福建电信网站备案wordpress的页面布局
non-blocking IO 非阻塞IO
一、三大组件
1.1 Channel
1.1.1 定义
是一种读写数据的双向通道
1.1.2 分类
- FileChannel
文件传输通道
- DatagramChannel
UDP传输通道
- SocketChannel
TCP传输通道,服务器和客户端都可以使用
- ServerChannel
TCP传输通道,专用于服务器通道
1.2 Buffer
1.2.1 定义
内存缓冲区,用来缓冲读写数据,读写数据都需要通过buffer
1.2.2 分类
- ByteBuffer
MappedByteBuffer
DirectByteBuffer
HeapByteBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
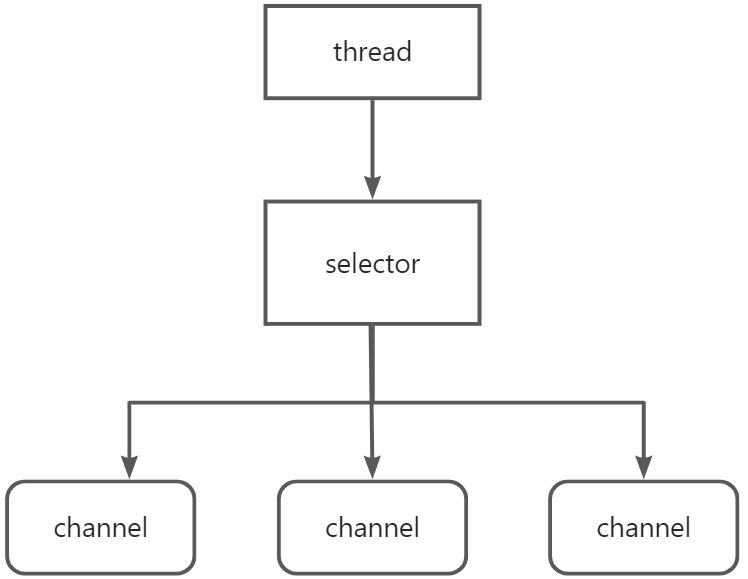
1.3 Selector
1.3.1 定义
配合一个线程,来管理多个Channel,获取这些Channel上发生的事件,这些Channel工作在非阻塞模式下;
1.3.2 优缺点
适合连接数多的场景
适合流量低的场景
1.3.3 数据模型
如果selector发现channel有执行事件,通知thread执行,selector可以发现哪些channel有可执行事件
1.4 其他
1.4.1 多线程
1.4.1.1 数据模型
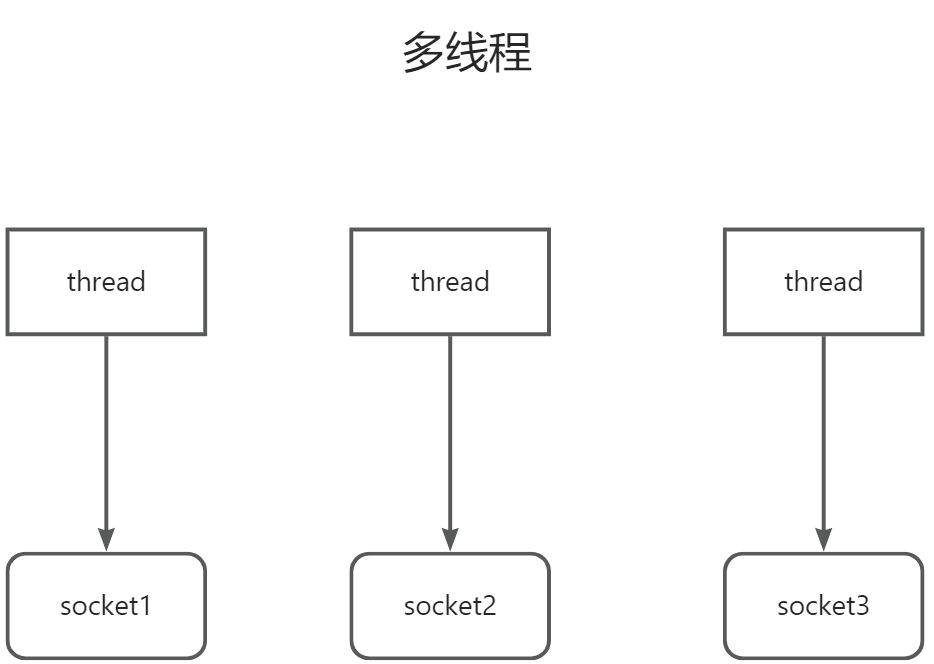
1.4.1.2 优缺点
内存占用高
线程切换成本高
只适合连接数少的场景
1.4.2 线程池
1.4.2.1 数据模型
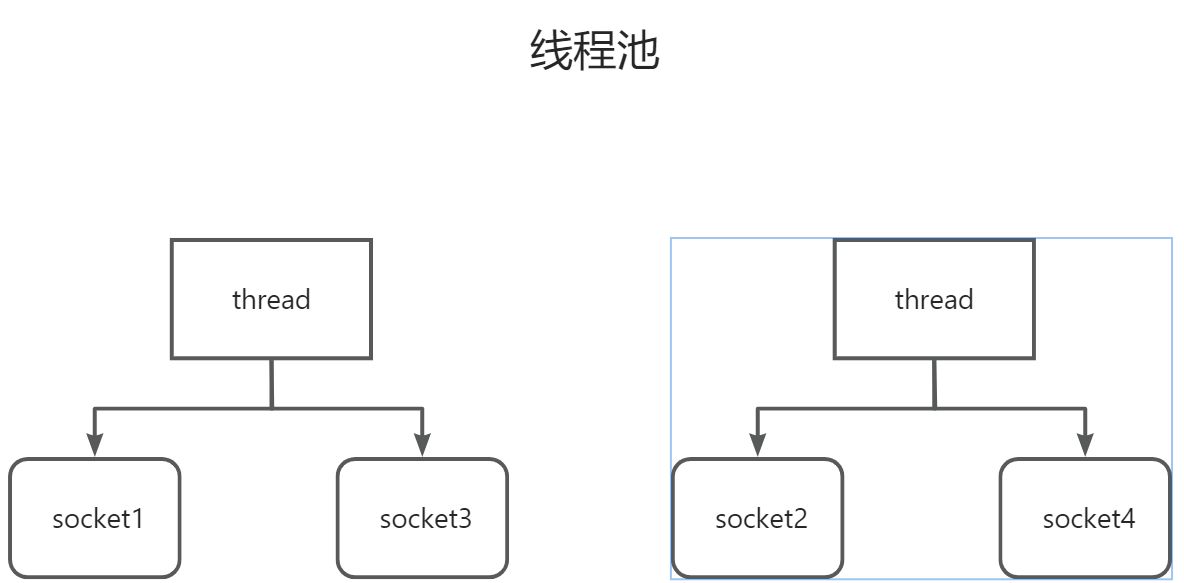
1.4.2.2 优缺点
阻塞模式下,只能处理一个socket
仅适用短连接场景
二、ByteBuffer
2.1 正确使用步骤
- 向buffer中写数据,例如:调用 channel.read(buffer)
- 调用flip()切换至读模式
- 从buffer中读数据,例如:buffer.get()
- 调用clear()或compact()切换至写模式
- clear与compact的区别:
- clear:如果buffer中数据还没有读完,会清除,从头写入数据
- compact:如果buffer中数据还没有读完,会继续从未读取数据的位置继续写入
- 重复1~4步
2.2 代码案例
public static void main(String[] args) {// FileChannel// 1. 输入输出流, 2. RandomAccessFiletry (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {// 准备缓冲区,初始化大小为10字节ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);while(true) {// 从 channel 读取数据,向 buffer 写入int len = channel.read(buffer);log.debug("读取到的字节数 {}", len);if(len == -1) { // 没有内容了break;}// 打印 buffer 的内容buffer.flip(); // 切换至读模式while(buffer.hasRemaining()) { // 是否还有剩余未读数据byte b = buffer.get();log.debug("实际字节 {}", (char) b);}buffer.clear(); // 切换为写模式 buffer.compact()}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}2.3 流程分析
ByteBuffer 有以下重要属性
- capacity 容量
- position 偏移量
- limit 读/写限制
一开始:
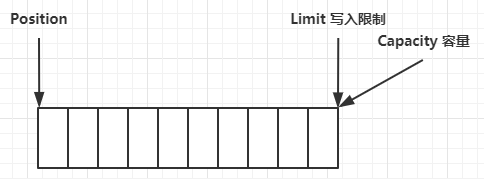
写模式下,position 是写入位置,limit 等于容量,下图表示写入了 4 个字节后的状态
