[MySQL] 联合查询
目录
1. 联合查询的由来
2. 笛卡尔积
2.1 理论介绍
2.2 SQL语句编写
2.3 联合查询的流程
2.4 内连接
2.5 外连接
2.6 自连接
2.7 子查询
2.8 合并查询
2.9 插入查询结果
1. 联合查询的由来
因为我们在创建数据表时候遵循范式的规则,将数据拆分成多个表,而我们想要查询表的所有属性列,就需要将几张表的数据结合起来显示,因此就产生了联合查询。比如:学生表和课程表,这里我们想要在一张表中显示学生表和课程表的信息,就需要用到联合查询。
2. 笛卡尔积
2.1 理论介绍
数据库中笛卡尔积指的是两个表之间的运算,我们可以将两个表进行笛卡尔积就能得到两个表的完整信息。
对下面这两个表进行笛卡尔积的运算:
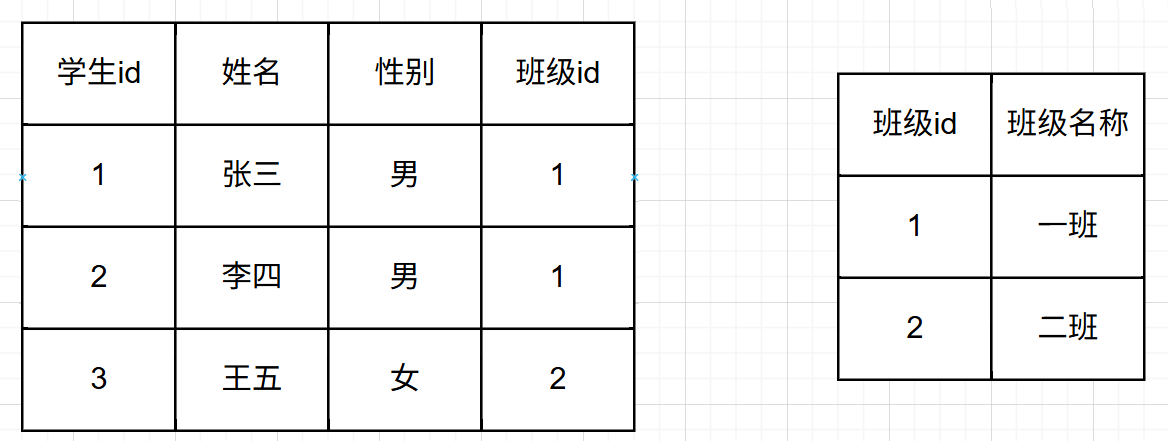
得到的结果表是:
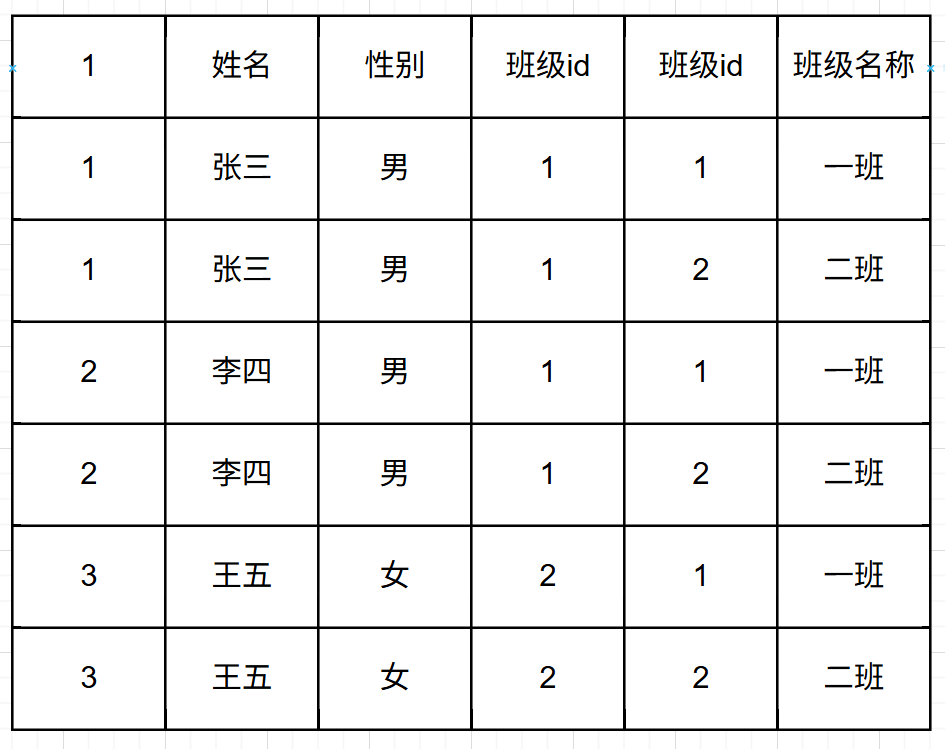
两个表通过笛卡尔积得到的 表的行数是两个表行数的乘积,表的列数是两个表列数的和。
我们观察新得到的表会发现这张表里面有很多无效数据,也就是张三应该是一班的,所以第二行是无效数据,那我们会发现无效数据是两个班级id不相同的数据,那我们在查询的时候可以添加一个where条件。
如何区分两个班级id呢?
我们可以这样表示 student.id 和 class.id。通过成员访问运算符 . 来实现。
2.2 SQL语句编写
下面是联合查询的代码实现:
create table class1(class_id int primary key, class_name varchar(20));
insert into class1 values(1,'一班'), (2,'二班');create table student1(id int primary key, name varchar(20), gender varchar(10), class_id int, foreign key (class_id) references class1(class_id));
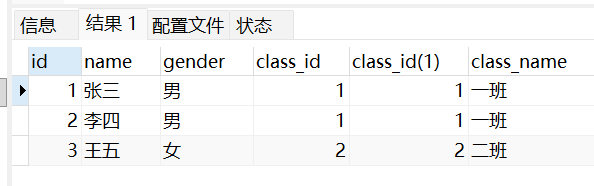
insert into student1 values(1,'张三','男',1), (2,'李四','男',1),(3,'王五','女',2);select * from student1, class1 where student1.class_id = class1.class_id;查询结果为:
2.3 联合查询的流程
- 我们先对两个表进行笛卡尔积。
- 接着添加连接条件。
- 然后根据需求添加其他条件。
- 最后针对列进行筛选/计算表达式/聚合查询等操作。
下面我举几个例子,帮助理解联合查询的流程:
首先我们先准备几张表进行查询,下面有学生表,班级表,成绩表,课程表四张表:
create table student(student_id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20), sno varchar(20), age int, gender int, enroll_date datetime, class_id int, foreign key (class_id) references class(class_id));
insert into student(name, sno, age, gender, enroll_date, class_id) values('唐三藏', '100001', 18, 1, '1986-09-01', 1),('孙悟空', '100002', 18, 1, '1986-09-01', 1),('猪悟能', '100003', 18, 1, '1986-09-01', 1),('沙悟净', '100004', 18, 1, '1986-09-01', 1),('宋江', '200001', 18, 1, '2000-09-01', 2),('武松', '200002', 18, 1, '2000-09-01', 2),('李逹', '200003', 18, 1, '2000-09-01', 2),('不想毕业', '200004', 18, 1, '2000-09-01', 2);create table class(class_id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
