数据结构的复习(1):
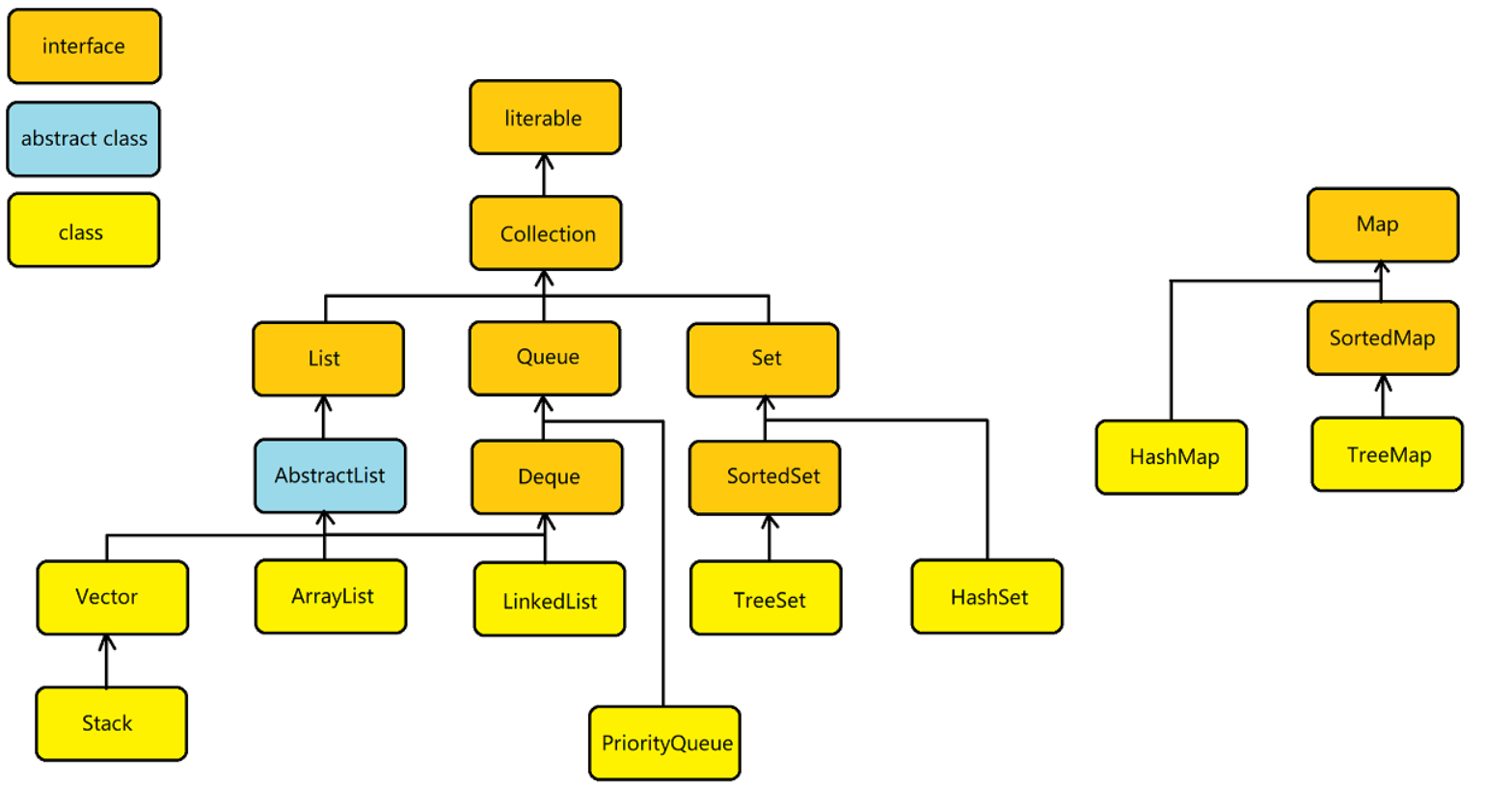
数据结构类和接口的总览
时间和空间复杂度
算法的效率一般由时间效率和空间效率而定,时间效率也就是时间复杂度,空间效率就是空间复杂夫,时间复杂度判断的是算法的运行速度,空间复杂度判断的是算法所需要空间的大小
常见的时间复杂度
O(1)<O(logN)<O(N)<O(N*logN)<O(N^2)
后续接着补充
装箱和拆箱
public class TestBaseType {public static void main(String[] args) {// 拆箱Integer a=1;int b=a.intValue();System.out.println(b);// 装箱int c=3;Integer d=Integer.valueOf(c);System.out.println(d);// 自动装箱int b1=2;Integer a1=b1;Integer b2=(Integer) b1;System.out.println(a1+" "+b2);
// 自动拆箱Integer a2=3;int a3=a2;int a4=(int)a2;System.out.println(a2+" "+a3);}
}
注:自动装箱Integer a =10,底层会帮我们调用Integer.valueOf()方法
面试题
判断代码输出的值是否相同
Integer a=127;Integer b=127;System.out.println(a==b);Integer c=128;Integer d=128;System.out.println(c==d);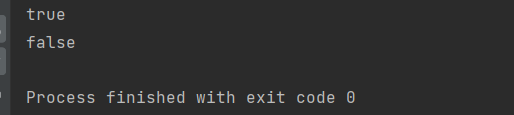
因为在Integer的源码中
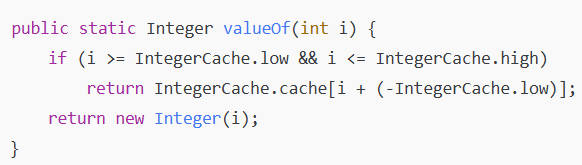
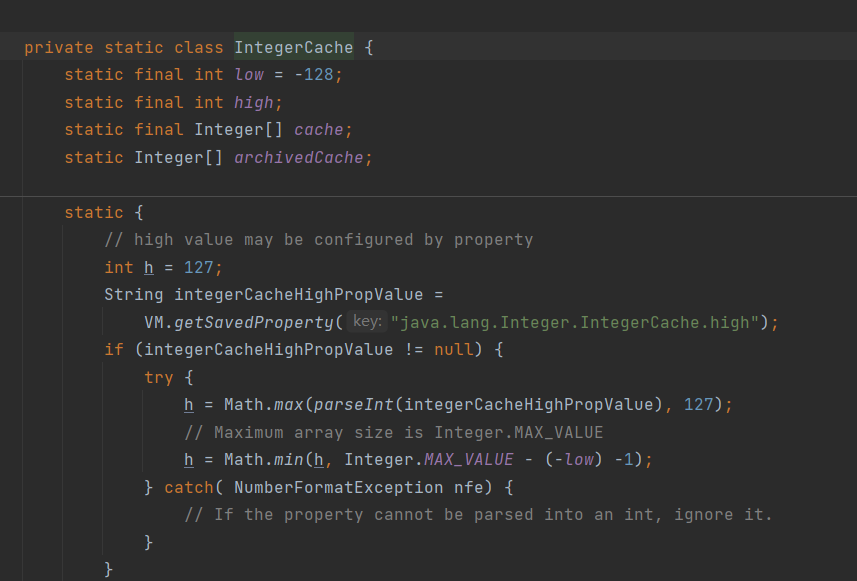
JVM 在启动时,会提前创建从 -128 到 127 的 Integer 对象,存放在 cache[] 里。
当调用 Integer.valueOf(x) 时,只要 x 在这个范围内,就直接取缓存引用
注:Integer a=127;就是一个自动的装箱过程,等同于Integer a=Integer.valueOf(127);
如果数值的范围在-128~127内,返回缓存中同一个对象进行引用,如果不在这个范围内就会创建一个新的对象。
所以在范围内,如果比较一个相同的数字,返回为true,是因为是同一个对象进行的访问,如果不是在范围内,则会返回为false,因为会创建不同的对象,所以就算数值相同,返回的还是false
泛型
泛型就是让类,接口,方法进行参数化操作不同类型的数据,不需要把每个类型都写一份代码
泛型可以在编译的时候就帮我检查类型,防止出错
注:泛型的<>中只能用包装类型(Integer),不能用基本类型(int)
泛型主要应用于类,接口,方法
泛型类的使用
class test2<T>{private T date;public void set(T date) {this.date = date;}public T get() {return date;}public static void main(String[] args) {test2<String> test2=new test2<>();test2.set("123");String s = test2.get();System.out.println(s);}
}泛型接口的应用
public interface swap<T>{int swapMethod(T a);}public class t1 implements swap<String>{@Overridepublic int swapMethod(String a) {return 0;}}泛型方法中的应用
泛型方法中的<T>代表一个占位符,是类型参数的申明,意思是告诉编译器这是一个泛型的方法,参数中由类型为T的参数
{
public static void main(String[] args) {utils.sq("123");utils.sq(666);}
}
class utils{public static <T> void sq(T date){System.out.println(date);}
}泛型的边界限定
有时候我们希望泛型不是任何的类型,而是某些类型的子类或者父类,在这时我们就需要定义泛型的上界和下界
泛型的上界规定,T只能是Number或者是其子类
class test2<T extends Number>{}因为他只是一个子类,不能确定的知道他是什么类型,所以只能读不能写
List<? super Integer> sup = new ArrayList<Number>();而泛型的下届规定他是某些类型的父类型,所以可以进行写入,但是在读取的时候,只能当作Object类型进行读取
泛型的擦除机制
Java在运行的时候会擦除所有的泛型类型,当成原始类型代替他们,基本泛型会被擦除成Object
泛型只是在编译的时候用作类型的检查,在运行的时候不会保留任何的泛型信息
当这样一份代码
public class Box<T> {private T value;public void set(T value) { this.value = value; }public T get() { return value; }
}
Box<String> box1 = new Box<>();
Box<Integer> box2 = new Box<>();
运行后,会被擦除为
public class Box {private Object value;public void set(Object value) { this.value = value; }public Object get() { return value; }
}
在运行时没有”泛型类型“一说,都是普通的object
泛型边界的擦除
class A<T> {T data;
}
⬇
class A {Object data;
}
上界的擦除
class B<T extends Number> {T data;
}
⬇
class B{Number date;
}注:如果有多重边界,则使用第一个边界
![]()
Java泛型时编译时期类型的安全机制,通过类型擦除在运行期兼容旧的JVM,所有的泛型类型信息在运行时都会消失
JDK17的语法新增特性
