', 'sequence': '我 想 明 天 去 她 家 吃 饭.'},# {'score': 0.2533259987831116, 'token': 872, 'token_str': '你', 'sequence': '我 想 明 天 去 你 家 吃 饭.'},# {'score': 0.1874391734600067, 'token': 800, 'token_str': '他', 'sequence': '我 想 明 天 去 他 家 吃 饭.'},# {'score': 0.1273055076599121, 'token': 2769, 'token_str': '我', 'sequence': '我 想 明 天 去 我 家 吃 饭.'},# {'score': 0.02162978984415531, 'token': 2644, 'token_str': '您', 'sequence': '我 想 明 天 去 您 家 吃 饭.'}]# 4 阅读理解任务(抽取式问答) 实现思路分析 dm04_test_question_answering():
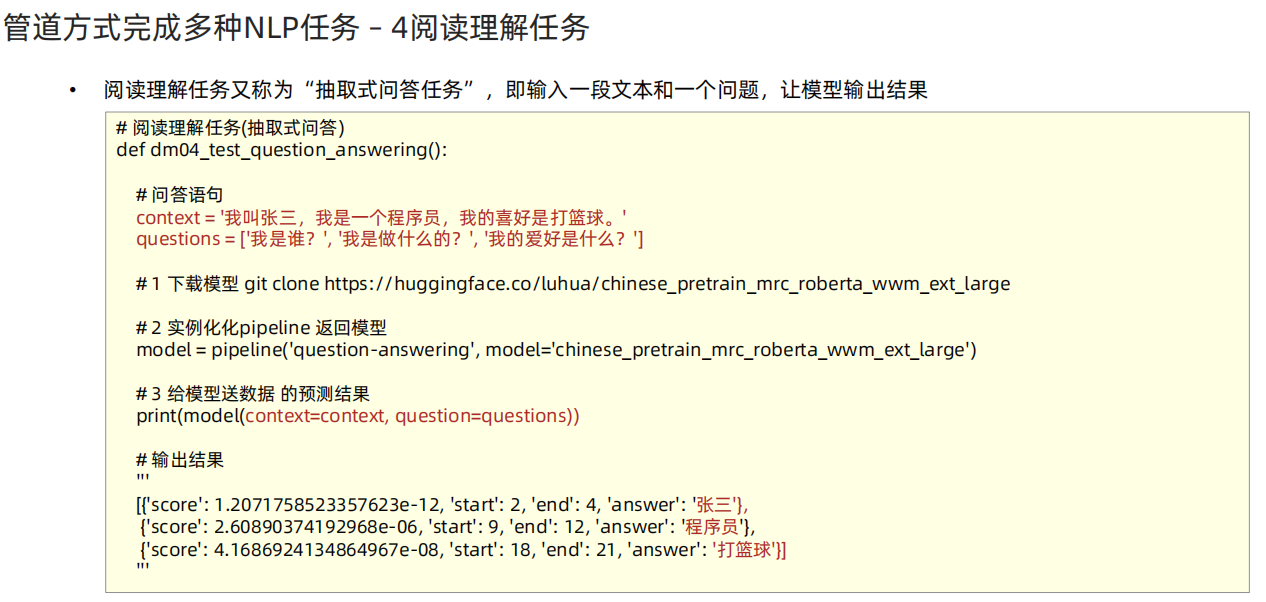
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/luhua/chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large
# 2 实例化pipeline对象
# my_model = pipeline('question-answering', model='./chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = model(context=context, question=questions)
def dm04_test_question_answering():# 问答语句context = '我叫张三,我是一个程序员,我的喜好是打篮球。'questions = ['我是谁?', '我是做什么的?', '我的爱好是什么?']# 1 下载模型 git clone https://huggingface.co/luhua/chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large# 2 实例化化pipeline 返回模型model = pipeline('question-answering', model='luhua/chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large')# 3 给模型送数据 的预测结果print(model(context=context, question=questions))# 输出结果'''[{'score': 1.2071758523357623e-12, 'start': 2, 'end': 4, 'answer': '张三'},{'score': 2.60890374192968e-06, 'start': 9, 'end': 12, 'answer': '程序员'},{'score': 4.1686924134864967e-08, 'start': 18, 'end': 21, 'answer': '打篮球'}]'''# 5 文本摘要 实现思路分析 dm_test_summarization():
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 chinese-bert-wwm
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/sshleifer/distilbart-cnn-12-6
# 2 实例化pipeline对象 返回模型
# my_model = pipeline(task='', model='')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = my_model('xxxx')
def dm05_test_summarization():# 1 下载模型 git clone https://huggingface.co/sshleifer/distilbart-cnn-12-6# 2 实例化pipline 返回模型my_model = pipeline(task = 'summarization', model="./distilbart-cnn-12-6")# 3 准备文本 送给模型text = "BERT is a transformers model pretrained on a large corpus of English data " \"in a self-supervised fashion. This means it was pretrained on the raw texts " \"only, with no humans labelling them in any way (which is why it can use lots " \"of publicly available data) with an automatic process to generate inputs and " \"labels from those texts. More precisely, it was pretrained with two objectives:Masked " \"language modeling (MLM): taking a sentence, the model randomly masks 15% of the " \"words in the input then run the entire masked sentence through the model and has " \"to predict the masked words. This is different from traditional recurrent neural " \"networks (RNNs) that usually see the words one after the other, or from autoregressive " \"models like GPT which internally mask the future tokens. It allows the model to learn " \"a