JDBC事务管理与DAO模式实践
一、什么是事务
事务是一个完整的业务,在这个业务中需要多条DML语句共同联合才能完成,而事务可以保证多条DML语句同时成功或者同时失败,从而保证数据的安全。
例如A账户向B账户转账一万,A账户减去一万(update)和B账户加上一万(update),必须同时成功或者同时失败,才能保证数据是正确的。
二、使用转账案例演示事务
1. 表和数据的准备


2.实现转账功能
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest19
* Description: 实现账户转账*
*/
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 转账金额
double money = 10000.0;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps1 = null;
PreparedStatement ps2 = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 更新 act-001 账户
String sql1 = "update t_act set balance = balance - ? where actno = ?";
ps1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps1.setDouble(1, money);
ps1.setString(2, "act-001");
int count1 = ps1.executeUpdate();
// 更新 act-002账户
String sql2 = "update t_act set balance = balance + ? where actno = ?";
ps2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ps2.setDouble(1, money);
ps2.setString(2, "act-002");
int count2 = ps2.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(null, ps1, null);
DbUtils.close(conn, ps1, null);
}
}
}
运行结果:


3.JDBC事务默认是自动提交的
JDBC事务默认情况下是自动提交的,所谓的自动提交是指:只要执行一条DML语句则自动提交一次。测试一下,在以下代码位置添加断点:
将数据改回去

让代码执行到断点处:
让程序停在此处,看看数据库表中的数据是否发生变化:

以看到,整个转账的业务还没有执行完毕,act-001 账户的余额已经被修改为 40000了,为什么修改为 40000了,因为JDBC事务默认情况下是自动提交,只要执行一条DML语句则自动提交一次。这种自动提交是极其危险的。如果在此时程序发生了异常,act-002账户的余额未成功更新,则钱会丢失一万。我们可以测试一下:测试前先将数据恢复到起初的时候
在以下代码位置,让其发生异常:

执行结果如下:

经过测试得知,丢失了一万元。
4.添加事务控制
如何解决以上问题,分三步:
第一步:将JDBC事务的自动提交机制修改为手动提交(即开启事务)
conn.setAutoCommit(false);第二步:当整个业务完整结束后,手动提交事务(即提交事务,事务结束)
conn.commit();第三步:在处理业务过程中,如果发生异常,则进入catch语句块进行异常处理,手动回滚事务(即回滚事务,事务结束)
conn.rollback();代码如下:
import oop3.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest19
* Description: 实现转账功能
*/
public class JDBCTest23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 转账金额
double money = 10000.0;
// 实现转账功能
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps1 = null;
PreparedStatement ps2 = null;
try {
// 获取连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 第一步:开启事务(将JDBC事务的自动提交机制修改为手动提交)
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// 将 act-001 账户的余额减去一万
String sql1 = "update t_act set balance = balance - ? where actno = ?";
ps1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps1.setDouble(1, money);
ps1.setString(2, "act-001");
int count1 = ps1.executeUpdate();
// 模拟异常的发生。
String s = null;
s.toString();
// 将 act-002 账户的余额加上一万
String sql2 = "update t_act set balance = balance + ? where actno = ?";
ps2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
ps2.setDouble(1, money);
ps2.setString(2, "act-002");
int count2 = ps2.executeUpdate();
// 第二步:当整个业务流程成功的完整的结束了,提交事务(事务结束)
conn.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 第三步:只要有任何一个异常发生,则回滚事务(事务结束)
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 释放资源
DbUtils.close(null, ps1, null);
DbUtils.close(null, ps2, null);
DbUtils.close(conn, null, null);
}
}
}
将数据恢复如初:

执行程序,仍然会出现异常:

但是数据库表中的数据是安全的:

当程序不出现异常时:

