ASP.NET Core MVC 路由逻辑初探
前言
说一下是怎么控制界面显示的,边用边写,看别人的文章大多太学术,以下是我看了一些视频教程后,浅显的理解,希望可以帮助新手同学学习。
新建的项目的结构:
在Program.cs中,框架创建了默认路由:
app.MapControllerRoute(name: "default",pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");其中各个属性说明:
name表示路由名称,默认值为default。
pattern 为匹配模板,默认值为"{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"。其中默认controller=Home,表示缺省值为HomeController,action=Index,表示默认缺省值为Index。id后面的?表示为可空类型,可以根据需要来填写。
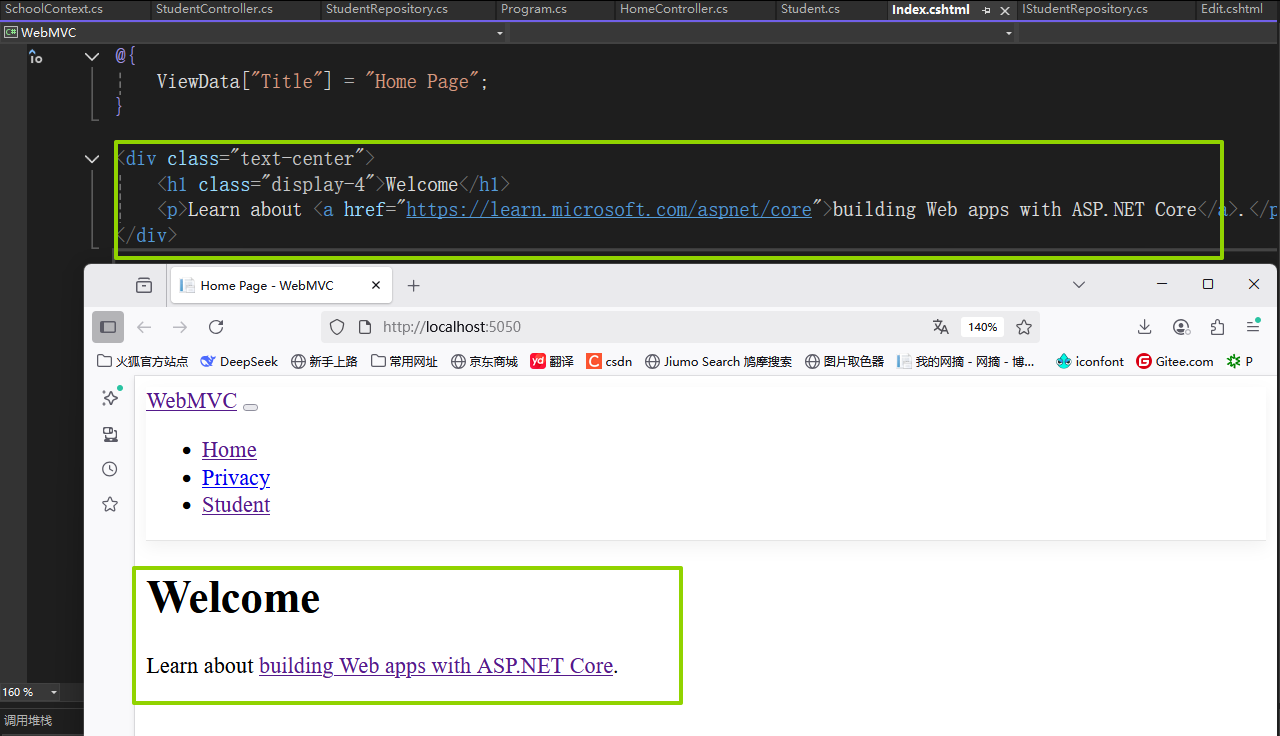
就是启动当前程序会显示项目Views/Home/Index.cshtml文件:
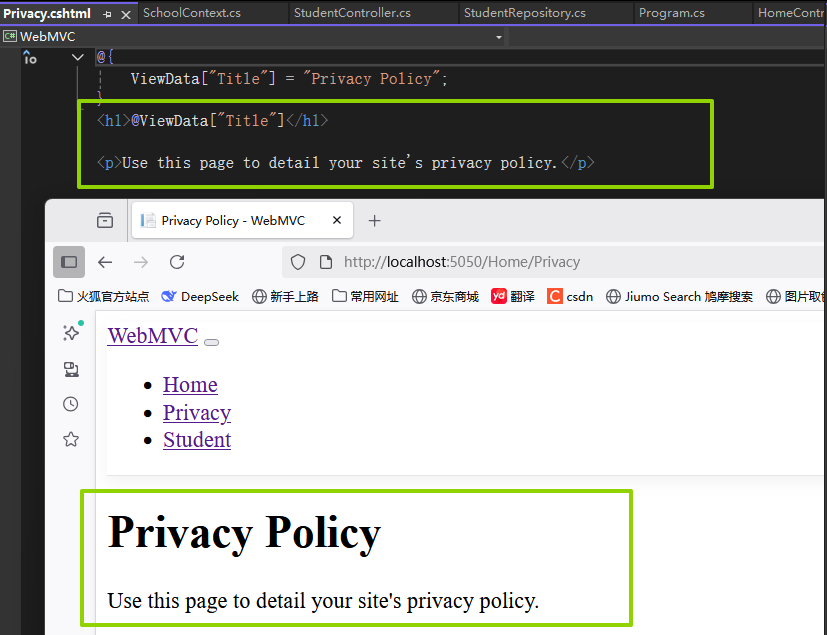
点击Privacy会显示Views/Home/Pricacy.cshtml文件:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
结合项目结构,可以发现Controller文件(如HomeController) 和 Views下的界面子文件夹有一个对应关系(如Views下的Home文件夹)。
打开HomeController类查看:
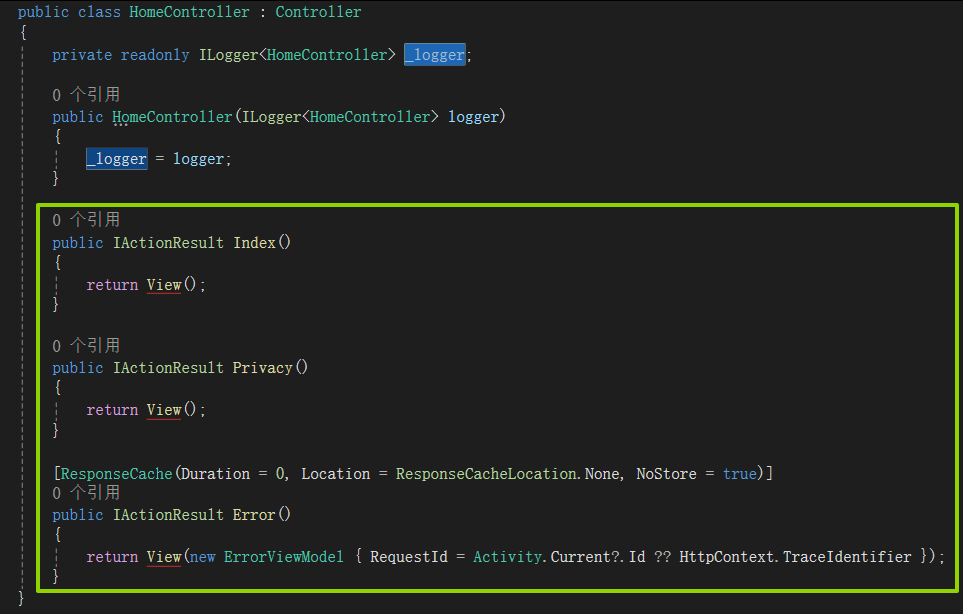
其中的方法,如Index、Privacy又对应上了Views下的Home文件夹中的Index.cshtml和Privacy.cshtml界面。(其中Error方法应该属于特殊情况,先不探讨。)
有了这些规律,再结合前面的匹配模板"{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}",得出MVC最基本的界面导航就是由一个controller的类名(可以省略后面的Controller,比如HomeController写成Home),和这个controller里面编写的方法(针对于实现界面显示的方法统称为Action)确认的。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
针对这个结论,写个新界面演示一下:
我会在主界面上添加一个按钮,点击这个按钮会显示我创建的一个新界面,上面有条目列表。
新建实体:
public class Student
{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public string Class { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }public string Sex { get; set; }
}模仿数据库提供数据源:
IStudentRepository:
public interface IStudentRepository
{DbSet<Student> List();Student Get(int id);Task<bool> Add(Student student);Task<bool> Update(Student student);Task<bool> Delete(int id);
}实现:
public class StudentRepository : IStudentRepository
