#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h> // 为了使用 bool 类型typedef struct ListNode {int data; // 数据域,这里以int为例struct ListNode* next; // 指针域,指向下一个节点
} ListNode, * LinkList;/*判断链表是否为空 (is_empty)检查链表中是否存在数据节点1.带头结点的链表 -- 第一个节点是头结点,不存储实际数据,其next指针指向第一个数据节点。2.不带头结点的链表 -- 头指针直接指向第一个数据节点。
*/// 判断链表是否为空(带头结点)
/*带头结点的链表通常有一个不存储实际数据的头结点,其 next 指针指向第一个有效结点。判断链表是否为空,只需检查头结点的 next 是否为 NULL。若 head->next 为 NULL,说明链表没有有效结点,返回 true。
*/
bool IsEmpty(ListNode* head)
{return head->next == NULL;
}// 创建一个只有头结点的空链表
ListNode* initList() {ListNode *head = (ListNode*) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (head == NULL) {printf("内存分配失败!\n");exit(1); // 或者返回NULL,由调用者处理错误}head->next = NULL; // 头结点指针域初始化为NULLreturn head;
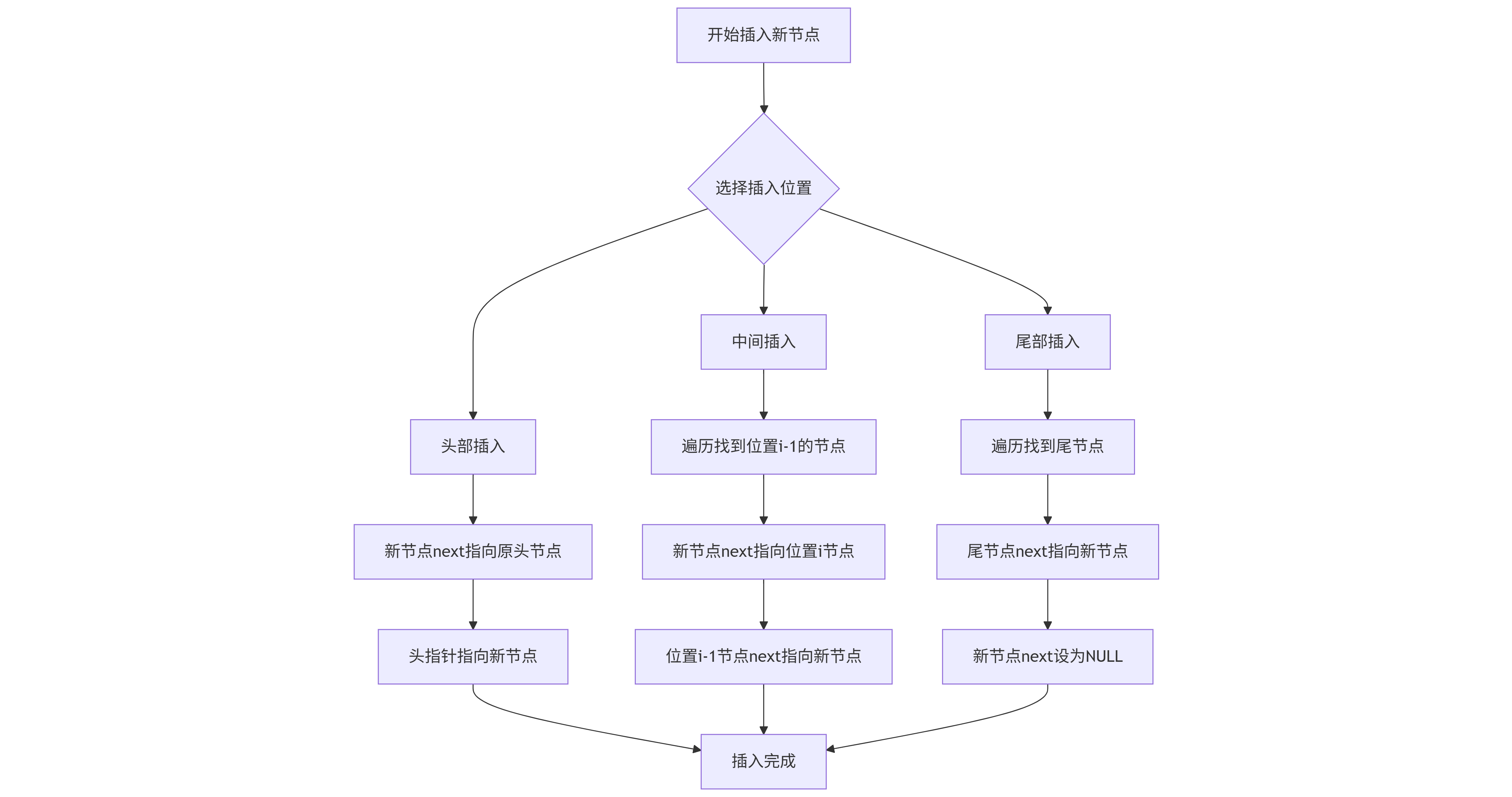
}// 头插法(在头结点后插入新节点)
void insertAtHead(ListNode *head, int value) {ListNode *newNode = (ListNode*) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newNode->data = value;newNode->next = head->next; // 新节点指向原首节点head->next = newNode; // 头结点指向新节点
}// 尾插法(在链表末尾插入新节点)
void insertAtTail(ListNode *head, int value) {ListNode* current = head;while (current->next != NULL) { // 找到最后一个节点current = current->next;}ListNode *newNode = (ListNode*) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newNode->data = value;newNode->next = NULL;current->next = newNode;
}// 指定位置插入
void insertAtIndex(ListNode *head, int index, int value) {if (index < 0) return;ListNode *current = head;for (int i = 0; current != NULL && i < index; i++) {current = current->next;}if (current == NULL) return; // 索引超出范围ListNode *newNode = (ListNode*) malloc(sizeof(ListNode));newNode->data = value;newNode->next = current->next;current->next = newNode;
}// 删除操作,按值删除
void deleteByValue(ListNode *head, int value) {ListNode *prev = head;ListNode *current = head->next;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == value) {prev->next = current->next;free(current);return;}prev = current;current = current->next;}printf("抱歉,此时链表中不存在value: %d \n",value);
}// 按位置删除