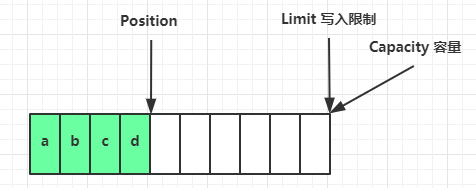
flip 动作发生后,position 切换为读取位置,limit 切换为读取限制
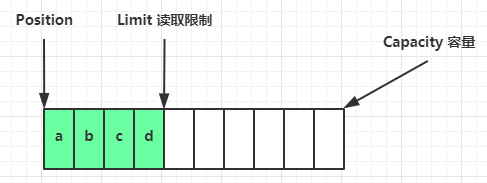
读取 4 个字节后,状态
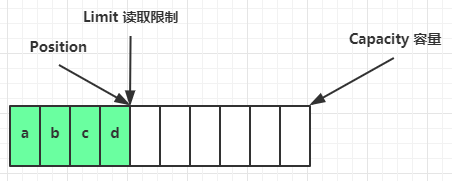
clear 动作发生后,状态
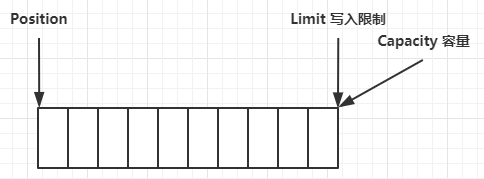
compact 方法,是把未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
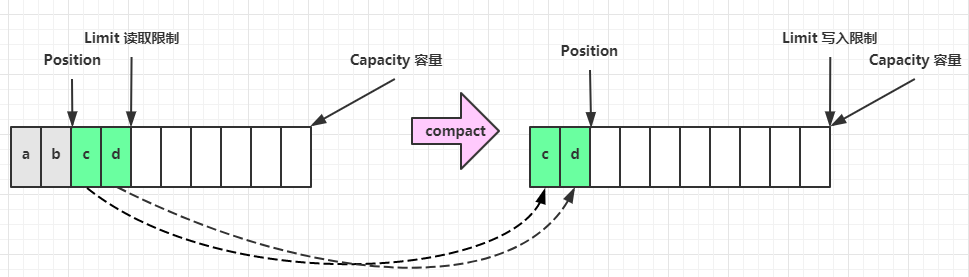
2.4 分配空间
两种方式:
- ByteBuffer.allocate(16):分配堆内存
特点:读写效率低,受GC影响(每进行一次GC,信息都需要来回copy,因此,效率比较低)
- ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16):分配直接内存
特点:读写效率高(少一次拷贝),不会受GC影响,分配效率低(需要调用内核API,使用不当,容易造成内存溢出)
2.5 向Buffer写数据
两种方式:
使用channel的read的方式
int readBytes = channel.read(byteBuffer);使用buffer的put的方式
buffer.put(127);
buffer.put((byte)127)2.6 从Buffer读数据
两种方式:
使用channel的write的方式
int writeBytes = channel.write(buffer);使用Buffer的get的方式
byte b = buffer.get();get()方法会让position指针向后走,如果想重复读取数据:
1、可以使用rewind()方法将position重置为0
2、或者调用get(int index),获取索引index的内容,指针不会移动
2.7 mark & reset
mark:打标记
reset:重置到mark的位置(偏移量会发生变化)
案例如下:
byte[] buffer = {q,w,e,r,t,y,u};
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.mark(); // 加标记,索引2 的位置
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
buffer.reset(); // 将 position 重置到索引 2
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());
System.out.println((char) buffer.get());2.8 Buffer常用方法
2.8.1 字符串转ByteBuffer
1、通过字符串转字节,再设置ByteBuffer(需要转成读模式,才可以读取)
2、使用Charset的方式 (会自动转成读模式)
3、使用wrap的方式 Nio的工具类 (会自动转成读模式)
public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 字符串转为 ByteBufferByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());debugAll(buffer1);// 2. CharsetByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");debugAll(buffer2);// 3. wrapByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());debugAll(buffer3);}2.8.2 ByteBuffer转字符串