{private readonly SchoolContext _context;public StudentRepository(SchoolContext context){_context = context;_context.Initialize();}public Task<bool> Add(Student student){Students.Add(student);return Task.FromResult(true);}public Task<bool> Delete(int id){var stu = Students.FirstOrDefault(s => s.Id == id);if (stu != null){Students.Remove(stu);}return Task.FromResult(true);}public Student Get(int id){return Students.FirstOrDefault(s => s.Id == id);}public DbSet<Student> Students => _context.Students;// 或者作为属性public DbSet<Student> List() { return _context.Students; }public Task<bool> Update(Student student){var stu = Students.FirstOrDefault(s => s.Id == student.Id);if (stu != null){Students.Remove(stu);}//Students.Add(student);return Task.FromResult(true);}
}数据源SchoolContext :
public class SchoolContext : DbContext
{public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder){optionsBuilder.UseInMemoryDatabase("TestDatabase"); // 使用内存数据库// 或者使用其他数据库:optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("你的连接字符串");}// 初始化数据的方法public void Initialize(){if (!Students.Any()){Students.AddRange(new Student { Id = 1, Name = "小红", Age = 10, Class = "1班", Sex = "女" },new Student { Id = 2, Name = "小明", Age = 11, Class = "2班", Sex = "男" },new Student { Id = 3, Name = "小强", Age = 12, Class = "3班", Sex = "男" });SaveChanges();}}
}新建Controller:
public class StudentController : Controller{//public IActionResult Index()//{// return View();//}private readonly IStudentRepository _studentRepository;public StudentController(IStudentRepository studentRepository){_studentRepository = studentRepository;}// GETpublic async Task<IActionResult> Index(){var a = _studentRepository.List().ToListAsync();return View(await _studentRepository.List().ToListAsync());}public async