ORB_SLAM2原理及代码解析:Tracking::TrackWithMotionModel() 函数
目录
1 作用
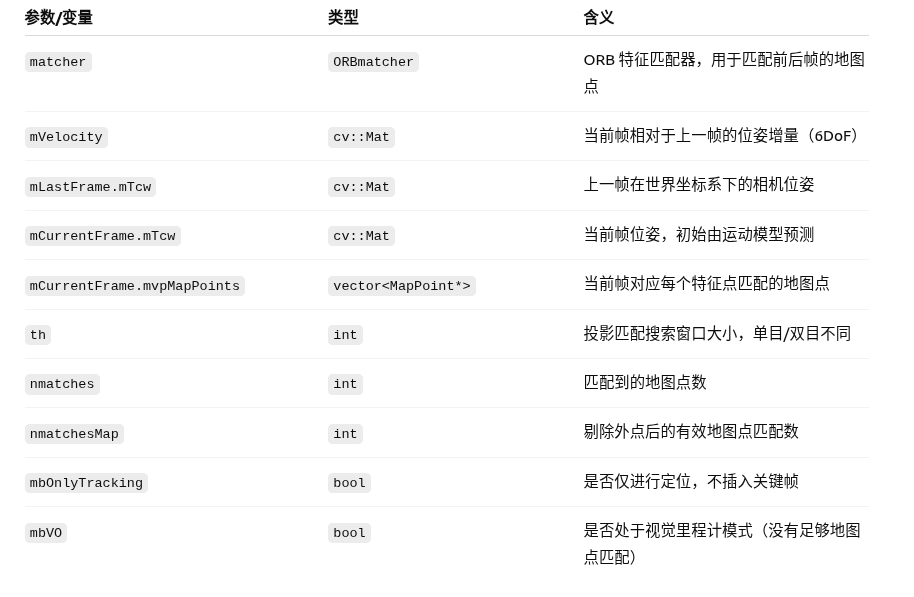
2 参数及含义
3 代码
4 解析
4.1 初始化匹配器
创建 ORB 匹配器,阈值 0.9,启用旋转一致性。
4.2 更新上一帧信息
4.2.1 UpdateLastFrame() 函数
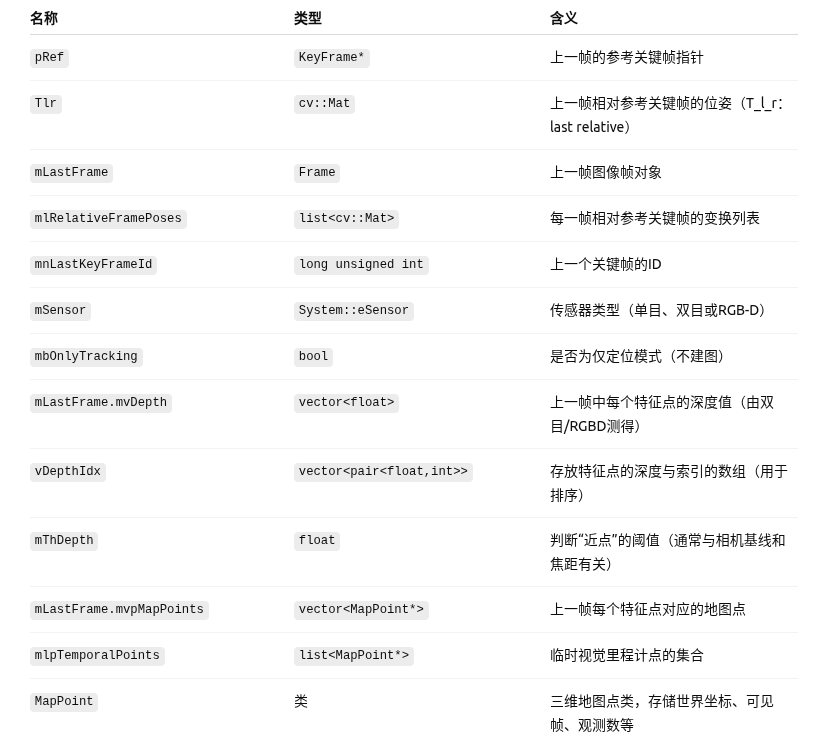
4.2.1.1 参数及含义
4.2.1.2 代码
4.2.1.3 UnprojectStereo() 函数
4.3 利用运动模型预测当前帧位姿
4.3.1 SetPose() 函数
4.4 清空当前帧地图点
4.5 投影匹配上一帧地图点
4.5.1 SearchByProjection() 函数
4.5.1.1 GetFeaturesInArea() 函数
4.6 匹配太少时扩大搜索模块
4.7 匹配数仍少则返回失败
4.8 优化当前帧位姿
4.8.1 PoseOptimization() 函数
4.9 剔除外点并统计有效地图点
4.10 判断是否为视觉里程计模式
4.11 返回普通模式结果
1 作用
运动模型(Motion Model)预测当前帧位姿,并尝试通过投影匹配跟踪上一帧的地图点来进行相机位姿估计。
2 参数及含义
3 代码
bool Tracking::TrackWithMotionModel() {ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);// Update last frame pose according to its reference keyframe// Create "visual odometry" points if in Localization ModeUpdateLastFrame();mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mVelocity*mLastFrame.mTcw);fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));// Project points seen in previous frameint th;if(mSensor!=System::STEREO)th=15;elseth=7;int nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);// If few matches, uses a wider window searchif(nmatches<20){fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,2*th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);}if(nmatches<20)return false;// Optimize frame pose with all matchesOptimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);// Discard outliersint nmatchesMap = 0;for(int i =0; i<mCurrentFrame.N; i++){if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]){if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]){MapPoint* pMP = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;pMP->mbTrackInView = false;pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;nmatches--;}else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)nmatchesMap++;}} if(mbOnlyTracking){mbVO = nmatchesMap<10;return nmatches>20;}return nmatchesMap>=10; }
4 解析
4.1 初始化匹配器
ORBmatcher matcher(0.9,true);创建 ORB 匹配器,阈值 0.9,启用旋转一致性。
4.2 更新上一帧信息
// Update last frame pose according to its reference keyframe// Create "visual odometry" points if in Localization ModeUpdateLastFrame();
4.2.1 UpdateLastFrame() 函数
4.2.1.1 参数及含义
4.2.1.2 代码
void Tracking::UpdateLastFrame() {// Update pose according to reference keyframeKeyFrame* pRef = mLastFrame.mpReferenceKF;//上一帧相对参考帧的位姿cv::Mat Tlr = mlRelativeFramePoses.back();//更新上一帧的世界坐标位姿mLastFrame.SetPose(Tlr*pRef->GetPose());if(mnLastKeyFrameId==mLastFrame.mnId || mSensor==System::MONOCULAR || !mbOnlyTracking)return;// Create "visual odometry" MapPoints// We sort points according to their measured depth by the