Kafka使用-Consumer
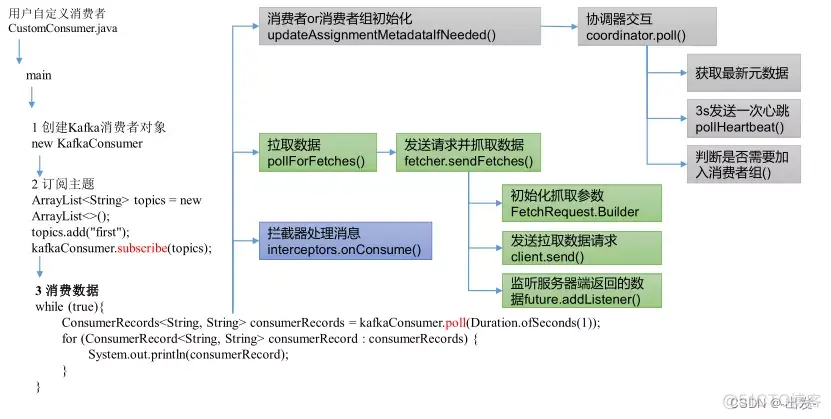
主要步骤
Kafka消费者的使用流程主要包括配置消费者、订阅主题、拉取消息、处理消息和提交偏移量等关键步骤。
-
消费者配置与初始化
必须配置bootstrap.servers(Kafka集群地址)、group.id(消费者组ID)和序列化器推荐使用手动提交偏移量以保证消息处理的可靠性consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop101:9092"); consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class.getName()); consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName()); consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "group1"); consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, false); -
主题订阅
支持订阅特定主题列表或使用正则表达式匹配多个主题。新主题匹配正则表达式时会触发再均衡。consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("first-topic")); -
消息拉取与处理
通过poll()方法批量拉取消息。在获取消息前可以使用自定义拦截器对消息进行处理。在消息处理完成后手动提交偏移量。ConsumerRecords<String, String> poll = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100)); -
消费者组管理
同一消费者组内的消费者共享主题分区。消费者数量变化或分区数变化时会触发再均衡。consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "qichsiii");
自定义拦截器
public class MyConsumerInceptor implements ConsumerInterceptor<Integer, String> {@Overridepublic ConsumerRecords<Integer, String> onConsume(ConsumerRecords<Integer, String> consumerRecords) {Iterator<ConsumerRecord<Integer, String>> iterator = consumerRecords.iterator();ConsumerRecords<Integer,String> cr = new ConsumerRecords<>(Collections.EMPTY_MAP);while(iterator.hasNext()){ConsumerRecord<Integer, String> record = iterator.next();if(record.key()%2==0){System.out.println("拦截器偶数key:"+record.key()+",value"+record.value());}}return consumerRecords;}@Overridepublic void onCommit(Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> map) {}@Overridepublic void close() {}@Overridepublic void configure(Map<String, ?> map) {}
}
public class KafkaConsumerTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 创建配置对象Map<String, Object> consumerConfig = new HashMap<>();consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop101:9092");consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, IntegerDeserializer.class.getName());consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName());
// consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, true);consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.INTERCEPTOR_CLASSES_CONFIG, MyConsumerInceptor.class.getName());consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "group1");consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "latest");// 创建消费者对象KafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(consumerConfig);// 订阅主题consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("first-topic"));while(true) {ConsumerRecords<String, String> poll = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> stringStringConsumerRecord : poll) {System.out.println("接收数据"+stringStringConsumerRecord);}Thread.sleep(1000L);}}
}
提交偏移量
kafka默认自动提交偏移量
- 消息重复消费风险
当enable.auto.commit=true时,默认每5秒(由auto.commit.interval.ms控制)提交一次偏移量。若在两次提交间隔内发生再均衡,新消费者会从上次提交的偏移量开始消费,导致已处理但未提交的消息被重复处理。例如:提交间隔5秒,第3秒发生再均衡,则3秒内的消息可能被重复消费。 - 提交时机不可控
自动提交基于时间间隔而非消息处理完成状态,可能提交未处理完的偏移量。若消费者在提交后崩溃,未处理的消息会被跳过(丢失)。
解决方法
- 手动提交:关闭自动提交(enable.auto.commit=false),在消息处理完成后调用commitSync()(同步)或commitAsync()(异步)。
- 幂等处理:业务逻辑中实现去重机制(如数据库唯一键校验)。
例子:
public class KafkaConsumerAutoOffsetTest {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建配置对象Map<String, Object> consumerConfig = new HashMap<>();consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "hadoop101:9092");consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName());consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class.getName());
// consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, true);consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "group1");consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.ENABLE_AUTO_COMMIT_CONFIG, false);
// consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.AUTO_OFFSET_RESET_CONFIG, "earliest");// 创建消费者对象KafkaConsumer<String,String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(consumerConfig);// 订阅主题consumer.subscribe(Collections.singletonList("first-topic"));while(true) {ConsumerRecords<String, String> poll = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> stringStringConsumerRecord : poll) {System.out.println("接收数据"+stringStringConsumerRecord);}// TODO 手动提交偏移量// TODO 拉取之后,还没处理数据就提交了。数据处理发生问题。出现露消费问题。
// consumer.commitAsync();//异步consumer.commitSync();// 同步}}
}
分区分配策略
通过 partition.assignment.strategy 配置分区分配策略:
RangeAssignor(默认):按分区范围分配。
RoundRobinAssignor:轮询分配分区。
StickyAssignor:尽量减少分区重新分配时的变动。
consumerConfig.put(ConsumerConfig.PARTITION_ASSIGNMENT_STRATEGY_CONFIG, StickyAssignor.class.getName());
