南京大学 LLM开发基础(二)大语言模型解析 -- 基于HF LlaMA实现的讲解
https://njudeepengine.github.io/llm-course-lecture/2025/lecture4.html#1
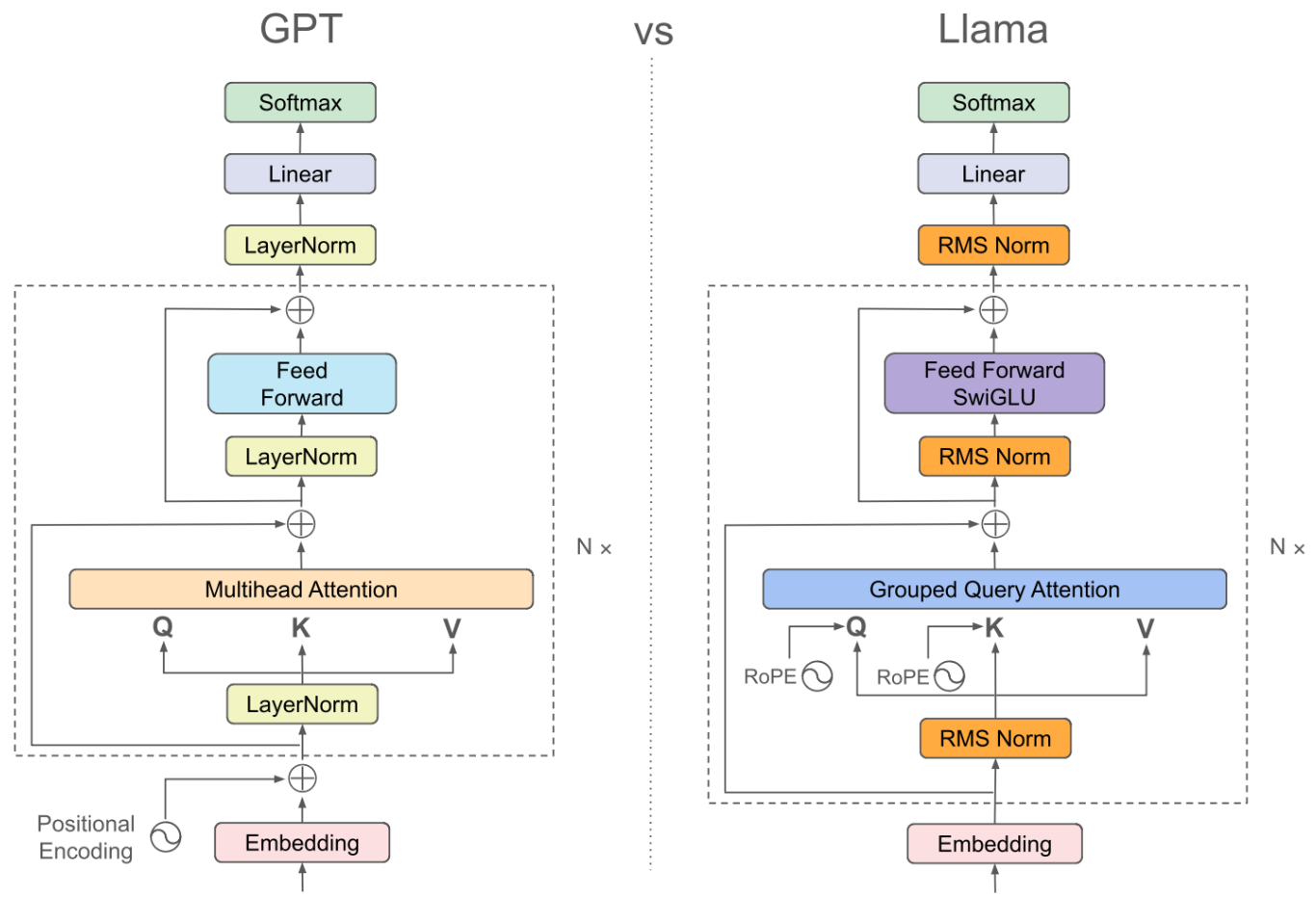
嵌入 + 位置掩码 + RMSNorm + 前馈神经网络FFN
作业:手搓多头注意力
目录
1. Input / Positional Embedding
Sinusoidal PE 绝对位置编码
旋转位置编码(Rotary PE)
2. Pytorch 中 tensor 的函数操作
3. Normalization
4. 前馈神经网络 FFN & SwiGLU模块