insert into class(name) values('001班'), ('002班'), ('003班');create table course(course_id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar(20));
insert into course(name) values('Java'),('C++'),('MySQL'),('操作系统'),('计算机网络'),('数据结构');create table score(score double, student_id int, course_id int, primary key(student_id,course_id));
insert into score(score,student_id,course_id) values (70.5, 1, 1),(98.5, 1, 3),(33, 1, 5),(98, 1, 6),(60, 2, 1),(59.5, 2, 5),
(33, 3, 1),(68, 3, 3),(99, 3, 5),(67, 4, 1),(23, 4, 3),(56, 4, 5),(72, 4, 6),
(81, 5, 1),(37, 5, 5),(56, 6, 2),(43, 6, 4),(79, 6, 6),(80, 7, 2),(92, 7, 6);查询学生姓名为孙悟空的详细信息,包括学生个人信息和班级信息。
1. 我们确定要查询的表来自那几张表,进行笛卡尔积运算。
学生表,班级表
select * from student, class;2. 确认连接条件,进行查询。
select * from student, class where student.class_id = class.class_id;3. 根据需求进一步增加条件。
select * from student, class
where student.class_id = class.class_idand student.name = '孙悟空';4. 根据需求来查找对应的列。
select student.name, student.sno, student.age, student.gender, student.enroll_date, class.name as '班级名称'
from student,class
where student.class_id = class.class_id and student.name = '孙悟空';
2.4 内连接
内连接相当于在原来的联合查询的语句上进行修改,这里用到 join on两个关键字。
原来查询是:
select * from student, class where student.class_id = class.class_id;改为内连接为:
select * from student join class on student.class_id = class.class_id;这两个SQL语句查询出来的内容都是一样的。
我们可以将上面的联合查询语句改成:
#内连接
# 1.笛卡尔积
select * from student join class;
# 2.添加连接条件
select * from student join class on student.class_id = class.class_id;
# 3.进一步添加条件
select * from student join class on student.class_id = class.class_id
where student.name = '孙悟空';