一些新增加的特性
yield关键字
正常的switch语句
String data = "one";int result = 0; //接收数据的返回值switch (data) {case "one":result = 1; //为result重新赋值break;case "two":result = 2; //为result 重新赋值break;default:result = -1; //为result重新赋值break;}简化
String data = "one" ;int result = switch (data) {case "one"->1;case "two"->2;default->-1;};使用yield关键字代替->
String data = "one" ;int result = switch (data) {case "one" : yield 1;case "two": yield 2;default : yield -1;};var关键字
var可以自动帮你推出类型
使⽤var可以使代码更简洁。有时候,类型名称可能会⾮常⻓,例如泛型。var就像是⼀个简化器,让 你不必反复写出繁琐的类型名
Map<String, List<Map<Integer, String>>> complexMap = new HashMap<String,
List<Map<Integer, String>>>();}var complexMap2 = new HashMap<String, List<Map<Integer, String>>>();List
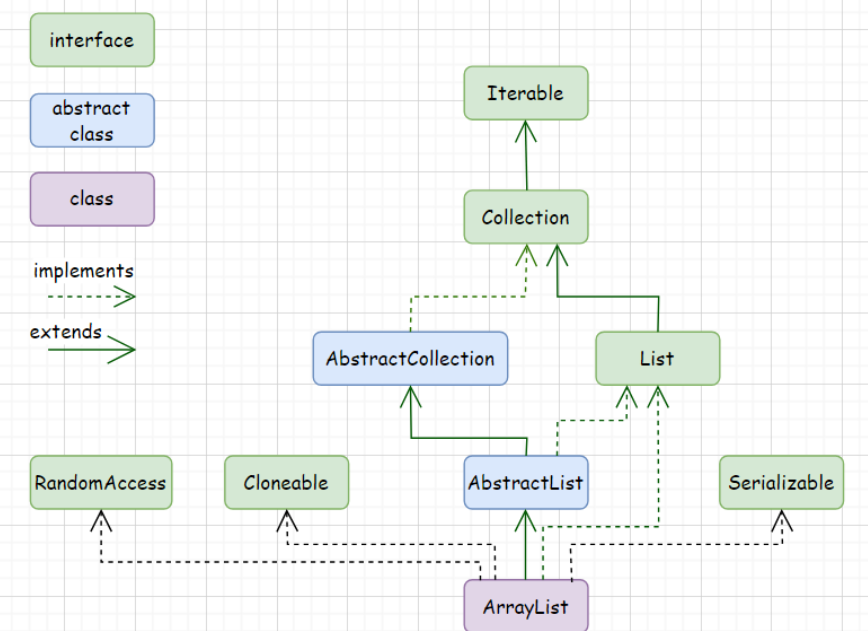
List是继承了Collection接口
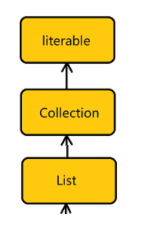
List就是一个线性表,即n个具有相同类型元素的有限序列,在该序列上可以执行增删改查以及变量等操作
List中的方法
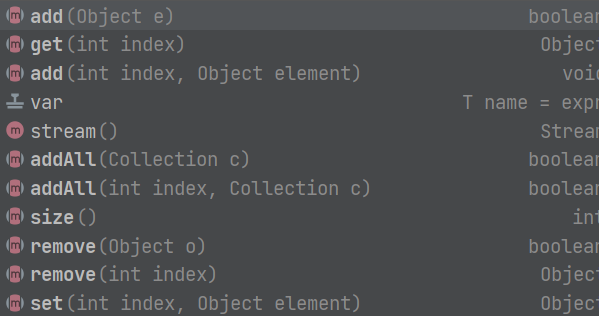
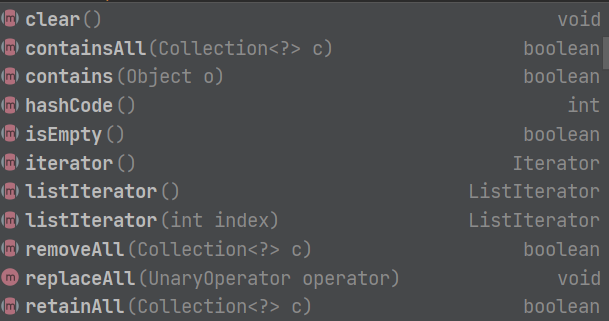
List中常用方法的使用
List是一个接口,并不能直接用来实例化,必须实例化List的实现类,ArrayList和LinkedList都实现了List接口
ArrayList
arrayList在本质上就是一个动态的顺序表
顺序表一般是在一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删查改
ArrayList的简介
arrayList是一个普通的类,实现了List接口
ArrayList的使用
class MyArrayList{public static void main(String[] args) {List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();//添加元素list.add("zhangsan");list.add("lisi");list.add("wangwu");display(list);System.out.println();//根据元素的下标获得元素String s = list.get(0);String s1 = list.get(1);String s2 = list.get(2);System.out.println(s+" "+s1+" "+s2);//获得顺序表的大小int size = list.size();System.out.println(size);//根据元素的下标删除元素list.remove(0);display(list);//判断是否包含某个元素list.contains("zhangsan");//查找某个元素对应的位置int index = list.indexOf("lisi");System.out.println(index);list.clear();display(list);}public static void display(List<String> list){for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");}if (list.isEmpty()){System.out.println("null");}}
}ArrayList的三个构造方法
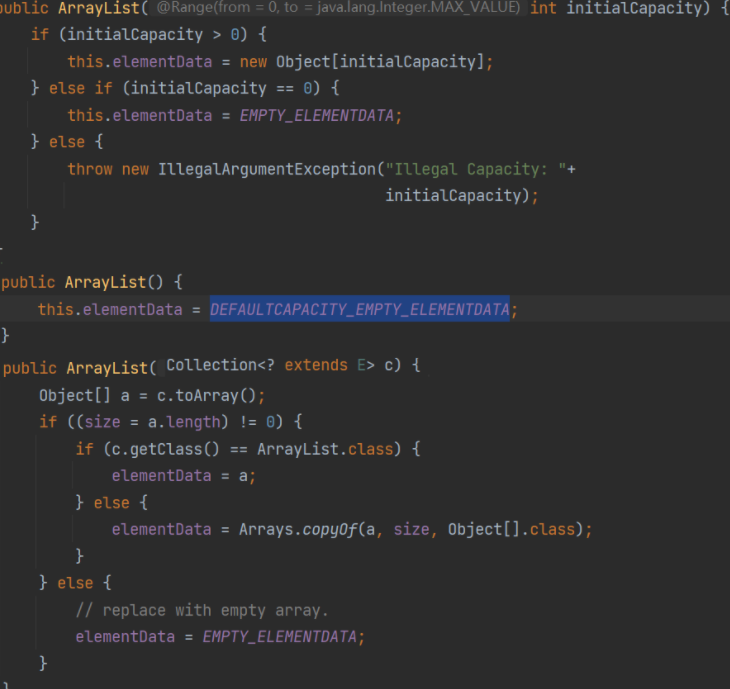
ArrayList的遍历
for循环遍历
// for循环进行遍历public static void display(List<String> list){for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.print(list.get(i)+" ");}if (list.isEmpty()){System.out.println("null");}}foreach遍历
// foreach进行遍历
public static void display1(List<String> list){for (String x:list) {System.out.print(x+" ");}
}迭代器遍历
public static void display2(List<String> list){Iterator<String> iterator=list.listIterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.print(iterator.next()+" ");}}ArrayList的扩容机制
ArrayList不是链表,而实一个可以自动扩容的顺序表,底层是由动态数组进行实现
![]()
执行的逻辑
当我们首次进行创建
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();源码底层创建了空数组变量并且进行调用,并没有直接的进行创建数组
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};public ArrayList() {this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}真正数组的创建是在实例化的对象第一次add()时候
list.add(1);底层源码调用ensureCapacityInternal()进行初始化容量