bidirectional representation of the sentence.Next sentence prediction (NSP): the models" \" concatenates two masked sentences as inputs during pretraining. Sometimes they correspond to " \"sentences that were next to each other in the original text, sometimes not. The model then " \"has to predict if the two sentences were following each other or not."output = my_model(text)# 4 打印摘要结果print('output--->', output)# 6 ner 实现思路分析 dm_test_ner()
# 1 使用中文预训练模型 chinese-bert-wwm
# 模型下载地址 git clone https://huggingface.co/uer/roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese
# 2 实例化pipeline对象 返回模型
# my_model = pipeline(task='', model='')
# 3 文本送给模型 进行文本分类
# output = my_model('xxxx')
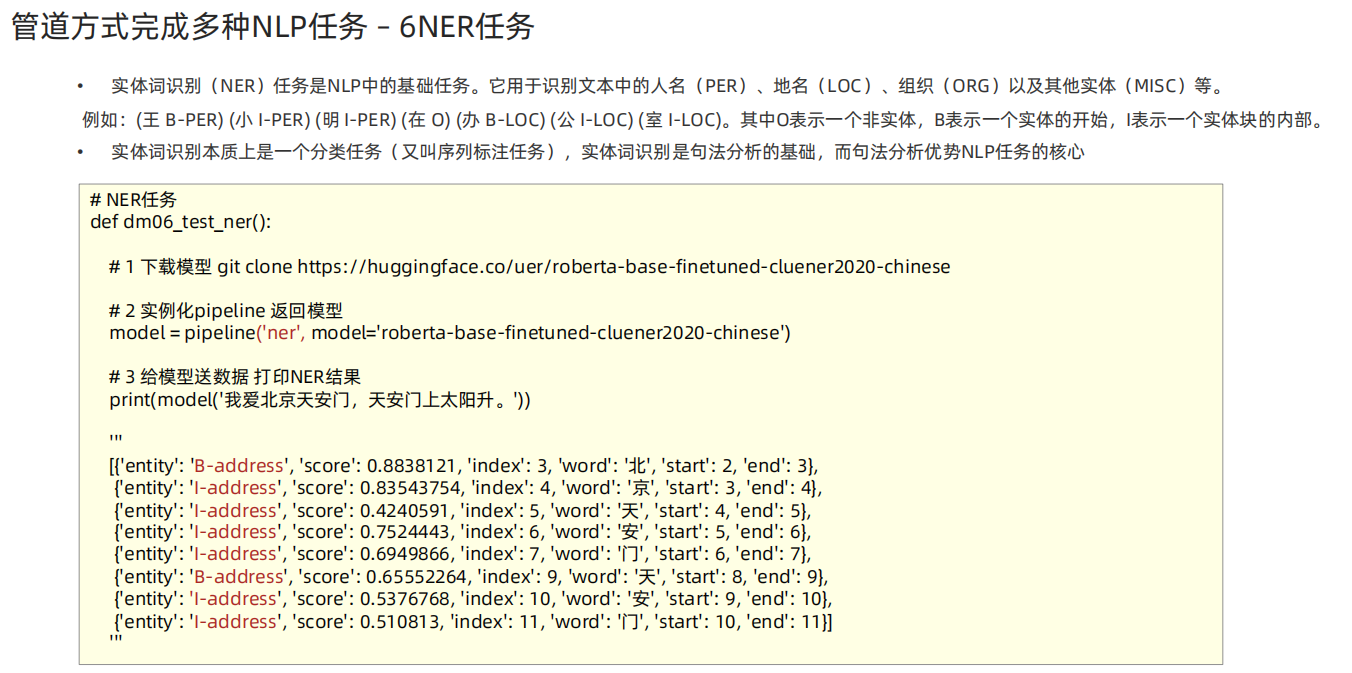
def dm06_test_ner():# 1 下载模型 git clone https://huggingface.co/uer/roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese# 2 实例化pipeline 返回模型model = pipeline('ner', model='./roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese')# 3 给模型送数据 打印NER结果print(model('我爱北京天安门,天安门上太阳升。'))'''[{'entity': 'B-address', 'score': 0.8838121, 'index': 3, 'word': '北', 'start': 2, 'end': 3},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.83543754, 'index': 4, 'word': '京', 'start': 3, 'end': 4},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.4240591, 'index': 5, 'word': '天', 'start': 4, 'end': 5},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.7524443, 'index': 6, 'word': '安', 'start': 5, 'end': 6},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.6949866, 'index': 7, 'word': '门', 'start': 6, 'end': 7},{'entity': 'B-address', 'score': 0.65552264, 'index': 9, 'word': '天', 'start': 8, 'end': 9},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.5376768, 'index': 10, 'word': '安', 'start': 9, 'end': 10},{'entity': 'I-address', 'score': 0.510813, 'index': 11, 'word': '门', 'start': 10, 'end': 11}]'''if __name__ == '__main__':# dm01_test_classification() # 文本分类任务# dm02_test_feature_extraction() # 文本特征提取# dm03_test_fill_mask() # 完形填空dm04_test_question_answering() # 阅读理解# dm05_test_summarization() # 摘要生成# dm06_test_ner()print('pipline方式使用Transformer库 End')passAutoModel——文本分类
AutoModel——特征提取


AutoModel——完形填空

AutoModel——阅读理解


AutoModel——文本摘要任务


AutoModel——命名实体识别


import torch
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoTokenizer
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoModelForMaskedLM, AutoModelForQuestionAnswering# AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM:文本摘要
# AutoModelForTokenClassification:ner
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoModelForTokenClassification# 学习目标
# 1 选用的是什么种类的模型 (eg: 分类模型、阅读理解模型)
# 2 每一种任务模型(eg: 分类模型)的 输入my_input 输出out_input数据格式是什么
# 3 每一种分词器模型的数据格式控制# 情感分类任务 实现思路 chinese_sentiment
# 1 加载 my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('')
# 2 加载模型 my_model AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('./chinese_sentiment')
# 3 文本转张量 my_tokenizer.encode(text,return_tensors,padding,truncation,max_length)
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model.eval() my_model(my_input1)
