JAVA EE初阶 2: 多线程-初阶

1.认识线程(Thread)



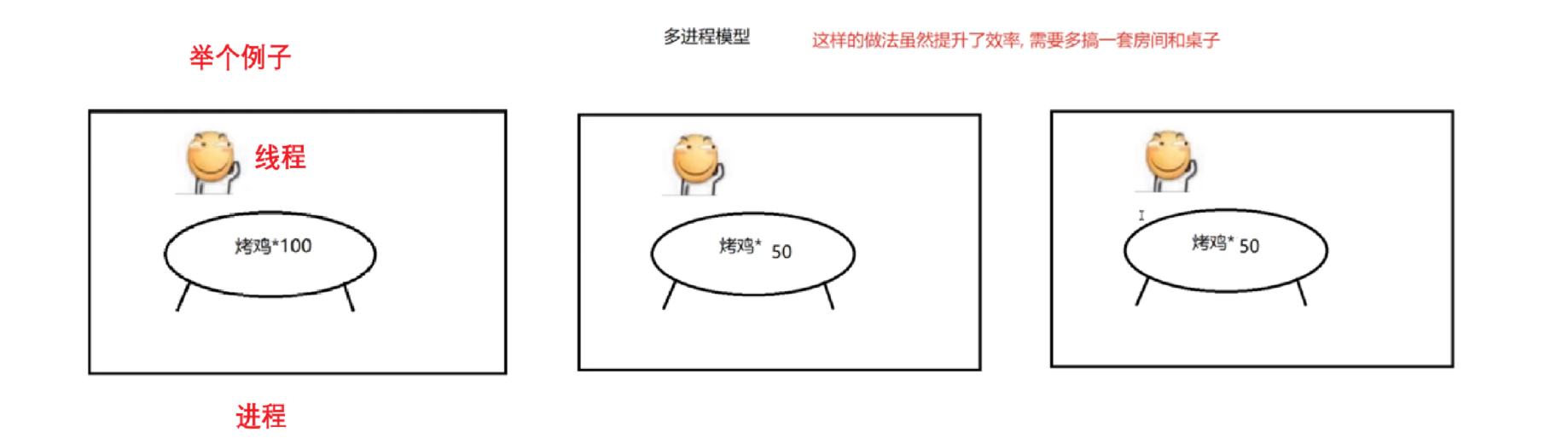
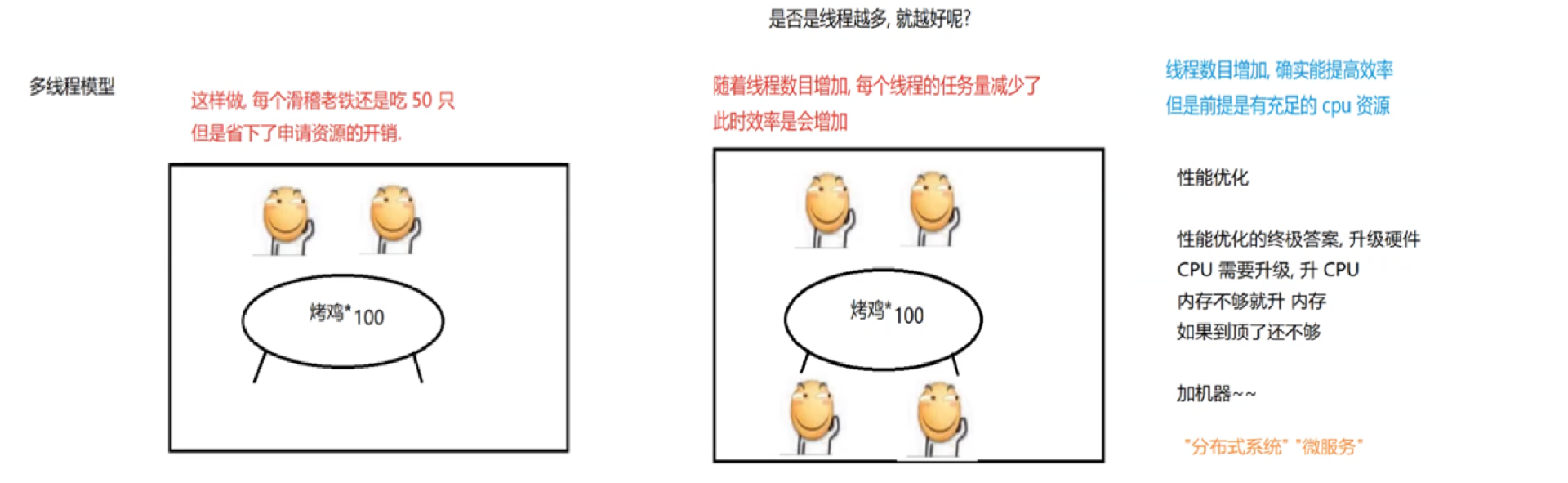


1.1 概念




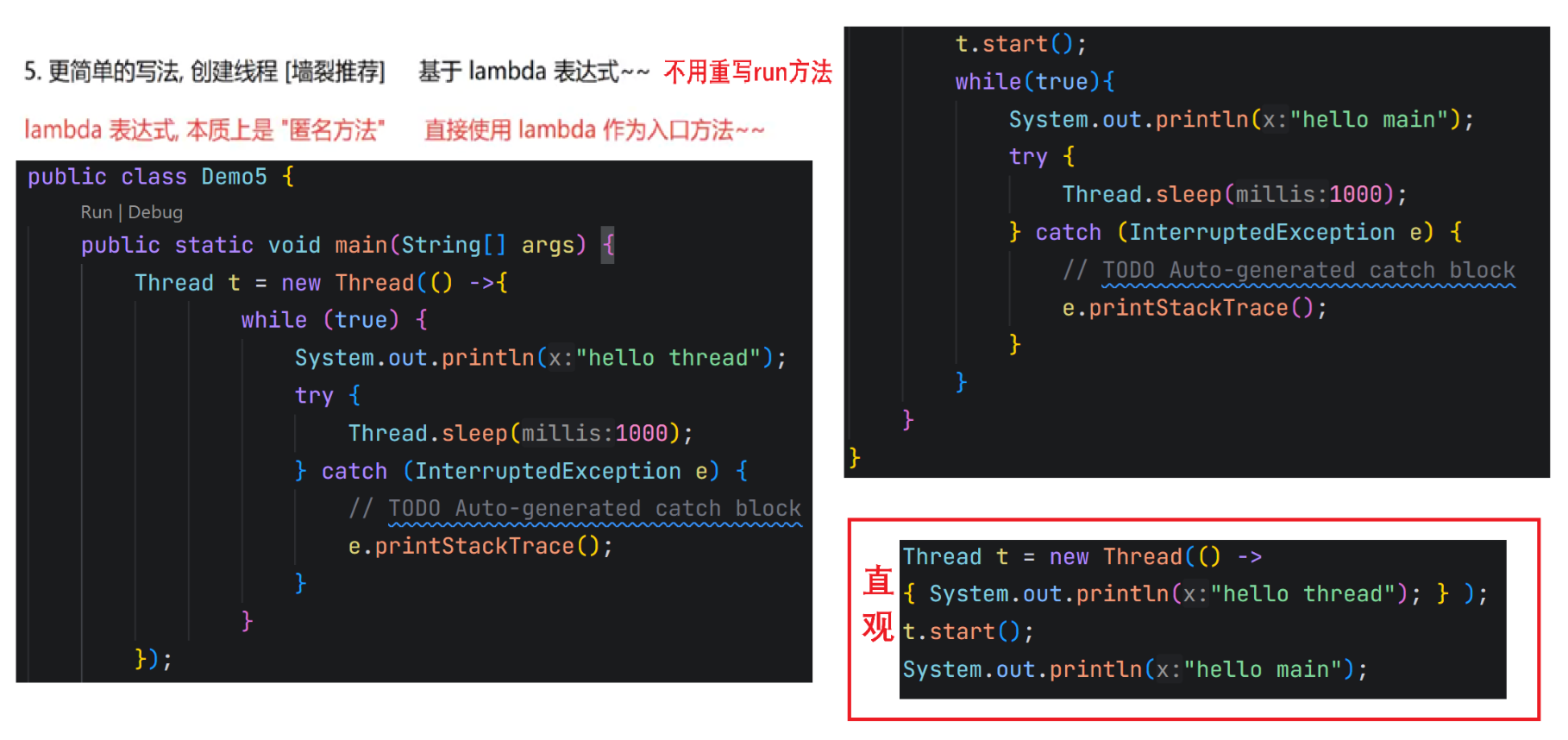
1.2 创建线程(lambda最常用)

1.2.1 方法1 - 继承Thread类


【 Ctrl + C 取消 终止 】



1.2.2 方法2 - 实现Runnable接口
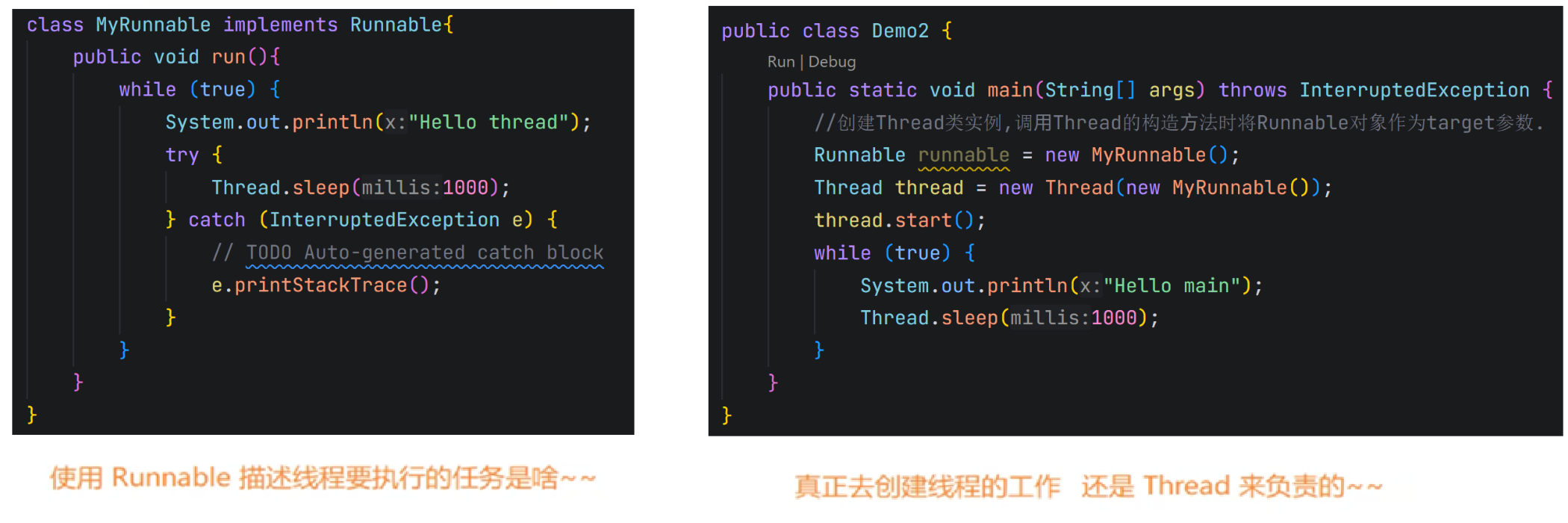
1.2.3 总结


1.2.4 匿名内部类



2.Thread类及常见方法
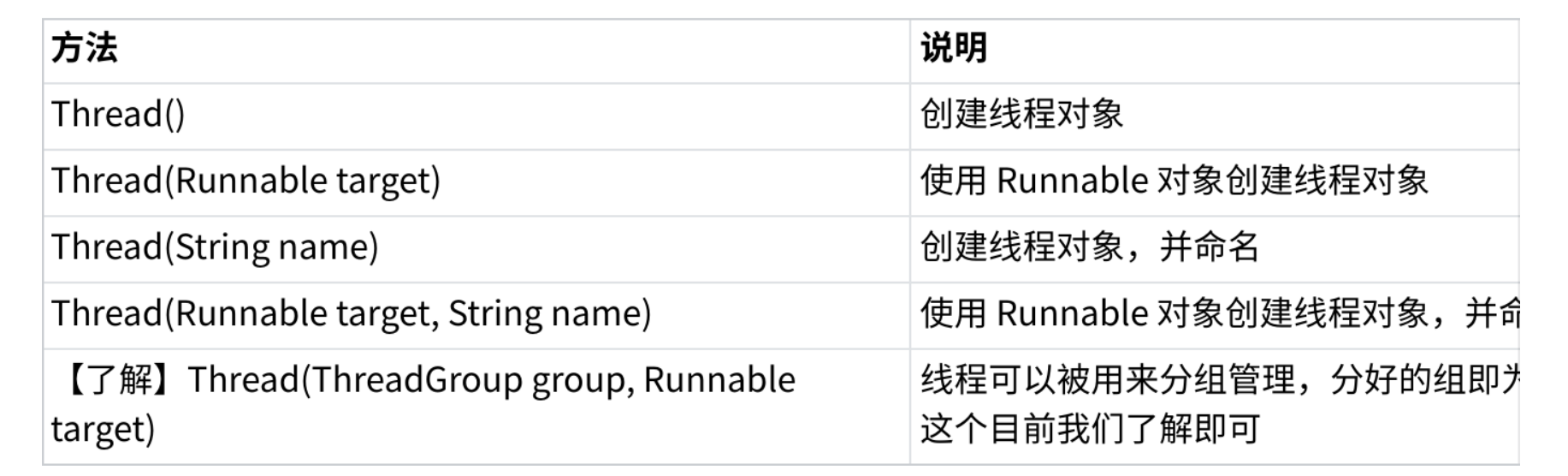
2.1 构造方法
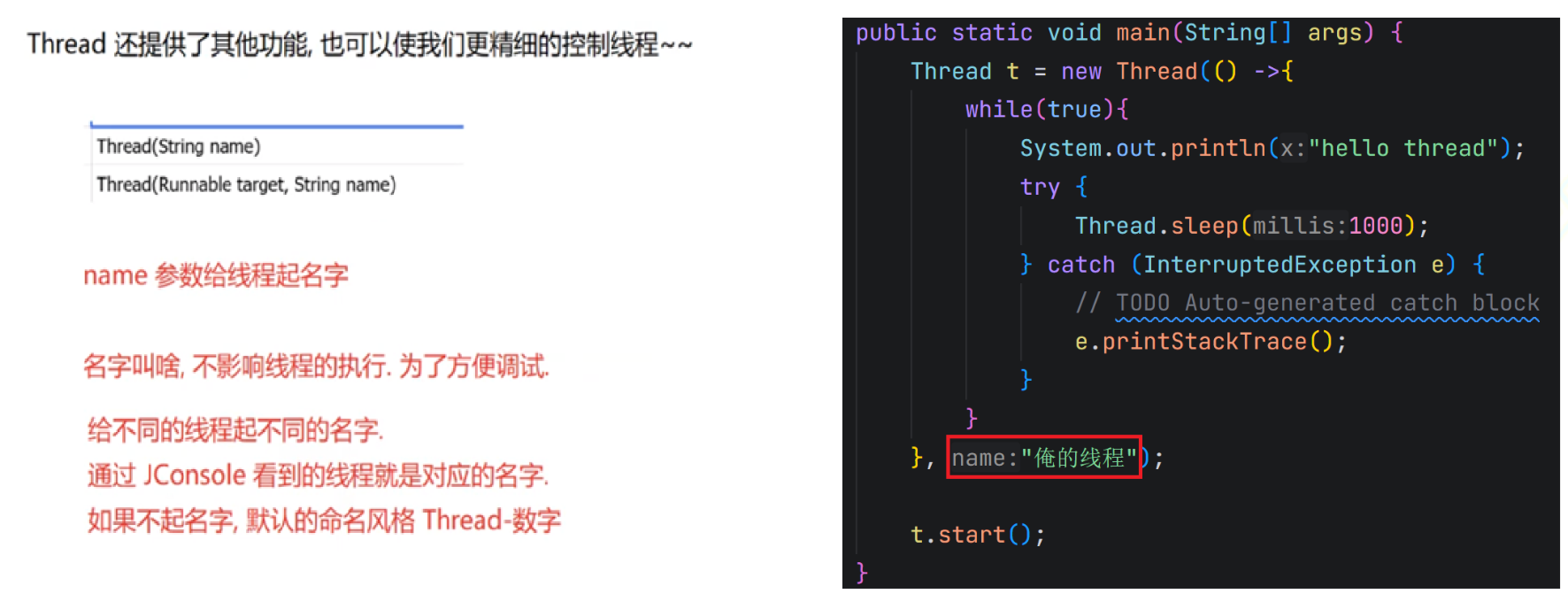

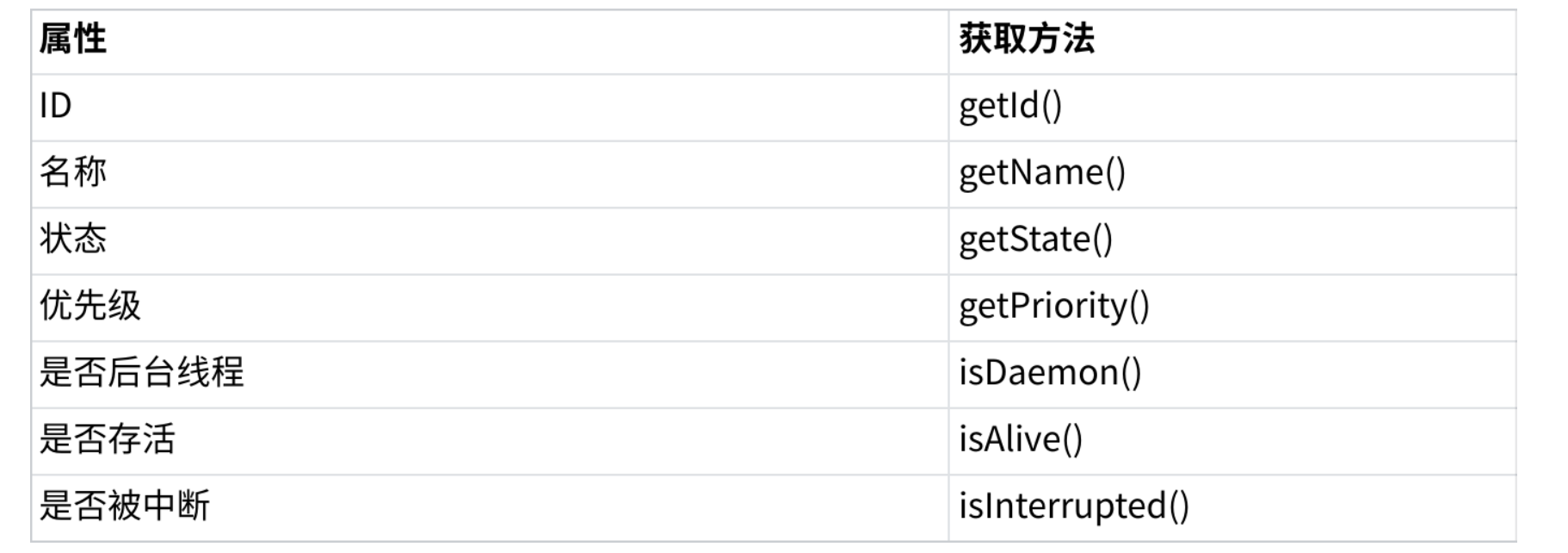
2.2 常见属性
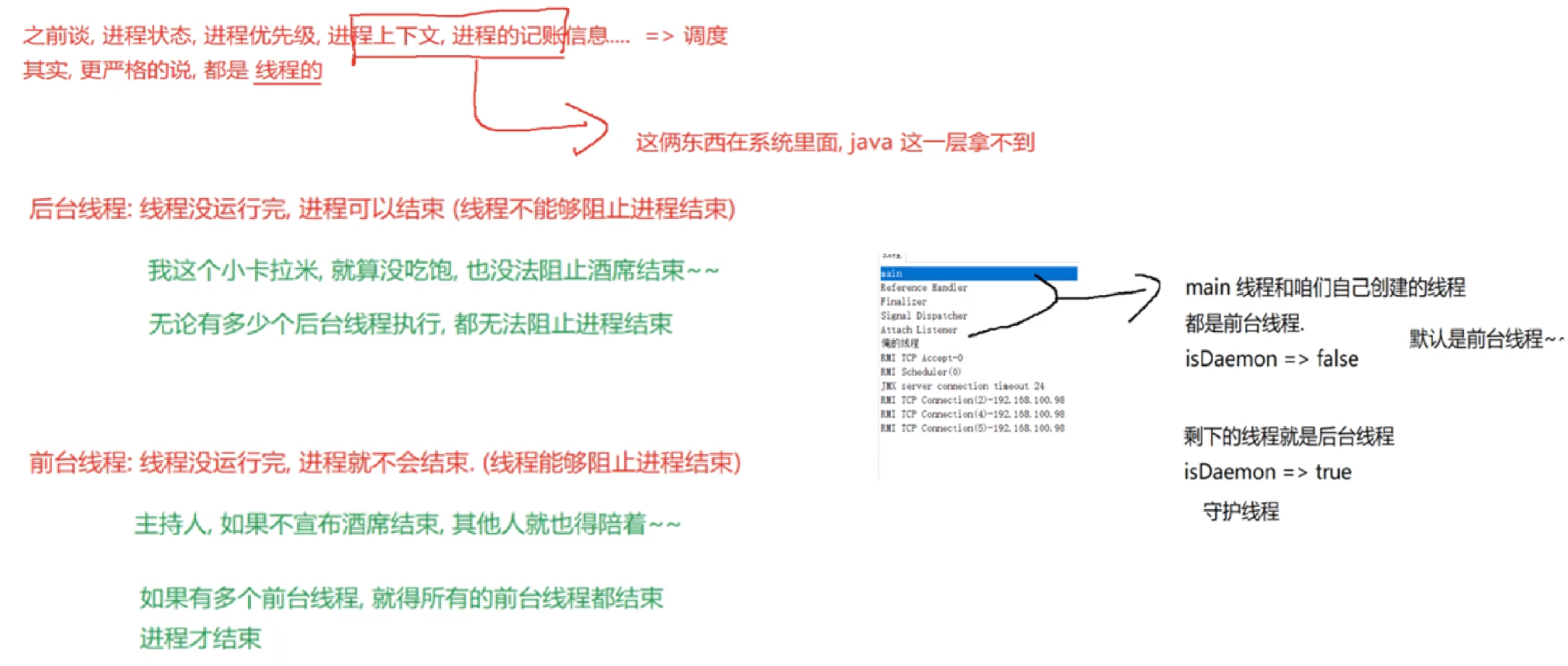
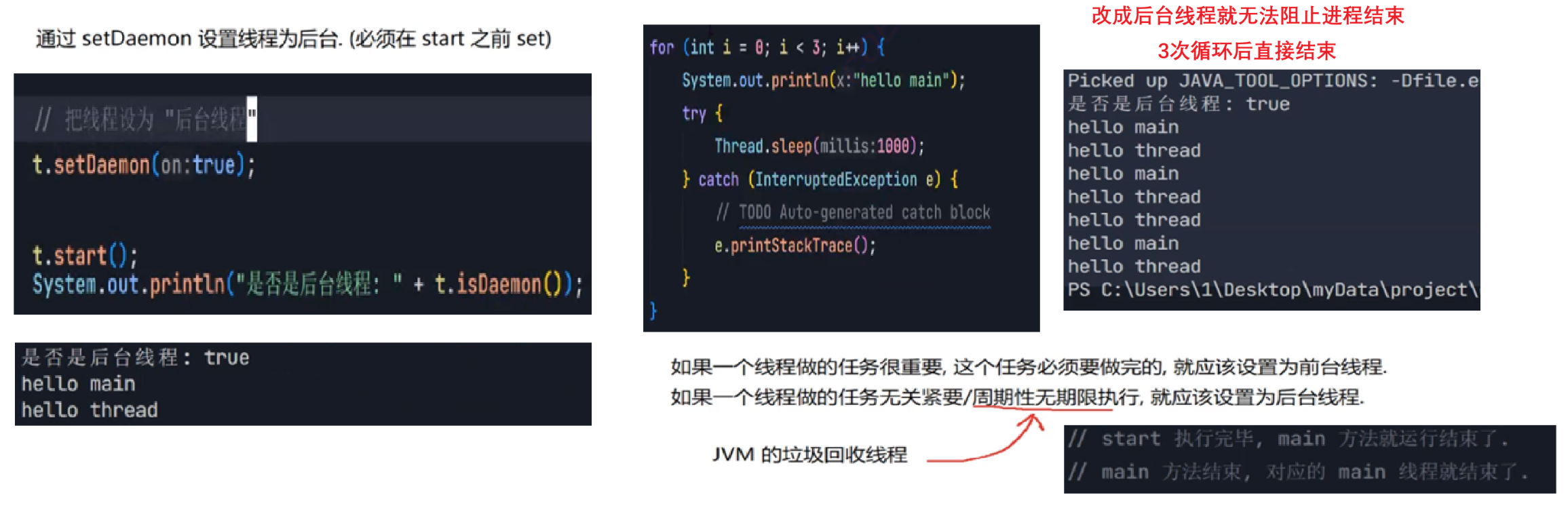

