02--CSS基础(1)
一.什么是CSS
前面我们介绍的是Html,这是web网页的骨架,决定web网页的结构,但是只有骨架网页会很难看,于是就有了CSS
二.基本语法规范
选择器+{1/N条声明}选择器决定了修改谁
声明决定修改哪些属性
声明的属性是键对值,用" ; "来区分键对值,用" : "来区分键和值
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style> p{/* 设置字体颜色 */color:green;/* 设置字体大小 */font-size: 80px; }</style>
</head>
<body><p>这是一段绿色的巨大的文字</p>
</body>
</html>CSS要写在style标签中(后面还有其他的写法)
style可以放在html页面的任意位置,但是一般放在head中(样式和结构尽量分离)
CSS使用/* */作为注释,//会报错
三.引入样式
1.内部样式表
写在style标签中,嵌入在html文件中,style标签放在哪里都无所谓,但是一般放在head中
可以让结构和样式进行分离,但是分离的不够彻底,尤其是CSS比较复杂的时候
2.行内样式表
通过style属性直接指定某个标签的属性
这种写法优先级很高,会覆盖掉内部样式表
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style> p{/* 设置字体颜色 */color:green;/* 设置字体大小 */font-size: 80px; }</style>
</head>
<body><p>这是一段绿色的巨大的文字</p><p style="color: red">这是一段绿色的巨大的文字</p>
</body>
</html>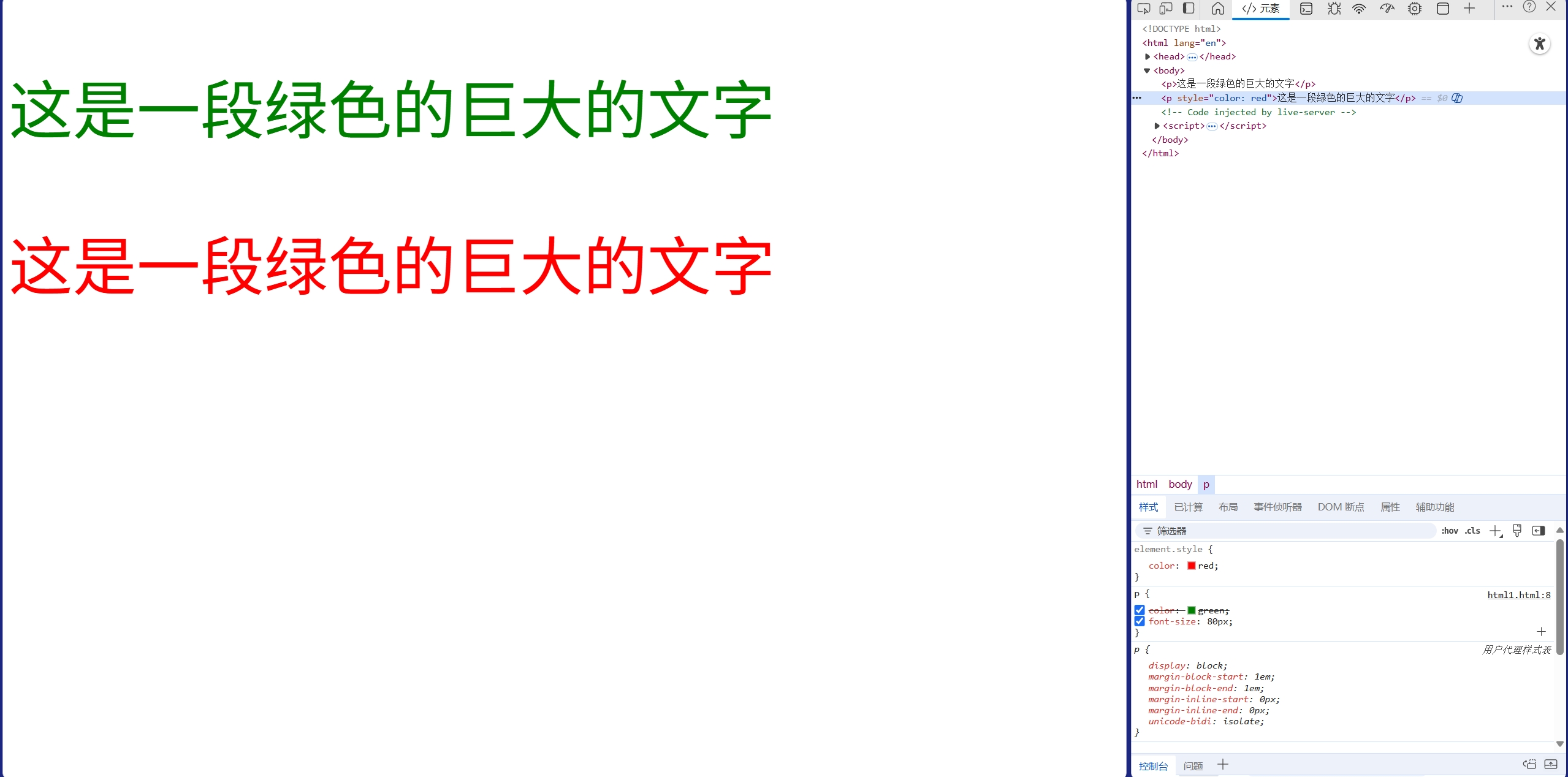
可以看到右下角我们的绿色被红色覆盖了
3.外部样式表
实际开发中最常用的方式
创建css文件
使用link标签进行引入css
<link rel="stylesheet" href="[CSS文件路径]">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style> p{/* 设置字体颜色 */color:green;/* 设置字体大小 */font-size: 80px; }</style><link rel="stylesheet" href="html1.css"></head>
<body><p>这是一段绿色的巨大的文字</p><p style="color: red">这是一段绿色的巨大的文字</p> <div>外部样式表</div>
</body>