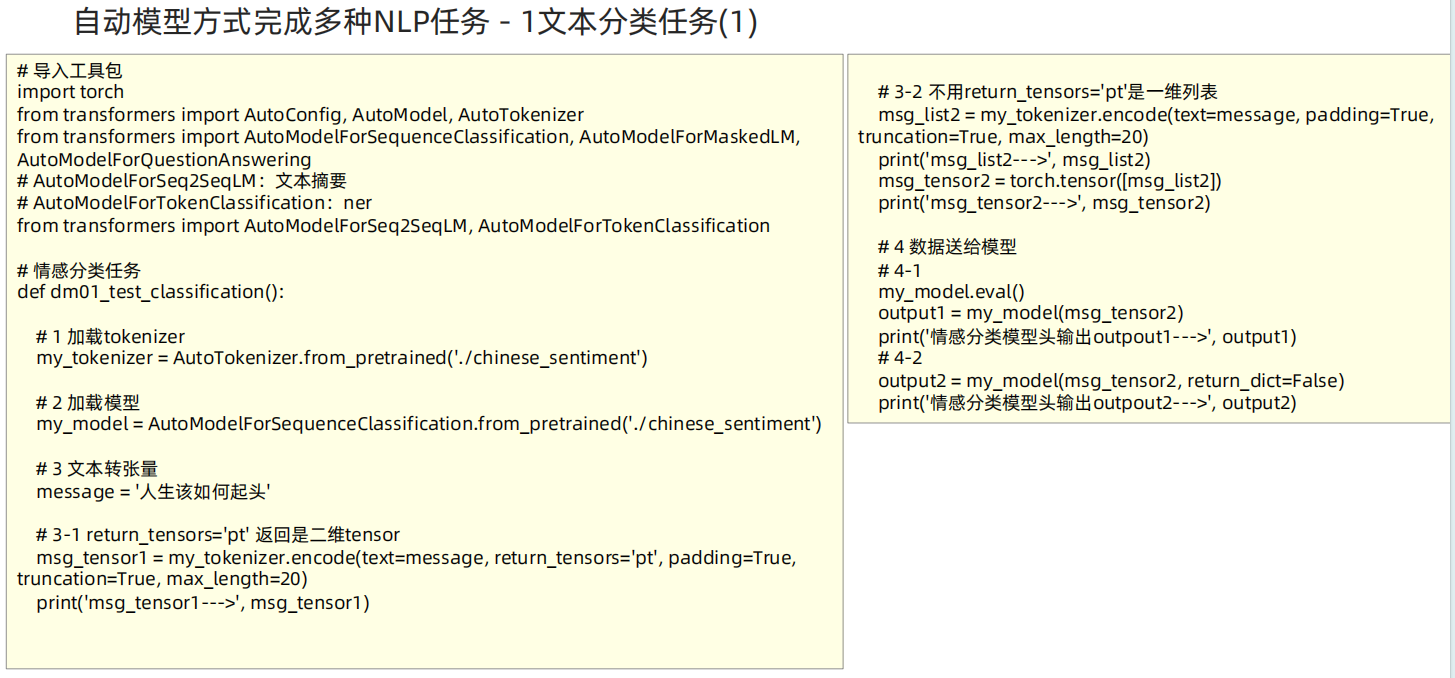
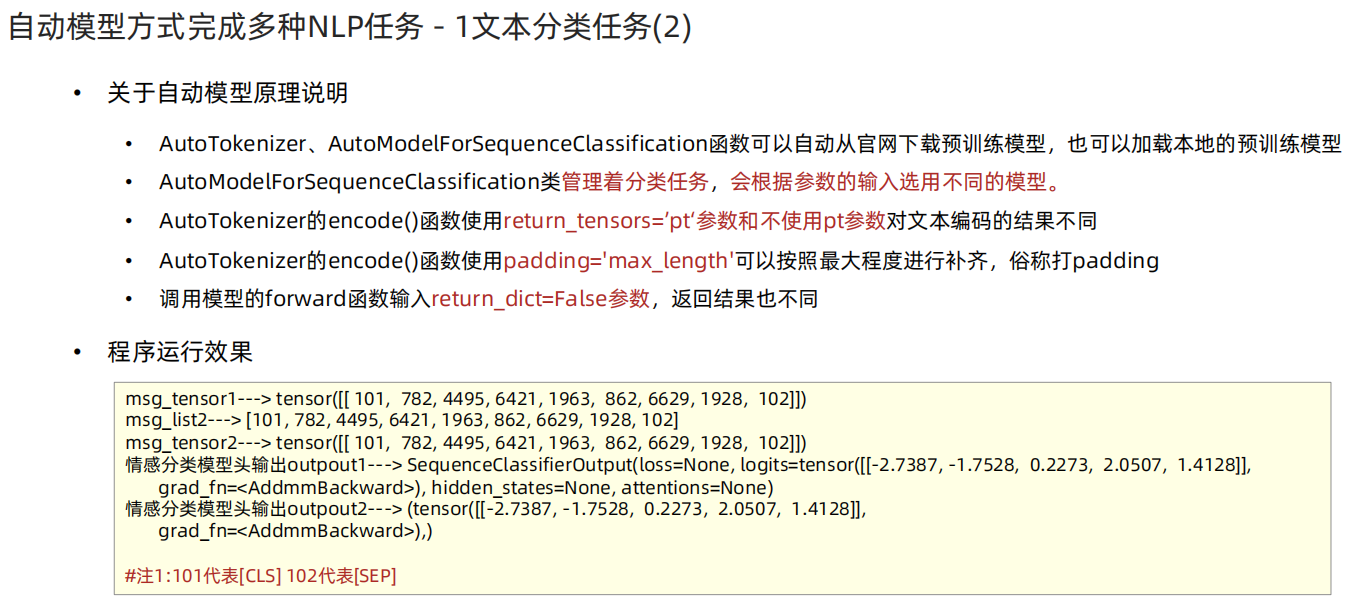
def dm01_test_classification():# 1 加载tokenizermy_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('/home/data/project/customer_AAA/NLP/Heima/012_Transformers/bert_base_chinese')print('my_tokenizer--->', my_tokenizer)# 2 加载模型my_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('/home/data/project/customer_AAA/NLP/Heima/012_Transformers/bert_base_chinese')# print('my_model--->', my_model)# 3 文本转张量message = '人生该如何起头'# 3-1 return_tensors='pt' 返回是二维tensormy_input1 = my_tokenizer.encode(text=message, return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=20)print('my_input1--->', my_input1)# 3-2 不用return_tensors='pt'是一维列表my_input2 = my_tokenizer.encode(text=message, padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=20)print('my_input2--->', my_input2)my_input2 = torch.tensor([my_input2])print('my_input2--->', my_input2)# 4 数据送给模型# 4-1my_model.eval()with torch.no_grad():my_output1 = my_model(my_input2)print('情感分类模型头输出my_output1--->', my_output1)print('情感分类模型头输出my_output1.logits--->', my_output1.logits)# 4-2my_output2 = my_model(my_input2, return_dict=False) # 不返回字典 直接直接5分类 结果print('情感分类模型头输出my_output2--->', my_output2)''' # 1 return_tensors='pt' 返回是二维数组my_input1---> tensor([[ 101, 782, 4495, 6421, 1963, 862, 6629, 1928, 102]])# 2 否则是一个list 需要手工的转成二维 torch.tensor([msg_list2])my_input2---> [101, 782, 4495, 6421, 1963, 862, 6629, 1928, 102]my_input2---> tensor([[ 101, 782, 4495, 6421, 1963, 862, 6629, 1928, 102]])# return_dict=False 返回结果是否字典形式情感分类模型头输出my_outpout1---> SequenceClassifierOutput(loss=None, logits=tensor([[-2.7387, -1.7528, 0.2273, 2.0507, 1.4128]],grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>), hidden_states=None, attentions=None)情感分类模型头输出my_outpout2---> (tensor([[-2.7387, -1.7528, 0.2273, 2.0507, 1.4128]],grad_fn=<AddmmBackward0>),)'''# 特征提取任务-不带任务输出头的任务 bert-base-chinese
# 1 加载 my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(...)
# 2 加载模型 my_model AutoModel.from_pretrained()
# 3 文本转张量 my_tokenizer.encode_plus(text,return_tensors,truncation,pad_to_max_length=True,max_length=30)
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model.eval() my_model(**msgs_tensor)
def dm02_test_feature_extraction():# 1 加载tokenizermy_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path='./bert-base-chinese')# 2 加载模型my_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path = './bert-base-chinese')# 3 文本转张量message = ['你是谁', '人生该如何起头']my_input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus(text=message, return_tensors='pt', truncation=True, pad_to_max_length=True, max_length=30)print('my_input--->', my_input)# 4 