# 4.对列进行精简
select student.name, student.sno, student.age, student.gender, student.enroll_date, class.name
from student join class on student.class_id = class.class_id
where student.name = '孙悟空';查询所有同学的总成绩和同学的个人信息。
确认从学生表和成绩表中查找。
# 笛卡尔积
select * from student join score;
# 添加连接条件
select * from student join score on student.student_id = score.student_id;
# 没有条件添加
#对列进行精简
select student.name, sum(score.score) as total_score
from student join score on student.student_id = score.student_id
group by student.name;查询所有同学每门课的成绩,及同学的个人信息。
确认从学生表,成绩表 和课程表中查找:
# 笛卡尔积
select * from score join student join course;
# 添加连接条件
select * from score
join student on student.student_id = score.student_id
join course on course.course_id = score.course_id;
#没有条件进行添加
#对列进行精简
select student.name, course.name as course_name, score.score
from score
join student on student.student_id = score.student_id
join course on course.course_id = score.course_id;
2.5 外连接
外连接分为左外连接,右外连接,全外连接,mysql不支持全外连接。
左外连接:如果左边表的数据在右边表中没有匹配记录,那么就会将对应右边记录为null。
右外连接:如果右边表对应左边表数据没有匹配记录,那么就会将对应左边记录为null。
全外连接:左右两张表互相存在不对应的匹配数据,就会为null。
创建新的两张表,学生表和成绩表:
create table student(id int, name varchar(20));
insert into student values(1,'张三'), (2,'李四'), (3,'王五');create table score(student_id int, score int);
insert into score values(1,88), (2,99), (4,77);内连接:
select * from student, score where student.id = score.student_id;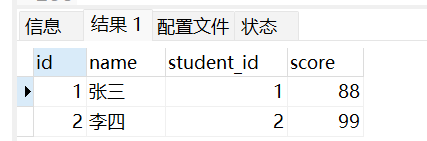
左外连接:
select * from student left join score on student.id = score.student_id;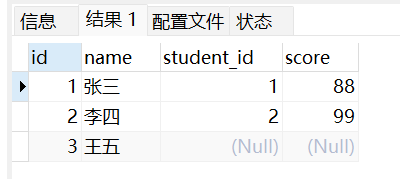
右外连接:
select * from student right join score on student.id = score.student_id;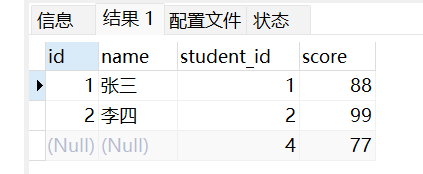
2.6 自连接
自连接是表自己对自己进行连接,我们可以把行变换成列,而列跟列之间能进行比较,所以相当于间接实现了行与行进行比较。我们在表连接时候,要为表起两个不同的别名。
显示所有"MySQL"成绩比"JAVA"成绩高的成绩信息:
这里我们是用成绩表进行自连接查询:
select s1.student_id, s1.course_id, s1.score, s2.course_id, s2.score