经典激活函数
Task1 多头注意力 - 多头乘法
1. 输入输出形状:
2. 计算步骤:
3. 代码实现
Task2 多头注意力 - 只算重要性高的 + 梯度
1. 题目要求
2. 重要性筛选 [b, s] -> t
3. 梯度计算
1. Input / Positional Embedding
https://tiktokenizer.vercel.app/ 不同分词器 embedding后
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
Sinusoidal PE 绝对位置编码
直接在每个token的 embedding 上线性叠加位置编码 xi+pi ,其中pi 为可训练的向量。
经典例:正弦余弦位置编码 第t个词的第i个维度。
不同的维度 根据奇偶正余弦,不同的周期。 不同的 t 对应正余弦值不同 体现位置。
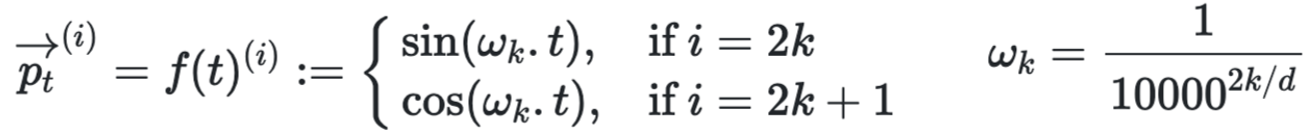
旋转位置编码(Rotary PE)
为每个 “维度对”旋转特定夹角 以下为 2维旋转&n维旋转
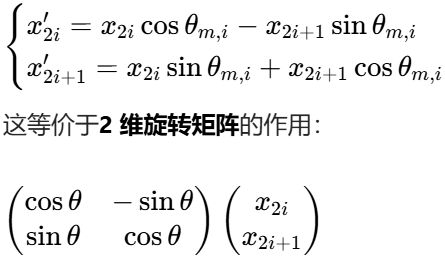
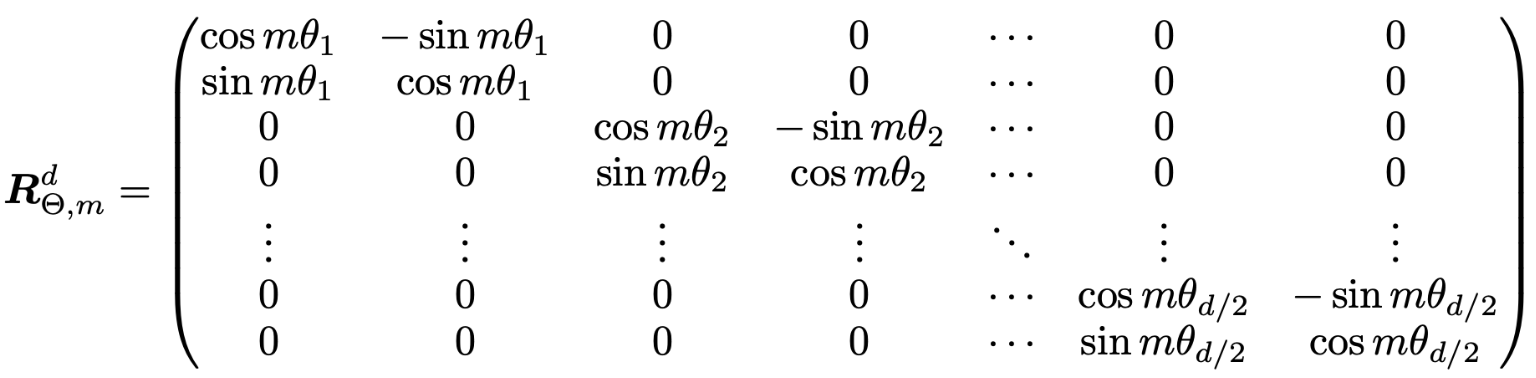
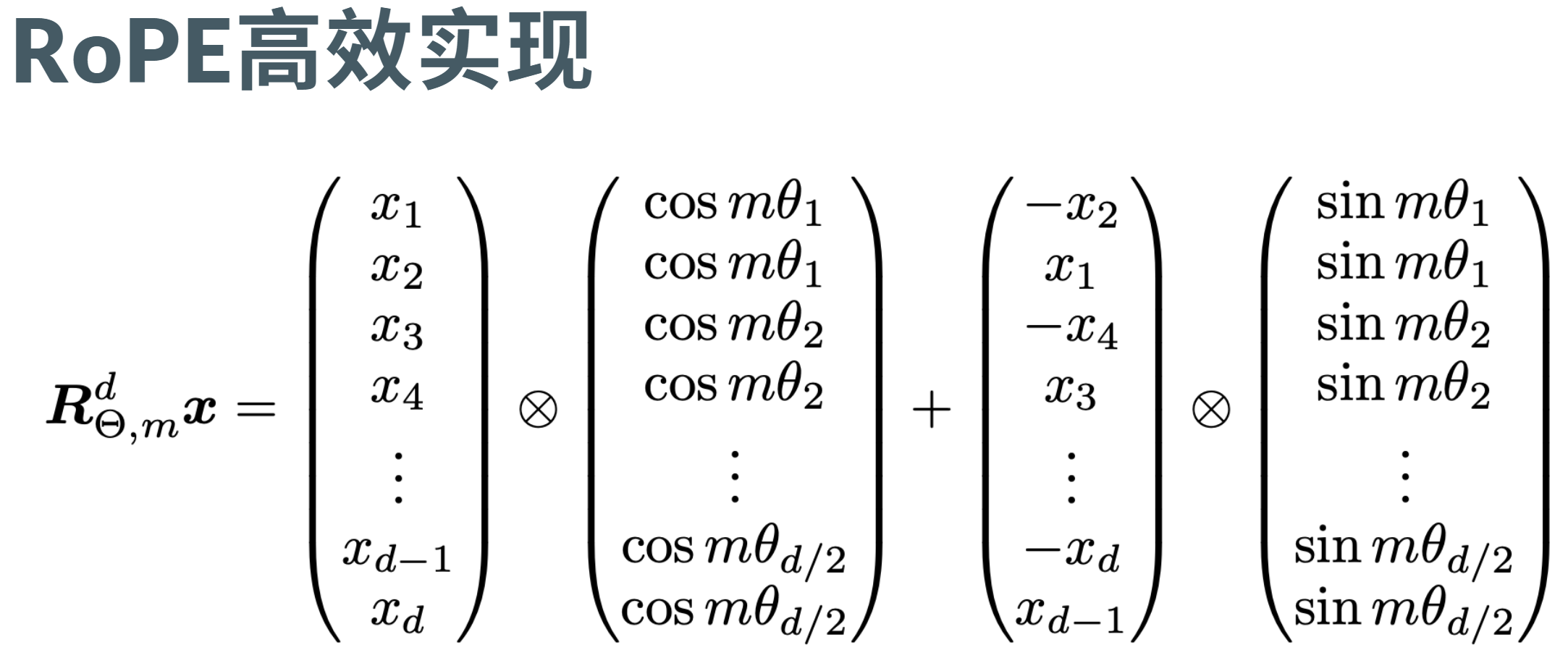
分半 取反 拼接; 变成右边 (-x2, x1, -x4, x3, ...)
