机器学习15:自监督式学习(Self-Supervised Learning)①
摘要
本周课程介绍了自监督式学习(Self-Supervised Learning)的基本概念与应用场景。自监督式学习是一种无需人工标注标签的学习方法,通过从无标签数据中自动构造监督信号进行模型预训练。课程以BERT模型为例,详细讲解了其自监督训练过程,包括遮码(Masking)和下一句预测(Next Sentence Prediction)等关键技术,并阐述了如何通过微调(Fine-tuning)将预训练模型适配到多种下游任务,如文本分类、序列标注、自然语言推理和问答系统。最后,通过通用语言理解评估基准(GLUE)展示了自监督学习模型在多项自然语言处理任务上的强大表现。
Abstract
This week's lesson introduces the basic concepts and applications of self-supervised learning. Self-supervised learning is a method that operates without human-annotated labels by automatically generating supervisory signals from unlabeled data for model pre-training. Using the BERT model as an example, the course explains in detail its self-supervised training process, including key techniques such as masking and next sentence prediction. It also describes how pre-trained models can be adapted through fine-tuning to various downstream tasks, such as text classification, sequence labeling, natural language inference, and question answering. Finally, the General Language Understanding Evaluation (GLUE) benchmark is used to demonstrate the strong performance of self-supervised learning models across multiple natural language processing tasks.
一.了解自监督式学习
本周开始学习自监督式学习,在了解之前我们不得不说到一个节目叫做《芝麻街》,因为其中一些人物的名字就对应一些模型的名称缩写,如下图分别代表了:通过知识集成增强表征(ERNIE)、来自语言模型的词嵌入(ELMo)、适用于更长序列的 Transformer 模型(Big Bird)、基于 Transformer 的双向编码器表征(BERT)。
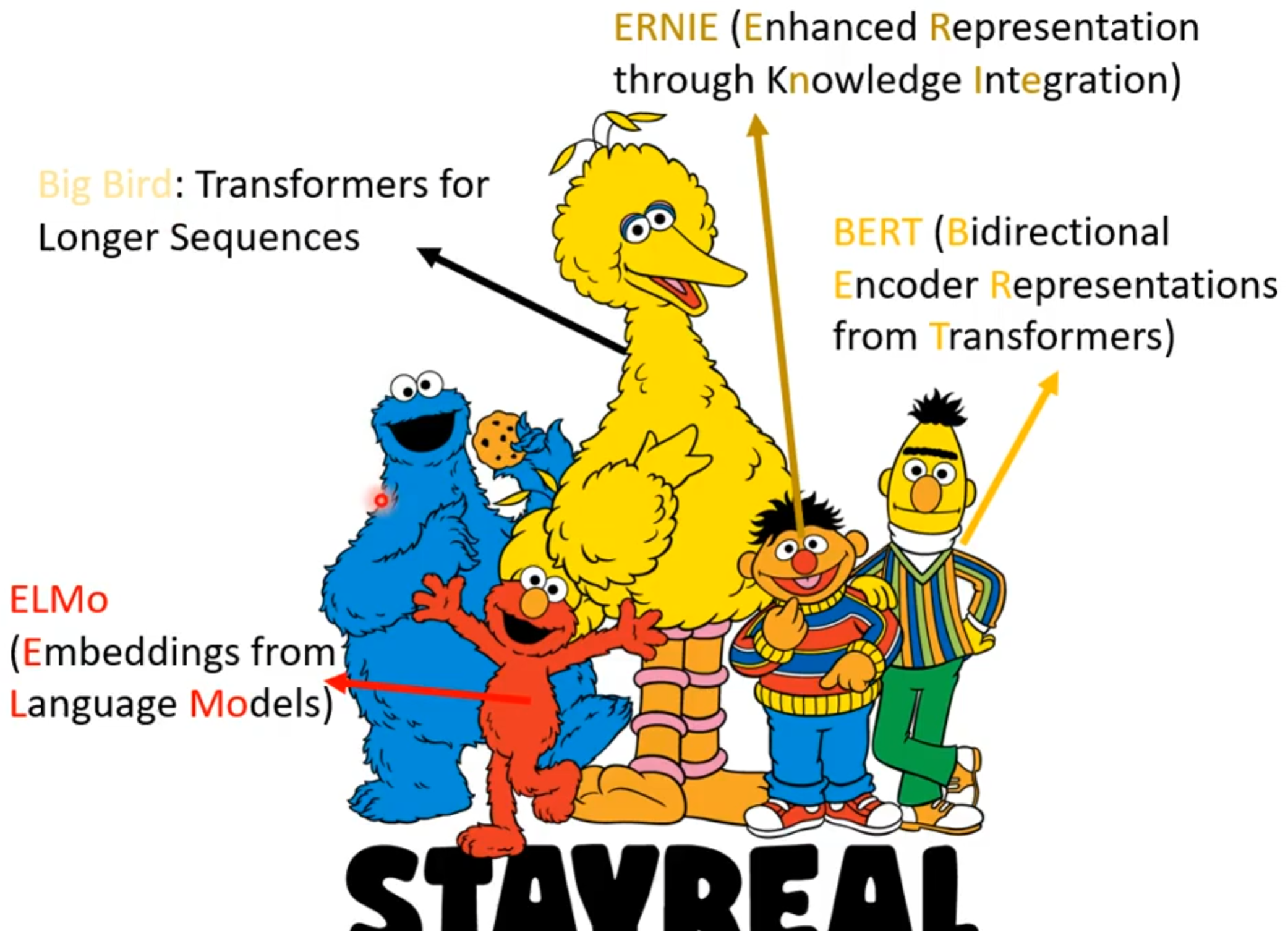
&n