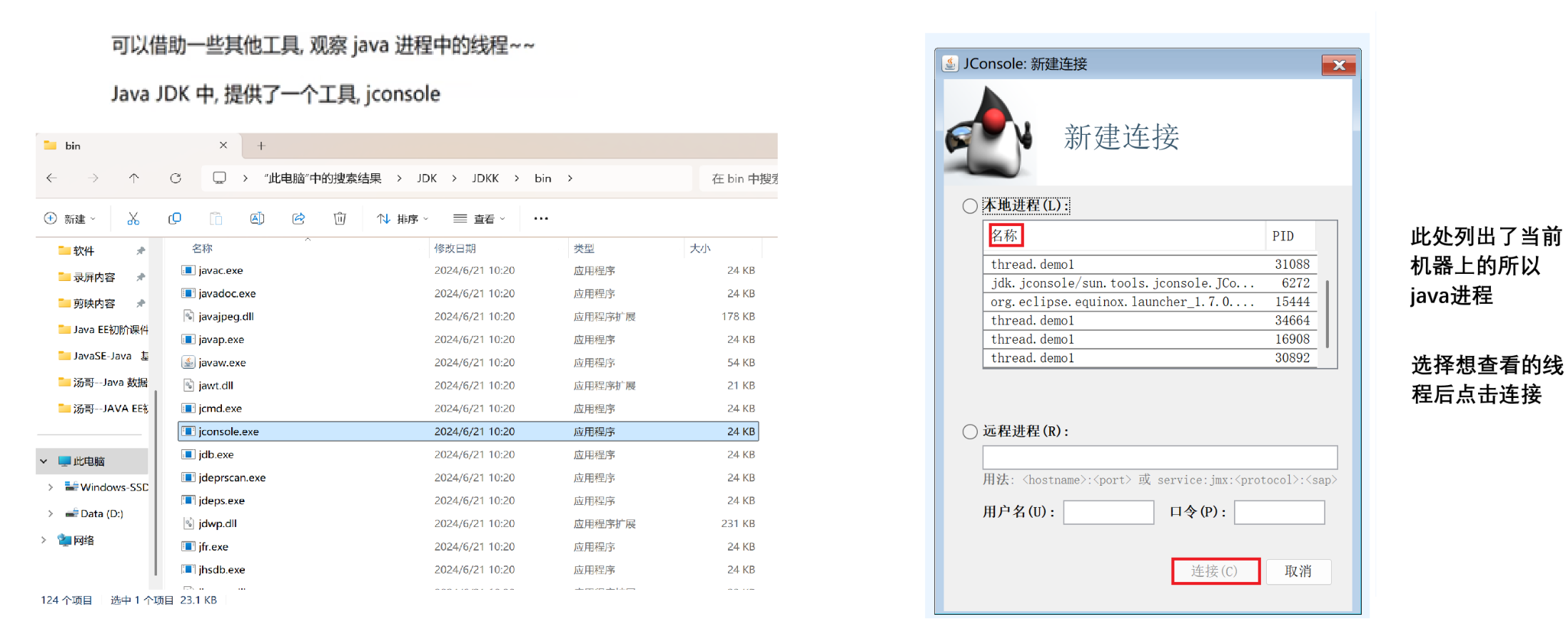
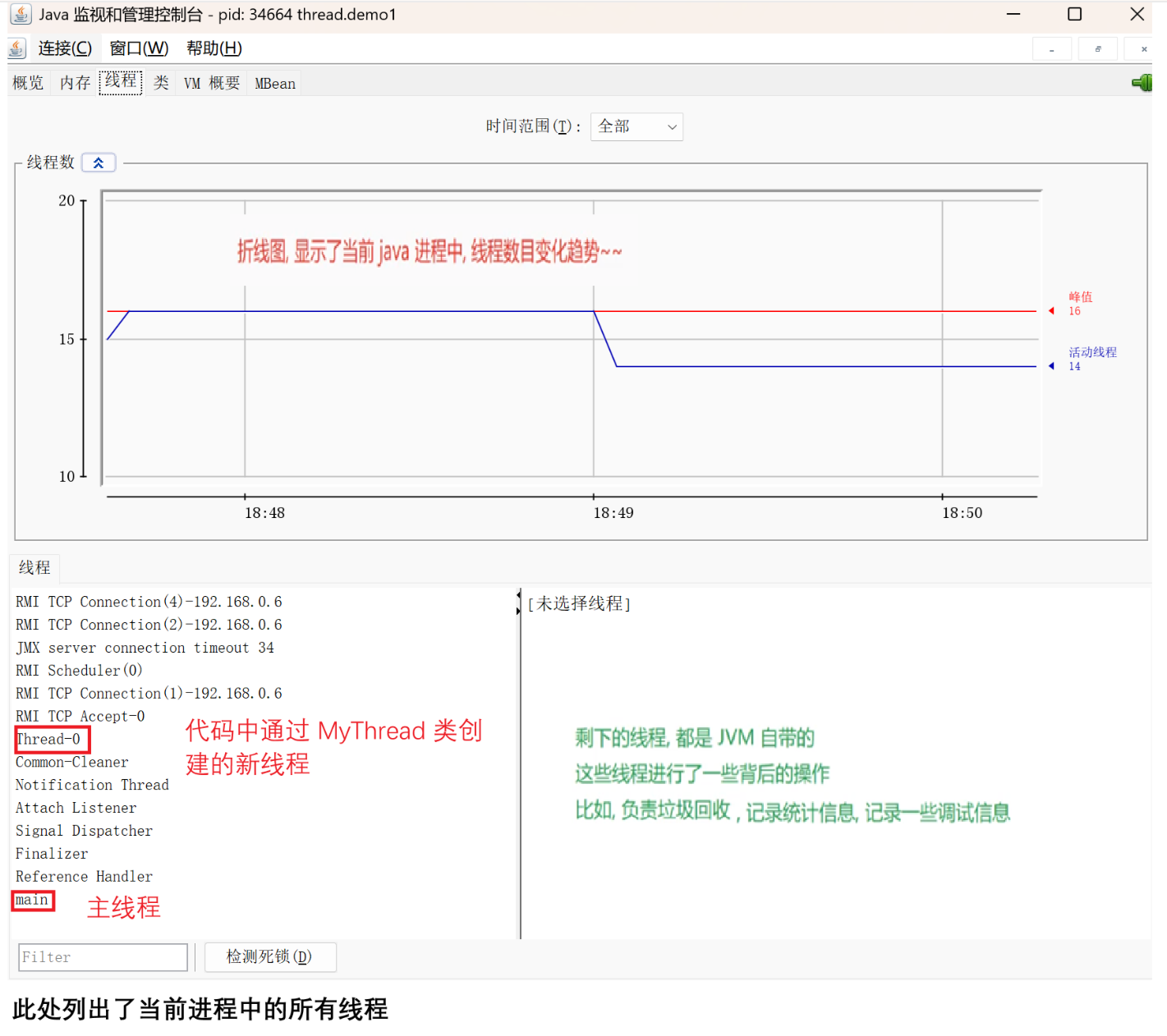
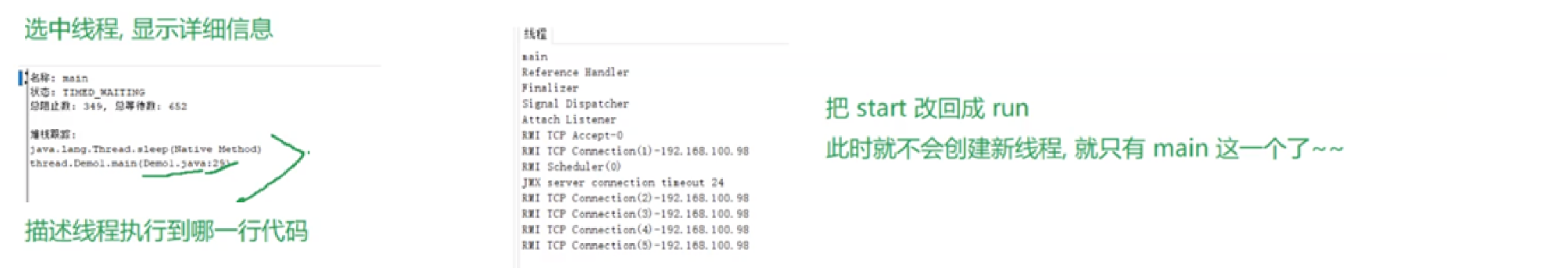
2.3 启动一个线程 start()

调用start方法,才真的在操作系统的底层创建出⼀个线程。


2.4 中断一个线程


package thread;public class Demo7 {private static boolean flag = true;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(() -> { while(flag){System.out.println("hello thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}});t.start();System.out.println("hello main");Thread.sleep(3000);flag = false;System.out.println("让 t 线程终止");}}
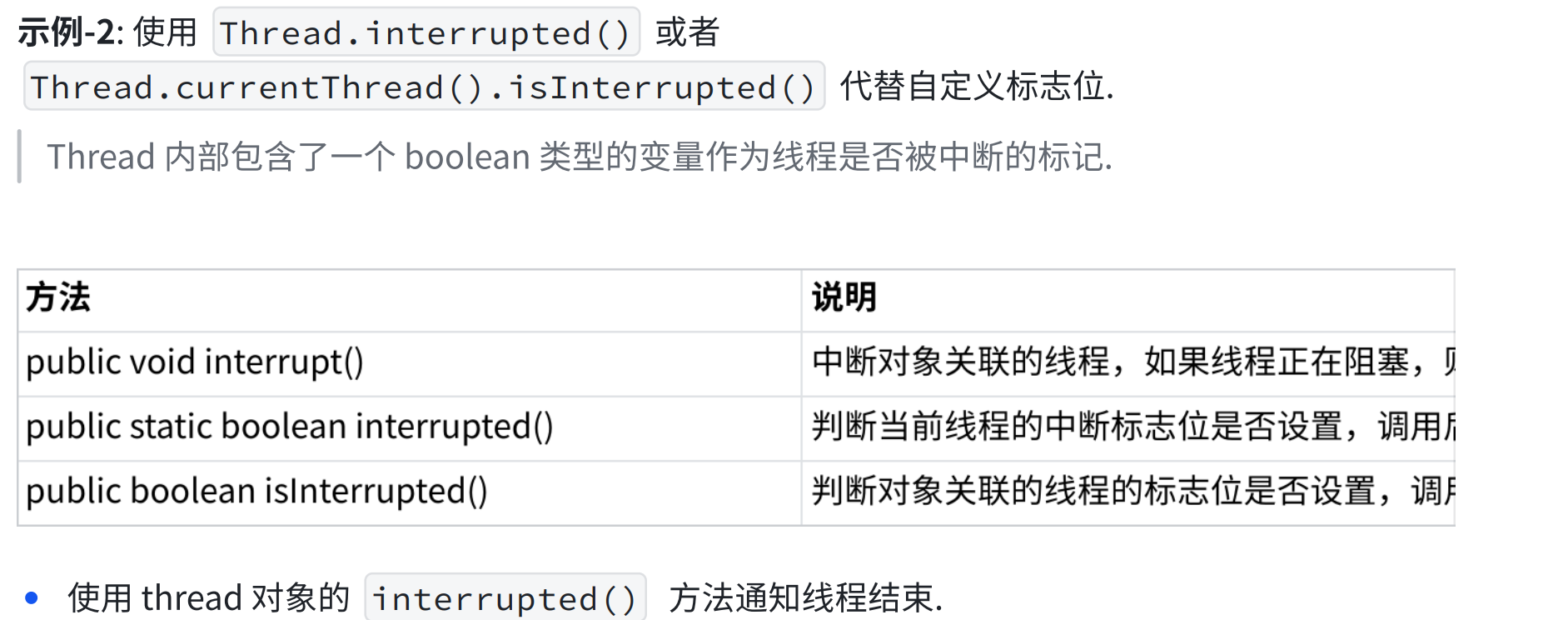

package thread;public class Demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(() -> { while(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){System.out.println("hello thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}});t.start();System.out.println("hello main");Thread.sleep(3000);t.interrupt();System.out.println("t 线程的中断标志位:" + t.isInterrupted());}}




2.5 等待一个线程 join()
有时,我们需要等待一个线程完成它的工作后,才能进的下⼀步工作,这时我们需要⼀个方法明确等待线程的结束。
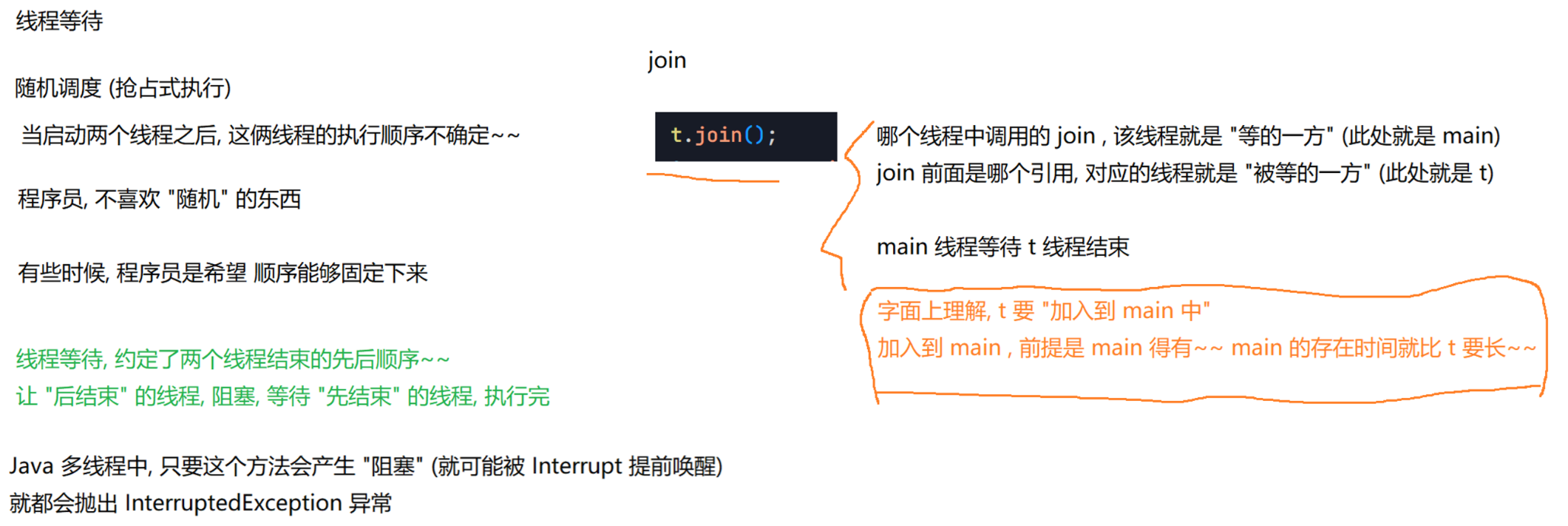
主线程等待代码
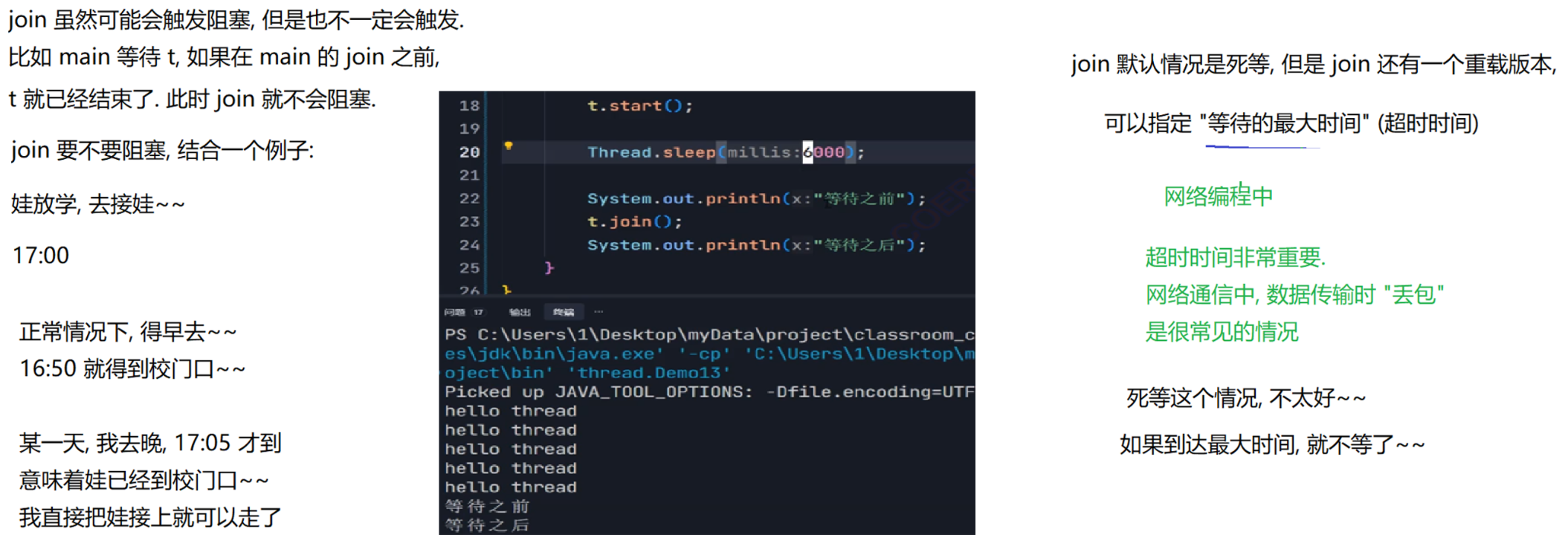
package thread;public class Demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t = new Thread(() -> {for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){System.out.println("hello thread");try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch block//e.printStackTrace();break;}}});System.out.println("主线程开始");t.start();System.out.println("主线程等待之前");t.join();System.out.println("主线程等待之后");System.out.println("主线程结束");}
}
t 线程等待代码
package thread;public class Demo7 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread mainThread = Thread.currentThread();Thread t = new Thread(() -> {try {System.out.println("t 线程等待之前");mainThread.join();System.out.println("t 线程等待之后");} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}});t.start();for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){System.out.println("hello main");Thread.sleep(1000);}}
}

