1.1、开篇:AI如何重塑网络安全攻防格局?
当攻击者开始使用AI,我们不能再依靠传统的手工防御。
一、新战场:从"Mirai"到"DeepLocker"的警示
2016年,Mirai僵尸网络通过感染15万台物联网设备,发动了史上最大规模的DDoS攻击,让大半个美国的互联网陷入瘫痪。这还只是传统攻击的威力。
2018年,IBM研究院演示了DeepLocker——一款使用AI技术精准锁定目标的勒索软件。它能够隐藏恶意代码,只在识别出特定人脸、声音或地理位置时才激活。这意味着,你的智能摄像头可能在"看见"你的一瞬间,才释放出致命的攻击载荷。
这就是AI带来的双重变革:
- 🔴 攻击方:获得了前所未有的精准度、隐蔽性和自动化能力
- 🔵 防御方:面临着指数级增长的攻击数据和日益复杂的威胁环境
传统的"特征码检测"和"规则引擎"正在失效,网络安全正从"人力密集型"转向"智能密集型"。
二、AI赋能防御:安全团队的"力量倍增器"
2.1 智能威胁检测:从"大海捞针"到"精准定位"
传统方案的困境:
# 传统的基于规则的检测
if request.source_ip in blacklist:
block_request()
elif "malicious_pattern" in request.payload:
block_request()
else:
allow_request()
这种方法的局限性显而易见:只能检测已知威胁,无法应对新型攻击。
AI驱动的智能检测:
# 基于机器学习的异常检测
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
# 训练正常行为基线
normal_traffic = collect_normal_traffic()
model = IsolationForest(contamination=0.01)
model.fit(normal_traffic)
# 实时检测异常
def detect_anomaly(current_traffic):
prediction = model.predict([current_traffic])
if prediction[0] == -1: # 异常
trigger_investigation()
return True
return False
实际应用场景:
- UEBA(用户实体行为分析)
- 学习每个用户的正常行为模式(登录时间、访问资源、操作习惯)
- 实时检测账户劫持、内部威胁
- 准确率比传统规则高3-5倍,误报率降低70%
- 网络流量异常检测
- 分析流量模式、协议行为、通信关系
- 及时发现DDoS攻击、数据渗出、C2通信
- 在攻击早期阶段发出预警,而非事后补救
2.2 自动化恶意软件分析
传统方案:安全分析师每天手动分析数百个样本,效率低下。
AI驱动方案:
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
# 将PE文件转换为灰度图进行分析
def analyze_malware(file_path):
# 读取二进制文件并转换为图像
with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
binary_data = f.read()
# 创建图像表示
file_size = len(binary_data)
width = 256
height = file_size // width + 1
# 转换为灰度图
image = Image.new('L', (width, height))
image.putdata(binary_data + b'\x00' * (width * height - file_size))
# 使用预训练的CNN模型分类
model = load_malware_classification_model()
prediction = model.predict(preprocess_image(image))
return prediction
实际效果:
- 分析速度:毫秒级 vs 人工分析的小时级
- 准确率:95%+的恶意软件家族识别准确率
- 规模:每天可处理数百万个样本
2.3 智能安全运营:从"救火队"到"预警系统"
传统SOC的困境:
- 安全分析师被海量告警淹没
- 平均每个告警处理时间:15-30分钟
- 平均每天处理告警数量:20-50个
- 结果:超过70%的告警被忽略
AI驱动的SOC:
class AISecurityAnalyst:
def __init__(self):
self.alert_priority_model = load_priority_model()
self.investigation_bot = load_investigation_agent()
self.response_automation = load_response_playbooks()
def process_alert(self, raw_alert):
# 智能优先级排序
priority_score = self.alert_priority_model.predict(raw_alert)