from score as s1, score as s2
where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.course_id = 3 and s2.course_id = 1 and s1.score > s2.score;2.7 子查询
子查询通常是把一个SQL语句的结果当作另一个SQL语句的条件来进行查询的。
但是这种查询方式比较难以阅读,违背软件开发的核心原则(将大问题转换为多个小问题),很少使用。
单行子查询:
查询与不想毕业的同学的同班同学:
select name from student where class_id =
(select class_id from student where name = '不想毕业');多行子查询:
查询mysql或Java课程的成绩信息:
select course_id,score from score where course_id in (
select course_id from course where name = 'MySQL' or name = 'Java');多列子查询:
查询重复录入的分数:
select * form score where (score,student_id,course_id) in (select score,student_id,course_id from score group by score,student_id,course_id having count(0) > 1);2.8 合并查询
这里我们可以将多个查询结果合并在一起进行,使用union 或者union all。
这里我们需要创建一个新表来进行演示:
create table student1 like student;
insert into student1 (name, sno, age, gender, enroll_date, class_id) values
('唐三藏', '100001', 18, 1, '1986-09-01', 1),
('刘备', '300001', 18, 1, '1993-09-01', 3),
('张飞', '300002', 18, 1, '1993-09-01', 3),
('关羽', '300003', 18, 1, '1993-09-01', 3);union操作符:
查询student表中id < 3 的同学和student1表中的所有同学:
select * from student where student_id < 3
union
select * from student1;查询结果:
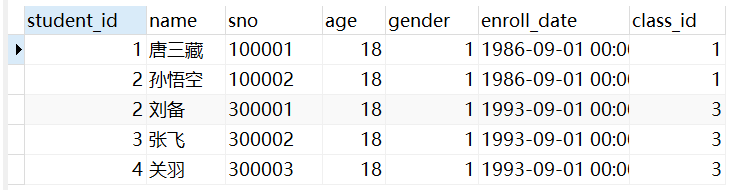
这里得union会把两个查询的结果取并集,并且会自动取出重复的行。
union all操作符:
查询student表中id < 3 的同学和student1表中的所有同学:
select * from student where student_id < 3
union all
select * from student1;
查询结果:
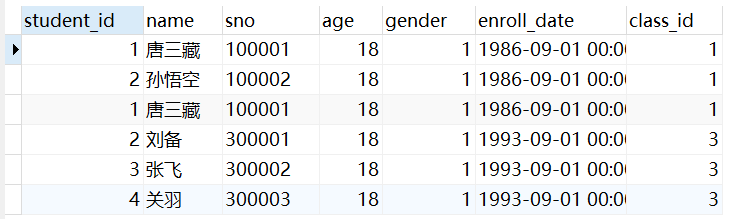
union all查询时候查询两个结果的并集,不会去除重复的行。
2.9 插入查询结果
将student表中的001班的学生复制到student1表中:
insert into student1(name,sno,age,gender,enroll_date,class_id)
select student.name,student.sno,student.age,student.gender,student.enroll_date,student.class_id
from student,class where student.class_id = class.class_id and class.name = '001班';这里后面的查询出来的条件应该与前面的条件类型和数量对应。