def rotate_half(x):"""Rotates half the hidden dims of the input."""x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2] # 取前一半维度 (x1, x3, x5, ...)x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :] # 取后一半维度 (x2, x4, x6, ...)return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1) # 交换并取负:(-x2, x1, -x4, x3, ...)def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin):cos = cos.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim) # 扩展维度以便广播sin = sin.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim) # 扩展维度以便广播# RoPE 核心计算q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)2. Pytorch 中 tensor 的函数操作
https://njudeepengine.github.io/llm-course-lecture/2025/lecture4.html#29
pytorch - tensor-operations
转置 / 维度交换操作
transpose() - 交换两个维度
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 4, 5)
y = x.transpose(1, 3) # 交换维度1和3
print(x.shape) # torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])
print(y.shape) # torch.Size([2, 5, 4, 3])permute() - 按制定顺序 重新排列所有维度
上两者操作会导致 张量不连续;可通过 .contiguous() 恢复连续性。
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 4, 5)
y = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2) # 重新排列维度
print(x.shape) # torch.Size([2, 3, 4, 5])
print(y.shape) # torch.Size([2, 5, 3, 4])x_contiguous = x_t.contiguous()形状变换操作:view vs reshape
reshape() 相当于检查连续性版本的 view()
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 4) # 形状:2×3×4
y = x.view(6, 4) # 成功:2×3=6x_transposed = x.transpose(0, 1) # 形状变为:3×2×4y = xx_transposed.view(12, 2) # 报错,因为转置后不连续 if x_transposed.is_contiguous():result = x_transposed.view(12, 2)
else:result = x_transposed.contiguous().view(12, 2) # 先复制再reshape移除 / 添加 大小为1的维度
squeeze() - 移除大小为1的维度
x = torch.randn(1, 3, 1, 4)
y = x.squeeze() # 移除所有大小为1的维度
z = x.squeeze(0) # 只移除第0维
print(x.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3, 1, 4])
print(y.shape) # torch.Size([3, 4])
print(z.shape) # torch.Size([3, 1, 4])unsqueeze() - 在指定位置插入大小为1的维度
x = torch.randn(3, 4)
y = x.unsqueeze(0) # 在第0维插入
z = x.unsqueeze(-1) # 在最后一维插入
print(x.shape) # torch.Size([3, 4])