给模型送数据提取特征my_model.eval()with torch.no_grad():output = my_model(**my_input)print('不带模型头输出output--->', output)print('outputs.last_hidden_state.shape--->', output.last_hidden_state.shape) # torch.Size([1, 30, 768])print('outputs.pooler_output.shape--->', output.pooler_output.shape) # torch.Size([1, 768])''' 1 return_tensors='pt' 返回是一个字典, input_ids 文本数值化后结果 句子分段信息token_type_ids 句子的掩码信息:attention_mask{input_ids': tensor([[ 101, 872, 3221, 6443, 102, 782, 4495, 6421, 1963, 862, 6629, 1928,102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), 'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])}2 output.last_hidden_state---> torch.Size([1, 30, 768]) # 返回类的对象BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndCrossAttentions3 output.pooler_output---> torch.Size([1, 768])'''# 完型填空任务 实现思路 ./chinese-bert-wwm bert-base-chinese
# 1 加载 my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained()
# 2 加载模型 my_model AutoModelForMaskedLM.from_pretrained()
# 3 文本转张量 input my_tokenizer.encode_plus('xx[MASK]xx',return_tensors='pt')
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model.eval() my_model(**input)
# 5 获取概率最高# mask_pred_idx = torch.argmax(output.logits[0][6]).item()# my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([mask_pred_idx]))
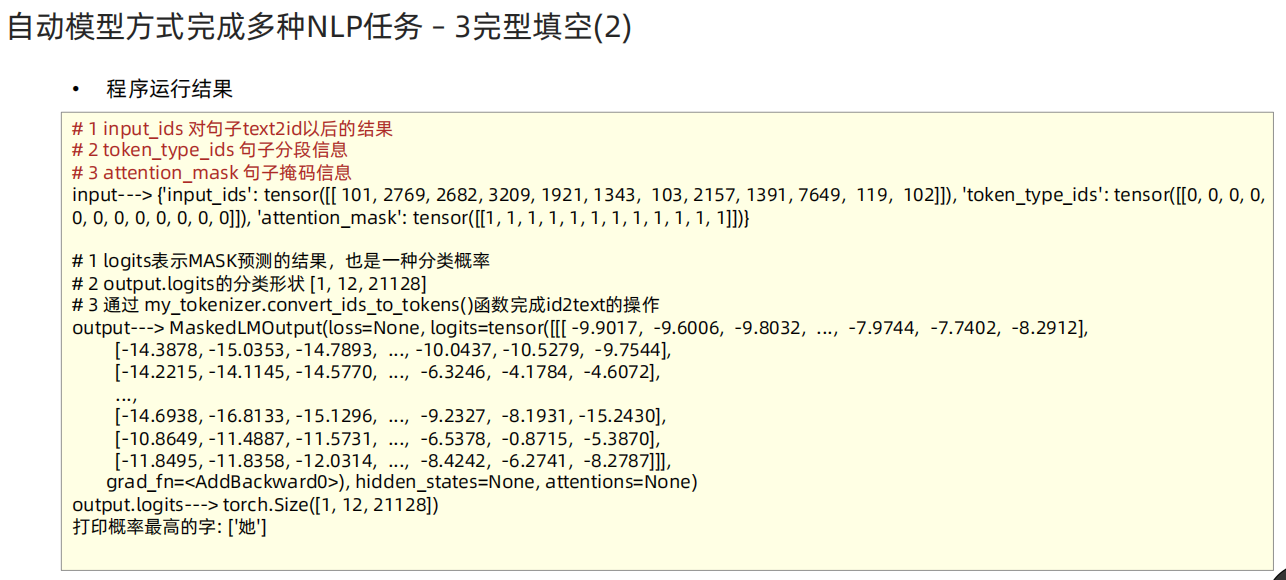
def dm03_test_fill_mask():# 1 加载tokenizermodename = "./chinese-bert-wwm"# modename = "bert-base-chinese"my_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(modename)# 2 加载模型my_model = AutoModelForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(modename)# 3 文本转张量my_input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus('我想明天去[MASK]家吃饭.', return_tensors='pt')print('my_input--->', my_input)# 4 给模型送数据提取特征my_model.eval()with torch.no_grad():output = my_model(**my_input)print('output--->', output)print('output.logits--->', output.logits.shape) # [1,12,21128]# 5 取概率最高mask_pred_idx = torch.argmax(output.logits[0][6]).item()mask_pred_idx = torch.argmax(output.logits[:,6,:]).item()print('打印概率最高的字:', my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([mask_pred_idx]))''' my_input---> {'input_ids': tensor([[ 101, 2769, 2682, 3209, 1921, 1343, 103, 2157, 1391, 7649, 119, 102]]), 'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]), '`attention_mask`': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])}output---> MaskedLMOutput(loss=None, logits=tensor([[[ -9.9017, -9.6006, -9.8032, ..., -7.9744, -7.7402, -8.2912],[-14.3878, -15.0353, -14.7893, ..., -10.0437, -10.5279, -9.7544],[-14.2215, -14.1145, -14.5770, ..., -6.3246, -4.1784, -4.6072],...,[-14.6938, -16.8133, -15.1296, ..., -9.2327, -8.1931, -15.2430],[-10.8649, -11.4887, -11.5731, ..., -6.5378, -0.8715, -5.3870],[-11.8495, -11.8358, -12.0314, ..., -8.4242, -6.2741, -8.2787]]],grad_fn=<AddBackward0>), hidden_states=None, attentions=None)output.logits---> torch.Size([1, 12, 21128])打印概率最高的字: ['她']'''# 阅读理解任务(抽取式问答) 实现思路 './chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large'
