【Mybatis从入门到入土】ResultMap映射、多表查询与缓存机制全解析


目录
- 0. 案例环境
- 0.1 案例数据初始化sql
- 0.2 实体类
- 0.2.1 User.java
- 0.2.2 Order.java
- 0.2.3 Role.java
- 1. ResultMap
- 1.1 基本使用
- 1.2 自动映射
- 1.3 继承映射关系
- 2. 多表查询
- 2.1 多表关联查询
- 2.1.1 一对一关系
- 2.1.1.1 使用ResultMap对所有字段进行映射
- 2.1.1.2 使用ResultMap中的association
- 2.1.2 一对多关系
- 2.1.2.1 使用ResultMap中的collection
- 2.2 分步查询
- 2.2.1实现步骤
- ①定义查询方法
- ②配置分步查询
- 2.2.2 设置按需加载
- 3.分页查询-PageHelper
- 3.1 实现步骤
- ①定义方法查询方法以及生成对应标签
- ② 引入依赖
- ③ 配置Mybatis核心配置文件使用分页插件
- ④ 开始分页查询
- 3.2 一对多多表查询分页问题
- 4.Mybatis缓存
- 4.1 一级缓存
- 4.2 二级缓存
- 4.2.1 开启二级缓存
- 4.2.2 使用建议
0. 案例环境
0.1 案例数据初始化sql
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`mybatis_db` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;USE `mybatis_db`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `orders`;
CREATE TABLE `orders` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`createtime` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间',`price` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '价格',`remark` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '备注',`user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户id',PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=4 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `orders`(`id`,`createtime`,`price`,`remark`,`user_id`) values (1,'2014-06-26 16:55:43',2000,'无',2),(2,'2021-02-23 16:55:57',3000,'无',3),(3,'2021-02-23 16:56:21',4000,'无',2);
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `role`;CREATE TABLE `role` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色名',`desc` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '角色描述',PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;/*Data for the table `role` */insert into `role`(`id`,`name`,`desc`) values (1,'总经理','一人之下'),(2,'CFO',NULL);/*Table structure for table `user` */DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;CREATE TABLE `user` (`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`username` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,`address` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=33 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;/*Data for the table `user` */insert into `user`(`id`,`username`,`age`,`address`) values (2,'pdd',26,NULL),(3,'UZI',19,'上海11'),(4,'RF',19,NULL);/*Table structure for table `user_role` */DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user_role`;CREATE TABLE `user_role` (`user_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,`role_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;/*Data for the table `user_role` */insert into `user_role`(`user_id`,`role_id`) values (2,2),(2,1),(3,1);
0.2 实体类
0.2.1 User.java
public class User {private Integer id;private String username;private Integer age;private String address;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "User{" +"id=" + id +", username='" + username + '\'' +", age=" + age +", address='" + address + '\'' +'}';}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getUsername() {return username;}public void setUsername(String username) {this.username = username;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age = age;}public String getAddress() {return address;}public void setAddress(String address) {this.address = address;}public User() {}public User(Integer id, String username, Integer age, String address) {this.id = id;this.username = username;this.age = age;this.address = address;}}0.2.2 Order.java
public class Order {private Integer id;private Date createtime;private Integer price;private String remark;private Integer userId;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Order{" +"id=" + id +", createtime=" + createtime +", price=" + price +", remark='" + remark + '\'' +", userId=" + userId +'}';}public Order() {}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public Date getCreatetime() {return createtime;}public void setCreatetime(Date createtime) {this.createtime = createtime;}public Integer getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(Integer price) {this.price = price;}public String getRemark() {return remark;}public void setRemark(String remark) {this.remark = remark;}public Integer getUserId() {return userId;}public void setUserId(Integer userId) {this.userId = userId;}public Order(Integer id, Date createtime, Integer price, String remark, Integer userId) {this.id = id;this.createtime = createtime;this.price = price;this.remark = remark;this.userId = userId;}
