深入浅出红黑树:C++ 完整实现与核心原理剖析
在数据结构的世界里,平衡二叉搜索树是解决 “二叉搜索树退化成链表” 问题的关键。红黑树作为其中的经典实现,通过巧妙的颜色约束实现近似平衡,既保证了 O(log N) 的时间复杂度,又比 AVL 树减少了旋转次数,成为 STL 中 map、set 等容器的底层核心。本文将结合完整 C++ 代码,从原理到实现,详细拆解红黑树的核心逻辑。
注:红黑树涉及旋转,如不了解请移步前文:深入理解 AVL 树:自平衡二叉搜索树的原理与实现-CSDN博客
1. 红黑树的核心概念与性质(重点)
红黑树是一棵二叉搜索树,每个节点增加了一个 “颜色” 属性(红色或黑色)。通过以下 4 条规则约束颜色分布,确保树的近似平衡(重点):
1.每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色;
2.根节点必须是黑色;
3.红色节点的两个子节点必须是黑色(无连续红色节点);
4.从任意节点到其所有空节点(NIL)的路径上,黑色节点数量相同。
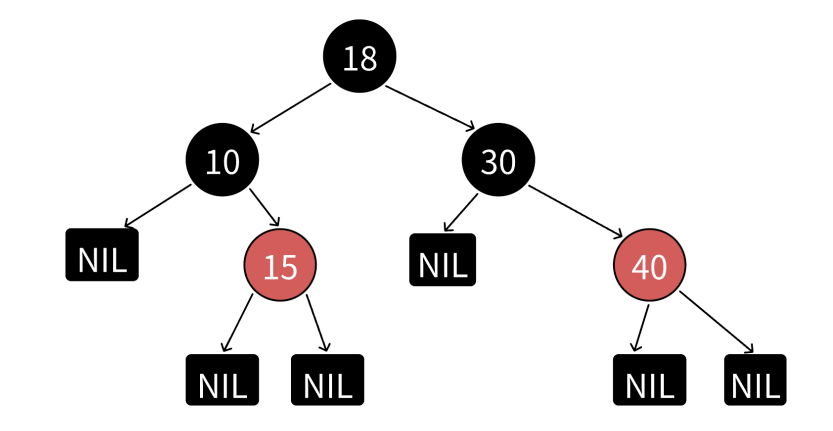
平衡的本质:最长路径不超过最短路径的 2 倍
最短路径:全由黑色节点组成(遵循规则4,全黑色);
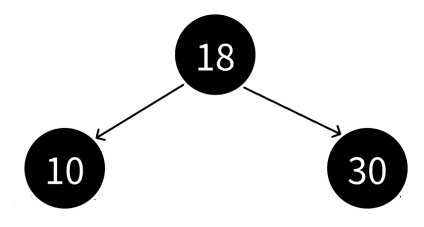
最长路径:黑红节点交替出现(遵循规则2、3,一黑一红);
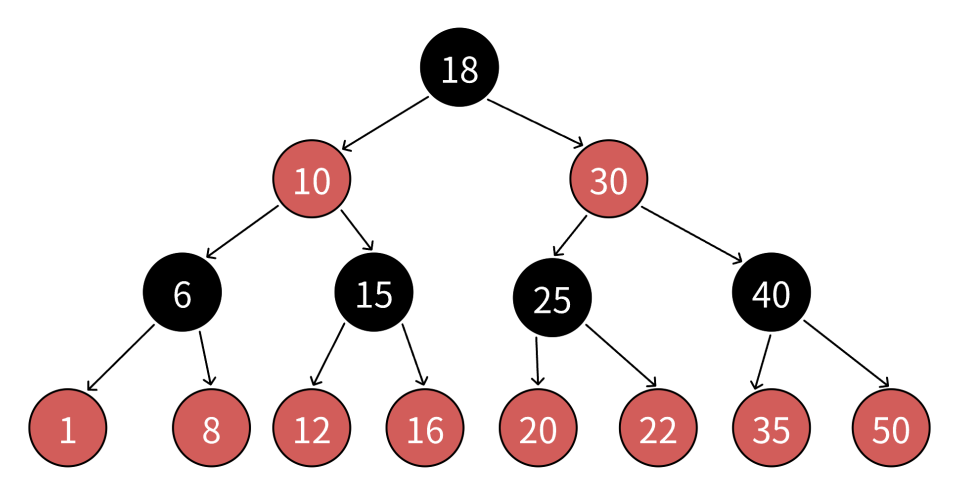
由此可推:最长路径长度 ≤ 2 × 最短路径长度,保证了树的近似平衡,使得增删查改的时间复杂度稳定在 O(log N)。
2. 红黑树结构设计
2.1 节点结构体定义
红黑树节点采用三叉链表结构(包含左、右子节点和父节点指针),同时存储键值对和颜色属性:
enum Color // 颜色枚举
{ RED, BLACK
}; template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{pair<K, V> _kv; // 键值对RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left; // 左子节点RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;// 右子节点RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;// 父节点(平衡调整必需)Color _col; // 节点颜色// 节点构造函数:初始化指针为nullptrRBTreeNode(const pair<K, V> kv): _kv(kv), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr), _col(RED) // 新节点默认红色(减少平衡调整次数){}
};2.2 红黑树类框架
template<class K, class V>
class RBTree {typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public://..具体函数private://..具体函数Node* _root = nullptr; // 根节点
};3. 红黑树的初始化与销毁
3.1 红黑树的初始化
(1)默认构造
我们先定义一个无参的构造函数,因为我们在定义拷贝构造之后编译器就不会再生成默认的构造函数了。
RBTree() {}(2)拷贝构造
采用后序递归拷贝策略,先拷贝当前节点,再递归拷贝左、右子树,最后修复子节点的父指针。深拷贝确保新树与原树内存独立,修改其中一棵不会影响另一棵。
// 拷贝构造函数:调用copy递归拷贝整棵树
RBTree(const RBTree<K, V>& t)
{_root = copy(t._root);
}// 递归拷贝辅助函数