数据库表中的数据也是正确的:
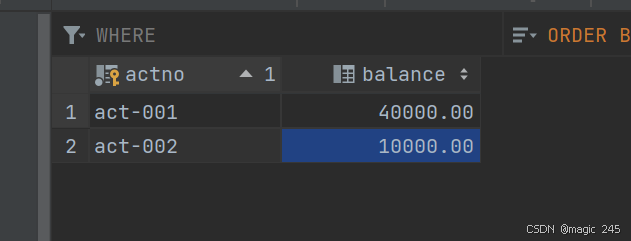
这样就采用了JDBC事务解决了数据安全的问题。
三、 设置JDBC事务隔离级别
设置事务的隔离级别也是比较重要的,在JDBC程序中应该如何设置事务的隔离级别呢?代码如下:
public class JDBCTest20 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
conn.setTransactionIsolation(Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, null, null);
}
}
}1. 在MySQL中创建存储过程
create procedure mypro(in n int, out sum int)
begin
set sum := 0;
repeat
if n % 2 = 0 then
set sum := sum + n;
end if;
set n := n - 1;
until n <= 0
end repeat;
end;2. 使用JDBC代码调用存储过程
import oop3.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Types;
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest21
* Description: 通过JDBC代码调用存储过程
*/
public class JDBCTest24 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
// 专门执行存储过程的。(CallableStatement 继承了 PreparedStatement)
CallableStatement cs = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 调用存储过程的SQL语句
// 注意:外边有一个大括号。
String sql = "{ call mypro(?,?) }";
// 对以上的SQL语句进行预编译
cs = conn.prepareCall(sql);
// 给占位符 ? 传值
cs.setInt(1, 100);
// 将第二个占位符 ? 注册为出参
// 并且出参的数据类型是整数型
cs.registerOutParameter(2, Types.INTEGER);
// 调用存储过程
cs.execute();
// 获取执行结果,执行结果在出参上。获取出参的值
int result = cs.getInt(2);
System.out.println(result);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, cs, null);
}
}
}执行结果:

程序解说:
使用JDBC代码调用存储过程需要以下步骤:
- 加载MySQL的JDBC驱动程序
使用以下代码加载MySQL的JDBC驱动程序:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");- 连接到MySQL数据库
使用以下代码连接到MySQL数据库:
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb", "user", "password");其中,第一个参数为连接字符串,按照实际情况修改;第二个参数为用户名,按照实际情况修改;第三个参数为密码,按照实际情况修改。
- 创建CallableStatement对象
使用以下代码创建CallableStatement对象:
CallableStatement cstmt = conn.prepareCall("{call mypro(?, ?)}");其中,第一个参数为调用存储过程的语句,按照实际情况修改;第二个参数是需要设定的参数。
- 设置输入参数
使用以下代码设置输入参数:
cstmt.setInt(1, n);其中,第一个参数是参数在调用语句中的位置,第二个参数是实际要传入的值。
- 注册输出参数
使用以下代码注册输出参数:
cstmt.registerOutParameter(2, Types.INTEGER);其中,第一个参数是要注册的参数在调用语句中的位置,第二个参数是输出参数的类型。
- 执行存储过程
使用以下代码执行存储过程:
cstmt.execute();- 获取输出参数值
使用以下代码获取输出参数的值:
int sum = cstmt.getInt(2);其中,第一个参数是输出参数在调用语句中的位置。
- 关闭连接
使用以下代码关闭连接和语句对象:
cstmt.close();
conn.close();上述代码中,可以根据实际情况适当修改存储过程名、参数传递方式、参数类型等内容。
四、JDBC实现员工管理
1. 数据库表的准备
drop table if exists t_employee;
create table t_employee(
id bigint primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(255),
job varchar(255),
hiredate char(10),
salary decimal(10,2),
address varchar(255)
);
insert into t_employee(name,job,hiredate,salary,address) values('张三','销售员','1999-10-11',5000.0,'北京朝阳');
insert into t_employee(name,job,hiredate,salary,address) values('李四','编码人员','1998-02-12',5000.0,'北京海淀');
insert into t_employee(name,job,hiredate,salary,address) values('王五','项目经理','2000-08-11',5000.0,'北京大兴');
insert into t_employee(name,job,hiredate,salary,address) values('赵六','产品经理','2022-09-11',5000.0,'北京东城');
insert into t_employee(name,job,hiredate,salary,address) values('钱七','测试员','2024-12-11',5000.0,'北京西城');
commit;
select * from t_employee;
2. 实现效果
⑴查看员工列表