}0.2.3 Role.java
public class Role {private Integer id;private String name;private String desc;@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Role{" +"id=" + id +", name='" + name + '\'' +", desc='" + desc + '\'' +'}';}public Role() {}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getDesc() {return desc;}public void setDesc(String desc) {this.desc = desc;}public Role(Integer id, String name, String desc) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.desc = desc;}
}1. ResultMap
1.1 基本使用
我们可以使用resultMap标签自定义结果集和实体类属性的映射规则。
<!--resultMap 用来自定义结果集和实体类的映射属性:id 相当于这个resultMap的唯一标识type 用来指定映射到哪个实体类id标签 用来指定主键列的映射规则属性:property 要映射的属性名column 对应的列名result标签 用来指定普通列的映射规则属性:property 要映射的属性名column 对应的列名--><resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" ><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="price" property="price"></result><result column="remark" property="remark"></result><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap><!--使用我们自定义的映射规则--><select id="findAll" resultMap="orderMap">SELECT id,createtime,price,remark,user_id FROM ORDERS</select>1.2 自动映射
我们定义resultMap时默认情况下自动映射是开启状态的。也就是如果结果集的列名和我们的属性名相同是会自动映射的我们只需要写特殊情况的映射关系即可。
例如:
下面这种写法和上面的写法会有相同的效果,因为其他属性的属性名和结果集的列名都是相同的会自动映射。
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" ><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap><!--使用我们自定义的映射规则--><select id="findAll" resultMap="orderMap">SELECT id,createtime,price,remark,user_id FROM ORDERS</select>
如有需要可以选择关闭自动映射可以把resultMap的autoMapping属性设置为false。
例如:
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false"><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="price" property="price"></result><result column="remark" property="remark"></result><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap>
1.3 继承映射关系
我们可以使用resultMap 的extends属性来指定一个resultMap,从而复用重复的映射关系配置。
例如:
<!--定义个父映射,供其他resultMap继承--><resultMap id="baseOrderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" ><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="price" property="price"></result><result column="remark" property="remark"></result></resultMap><!--继承baseOrderMap,然后只需要写自己特有的映射关系即可--><resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false" extends="baseOrderMap"><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap>
2. 多表查询
有的时候我们需要查询多张表的数据才可以得到我们要的结果。
我们可以直接写一个多表关联的SQL进行查询。也可以分步进行多次的查询来拿到我们需要的结果。
Mybatis就提供了对应的配置,可以让我们去更方便的进行相应的查询和对应的结果集处理。
2.1 多表关联查询
2.1.1 一对一关系
两个实体之间是一对一的关系。(例如我们需要查询订单,要求还需要下单用户的数据。这里的订单相对于用户是一对一。)
例如:
方法定义如下
//根据订单id查询订单,要求把下单用户的信息也查询出来Order findById(Integer id);
因为期望Order中还能包含下单用户的数据,所以可以再Order中增加一个属性
private User user;
SQL语句如下
SELECT o.id,o.`createtime`,o.`price`,o.`remark`,o.`user_id`,u.`id` uid,u.`username`,u.`age`,u.`address`
FROM orders o,USER u
WHEREo.`user_id` = u.`id`AND o.id = 2
结果集
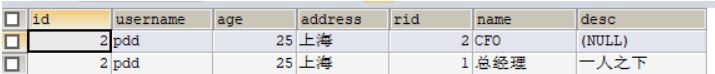
我们可以使用如下两种方式封装结果集。
2.1.1.1 使用ResultMap对所有字段进行映射
可以使用ResultMap设置user对象的属性的映射规则。
①resultMap定义,主要是对user对象的属性设置映射规则
<resultMap id="baseOrderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" ><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="price" property="price"></result><result column="remark" property="remark"></result></resultMap><resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false" extends="baseOrderMap"><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap><!--Order和User关联的映射--><resultMap id="orderUserMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false" extends="orderMap"><result property="user.id" column="uid"></result><result property="user.username" column="username"></result><result property="user.age" column="age"></result><result property="user.address" column="address"></result></resultMap>
②使用定义好的resultMap
<!--根据订单id查询订单,要求把下单用户的信息也查询出来--><select id="findById" resultMap="orderUserMap">SELECTo.`id`,o.`createtime`,o.`price`,o.`remark`,o.`user_id`,u.`id` uid,u.`username`,u.`age`,u.`address`FROMorders o,`user` uWHEREo.id = #{id} ANDo.`user_id`=u.`id`</select>
2.1.1.2 使用ResultMap中的association
可以使用ResultMap中的子标签association 来设置关联实体类的映射规则.