public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 字符串转为 ByteBufferByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);buffer1.put("hello".getBytes());debugAll(buffer1);// 2. CharsetByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello");debugAll(buffer2);// 3. wrapByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes());debugAll(buffer3);// 4. 转为字符串String str1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString();System.out.println(str1);buffer1.flip();String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString();System.out.println(str2);}2.9 分散读集中写
思想:减少数据在 ByteBuffer间的copy次数,间接提高性能;
3.0 黏包、半包
黏包产生的原因:因为客户端要提高效率,所以会把数据合并发送
半包产生的原因:因为服务器端ByteBuffer的大小限制
解决方法案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {/*网络上有多条数据发送给服务端,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔但由于某种原因这些数据在接收时,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有3条为Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHow are you?\n变成了下面的两个 byteBuffer (黏包,半包)Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHow are you?\n现在要求你编写程序,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按 \n 分隔的数据*/// 模拟产生黏包半包,分两次接收数据ByteBuffer source = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);// 第一次接收并处理source.put("Hello,world\nI'm zhangsan\nHo".getBytes());split(source);// 第二次接收并处理source.put("w are you?\n".getBytes());split(source);}/**** @param source 接收的ByteBuffer**/private static void split(ByteBuffer source) {// 转读模式source.flip();// 遍历接收到数据的长度for (int i = 0; i < source.limit(); i++) {// 找到一条完整消息 source.get(index),source的position不发生变化if (source.get(i) == '\n') {int length = i + 1 - source.position();// 把这条完整消息存入新的 ByteBufferByteBuffer target = ByteBuffer.allocate(length);// 从 source 读,向 target 写for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {target.put(source.get());}debugAll(target);}}source.compact();}