⑵查看员工详情

⑶新增员工

⑷修改员工

⑸删除员工

⑹ 退出系统

package oop3;
import oop3.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest25
* Description: 使用JDBC实现员工信息管理
*/
public class JDBCTest25 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 显示系统欢迎信息和功能菜单
System.out.println("欢迎使用员工信息管理,请认真阅读使用说明:");
System.out.println("本系统的功能主要包括:查看员工列表、查看某个员工详细信息、新增员工、修改员工、删除员工");
System.out.println("请输入对应的功能编号选择功能:");
System.out.println("[1]查看员工列表");
System.out.println("[2]查看某个员工详细信息");
System.out.println("[3]新增员工");
System.out.println("[4]修改员工");
System.out.println("[5]删除员工");
System.out.println("[0]退出系统");
// 创建Scanner对象用于接收用户输入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 进入循环,持续接收用户输入的功能编号
while (true) {
System.out.print("请输入功能编号:");
int no = scanner.nextInt();
if (1 == no) {
// 查看员工列表
System.out.println("员工信息列表如下:");
doList();
} else if (2 == no) {
// 查看某个员工的详细信息
doList();
System.out.print("请输入员工的id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的详细信息如下:");
doDetail(id);
} else if (3 == no) {
// 接收员工的信息
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 新增员工
doSave(name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("新增员工[" + name + "]成功!!!");
doList();
} else if (4 == no) {
// 显示员工列表
doList();
// 显示员工详细信息
System.out.print("请输入您要修改的员工id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
doDetail(id);
// 接收新的信息(注意:修改员工时,id不能修改)
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 修改员工
doModify(id, name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的信息更新成功!!!!");
} else if (5 == no) {
doList();
System.out.print("请输入要删除的员工id:");
Long id = scanner.nextLong();
// 删除员工
doDel(id);
System.out.println("删除员工[" + id + "]成功了!");
doList();
} else if (0 == no) {
System.out.println("下次再见!");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("对不起,您输入的功能暂不支持!");
}
}
}
/**
* 根据员工id删除员工信息
* @param id 要删除的员工的id
*/
private static void doDel(Long id) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 定义删除员工信息的SQL语句
String sql = "delete from t_employee where id = ?";
// 创建PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 为SQL语句中的占位符赋值
ps.setLong(1, id);
// 执行删除SQL语句
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接、PreparedStatement对象和ResultSet对象
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
}
/**
* 根据员工id修改员工信息
* @param id 要修改的员工的id
* @param name 员工姓名
* @param job 员工岗位
* @param salary 员工月薪
* @param hiredate 员工入职日期
* @param address 员工住址
*/
private static void doModify(Long id, String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 定义修改员工信息的SQL语句
String sql = "update t_employee set name=?, job=?, salary=?, hiredate=?, address=? where id=?";
// 创建PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 为SQL语句中的占位符赋值
ps.setString(1, name);
ps.setString(2, job);
ps.setDouble(3, salary);
ps.setString(4, hiredate);
ps.setString(5, address);
ps.setLong(6, id);
// 执行更新SQL语句
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接、PreparedStatement对象和ResultSet对象
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
}
/**
* 新增员工信息
* @param name 员工姓名
* @param job 员工岗位
* @param salary 员工月薪
* @param hiredate 员工入职日期
* @param address 员工住址
*/
private static void doSave(String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 定义插入员工信息的SQL语句
String sql = "insert into t_employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
// 创建PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 为SQL语句中的占位符赋值
ps.setString(1, name);
ps.setString(2, job);
ps.setDouble(3, salary);
ps.setString(4, hiredate);
ps.setString(5, address);
// 执行保存SQL语句
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接、PreparedStatement对象和ResultSet对象
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
}
/**
* 根据员工id查看员工详细信息
* @param id 要查看的员工的id
*/
private static void doDetail(Long id) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 定义查询员工详细信息的SQL语句
String sql = "select * from t_employee where id = ?";
// 创建PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 为SQL语句中的占位符赋值
ps.setLong(1, id);
// 执行查询SQL语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
// 获取员工信息
String name = rs.getString("name");
String job = rs.getString("job");
String hiredate = rs.getString("hiredate");
Double salary = rs.getDouble("salary");
String address = rs.getString("address");
// 输出员工详细信息
System.out.println("id = " + id);
System.out.println("姓名 = " + name);
System.out.println("岗位 = " + job);
System.out.println("入职日期 = " + hiredate);
System.out.println("月薪 = " + salary);
System.out.println("住址 = " + address);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接、PreparedStatement对象和ResultSet对象
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
}
/**
* 查看所有员工的简要信息列表
*/
private static void doList() {
// 编写JDBC代码,连接数据库,查询所有的员工信息,展示
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 获取数据库连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 定义查询员工简要信息的SQL语句
String sql = "select id,name,job from t_employee";
// 创建PreparedStatement对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 执行查询SQL语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 输出表头
System.out.println("id\tname\tjob");
System.out.println("----------------------------");
while (rs.next()) {
// 获取员工简要信息
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
String job = rs.getString("job");
// 输出员工简要信息
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + job);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
// 关闭数据库连接、PreparedStatement对象和ResultSet对象
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
}
}代码说明:
main方法:程序的入口点,负责显示系统欢迎信息和功能菜单,接收用户输入的功能编号,并根据编号调用相应的方法来实现不同的功能。doDel方法:根据员工的id删除员工信息。doModify方法:根据员工的id修改员工的姓名、岗位、月薪、入职日期和住址信息。doSave方法:新增员工信息,将员工的姓名、岗位、月薪、入职日期和住址信息插入到数据库中。doDetail方法:根据员工的id查询员工的详细信息,并将其输出。doList方法:查询所有员工的简要信息(id、姓名、岗位),并将其输出
运行结果:


五、DAO
1. 什么是DAO
DAO是:Data Access Object,翻译为:数据访问对象。
一种JavaEE的设计模式,专门用来做数据增删改查的类。
在实际的开发中,通常我们会将数据库的操作封装为一个单独的DAO去完成,这样做的目的是:提高代码的复用性,另外也可以降低程序的耦合度,提高扩展力。
例如:操作用户数据的叫做UserDao,操作员工数据的叫做EmployeeDao,操作产品数据的叫做ProductDao,操作订单数据的叫做OrderDao等。
2. 使用DAO改造员工信息管理
⑴ 定义Employee封装数据
Employee类是一个Java Bean,专门用来封装员工的信息:

Employee类:
package oop3.beans;
/**
* ClassName: Employee
* Description: 员工类,专门做数据封装的。封装了员工信息。
* 这个类被称为bean,或者pojo类。也就是:普通的java类。
*/
public class Employee {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String job;
private Double salary;
private String hiredate;
private String address;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Long id, String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
this.salary = salary;
this.hiredate = hiredate;
this.address = address;
}
public Employee(String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
this.salary = salary;
this.hiredate = hiredate;
this.address = address;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public Double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getHiredate() {
return hiredate;
}
public void setHiredate(String hiredate) {
this.hiredate = hiredate;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", job='" + job + '\'' +
", salary=" + salary +
", hiredate='" + hiredate + '\'' +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}⑵.定义EmployeeDao
定义五个方法,分别完成五个功能:新增,修改,删除,查看一个,查看所有。