print(y.shape) # torch.Size([1, 3, 4])
print(z.shape) # torch.Size([3, 4, 1])乘法
torch.matmul()/@: 通用矩阵乘法,支持广播torch.bmm(): 批量矩阵乘法,专门用于3D tensortorch.mm(): 2D矩阵乘法-
torch.einsum 爱因斯坦求和约定 通过字符串要求格式
如后面多头中用到的 output = torch.einsum('bshd,hde->bshe', input, weight)
gather 拿 scatter 插
torch.gather() - 按索引收集元素 把对应位置的拿出来
x = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3],[4, 5, 6],[7, 8, 9]])indices = torch.tensor([[0, 1],[1, 2], [0, 2]])y = torch.gather(x, 1, indices) # 1代表处理每行
# 结果:每行按索引选取对应列的元素
# [[1, 2], # 第0行:列0=1, 列1=2
# [5, 6], # 第1行:列1=5, 列2=6
# [7, 9]] # 第2行:列0=7, 列2=9torch.scatter_() - 将元素分散到指定位置 插到对应位置
x = torch.zeros(3, 4)
values = torch.randn(3, 2)
indices = torch.tensor([[0, 2], [1, 3], [0, 1]])
x.scatter_(1, indices, values)detach() 函数:从计算图中分离张量,阻止梯度传播
3. Normalization
![]()
使得梯度下降的时候 加速收敛,降低过拟合(overfitting),增强泛化(generalization)
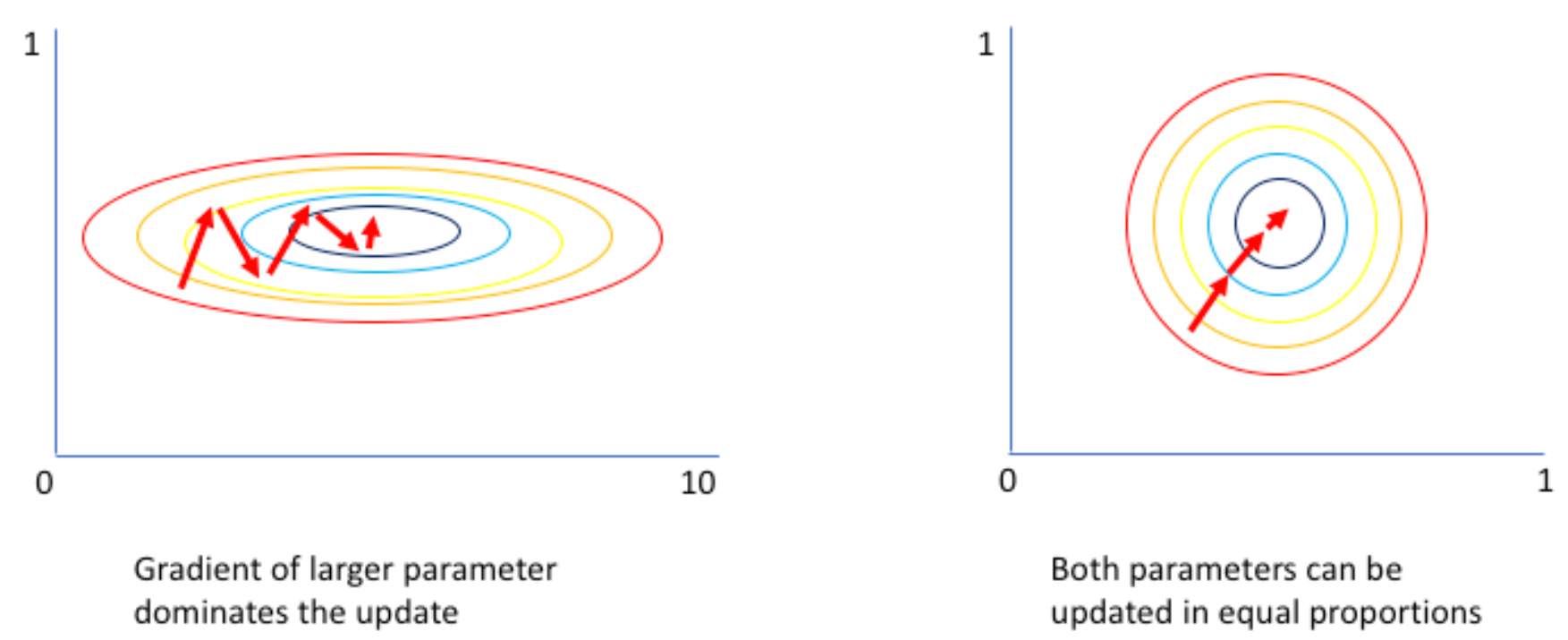
在大模型中,调整数据分布。
-
Batch Norm(批归一化):对每个通道,在整个批次的空间维度(如图像的高、宽)上统计均值和方差。类比:全班学生(批量)的某一门科目(通道)成绩整体归一化。(依赖于batch长度 足够多的batch才能进行 批归一化)
-
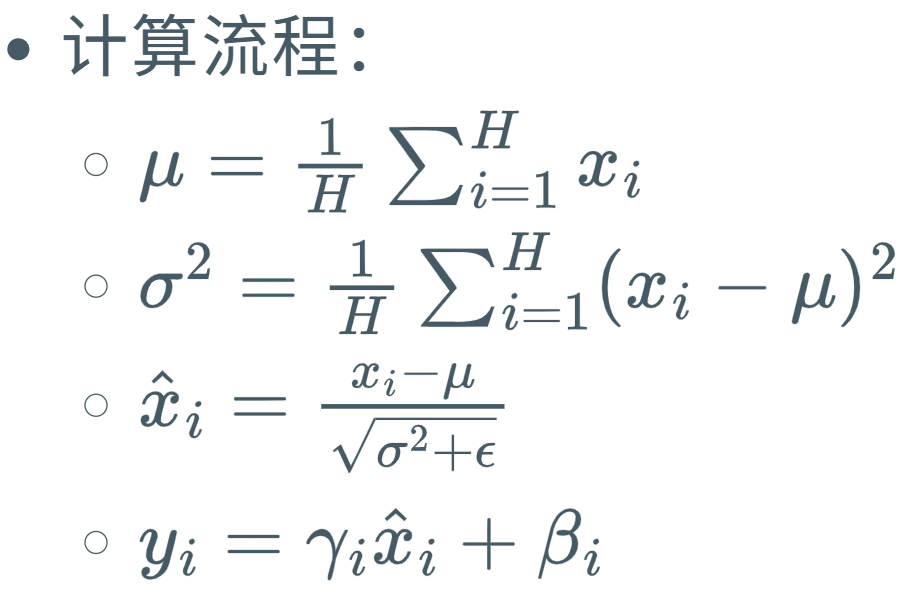
Layer Norm(层归一化):对单个样本的所有通道和空间维度统计均值和方差。类比:单个学生的所有科目成绩整体归一化。
-
两个可学习参数 灵活性;但进行求和比较麻烦。

-
Group Normalization(组归一化):将通道分成若干组,对每个组内的通道在单个样本的空间维度上统计均值和方差。类比:把科目分成 “文科组”“理科组”,对每个组内的科目成绩归一化。
RMSNorm -- Root Mean Square Layer Normalization
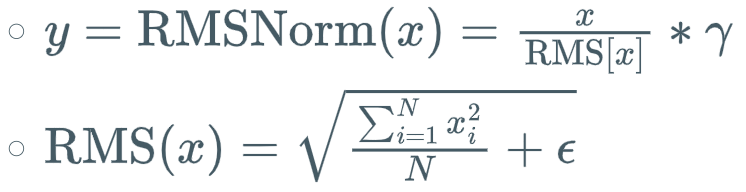
手搓
input =input.to(torch.float32)
variance =input.pow(2).mean(-1,keepdim=True)
hidden_states =input * torch.rsqrt(variance + variance_epsilon)直接调用 nn.RMSNorm
rms_norm = nn.RMSNorm(normalized_shape=512)# 随机生成一个输入张量 (batch_size=2, seq_len=10, feature_dim=512)
x = torch.randn(2, 10, 512)# 应用RMSNorm
output = rms_norm(x)4. 前馈神经网络 FFN & SwiGLU模块
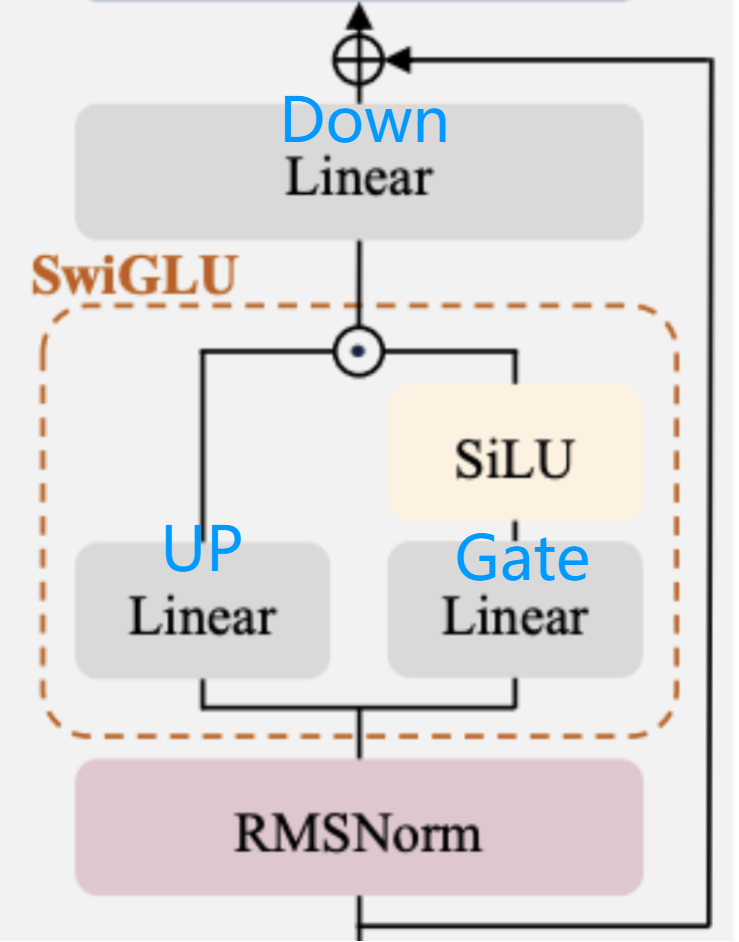 2048 -> 8192 -> 2048
2048 -> 8192 -> 2048

(mlp): LlamaMLP((gate_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=8192, bias=False)(up_proj): Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=8192, bias=False)(down_proj): Linear(in_features=8192, out_features=2048, bias=False)(act_fn): SiLU()
)pytorch - SiLU激活函数