stereo/RGB-D sensorvector<pair<float,int> > vDepthIdx;vDepthIdx.reserve(mLastFrame.N);for(int i=0; i<mLastFrame.N;i++){float z = mLastFrame.mvDepth[i];if(z>0){vDepthIdx.push_back(make_pair(z,i));}}if(vDepthIdx.empty())return;sort(vDepthIdx.begin(),vDepthIdx.end());// We insert all close points (depth<mThDepth)// If less than 100 close points, we insert the 100 closest ones.int nPoints = 0;for(size_t j=0; j<vDepthIdx.size();j++){int i = vDepthIdx[j].second;bool bCreateNew = false;MapPoint* pMP = mLastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];if(!pMP)bCreateNew = true;//如果地图点没有被观测,则创建新的点else if(pMP->Observations()<1){bCreateNew = true;}if(bCreateNew){cv::Mat x3D = mLastFrame.UnprojectStereo(i);MapPoint* pNewMP = new MapPoint(x3D,mpMap,&mLastFrame,i);mLastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=pNewMP;mlpTemporalPoints.push_back(pNewMP);nPoints++;}else{nPoints++;}if(vDepthIdx[j].first>mThDepth && nPoints>100)break;} }
4.2.1.3 UnprojectStereo() 函数
详见:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45728280/article/details/152324125?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502
4.3 利用运动模型预测当前帧位姿
mCurrentFrame.SetPose(mVelocity*mLastFrame.mTcw);
4.3.1 SetPose() 函数
详见:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45728280/article/details/152333209?spm=1011.2415.3001.5331
4.4 清空当前帧地图点
fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));开始当前帧跟踪前,清空当前帧关联的地图点指针,否则是上一帧的数据。
4.5 投影匹配上一帧地图点
// Project points seen in previous frame//投影匹配搜索半径int th;if(mSensor!=System::STEREO)th=15;elseth=7;int nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);
4.5.1 SearchByProjection() 函数
(1)作用:
通过将上一帧(LastFrame)的地图点投影到当前帧(CurrentFrame)图像平面,然后在投影附近搜索匹配特征点,实现帧间地图点匹配。
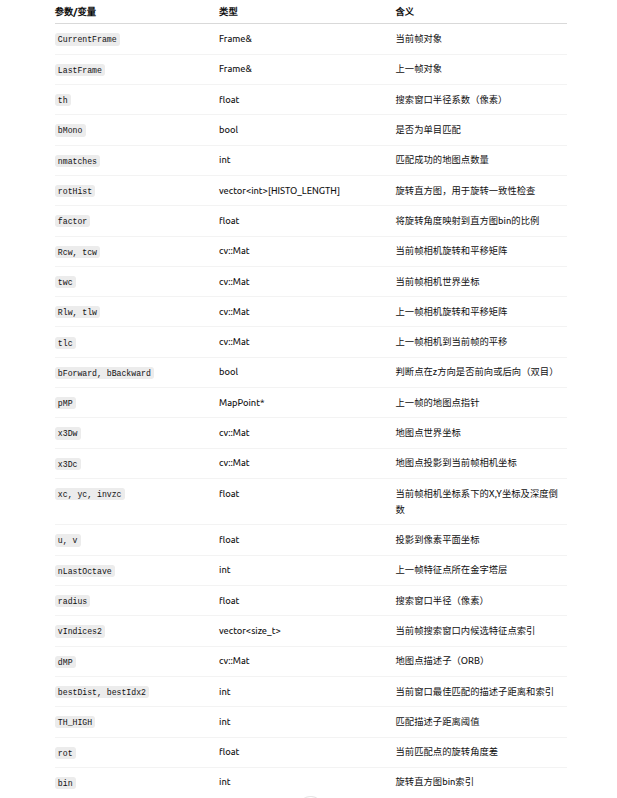
(2)参数及含义:
(3)声明:ORBmatcher.h
// Project MapPoints tracked in last frame into the current frame and search matches.// Used to track from previous frame (Tracking)int SearchByProjection(Frame &CurrentFrame, const Frame &LastFrame, const float th, const bool bMono);(4)定义:ORBmatcher.cc
int ORBmatcher::SearchByProjection(Frame &CurrentFrame, const Frame &LastFrame, const float th, const bool bMono) {//初始化,匹配计数器nmatches置0int nmatches = 0;// Rotation Histogram (to check rotation consistency)//创建旋转直方图rotHist,用于检查旋转一致性vector<int> rotHist[HISTO_LENGTH];//给每个bin预留500的空间,HISTO_LENGTH指拆分出来的bin个数for(int i=0;i<HISTO_LENGTH;i++)rotHist[i].reserve(500);//factor将旋转角度映射到直方图的binconst float factor = 1.0f/HISTO_LENGTH;//当前帧相机旋转和平移矩阵const cv::Mat Rcw = CurrentFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3);const cv::Mat tcw = CurrentFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3);//当前帧相机世界坐标twcconst