void deleteByIndex(ListNode *head, int index) {if (index < 0) return;ListNode *prev = head;ListNode *current = head->next;for (int i = 0; current != NULL && i < index; i++) {prev = current;current = current->next;}if (current == NULL) return; // 索引超出范围prev->next = current->next;free(current);
}// 查找操作,按值查找
ListNode* searchByValue(ListNode *head, int value) {int count = 0;ListNode *current = head->next;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == value) {printf("value:%d 当前位置为 %d \n",value, count);return current;}current = current->next;count++;}return NULL; // 未找到
}// 按位置查找
ListNode* searchByIndex(ListNode *head, int index) {if (index < 0) return NULL;ListNode *current = head->next;for (int i = 0; current != NULL && i < index; i++) {current = current->next;}return current; // 可能返回NULL(索引超限)
}// 遍历链表
void traverseList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head->next;while (current != NULL) {printf("%d ", current->data);current = current->next;}printf("\n");
}// 销毁链表
void destroyList(ListNode *head) {ListNode *current = head;while (current != NULL) {ListNode *temp = current;current = current->next;free(temp);}
}int main()
{printf("Hello, World!\n");LinkList * head = initList();insertAtHead(head,5);insertAtHead(head,10);insertAtTail(head,20);traverseList(head);ListNode* pos = searchByValue(head,20);deleteByValue(head,20);traverseList(head);deleteByValue(head,20);bool isEmpty = IsEmpty(head);printf("此链表是否为空? %s",isEmpty ? "true" : "false");return 0;
}
相交链表的实现:
/*** 相交链表* 方法一:双指针法(推荐)* 算法原理让指针 pA 和 pB 分别从 headA 和 headB 开始遍历。当 pA 到达链表 A 的末尾时,让它从链表 B 的头节点重新开始;同样,当 pB 到达链表 B 的末尾时,让它从链表 A 的头节点重新开始。如果两个链表相交,那么 pA 和 pB 最终会走过相同的路程(LenA + LenB),并在相交节点相遇。如果链表不相交,两个指针最终会同时变为 NULL。* @return*/bool getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB){if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL) {return NULL;}struct ListNode *pA = headA;struct ListNode *pB = headB;while (pA != pB) {// pA走到头后,转去遍历链表BpA = (pA == NULL) ? headB : pA->next;// pB走到头后,转去遍历链表ApB = (pB == NULL) ? headA : pB->next;}return pA;}