if priority_score > 0.8: # 高优先级
# 自动化调查
investigation_result = self.investigation_bot.investigate(raw_alert)
if investigation_result.confidence > 0.9:
# 自动化响应
self.response_automation.execute(investigation_result)
else:
# 转交人类分析师,附上初步分析结果
human_analyst.review(investigation_result)
else:
# 低优先级告警,记录后忽略
self.log_low_priority_alert(raw_alert)
三、AI驱动攻击:攻击者的"智能武器库"
3.1 智能化的社会工程学攻击
传统钓鱼邮件:
主题:您的账户出现异常
内容:亲爱的用户,我们发现您的账户有异常活动,请立即点击链接验证。
AI生成的钓鱼邮件:
# 使用GPT模型生成个性化钓鱼邮件
def generate_spear_phishing(target_info):
prompt = f"""
根据以下信息生成一封个性化的商务邮件:
- 目标姓名:{target_info['name']}
- 公司:{target_info['company']}
- 职位:{target_info['position']}
- 最近活动:{target_info['recent_activity']}
邮件目的是让目标点击恶意链接,但要看起来完全合法。
"""
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
生成效果:
- 语言自然流畅,无语法错误
- 内容高度个性化,引用真实事件
- 检测逃避:避免使用敏感关键词
- 成功率比传统钓鱼高5-10倍
3.2 智能漏洞挖掘
传统fuzzing:随机生成测试用例,效率低下
AI驱动的fuzzing:
class AIFuzzer:
def __init__(self, target_program):
self.target = target_program
self.lstm_model = load_language_model()
self.reward_model = load_reward_model()
def generate_test_cases(self):
# 基于程序输入语法学习生成测试用例
learned_grammar = self.lstm_model.learn_grammar(self.target)
for i in range(1000):
# 生成符合语法的输入
test_input = self.lstm_model.generate_input(learned_grammar)
# 执行测试
result = self.execute_test(test_input)
# 基于执行结果奖励模型
reward = self.reward_model.calculate_reward(result)
self.lstm_model.update(reward)
if result.crashed:
log_crash(test_input, result)
实际效果:
- 漏洞发现效率提升10-50倍
- 能够发现复杂的逻辑漏洞
- 7×24小时不间断工作
3.3 对抗性攻击:欺骗AI安全系统
import torch
def generate_adversarial_example(model, original_sample, target_class):
"""
生成对抗样本,欺骗AI分类器
"""
original_sample.requires_grad = True
# 前向传播
output = model(original_sample)
loss = torch.nn.functional.cross_entropy(output, target_class)
# 反向传播获取梯度
model.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
# 生成对抗扰动
gradient_sign = original_sample.grad.data.sign()
adversarial_sample = original_sample + 0.1 * gradient_sign
return adversarial_sample
# 使用示例:让恶意软件绕过AI检测
malicious_feature = extract_features(malware_file)
adversarial_malware = generate_adversarial_sample(ai_detector, malicious_feature, benign_class)
四、AI自身安全:新的攻防前线
4.1 模型安全:保护我们的"智能大脑"
主要威胁:
- 模型窃取攻击
# 攻击者通过API查询重建模型
def model_stealing_attack(target_api, num_queries=10000):
