Java基础——常用API2
一、System

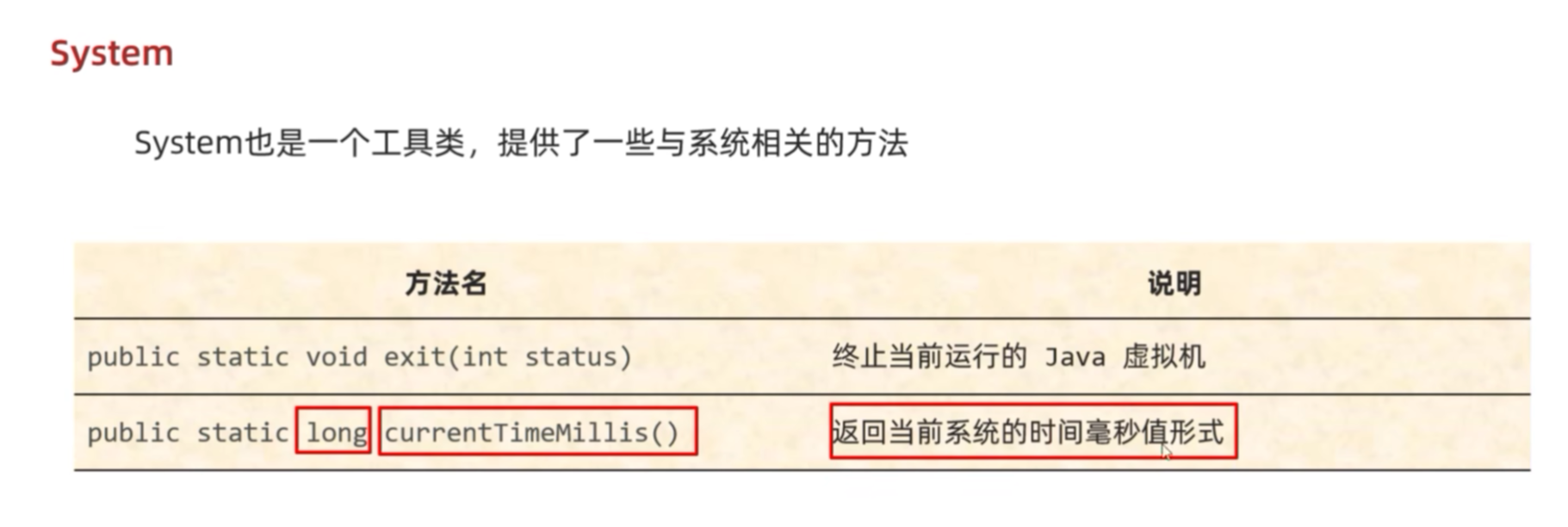
1.1 计算机中的时间原点
它表示最初的开始时间,是1970年1月1日00.00。

在我们国家,因为时差的原因实际上是:


那么这句话的意思就是,从时间原点开始到现在你执行这个代码一共过了多少毫秒。



package com.lkbhua.MyApi.System;public class demo2 {public static void main(String[] args){// -------------------------------数据源数组------起始索引-----目的地数组------起始索引-------拷贝个数// 3、public static void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length): 数组拷贝// 细节:// 1、如果数组源和目的数组都是基本数据类型,那么两者的类型一定要保持一致,否则会报错int []arr = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};double []arr1 = new int[10];System.arraycopy(arr, 0, arr1, 0, arr.length);for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr1[i] + " ");}// 2、在拷贝的时候需要考虑数组的长度,如果超过范围也会报错int []arr2 = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};int []arr3 = new int[5];System.arraycopy(arr2, 0, arr3, 0, arr2.length);for (int i = 0; i < arr3.length; i++) {System.out.print(arr3[i] + " ");}// 3、如果数组源和目的数组都是引用数据类型,那么子类类型可以赋值给父类类型Student s1 = new Student("张三", 18);Student s2 = new Student("李四", 19);Student s3 = new Student("王五", 20);Student []students = {s1,s2,s3};Person []students1 = new Student[3];// 4、数组拷贝System.arraycopy(students, 0, students1, 0, students.length);// 只不过遍历的时候需要强转for (int i = 0; i<arr2.length;i++){Student stu = (Student)students1[i];System.out.println(stu.getName() + " " + stu.getAge());}}
}class Person{private String name;private int age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}class Student extends Person{public Student() {}public Student(String name, int age) {super(name, age);}
}声明:
以上均来源于B站@ITheima的教学内容!!!
本人跟着视频内容学习,整理知识引用