EmployeeDao1类:
import oop3.beans.Employee;
import oop3.utils.DbUtils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* ClassName: EmployeeDao
*/
public class EmployeeDao1 {
/**
* 新增员工
* @param employee
* @return
*/
public int insert(Employee employee) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into t_employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, employee.getName());
ps.setString(2, employee.getJob());
ps.setDouble(3, employee.getSalary());
ps.setString(4, employee.getHiredate());
ps.setString(5, employee.getAddress());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 修改员工
* @param employee
* @return
*/
public int update(Employee employee){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "update t_employee set name=?, job=?, salary=?, hiredate=?, address=? where id=?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, employee.getName());
ps.setString(2, employee.getJob());
ps.setDouble(3, employee.getSalary());
ps.setString(4, employee.getHiredate());
ps.setString(5, employee.getAddress());
ps.setLong(6, employee.getId());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据id删除员工信息
* @param id 员工id
* @return 1表示成功
*/
public int deleteById(Long id){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from t_employee where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 根据id查询所有员工
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Employee selectById(Long id){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Employee employee = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from t_employee where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(id);
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setJob(rs.getString("job"));
employee.setSalary(rs.getDouble("salary"));
employee.setHiredate(rs.getString("hiredate"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return employee;
}
/**
* 查询所有员工信息
* @return 员工列表
*/
public List<Employee> selectAll(){
List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from t_employee";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setJob(rs.getString("job"));
employee.setSalary(rs.getDouble("salary"));
employee.setHiredate(rs.getString("hiredate"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
employees.add(employee);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return employees;
}
}测试类:
import oop3.beans.Employee;
import oop3.dao.EmployeeDao1;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest23
* Description: 员工信息管理(使用DAO进行改造)
* beans包创建EMployee对象,dao包下完成CRUD,测试类调用功能
*/
public class JDBCTest26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用员工信息管理,请认真阅读使用说明:");
System.out.println("本系统的功能主要包括:查看员工列表、查看某个员工详细信息、新增员工、修改员工、删除员工");
System.out.println("请输入对应的功能编号选择功能:");
System.out.println("[1]查看员工列表");
System.out.println("[2]查看某个员工详细信息");
System.out.println("[3]新增员工");
System.out.println("[4]修改员工");
System.out.println("[5]删除员工");
System.out.println("[0]退出系统");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入功能编号:");
int no = scanner.nextInt();
if(1 == no){
// 查看员工列表
System.out.println("员工信息列表如下:");
doList();
} else if(2 == no){
// 查看某个员工的详细信息
doList();
System.out.print("请输入员工的id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的详细信息如下:");
doDetail(id);
} else if(3 == no){
// 接收员工的信息
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 新增员工
doSave(name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("新增员工[" + name + "]成功!!!");
doList();
} else if(4 == no){
// 显示员工列表
doList();
// 显示员工详细信息
System.out.print("请输入您要修改的员工id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
doDetail(id);
// 接收新的信息(注意:修改员工时,id不能修改)
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 修改员工
doModify(id, name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的信息更新成功!!!!");
} else if(5 == no){
doList();
System.out.print("请输入要删除的员工id:");
Long id = scanner.nextLong();
// 删除员工
doDel(id);
System.out.println("删除员工[" + id + "]成功了!");
doList();
} else if(0 == no){
System.out.println("下次再见!");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("对不起,您输入的功能暂不支持!");
}
}
}
private static EmployeeDao1 employeeDao = new EmployeeDao1();
private static void doDel(Long id) {
employeeDao.deleteById(id);
}
private static void doModify(Long id, String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Employee employee = new Employee(id,name,job,salary,hiredate,address);
employeeDao.update(employee);
}
private static void doSave(String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Employee employee = new Employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address);
employeeDao.insert(employee);
}
private static void doDetail(Long id) {
Employee employee = employeeDao.selectById(id);
System.out.println("id = " + employee.getId());
System.out.println("姓名 = " + employee.getName());
System.out.println("岗位 = " + employee.getJob());
System.out.println("入职日期 = " + employee.getHiredate());
System.out.println("月薪 = " + employee.getSalary());
System.out.println("住址 = " + employee.getAddress());
}
private static void doList() {
List<Employee> employees = employeeDao.selectAll();
System.out.println("id\tname\tjob");
System.out.println("----------------------------");
// 遍历List集合
for (Employee e : employees){
System.out.println(e.getId() + "\t" + e.getName() + "\t" + e.getJob());
}
}
}运行结果:

3. BaseDao的封装


BaseDao类:
import oop3.utils.DbUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* ClassName: BaseDao
* Description: 最基础的Dao,所有的Dao应该去继承该BaseDao
*/
public class BaseDao {
/**
* 这是一个通用的执行insert delete update语句的方法。
* @param sql
* @param params
* @return
*/
public int executeUpdate(String sql, Object... params) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
// 获取连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 获取预编译的数据库操作对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给 ? 占位符传值
if(params != null && params.length > 0){
// 有占位符 ?
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
}
// 执行SQL语句
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;
}
/**
* 这是一个通用的查询语句
* @param clazz
* @param sql
* @param params
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> List<T> executeQuery(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... params){
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 获取连接
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
// 获取预编译的数据库操作对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
// 给?传值
if(params != null && params.length > 0){
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
ps.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
}
// 执行SQL语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();
// 获取查询结果集元数据
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
// 获取列数
int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
// 处理查询结果集
while(rs.next()){
// 封装bean对象
T obj = clazz.newInstance();
// 给bean对象属性赋值
/*
比如现在有一张表:t_user,然后表中有两个字段,一个是 user_id,一个是user_name
现在javabean是User类,该类中的属性名是:userId,username
执行这样的SQL语句:select user_id as userId, user_name as username from t_user;
*/
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
// 获取查询结果集中的列的名字
// 这个列的名字是通过as关键字进行了起别名,这个列名就是bean的属性名。
String fieldName = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i);
// 获取属性Field对象
Field declaredField = clazz.getDeclaredField(fieldName);
// 打破封装
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
// 给属性赋值
declaredField.set(obj, rs.getObject(i));
}
// 将对象添加到List集合
list.add(obj);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
// 返回List集合
return list;
}
/**
*
* @param clazz
* @param sql
* @param params
* @return
* @param <T>
*/
public <T> T queryOne(Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... params){
List<T> list = executeQuery(clazz, sql, params);
if(list == null || list.size() == 0){
return null;
}
return list.get(0);
}
}EmployeeDao类:
import oop3.beans.Employee;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* ClassName: EmployeeDao
* Description: 完成员工表t_employee中数据的增删改查。
* 增删改查也被简称为:CRUD。
* C:Create 增
* R:Read 查
* U:Update 改
* D:Delete 删
* 注意:
* DAO不负责任何业务逻辑的处理。只负责CRUD操作。
* DAO是JavaEE的设计模式之一。
* DAO中方法名起名也有讲究,一般都是以:insert delete update select开头。
*/
public class EmployeeDao extends BaseDao{
/**
* 新增员工
* @param employee 员工数据
* @return 1表示新增了1条记录。返回其他值表示新增失败。
*/
public int insert(Employee employee){
/*Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into t_employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, employee.getName());
ps.setString(2, employee.getJob());
ps.setDouble(3, employee.getSalary());
ps.setString(4, employee.getHiredate());
ps.setString(5, employee.getAddress());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;*/
String sql = "insert into t_employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address) values(?,?,?,?,?)";
return executeUpdate(sql, employee.getName(), employee.getJob(), employee.getSalary(), employee.getHiredate(), employee.getAddress());
}
/**
* 根据id删除员工信息
* @param id 员工id
* @return 1表示删除成功,其他值表示删除失败
*/
public int deleteById(Long id){
/*Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "delete from t_employee where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;*/
String sql = "delete from t_employee where id = ?";
return executeUpdate(sql, id);
}
/**
* 修改员工信息
* @param newEmployee 新的员工信息(注意:新的员工信息和旧的员工信息id是不变的。)
* @return 1表示修改成功,其他值表示修改失败
*/
public int update(Employee newEmployee){
/*Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
int count = 0;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "update t_employee set name=?, job=?, salary=?, hiredate=?, address=? where id=?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, newEmployee.getName());
ps.setString(2, newEmployee.getJob());
ps.setDouble(3, newEmployee.getSalary());
ps.setString(4, newEmployee.getHiredate());
ps.setString(5, newEmployee.getAddress());
ps.setLong(6, newEmployee.getId());
count = ps.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, null);
}
return count;*/
String sql = "update t_employee set name=?, job=?, salary=?, hiredate=?, address=? where id=?";
return executeUpdate(sql, newEmployee.getName(), newEmployee.getJob(), newEmployee.getSalary(), newEmployee.getHiredate(), newEmployee.getAddress(),newEmployee.getId());
}
/**
* 根据id获取员工信息
* @param id 员工id
* @return 员工信息
*/
public Employee selectById(Long id){
/*Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Employee employee = null;
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select name,job,salary,hiredate,address from t_employee where id = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setLong(1, id);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if(rs.next()){
// 完成数据的封装,将数据库表查询出来的数据封装成员工对象。
employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(id);
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setJob(rs.getString("job"));