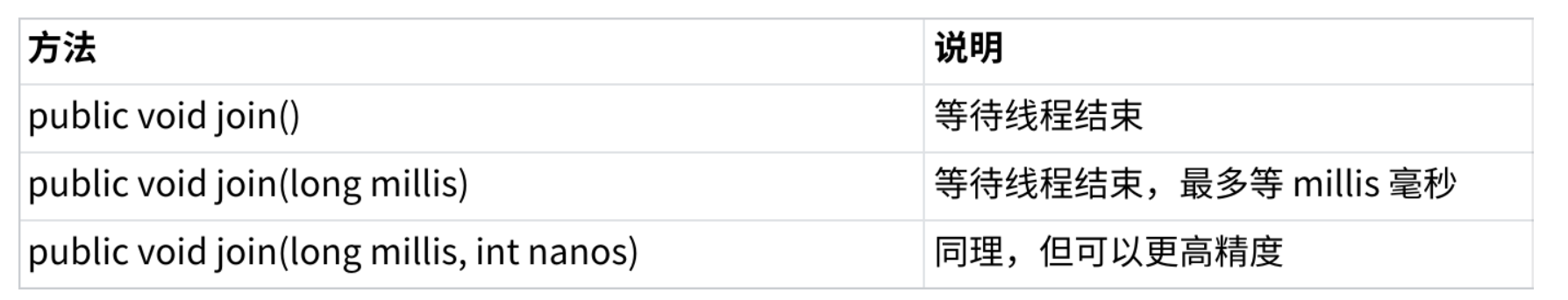

2.6 获取当前线程引用
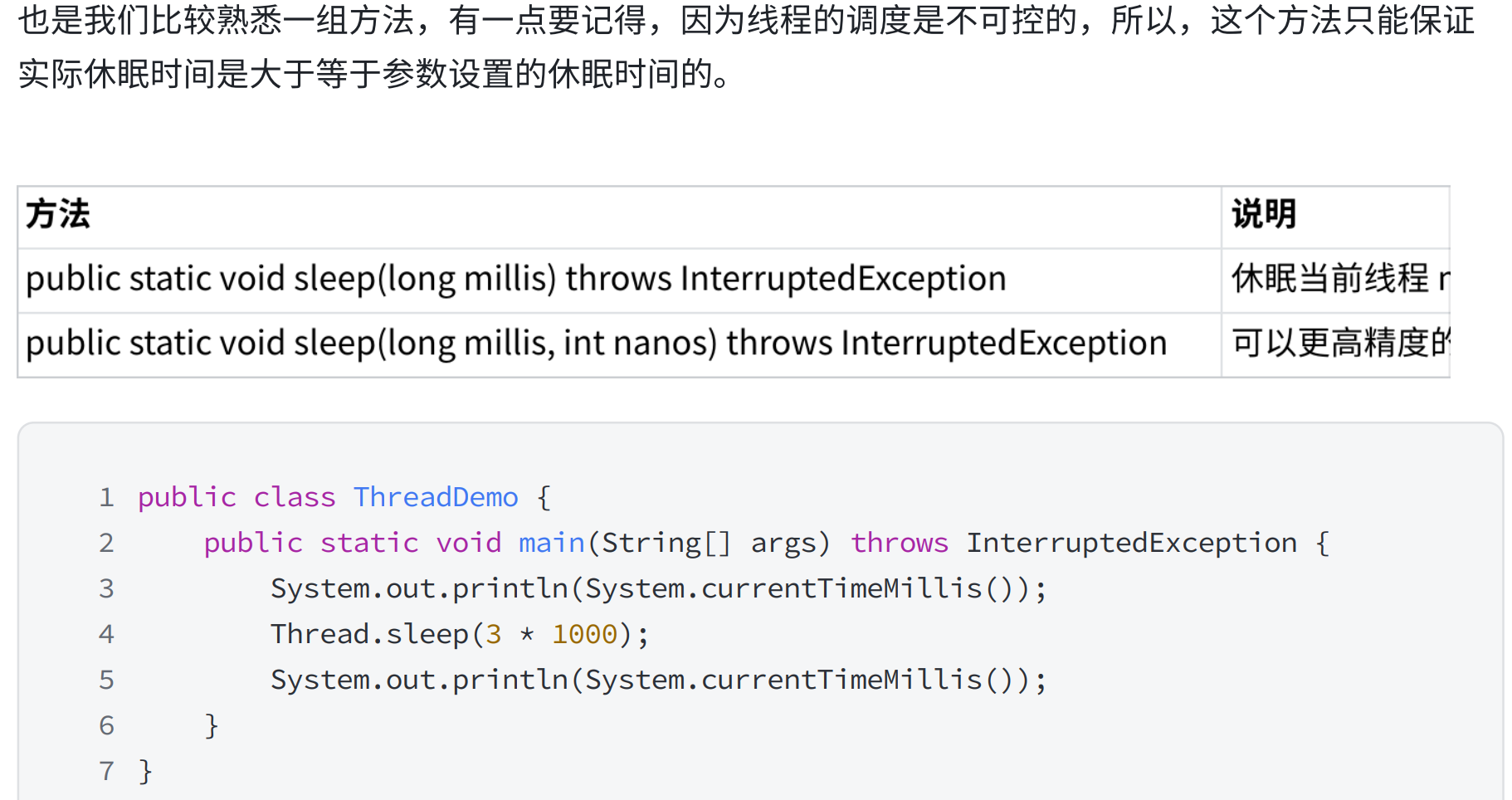
2.7 休眠当前线程

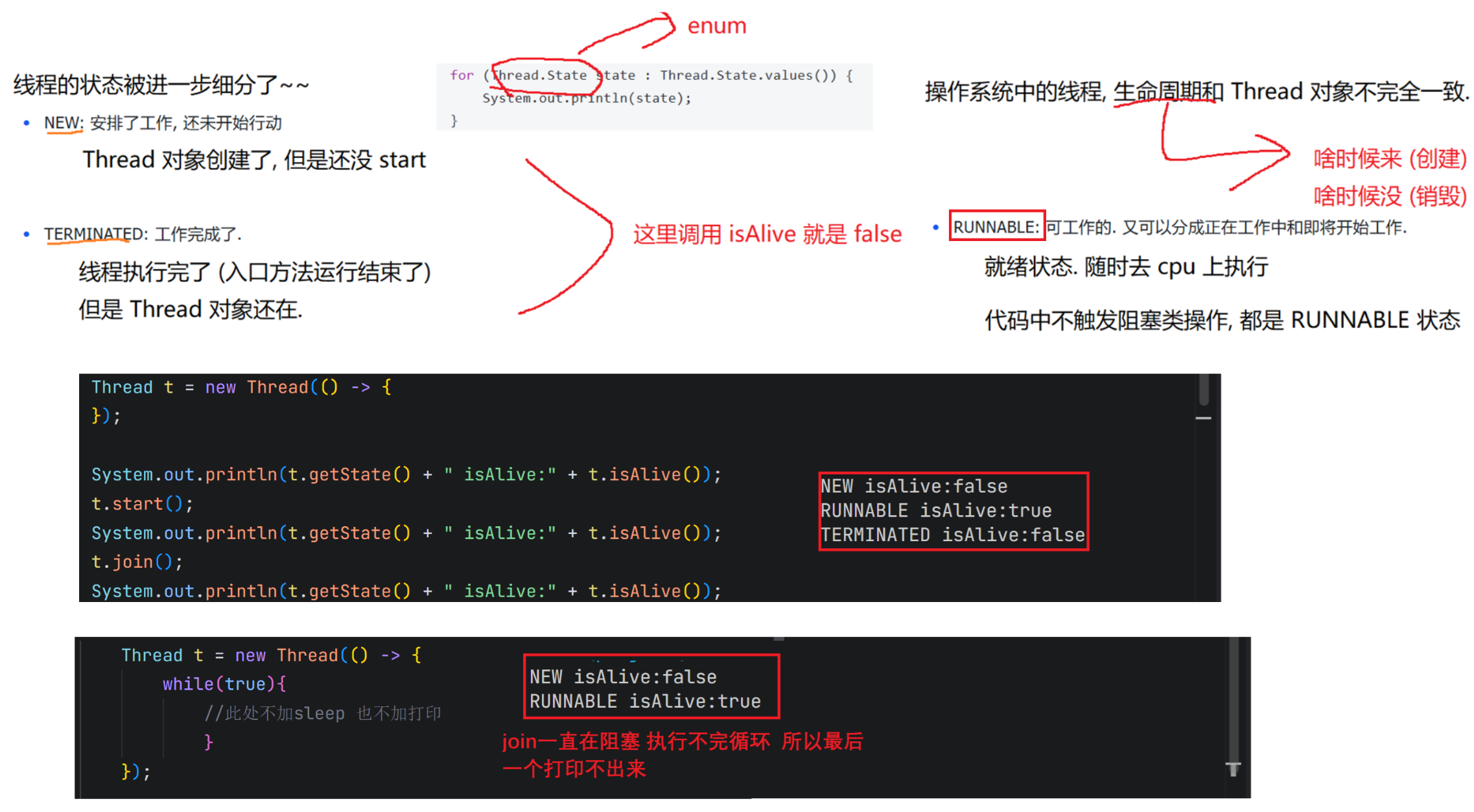
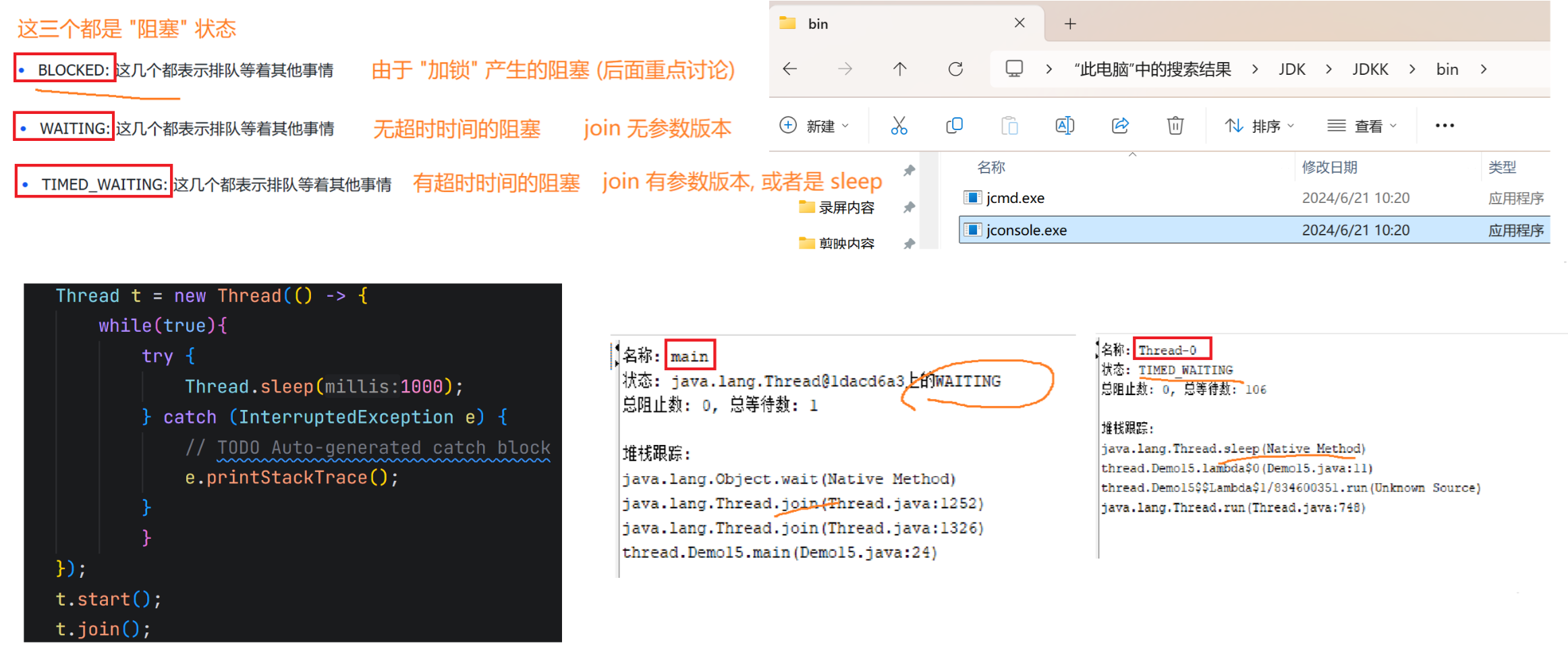
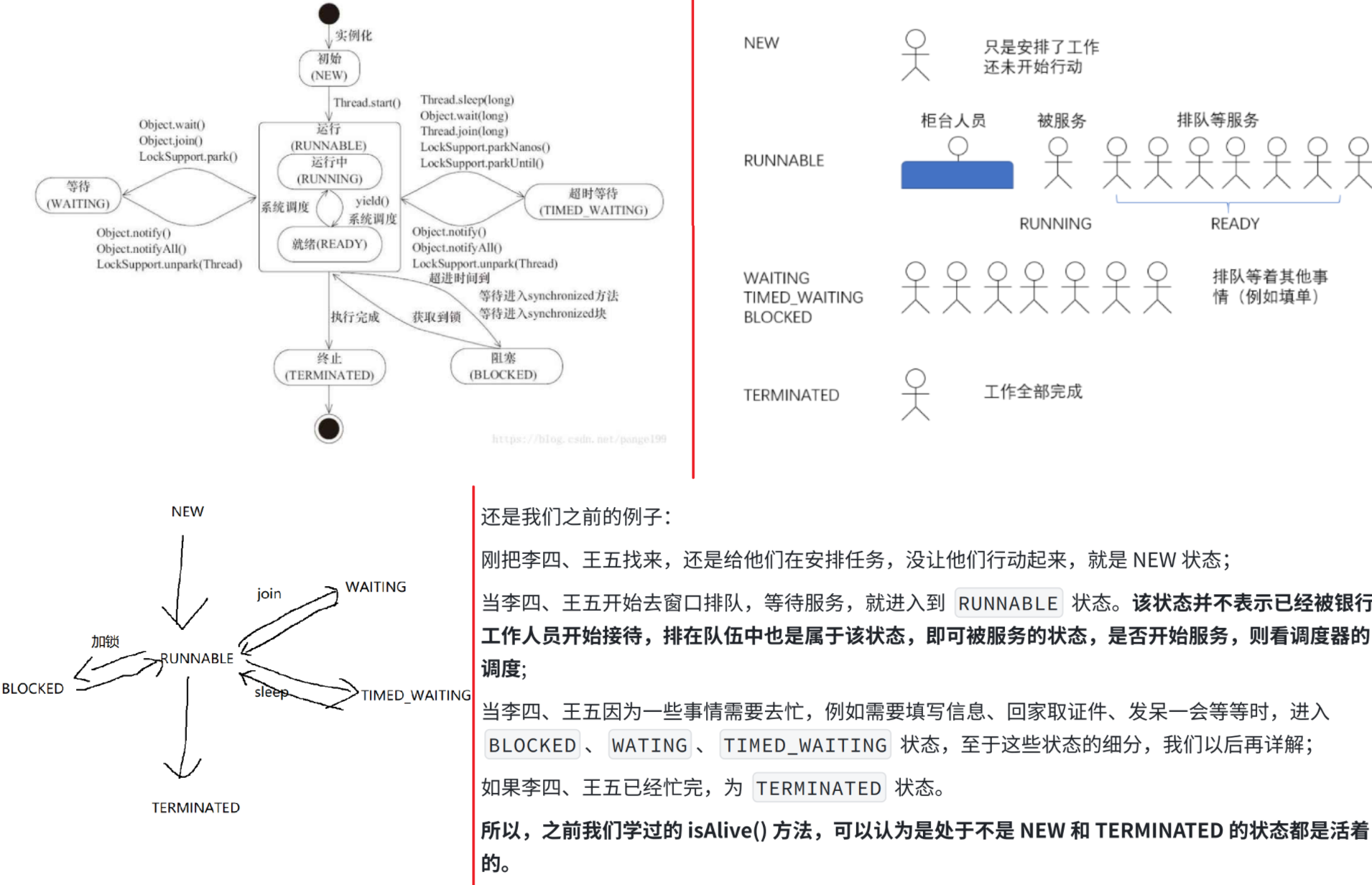
3.线程的状态
线程的状态是⼀个枚举类型 Thread.State

4.多线程带来的的风险-线程安全(重点!)
4.1 概念 例子

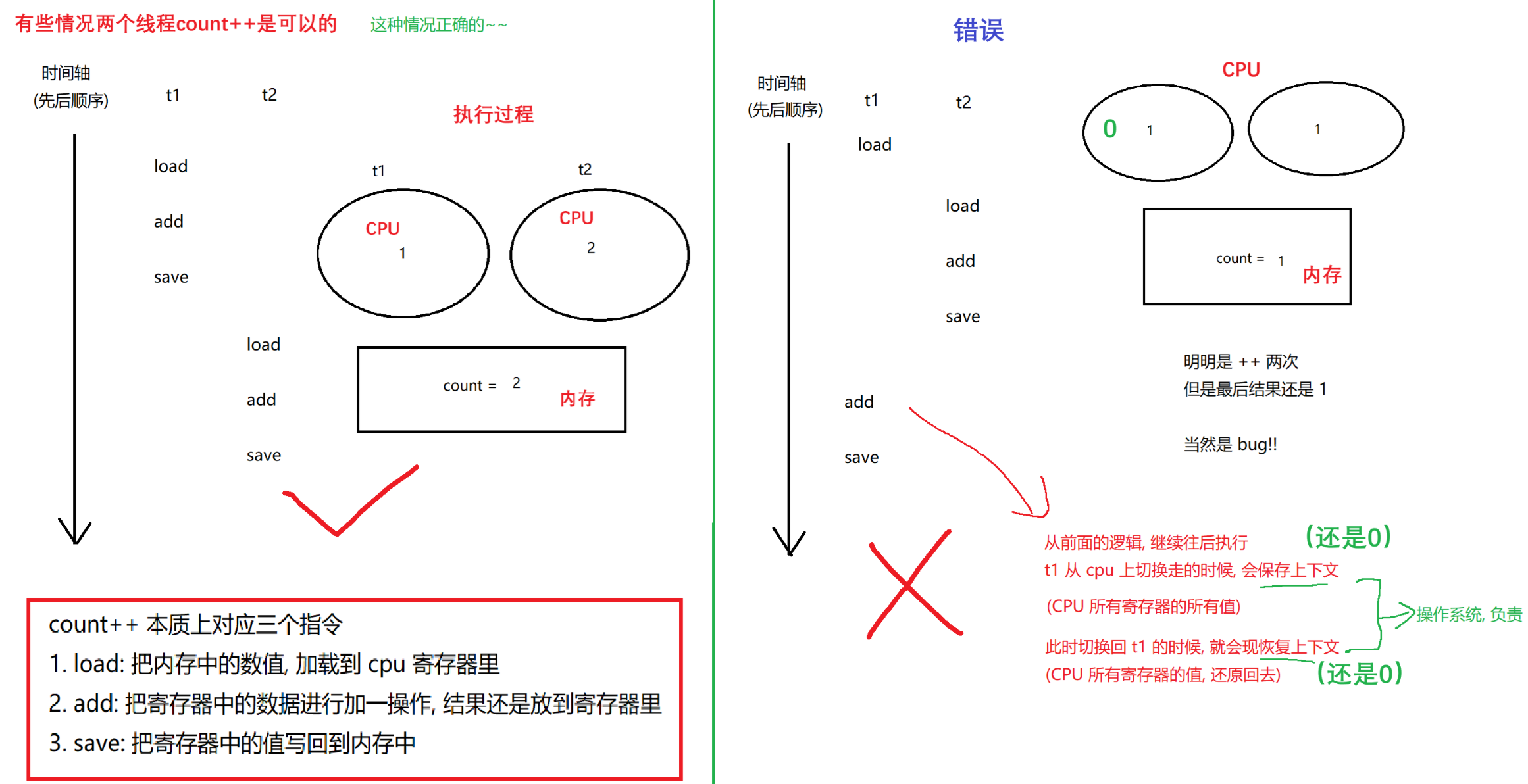

4.2 线程不安全的原因

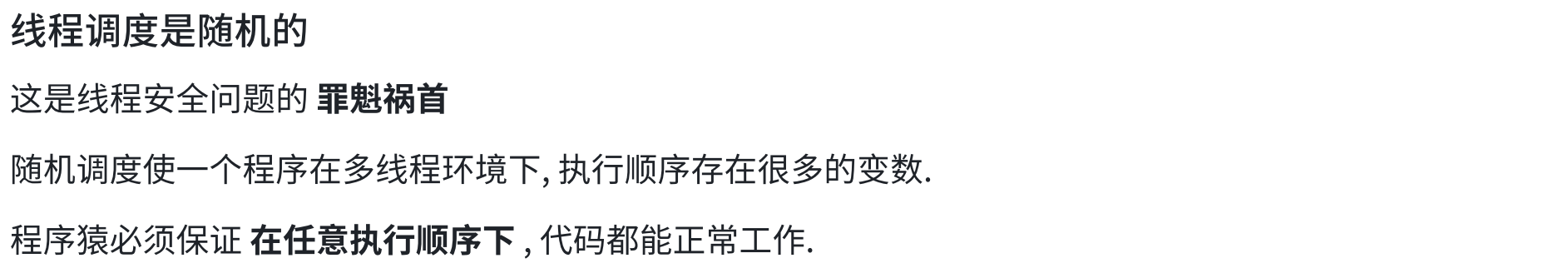



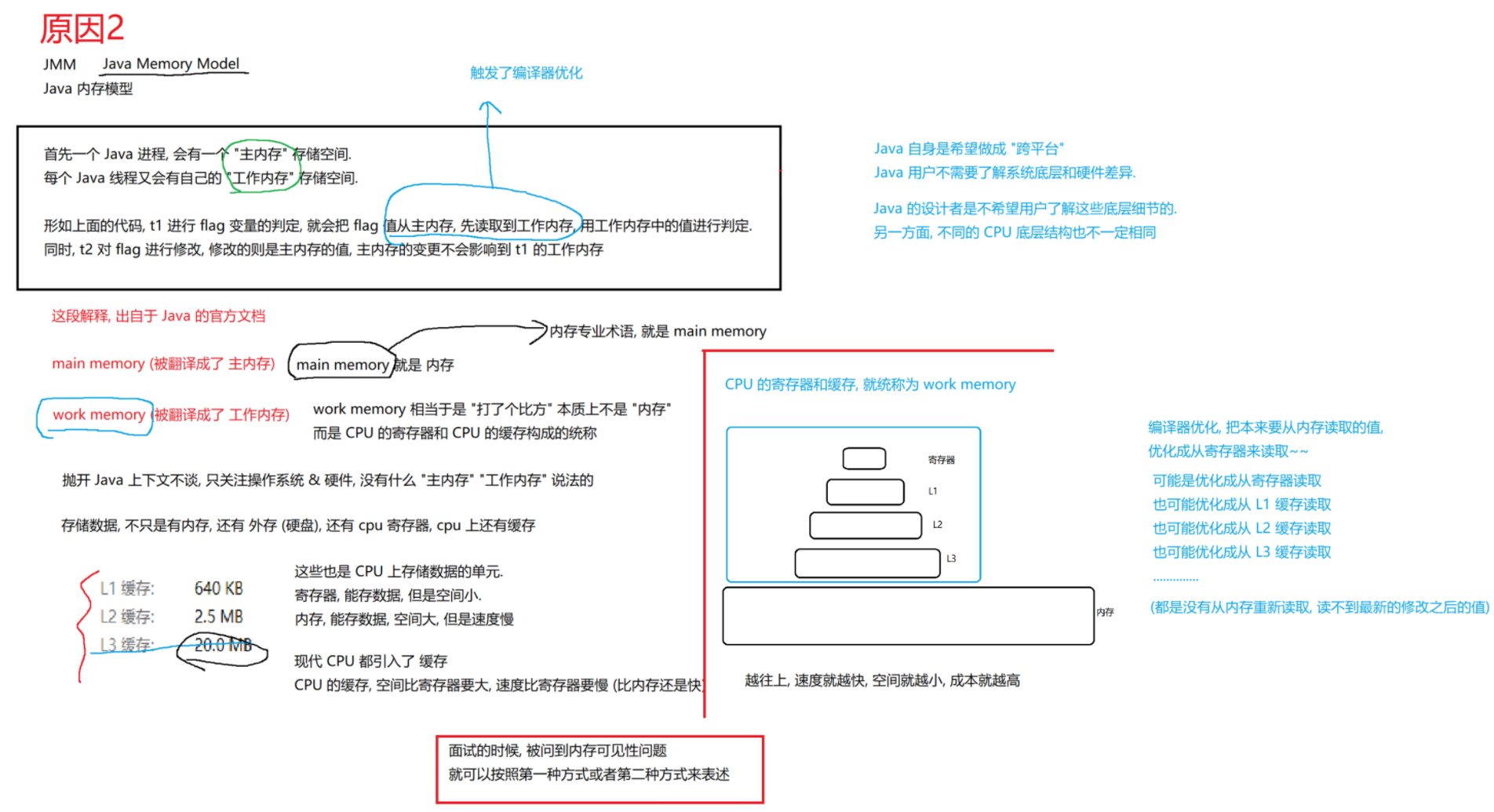

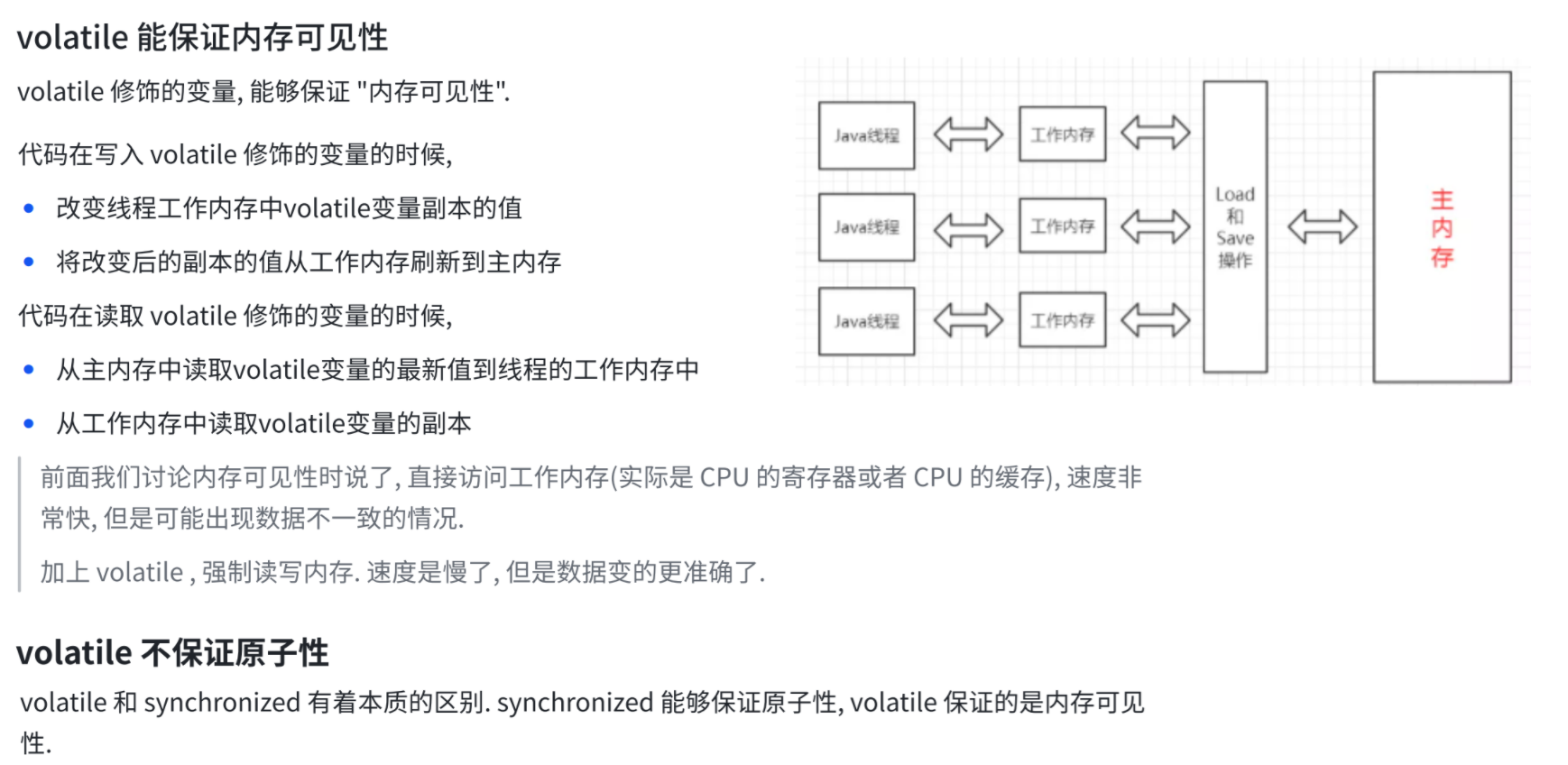


5.死锁(重点)