初始化的DEFAULT_CAPACITY值为10
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
当容量不够的时候,源码进行判断,是否需要扩容
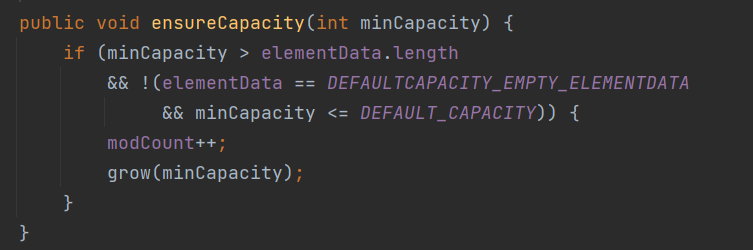
源码自动进行扩容
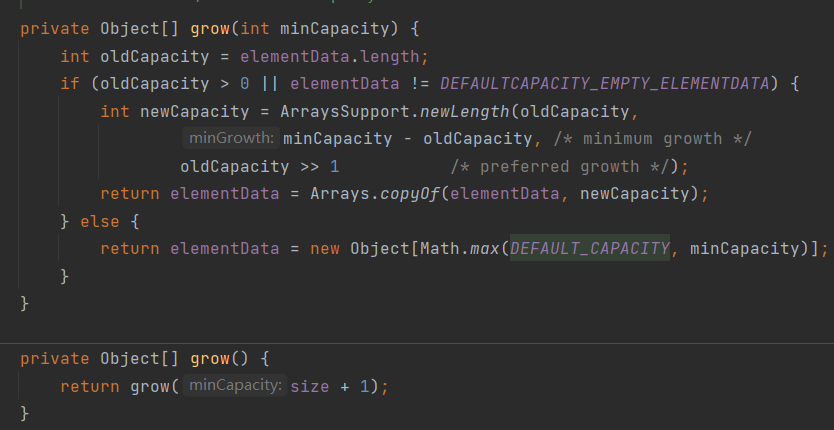
ArrayList扩容机制的底层源码逻辑
注:扩容需要申请新数组,拷贝旧数组,会影响性能,所以如果你提前知道元素的多少,建议在实例化对象的时候,直接用含参数的构造方法,传入你需要的大小,后续无需扩容
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(1000);通过制作一个发牌模式,练习一下ArrayList
public class Card {private String suit;private int number;public Card(){}public Card(String suit,int number){this.suit=suit;this.number=number;}public String toString() {return String.format("[%s %d]", suit, number);}
}class CardDemo{private static final String[] SUIT={"♣","♥","♦","♠"};// 定义一副牌public static final List<Card> cards() {List<Card> cards = new ArrayList<>(52);for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {for (int j = 1; j <= 13; j++) {String s = SUIT[i];int number = j;Card card = new Card(s, number);cards.add(card);}}return cards;}// 洗牌public static final List<Card> randomCard(List<Card> cards){Random random=new Random();for (int i = cards.size()-1; i >0; i--) {int r=random.nextInt(i);swap(cards,i,r);}return cards;}private static void swap(List<Card> cards, int i, int r) {Card cardI = cards.get(i);cards.set(i,cards.get(r));cards.set(r,cardI);}//玩牌public static void main(String[] args) {List<Card> cards = cards();System.out.println(cards);System.out.println();randomCard(cards);System.out.println(cards);// 发牌List<List<Card>> p=new ArrayList<>();p.add(new ArrayList<>());p.add(new ArrayList<>());p.add(new ArrayList<>());for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {p.get(j).add(cards.remove(0));}}System.out.println(p.get(0));System.out.println(p.get(1));System.out.println(p.get(2));}
}
ArrayList的缺陷
当arrayList添加元素或者删除元素的时候需要往前或者往后移动其他的元素,时间复杂度为O(N),效率很低,因此ArrayList不适合作很多元素的删除或者插入
链表(LinkedList)
是一种通过节点连接起来的线性的数据结构
节点中一般存放着数据的值和下一个连接的节点地址
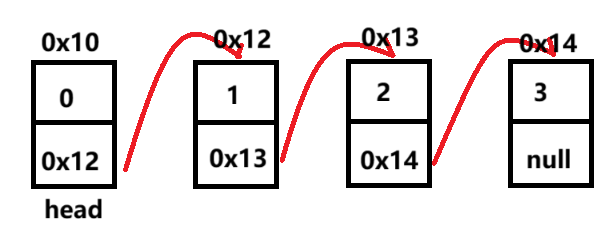
LinkedList的简单使用
public static void main(String[] args) {LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>();list.add("a");list.add("b");list.add("c");list.addFirst("66");list.addLast("99");for (String s : list) {System.out.println(s);}System.out.println(list);list.remove(0);System.out.println(list);}LinkedNode的简单实现
class RealizeLinkedList implements SingleLinkedList{static class ListNode{private int val;private ListNode next;public ListNode(int val){this.val=val;}}public ListNode head;// 创建一个链表public void createLinkedList(){ListNode node=new ListNode(12);ListNode node1=new ListNode(12);ListNode node2=new ListNode(34);ListNode node3=new ListNode(45);node.next=node1;node1.next=node2;node2.next=node3;node3.next=null;this.head=node;}@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node=new ListNode(data);ListNode cur=head;node.next=cur;head=node;}@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {if(head==null){return;}ListNode node =new ListNode(data);ListNode cur =head;while (cur.next!