cv::Mat twc = -Rcw.t()*tcw;//上一帧相机旋转和平移矩阵const cv::Mat Rlw = LastFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).colRange(0,3);const cv::Mat tlw = LastFrame.mTcw.rowRange(0,3).col(3);//上一帧相机到当前帧的平移const cv::Mat tlc = Rlw*twc+tlw;//双目/RGBD用,判断相机在Z轴前后运动(tlc.at<float>(2)),mb相机基线长度,单位mconst bool bForward = tlc.at<float>(2)>CurrentFrame.mb && !bMono;const bool bBackward = -tlc.at<float>(2)>CurrentFrame.mb && !bMono;for(int i=0; i<LastFrame.N; i++){MapPoint* pMP = LastFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];if(pMP){if(!LastFrame.mvbOutlier[i]){// Project//地图点在世界坐标系下的位置cv::Mat x3Dw = pMP->GetWorldPos();//把世界坐标系下的三维点投影到当前相机坐标系下,//x3Dc 就是 相机坐标系下的三维点,Z 轴朝相机前方cv::Mat x3Dc = Rcw*x3Dw+tcw;const float xc = x3Dc.at<float>(0);const float yc = x3Dc.at<float>(1);const float invzc = 1.0/x3Dc.at<float>(2);if(invzc<0)continue;//转化为像素坐标float u = CurrentFrame.fx*xc*invzc+CurrentFrame.cx;float v = CurrentFrame.fy*yc*invzc+CurrentFrame.cy;//投影之后检查点是否落在图像可视范围内if(u<CurrentFrame.mnMinX || u>CurrentFrame.mnMaxX)continue;if(v<CurrentFrame.mnMinY || v>CurrentFrame.mnMaxY)continue;int nLastOctave = LastFrame.mvKeys[i].octave;// Search in a window. Size depends on scale//确定投影点附近的搜索区域//radius:在图像平面上搜索候选特征的半径,单位像素float radius = th*CurrentFrame.mvScaleFactors[nLastOctave];//vIndices2用来存储当前帧中落在搜索窗口内的特征点索引vector<size_t> vIndices2;if(bForward)//搜索上一帧特征的同一尺度层vIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(u,v, radius, nLastOctave);else if(bBackward)//从最底层到上一帧特征所在层vIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(u,v, radius, 0, nLastOctave);elsevIndices2 = CurrentFrame.GetFeaturesInArea(u,v, radius, nLastOctave-1, nLastOctave+1);if(vIndices2.empty())continue;//获取地图点描述子const cv::Mat dMP = pMP->GetDescriptor();//初始化候选点中最小描述子距离、当前帧候选特征点索引int bestDist = 256;int bestIdx2 = -1;//在候选特征点中寻找与 MapPoint 最佳匹配的描述子for(vector<size_t>::const_iterator vit=vIndices2.begin(), vend=vIndices2.end(); vit!=vend; vit++){const size_t i2 = *vit;//CurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i2]//表示当前帧第 i2 个特征点是否已经关联了MapPointif(CurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i2])if(CurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i2]->Observations()>0)continue;if(CurrentFrame.mvuRight[i2]>0){//根据深度计算左图投影到右图的理论坐标const float ur = u - CurrentFrame.mbf*invzc;//实际右图坐标与预测右图坐标的误差const float er = fabs(ur - CurrentFrame.mvuRight[i2]);if(er>radius)continue;}const cv::Mat &d = CurrentFrame.mDescriptors.row(i2);//计算 MapPoint 描述子与候选特征的 汉明距离const int dist = DescriptorDistance(dMP,d);//更新最佳匹配if(dist<bestDist){bestDist=dist;bestIdx2=i2;}}//最佳匹配距离小于阀值if(bestDist<=TH_HIGH){CurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[bestIdx2]=pMP;nmatches++;if(mbCheckOrientation){float