</html>这样样式和结构就完全分离了,但是有时会受浏览器缓存的影响,不会立即生效
四.代码样式
1.样式格式
紧凑格式
p { color: red; font-size: 20px; }
展开风格(推荐)
p {color:red;font-size:20px;
}2.大小写
css并不区分大小写,但为了规范统一使用小写
3.空格规范
选择器和{之间加一个空格
冒号后面也加一个空格
五.选择器
1.功能
选中页面中指定的标签元素,选中之后才能对元素设置属性
2.选择器的种类
这里按CSS2的标准来(CSS3向下兼容2)
基础选择器:单个选择器构成的
标签选择器
类选择器
id选择器
通配符选择器
复合选择器:把多种选择器综合运用起来
后代选择器
伪类选择器
子选择器
并集选择器
参考文档:CSS 选择器参考手册
先看效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>/* 标签选择器 */p {color:brown;}div {color:blue;}/* 类选择器 */.classp1 {color:aqua;}.classp2 {color:darkorange}.classp3 {font-size: 80px;}/* id选择器 */#id1 {color:lawngreen}/* 通配符选择器 */* {color:rgb(230, 22, 22);}</style>
</head>
<body><!-- 标签选择器 --><p>p1</p><p>p2</p><p>p3</p><div>div1</div><div>div2</div><div>div3</div><!-- 类选择器 --><p class="classp1">classp1</p><p class="classp2 classp3">classp2</p><!-- id选择器 --><div id="id1">id1</div><!-- 验证通配符选择器 --><input type="button" value="通配符配置颜色">
</body>
</html>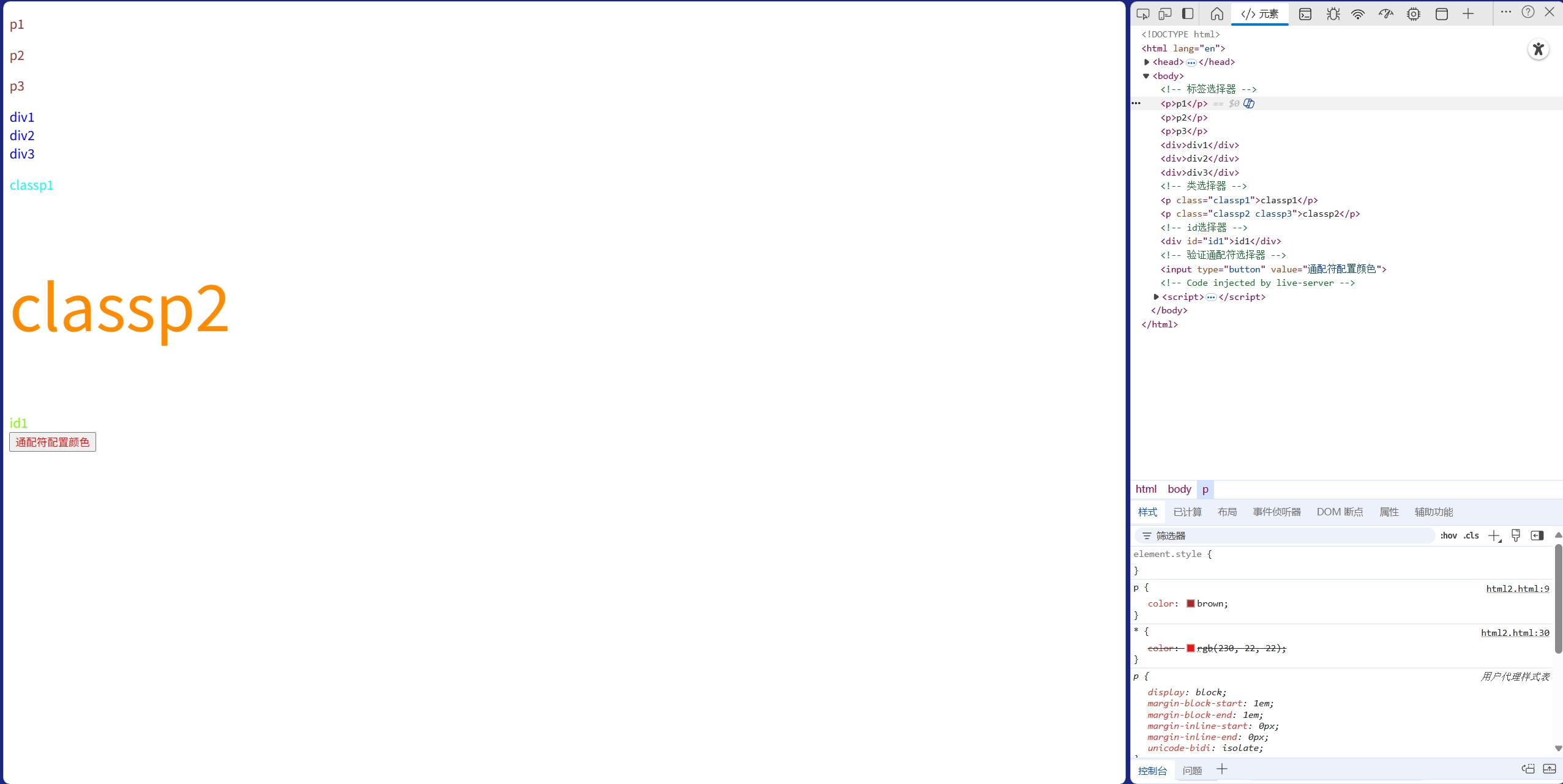
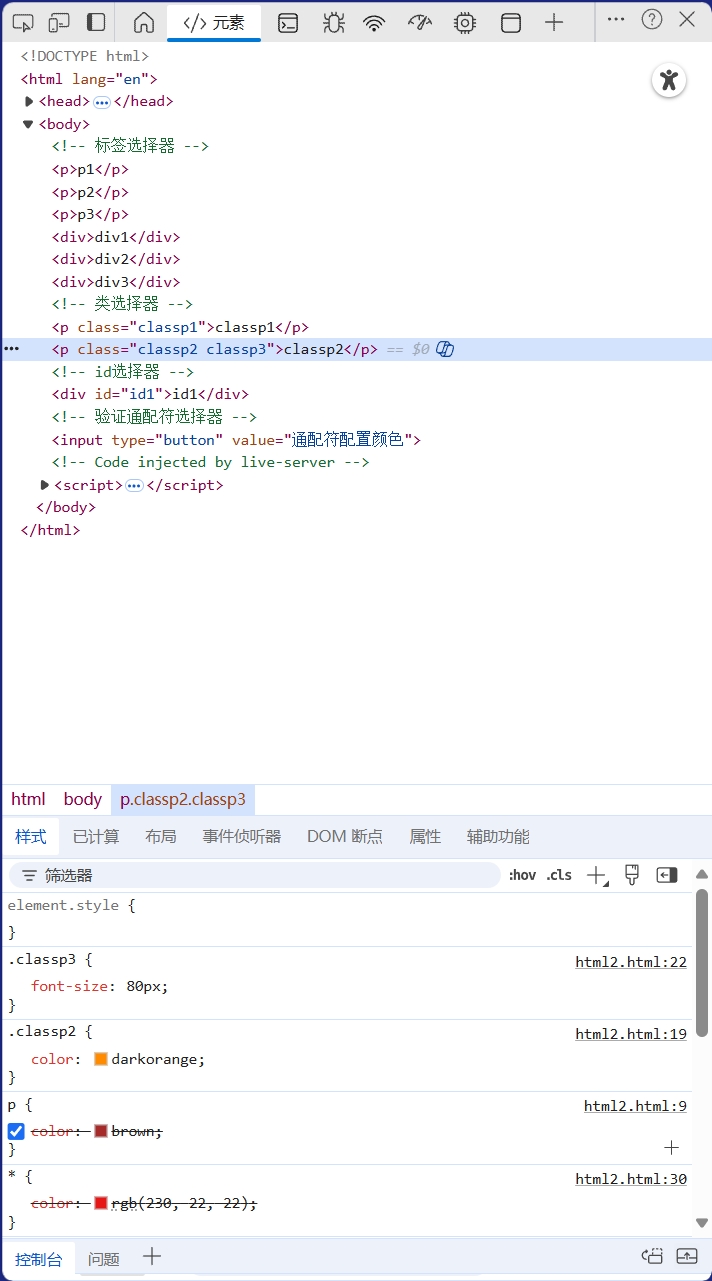
注意选择器之间存在覆盖的关系
标签选择器
可以将同一类标签快速选择出来
不能差异化选择
类选择器
差异化表示不同的标签
可以让多个标签都使用同一个标签
语法细节
多类名实例
一个标签使用多个类名就可以将相同属性提出来,简化代码
<style> .box {width: 200px;height: 150px;}.red {background-color: red;}.green {background-color: green;}
</style>