上采样 * 门控&激活 -> 下采样 维度回投
down_proj = self.down_proj (self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x) )经典激活函数
增加模型非线性能力

Task1 多头注意力 - 多头乘法
朴素的矩阵乘法仅对 A1 中 batch_size 维度,针对每个序列索引i,都执行 O1[i] = A1[i] @ W1 计算,从而得到形状为 [b, s, e] 的张量 O1。
在多头矩阵乘法中,我们首先将输入张量 A1 和权重张量 W1 的 h 维度均分为 num_heads 个子维度(记为 nh,表示头的数量),由此得到形状为 [b, s, nh, hd] 的四维张量 A2 和形状为 [nh, hd, e] 的三维张量 W2。
接下来,对于 A2 中 batch_size 维度下的每个序列,遍历其 num_heads 维度上的每个 [s, hd] 矩阵,并将其与 W2 中 num_heads 维度下对应的 [hd, e] 矩阵进行乘法运算。通过多头并行计算,最终输出一个形状为 [b, s, nh, e] 的四维张量 O2。
1. 输入输出形状:
-
输入A1:
[b, s, h]= [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size] -
权重W1:
[h, e]= [hidden_size, embed_size] -
输出O2:
[b, s, nh, e]= [batch_size, seq_len, num_heads, embed_size]
2. 计算步骤:
-
维度分割:
-
将
h维度分割为nh个头,每个头维度为hd = h / nh -
A1 重塑为
[b, s, nh, hd] -
W1 重塑为
[nh, hd, e]
-
-
并行矩阵乘法:
-
对于每个头
i(0 ≤ i < nh):-
取 A1 的
[:, :, i, :]形状为[b, s, hd] -
取 W1 的
[i, :, :]形状为[hd, e] -
计算矩阵乘法:
[b, s, hd] @ [hd, e] = [b, s, e]
-
-
-
组合结果:
-
将所有头的输出堆叠在维度2,得到
[b, s, nh, e]
-
3. 代码实现
Args: input (torch.Tensor): # TODO中的输入输出规约
input tensor in the range of [-1, 1], with shape: [batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size]
weight (torch.Tensor): weight tensor in the range of [-1, 1], with shape: [hidden_size, embed_size]
num_heads (int): number of heads to split hidden_size
Returns: output (torch.Tensor): output tensor, with shape: [batch_size, seqlen, num_heads, embed_size]
def matmul_with_multi_head(input: torch.Tensor,weight: torch.Tensor,num_heads: int = 1,
) -> torch.Tensor:# 获取输入形状batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size = input.shapeembed_size = weight.shape[1]# 检查hidden_size是否能被num_heads整除if hidden_size % num_heads != 0:raise ValueError(f"hidden_size ({hidden_size}) must be divisible by num_heads ({num_heads})")# 计算每个头的维度head_dim = hidden_size // num_heads# 重塑输入张量: [b, s, h] -> [b, s, nh, hd]input_reshaped = input.view(batch_size, seq_len, num_heads, head_dim)# 重塑权重张量: [h, e] -> [nh, hd, e]weight_reshaped = weight.view(num_heads, head_dim, embed_size)# 使用einsum进行批量矩阵乘法# b: batch_size, s: seq_len, h: head_index, d: head_dim, e: embed_sizeoutput = torch.einsum('bshd,hde->bshe', input_reshaped, weight_reshaped)return outputTask2 多头注意力 - 只算重要性高的 + 梯度