rot = LastFrame.mvKeysUn[i].angle-CurrentFrame.mvKeysUn[bestIdx2].angle;if(rot<0.0)rot+=360.0f;int bin = round(rot*factor);if(bin==HISTO_LENGTH)bin=0;assert(bin>=0 && bin<HISTO_LENGTH);rotHist[bin].push_back(bestIdx2);}}}}}//Apply rotation consistencyif(mbCheckOrientation){//初始化最大bin索引int ind1=-1;int ind2=-1;int ind3=-1;//计算前三大 binComputeThreeMaxima(rotHist,HISTO_LENGTH,ind1,ind2,ind3);//如果计算出来的bin不是前三大,则认为方向不一致,剔除for(int i=0; i<HISTO_LENGTH; i++){if(i!=ind1 && i!=ind2 && i!=ind3){for(size_t j=0, jend=rotHist[i].size(); j<jend; j++){CurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[rotHist[i][j]]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);nmatches--;}}}}return nmatches; }
4.5.1.1 GetFeaturesInArea() 函数
该函数作用为在图像坐标系下快速找到某个区域内的特征点索引,Frame.cc和KeyFrame.cc中都有定义,Frame.cc用于Tracking 阶段,KeyFrame.cc用于MapPoint 投影、回环检测。此处调用Frame.cc。
(1)声明:Frame.h
vector<size_t> GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r, const int minLevel=-1, const int maxLevel=-1) const;(2)定义:Frame.cc
vector<size_t> Frame::GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r, const int minLevel, const int maxLevel) const {vector<size_t> vIndices;vIndices.reserve(N);//计算需要搜索的网格范围,圆的上下左右const int nMinCellX = max(0,(int)floor((x-mnMinX-r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));if(nMinCellX>=FRAME_GRID_COLS)return vIndices;const int nMaxCellX = min((int)FRAME_GRID_COLS-1,(int)ceil((x-mnMinX+r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));if(nMaxCellX<0)return vIndices;const int nMinCellY = max(0,(int)floor((y-mnMinY-r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));if(nMinCellY>=FRAME_GRID_ROWS)return vIndices;const int nMaxCellY = min((int)FRAME_GRID_ROWS-1,(int)ceil((y-mnMinY+r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));if(nMaxCellY<0)return vIndices;//遍历范围内的特征点,跳过不在要求的金字塔层const bool bCheckLevels = (minLevel>0) || (maxLevel>=0);for(int ix = nMinCellX; ix<=nMaxCellX; ix++){for(int iy = nMinCellY; iy<=nMaxCellY; iy++){const vector<size_t> vCell = mGrid[ix][iy];if(vCell.empty())continue;for(size_t j=0, jend=vCell.size(); j<jend; j++){const cv::KeyPoint &kpUn = mvKeysUn[vCell[j]];if(bCheckLevels){if(kpUn.octave<minLevel)continue;if(maxLevel>=0)if(kpUn.octave>maxLevel)continue;}//如特征点在范围内则保存const float distx = kpUn.pt.x-x;const float disty = kpUn.pt.y-y;if(fabs(distx)<r && fabs(disty)<r)vIndices.push_back(vCell[j]);}}}return vIndices; }
(1)声明:KeyFrame.h
std::vector<size_t> GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r) const;(2)定义:KeyFrame.cc
