育苗盘补苗路径规划研究_2.5
文章目录
- 第一个代码
- 第二个代码
- 代码逻辑摘要
- 1. 基础参数
- 2. 盘子生成与初始化
- 3. **固定列顺序算法 (fixed\_order\_algorithm)**
- 4. **贪心算法 (greedy\_algorithm)**
- 5. 绘图函数
- 6. 主程序对比 (`run_comparison()`)
- 对比
- 核心内容摘要:
- 贪心算法相较于固定列顺序算法的优点
- 未来算法比较
- 加模拟退火算法
- 混合算法框架
- 对比指标
- **启发式贪心算法** 和 **启发式贪心 + 模拟退火** 的原理和公式
- # 1. 启发式贪心 (Heuristic Greedy)
- **原理**
- **公式推导**
- # 2. 启发式贪心 + 模拟退火 (Heuristic Greedy + SA)
- **原理**
- **公式推导**
- **总代价**
- # 总结对比
- 代码见代码仓库
第一个代码
“自动移栽(取苗-放苗)”的模拟过程,包含目标盘(Target Plate)和供苗盘(Source Plate),
并采用 按列固定顺序取苗的算法。
代码整体逻辑
-
参数设定
- 定义了孔径、行列数、盘子间距、盘子尺寸等基础参数。
- 每个盘子就是一个带有行、列坐标的孔阵列。
-
生成盘子函数
generate_plate_positions:生成一个盘的所有孔坐标,并标记状态(默认"Normal")。initialize_target_plate:生成目标盘,并随机挑选 10~15 个孔设为"Empty"(需要填充)。initialize_source_plate:生成供苗盘,并随机挑选 10~15 个孔设为"Empty"(没有苗)。
-
固定列顺序算法(核心)
-
一次性初始化 供苗盘。
-
按照“列优先,列内从下到上”的顺序,生成一个全局的取苗序列。
-
不断生成新的目标盘:
-
找到目标盘上所有
"Empty"的孔(需要填充),排序(按行列)。 -
对每个空孔:
- 从供苗盘取出一个
"Normal"苗(按列顺序)。 - 走到供苗孔 → 再走到目标孔,完成移栽。
- 更新状态(供苗孔变
"Taken",目标孔变"Filled")。
- 从供苗盘取出一个
-
每个目标盘填完后,路径回到起点 (0,0)。
-
-
重复直到供苗盘没有苗可用。
-
-
路径与统计
- 记录每次移动的路径、累计的移动距离和耗时(简单用
time.time()模拟)。 - 统计完成的目标盘数量和剩余苗数。
- 记录每次移动的路径、累计的移动距离和耗时(简单用
-
可视化
plot_result:绘制供苗盘和目标盘的孔分布、路径和状态变化。- 空孔、填充孔、取走孔都用不同颜色和标记区分。
-
输出结果
- 打印总路径距离、总耗时、完成目标盘数量、剩余苗数。
代码模拟了一个 移栽机器人 的工作过程:
- 从供苗盘中 按列顺序取苗,
- 将苗移植到目标盘的 空孔,
- 计算并绘制路径,统计总距离、耗时和完成情况。
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random# -------------------------
# Base Parameters
# -------------------------
hole_diameter = 32 # Diameter of each hole
num_cols = 8 # Number of holes per row
num_rows = 16 # Number of rows
plate_spacing = 100 # Spacing between plates
plate_width = num_cols * hole_diameter
plate_height = num_rows * hole_diameter# -------------------------
# Generate Plate Positions
# -------------------------
def generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name):"""Generate coordinates for the holes on the plate, with x and y values."""positions = []for i in range(rows):for j in range(cols):positions.append({"plate": plate_name,"row": i + 1,"col": j + 1,"x": x0 + j * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"y": y0 + i * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"status": "Normal"})return positions# -------------------------
# Initialize Target Plate
# -------------------------
def initialize_target_plate(x0, y0, rows, cols):"""Initialize target plate, randomly fill 10-15 empty positions."""target_plate = generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, "Target Plate")# Randomly generate 10-15 empty holesnum_empty = random.randint(10, 15)empty_holes = sorted(random.sample(target_plate, num_empty), key=lambda k: (k["row"], k["col"]))# Mark these holes as "Empty"for hole in empty_holes:hole["status"] = "Empty"return target_plate, empty_holes# -------------------------
# Initialize Source Plate
# -------------------------
def initialize_source_plate(x0, y0, rows, cols):"""Initialize source plate, randomly fill 10-15 empty positions."""source_plate = generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, "Source Plate")# Randomly generate 10-15 empty holesnum_empty = random.randint(10, 15)empty_holes = sorted(random.sample(source_plate, num_empty), key=lambda k: (k["row"], k["col"]))# Mark these holes as "Empty"for hole in empty_holes:hole["status"] = "Empty"return source_plate, empty_holes# -------------------------
# Fixed Order Algorithm
# -------------------------
def fixed_order_algorithm():total_distance = 0total_time = 0completed_plates = 0last_plate_incomplete = 0current_pos = np.array([0, 0])# 初始化供苗盘(只生成一次)source_plate, empty_holes_source = initialize_source_plate(30 + plate_width + plate_spacing, 30, num_rows, num_cols)while True:# 每次循环只重新生成目标盘target_plate, empty_holes_target = initialize_target_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols)empty_indices_target = [(h["row"], h["col"]) for h in empty_holes_target]fixed_empty_holes = []for hole in target_plate:if (hole["row"], hole["col"]) in empty_indices_target:hole["status"] = "Empty"fixed_empty_holes.append(hole)# 按行列排序fixed_empty_holes.sort(key=lambda h: (h["row"], h["col"]))# 供苗盘可用苗(Normal 才能取,Empty 和 Taken 不能用)seedlings_by_row = {r: [] for r in range(1, num_rows + 1)}for s in source_plate:if s["status"] == "Normal":seedlings_by_row[s["row"]].append(s)for r in seedlings_by_row:seedlings_by_row[r].sort(key=lambda s: s["col"])path = [(0, 0)]start_time = time.time()# 填充目标盘for hole in fixed_empty_holes:row = hole["row"]if seedlings_by_row[row]:seedling = seedlings_by_row[row].pop(0)else:last_plate_incomplete = rowbreak# current -> seedlingpath.append((seedling["x"], seedling["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]))seedling["status"] = "Taken"# seedling -> holepath.append((hole["x"], hole["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]) - np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]]))hole["status"] = "Filled"current_pos = np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]])# 回到起点path.append((0, 0))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([0, 0]))end_time = time.time()total_time += end_time - start_timecompleted_plates += 1plot_result(path,target_plate,source_plate,f"Fixed Order Algorithm (Distance={total_distance:.2f}, Time={total_time:.10f}s)")if last_plate_incomplete > 0:breakremaining_seedlings = sum([1 for s in source_plate if s["status"] == "Normal"])return path, total_distance, total_time, completed_plates, last_plate_incomplete, remaining_seedlings, target_plate, source_plate# -------------------------
# Plotting Function
# -------------------------
def plot_result(path, target_plate, source_plate, title):"""Plot the allocation of target and source plates, display the path and status."""fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))ax.set_aspect('equal')# Plot target platefor hole in target_plate:if hole["status"] == "Empty":ax.text(hole["x"], hole["y"], "X", color="blue", fontsize=12, ha="center", va="center")elif hole["status"] == "Filled":ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=80, c="red", marker="o")else:ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=40, facecolors='none', edgecolors='blue')# Plot source platefor hole in source_plate:if hole["status"] == "Taken":ax.text(hole["x"], hole["y"], "X", color="red", fontsize=12, ha="center", va="center")elif hole["status"] == "Empty":ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=150, c="red", marker="o") # 初始空位 -> 大红点else:ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=40, facecolors='none', edgecolors='red')# Plot pathfor i in range(len(path) - 1):ax.annotate('', xy=path[i + 1], xytext=path[i],arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", color='green', lw=1.5))# Start point markerax.scatter(0, 0, s=100, c="black", marker="*", label="Start (0,0)")# Set plot parametersax.set_xlim(-50, plate_width * 2 + plate_spacing + 100)ax.set_ylim(-50, plate_height + 100)ax.set_xlabel("X / mm")ax.set_ylabel("Y / mm")ax.set_title(title)ax.legend()plt.tight_layout()plt.show()# -------------------------
# Main Program
# -------------------------
path_fixed, dist_fixed, time_fixed, completed_plates, last_plate_incomplete, remaining_seedlings, tp_fixed, sp_fixed = fixed_order_algorithm()# Output results
print("Total Path Distance =", dist_fixed)
print("Total Time =", time_fixed)
print("Completed Plates =", completed_plates)
print("Last Incomplete Row =", last_plate_incomplete)
print("Remaining Seedlings =", remaining_seedlings)第二个代码
对比两种移栽算法:固定列顺序算法 vs 贪心算法。
代码逻辑摘要
1. 基础参数
- 定义孔径、行数、列数、盘子间距和盘子大小。
- 一个“盘”就是带有行列坐标的孔阵列,每个孔有状态(
Normal / Empty / Taken / Filled)。
2. 盘子生成与初始化
generate_plate_positions():生成某个盘所有孔的坐标和状态(默认"Normal")。initialize_plate():初始化盘子,随机挑出 10~15 个空孔,标记为"Empty";也可以传入固定的空孔索引。
3. 固定列顺序算法 (fixed_order_algorithm)
-
生成供苗盘的 全局顺序:按列,从下到上。
-
循环生成目标盘:
- 找出所有空孔,按行列排序。
- 按照全局顺序依次取苗,填充目标盘的空孔。
- 路径计算:当前点 → 取苗孔 → 移栽孔 → 更新状态。
- 每个目标盘完成后回到 (0,0)。
-
统计总路径长度、耗时、完成的目标盘数量。
4. 贪心算法 (greedy_algorithm)
-
在每一步:
- 找到 离当前位置最近的苗。
- 从该苗出发,找 离它最近的空孔。
- 移栽并更新状态。
-
不断重复,直到所有苗或空孔用完。
-
同样统计总路径长度、耗时、完成的目标盘数量。
5. 绘图函数
-
plot_result():画出供苗盘、目标盘和路径:- 不同状态的孔用不同颜色/标记表示。
- 箭头显示路径。
- 起点 (0,0) 用黑色星号标记。
6. 主程序对比 (run_comparison())
-
初始化相同的供苗盘和目标盘空孔(保证公平比较)。
-
拷贝数据,分别交给 固定列顺序算法 和 贪心算法。
-
输出对比结果:
- 总路径距离
- 总耗时
- 完成的目标盘数
这段代码模拟了一个移栽机器人,用 两种策略把供苗盘的苗移植到目标盘的空孔里:
- 固定列顺序:按列逐个搬运,规则简单。
- 贪心算法:每次选择最近的苗和最近的孔,路径更短。
最后通过绘图和数据统计对比两种算法的效率(距离、时间、完成盘数)。
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import copy# -------------------------
# Base Parameters
# -------------------------
hole_diameter = 32
num_cols = 8
num_rows = 16
plate_spacing = 100
plate_width = num_cols * hole_diameter
plate_height = num_rows * hole_diameter# -------------------------
# Generate Plate Positions
# -------------------------
def generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name):positions = []for i in range(rows):for j in range(cols):positions.append({"plate": plate_name,"row": i + 1,"col": j + 1,"x": x0 + j * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"y": y0 + i * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"status": "Normal"})return positions# -------------------------
# Initialize Plate with Fixed Empty Holes
# -------------------------
def initialize_plate(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name, empty_indices=None):plate = generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name)if empty_indices is None:num_empty = random.randint(10, 15)empty_holes = random.sample(range(len(plate)), num_empty)else:empty_holes = empty_indicesfor idx in empty_holes:plate[idx]["status"] = "Empty"return plate, empty_holes# -------------------------
# Fixed Column-Order Algorithm (Multi Plates)
# -------------------------
def fixed_order_algorithm(source_plate, empty_indices_target):total_distance = 0total_time = 0completed_plates = 0current_pos = np.array([0, 0])path = []# 全局顺序:按列,从下到上column_order = []for c in range(1, num_cols + 1):col_seeds = [s for s in source_plate if s["col"] == c and s["status"] == "Normal"]col_seeds.sort(key=lambda s: s["row"])column_order.extend(col_seeds)seed_index = 0while seed_index < len(column_order):target_plate, _ = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate", empty_indices_target)fixed_empty_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]fixed_empty_holes.sort(key=lambda h: (h["row"], h["col"]))local_path = [(0, 0)]start_time = time.time()for hole in fixed_empty_holes:if seed_index >= len(column_order):breakseedling = column_order[seed_index]while seed_index < len(column_order) and seedling["status"] != "Normal":seed_index += 1if seed_index < len(column_order):seedling = column_order[seed_index]if seed_index >= len(column_order):break# current -> seedlinglocal_path.append((seedling["x"], seedling["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]))seedling["status"] = "Taken"# seedling -> holelocal_path.append((hole["x"], hole["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]) - np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]]))hole["status"] = "Filled"current_pos = np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]])seed_index += 1# 回到起点local_path.append((0, 0))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([0, 0]))end_time = time.time()total_time += end_time - start_timecompleted_plates += 1path.append(local_path)# 绘制每个目标盘结果plot_result(local_path, target_plate, source_plate,f"Fixed Order Plate {completed_plates} (Dist={total_distance:.2f}, Time={total_time:.5f}s)")return path, total_distance, total_time, completed_plates# -------------------------
# Greedy Algorithm (Multi Plates)
# -------------------------
def greedy_algorithm(source_plate, empty_indices_target):total_distance = 0total_time = 0completed_plates = 0current_pos = np.array([0, 0])path = []available_seedlings = [s for s in source_plate if s["status"] == "Normal"]while available_seedlings:target_plate, _ = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate", empty_indices_target)available_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]local_path = [(0, 0)]start_time = time.time()while available_seedlings and available_holes:# 找到最近的苗nearest_seedling = min(available_seedlings,key=lambda s: np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([s["x"], s["y"]])))local_path.append((nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]))# 找最近的空穴nearest_hole = min(available_holes,key=lambda h: np.linalg.norm(np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]) - np.array([h["x"], h["y"]])))local_path.append((nearest_hole["x"], nearest_hole["y"]))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]) - np.array([nearest_hole["x"], nearest_hole["y"]]))nearest_seedling["status"] = "Taken"nearest_hole["status"] = "Filled"current_pos = np.array([nearest_hole["x"], nearest_hole["y"]])available_seedlings = [s for s in source_plate if s["status"] == "Normal"]available_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]# 回到起点local_path.append((0, 0))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([0, 0]))end_time = time.time()total_time += end_time - start_timecompleted_plates += 1path.append(local_path)plot_result(local_path, target_plate, source_plate,f"Greedy Plate {completed_plates} (Dist={total_distance:.2f}, Time={total_time:.5f}s)")return path, total_distance, total_time, completed_plates# -------------------------
# Plotting Function
# -------------------------
def plot_result(path, target_plate, source_plate, title):fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(12, 8))ax.set_aspect('equal')# Target platefor hole in target_plate:if hole["status"] == "Empty":ax.text(hole["x"], hole["y"], "X", color="blue", fontsize=12, ha="center", va="center")elif hole["status"] == "Filled":ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=80, c="red", marker="o")else:ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=40, facecolors='none', edgecolors='blue')# Source platefor hole in source_plate:if hole["status"] == "Taken":ax.text(hole["x"], hole["y"], "X", color="red", fontsize=12, ha="center", va="center")elif hole["status"] == "Empty":ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=150, c="red", marker="o")else:ax.scatter(hole["x"], hole["y"], s=40, facecolors='none', edgecolors='red')# Pathfor i in range(len(path) - 1):ax.annotate('', xy=path[i + 1], xytext=path[i],arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", color='green', lw=1.5))ax.scatter(0, 0, s=100, c="black", marker="*", label="Start (0,0)")ax.set_xlim(-50, plate_width * 2 + plate_spacing + 100)ax.set_ylim(-50, plate_height + 100)ax.set_xlabel("X / mm")ax.set_ylabel("Y / mm")ax.set_title(title)ax.legend()plt.tight_layout()plt.show()# -------------------------
# Main Program
# -------------------------
def run_comparison():# 生成相同的随机空位source_plate, empty_indices_source = initialize_plate(30 + plate_width + plate_spacing, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Source Plate")_, empty_indices_target = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate")# 深拷贝,保证两个算法用相同数据source_plate_fixed = copy.deepcopy(source_plate)source_plate_greedy = copy.deepcopy(source_plate)# 固定列序算法_, dist_fixed, time_fixed, completed_fixed = fixed_order_algorithm(source_plate_fixed, empty_indices_target)# 贪心算法_, dist_greedy, time_greedy, completed_greedy = greedy_algorithm(source_plate_greedy, empty_indices_target)print("=== Result Comparison ===")print(f"Fixed Order -> Distance: {dist_fixed:.2f}, Time: {time_fixed:.5f}s, Plates: {completed_fixed}")print(f"Greedy -> Distance: {dist_greedy:.2f}, Time: {time_greedy:.5f}s, Plates: {completed_greedy}")if __name__ == "__main__":run_comparison()对比
移栽路径规划对比实验,比较 固定列序算法 和 贪心算法
核心内容摘要:
-
实验背景
- 模拟苗盘(Source Plate)和目标盘(Target Plate),每个盘有固定的孔洞阵列。
- 孔洞里有的空、有的正常,有苗的孔需要被移到目标盘的空孔中。
-
算法设计
- 固定列序算法(Fixed Order):按固定顺序(逐列,从下到上)依次取苗并填充目标盘空位。
- 贪心算法(Greedy):每次选择距离当前位置最近的苗孔,再将其放到距离最近的目标空孔。
-
指标统计
- 累计路径长度(total distance):机器人臂在取苗、移苗、回归起点过程中的移动距离总和。
- 完成目标盘数量与对应的累计路径长度。
-
实验流程
- 多次随机生成供苗盘和目标盘(含随机空孔位置)。
- 运行两种算法,记录每完成一个目标盘后的累计路径长度。
- 汇总 20 次实验结果,计算均值和标准差。
-
结果输出
- 绘制折线图,横轴为“完成的目标盘数”,纵轴为“累计路径长度”。
- 曲线包含 均值 ± 标准差,便于比较两种算法的稳定性与效率。
- 标题中还显示了源盘和目标盘的平均空孔数。
👉 总体来说,这个程序用于验证 固定顺序搬运 vs 贪心搬运 的效率差异,并可视化对比实验结果。
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import random
import copy# -------------------------
# Base Parameters
# -------------------------
hole_diameter = 32
num_cols = 8
num_rows = 16
plate_spacing = 100
plate_width = num_cols * hole_diameter
plate_height = num_rows * hole_diameter# -------------------------
# Generate Plate Positions
# -------------------------
def generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name):positions = []for i in range(rows):for j in range(cols):positions.append({"plate": plate_name,"row": i + 1,"col": j + 1,"x": x0 + j * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"y": y0 + i * hole_diameter + hole_diameter / 2,"status": "Normal"})return positions# -------------------------
# Initialize Plate
# -------------------------
def initialize_plate(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name, empty_indices=None):plate = generate_plate_positions(x0, y0, rows, cols, plate_name)if empty_indices is None:num_empty = random.randint(10, 15)empty_holes = random.sample(range(len(plate)), num_empty)else:empty_holes = empty_indicesfor idx in empty_holes:plate[idx]["status"] = "Empty"return plate, empty_holes# -------------------------
# Fixed Column-Order Algorithm (Multi Plates)
# -------------------------
def fixed_order_algorithm(source_plate, empty_indices_target):total_distance = 0completed_plates = 0current_pos = np.array([0, 0])dist_progress = []# 全局顺序:按列,从下到上column_order = []for c in range(1, num_cols + 1):col_seeds = [s for s in source_plate if s["col"] == c and s["status"] == "Normal"]col_seeds.sort(key=lambda s: s["row"])column_order.extend(col_seeds)seed_index = 0while seed_index < len(column_order):target_plate, _ = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate", empty_indices_target)fixed_empty_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]fixed_empty_holes.sort(key=lambda h: (h["row"], h["col"]))for hole in fixed_empty_holes:if seed_index >= len(column_order):breakseedling = column_order[seed_index]while seed_index < len(column_order) and seedling["status"] != "Normal":seed_index += 1if seed_index < len(column_order):seedling = column_order[seed_index]if seed_index >= len(column_order):break# 移动 current -> seedlingtotal_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]))seedling["status"] = "Taken"# 移动 seedling -> holetotal_distance += np.linalg.norm(np.array([seedling["x"], seedling["y"]]) - np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]]))hole["status"] = "Filled"current_pos = np.array([hole["x"], hole["y"]])seed_index += 1# 回到起点total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([0, 0]))current_pos = np.array([0, 0])completed_plates += 1dist_progress.append(total_distance)return dist_progress# -------------------------
# Greedy Algorithm (Multi Plates)
# -------------------------
def greedy_algorithm(source_plate, empty_indices_target):total_distance = 0completed_plates = 0current_pos = np.array([0, 0])dist_progress = []available_seedlings = [s for s in source_plate if s["status"] == "Normal"]while available_seedlings:target_plate, _ = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate", empty_indices_target)available_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]while available_seedlings and available_holes:nearest_seedling = min(available_seedlings,key=lambda s: np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([s["x"], s["y"]])))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]))nearest_hole = min(available_holes,key=lambda h: np.linalg.norm(np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]) - np.array([h["x"], h["y"]])))total_distance += np.linalg.norm(np.array([nearest_seedling["x"], nearest_seedling["y"]]) - np.array([nearest_hole["x"], nearest_hole["y"]]))nearest_seedling["status"] = "Taken"nearest_hole["status"] = "Filled"current_pos = np.array([nearest_hole["x"], nearest_hole["y"]])available_seedlings = [s for s in source_plate if s["status"] == "Normal"]available_holes = [h for h in target_plate if h["status"] == "Empty"]# 回到起点total_distance += np.linalg.norm(current_pos - np.array([0, 0]))current_pos = np.array([0, 0])completed_plates += 1dist_progress.append(total_distance)return dist_progress# -------------------------
# Single Experiment
# -------------------------
def run_single_experiment():# 生成供苗盘 & 目标盘空位source_plate, empty_indices_source = initialize_plate(30 + plate_width + plate_spacing, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Source Plate")_, empty_indices_target = initialize_plate(30, 30, num_rows, num_cols, "Target Plate")# 记录空位数量source_empty_count = len(empty_indices_source)target_empty_count = len(empty_indices_target)# 固定列序fixed_progress = fixed_order_algorithm(copy.deepcopy(source_plate), empty_indices_target)# 贪心greedy_progress = greedy_algorithm(copy.deepcopy(source_plate), empty_indices_target)return fixed_progress, greedy_progress, source_empty_count, target_empty_count# -------------------------
# Multiple Experiments with Averaging
# -------------------------
def run_multiple_experiments(n=20):all_fixed = []all_greedy = []source_empty_counts = []target_empty_counts = []for _ in range(n):fixed_prog, greedy_prog, src_empty, tgt_empty = run_single_experiment()all_fixed.append(fixed_prog)all_greedy.append(greedy_prog)source_empty_counts.append(src_empty)target_empty_counts.append(tgt_empty)# 对齐长度max_len = max(max(len(f) for f in all_fixed), max(len(g) for g in all_greedy))fixed_array = np.full((n, max_len), np.nan)greedy_array = np.full((n, max_len), np.nan)for i in range(n):fixed_array[i, :len(all_fixed[i])] = all_fixed[i]greedy_array[i, :len(all_greedy[i])] = all_greedy[i]# 均值和标准差fixed_mean = np.nanmean(fixed_array, axis=0)fixed_std = np.nanstd(fixed_array, axis=0)greedy_mean = np.nanmean(greedy_array, axis=0)greedy_std = np.nanstd(greedy_array, axis=0)# 绘制均值 ± 标准差曲线plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))x = np.arange(1, max_len+1)plt.plot(x, fixed_mean, label="Fixed Order", color="blue")plt.fill_between(x, fixed_mean-fixed_std, fixed_mean+fixed_std, color="blue", alpha=0.2)plt.plot(x, greedy_mean, label="Greedy", color="red")plt.fill_between(x, greedy_mean-greedy_std, greedy_mean+greedy_std, color="red", alpha=0.2)plt.xlabel("Number of Target Plates Completed")plt.ylabel("Cumulative Path Distance (mm)")plt.title(f"Average over {n} Experiments\n"f"Source empty avg={np.mean(source_empty_counts):.1f}, "f"Target empty avg={np.mean(target_empty_counts):.1f}")plt.legend()plt.grid(True)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()# -------------------------
# Run
# -------------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":run_multiple_experiments(n=20)
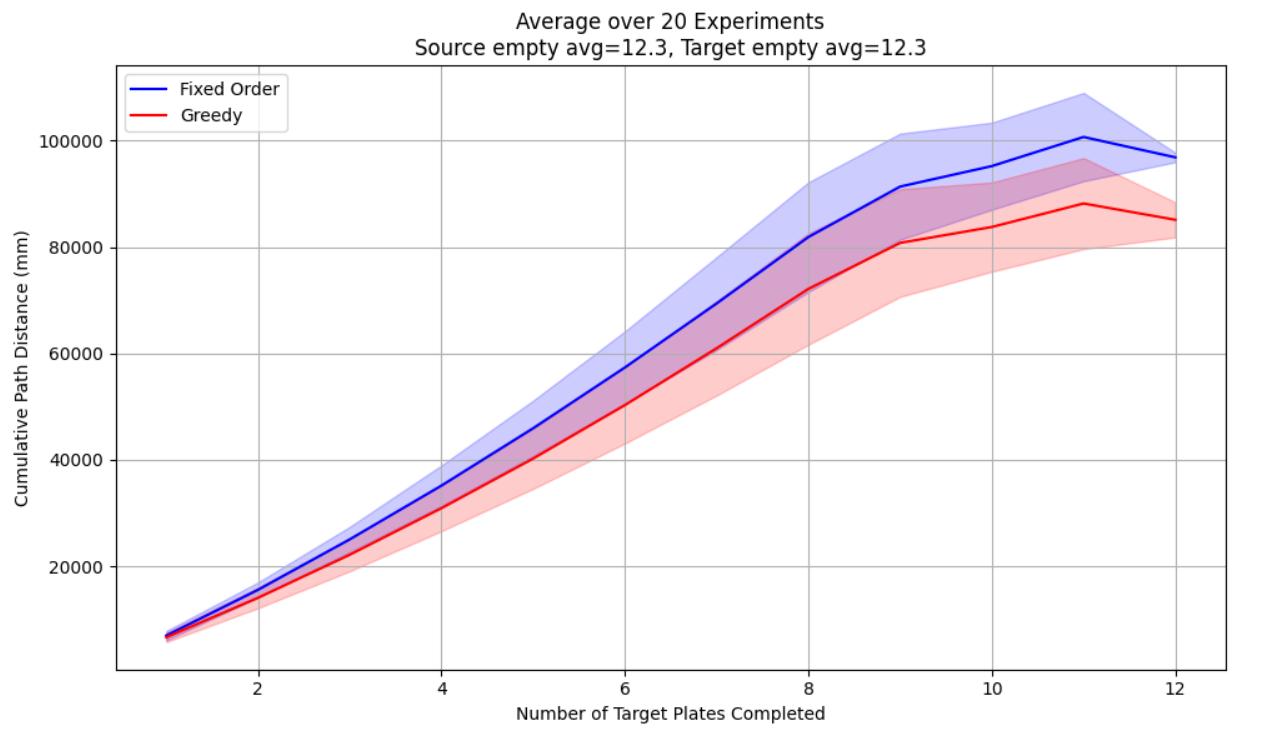
贪心算法相较于固定列顺序算法的优点
路径更短
固定列顺序可能会“绕远路”,因为它严格按列走。
贪心会优先选择最近的苗孔/目标孔,减少不必要的移动。
效率更高
因为路径缩短,累计距离和时间消耗更小。
更贴近实际自动化机械臂/机器人需要的“节能”操作。
自适应性强
固定顺序不考虑孔的实际分布(比如供苗孔正好在目标孔旁边,仍要等到顺序轮到)。
贪心可以动态调整,随时根据当前坐标选择最优。
利用资源更均衡
固定顺序可能导致某些供苗盘区域很快被取空,导致后续操作都要跨大范围移动。
贪心倾向于“就近取苗”,自然会让供苗区域消耗得更均匀。
未来算法比较
| 算法 | 核心思路 | 优点 | 缺点 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 固定列顺序 | 按列优先、列内自下而上依次取苗、填孔 | 简单、可预测、实现容易 | 路径可能很长、效率低、不能适应随机空孔 | 规则化实验、对效率要求不高的情况 |
| 贪心 (Greedy) | 每次选择最近的供苗孔,再选择最近的目标孔 | 路径更短,效率比固定顺序高,自适应性强 | 只考虑局部最优,可能导致整体路径不优 | 动态目标盘、需要一定效率的情况 |
| 批量规划 (TSP简化版) | 一次选定多个目标孔,按近似最短路径顺序完成 | 路径更顺滑,减少来回跑,全局效率高 | 算法复杂度高,需批次划分逻辑 | 任务量大、对效率要求极高的自动化 |
| 启发式贪心 (A*思路) | 选择时考虑“当前位置→苗孔+苗孔→目标孔+未来代价” | 兼顾当前与未来,避免局部最优,实时性好 | 启发函数需要设计,仍非绝对最优 | 动态任务、需要平衡效率与计算成本 |
加模拟退火算法
启发式贪心 + 模拟退火(SA)就是 实时性 + 全局优化 的组合,可以写成这样:
混合算法框架
-
启发式贪心阶段
- 根据当前位置、苗孔 → 目标孔距离 + 启发式“未来代价”
- 快速生成一条“可行路径”
- 保证实时性(系统马上能用)
-
模拟退火阶段
- 以启发式贪心的结果作为初始解
- 在后台运行,尝试局部交换路径(比如调整访问顺序)
- 温度逐渐下降,少量接受“更差解”,避免局部最优
- 得到更短的路径
-
动态更新
- 如果 SA 找到更优解 → 更新给执行系统
- 如果来不及优化 → 继续用原来的启发式贪心路径,保证不会卡住
对比指标
我们可以比较三方面:
-
路径长度
- 固定列顺序(基线,最差)
- 贪心(改进)
- 启发式贪心(更好)
- 启发式贪心 + 模拟退火(最优或接近最优)
-
算法运行时间
- 固定列顺序:O(n),非常快
- 贪心:O(n²) 左右(找最近点)
- 启发式贪心:O(n²),但比单纯贪心更聪明
- 启发式贪心 + SA:O(n²) + O(iter × swap),取决于迭代次数
-
实时性 vs 全局性
- 启发式贪心:实时可用
- SA:慢,但后台可优化
- 混合策略:前台保证可执行,后台逐步改进
启发式贪心 + 模拟退火:
- 优点:路径最短(接近全局最优),实时性好
- 缺点:计算时间更长(但后台可容忍)
- 创新点:把实时启发式和全局优化结合,兼顾速度与质量,非常适合论文/项目展示
启发式贪心算法 和 启发式贪心 + 模拟退火 的原理和公式
# 1. 启发式贪心 (Heuristic Greedy)
原理
-
普通贪心只看 当前位置 → 候选点的距离,容易陷入局部最优。
-
启发式贪心引入“未来代价”估计,即:
不仅考虑当前位置到候选点的距离,还考虑候选点继续走向其他未访问点的潜在开销。实际是一种全局算法
公式推导
设:
- 当前点:ccc
- 候选点集(未访问):U={q1,q2,…,qm}U = \{q_1, q_2, \dots, q_m\}U={q1,q2,…,qm}
- 距离函数:
d(p,q)=(xp−xq)2+(yp−yq)2d(p, q) = \sqrt{(x_p - x_q)^2 + (y_p - y_q)^2} d(p,q)=(xp−xq)2+(yp−yq)2
启发式代价函数:
h(c,q)=d(c,q)+minr∈U∖{q}d(q,r)h(c, q) = d(c, q) + \min_{r \in U \setminus \{q\}} d(q, r) h(c,q)=d(c,q)+r∈U∖{q}mind(q,r)
解释:
- d(c,q)d(c, q)d(c,q):当前位置到候选点的即时开销
- minr∈U∖{q}d(q,r)\min_{r \in U \setminus \{q\}} d(q, r)minr∈U∖{q}d(q,r):候选点到未来最近点的估计开销
选择规则:
q∗=argminq∈Uh(c,q)q^* = \arg\min_{q \in U} h(c, q) q∗=argq∈Uminh(c,q)
总代价(路径长度):
Lheur=∑i=0∣π∣−2d(πi,πi+1)L_{\text{heur}} = \sum_{i=0}^{|\pi|-2} d(\pi_i, \pi_{i+1}) Lheur=i=0∑∣π∣−2d(πi,πi+1)
其中 π=[p0,q1,q2,…,qm,p0]\pi = [p_0, q_1, q_2, \dots, q_m, p_0]π=[p0,q1,q2,…,qm,p0] 表示完整路径。
# 2. 启发式贪心 + 模拟退火 (Heuristic Greedy + SA)
原理
- 启发式贪心生成一条“较优”的初始解 π0\pi_0π0。
- 模拟退火 (SA) 在邻域中搜索,通过“有概率接受坏解”的机制跳出局部最优,逐步接近全局最优。
公式推导
- 初始解
π0=HeuristicGreedy(p0,U)\pi_0 = \text{HeuristicGreedy}(p_0, U) π0=HeuristicGreedy(p0,U)
-
邻域生成
随机交换路径中两个位置 i,ji, ji,j,得到新路径 π′\pi'π′。 -
代价差
ΔE=L(π′)−L(π)\Delta E = L(\pi') - L(\pi) ΔE=L(π′)−L(π)
- 接受概率
P(π→π′)={1,ΔE≤0exp(−ΔET),ΔE>0P(\pi \to \pi') = \begin{cases} 1, & \Delta E \leq 0 \\ \exp\left(-\dfrac{\Delta E}{T}\right), & \Delta E > 0 \end{cases} P(π→π′)=⎩⎨⎧1,exp(−TΔE),ΔE≤0ΔE>0
- 温度更新
Tk+1=α⋅Tk(0<α<1)T_{k+1} = \alpha \cdot T_k \quad (0 < \alpha < 1) Tk+1=α⋅Tk(0<α<1)
- 终止条件
当温度 T<TminT < T_{\min}T<Tmin 或迭代次数达到上限时停止,输出当前最优解 π∗\pi^*π∗。
总代价
LSA=∑i=0∣π∗∣−2d(πi∗,πi+1∗)L_{\text{SA}} = \sum_{i=0}^{|\pi^*|-2} d(\pi^*_i, \pi^*_{i+1}) LSA=i=0∑∣π∗∣−2d(πi∗,πi+1∗)
# 总结对比
| 算法 | 选择公式 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 启发式贪心 | q∗=argminq∈U{d(c,q)+minrd(q,r)}q^* = \arg\min_{q \in U} \{ d(c,q) + \min_{r} d(q,r) \}q∗=argminq∈U{d(c,q)+minrd(q,r)} | 快速、实时性好,优于单纯贪心 |
| 启发式贪心 + SA | 以启发式贪心路径为初始解,用 SA 改进 | 路径最优或接近全局最优,代价是计算时间增加 |