Node* copy(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr) // 空节点直接返回return nullptr; // 1. 拷贝当前节点(值和颜色)Node* newnode = new Node(root->_kv);newnode->_col = root->_col;newnode->_parent = nullptr; // 新节点父指针先置空// 2. 递归拷贝左、右子树newnode->_left = copy(root->_left);newnode->_right = copy(root->_right);// 3. 维护子节点的父指针(关键:确保三叉链表结构完整)if (newnode->_left){newnode->_left->_parent = newnode;}if (newnode->_right){newnode->_right->_parent = newnode;}return newnode;
}(3)赋值重载
函数参数为值传递,会自动调用拷贝构造函数生成临时树 t,然后交换当前树的 _root 和临时树的 _root,当前树获得临时树的资源;函数结束时,临时树带着原当前树的旧资源销毁(调用析构函数),无需手动释放旧资源,简洁且安全。
RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> t)
{swap(_root, t._root); // 交换当前树和临时树的根节点return *this;
}3.2 红黑树的销毁
(1)析构函数
采用后序递归销毁策略,确保每个节点的子节点都被释放后,再释放当前节点,避免悬空指针。无需手动置空 _root(析构后对象生命周期结束,不再访问)。
// 析构函数:调用Destroy递归销毁整棵树
~RBTree()
{Destroy(_root);
}// 递归销毁辅助函数
void Destroy(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr) // 空节点直接返回return;// 后序遍历:先销毁左、右子树,再销毁当前节点Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root; // 释放当前节点内存
}4. 红黑树的插入(重点)
插入是红黑树最复杂的操作,需遵循 “二叉搜索树插入规则”+“红黑树平衡修复” 两步走。
4.1 插入流程概述
1. 空树直接插入根节点(颜色设为黑色);
2. 非空树按二叉搜索树规则找到插入位置,新增节点设为红色(减少规则 4 的破坏);
3. 若父节点为黑色,插入结束(无规则破坏);
4. 若父节点为红色,触发平衡调整(破坏规则 3:连续红色节点)。
这里我们注意,为什么设置新插入节点为红色呢?因为如果新插入节点是黑色的话对规则4造成了破坏,而要维护规则4的话需要调整所有路径,是非常麻烦的,所以这里我们设置新插入节点默认为红色。
4.2 平衡调整
设新增节点为 cur(红)、父节点为 parent(红)、祖父节点为 grandfather(黑,因规则 3)、叔叔节点为 uncle,四个节点简称为c、p、g、u,调整逻辑分三种场景:
(1)场景 1
叔叔节点存在且为红色
处理逻辑:变色(parent 和 uncle 变黑,grandfather 变红),然后将 cur 指向 grandfather,继续向上校验;
原理:保持每条路径的黑色节点数不变,消除连续红色节点。
分析:因为p和u都是红色,g是黑色,把p和u变黑,左边子树路径各增加一个黑色结点,g再变红,相当于保持g所在子树的黑色结点的数量不变,同时解决了c和p连续红色结点的问题,需要继续往上更新是因为,g是红色,如果g的父亲还是红色,那么就还需要继续处理;如果g的父亲是黑色,则处理结束了;如果g就是整棵树的根,再把g变回黑色。
场景1只变色,不旋转。所以无论c是p的左还是右,p是g的左还是右,都是上面的变色处理方式。
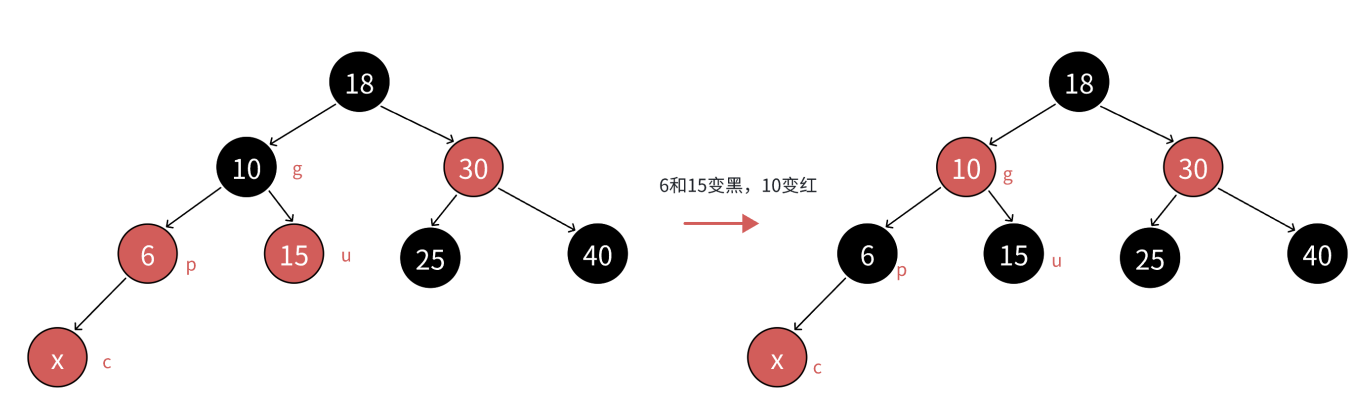
这里的c可能是新插入节点,也可能是下面节点的祖父节点(g):

(2)场景 2
叔叔节点不存在或为黑色(cur 是 parent 的同方向子节点)
处理逻辑:单旋转 + 变色(如 parent 是 grandfather 的左子节点,cur 是 parent 的左子节点 → 右旋转 grandfather,parent 变黑,grandfather 变红);
原理:通过旋转调整树结构,再变色消除连续红色节点。
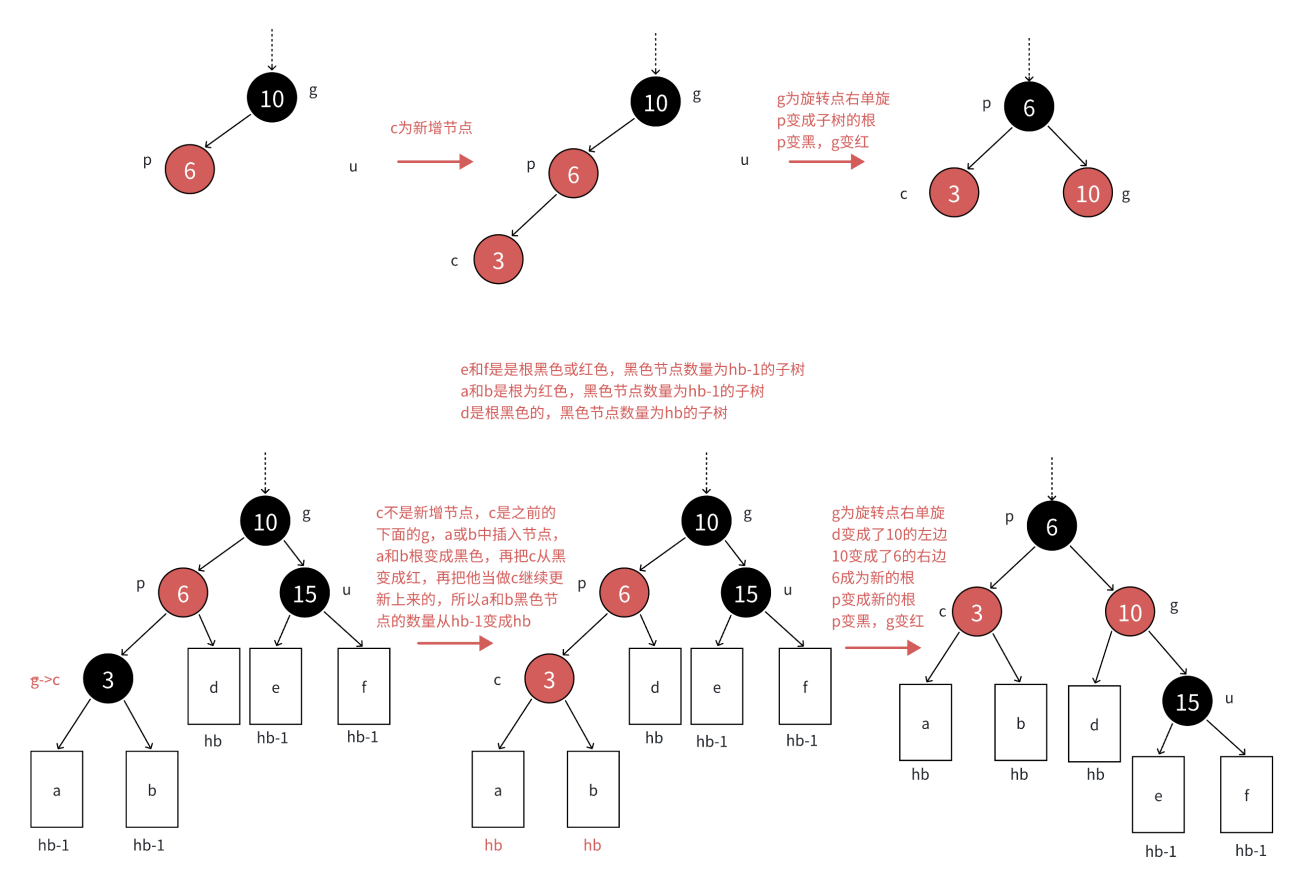