=null){cur=cur.next;}cur.next=node;node.next=null;}@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {if(index<0 || index>size()){throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("索引不合法");}if(index==0){addFirst(data);}ListNode node=new ListNode(data);ListNode cur=head;while (index-1!=0){cur=cur.next;index--;}ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next=node;node.next=curNext;}@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur=head;if(cur==null){return false;}while (cur!=null){if(cur.val==key){return true;}cur=cur.next;}return false;}@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if(head==null){return;}if(head.val==key){head=head.next;return;}ListNode cur=findNodeOfKey(key);if (cur != null && cur.next != null) {cur.next = cur.next.next;}}private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {ListNode cur=head;while (cur.next!=null){if(cur.next.val==key){return cur;}cur=cur.next;}return null;}@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if(head==null){return;}ListNode prev=head;ListNode cur=head.next;while (cur!=null){if(cur.val==key){prev.next=cur.next;cur=cur.next;}else {prev=cur;cur=cur.next;}}if(head.val==key){head=head.next;}}@Overridepublic int size() {ListNode cur=head;int len=0;while (cur!=null){len++;cur=cur.next;}return len;}@Overridepublic void clear() {this.head=null;}@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur=head;while (cur!=null){System.out.print(cur.val+" ");cur=cur.next;}System.out.println();}
}测试
public static void main(String[] args) {RealizeLinkedList realizeLinkedList=new RealizeLinkedList();realizeLinkedList.createLinkedList();realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.addFirst(3);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.addLast(5);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.addIndex(2,6);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.remove(6);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.removeAllKey(12);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.contains(3);realizeLinkedList.display();realizeLinkedList.size();realizeLinkedList.clear();realizeLinkedList.display();}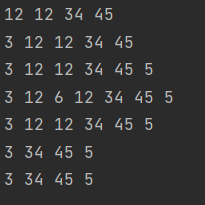
移除链表元素
203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
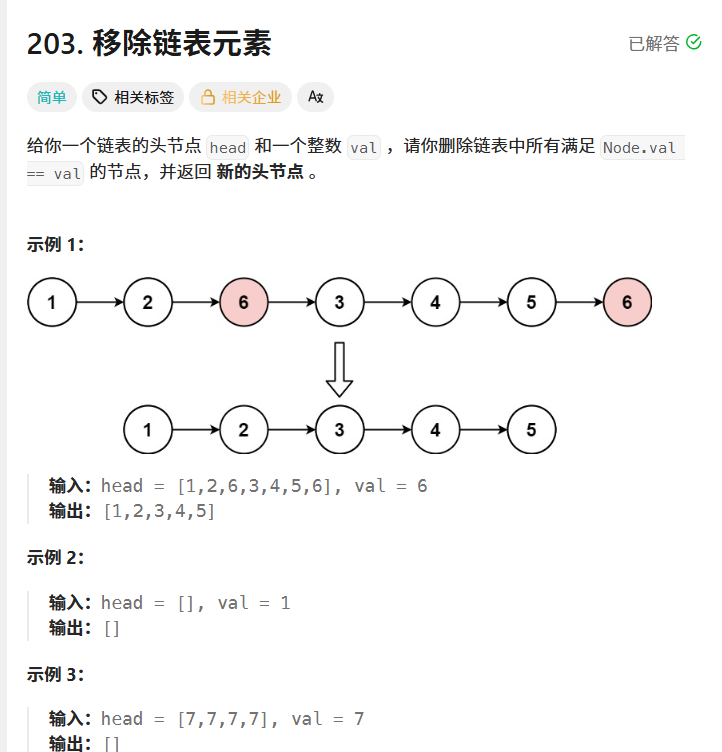
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if(head==null){return null;}ListNode prev=head;ListNode cur=head.next;while(cur!=null){if(cur.val==val){prev.next=cur.next;cur=cur.next;}else{prev=cur;cur=cur.next;}}if(head.val==val){head=head.next;}return head;}
}反转链表
206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
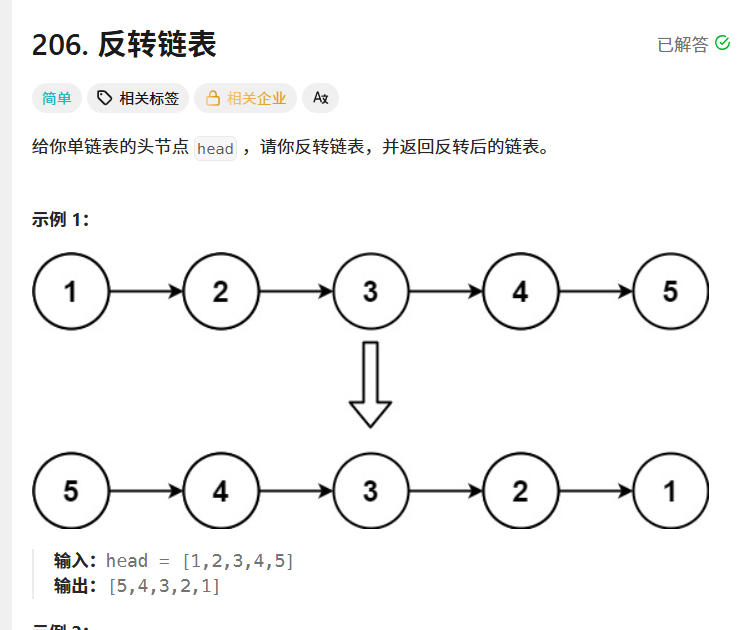