①定义resultMap
<resultMap id="baseOrderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" ><id column="id" property="id"></id><result column="createtime" property="createtime"></result><result column="price" property="price"></result><result column="remark" property="remark"></result></resultMap><resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false" extends="baseOrderMap"><result column="user_id" property="userId"></result></resultMap><!--Order和User关联的映射(使用association)--><resultMap id="orderUserMapUseAssociation" type="com.sangeng.pojo.Order" autoMapping="false" extends="orderMap"><association property="user" javaType="com.sangeng.pojo.User"><id property="id" column="uid"></id><result property="username" column="username"></result><result property="age" column="age"></result><result property="address" column="address"></result></association></resultMap>
②使用resultMap
<!--根据订单id查询订单,要求把下单用户的信息也查询出来--><select id="findById" resultMap="orderUserMapUseAssociation">SELECTo.`id`,o.`createtime`,o.`price`,o.`remark`,o.`user_id`,u.`id` uid,u.`username`,u.`age`,u.`address`FROMorders o,`user` uWHEREo.id = #{id} ANDo.`user_id`=u.`id`</select>
2.1.2 一对多关系
两个实体之间是一对多的关系。(例如我们需要查询用户,要求还需要该用户所具有的角色信息。这里的用户相对于角色是一对多的。)
例如:
方法定义如下
//根据id查询用户,并且要求把该用户所具有的角色信息也查询出来User findById(Integer id);
因为期望User中还能包含该用户所具有的角色信息,所以可以在User中增加一个属性
// 该用户所具有的角色private List<Role> roles;
SQL语句如下
SELECT u.`id`,u.`username`,u.`age`,u.`address`,r.id rid,r.name,r.desc
FROM USER u,user_role ur,role r
WHERE u.id=ur.user_id AND ur.role_id = r.idAND u.id = 2
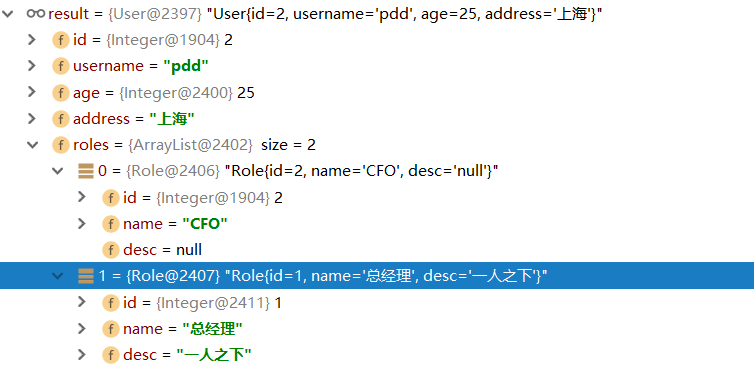
结果集
我们可以使用如下的方式封装结果集。
2.1.2.1 使用ResultMap中的collection
可以使用ResultMap中的子标签association 来设置关联实体类的映射规则.
①定义ResultMap
<!--定义User基本属性映射规则--><resultMap id="userMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.User"><id property="id" column="id"></id><result property="username" column="username"></result><result property="age" column="age"></result><result property="address" column="address"></result></resultMap><resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.User" extends="userMap"><collection property="roles" ofType="com.sangeng.pojo.Role" ><id property="id" column="rid"></id><result property="name" column="name"></result><result property="desc" column="desc"></result></collection></resultMap>②使用ResultMap
<select id="findById" resultMap="userRoleMap" >SELECT u.`id`,u.`username`,u.`age`,u.`address`,r.id rid,r.name,r.descFROM USER u,user_role ur,role rWHERE u.id=ur.user_id AND ur.role_id = r.idAND u.id = #{id}</select>
最终封装完的结果如下:
2.2 分步查询
如果有需要多表查询的需求我们也可以选择用多次查询的方式来查询出我们想要的数据。Mybatis也提供了对应的配置。
例如我们需要查询用户,要求还需要查询出该用户所具有的角色信息。我们可以选择先查询User表查询用户信息。然后在去查询关联的角色信息。
2.2.1实现步骤
具体步骤如下:
①定义查询方法
因为我们要分两步查询: 1.查询User 2.根据用户的id查询Role 所以我们需要定义下面两个方法,并且把对应的标签也先写好
1.查询User
//根据用户名查询用户,并且要求把该用户所具有的角色信息也查询出来User findByUsername(String username);
<!--根据用户名查询用户--><select id="findByUsername" resultType="com.sangeng.pojo.User">select id,username,age,address from user where username = #{username}</select>
2.根据user_id查询Role
public interface RoleDao {//根据userId查询所具有的角色List<Role> findRoleByUserId(Integer userId);
} <!--根据userId查询所具有的角色--><select id="findRoleByUserId" resultType="com.sangeng.pojo.Role">select r.id,r.name,r.descfrom role r,user_role urwhere ur.role_id = r.idand ur.user_id = #{userId}</select>
②配置分步查询