1. 题目要求
在多头矩阵乘法的基础上,我们引入一个表示“重要性”的概率张量 P,其形状为 [b, s]。P 中的每个元素表示 A1 中对应位置的元素的重要程度。基于这个重要性概率,我们的目标是只对每个序列中的 “重要” 元素执行矩阵乘法运算。
( [b, s] -> t)重要元素总共有t 个,计算结果收集到输出张量 O3 中,形状为 [t, nh, e]。
如果提供了输出张量的可选梯度(记为 dO3,其形状与 O3 相同),我们还需要计算输入张量的梯度(记为 dA1,形状与 A1 相同)和权重张量的梯度(记为 dW1,形状与 W1 相同)。否则均返回 None。
2. 重要性筛选 [b, s] -> t
weight_reshaped 同Task1 分为多头;
def matmul_with_importance(input: torch.Tensor,weight: torch.Tensor,probs: torch.Tensor,grad_output: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,num_heads: int = 1,top_p: float = 1.0,top_k: Optional[int] = None,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[torch.Tensor]]:batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size = input.shapeembed_size = weight.shape[1]# 检查hidden_size是否能被num_heads整除if hidden_size % num_heads != 0:raise ValueError(f"hidden_size ({hidden_size}) must be divisible by num_heads ({num_heads})")head_dim = hidden_size // num_heads# 重塑权重张量: [h, e] -> [nh, hd, e]weight_reshaped = weight.view(num_heads, head_dim, embed_size)进行矩阵的与&操作,进行重要性高的筛选。
torch.topk 返回前k大的值和对应索引。
# 筛选重要的元素mask = torch.ones_like(probs, dtype=torch.bool)# 应用top-p筛选 (保留大于等于top_p的概率)if top_p < 1.0:top_p_mask = probs >= top_pmask = mask & top_p_mask # 矩阵与&一下# 应用top-k筛选if top_k is not None and top_k < seq_len:# 获取每个batch中top_k的概率索引_, topk_indices = torch.topk(probs, top_k, dim=1) # indices 前k的索引topk_mask = torch.zeros_like(probs, dtype=torch.bool)for i in range(batch_size):topk_mask[i, topk_indices[i]] = True # 把前k的索引位置置为Truemask = mask & topk_mask # 矩阵与&一下特判如果没有重要元素,返回空张量;要返回梯度 就返回0张量。
# 如果没有重要元素,返回空张量if len(batch_indices) == 0:empty_output = torch.empty(0, num_heads, embed_size,device=input.device, dtype=input.dtype)if grad_output is not None: # Task 3 要返回梯度 都零张量empty_grad_input = torch.zeros_like(input)empty_grad_weight = torch.zeros_like(weight)return empty_output, empty_grad_input, empty_grad_weightelse:return empty_output, None, Nonetorch.where 返回符合重要性的(b,s) 位置索引。
把索引对应的元素拿出来,拼成 t 个元素。再进行多头乘法。