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head==null){return null;}if(head.next==null){return head;}ListNode cur=head.next;head.next=null;ListNode curN=cur.next;ListNode prev=head;while(cur.next!=null){cur.next=prev;prev=cur;cur=curN;curN=curN.next;}cur.next=prev;return cur;}
}链表的中间结点
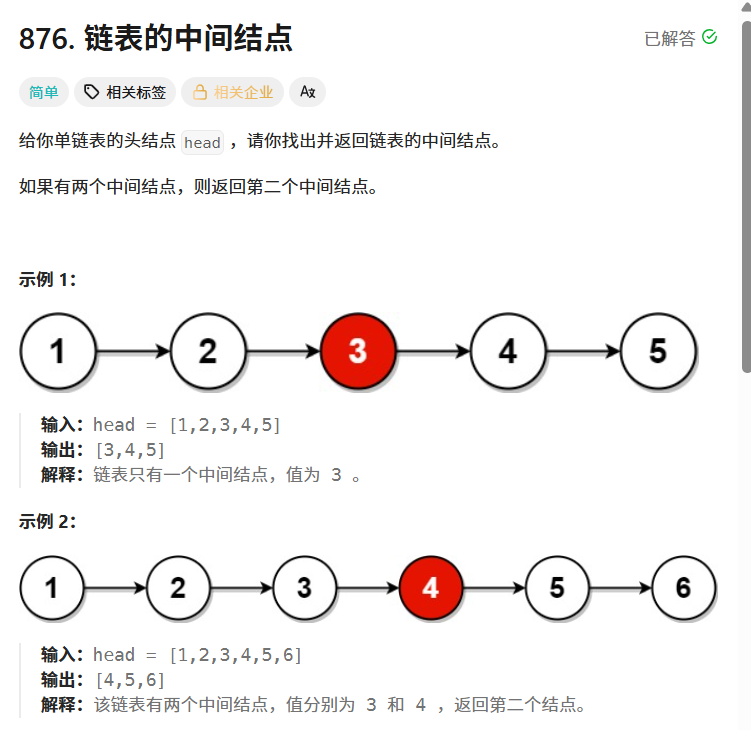
876. 链表的中间结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head==null){return null;}if(head.next==null){return head;}ListNode quick=head;ListNode slow=head;while(quick!=null && quick.next!=null){quick=quick.next.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;}
}链表中倒数最后k个结点
链表中倒数最后k个结点_牛客题霸_牛客网

public class Solution {/*** 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可** * @param pHead ListNode类 * @param k int整型 * @return ListNode类*/public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {if(pHead==null){return null;}ListNode cur=pHead;int len=0;while(cur!=null){len++;cur=cur.next;}if(k==len){return pHead;}if(k>len){return null;}cur=pHead;int num=len-k;while(num!=0){cur=cur.next;num--;}return cur;}
}合并两个有序列表
21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
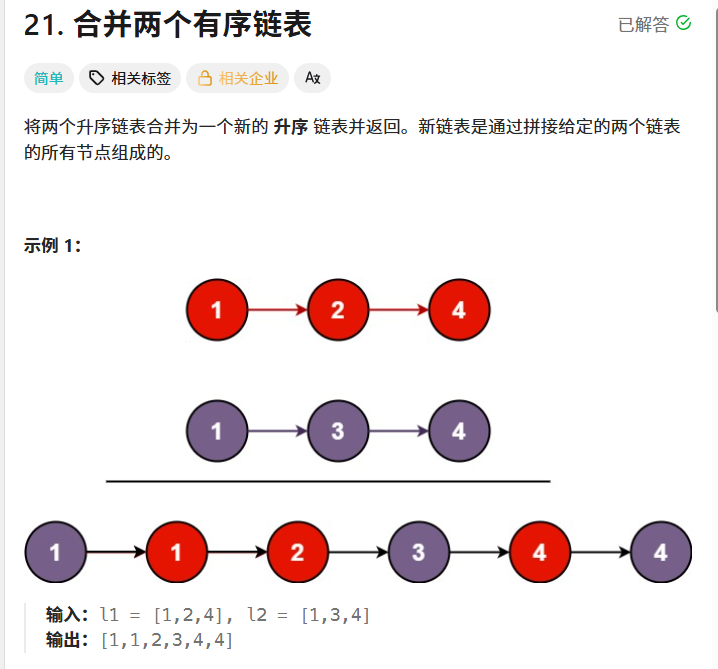
通过递归的方法
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if(list1==null){return list2;}if(list2==null){return list1;}if(list1.val<=list2.val){list1.next=mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);return list1; }else{list2.next=mergeTwoLists(list2.next,list1);return list2;}}
}使用链表的方法
class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {if(list1==null){return list2;}if(list2==null){return list1;}ListNode node=new ListNode(-1);ListNode cur=node;while(list1!=null && list2!=null){if(list1.val<=list2.val){cur.next=list1;list1=list1.next;}else{cur.next=list2;list2=list2.next;}cur=cur.next;}// 拼接后面的部分cur.next=(list1==null)?list2:list1;return node.next;}
}链表的分割
链表分割_牛客题霸_牛客网
定义两个新的链表,将小于x的放在一个链表中,将大于x的放到另一个链表中,当放完整个链表,将大于x的链表接到小于x链表的后面
public class Partition {public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {ListNode bs=null;ListNode be=null;ListNode as=null;ListNode ae=null;ListNode cur=pHead;while(cur!=null){if(cur.val<x){if(bs==null){bs=be=cur;}else{be.next=cur;be=be.next;}}else{if(as==null){as=ae=cur;}else{ae.next=cur;ae=ae.next;}}cur=cur.next;}if(bs==null){ae.next=null;return as;}be.next=as;if(as!=null){ae.next=null;}return bs;}
}判断链表是否是回文结构
链表的回文结构_牛客题霸_牛客网
定义一个快指针,一个慢指针,让快指针每次走两步,慢指针一步,这样走完时,慢指针的位置刚刚好是链表的中间节点,然后让后半部分链表进行反转,拿反转后的链表和前半部分的链表进行比较,看是否相同
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode head) {if(head==null){return true;}ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){slow=slow.next;fast=fast.next.next;}ListNode cur=null; while(slow!=null){ListNode pHead=slow.next;slow.next=cur;cur=slow;slow=pHead;}while(cur!=null){if(head.val!=cur.val){return false;}head=head.next;cur=cur.next;}return true;}
}相交链表
160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)