stolen_model = create_shadow_model()
for i in range(num_queries):
# 生成查询数据
query_data = generate_query_data()
# 获取目标API预测结果
prediction = target_api.predict(query_data)
# 用查询结果训练影子模型
stolen_model.train(query_data, prediction)
return stolen_model # 现在攻击者有了功能相似的模型
- 数据投毒攻击
# 在训练数据中注入后门
def data_poisoning(training_data, poison_ratio=0.05):
poisoned_data = training_data.copy()
num_poison = int(len(training_data) * poison_ratio)
for i in range(num_poison):
# 选择样本并添加后门触发器
sample = training_data[i]
poisoned_sample = add_backdoor_trigger(sample)
# 修改标签为攻击者期望的目标
poisoned_data[i] = (poisoned_sample, target_label)
return poisoned_data
4.2 隐私保护:联邦学习的兴起
class FederatedLearningSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.global_model = create_initial_model()
self.clients = []
def federated_training_round(self):
# 1. 将全局模型分发给客户端
client_models = [self.global_model.copy() for _ in self.clients]
# 2. 各客户端在本地训练(数据不出域)
client_updates = []
for client, model in zip(self.clients, client_models):
local_update = client.train_locally(model)
client_updates.append(local_update)
# 3. 聚合模型更新
global_update = aggregate_updates(client_updates)
# 4. 更新全局模型
self.global_model.update(global_update)
return self.global_model
五、构建智能安全运营体系
5.1 AISecOps成熟度模型
Level 1: 基础分析 → Level 2: 智能检测 → Level 3: 预测防御 → Level 4: 智能自适应
↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
手工分析 机器学习检测 威胁预测 自主响应
规则引擎 异常检测 攻击路径预测 自适应防御
5.2 技术架构蓝图
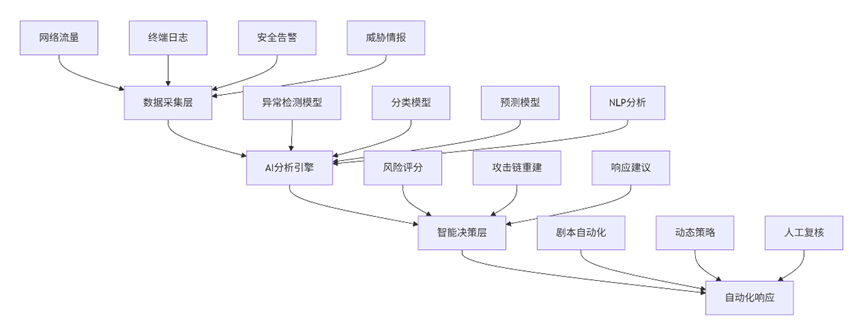
5.3 实施路线图
第一阶段:基础建设(1-3个月)
- 建立数据收集和预处理管道
- 部署基础的机器学习检测模型
- 训练团队掌握AI工具使用
第二阶段:能力提升(3-6个月)
- 实现自动化调查和响应
- 建立模型持续训练流程
- 开展红蓝对抗测试AI系统
第三阶段:智能运营(6-12个月)
- 实现预测性威胁狩猎
- 建立自适应防御体系
- 形成AI驱动的安全文化
六、挑战与未来展望
6.1 当前主要挑战
- 数据质量与数量
- 高质量标注数据稀缺
- 数据隐私与合规限制
- 数据偏见导致模型偏差
- 技术复杂性
- 需要跨学科人才(安全+AI+工程)
- 模型可解释性难题
- 系统集成复杂度高
- 对抗性环境
- 攻击者也在使用AI
- 模型本身成为攻击目标
- 需要持续更新和适应
6.2 未来趋势
- 大语言模型在安全中的应用
- 自动化安全报告生成
- 智能代码安全审查
- 自然语言交互的安全助手
- 自主安全系统
- 基于强化学习的自适应防御
- 自动化的攻防演练
- 预测性漏洞修复
- 隐私增强技术
- 同态加密下的安全分析
- 差分隐私保护
- 安全多方计算
七、总结:拥抱智能安全新时代
AI正在从根本上改变网络安全的游戏规则:
- 防御方获得了处理海量数据、发现未知威胁、自动化响应的能力
- 攻击方获得了精准 targeting、自动化攻击、逃避检测的新手段
- 新的战场在AI模型本身展开,模型安全成为必争之地
关键认知转变:
- 从"特征检测"到"行为分析"
- 从"被动响应"到"预测防御"
- 从"工具堆砌"到"智能体系"
- 从"人力密集"到"人机协同"
未来的安全团队不再是传统的"防火墙管理员"或"漏洞分析员",而是安全数据科学家、AI模型工程师和威胁狩猎专家的组合。
这场AI安全革命不是未来,而是现在。要么主动拥抱,要么被动淘汰。
