PySide与Ollama连接交互
Ollama 简介
Ollama 是一个开源工具,专注于本地运行和管理大型语言模型(LLMs)。它简化了在个人计算机上部署和操作 LLM 的过程,为用户提供了一种高效且隐私友好的方式来利用先进的语言模型技术。
Ollama 支持多种流行的开源模型,如 LLaMA、Mistral 和 Gemma。用户可以通过简单的命令行界面下载、运行这些模型,无需复杂的配置或依赖云服务。该工具支持跨平台操作,兼容 macOS、Linux 和 Windows 系统。其模块化架构便于集成到现有工作流程中,也适合开发者进行二次开发。

Ollama端点
通过 pip install ollama安装ollama的python库,在连接之前确保Ollama 已在本地安装并启动。默认情况下,它会在 http://localhost:11434 提供服务。你可以在终端输入 ollama serve 来启动服务。
服务启动后,可以通过curl来验证ollama测试:
curl http://localhost:11434/api/tags
如果已经正常启动,就能看到已安装模型的JSON列表。
Ollama主要提供三个核心API端点:
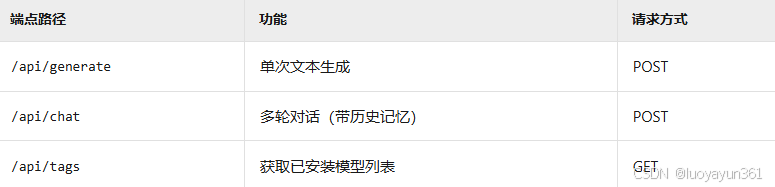
所以,在本地运行 Ollama 服务后,它默认会在 http://localhost:11434 这个地址监听 API 请求。只要你的 PySide 应用程序与 Ollama 在同一台机器上运行,就可以通过这个地址与 Ollama 通信。
PySide连接示例
来看一个基础的连接示例,向ollama的模型发送信息:
def send_message(self):user_input = self.input_field.text()if not user_input.strip():return# 显示用户消息self.chat_display.append(f"<b>You:</b> {user_input}")self.input_field.clear()# 调用Ollamatry:response = self.call_ollama(user_input)self.chat_display.append(f"<b>AI:</b> {response}")except Exception as e:self.chat_display.append(f"<font color='red'>Error: {str(e)}</font>")def call_ollama(self, prompt):url = "http://localhost:11434/api/generate"payload = {"model": "qwen2:1.5b","prompt": prompt,"stream": False}response = requests.post(url, json=payload)if response.status_code == 200:return response.json()["response"]else:raise Exception(f"API Error {response.status_code}: {response.text}")
项目延伸
在实际的项目中,ollama中部署了模型后,正常流程是我们的程序启动时去连接ollama对模型进行访问。但是实际开发时还要考虑更完整的流程,如:在连接ollama的时候,判断ollama服务是否已经启动,防止重复去启动服务;其次,连接的时候如果端口被占用,也需要提供处理方案;另外,启动的时候也要考虑阻塞问题,所以启动流程可能需要放到子线程中处理。
检查服务状态
核心方法是向 Ollama 的 API 发送一个简单的请求(如检查模型列表),根据响应判断服务状态:
import requests
import subprocess
import time
from PySide6.QtCore import QThread, Signaldef check_ollama_service(base_url='http://localhost:11434', timeout=5):"""检查 Ollama 服务是否正在运行返回值: bool, 服务正常运行返回 True,否则返回 False"""try:response = requests.get(f"{base_url}/api/tags", timeout=timeout)return response.status_code == 200except (requests.ConnectionError, requests.Timeout):return False
安全启动 Ollama 服务
如果检测到服务未运行,再启动它。关键在于处理可能出现的端口占用问题
def start_ollama_service():"""启动 Ollama 服务返回值: bool, 成功启动返回 True,否则返回 False"""# 首先检查服务是否已运行,避免重复启动[6](@ref)if check_ollama_service():print("Ollama 服务已在运行")return Truetry:# 使用 subprocess 启动 ollama serve# 注意:确保 ollama 命令在第三方电脑的 PATH 环境变量中process = subprocess.Popen(['ollama', 'serve'],stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE,text=True)# 等待一段时间让服务初始化time.sleep(5)# 再次检查服务是否成功启动if check_ollama_service():print("Ollama 服务启动成功")return Trueelse:print("Ollama 服务启动后仍不可用")return Falseexcept FileNotFoundError:print("错误:未找到 ollama 命令。请确保 Ollama 已正确安装。")return Falseexcept Exception as e:print(f"启动 Ollama 服务时发生错误: {str(e)}")return False
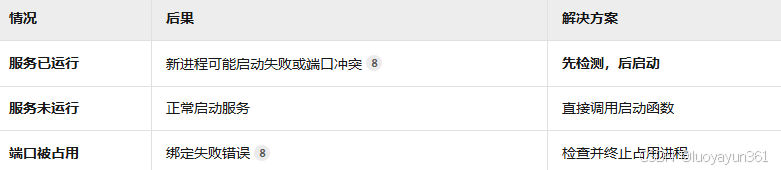
重复启动的影响与处理
关于重复启动的应对策略,可参考:
集成到项目中
一个简单的示例,为了避免阻塞图形界面,建议将服务检查和启动放在单独的线程中执行。
class OllamaServiceThread(QThread):"""用于在后台检查和启动 Ollama 服务的线程"""status_signal = Signal(str) # 用于向主线程发送状态信号finished_signal = Signal(bool) # 发送最终成功与否的信号def __init__(self):super().__init__()def run(self):self.status_signal.emit("正在检查 Ollama 服务状态...")if check_ollama_service():self.status_signal.emit("Ollama 服务正常运行")self.finished_signal.emit(True)returnself.status_signal.emit("正在启动 Ollama 服务...")if start_ollama_service():self.status_signal.emit("Ollama 服务启动成功")self.finished_signal.emit(True)else:self.status_signal.emit("Ollama 服务启动失败")self.finished_signal.emit(False)# 在主窗口类中使用