vector<size_t> KeyFrame::GetFeaturesInArea(const float &x, const float &y, const float &r) const {vector<size_t> vIndices;vIndices.reserve(N);const int nMinCellX = max(0,(int)floor((x-mnMinX-r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));if(nMinCellX>=mnGridCols)return vIndices;const int nMaxCellX = min((int)mnGridCols-1,(int)ceil((x-mnMinX+r)*mfGridElementWidthInv));if(nMaxCellX<0)return vIndices;const int nMinCellY = max(0,(int)floor((y-mnMinY-r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));if(nMinCellY>=mnGridRows)return vIndices;const int nMaxCellY = min((int)mnGridRows-1,(int)ceil((y-mnMinY+r)*mfGridElementHeightInv));if(nMaxCellY<0)return vIndices;for(int ix = nMinCellX; ix<=nMaxCellX; ix++){for(int iy = nMinCellY; iy<=nMaxCellY; iy++){const vector<size_t> vCell = mGrid[ix][iy];for(size_t j=0, jend=vCell.size(); j<jend; j++){const cv::KeyPoint &kpUn = mvKeysUn[vCell[j]];const float distx = kpUn.pt.x-x;const float disty = kpUn.pt.y-y;if(fabs(distx)<r && fabs(disty)<r)vIndices.push_back(vCell[j]);}}}return vIndices; }
4.6 匹配太少时扩大搜索模块
// If few matches, uses a wider window searchif(nmatches<20){fill(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.begin(),mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints.end(),static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL));nmatches = matcher.SearchByProjection(mCurrentFrame,mLastFrame,2*th,mSensor==System::MONOCULAR);}
4.7 匹配数仍少则返回失败
if(nmatches<20)return false;
4.8 优化当前帧位姿
// Optimize frame pose with all matchesOptimizer::PoseOptimization(&mCurrentFrame);
4.8.1 PoseOptimization() 函数
详见ORB_SLAM2原理及代码解析:Tracking::TrackReferenceKeyFrame() 函数-4.5.1:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45728280/article/details/152559357?spm=1011.2415.3001.5331
4.9 剔除外点并统计有效地图点
// Discard outliers//当前帧中与地图中已存在的 MapPoint 成功匹配的数量int nmatchesMap = 0;for(int i =0; i<mCurrentFrame.N; i++){if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]){if(mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]){MapPoint* pMP = mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i];mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]=static_cast<MapPoint*>(NULL);//当前帧外点记作非外点mCurrentFrame.mvbOutlier[i]=false;//该地图点在当前帧不可见pMP->mbTrackInView = false;//地图点上次被观测到是当前帧下pMP->mnLastFrameSeen = mCurrentFrame.mnId;nmatches--;}//这个地图点不是外点,被观测过else if(mCurrentFrame.mvpMapPoints[i]->Observations()>0)nmatchesMap++;}}
4.10 判断是否为视觉里程计模式
if(mbOnlyTracking){//小于10VO模式,不依赖地图,否则SLAM模式mbVO = nmatchesMap<10;//大于20相机跟踪成功,否则失败return nmatches>20;}
4.11 返回普通模式结果
return nmatchesMap>=10;4.10、4.11逻辑含义:
如果在“仅定位”mbOnlyTracking模式下,少于 10 个地图点匹配 → VO 模式;匹配总数大于 20 → 跟踪成功。
如果在“建图”模式下,至少 10 个地图点匹配 → 跟踪成功。