# 获取筛选后的二维索引 (b,s) 对应非零位置 batch_indices, seq_indices = torch.where(mask)# 收集筛选后的输入selected_input = input[batch_indices, seq_indices] # [t, h]# 重塑输入: [t, h] -> [t, nh, hd]selected_input_reshaped = selected_input.view(-1, num_heads, head_dim)# 多头矩阵乘法: [t, nh, hd] @ [nh, hd, e] -> [t, nh, e]output = torch.einsum('tnh,nhd->tnd', selected_input_reshaped, weight_reshaped)# Task2: 如果没有梯度输出,直接返回结果if grad_output is None:return output, None, None3. 梯度计算
多头乘法算梯度
grad_input_selected = grad_output @ weight_reshaped^T维度: grad_output: [t, nh, e] weight_reshaped^T: [nh, e, hd] (对最后两个维度转置) 结果: [t, nh, hd]
# Task3: 如果有梯度输出,计算梯度# 检查grad_output形状是否正确expected_shape = (len(batch_indices), num_heads, embed_size)if grad_output.shape != expected_shape:raise ValueError(f"grad_output shape {grad_output.shape} doesn't match expected shape {expected_shape}")# 初始化梯度张量grad_input = torch.zeros_like(input)# 1. 计算输入梯度 (grad_input)# 原理: ∂L/∂input = ∂L/∂output * ∂output/∂input = grad_output * weight^T# weight_reshaped: [nh, hd, e] -> 转置为 [nh, e, hd]weight_T = weight_reshaped.transpose(1, 2) # [nh, e, hd]# 计算筛选位置的梯度: [t, nh, hd] = [t, nh, e] @ [nh, e, hd]grad_input_selected = torch.einsum('tne,neh->tnh', grad_output, weight_T)# 重塑为原始hidden_size维度: [t, nh, hd] -> [t, h]grad_input_selected_flat = grad_input_selected.reshape(-1, hidden_size)# 将梯度放回原始位置(只对筛选出的位置有梯度)grad_input[batch_indices, seq_indices] = grad_input_selected_flat# 2. 计算权重梯度 (grad_weight) # 原理: ∂L/∂weight = ∂L/∂output * ∂output/∂weight = input^T * grad_output # 计算每个头的权重梯度: [nh, hd, e] = [t, nh, hd]^T @ [t, nh, e]
# 2. 计算权重梯度 (grad_weight)# 原理: ∂L/∂weight = ∂L/∂output * ∂output/∂weight = input^T * grad_output# 计算每个头的权重梯度: [nh, hd, e] = [t, nh, hd]^T @ [t, nh, e]grad_weight_reshaped = torch.einsum('tnh,tne->nhe', selected_input_reshaped, grad_output)# 重塑回原始权重形状: [nh, hd, e] -> [h, e]grad_weight = grad_weight_reshaped.reshape(hidden_size, embed_size)return output, grad_input, grad_weight