employee.setSalary(rs.getDouble("salary"));
employee.setHiredate(rs.getString("hiredate"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return employee;*/
String sql = "select id,name,job,salary,hiredate,address from t_employee where id = ?";
return queryOne(Employee.class, sql, id);
}
/**
* 获取所有员工信息
* @return 员工列表
*/
public List<Employee> selectAll(){
/*Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
try {
conn = DbUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name,job,salary,hiredate,address from t_employee";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
// 完成数据的封装,将数据库表查询出来的数据封装成员工对象。
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(rs.getLong("id"));
employee.setName(rs.getString("name"));
employee.setJob(rs.getString("job"));
employee.setSalary(rs.getDouble("salary"));
employee.setHiredate(rs.getString("hiredate"));
employee.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
// 将员工对象添加到List集合中
employeeList.add(employee);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
DbUtils.close(conn, ps, rs);
}
return employeeList;*/
String sql = "select id,name,job,salary,hiredate,address from t_employee";
return executeQuery(Employee.class, sql);
}
}Dbutils类:
package oop3.utils;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* ClassName: DbUtils
* Description: JDBC工具类
*/
public class DbUtils {
/**
* 工具类的构造方法一般都是私有化的,因为工具类中的一般都是静态的,
* 工具类就是为了方便编程,所以工具类中的方法都是直接采用“类名.”
* 的方式访问,因此不需要new对象。
*/
private DbUtils(){}
// 静态变量
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
// 静态代码块
static {
// 在这里读取属性配置文件,给静态变量赋值
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
driver = bundle.getString("driver");
url = bundle.getString("url");
user = bundle.getString("user");
password = bundle.getString("password");
// 在类加载的时候,注册驱动,对于整个应用程序来说,注册驱动只需要做一次即可。所以选择静态代码块。
// 静态代码块在类加载时执行,并且只执行一次。
try {
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库连接对象
* @return 连接对象
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
// 实际上这里每一次调用 getConnection() 方法时都会获取一个全新的数据库连接对象,实际上这样效率是比较低的,后期会使用连接池进行改造。
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param conn 连接对象
* @param stmt 数据库操作对象
* @param rs 结果集对象
*/
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
测试类:
import oop3.beans.Employee;
import oop3.dao.EmployeeDao;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* ClassName: JDBCTest23
* Description: 员工信息管理(使用DAO进行改造)
* beans包创建EMployee对象,dao包下完成CRUD,测试类调用功能
*/
public class JDBCTest26 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("欢迎使用员工信息管理,请认真阅读使用说明:");
System.out.println("本系统的功能主要包括:查看员工列表、查看某个员工详细信息、新增员工、修改员工、删除员工");
System.out.println("请输入对应的功能编号选择功能:");
System.out.println("[1]查看员工列表");
System.out.println("[2]查看某个员工详细信息");
System.out.println("[3]新增员工");
System.out.println("[4]修改员工");
System.out.println("[5]删除员工");
System.out.println("[0]退出系统");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入功能编号:");
int no = scanner.nextInt();
if(1 == no){
// 查看员工列表
System.out.println("员工信息列表如下:");
doList();
} else if(2 == no){
// 查看某个员工的详细信息
doList();
System.out.print("请输入员工的id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的详细信息如下:");
doDetail(id);
} else if(3 == no){
// 接收员工的信息
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 新增员工
doSave(name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("新增员工[" + name + "]成功!!!");
doList();
} else if(4 == no){
// 显示员工列表
doList();
// 显示员工详细信息
System.out.print("请输入您要修改的员工id:");
long id = scanner.nextLong();
doDetail(id);
// 接收新的信息(注意:修改员工时,id不能修改)
System.out.print("请输入员工姓名:");
String name = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工岗位:");
String job = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工月薪:");
Double salary = scanner.nextDouble();
System.out.print("请输入员工入职日期:");
String hiredate = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入员工住址:");
String address = scanner.next();
// 修改员工
doModify(id, name, job, salary, hiredate, address);
System.out.println("员工[" + id + "]的信息更新成功!!!!");
} else if(5 == no){
doList();
System.out.print("请输入要删除的员工id:");
Long id = scanner.nextLong();
// 删除员工
doDel(id);
System.out.println("删除员工[" + id + "]成功了!");
doList();
} else if(0 == no){
System.out.println("下次再见!");
System.exit(0);
} else {
System.out.println("对不起,您输入的功能暂不支持!");
}
}
}
private static EmployeeDao employeeDao = new EmployeeDao();
private static void doDel(Long id) {
employeeDao.deleteById(id);
}
private static void doModify(Long id, String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Employee employee = new Employee(id,name,job,salary,hiredate,address);
employeeDao.update(employee);
}
private static void doSave(String name, String job, Double salary, String hiredate, String address) {
Employee employee = new Employee(name,job,salary,hiredate,address);
employeeDao.insert(employee);
}
private static void doDetail(Long id) {
Employee employee = employeeDao.selectById(id);
System.out.println("id = " + employee.getId());
System.out.println("姓名 = " + employee.getName());
System.out.println("岗位 = " + employee.getJob());
System.out.println("入职日期 = " + employee.getHiredate());
System.out.println("月薪 = " + employee.getSalary());
System.out.println("住址 = " + employee.getAddress());
}
private static void doList() {
List<Employee> employees = employeeDao.selectAll();
System.out.println("id\tname\tjob");
System.out.println("----------------------------");
// 遍历List集合
for (Employee e : employees){
System.out.println(e.getId() + "\t" + e.getName() + "\t" + e.getJob());
}
}
}运行结果:

