(五)Gradle 依赖传递与冲突处理
一、依赖解析
1.1 传递依赖
当项目声明一个直接依赖(Direct Dependency)时,Gradle 会自动引入该依赖所需要的其他依赖(传递依赖),并将其加入项目构建路径,无需手动声明。
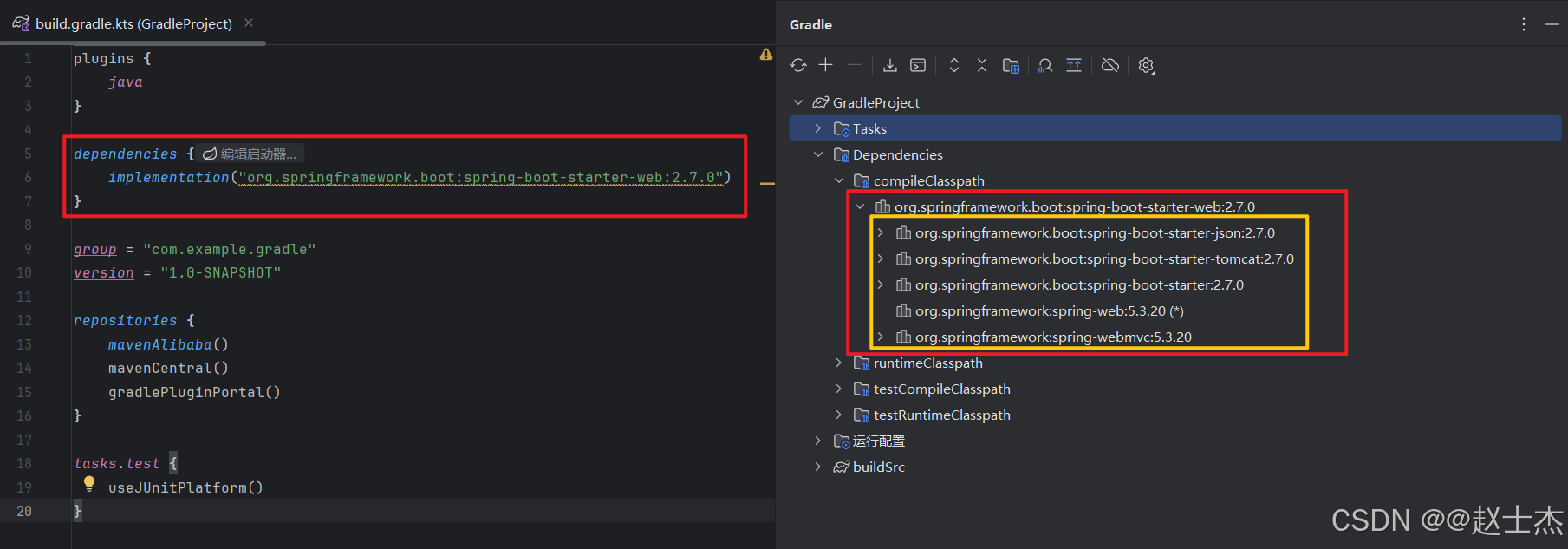
例如,当我们在项目中引入 spring-boot-starter-web 时:
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:2.7.0")
Gradle 不仅会下载 spring-boot-starter-web 本身,还会自动引入 spring-boot-starter(父依赖)、tomcat-embed-core(Web 容器依赖)等间接依赖,以及这些库的依赖,直至形成完整的依赖链(间接依赖的版本由 “直接依赖的 POM 文件” 定义):
1.2 禁用传递依赖
Gradle 提供了 isTransitive 属性来传递依赖, 通过 isTransitive = false 可以移除其所有间接依赖,不影响其他依赖。
例如,项目依赖 spring-boot-starter-web,但不需要它的传递依赖,可在声明时通过以下方式禁用:
dependencies {implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:3.2.0"){isTransitive = false}
}
此时,执行 gradle dependencies 查看依赖树,会发现 spring-boot-starter-web 的间接依赖不再被引入:
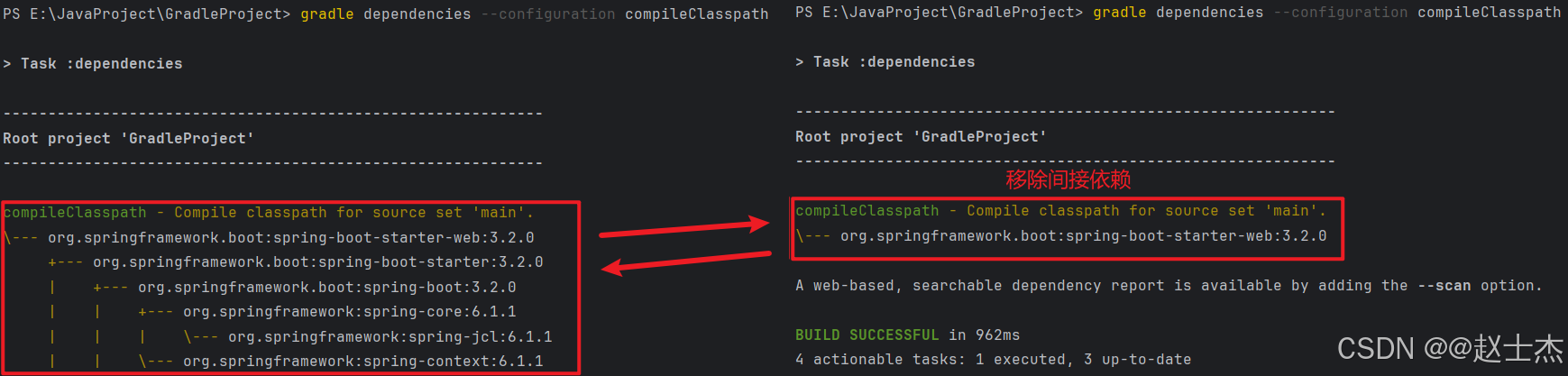
如果需要全局禁用所有传递依赖,可以通过 configurations.all 配置禁用:
// 全局禁用所有传递依赖(谨慎使用)
configurations.all {isTransitive = false
}
该方式会导致所有依赖的间接依赖都被移除,可能引发大量 ClassNotFoundException(需手动声明所有间接依赖)。
二、依赖约束
依赖约束(Dependency Constraints)是 Gradle 用于为项目中所有直接或间接引入的依赖设定版本规则,在依赖解析阶段通过预先定义的规则干预版本选择逻辑,明确 “应该用哪个版本”“禁止用哪个版本”“优先用哪个版本”。
Gradle 在 dependencies 块中通过 constraints 统一声明约束,基本结构如下:
dependencies {constraints {implementation("group:module:version")}
}
例如要求 slf4j-api 依赖版本必须使用 2.0.7 版本,不接受其他版本:
dependencies {// 定义依赖约束constraints {implementation("org.slf4j:slf4j-api:2.0.7!!")// 可添加更多约束// implementation("group:module:version")}
}
💡 注意:与依赖声明不同的是,依赖约束 不会主动添加新依赖,仅对项目中已存在的依赖(无论是直接声明的还是传递引入的)生效。
三、依赖冲突
当项目中 直接依赖 或 传递依赖 引入了 同一库的多个版本 时,就会发生依赖冲突。
例如我们在 Gradle 依赖配置引入 spring-boot-starter-web:3.2.0 版本:
dependencies {// Spring Boot Web Starterimplementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:3.2.0")
}
spring-boot-starter-web 作为一个 “starter 库”,会自动引入一系列传递依赖(如日志框架、Web 容器等),可执行以下命令输出完整的依赖树:
gradle dependencies --configuration compileClasspath
在依赖树中,Gradle 会用 -> 标记冲突及最终选择的版本。例如:

此时,Gradle 发现多个依赖传递引入了 slf4j-api 的不同版本,最终自动选择了一个统一版本来消除冲突。但无论选择哪个版本,都可能版本不兼容,引发 ClassNotFoundException(类找不到)、MethodNotFoundError(方法签名不匹配)等运行时异常。
3.1 如何检测依赖冲突?