我们期望的效果是调用findByUsername方法查询出来的结果中就包含角色的信息。所以我们可以设置findByUsername方法的RestltMap,指定分步查询
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.sangeng.pojo.User"><id property="id" column="id"></id><result property="username" column="username"></result><result property="age" column="age"></result><result property="address" column="address"></result></resultMap><!--select属性:指定用哪个查询来查询当前属性的数据 写法:包名.接口名.方法名column属性:设置当前结果集中哪列的数据作为select属性指定的查询方法需要参数--><resultMap id="userRoleMapBySelect" type="com.sangeng.pojo.User" extends="userMap"><collection property="roles"ofType="com.sangeng.pojo.Role"select="com.sangeng.dao.RoleDao.findRoleByUserId"column="id"></collection></resultMap>
指定findByUsername使用我们刚刚创建的resultMap
<!--根据用户名查询用户--><select id="findByUsername" resultMap="userRoleMapBySelect">select id,username,age,address from user where username = #{username}</select>
2.2.2 设置按需加载
我们可以设置按需加载,这样在我们代码中需要用到关联数据的时候才会去查询关联数据。
有两种方式可以配置分别是全局配置和局部配置
-
局部配置
设置fetchType属性为lazy
<resultMap id="userRoleMapBySelect" type="com.sangeng.pojo.User" extends="userMap"><collection property="roles"ofType="com.sangeng.pojo.Role"select="com.sangeng.dao.RoleDao.findRoleByUserId"column="id" fetchType="lazy"></collection></resultMap> -
全局配置
设置lazyLoadingEnabled为true
<settings><setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
3.分页查询-PageHelper
我们可以使用PageHelper非常方便的帮我们实现分页查询的需求。不需要自己在SQL中拼接SQL相关参数,并且能非常方便的获取的总页数总条数等分页相关数据。
3.1 实现步骤
①定义方法查询方法以及生成对应标签
List<User> findAll();
<select id="findAll" resultType="com.sangeng.pojo.User">select id,username,age,address from user</select>
② 引入依赖
<dependency><groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId><artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId><version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>
③ 配置Mybatis核心配置文件使用分页插件
<plugins><!-- 注意:分页助手的插件 配置在通用馆mapper之前 --><plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper"><!-- 指定方言 --><property name="dialect" value="mysql"/></plugin></plugins>
④ 开始分页查询
我们只需要在使用查询方法前设置分页参数即可
//设置分页参数UserDao userDao = session.getMapper(UserDao.class);//设置分页查询参数PageHelper.startPage(1,1);List<User> users = userDao.findAll();System.out.println(users.get(0));
如果需要获取总页数总条数等分页相关数据,只需要创建一个PageInfo对象,把刚刚查询出的返回值做为构造方法参数传入。然后使用pageInfo对象获取即可。
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<User>(users);System.out.println("总条数:"+pageInfo.getTotal());System.out.println("总页数:"+pageInfo.getPages());System.out.println("当前页:"+pageInfo.getPageNum());System.out.println("每页显示长度:"+pageInfo.getPageSize());
3.2 一对多多表查询分页问题
我们在进行一对多的多表查询时,如果使用了PageHelper进行分页。会出现关联数据不全的情况。我们可以使用分步查询的方式解决该问题。
4.Mybatis缓存
Mybatis的缓存其实就是把之前查到的数据存入内存(map),下次如果还是查相同的东西,就可以直接从缓存中取,从而提高效率。
Mybatis有一级缓存和二级缓存之分,一级缓存(默认开启)是sqlsession级别的缓存。二级缓存相当于mapper级别的缓存。
4.1 一级缓存
几种不会使用一级缓存的情况
1.调用相同方法但是传入的参数不同
2.调用相同方法参数也相同,但是使用的是另外一个SqlSession
3.如果查询完后,对同一个表进行了增,删改的操作,都会清空这sqlSession上的缓存
4.如果手动调用SqlSession的clearCache方法清除缓存了,后面也使用不了缓存
4.2 二级缓存
注意:只在sqlsession调用了close或者commit后的数据才会进入二级缓存。
4.2.1 开启二级缓存
①全局开启
在Mybatis核心配置文件中配置
<settings><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/></settings>
②局部开启
在要开启二级缓存的mapper映射文件中设置 cache标签
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd" >
<mapper namespace="com.sangeng.dao.RoleDao"><cache></cache>
</mapper>
4.2.2 使用建议
二级缓存在实际开发中基本不会使用。
如果我的内容对你有帮助,请辛苦动动您的手指为我点赞,评论,收藏。感谢大家!!