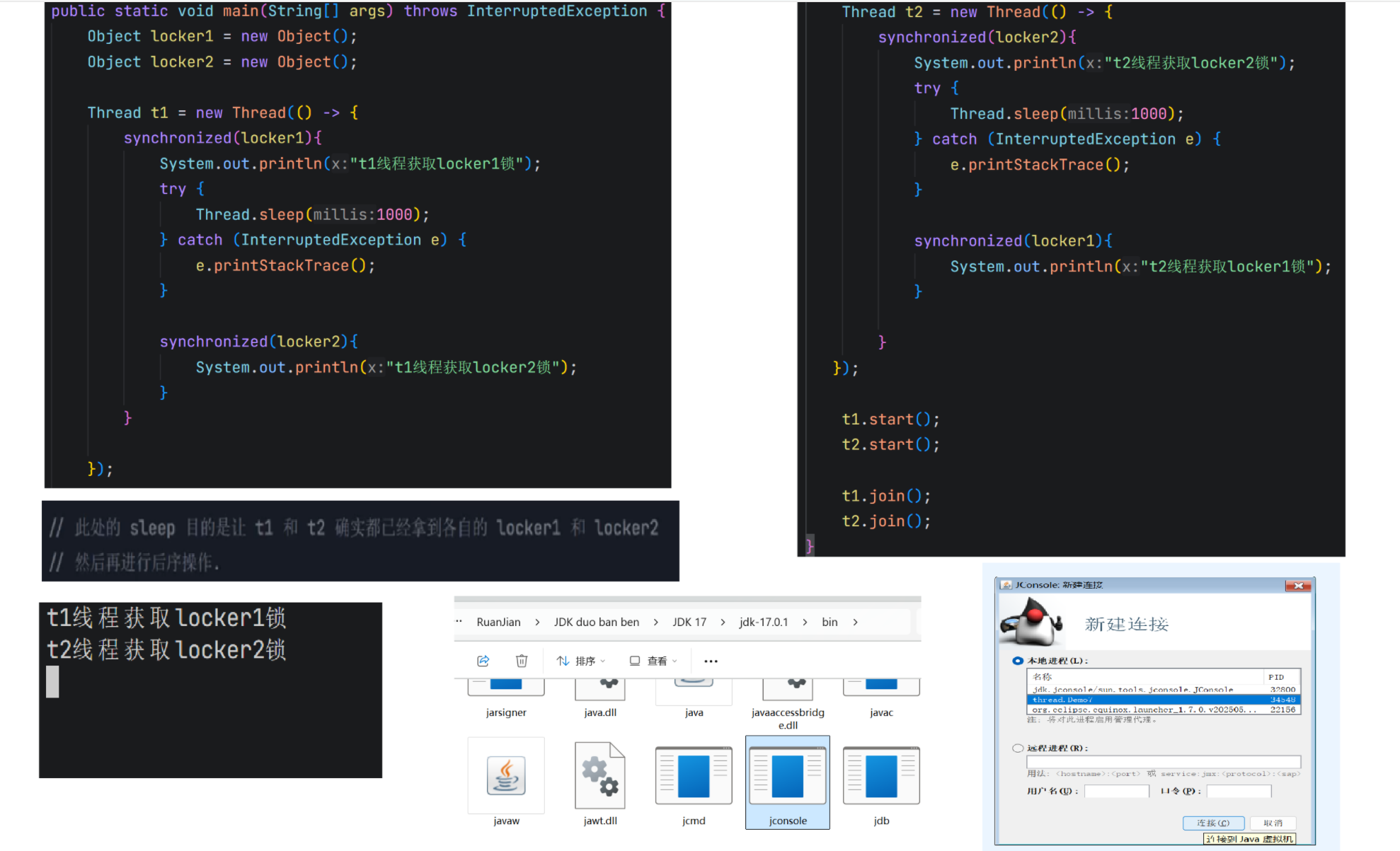
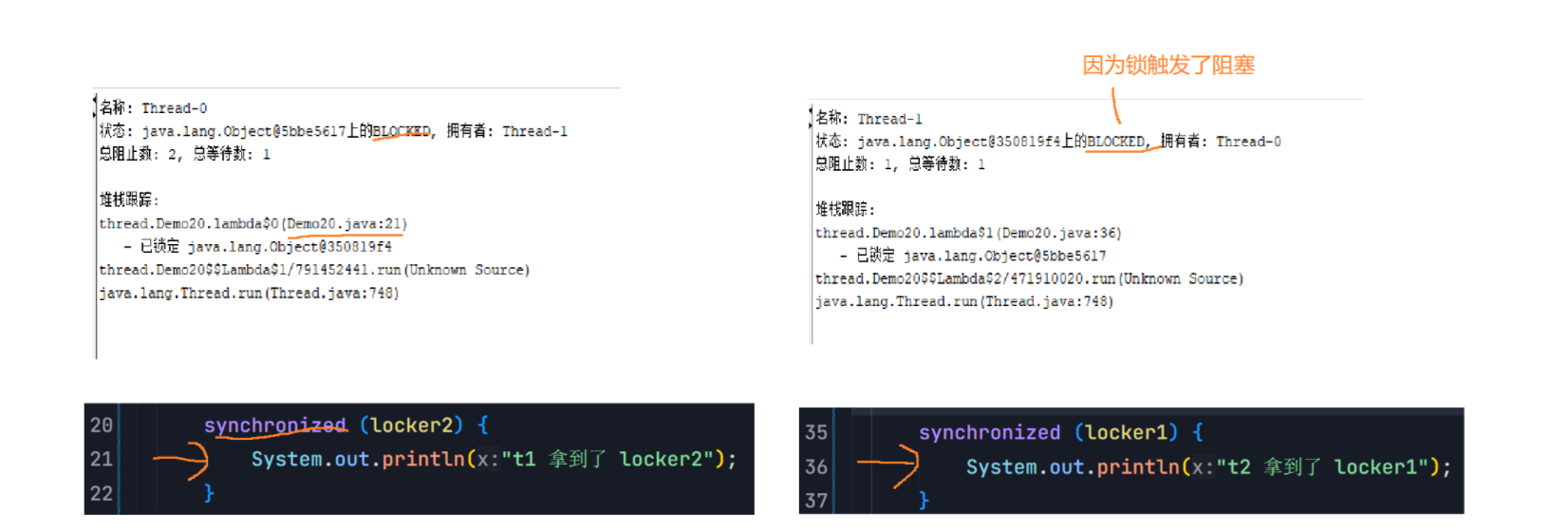



Object lock1 = new Object();Object lock2 = new Object();Thread t1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock1) {synchronized (lock2) {// do something...}}}};t1.start();Thread t2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock2) {synchronized (lock1) {// do something...}}}};t2.start();不会产生环路等待的代码:约定好先获取lock1,再获取lock2,就不会环路等待。
Object lock1 = new Object();Object lock2 = new Object();Thread t1 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock1) {synchronized (lock2) {// do something...}}}};t1.start();Thread t2 = new Thread() {@Overridepublic void run() {synchronized (lock1) {synchronized (lock2) {// do something...}}}};t2.start();6.synchronized关键字 - 监视器锁(monitor lock)
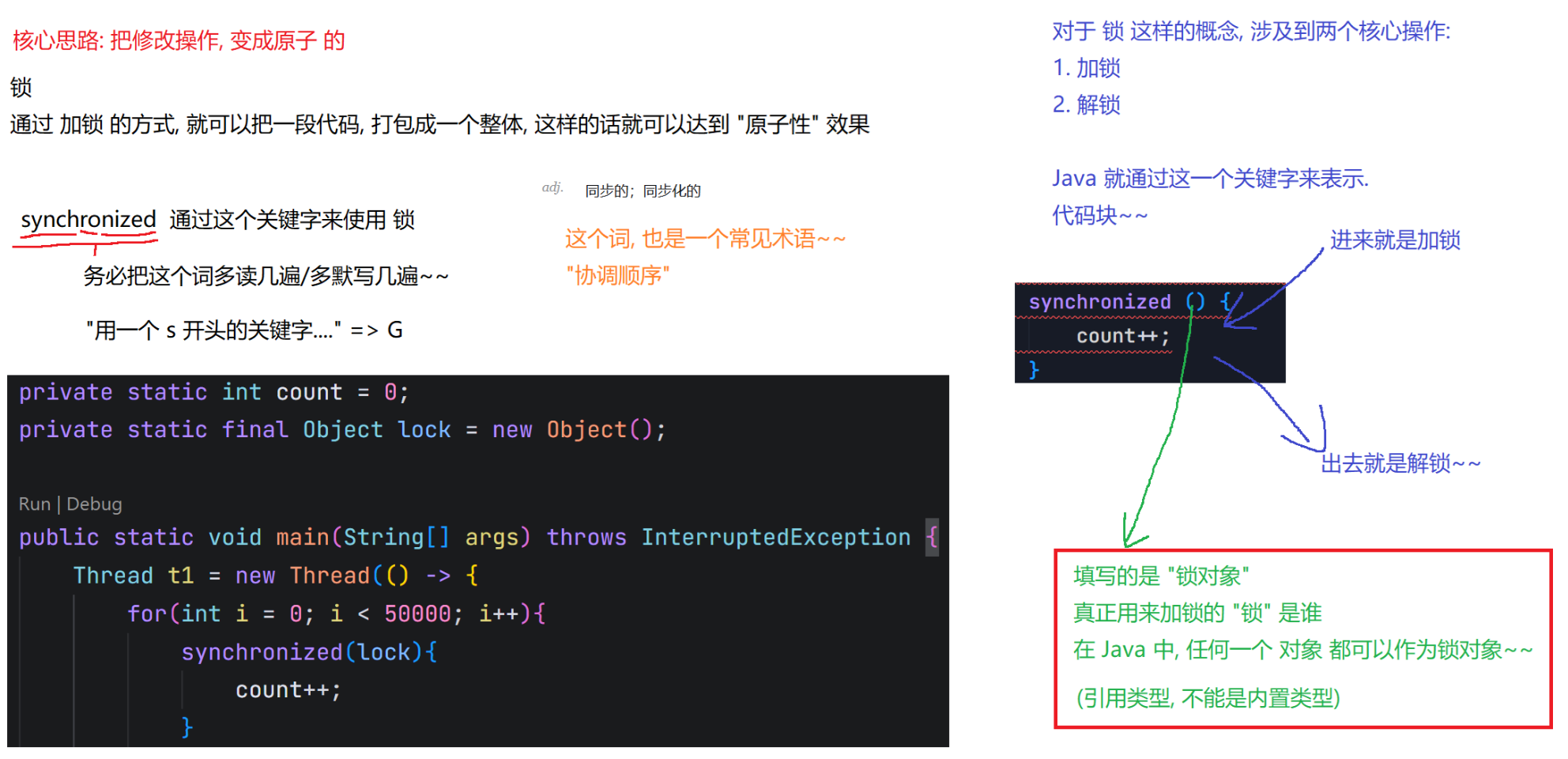

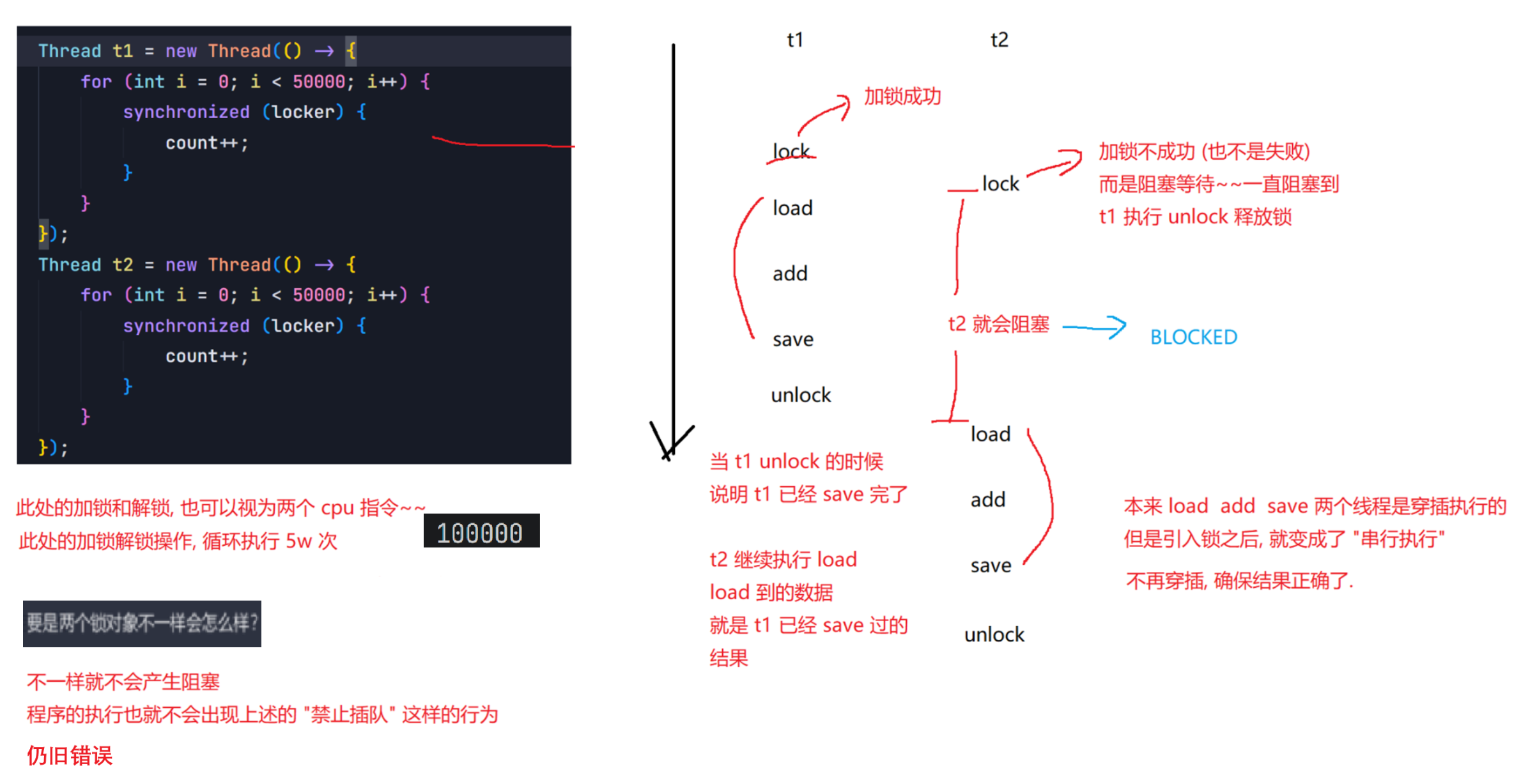
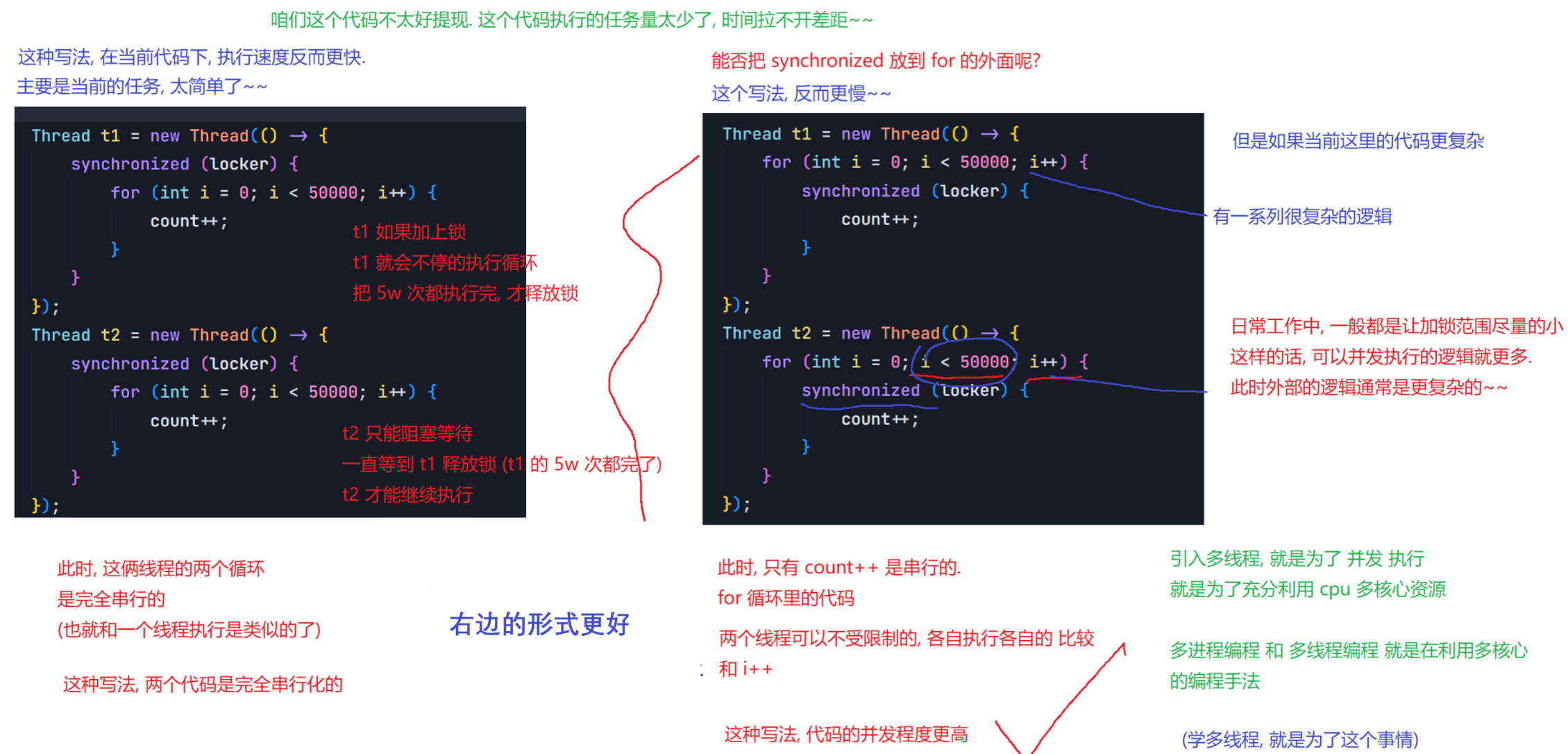
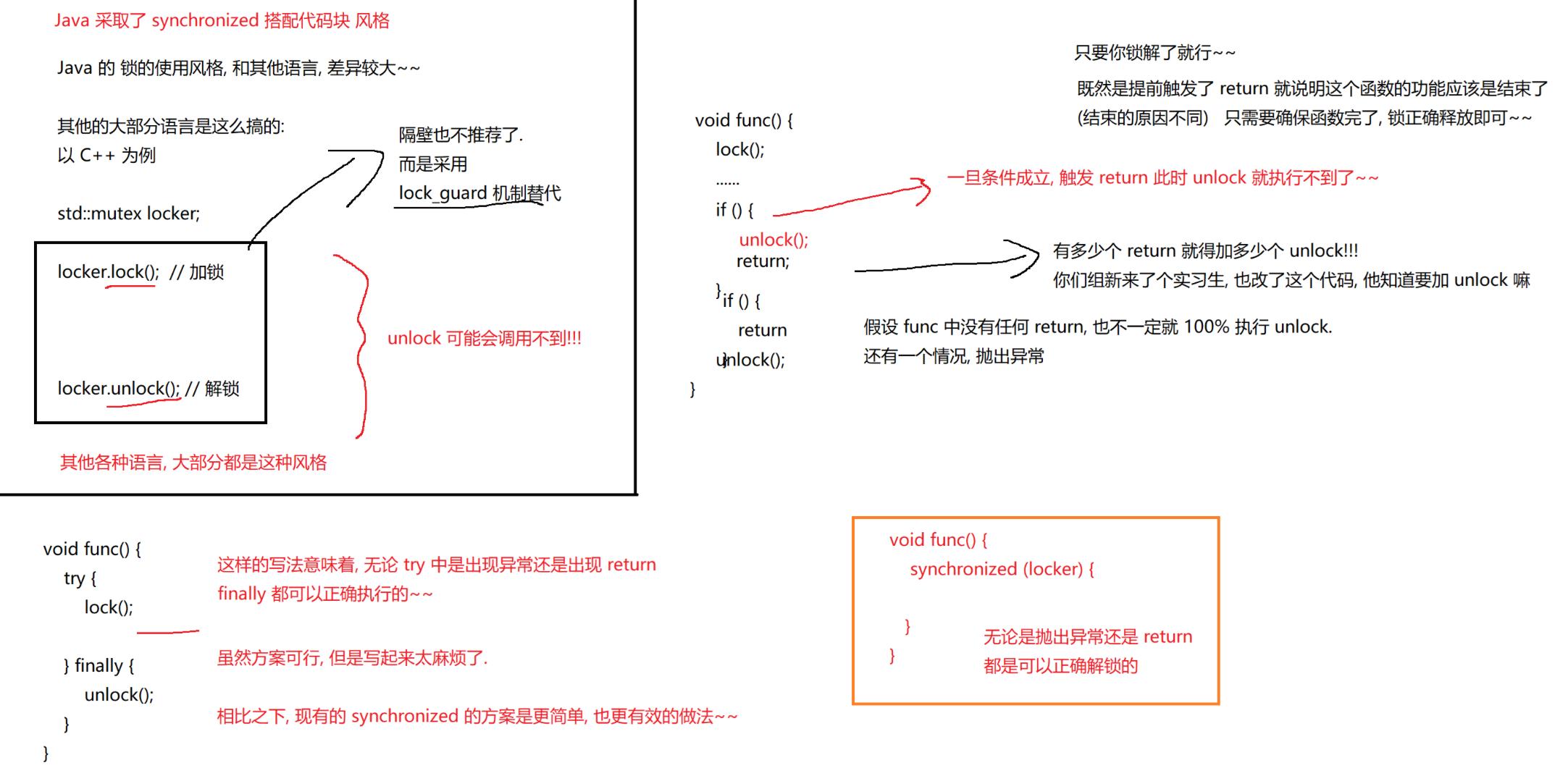
6.1 synchronized的特性