public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {int lenA=0;int lenB=0;ListNode cur1=headA;ListNode cur2=headB;while(headA!=null){lenA++;headA=headA.next;}while(headB!=null){lenB++;headB=headB.next;}headA=cur1;headB=cur2;int len=lenA-lenB;if(len>0){while(len>0){headA=headA.next;len--;}}else{while(len<0){headB=headB.next;len++;}}while(headA!=null && headB!=null){if(headA==headB){return headA;}headA=headA.next;headB=headB.next;}return null;}
}判断是否是环形链表
141. 环形链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
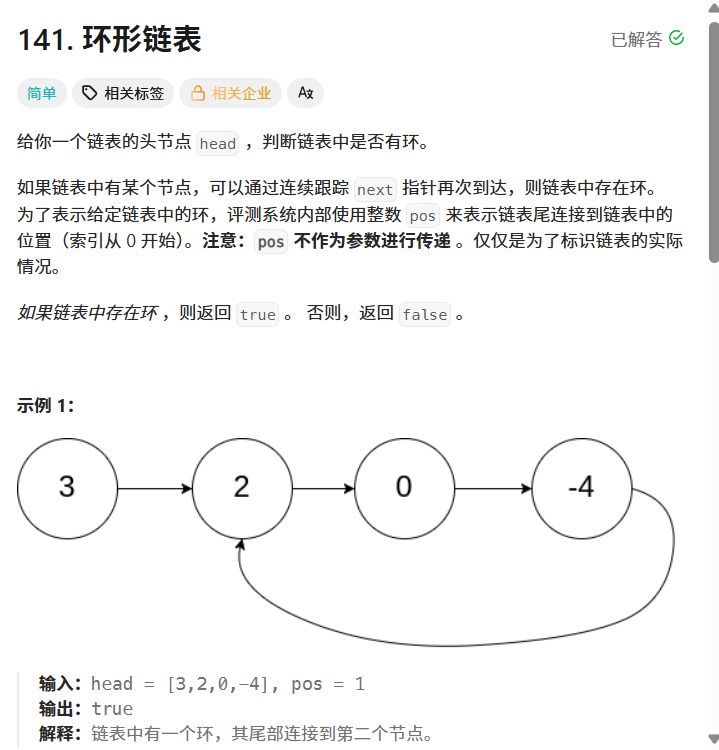
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if(head==null){return false;}ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if(fast==slow){return true;}}return false;}
}环形链表,返回成环的第一个节点
142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
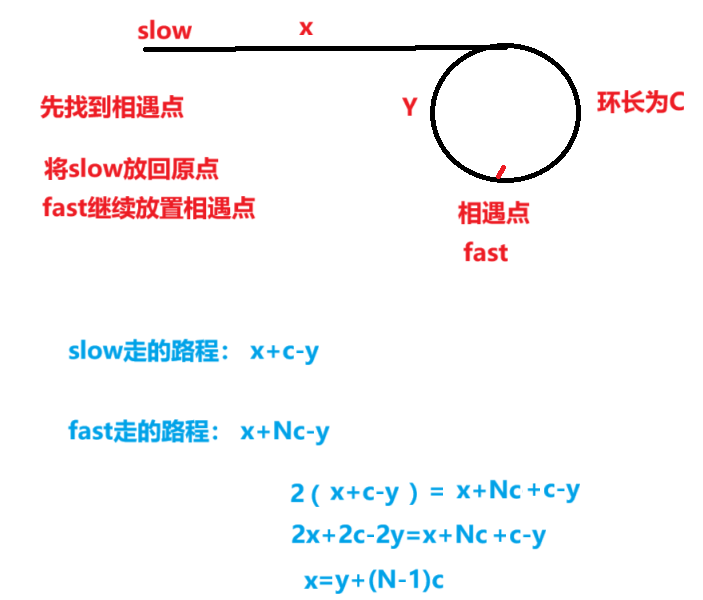
根据推出的公式得出:x=y+(N-1)c
两个指针每次都走一步;当 slow == fast 时,它们正好都走到了 环的入口节点
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast=head;ListNode slow=head;// 判断是环while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){fast=fast.next.next;slow=slow.next;if(fast==slow){break;}}// 不是环,返回为nullif(fast==null || fast.next==null){return null;}slow=head;while(fast!=slow){fast=fast.next;slow=slow.next;}return slow;}
}
栈(Stack)
其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作
栈是先进后出的,进入和出去的时间复杂度为O(1)
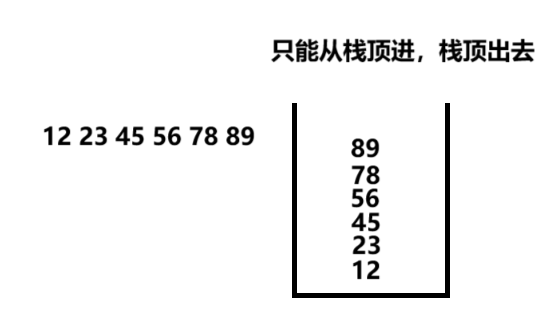
栈中的方法
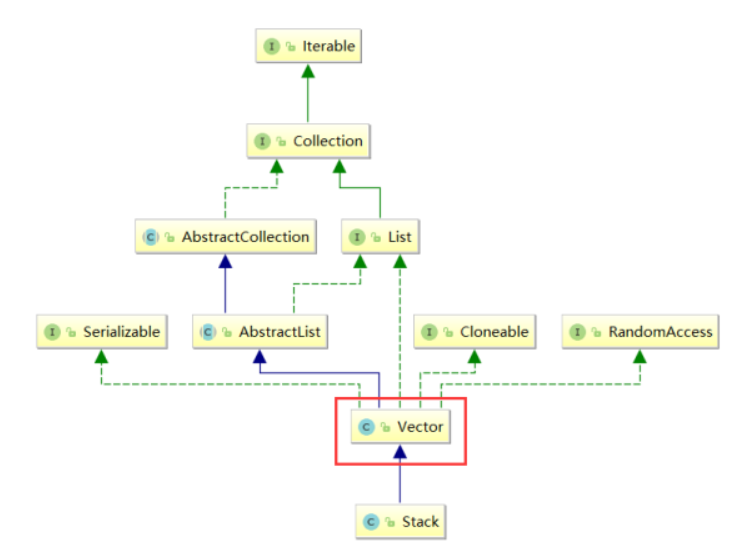
栈的使用
public class MyStack {public static void main(String[] args) {Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();stack.push(12);stack.push(23);stack.push(34);stack.push(45);stack.push(56);stack.push(67);stack.push(78);stack.push(89);System.out.println(stack);stack.pop();stack.pop();System.out.println(stack);Integer peek = stack.peek();System.out.println(peek);boolean empty = stack.isEmpty();System.out.println(empty);}
}栈的模拟实现
使用数组的形式实现一个栈
public class StackReceive {private int[] elem;private int userSize;public StackReceive() {this.elem = new int[10];}// 将元素存到栈中public void push(int val) {if(isFull()){this.elem= Arrays.copyOf(elem,userSize*2);}elem[userSize]=val;}
// 判断栈的空间是否满public boolean isFull() {return elem.length==userSize;}
// 取出栈顶元素public int pop() {if (isEmpty()){throw new NullPointerException();}int val=elem[userSize-1];userSize--;return val;}
// 查询栈顶元素,但是不进行删除public int peek() {if (isEmpty()){throw new NullPointerException();}return elem[userSize-1];}public boolean isEmpty(){return this.userSize==0;}
}有效的括号
20. 有效的括号 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {public boolean isValid(String s) {Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<>();for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){char ch=s.charAt(i);if(ch=='(' ||ch=='[' || ch=='{'){stack.push(ch);}else{if(stack.isEmpty()){return false;}char ch1=stack.pop();if((ch1!='(' && ch==')')||(ch1!='[' && ch==']')||(ch1!='{' && ch=='}'))return false;}}return stack.isEmpty();}}逆波兰表达式求值