# 1 加载my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(...)
# 2 加载模型 my_model AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained()
# 3 文本转张量 for q in qs: input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus(question, context, return_tensors='pt')
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model(**input)
# 5 根据最大概率取对应位置数据
# start, end = torch.argmax(output.start_logits), torch.argmax(output.end_logits) + 1
# answer = my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(input['input_ids'][0][start:end])
def dm04_test_question_answering():# path = 'bert-base-chinese'path = './chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large'# 1 加载tokenizermy_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(path)# 2 加载模型my_model = AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(path)# 3 文本转张量# 文字中的标点符号如果是中文的话,会影响到预测结果 也可以去掉标点符号context = '我叫张三 我是一个程序员 我的喜好是打篮球' # 从上下文中 抽取答案questions = ['我是谁?', '我是做什么的?', '我的爱好是什么?']# questions = ['你是男孩还是女孩?', '我是做什么的?', '我的爱好是什么?']# 4 给模型送数据 模型做抽取式 问答my_model.eval()for question in questions:my_input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus(question, context, return_tensors='pt')# print('my_input--->', my_input)my_output = my_model(**my_input)# print('my_output--->', my_output)# print('output.start_logits.shape--->', my_output.start_logits.shape)start, end = torch.argmax(my_output.start_logits), torch.argmax(my_output.end_logits) +1answer = my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(my_input['input_ids'][0][start:end] )print('question:', question, 'answer:', answer)# breakpasspass''' input---> {'input_ids': tensor([[ 101, 2769, 3221, 6443, 8043, 102, 2769, 1373, 2476, 676, 2769, 3221,671, 702, 4923, 2415, 1447, 2769, 4638, 1599, 1962, 3221, 2802, 5074,4413, 102]]), 'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,1, 1]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,1, 1]])}output---> QuestionAnsweringModelOutput(loss=None, start_logits=tensor([[ -1.9978, -11.4788, -12.6324, -11.8324, -12.4148, -11.9371, -2.7246,-6.6402, 3.9131, -2.9533, -7.0866, -9.5696, -4.2775, -8.9042,0.5753, -6.9468, -7.0469, -8.5334, -11.3796, -9.3905, -11.0242,-11.1047, -5.7124, -2.7293, -7.5896, -12.6013]],grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>), end_logits=tensor([[ -1.3483, -12.0141, -11.6312, -11.6629, -11.9607, -12.0039, -4.6118,-7.4034, -2.3499, 4.7159, -7.2880, -9.5317, -6.6742, -6.0915,-7.0023, -4.9691, 1.4515, -7.8329, -9.0895, -10.3742, -8.7482,-9.8567, -7.2930, -5.8163, -1.7323, -12.2525]],grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>), hidden_states=None, attentions=None)output.start_logits.shape---> torch.Size([1, 26])question: 我是谁? answer: ['张', '三']'''# 文本摘要 实现思路 path = "./distilbart-cnn-12-6"