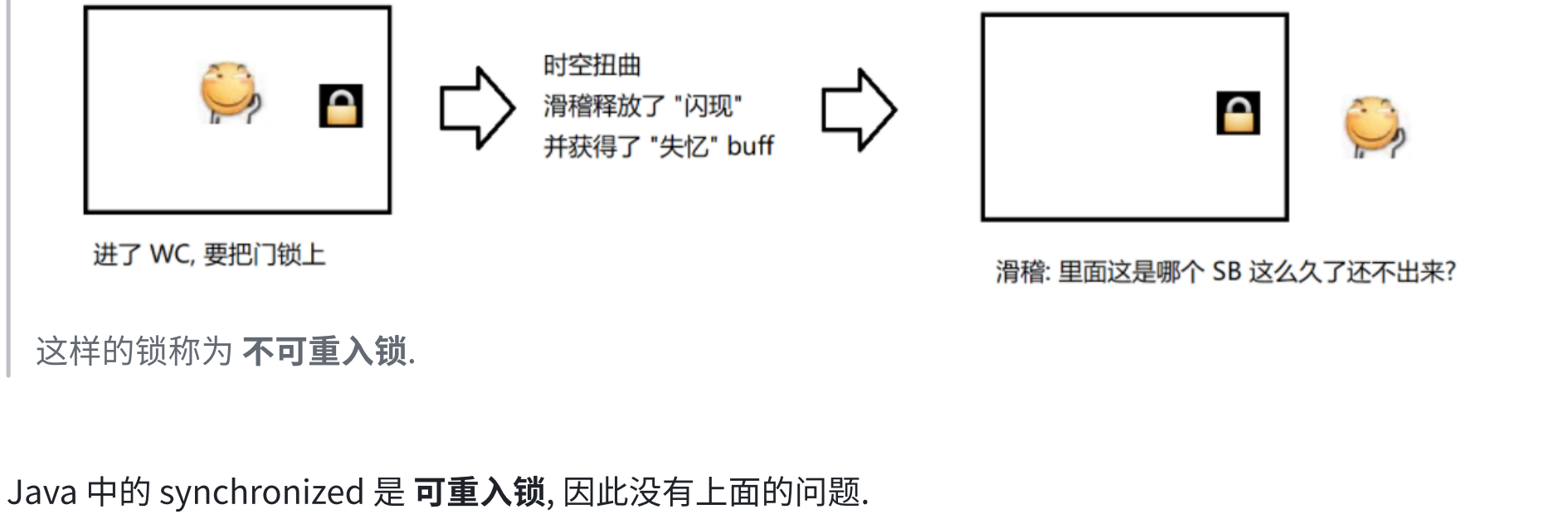




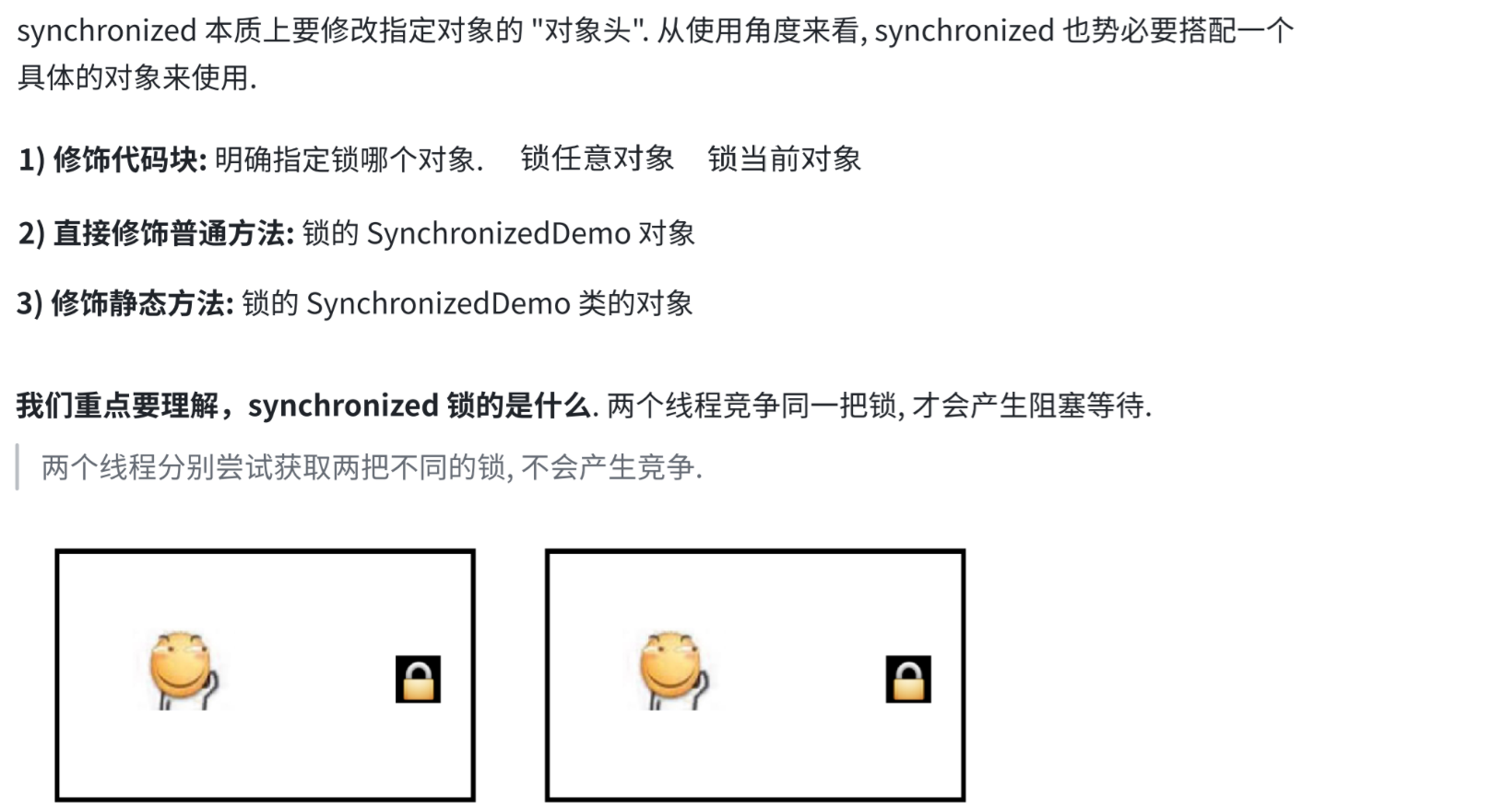
6.2 synchronized使用示例
重点是第一种,也是最常用的。

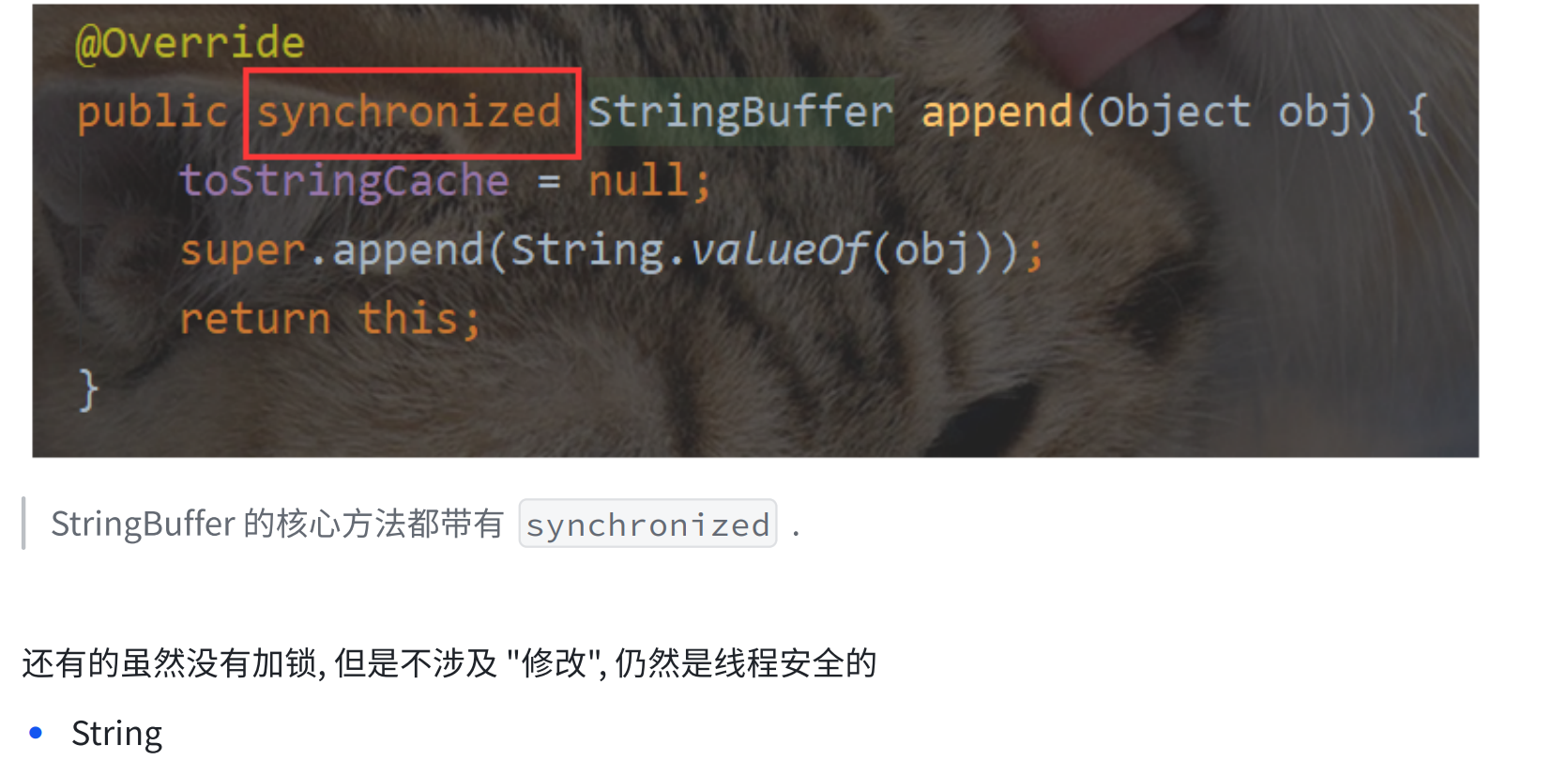
6.3 Java标准库中的线程安全类

7.wait和notify

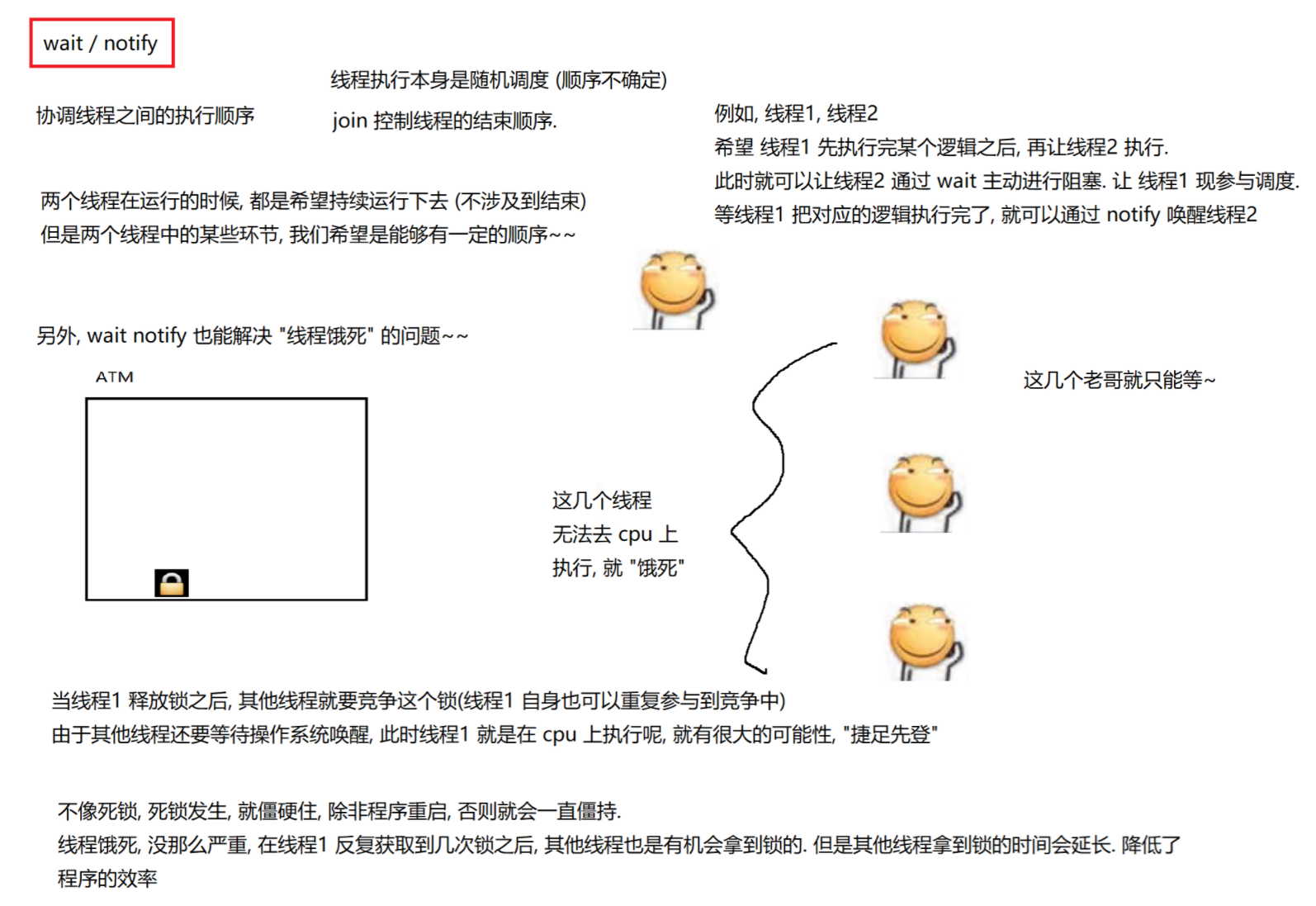

7.1 wait()方法


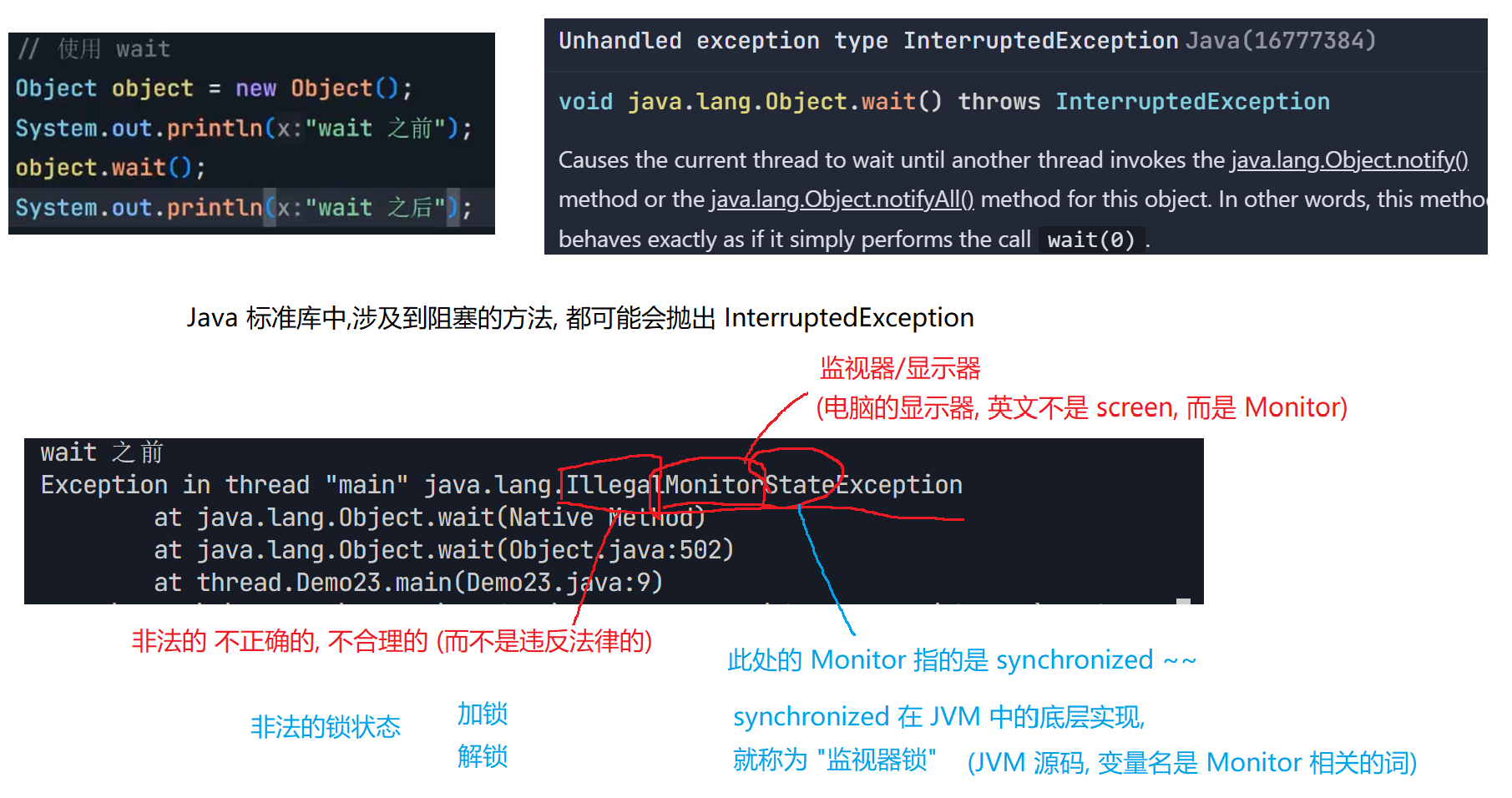
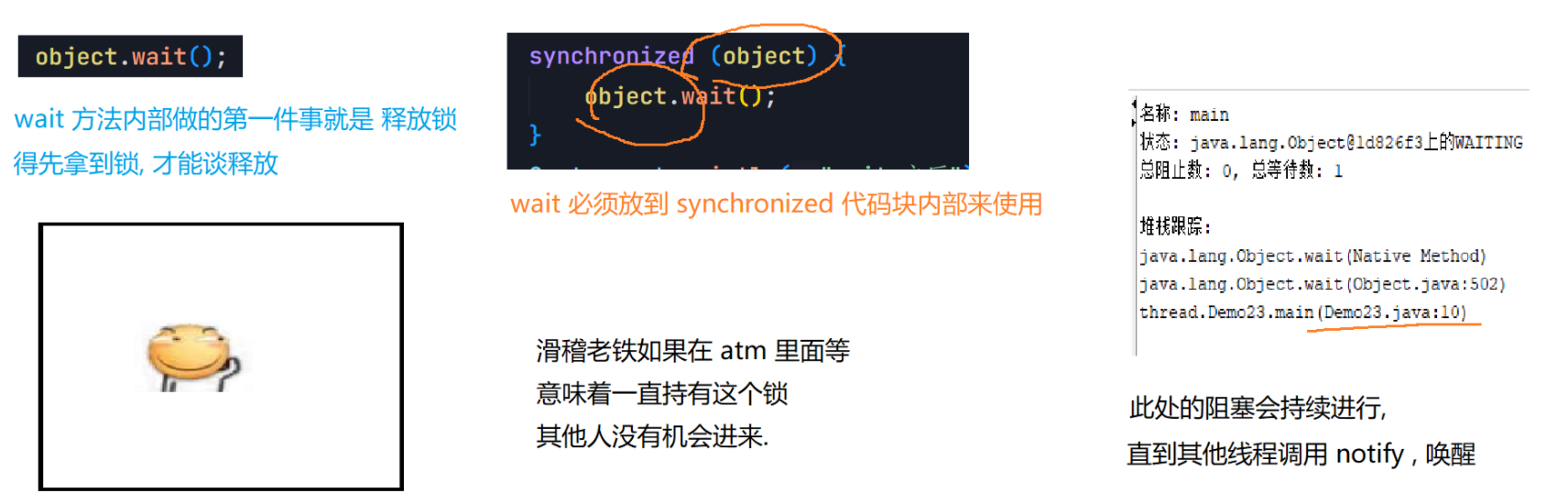
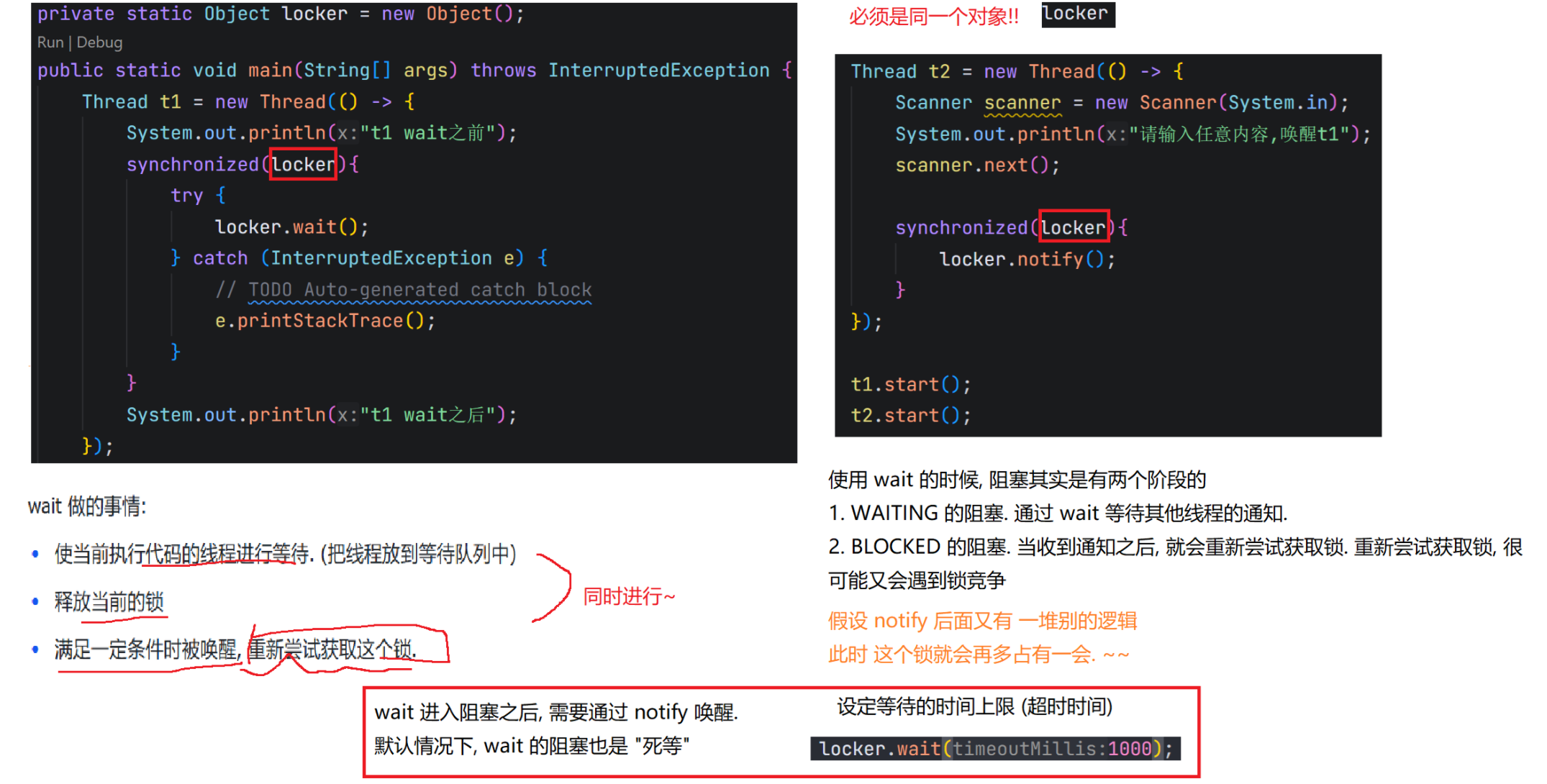
7.2 notify() notifyAll() 方法

![]()



7.3 wait和sleep的对比(面试题)


8.多线程案例
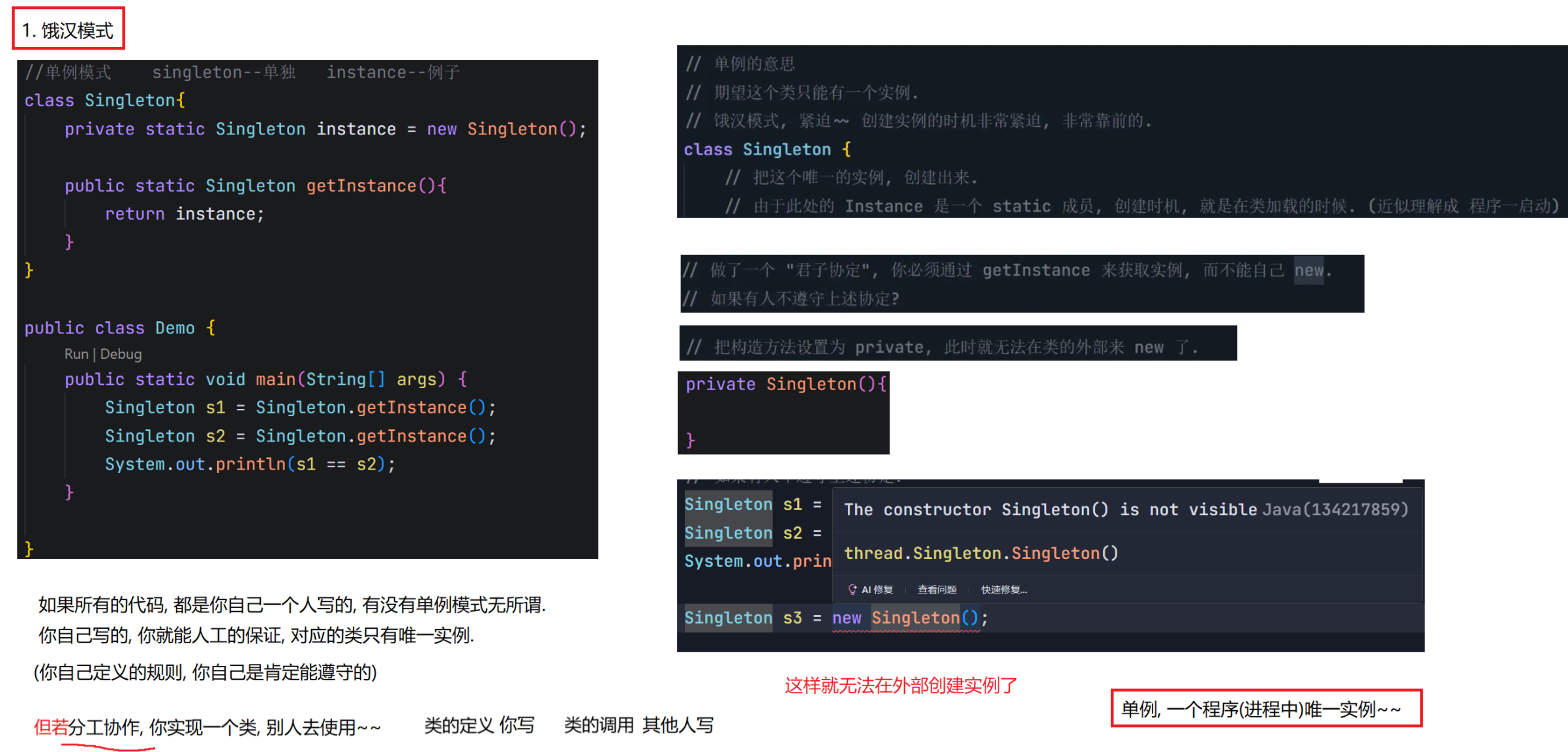
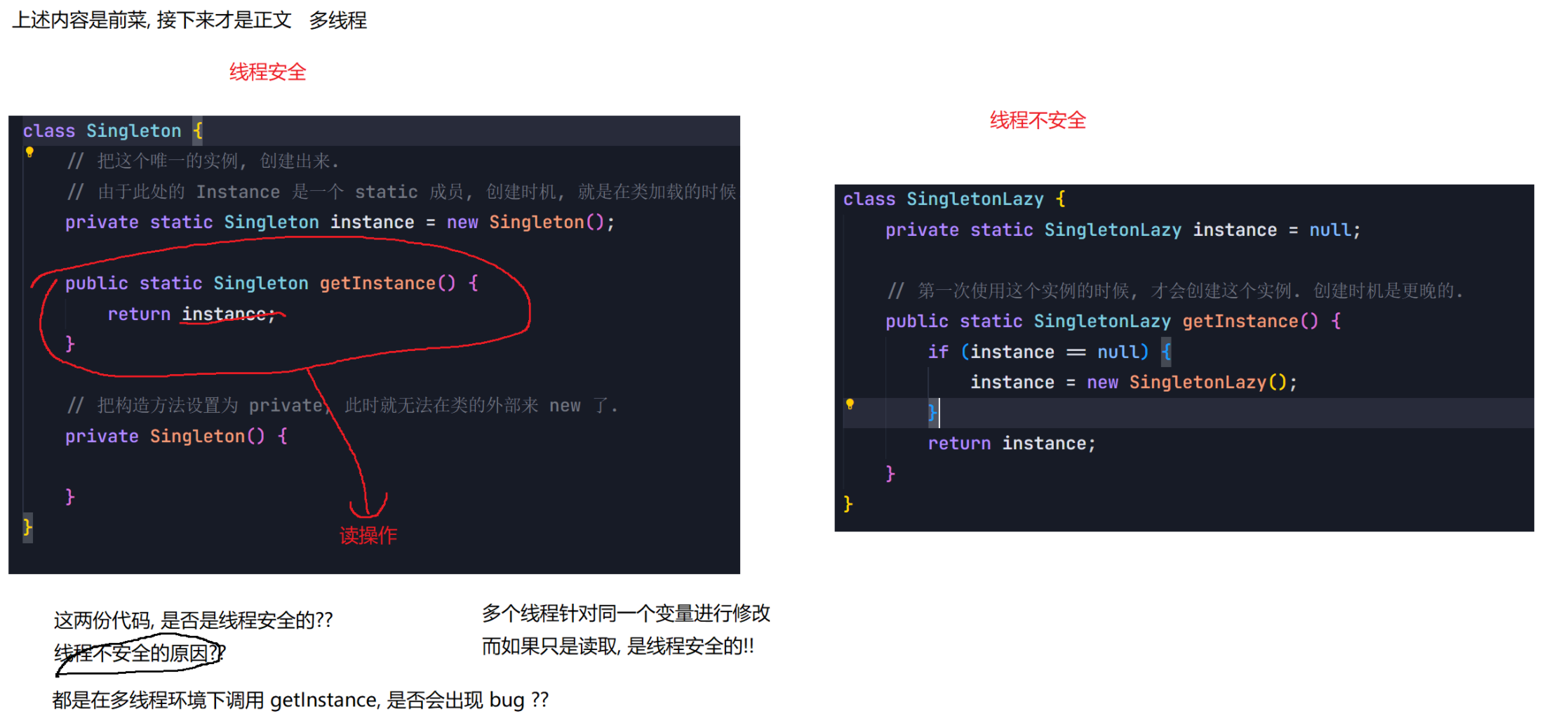
8.1 单例模式(面试常考)
单例模式是校招中最常考的设计模式之一