场景解析:c为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在或者u存在且为黑,u不存在,则c一定是新增结点,u存在且为黑,则c一定不是新增,c之前是黑色的,是在c的子树中插入,符合场景1,变色将c从黑色变成红色,更新上来的。
p必须变黑,才能解决连续红色结点的问题,u不存在或者是黑色的,这里单纯的变色无法解决问题,需要旋转+变色。
如果p是g的左子节点,c是p的左子节点,那么以g为旋转点进行右单旋,再把p变黑,g变红即可。p变成这颗树新的根,这样子树黑色结点的数量不变,没有连续的红色结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为p的父亲是黑色还是红色或者空都不违反规则。

同上,逻辑类似,这里以g为旋转点左单旋加p、g变色即可。
这里的c可能是新插入节点,也可能是下面节点的祖父节点(g):
(3)场景 3
叔叔节点不存在或为黑色(cur 是 parent 的反方向子节点)
处理逻辑:双旋转 + 变色(如 parent 是 grandfather 的左子节点,cur 是 parent 的右子节点 → 先左旋转 parent,再右旋转 grandfather,cur 变黑,grandfather 变红);
原理:先将 cur 调整为 parent 的同方向子节点,转化为场景 2 再处理。
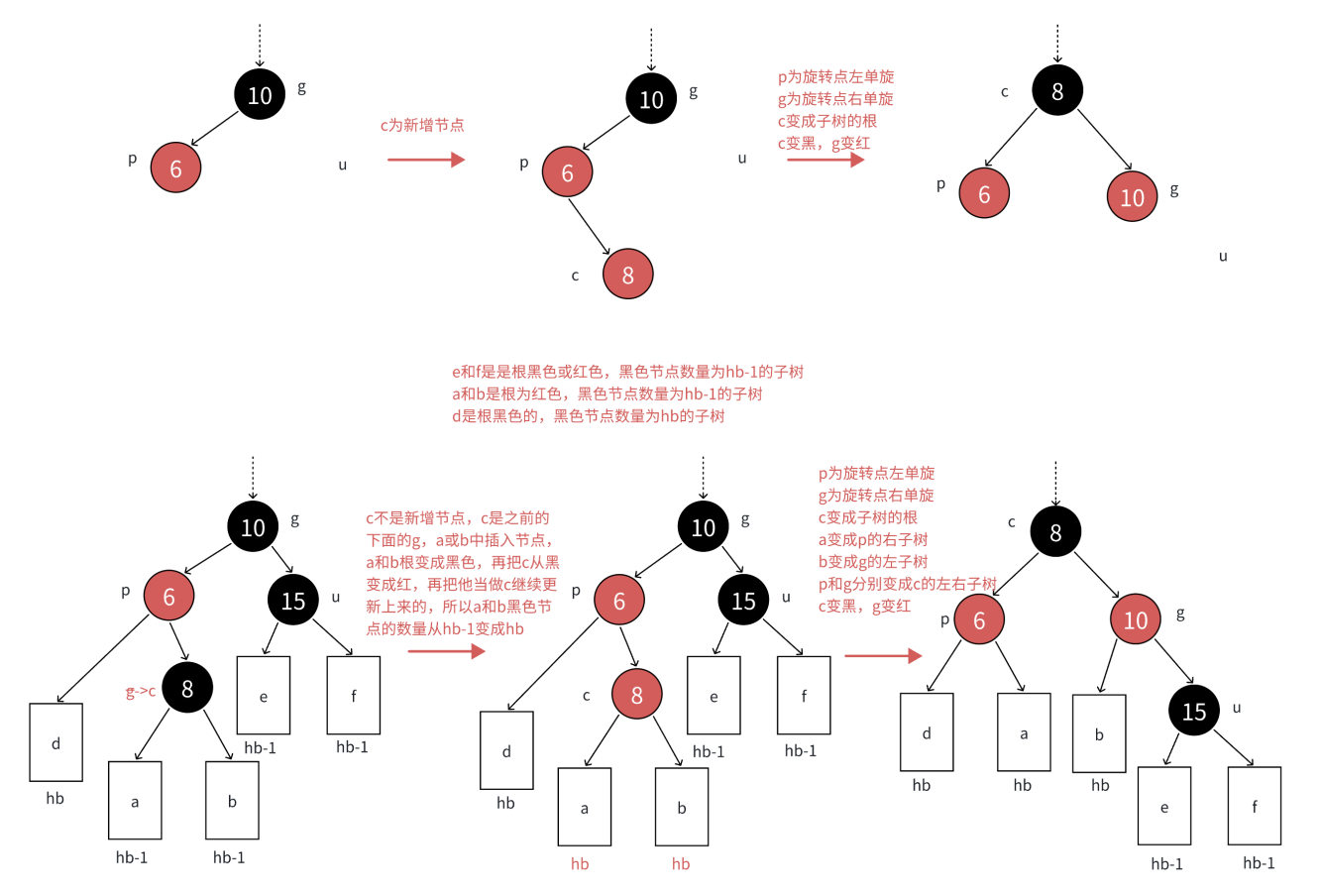
场景解析:c为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在或者u存在且为黑,u不存在,则c一定是新增结点,u存在且为黑,则c一定不是新增,c之前是黑色的,是在c的子树中插入,符合情况1,变色将c从黑色变成红色,更新上来的。
p必须变黑,才能解决连续红色结点的问题,u不存在或者是黑色的,这里单纯的变色无法解决问题,需要旋转+变色。
如果p是g的左子节点,c是p的右子节点,那么先以p为旋转点进行左单旋,再以g为旋转点进行右单旋,再把c变黑,g变红即可。c变成这棵树新的根,这样子树黑色结点的数量不变,没有连续的红色结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为c的父亲是黑色还是红色或者空都不违反规则。

如果p是g的右子,c是p的左子,那么先以p为旋转点进行右单旋,再以g为旋转点进行左单旋,再把c变黑,g变红即可。c变成这棵树新的根,这样子树黑色结点的数量不变,没有连续的红色结点了,且不需要往上更新,因为c的父亲是黑色还是红色或者空都不违反规则。
这里的c可能是新插入节点,也可能是下面节点的祖父节点(g):
4.3 插入代码实现
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{// 1. 空树插入根节点(黑色)if (_root == nullptr) {_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}// 2. 按二叉搜索树规则找插入位置Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) {if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first) {parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else {return false; // 键值已存在,插入失败}}// 3. 插入新节点(红色)cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first) {parent->_left = cur;}else {parent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parent; // 维护父指针// 4. 