150. 逆波兰表达式求值 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();for(String s:tokens){if(!isOperator(s)){int num=Integer.parseInt(s);stack.push(num);}else{int val2=stack.pop();int val1=stack.pop();switch(s){case "+":stack.push(val1+val2);break;case "-":stack.push(val1-val2);break;case "*":stack.push(val1*val2);break;case "/":stack.push(val1/val2);break;}}}return stack.pop();}public boolean isOperator(String s){if(s.equals("+") || s.equals("-") || s.equals("*") ||s.equals("/")){return true;}return false;}
}栈的压入,弹出序列
栈的压入、弹出序列_牛客题霸_牛客网
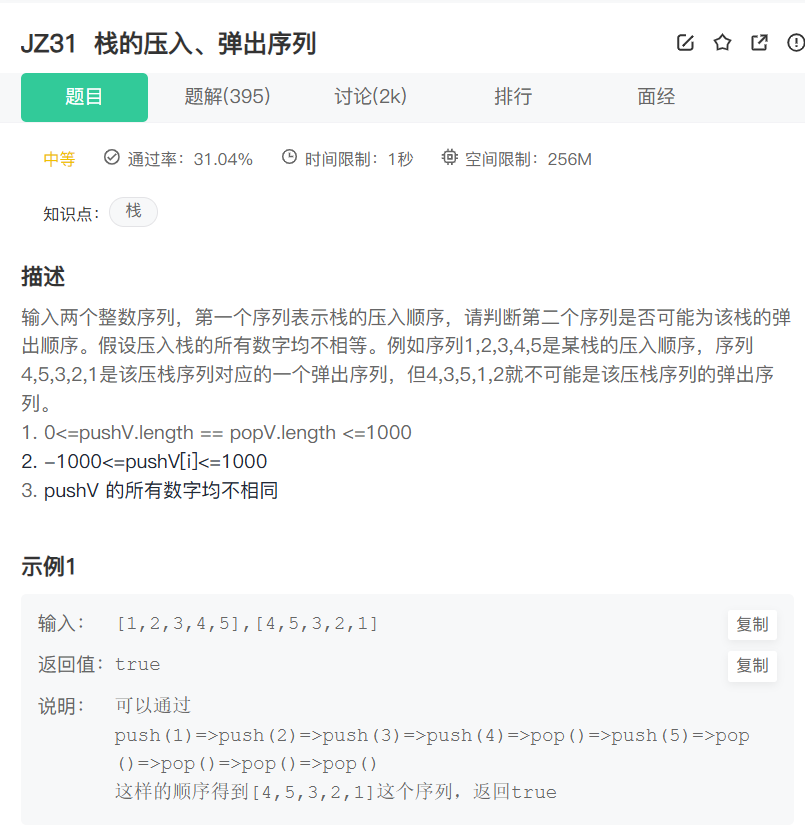
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {if(pushV==null || popV ==null || popV.length!=pushV.length){return false;}Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();int num=0;for(int i=0;i<pushV.length;i++){stack.push(pushV[i]);// 持续的检查栈中的元素是否满足条件,如果取出一个元素后,继续的进行遍历,判断下一个元素是否也满足条件while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()==popV[num]){stack.pop();num++;}}return stack.isEmpty();}最小栈
155. 最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class MinStack {public Stack<Integer> stack;public Stack<Integer> minStack;public MinStack() {stack=new Stack();minStack=new Stack();}public void push(int val) {stack.push(val);if(minStack.isEmpty()){minStack.push(val);}else{if(minStack.peek()>=val){minStack.push(val);}}}public void pop() {if(stack.isEmpty()){return ;}int val=stack.pop();if(val==minStack.peek()){minStack.pop();}}public int top() {return stack.peek();}public int getMin() {if(minStack.isEmpty()){return -1;}return minStack.peek();}
}栈,虚拟机栈,栈帧的区别
栈:数据结构上的栈,进行存储
虚拟机栈:Java虚拟机栈,属于JVM内存结构的一部分,每个线程都有独特的虚拟机栈,用来支持Java方法的调用和执行,每当一个线程启动时,JVM都会为它创建一个虚拟机栈,每当调用一个方法,都会在这个栈中创建一个新的栈帧,当方法进行返回时,就会销毁对应的栈帧
栈帧:是虚拟机栈中的一个元素,对应一次方法的调用
队列(Queue)
队列是只允许在一端进行元素的插入,在另一端进行元素的删除
Queue是一个接口,底层是LinkedList实现的
队列的使用
public class UserQueue {public static void main(String[] args) {Queue<Integer> queue=new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(1);queue.offer(2);queue.offer(3);queue.offer(4);System.out.println(queue);queue.poll();System.out.println(queue);queue.offer(5);System.out.println(queue);System.out.println(queue.peek());System.out.println(queue.size());System.out.println(queue.isEmpty());}}队列的模拟实现
用双向链表实现队列
public class QueueReceive {static class ListNode{private ListNode next;private ListNode prev;private int val;public ListNode(int val){this.val=val;}public ListNode(){}}private ListNode first=null;private ListNode last=null;private int userSize;public void offer(int val) {ListNode node=new ListNode(val);if(isEmpty()){first=last=node;}else{last.next=node;node.prev=last;last=node;}userSize++;}public int poll() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}int val= first.val;first=first.next;if(first!=null){first.prev=null;}userSize--;return val;}public int peek() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}return first.val;}public boolean isEmpty() {return userSize==0;}