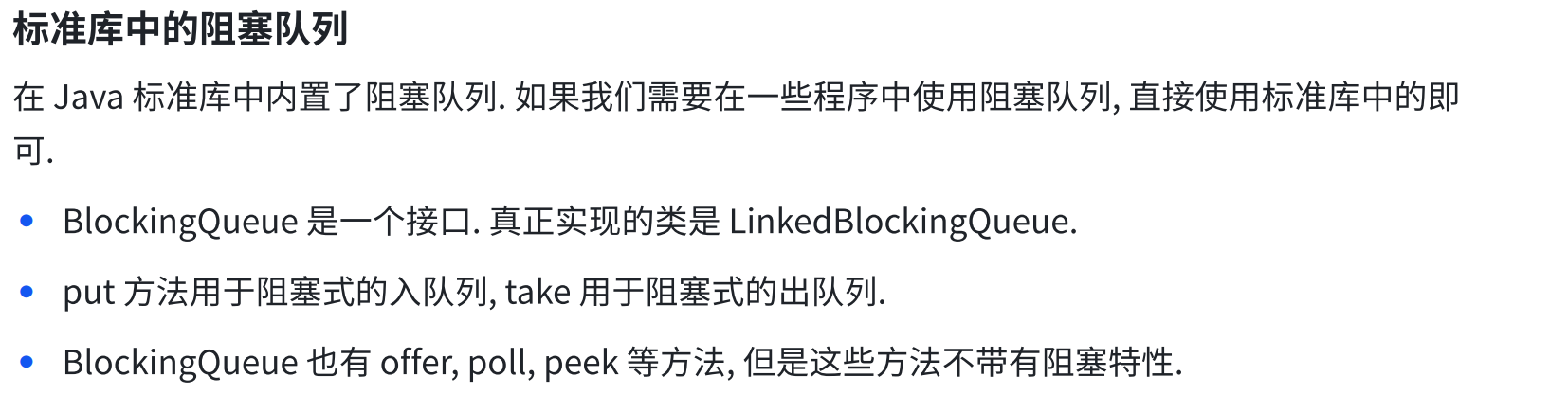
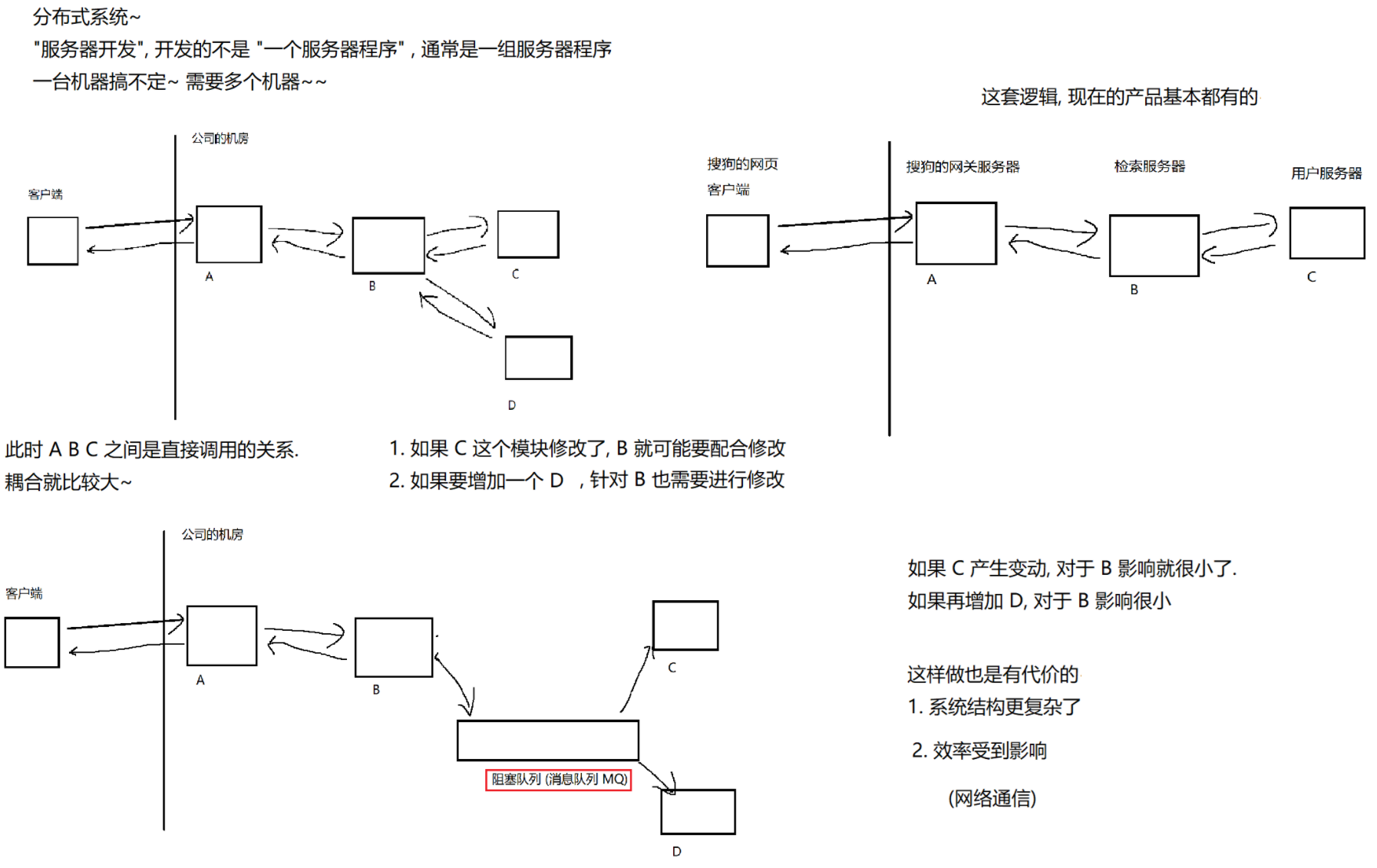
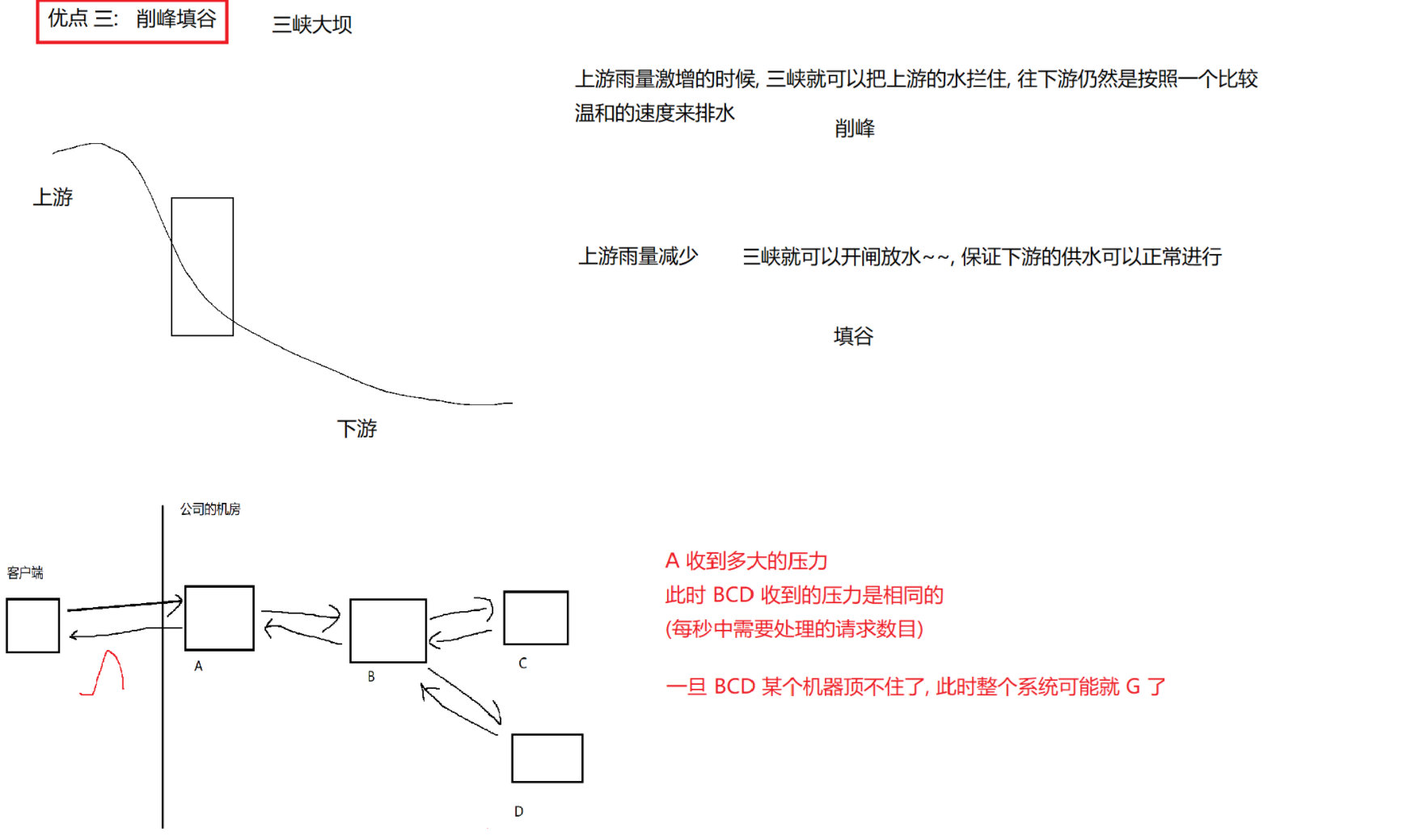
8.2 阻塞队列



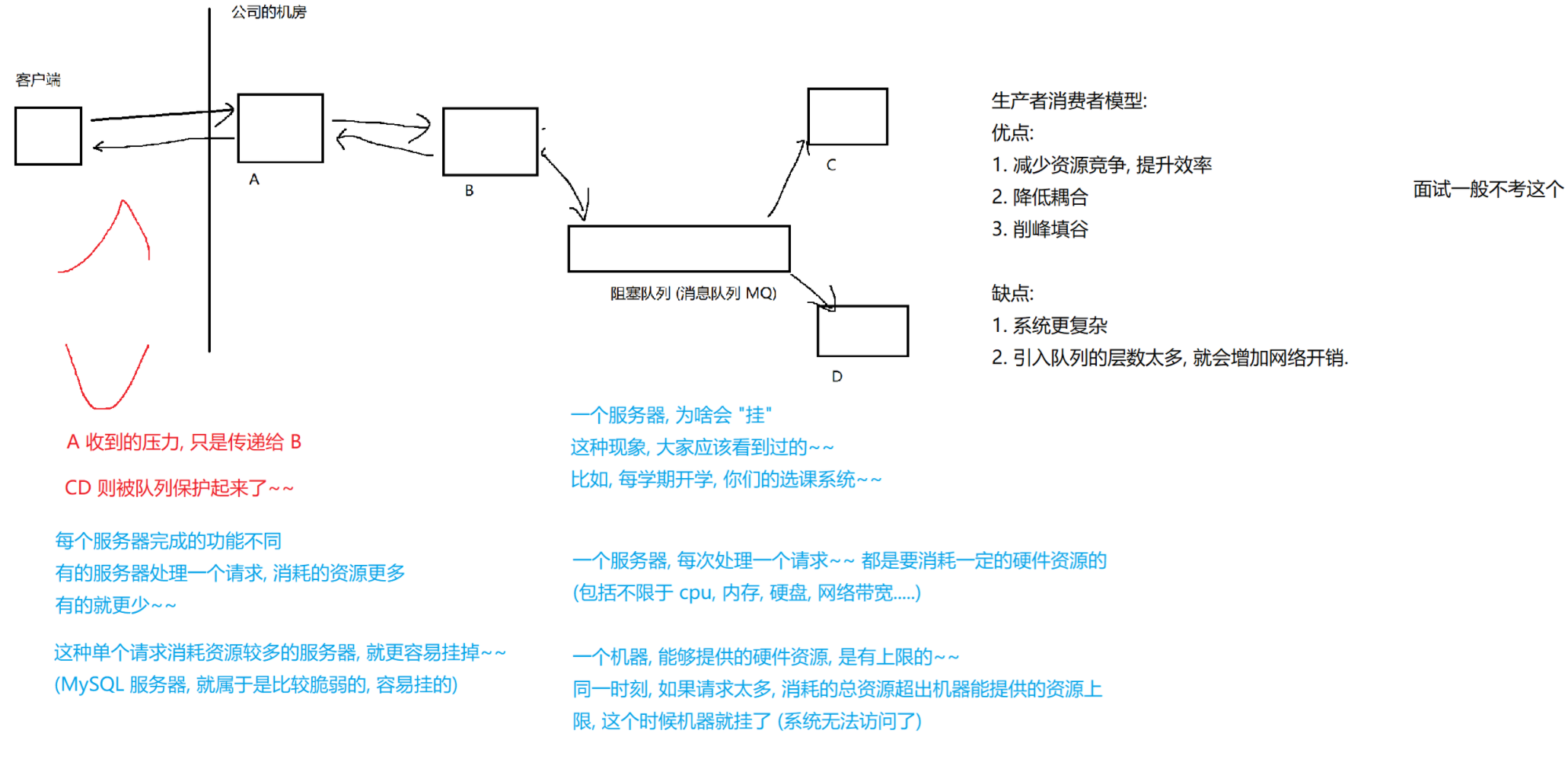
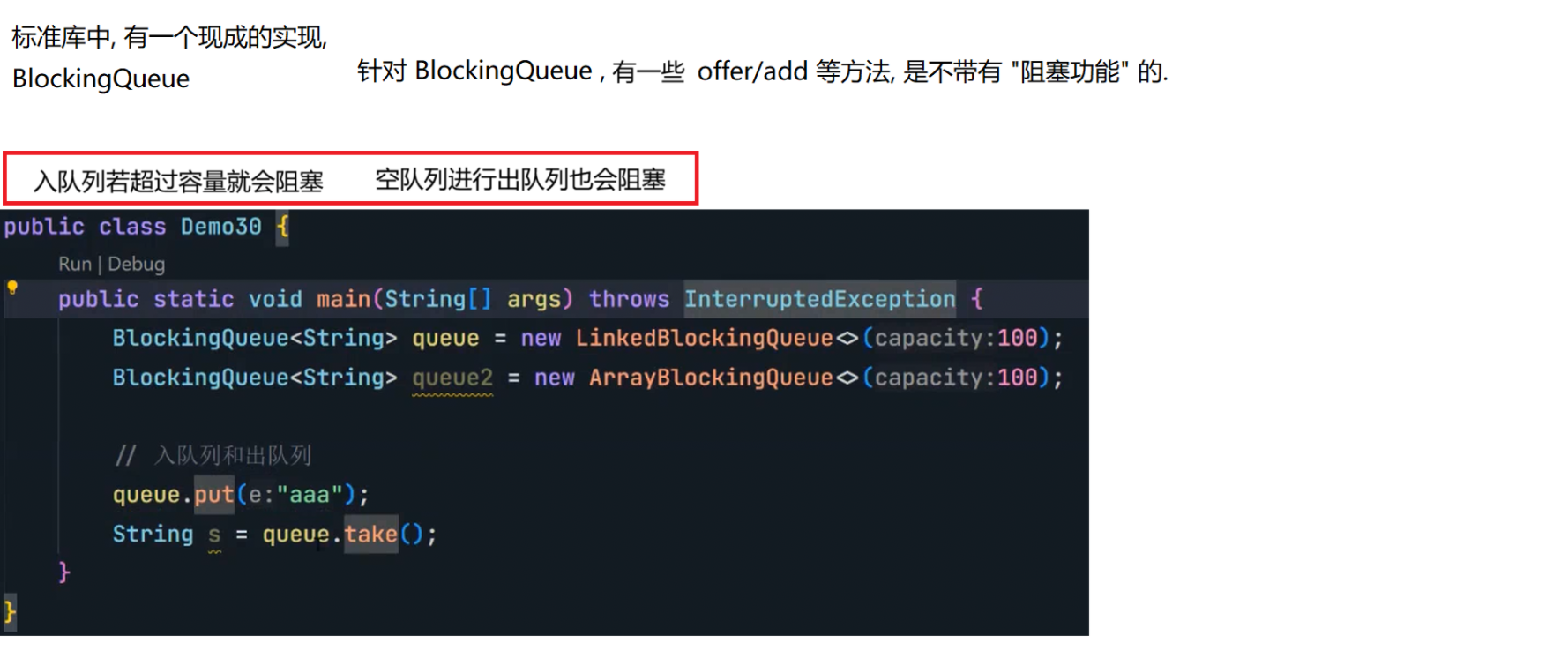
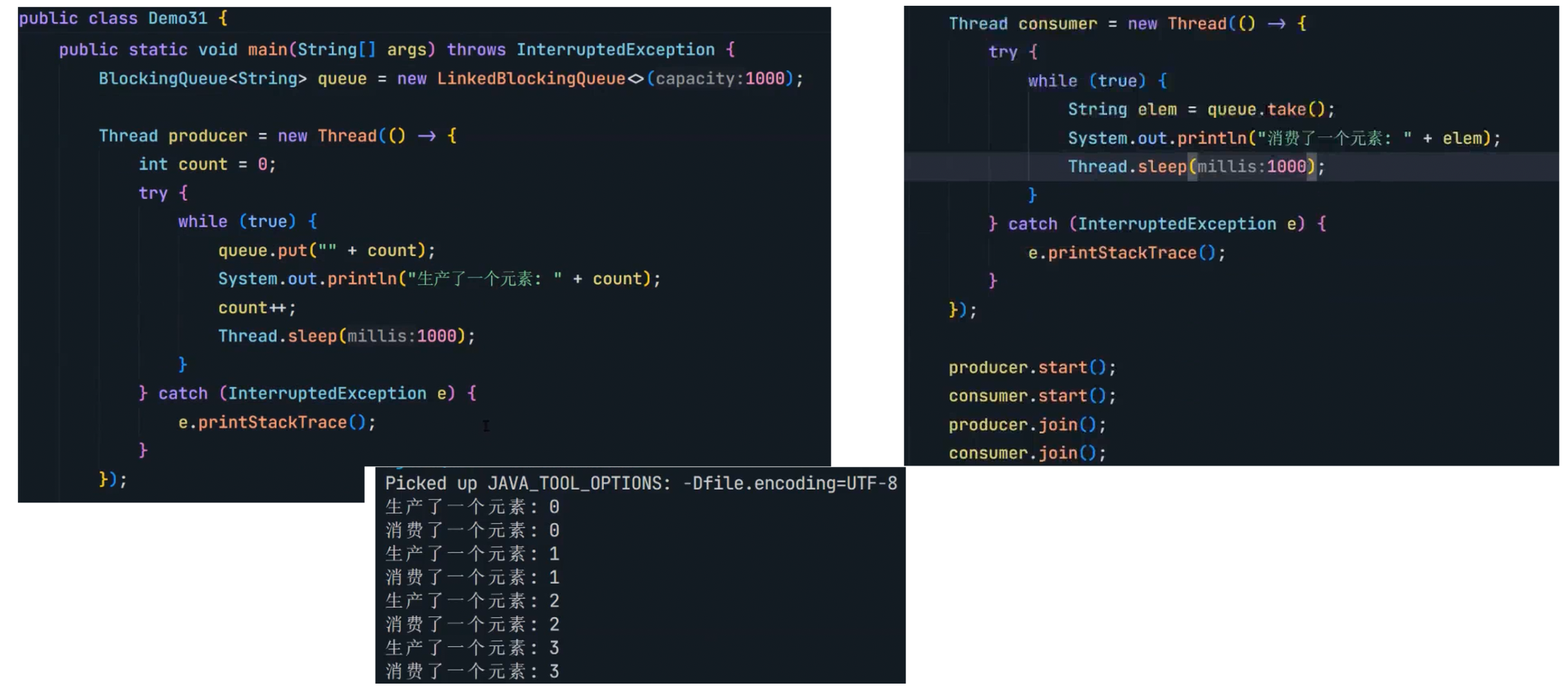