<div class="box red"></div>
<div class="box green"></div>
<div class="box red"></div>这里三个标签的尺寸属性是相同的,就设置一个类统一处理,差异化部分再设置类即可
id选择器
CSS中使用#开头表示id选择器
通配符选择器
使用*的定义,选取所有标签
不需要被页面结构调用
常用于重置默认样式(如margin、padding归零)
优先级顺序
ID选择器 > 类选择器 > 标签选择器 > 通配符选择器
后代选择器
又叫包含选择器,选择某个父元素中的所有后代元素
元素1 元素2 {样式声明}元素1和元素2之间要用空格进行分隔
选中的是元素1中的元素2,只修改元素2,对元素1不会产生影响
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>/* 案例一:父子关系 */ul li {color:blue;}/* 案例二:爷孙关系 */ol a {color:crimson;}/* 案例三:多个选择器叠加 */.example3 li {color:goldenrod;}</style>
</head>
<body><!-- 案例一 --><ul><li>ul1</li><li>ul2</li><li>ul3</li></ul><!-- 案例二 --><ol><li>ol1</li><li>ol2</li><li><a href="#">#</a></li></ol><!-- 案例三 --><ol class="example3"><li>ol1</li><li>ol2</li><li><a href="#">#</a></li></ol>
</body>
</html>
子选择器
和后代选择器类似,但是只能选择子标签
元素1>元素2 {样式声明}使用大于号分隔两个选择器
只选亲儿子,不选孙子元素
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>/* 后代选择器和子选择器对比 */.one a {color:green;}.two>a {color:red;}/* 并集选择器 */</style>
</head>
<body><!-- 后代选择器和子选择器对比 --><div class="one"><a href="#">亲儿子</a><p><a href="#">孙子</a></p></div><div class="two"><a href="#">亲儿子</a><p><a href="#">孙子</a></p></div>
</body>
</html>
并集选择器
元素1,元素2 {样式声明}用于选择多组标签(集体声明)
通过" , "进行分隔各个元素,表示同时选中元素1 元素2
