队列queue
一、定义
队列(queue)是一个线性表,其插入和删除操作分别在表的不同端进行
添加新元素的那一端被称为队尾(queueBack) 或qBack
删除元素的那一端被成为队首(queueFront) 或qFront
队列是一个先进先出(first-in-first-out, FIFO)的线性表
抽象类(queue.h):
#ifndef queue_
#define queue_using namespace std;template<class T>
class queue
{public:virtual ~queue() {}virtual bool empty() const = 0;// return true iff queue is emptyvirtual int size() const = 0;// return number of elements in queuevirtual T& front() = 0;// return reference to the front elementvirtual T& back() = 0;// return reference to the back elementvirtual void pop() = 0;// remove the front elementvirtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0;// add theElement at the back of the queue
};
#endif二、队列 数组描述(循环队列)
int queueFront;删除
int queueBack;添加
int arrayLength;数组长度
T *queue;数组指针
描述队列的数组被视为一个“环” ,qBack抵达数组最后可使用数组开始的空间。
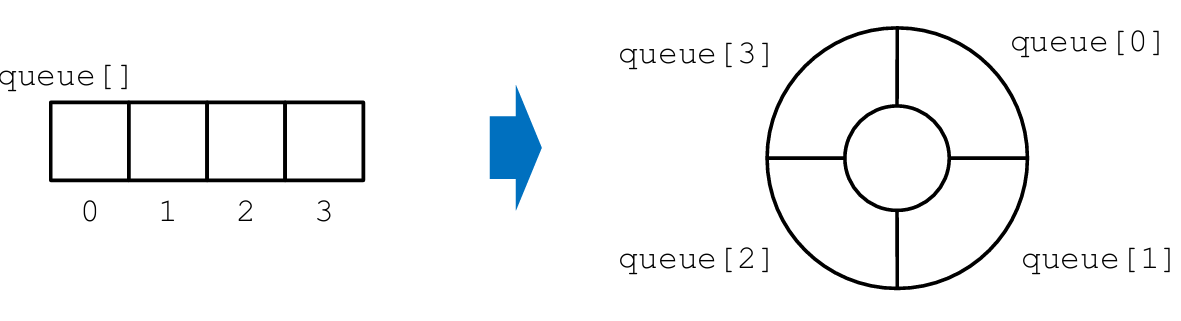
使用 i % n 表示队列的第i个元素到数组对应位置的映射:
第0,1,2,3个元素映射到第0,1,2,3个位置,第4个元素映射到第0个位置。
qFront修改为指向队头前一个位 置(总为空)队列不能插满:最多n-1个元素
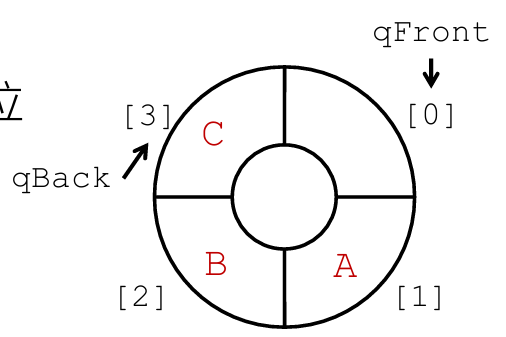
此时:
队列不能插满:最多n-1个元素
qFront修改为指向队头前一个位置(总为空)
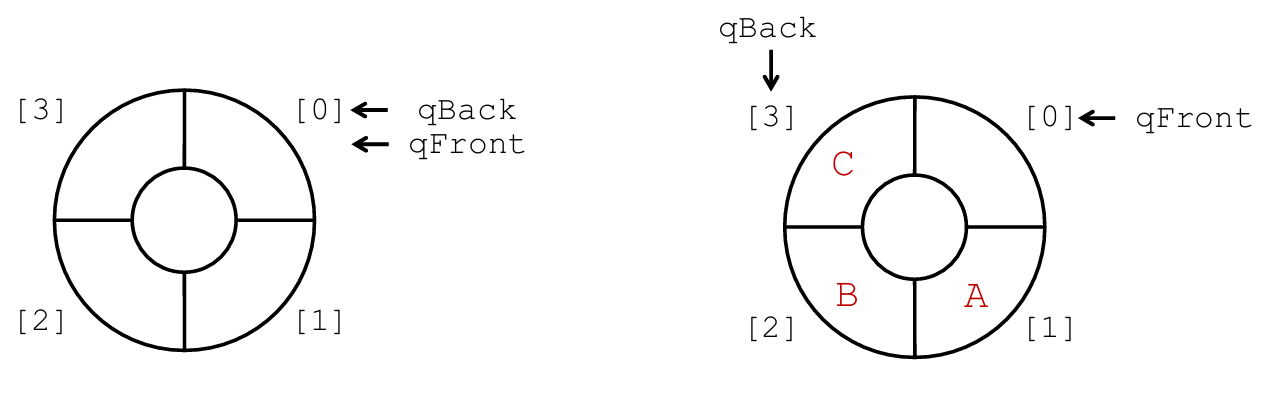
队列为空:qFront == qBack 队列为满:(qBack + 1)%n == qFront
arrayQueue:
template <typename T>class arrayQueue: public queue<T>{private:int queueFront;int queueBack;int arrayLength;T *queue;public:arrayQueue(intinitialCapacity = 10);~arrayQueue () { delete [] queue; }bool empty()const{ return queueFront== queueBack; }//队列为空:qFront == qBackint size()const{ return (arrayLength + queueBack- queueFront) % arrayLength;}T& front()const;T& back()const;voidpop();voidpush(constT& theElement);};(arrayLength + queueBack- queueFront) % arrayLength是为了使得出结果为正数。
构造函数:
template<class T>
arrayQueue<T>::arrayQueue(int initialCapacity)
{if (initialCapacity < 1){ throwillegalParameterException("");}arrayLength = initialCapacity;queue = new T[arrayLength];theFront =theBack= 0;
}读队头/尾:
template<classT>T&arrayQueue<T>::front() const{if(queueFront == queueBack) throwqueueEmpty();return queue[(queueFront + 1) % arrayLength];}template<classT>T&arrayQueue<T>::back()const{if(queueFront == queueBack) throwqueueEmpty();return queue[queueBack];}先判断是否为空,非空时返回头/尾。头时需要计算+1,需要取模保证指针指向队头元素,而尾未进行运算不需要取模。
push与pop:
pop:
template<classT>void arrayQueue <T>::pop(){if (queueFront == queueBack) throwqueueEmpty();queueFront=(queueFront + 1) % arrayLength;queue[queueFront].~T();}
先判断是否为空,非空时queueFront+1取模,然后调用该元素类型析构函数。
push:
template<classT>void arrayQueue<T>::push(const T& theElement){if ((queueBack + 1)% arrayLength == queueFront){…}//扩展队列queueBack= (queueBack+ 1)% arrayLength;queue[queueBack] = theElement;}数组扩展:
if ((theBack + 1) % arrayLength == theFront)
{//扩容二倍T* newQueue = new T[2 * arrayLength]; //容量为二倍的数组int start = (theFront + 1) % arrayLength;//theFront为第一个元素前一个位置,start为队列第一个元素的位置if (start < 2)//start<2时无回绕copy(queue + start, queue + start + arrayLength - 1, newQueue);//从start位置开始,复制arrayLength - 1个元素(原队列的全部元素)到新数组的起始位置else{ //有回绕copy(queue + start, queue + arrayLength, newQueue);//先复制start到原数组末尾的元素到新数组开头copy(queue, queue + theBack + 1, newQueue + arrayLength - start);//再复制原数组开头到queueBack的元素,拼接在前一部分之后(偏移量为arrayLength - start,//即第一部分的元素个数)}theFront = 2 * arrayLength - 1;theBack = arrayLength - 2; // queue size arrayLength - 1arrayLength *= 2;queue = newQueue;}队列 链表描述
两个指针指头和尾,一个queueSize表示大小
队头就是链表头,队尾就是链表尾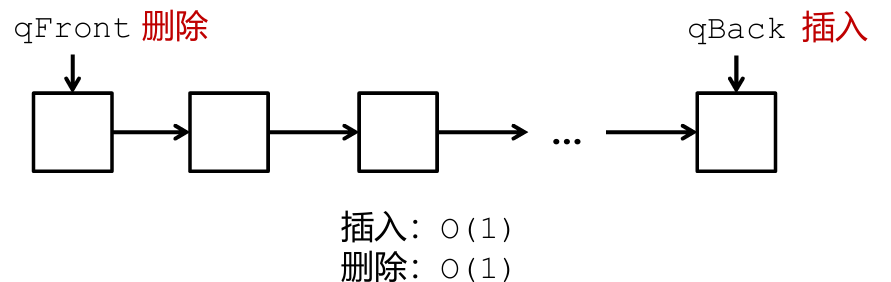
template<typenameT>class LinkedQueue:publicqueue<T>{private:chainNode<T>* queueFront;chainNode<T>* queueBack;int queueSize;public:LinkedQueue(intinitialCapacity = 10);~LinkedQueue();boolempty()const {returnqueueSize== 0; }int size()const { return queueSize; }T& front();T& back();voidpush(constT& theElement);voidpop();};front和back:
template<classT>T& LinkedQueue<T>::front(){if (queueSize == 0)throw queueEmpty();return queueFront->element;}template<classT>T& LinkedQueue<T>::back(){if (queueSize == 0)throw queueEmpty();return queueBack->element;}push和pop:
template<classT>void LinkedQueue<T>::push(constT&theElement){chainNode<T>* newNode =new chainNode<T>(theElement, nullptr);if(queueSize!=0)queueBack->next = newNode;elsequeueFront=newNode;queueBack= newNode;queueSize++;}template<classT>void LinkedQueue<T>::pop(){if(queueFront == NULL)throw queueEmpty();chainNode<T>* nextNode= queueFront->next;delete queueFront;queueFront=nextNode;queueSize--;}
三、应用:列车重排
int NowOut =1; // NowOut:下一次要输出的车厢号
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){ //从前至后依次检查的所有车厢
1.车厢p[i]从入轨上移出
2.if(p[i] == NowOut) // NowOut:下一次要输出的车厢号
2.1使用缓冲铁轨Hk把p[i]放到出轨上去; NowOut++;2.2 while (minH (当前缓冲铁轨中编号最小的车厢) == NowOut) {
把minH放到出轨上去;
更新minH,minQ(minH所在的缓冲铁轨);NowOut++;}else按照分配规则将车厢p[i]送入某个缓冲铁轨
}
// railroad car rearrangement using queues#include <iostream>
#include "arrayQueue.h"using namespace std;// global variables
arrayQueue<int>* track; // array of holding tracks
int numberOfCars;
int numberOfTracks;
int smallestCar; // smallest car in any holding track
int itsTrack; // holding track with car smallestCarvoid outputFromHoldingTrack()