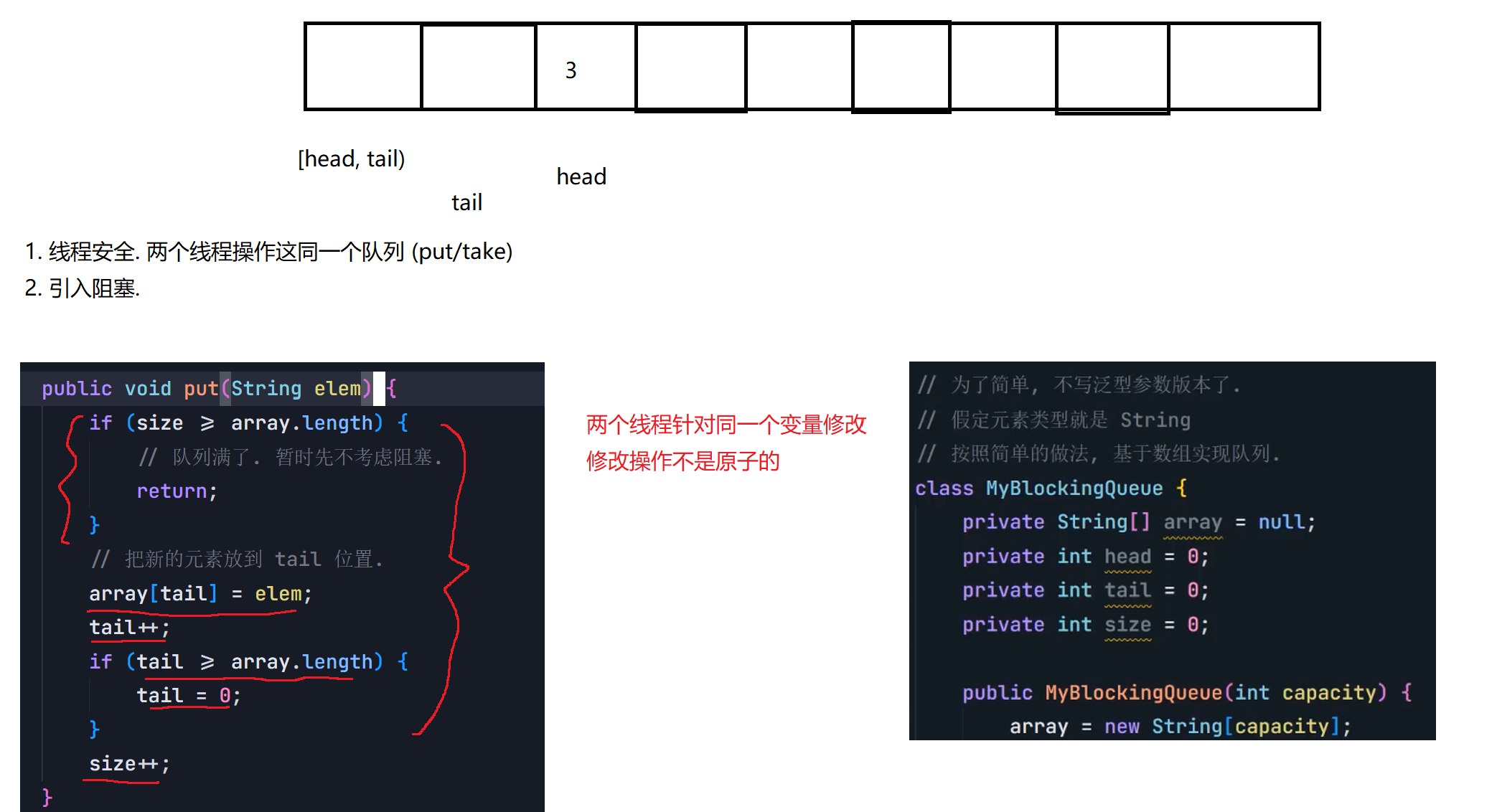
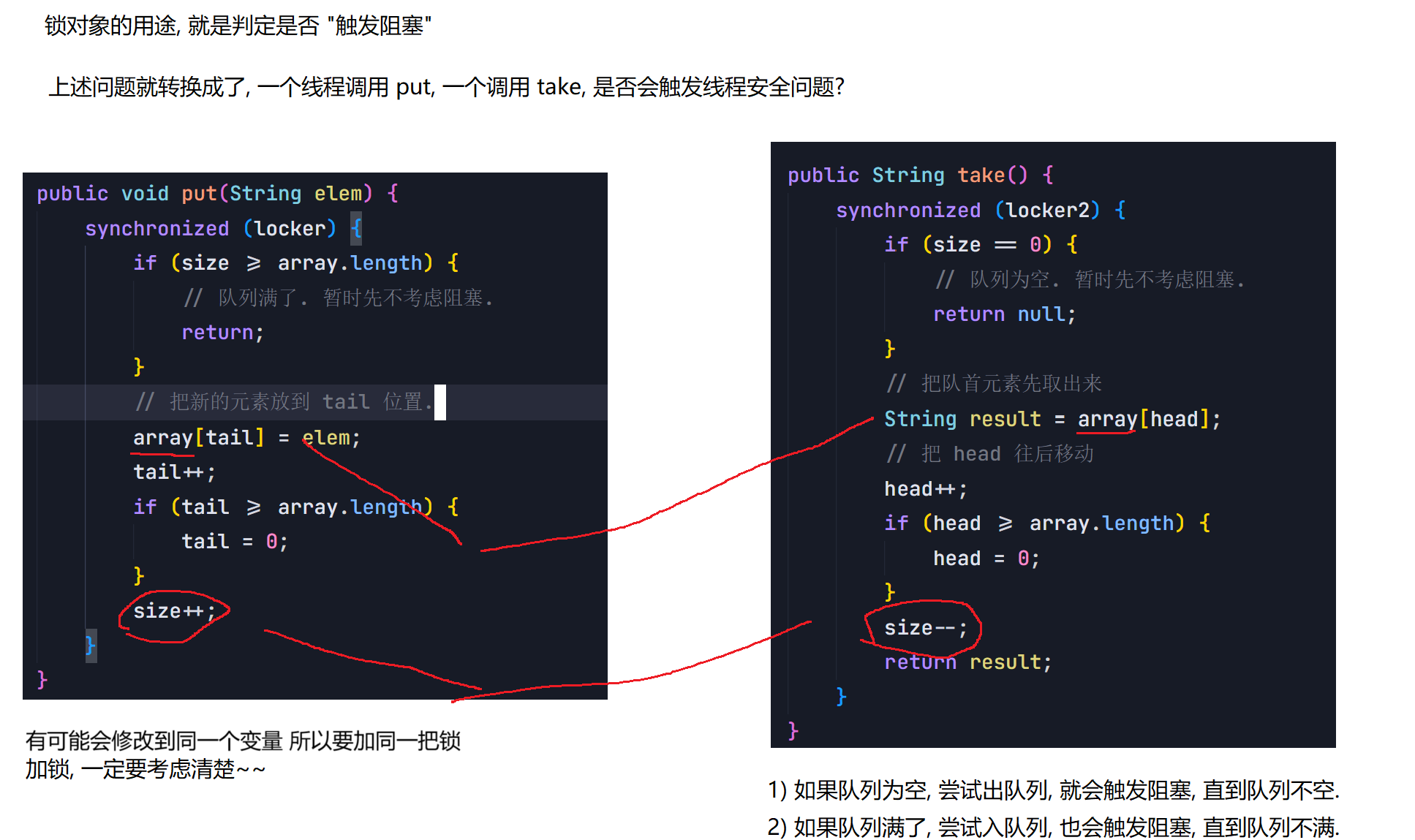
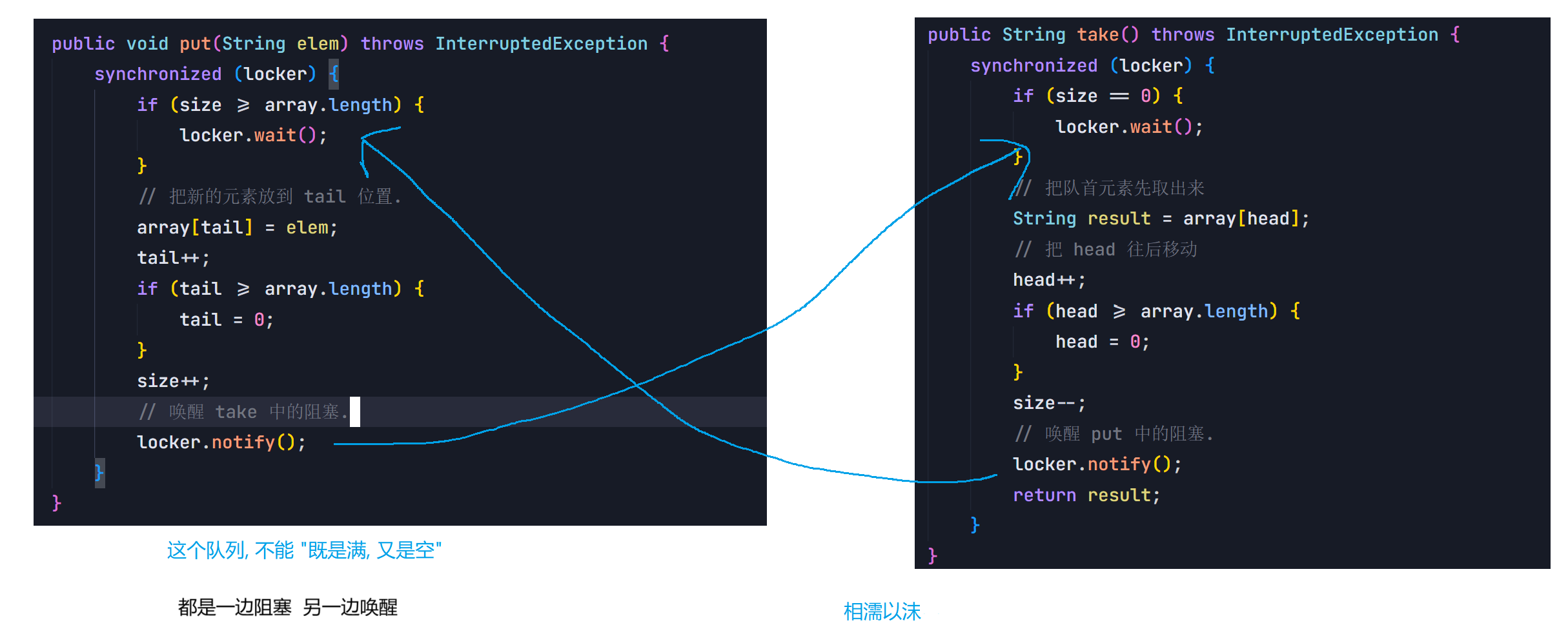
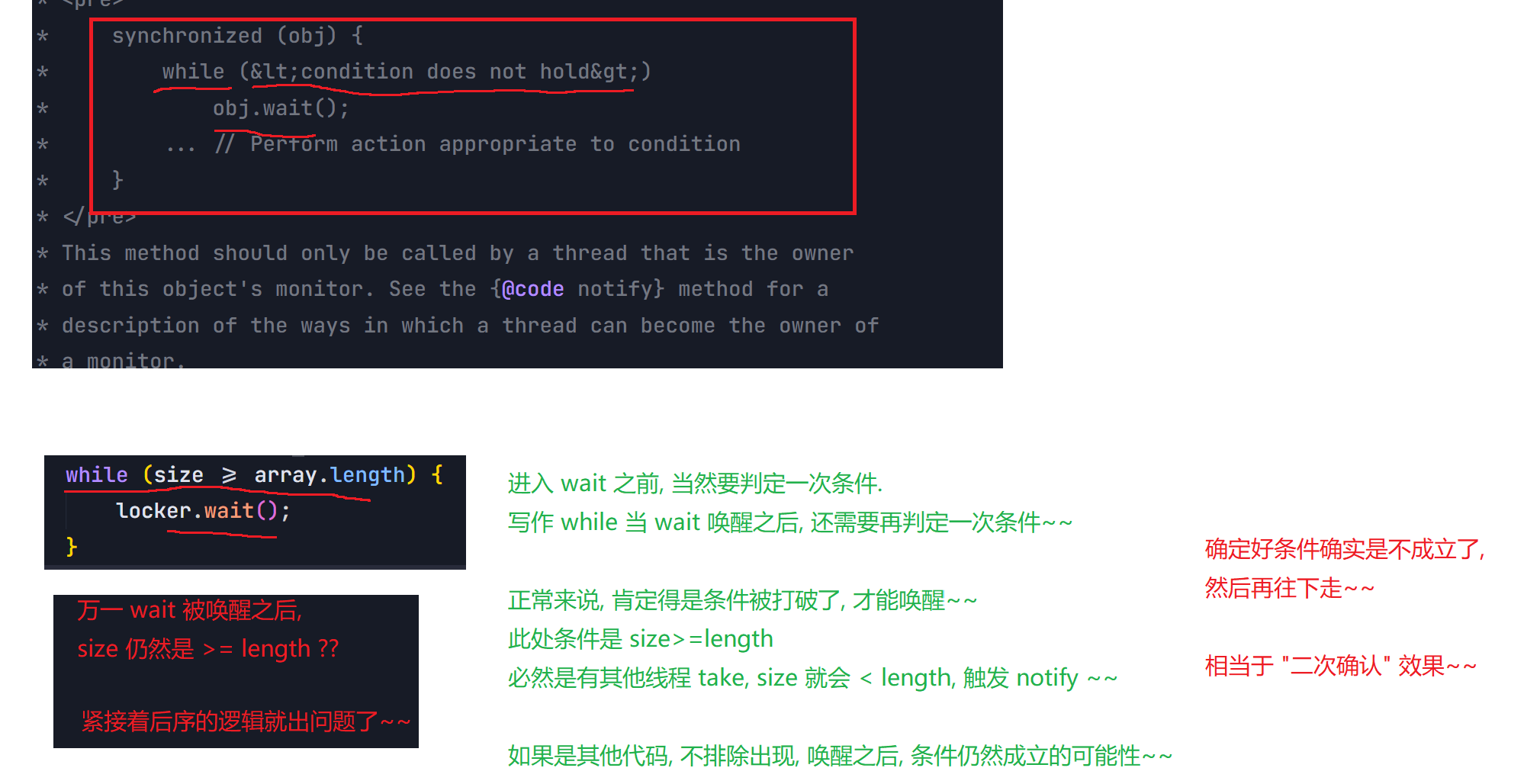
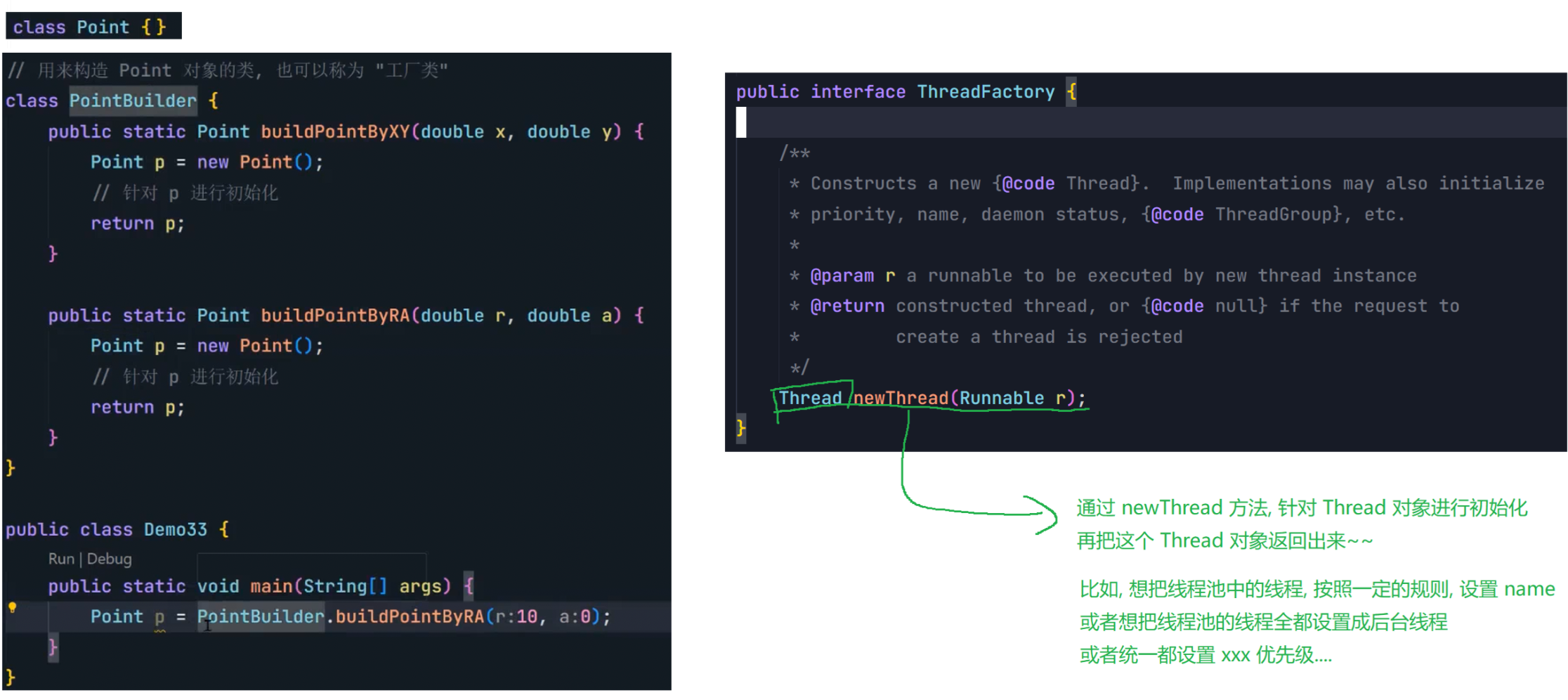
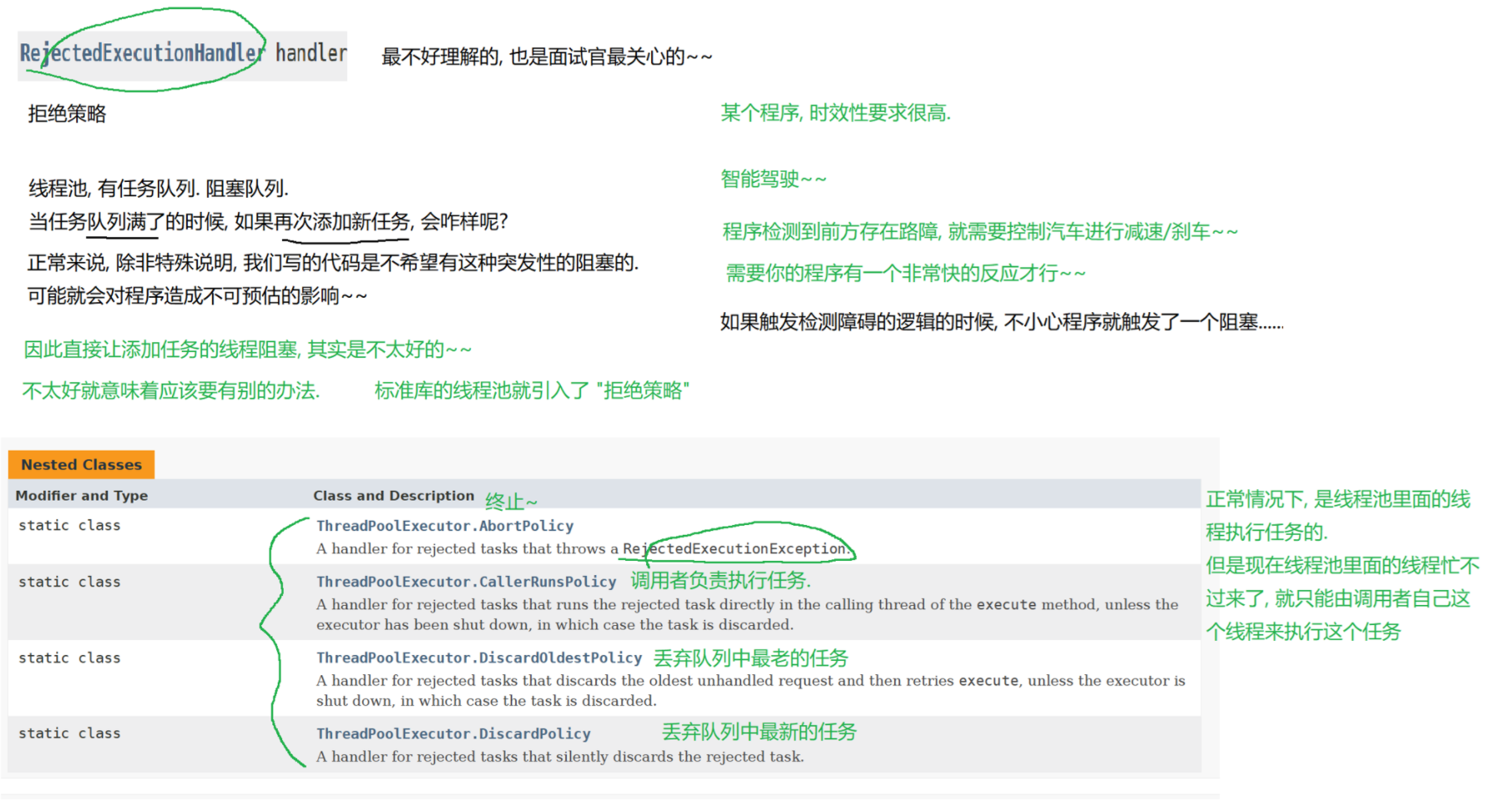
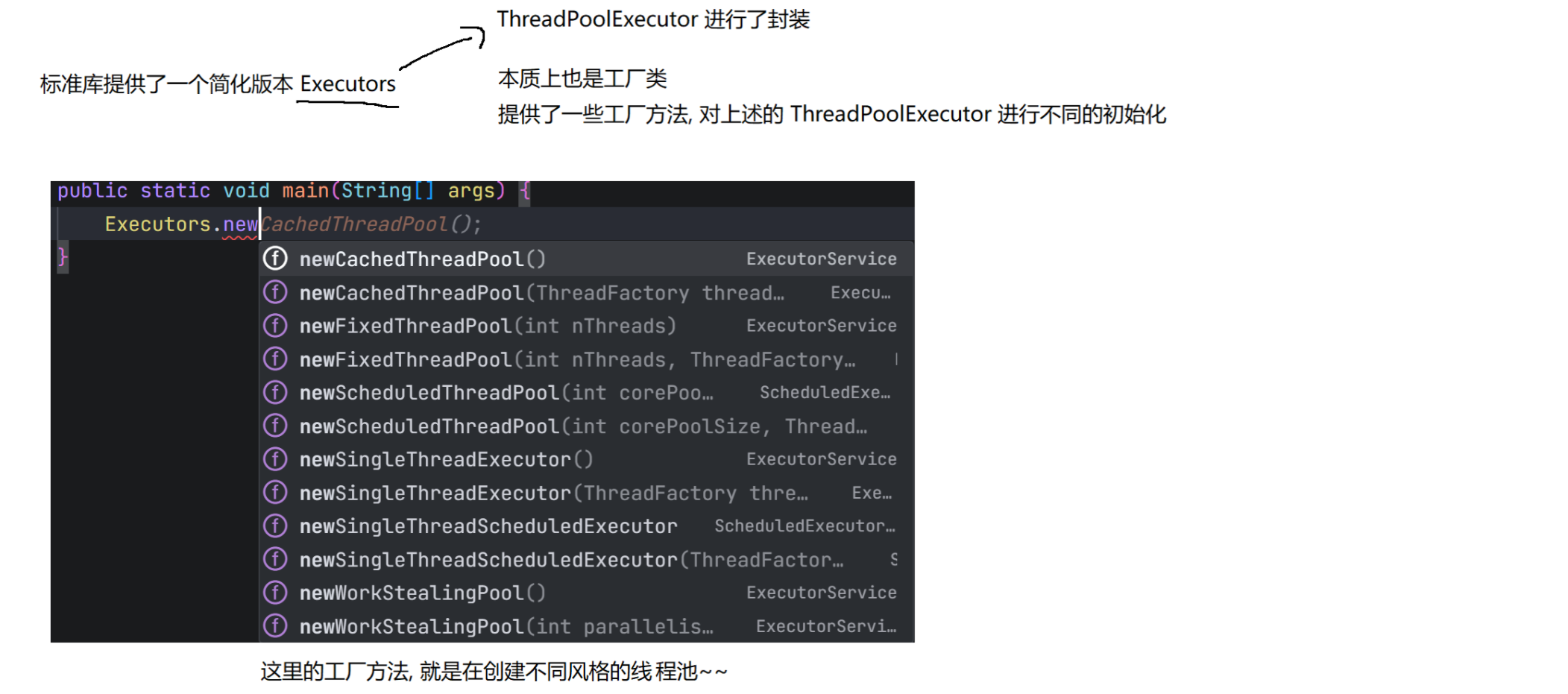
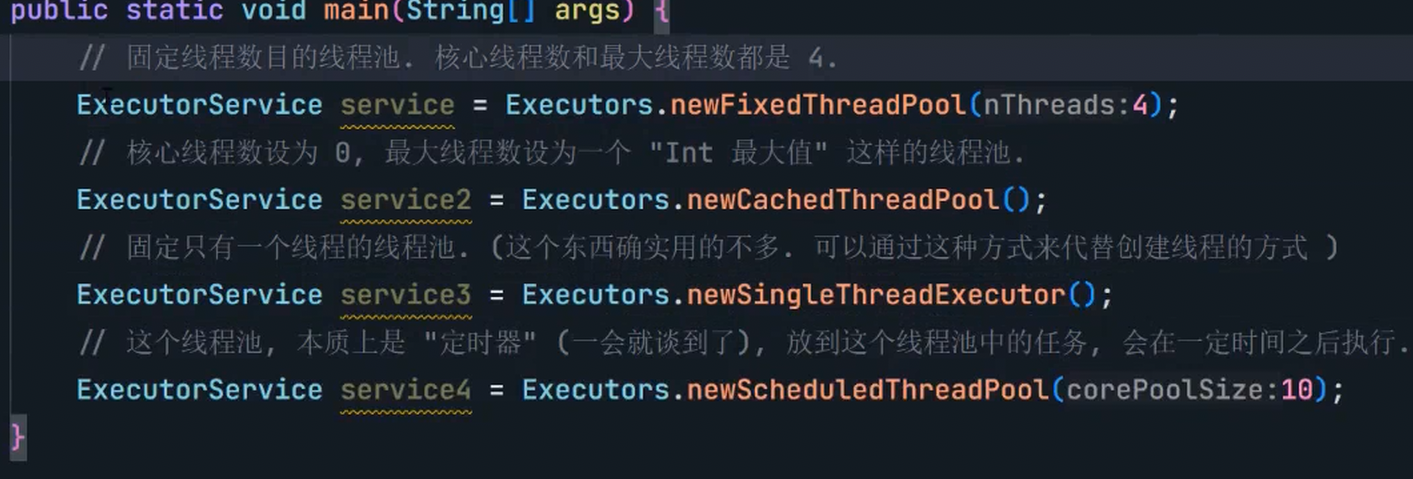
8.3 线程池
(1)概念
 线程池最大的好处就是减少每次启动、销毁线程的损耗。
线程池最大的好处就是减少每次启动、销毁线程的损耗。
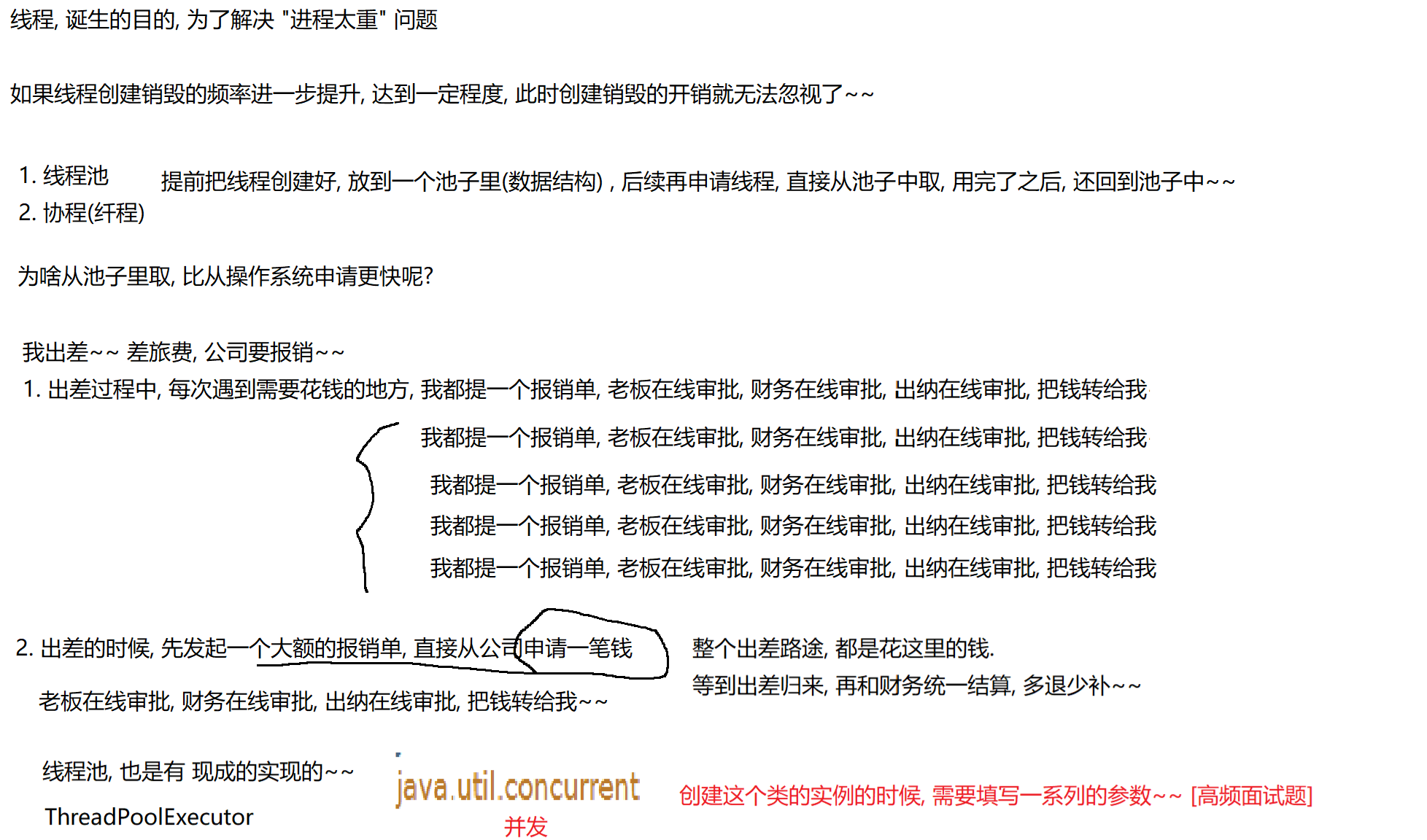