任何基础选择器都可以使用并集选择器
并集选择器建议竖着写,每一个选择器后面都加上一个,(最后一个选择器不需要加,)
伪类选择器
链接伪类选择器
a:link 选择未被访问过的链接
a:visited 选择已经被访问过的链接
a:hover 选择鼠标指针悬停上的链接
a:active 选择活动链接(鼠标按下了但是未弹起)a {color: black;
}
a:hover {color: red;
}force伪类选择器
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>Document</title><style>/* 并集选择器 */div,p,input {color:red;}/* 伪类选择器 *//* 链接伪类选择器 *//* 选择未被访问过的链接 */a:link {color:black;/* 去掉下划线 */text-decoration: none;}/* 选择已经被访问过的链接 */a:visited {color: blue;text-decoration: dashed;}/* 鼠标悬停 */a:hover {color:red;}/* 鼠标点击但未弹起 */a:active {color:gold;}/* force伪类选择器 */.three>input:focus {color:red;}</style>
</head>
<body><!-- 并集选择器 --><div>div</div><p>p</p><input type="button" value="button"><!-- 伪类选择器 --><!-- 链接伪类选择器 --><div><a href="https://www.baidu.com/">百度一下,你就知道</a></div><!-- force伪类选择器 --><div class="three"><input type="text"><input type="text"><input type="text"></div>
</body>
</html>
小结
| 选择器类型 | 语法 | 匹配规则 | 优先级 | 性能 | 典型场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 后代选择器 | A B | 所有层级的后代 | 组合计算 | 低 | 容器内元素样式 |
| 子选择器 | A > B | 仅直接子元素 | 组合计算 | 中 | 精确控制层级 |
| 并集选择器 | A, B, C | 同时匹配多个选择器 | 最高优先级 | 高 | 统一多个元素样式 |
| 伪类选择器 | :hover, :nth-child(n) | 元素状态或位置 | 类选择器优先级 | 中 | 交互效果、结构样式 |