{// output the smallest car from the holding tracks// pop smallestCar from itsTracktrack[itsTrack].pop();cout << "Move car " << smallestCar << " from holding track "<< itsTrack << " to output track" << endl;// find new smallestCar and itsTrack by checking all queue frontssmallestCar = numberOfCars + 2;for (int i = 1; i <= numberOfTracks; i++)if (!track[i].empty() && track[i].front() < smallestCar){smallestCar = track[i].front();itsTrack = i;}
}bool putInHoldingTrack(int c)
{// Put car c into a holding track.// Return false iff there is no feasible holding track for this car.// find best holding track for car c// initializeint bestTrack = 0, // best track so farbestLast = 0; // last car in bestTrack// scan tracksfor (int i = 1; i <= numberOfTracks; i++)if (!track[i].empty()){// track i not emptyint lastCar = track[i].back();if (c > lastCar && lastCar > bestLast){// track i has bigger car at its rearbestLast = lastCar;bestTrack = i;}}else // track i emptyif (bestTrack == 0)bestTrack = i;if (bestTrack == 0)return false; // no feasible track// add c to bestTracktrack[bestTrack].push(c);cout << "Move car " << c << " from input track "<< "to holding track " << bestTrack << endl;// update smallestCar and itsTrack if neededif (c < smallestCar){ smallestCar = c;itsTrack = bestTrack;}return true;
}bool railroad(int* inputOrder,int theNumberOfCars, int theNumberOfTracks)
{// Rearrange railroad cars beginning with the initial order.// inputOrder[1:theNumberOfCars]// Return true if successful, false if impossible.numberOfCars = theNumberOfCars;// keep last track open for outputnumberOfTracks = theNumberOfTracks - 1;// create queues track[1:numberOfTracks] for use as holding trackstrack = new arrayQueue<int> [numberOfTracks + 1];int nextCarToOutput = 1;smallestCar = numberOfCars + 1; // no car in holding tracks// rearrange carsfor (int i = 1; i <= numberOfCars; i++)if (inputOrder[i] == nextCarToOutput){// send car inputOrder[i] straight outcout << "Move car " << inputOrder[i] << " from input "<< "track to output track" << endl;nextCarToOutput++;// output from holding trackswhile (smallestCar == nextCarToOutput){outputFromHoldingTrack();nextCarToOutput++;}}else// put car inputOrder[i] in a holding trackif (!putInHoldingTrack(inputOrder[i]))return false;return true;
}// test program
int main()
{//int p[] = {0, 5, 8, 1, 7, 4, 2, 9, 6, 3};//cout << "Input permutation is 581742963" << endl;int p[] = {0, 3, 6, 9, 2, 4, 7, 1, 8, 5};cout << "Input permutation is 369247185" << endl;railroad(p, 9, 3);return 0;
}