(2)模拟实现
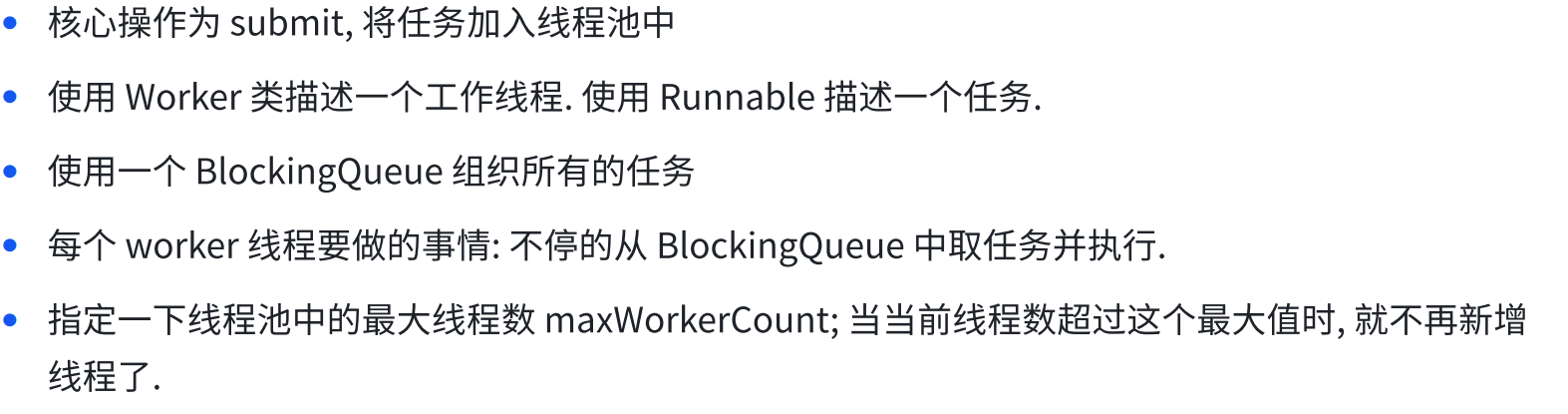

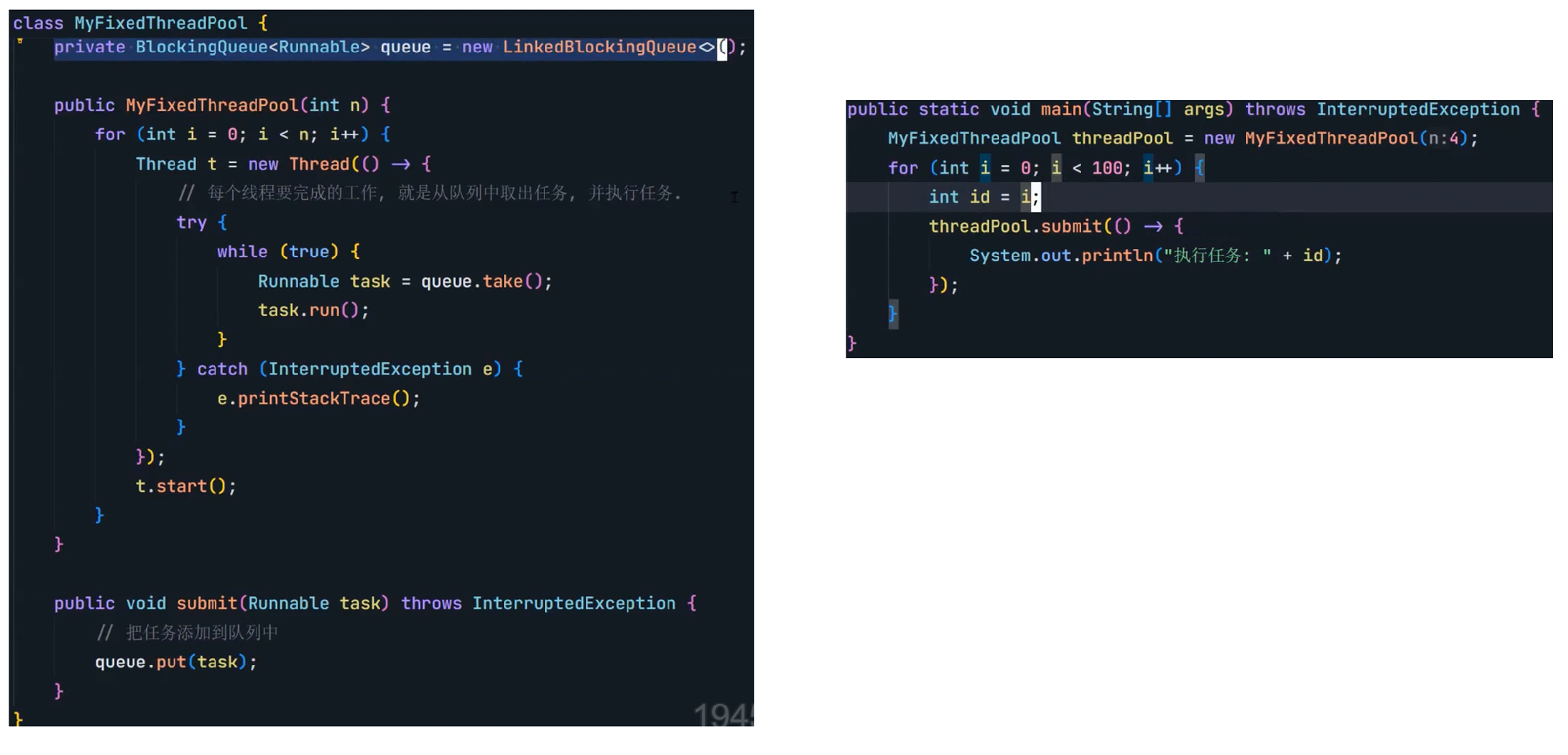
8.4 定时器
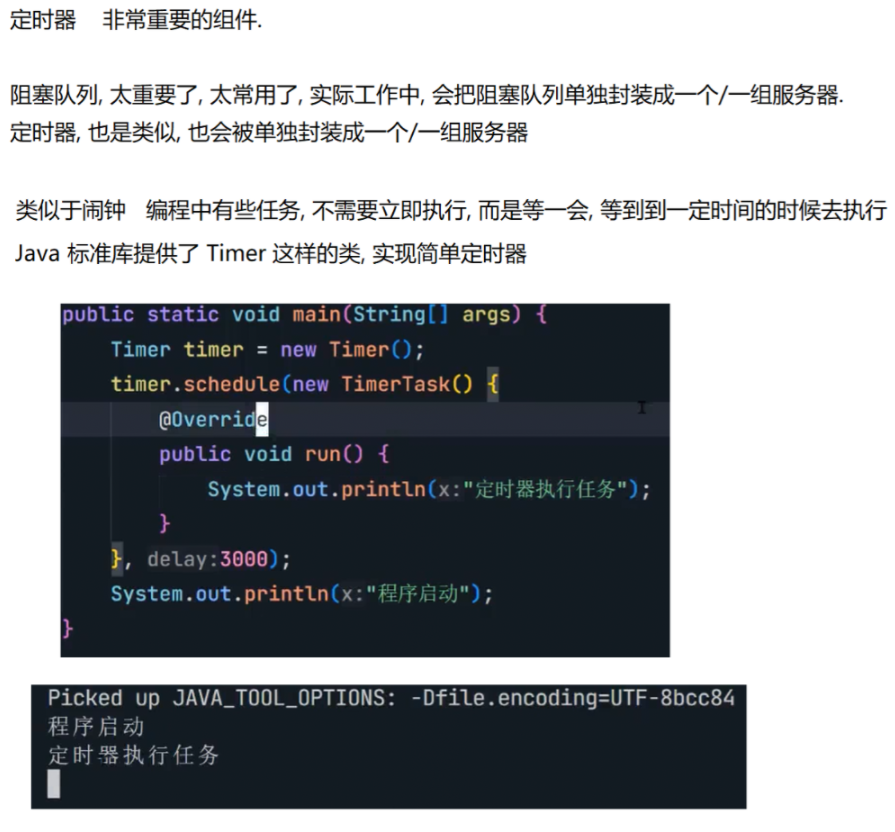

自行实现一个定时器
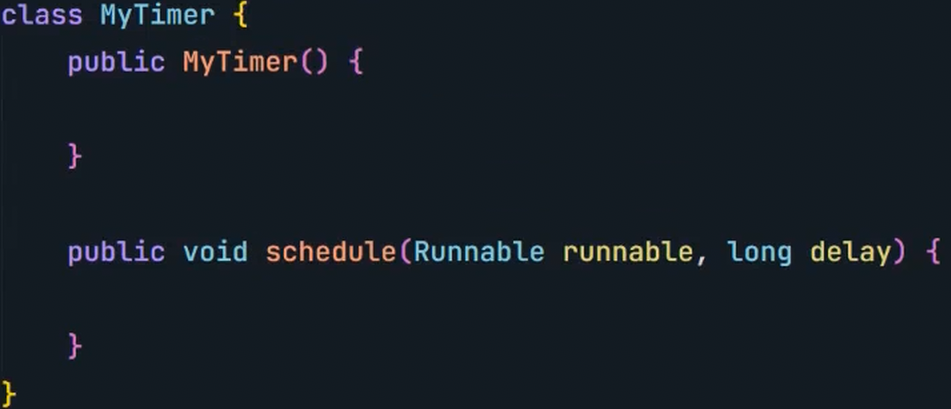
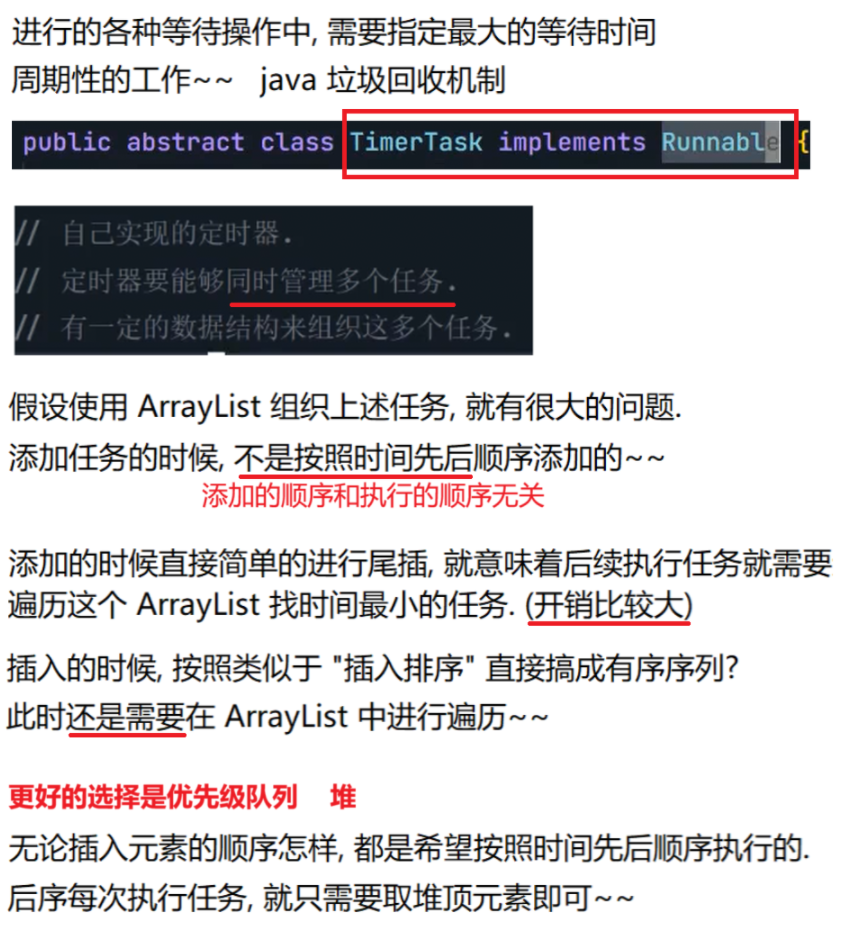
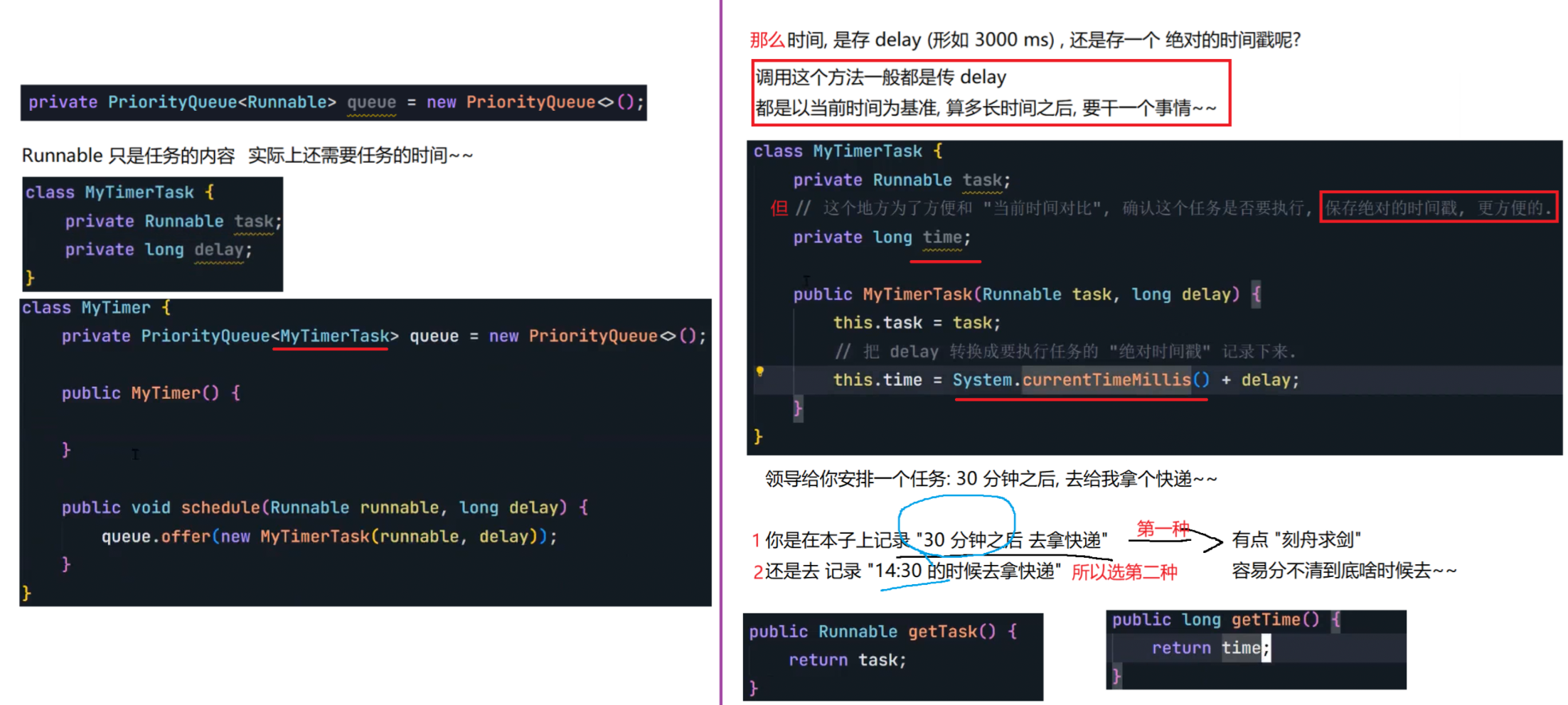
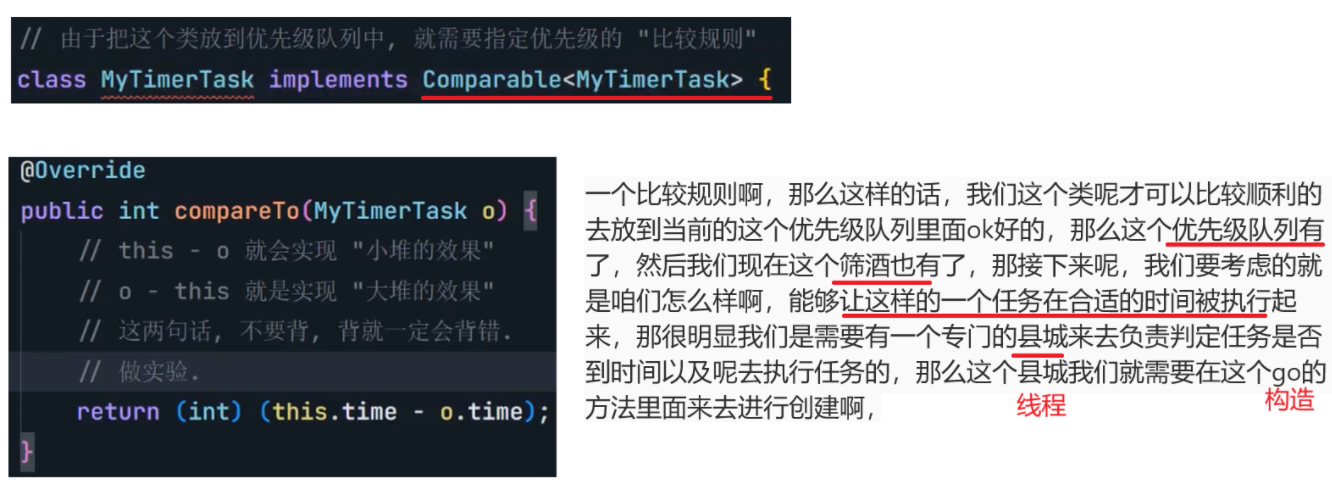
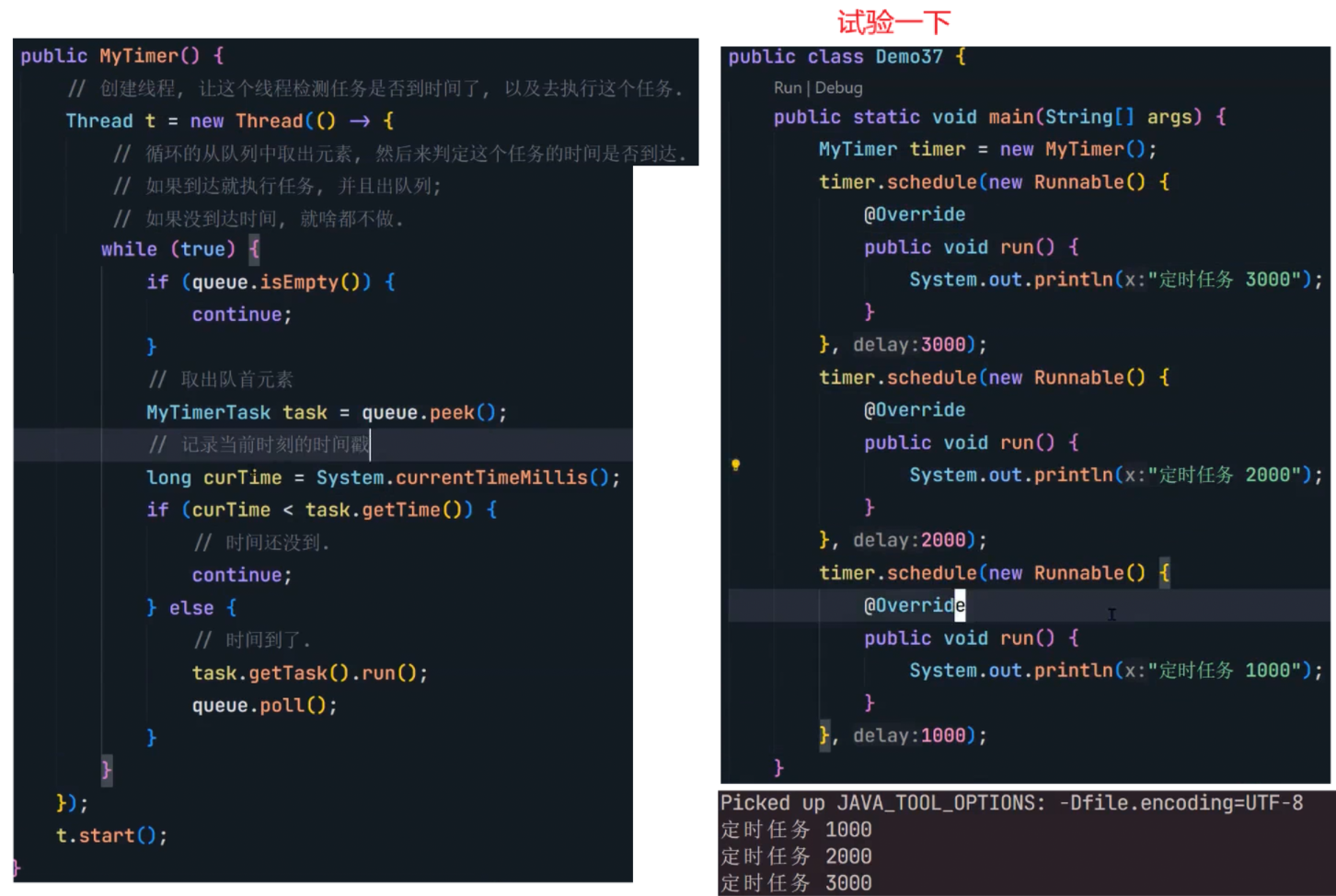
虽然执行结果看起来对了,但其实还是有几个问题的。




9.总结