class MainWindow(QMainWindow):def __init__(self):super().__init__()# ... 其他初始化代码 ...self.init_ollama_service()def init_ollama_service(self):"""初始化 Ollama 服务"""self.status_label.setText("正在初始化 Ollama 服务...")self.ollama_thread = OllamaServiceThread()self.ollama_thread.status_signal.connect(self.update_status)self.ollama_thread.finished_signal.connect(self.on_service_ready)self.ollama_thread.start()def update_status(self, message):"""更新状态标签"""self.status_label.setText(message)def on_service_ready(self, success):"""服务准备就绪后的回调"""if success:self.status_label.setText("✅ 就绪")self.chat_input.setEnabled(True)self.send_button.setEnabled(True)else:self.status_label.setText("❌ Ollama 服务异常")# 可以在这里提供手动重试或安装指导
模型是否存在
另外,我们还可以判断需要使用的模型是否存在,这个条件用于在应用中处理任务前进行判断,防止意外出错。
示例:
def ensure_model_available(model_name='qwen2:1.5b'):"""确保模型已下载"""try:client = ollama.Client()models = client.list()if not any(model['name'] == model_name for model in models['models']):subprocess.run(['ollama', 'pull', model_name], check=True)except Exception as e:print(f"确保模型可用时出错: {e}")
关闭Ollama服务
在你开发的应用关闭时,妥善关闭 Ollama 服务是个好习惯,这能确保资源被正确释放。
那么,关闭服务可以通过几种方式来实现。
1.通过子进程对象终止
如果你的应用启动了 Ollama 服务并保存了 Popen 对象,这是最直接的方法。
import signal
import subprocess
import time# 启动服务时保存进程对象
ollama_process = subprocess.Popen(['ollama', 'serve'])def stop_ollama_service(process):"""停止由本应用启动的 Ollama 服务"""if process is None:return Truetry:# 1. 尝试优雅终止process.terminate() # 发送 SIGTERM 信号[7,8](@ref)process.wait(timeout=10) # 等待最多10秒return Trueexcept subprocess.TimeoutExpired:# 2. 优雅终止失败,强制终止try:process.kill() # 发送 SIGKILL 信号[7,8](@ref)process.wait()return Trueexcept Exception as e:print(f"强制终止失败: {e}")return Falseexcept Exception as e:print(f"终止过程出错: {e}")return False
2.通过系统命令终止
如果你没有保存进程对象,可以通过系统命令来查找并终止进程。
Windows系统:
import osdef stop_ollama_windows():"""在 Windows 上停止 Ollama 服务"""try:# 使用 taskkill 命令终止所有 ollama 进程os.system('taskkill /F /IM ollama.exe')return Trueexcept Exception as e:print(f"终止 Ollama 进程失败: {e}")return False
Linux/maxOS系统:
import subprocess
import signaldef stop_ollama_unix():"""在 Unix 系统上停止 Ollama 服务"""try:# 查找 ollama 相关进程result = subprocess.run(['pgrep', '-f', 'ollama'], capture_output=True, text=True)if result.returncode == 0:# 获取所有相关进程IDpids = result.stdout.strip().split('\n')for pid in pids:try:# 先尝试优雅终止[1](@ref)os.kill(int(pid), signal.SIGTERM)time.sleep(2) # 等待2秒# 如果进程仍在,强制终止[1](@ref)os.kill(int(pid), signal.SIGKILL)except ProcessLookupError:pass # 进程已退出return Trueexcept Exception as e:print(f"终止 Ollama 进程失败: {e}")return False
将关闭逻辑集成到应用的退出事件中:
from PySide6.QtWidgets import QMainWindow, QApplication
from PySide6.QtCore import QTimer
import sysclass MainWindow(QMainWindow):def __init__(self):super().__init__()self.ollama_process = None # 保存启动的进程def closeEvent(self, event):"""重写关闭事件,在窗口关闭时执行"""# 延迟实际关闭,先处理清理工作event.ignore()self.prepare_to_exit()def prepare_to_exit(self):"""准备退出应用"""# 停止 Ollama 服务if self.ollama_process:stop_ollama_service(self.ollama_process)# 也可以检查并终止任意运行的 Ollama 服务if is_ollama_running():# 根据操作系统选择终止方法if sys.platform == "win32":stop_ollama_windows()else:stop_ollama_unix()# 稍后真正退出应用QTimer.singleShot(100, QApplication.instance().quit)# 应用启动时
if __name__ == "__main__":app = QApplication(sys.argv)# 启动 Ollama 服务ollama_process = start_ollama_service() # 你的启动函数window = MainWindow()window.ollama_process = ollama_processwindow.show()sys.exit(app.exec())
优先考虑第一种方式关闭服务,让 Ollama 有时间完成正在进行的操作,终止进程后,调用 wait() 确保资源释放,避免“僵尸进程”。