# 1 加载 my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(...)
# 2 加载模型 my_model AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained()
# 3 文本转张量my_input my_tokenizer([text], return_tensors='pt')
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model.generate(my_input.input_ids) # 文本摘要是生成式任务 给模型喂数据输入my_input.input_ids 不需要掩码 句子分度信息
# 5 分词器decode [my_tokenizer.decode(g, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False) for g in my_output])# skip_special_tokens 单词id2word中跳过特殊字符 clean_up_tokenization_spaces=Fasle 句子之间的空格不去除
def dm05_test_summarization():text = "BERT is a transformers model pretrained on a large corpus of English data " \"in a self-supervised fashion. This means it was pretrained on the raw texts " \"only, with no humans labelling them in any way (which is why it can use lots " \"of publicly available data) with an automatic process to generate inputs and " \"labels from those texts. More precisely, it was pretrained with two objectives:Masked " \"language modeling (MLM): taking a sentence, the model randomly masks 15% of the " \"words in the input then run the entire masked sentence through the model and has " \"to predict the masked words. This is different from traditional recurrent neural " \"networks (RNNs) that usually see the words one after the other, or from autoregressive " \"models like GPT which internally mask the future tokens. It allows the model to learn " \"a bidirectional representation of the sentence.Next sentence prediction (NSP): the models" \" concatenates two masked sentences as inputs during pretraining. Sometimes they correspond to " \"sentences that were next to each other in the original text, sometimes not. The model then " \"has to predict if the two sentences were following each other or not."# 1 加载tokenizermy_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path="./distilbart-cnn-12-6")# 2 加载模型my_model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path='./distilbart-cnn-12-6')# 3 文本转张量my_input = my_tokenizer([text], return_tensors='pt')print('my_input--->', my_input)# 4 送给模型做摘要my_model.eval()my_output = my_model.generate(my_input.input_ids)print('my_output--->', my_output)# 5 处理摘要结果# 5-1 skip_special_tokens=TRUE 一些特殊的控制token跳过,不解码# clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False 解码过程中空格不去除print([my_tokenizer.decode(g, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False) for g in my_output])pass# 5-2 convert_ids_to_tokens 函数只能将 ids 还原为 token 不能去除一些控制字符# print(my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(output[0]))# ner任务
# ner任务 实现思路 './chinese_pretrain_mrc_roberta_wwm_ext_large'
# 1-1 加载 my_tokenizer AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(...)
# 1-2 加载模型 my_model AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained()
# 1-3 加载ner_label配置 my_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(my_path)
# 2 文本转张量 my_input my_tokenizer(msg, return_tensors='pt')
# 3 给模型喂数据 my_model.generate(my_input.input_ids)
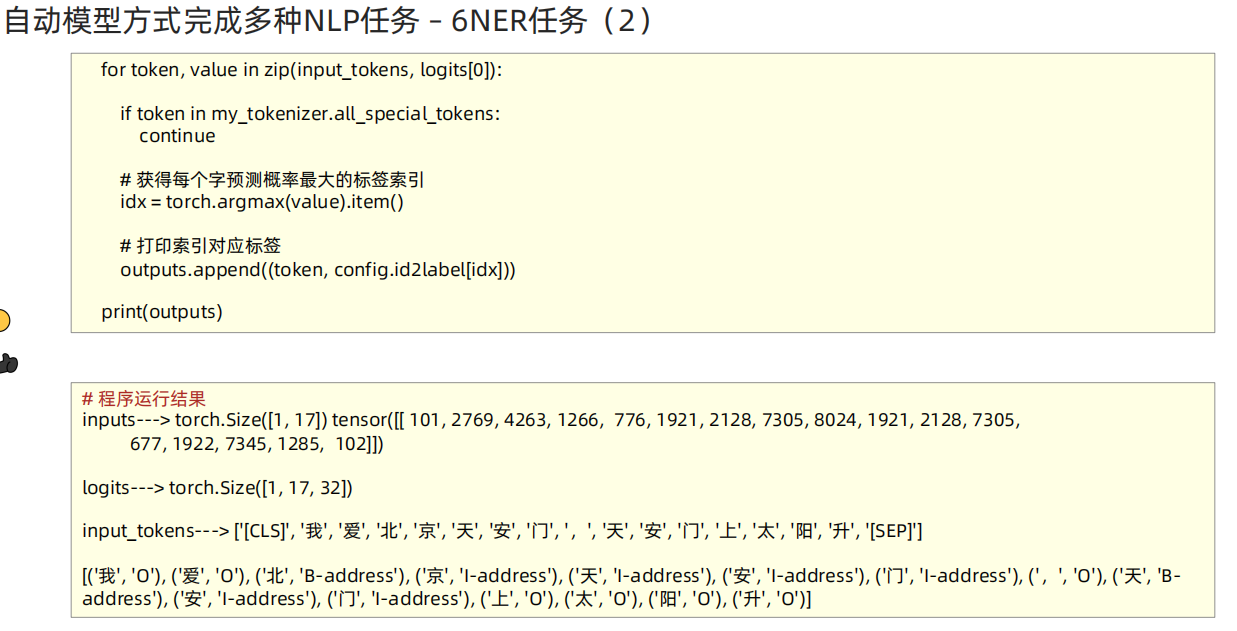