平衡调整(父节点为红色时才需要)while (parent && parent->_col == RED) {Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; // 祖父节点必存在(父红→祖父黑)if (parent == grandfather->_left) // 父是祖父的左子节点{ Node* uncle = grandfather->_right; // 叔叔节点// 场景1:叔叔存在且为红 → 变色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) {parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上校验cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else { // 场景2、3:叔叔不存在或为黑 → 旋转+变色if (cur == parent->_left) // 场景2:cur是parent的左子节点 → 右单旋{ RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else // 场景3:cur是parent的右子节点 → 双旋(左旋parent+右旋grandfather){RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break; // 旋转后已平衡,无需向上}}else // 父是祖父的右子节点(对称逻辑){ Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) // 场景1:变色{ parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 场景2、3:旋转+变色{ if (cur == parent->_right) // 场景2:左单旋{ RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else // 场景3:双旋(右旋parent+左旋grandfather){ RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK; // 确保根节点始终为黑(防止调整后根变红)return true;
}5. 辅助函数
5.1 查找
按二叉搜索树规则查找,时间复杂度 O(log N):
Node* Find(const K& key)
{Node* cur = _root;while (cur) {if (cur->_kv.first < key) {cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key) {cur = cur->_left;}else {return cur; // 找到返回节点指针}}return nullptr; // 未找到
}5.2 中序遍历
验证红黑树的有序性(二叉搜索树中序遍历为升序):
void _InOrder(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);
}5.3 高度与节点数量
递归计算树高和节点数量,用于性能分析:
int _Height(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr){return 0;}int leftH = _Height(root->_left);int rightH = _Height(root->_right);return max(leftH, rightH) + 1;
}int _Size(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr){return 0;}return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;
}5.4 平衡校验(重点)
验证红黑树的 4 条规则,确保树结构合法:
IsBalance():入口函数,负责前置规则校验(空树、根节点颜色),计算黑色节点参考值,触发递归校验。
Check(...):递归辅助函数,负责遍历所有路径,校验 “无连续红节点” 和 “各路径黑节点数一致” 两大规则。
bool IsBalance()
{if (_root == nullptr) // 空树平衡return true; if (_root->_col == RED) // 根节点必须为黑return false; // 计算最左路径的黑色节点数(作为参考值)int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur) {if (cur->_col == BLACK) refNum++;cur = cur->_left;}// 递归校验所有路径return Check(_root, 0, refNum);
}bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum)
{if (root == nullptr) { // 一条路径结束if (blackNum != refNum) {cout << "错误:黑色节点数量不一致" << endl;return false;}return true;}// 校验规则3:无连续红色节点if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED) {cout << "错误:节点" << root->_kv.first << "存在连续红色节点" << endl;return false;}// 累计黑色节点数if (root->_col == BLACK) blackNum++;// 递归校验左、右子树return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);
}6. 源码
RBTree.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};template<class K, class V>
struct RBTreeNode
{pair<K, V> _kv;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V> kv):_kv(kv),_left(nullptr),_right(nullptr),_parent(nullptr){}
};template<class K, class V>
class RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node;
public://默认构造RBTree(){}//拷贝构造RBTree(const RBTree<K, V>& t){_root = copy(t._root);}Node* copy(Node* root){// 如果原始节点为空,直接返回空指针if (root == nullptr){return nullptr;}// 为新节点分配内存并拷贝原始节点的值Node* newnode = new Node(root->_kv);// 递归拷贝左子树newnode->_left = copy(root->_left);// 递归拷贝右子树newnode->_right = copy(root->_right);// 将新节点的父节点指针置为空newnode->_parent = nullptr;// 拷贝原始节点的颜色信息newnode->_col = root->_col;// 如果新节点的左子节点存在,设置其父节点为新节点if (newnode->_left){newnode->_left->_parent = newnode;}// 如果新节点的右子节点存在,设置其父节点为新节点if (newnode->_right){newnode->_right->_parent = newnode;}return newnode;}//赋值重载RBTree<K, V>& operator =(RBTree<K, V> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}//析构函数~RBTree(){Destroy(_root);}void Destroy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}//递归销毁左子树Destroy(root->_left);//递归销毁右子树Destroy(root->_right);//销毁根节点delete root;}bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(kv);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;//遍历寻找插入位置while (cur){if (kv.first < cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else if (kv.first > cur->_kv.first){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else{return false; //如果等于则插入失败}}cur = new Node(kv);cur->_col = RED;if (kv.first < parent->_kv.first){parent->_left = cur;}else{parent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//父节点为组父节点左孩子if (parent == grandfather->_left){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//叔叔节点存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){//变色parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//继续向上遍历cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //叔叔节点不存在或存在但是为黑色{if (cur == parent->_left){RotateR(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}else{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;//叔叔节点存在且为红色if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED){//变色parent->_col = BLACK;uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;//继续向上遍历cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else //叔叔节点不存在或存在但是为黑色{if (cur == parent->_right){RotateL(grandfather);parent->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);cur->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;}break;}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* subL = parent->_left;Node* subLR = subL->_right;parent->_left = subLR;if (subLR){subLR->_parent = parent;}Node* pParent = parent->_parent;subL->_right = parent;parent->_parent = subL;if (parent == _root){_root = subL;subL->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (pParent->_left == parent){pParent->_left = subL;}else{pParent->_right = subL;}subL->_parent = pParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* subR = parent->_right;Node* subRL = subR->_left;parent->_right = subRL;if (subRL){subRL->_parent = parent;}Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;subR->_left = parent;parent->_parent = subR;if (parentParent == nullptr){_root = subR;subR->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parent == parentParent->_left){parentParent->_left = subR;}else{parentParent->_right = subR;}subR->_parent = parentParent;}}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}int Height(){return _Height(_root);}int Size(){return _Size(_root);}Node* Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_kv.first > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return cur;}}return nullptr;}bool IsBalance(){if (_root == nullptr)return true;if (_root->_col == RED)return false;//黑色节点参考值int refNum = 0;Node* cur = _root;//遍历最左路径,得出该路径黑色节点数,然后拿该节点数跟其他路径的对比while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK){refNum++;}cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, 0, refNum);}private:bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum){if (root == nullptr){// 前序遍历走到空时,意味着一条路径走完了//cout << blackNum << endl;if (refNum != blackNum){cout << "存在黑色结点的数量不相等的路径" << endl;return false;}return true;}// 检查孩子不太方便,因为孩子有两个,且不一定存在,反过来检查父亲就方便多了if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED){//检查红节点的父节点,如果也为红返回falsecout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色结点" << endl;return false;}if(root->_col == BLACK){blackNum++;}return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum)&& Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum);}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left);int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right);return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1;}int _Size(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1;}Node* _root = nullptr;
};test.cpp
#include"RBTree.h"void TestRBTree1()
{RBTree<int, int> t;// 常规的测试用例int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };// 特殊的带有双旋场景的测试用例//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };for (auto e : a){t.Insert({ e, e });}t.InOrder();cout << t.IsBalance() << endl;
}int main()
{TestRBTree1();return 0;
}结语
好好学习,天天向上!有任何问题请指正,谢谢观看!