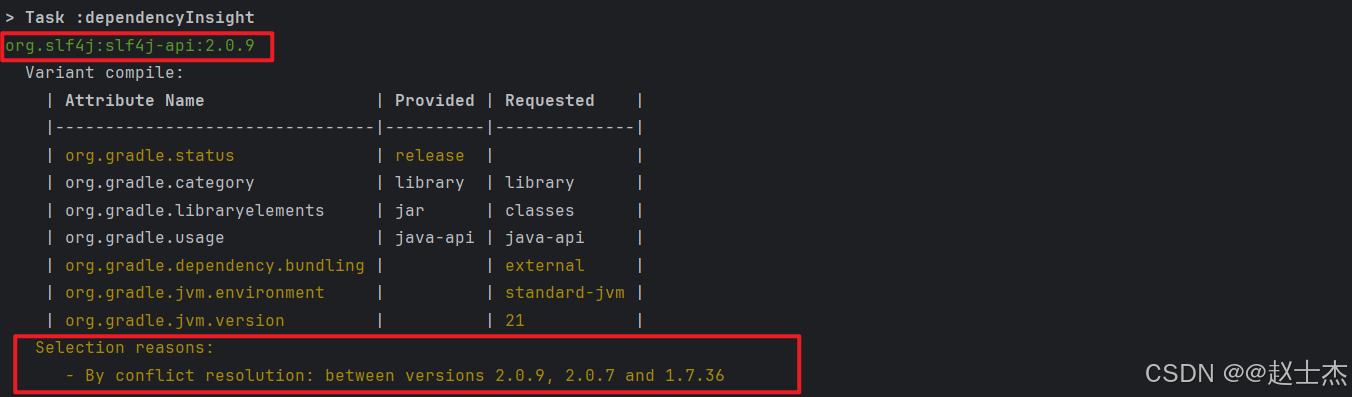
执行 dependencyInsight 命令分析 slf4j-api 依赖的所有引入路径和最终选择的版本:
gradle dependencyInsight --configuration compileClasspath --dependency slf4j-api
红色框标注了 slf4j-api 存在 三个冲突版本(2.0.9、2.0.7、1.7.36),Gradle 通过「冲突解决策略」选择了 2.0.9 版本,最终项目实际使用 slf4j-api:2.0.9 版本:
该命令也会输出 slf4j-api 依赖对应的三条 传递引入路径:

这些路径清晰展示了 “哪些依赖间接引入了 slf4j-api 的不同版本”,帮助我们定位冲突的源头依赖:
- 路径一:
spring-boot-starter-logging→jul-to-slf4j→slf4j-api:2.0.9; - 路径二:
spring-boot-starter-logging→log4j-to-slf4j→slf4j-api:1.7.36(被 Gradle 升级到2.0.9); - 路径三:
spring-boot-starter-logging→logback-classic→slf4j-api:2.0.7(被 Gradle 升级到2.0.9)。
3.2 默认冲突解决策略
Gradle 默认采用 “最新版本获胜”(Newest Version Wins) 策略:当同一库的不同版本冲突时,自动选择版本号最高的那个。
例如,上述 slf4j-api 三个冲突版本(2.0.9、2.0.7、1.7.36) 时,Gradle 会默认选择 2.0.9。
注意:与 Maven 的 “最短路径优先” 不同,Gradle 默认不考虑依赖路径长度,仅以版本号高低决定。
3.3 解决依赖冲突的方法
3.3.1 force 强制依赖版本
若确定某个版本兼容所有依赖它的库,可以在 configurations 的 resolutionStrategy 模块中使用 force 关键字强制依赖使用指定版本:
// 强制所有依赖配置使用指定版本(如 implementation、api、runtimeOnly 等)
configurations.all {resolutionStrategy {// 强制所有模块使用 slf4j-api:2.0.7force("org.slf4j:slf4j-api:2.0.7"// 可以在此处添加更多依赖强制版本// force("group:name:version"))}
}dependencies {implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:3.2.0")
}
如果只希望某个特定配置的依赖(例如 compileClasspath)使用指定版本,可以这样写:
// 对所有 compileClasspath 依赖,强制使用指定版本
configurations.named("compileClasspath") {resolutionStrategy {force("org.slf4j:slf4j-api:2.0.7")}
}
3.3.2 exclude 排除指定依赖
若某个库的传递依赖与其他库冲突,可在依赖声明时通过 exclude 关键字排除传递依赖:
dependencies {implementation('依赖坐标') {exclude(group = "冲突依赖的 group", module = "冲突依赖的 module")}
}
例如,排除 spring-boot-starter-web 传递的 slf4j-api 依赖:
dependencies {implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web:3.2.0"){exclude(group = "org.slf4j", module = "slf4j-api")}
}
如果多个依赖都传递了同一个不必要的依赖,可在 configurations 中全局配置排除,避免重复操作:
configurations.all {exclude(group = "org.slf4j", module = "slf4j-api")
}
💡 排除依赖时需明确
Group和Module,避免仅按Group排除导致误删必要依赖。