# 4 对输入token反显 对预测结果反显
# 4-1 input_tokens = my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(my_input.input_ids[0])
# 4-2 zip方式输出[输入的token, 预测的label]
# for token, value in zip(input_tokens, my_output.logits[0]):
def dm06_test_ner():# 1-1 加载tokenizer 加载模型 加载配置文件# https://huggingface.co/uer/roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinesemy_path = './roberta-base-finetuned-cluener2020-chinese'my_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(my_path)my_model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained(my_path)my_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(my_path)# 2 数据张量化my_input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus('我爱北京天安门,天安门上太阳升', return_tensors='pt')print('my_input--->', my_input)print('my_input.input_ids.shape--->', my_input.input_ids.shape, my_input.input_ids) # torch.Size([1, 17])# 3 送入模型 预测ner概率 每个字预测的标签概率my_model.eval()my_output = my_model(my_input.input_ids)# print('my_output--->', my_output) # TokenClassifierOutput 返回类对象(loss, logits,grad_fn, hidden_states, attentions)print('my_output.logits.shape--->', my_output.logits.shape) # torch.Size([1, 17, 32])# 4 反显有2个:对输入token反显 对预测结果反显# 4-1 对输入token反显 id2tokeninput_tokens = my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(my_input.input_ids[0])print('input_tokens--->', input_tokens)# 4-2 zip方式输出[输入的token, 预测的label]ner_result = []# my_output.logits[0][1,17,32] --> [17,32] # 每个单词有32种预测结果 反显预测结果for token, value in zip(input_tokens, my_output.logits[0]):if token in my_tokenizer.all_special_tokens:continue# 获得每个字预测概率最大的标签索引idx = torch.argmax(value).item()# 预测结果进行反显, 组成元组对, 进行输出ner_result.append((token, my_config.id2label[idx]))print('最终ner结果输出ner_result--->\n', ner_result)''' # 没有看不懂的代码 只有看不懂的业务 [('我', 'O'), ('爱', 'O'), ('北', 'B-address'), ('京', 'I-address'), ('天', 'I-address'), ('安', 'I-address'),('门', 'I-address'), (',', 'O'), ('天', 'B-address'), ('安', 'I-address'), ('门', 'I-address'), ('上', 'O'), ('太', 'O'),('阳', 'O'), ('升', 'O')]'''if __name__ == '__main__':dm01_test_classification() # 文本分类dm02_test_feature_extraction() # 特征提取dm03_test_fill_mask() # 完形填空dm04_test_question_answering() # 阅读理解# dm05_test_summarization() # 摘要生成# dm06_test_ner()# print('AutoModel方式使用Transformer库 End')pass直接使用Bert模型

import torch
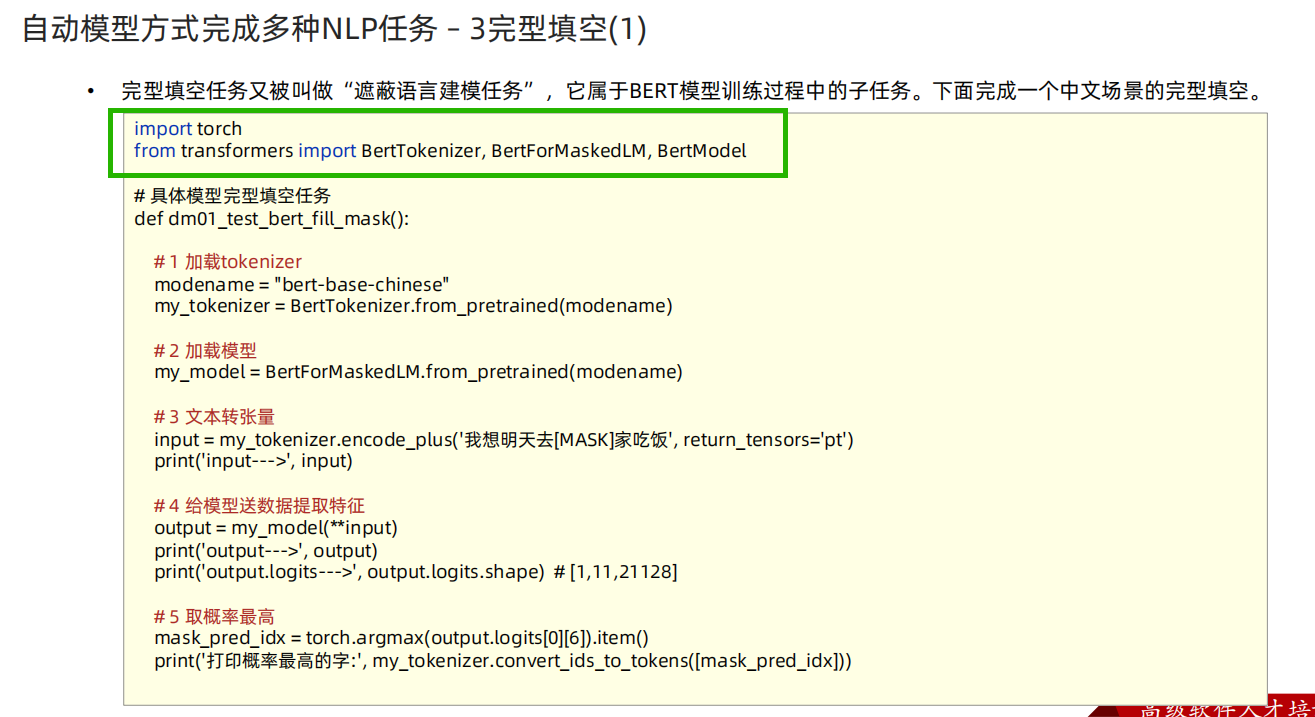
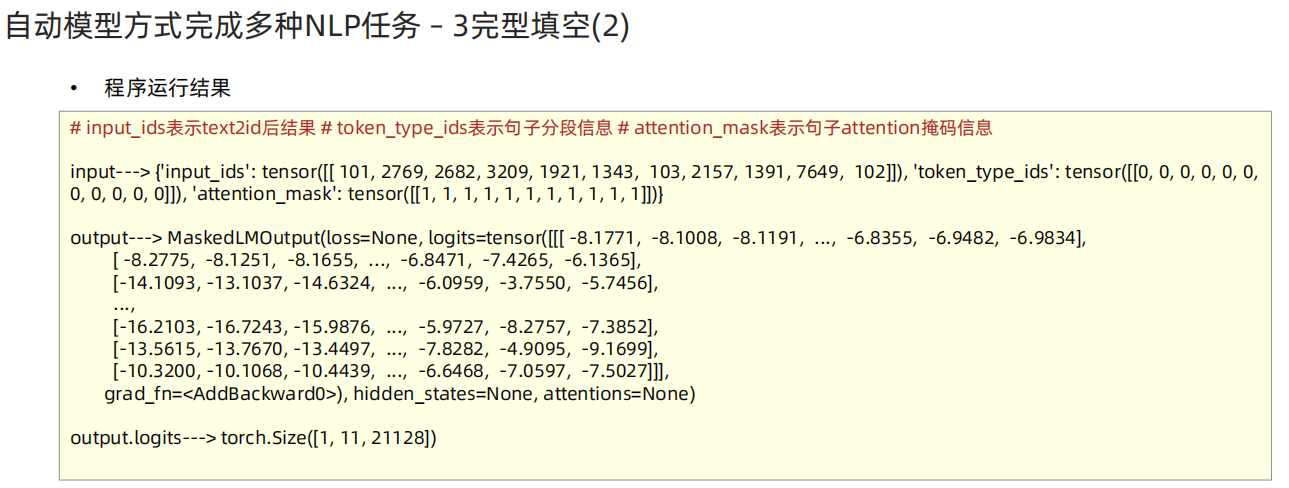
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertForMaskedLM, BertModel# 完型填空任务 实现思路 ."./bert-base-chinese"
# 1 加载 my_tokenizer BertTokenizer.from_pretrained()
# 2 加载模型 my_model BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained()
# 3 文本转张量 input my_tokenizer.encode_plus('xx[MASK]xx',return_tensors='pt')
# 4 给模型喂数据 my_model.eval() my_model(**input)
# 5 获取概率最高# mask_pred_idx = torch.argmax(output.logits[0][6]).item()# my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([mask_pred_idx])
def dm01_test_bert_fill_mask():# 1 加载path = './bert-base-chinese'my_tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(path)# 2 加载模型my_model= BertForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(path)# 3 文本转张量my_input = my_tokenizer.encode_plus('我想明天去[MASK]家吃饭',return_tensors='pt')# 4 给模型喂数据my_model.eval()my_output = my_model(**my_input)# 5 获取概率最高mask_pred_idx = torch.argmax(my_output.logits[0][6]).item()res = my_tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens([mask_pred_idx])print(res)passfrom transformers import BertModel, BertConfig
def dm03_bert():mybertconfig = BertConfig()print('mybertconfig-->', mybertconfig)mymodel = BertModel(config=mybertconfig)passif __name__ == '__main__':dm01_test_bert_fill_mask()# dm03_bert()print('具体模型 End')pass# from transformers import BertModel