}循环队列的实现
public class CircleQueue {private int front;private int rear;private int size;private int[] elem;public CircleQueue(int k) {elem = new int[k + 1]; // +1 是关键!留一个空位区分满和空front = 0;rear = 0;size = k + 1;}
//入队列public boolean enQueue(int val) {if(isFull()){return false;}elem[rear]=val;rear=(rear+1)%size;return true;}
//出队列public boolean deQueue() {if(isEmpty()){return false;}front=(front+1)%size;return true;}
//获得队头元素public int Front() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}return elem[front];}
//获得队尾元素public int Rear() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}//当rear为0时,0-1会为-1,所以需要让其加size再%sizereturn elem[(rear-1+size)%size];}
//判空public boolean isEmpty() {return rear==front;}
//判满public boolean isFull() {return (rear+1)%size==front;}}设计循环队列
622. 设计循环队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)

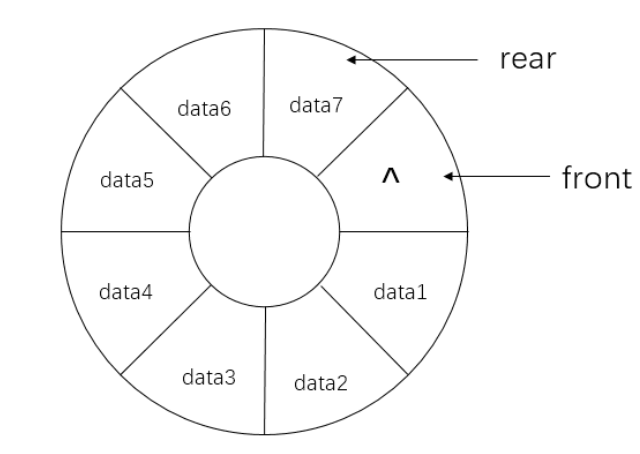
class MyCircularQueue {private int[] elem;private int front;private int rear;private int size;public MyCircularQueue(int k) {rear=0;front=0;size=k+1;elem=new int[k+1];}public boolean enQueue(int value) {if(isFull()){return false;}elem[rear]=value;rear=(rear+1)%size;return true;}public boolean deQueue() {if(isEmpty()){return false;}front=(front+1)%size;return true;}public int Front() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}return elem[front];}public int Rear() {if(isEmpty()){return -1;}return elem[(rear-1+size)%size];}public boolean isEmpty() {return front==rear;}public boolean isFull() {return (rear+1)%size==front;}
}
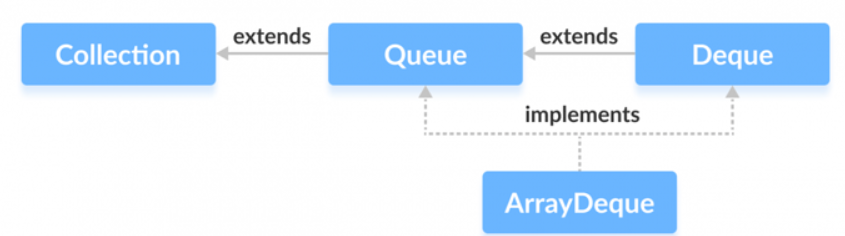
双端队列(Deque)
每一端既可以进,又可以出
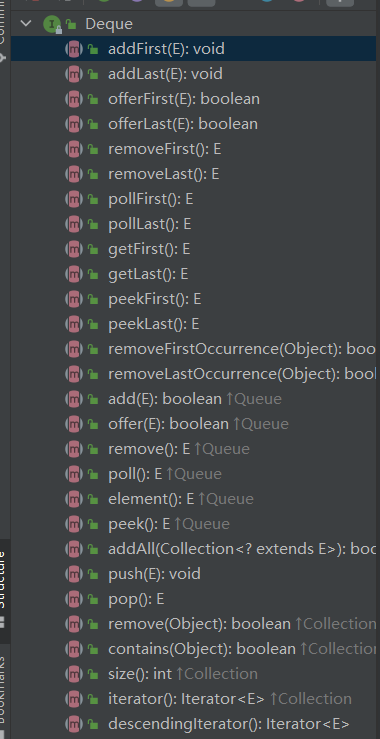
接口中的方法
用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class MyStack {Queue<Integer> queue;public MyStack() {queue=new LinkedList<>();}public void push(int x) {queue.offer(x);for(int i=0;i<queue.size()-1;i++){queue.offer(queue.poll());}}public int pop() {return queue.poll();}public int top() {return queue.peek();}public boolean empty() {return queue.isEmpty();}
}用栈实现队列
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class MyQueue {Stack<Integer> in;Stack<Integer> out;public MyQueue() {in=new Stack<>();out=new Stack<>();}public void push(int x) {in.push(x);}public int pop() {if(out.empty()){while(!in.empty()){out.push(in.pop());}}return out.pop();}public int peek() {if(out.empty()){while(!in.empty()){out.push(in.pop());}}return out.peek();}public boolean empty() {return in.isEmpty() && out.isEmpty();}
}/*** Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();* obj.push(x);* int param_2 = obj.pop();* int param_3 = obj.peek();* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();*/