# # bert
# # 静态词向量和动态词向量:模型训练完毕以后(模型的参数就固定下来了),还有没有能力根据再根据上下文,重新生成生成词向量
# # word2vec fasttext
# # - eg:我是中国人
# # - eg:我站在两个楼的中间
# # - 上下文不同,”中“的词向量也应该不同!
#
# # 1. Embedding层:输入无论任何的词,不关心位置、不关心上下文:静态词向量
# # 2. 加上位置新(POS + 上下文(MHA)==> last hidden state
#
#
# # 模型训练完毕以后,能根据上下文语言来生成词向量。
# # 比如:'我是中国人','我站在两个楼中间的位置',在不同语义的"中"应该有不同的词向量表达。
# # 4 bert模型对静态词向量、动态词向量的实验支持!
# # 5 如何拿到bert模型的静态词向量
#
#
# def dm05_bert_vector():
#
# s1 = '我是中国人'
# s2 = '我站在两个楼中间的位置'
#
# my_tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('./bert-base-chinese')
# my_model = BertModel.from_pretrained('./bert-base-chinese')
#
# input1 = my_tokenizer.encode_plus(s1, return_tensors='pt')
# print('input1-->', input1)
#
# input2 = my_tokenizer.encode_plus(s2, return_tensors='pt')
# print('input2-->', input2)
#
# # 让模型产生词向量
# output1 = my_model(**input1)
# print("output1-->", output1.last_hidden_state.shape, '\ns1 中词向量', output1.last_hidden_state[0][3][0:10])
#
# # 让模型产生词向量
# input2 = my_model(**input2)
# print("input2-->", input2.last_hidden_state.shape, '\ns2 中词向量', input2.last_hidden_state[0][7][0:10])
#
# print('bert模型静态词向量矩阵', my_model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight.shape) # 21128 * 768
# idx = my_tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("中")
# print('idx--->', idx)
# print('中 静态词向量===>',my_model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight[idx][:10])
#
# # self.embeddings = BertEmbeddings(config)
# # self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, padding_idx=config.pad_token_id)
#
# pass# def dm02_bert_vector():
#
# torch.set_printoptions(precision=6, sci_mode=False)
# bert_tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('./bert-base-chinese')
# bert_model = BertModel.from_pretrained('./bert-base-chinese')
#
# s1 = '我是中国人'
# s2 = '我站在两个楼中间的位置'
# s1 = bert_tokenizer.encode_plus(s1, return_tensors='pt')
# s2 = bert_tokenizer.encode_plus(s2, return_tensors='pt')
# idx = bert_tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids('中')
# print('s1--->', s1)
# print('s2--->', s2)
#
# #
# output1 = bert_model(**s1)
# output2 = bert_model(**s2)
# print('查看中的动态词向量')
#
# # self.embeddings = BertEmbeddings(config)
# # self.word_embeddings = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, padding_idx=config.pad_token_id)
# # self.weight
#
# print('句子1的"中",动态词向量output1--->',output1.last_hidden_state[0][3].shape,
# output1.last_hidden_state[0][3][:10].tolist())
# print('句子2的"中",动态词向量output2--->',output2.last_hidden_state[0][7].shape,
# output2.last_hidden_state[0][7][:10].tolist())
#
# print('查看中的静态词向量')
#
# print("bert词向量矩阵", bert_model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight.shape)
# print('bert词向量矩阵', bert_model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight.shape) # torch.Size([21128, 768])
# print('bert词向量矩阵的"中的词向量', bert_model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight[704][:10].tolist())
#
#
# def dm03_bert_vector():
# s1 = '我是中国人'
# s2 = '我站在两个楼中间的位置'
#
# model = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-chinese')
# tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-chinese')
#
# s1 = tokenizer(s1, return_tensors='pt', return_token_type_ids=False, add_special_tokens=False)
# print(s1)
#
# s2 = tokenizer(s2, return_tensors='pt', return_token_type_ids=False, add_special_tokens=False)
# print(s2)
#
# print(tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids('中'))
#
# output1 = model(**s1)
# output2 = model(**s2)
#
# print(model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight.shape)
# print(model.embeddings.word_embeddings.weight[704][:10].tolist())
# print('-' * 100)
# # "中" 动态向量表示
# print(output1.last_hidden_state.squeeze()[2][:10].tolist())
# print('-' * 100)
# print(output2.last_hidden_state.squeeze()[6][:10].tolist())
#
# # import torch.nn as nn
# # nn.Embedding().weight