Task<IActionResult> Create(){return View();}// GET: Students/Edit/5public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(int? id){if (id == null){return NotFound();}var movie = await _studentRepository.List().FindAsync(id);if (movie == null){return NotFound();}return View(movie);}// POST: Students/Edit/5// To protect from overposting attacks, enable the specific properties you want to bind to.// For more details, see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=317598.[HttpPost][ValidateAntiForgeryToken]public async Task<IActionResult> Edit(int id, [Bind("Id,Name,Class,Age,Sex")] Student movie){if (id != movie.Id){return NotFound();}if (ModelState.IsValid){try{await _studentRepository.Update(movie);}catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException){throw;}return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));}return View(movie);}// GET: Students/Details/5public async Task<IActionResult> Details(int? id){if (id == null){return NotFound();}var movie = await _studentRepository.List().FirstOrDefaultAsync(m => m.Id == id);if (movie == null){return NotFound();}return View(movie);}// GET: Students/Delete/5public async Task<IActionResult> Delete(int? id){if (id == null){return NotFound();}var movie = await _studentRepository.List().FirstOrDefaultAsync(m => m.Id == id);if (movie == null){return NotFound();}return View(movie);}// POST: Students/Delete/5[HttpPost, ActionName("Delete")][ValidateAntiForgeryToken]public async Task<IActionResult> DeleteConfirmed(int id){var movie = await _studentRepository.List().FindAsync(id);if (movie != null){_studentRepository.List().Remove(movie);}//await _context.SaveChangesAsync();return RedirectToAction(nameof(Index));}}新建对应界面:
我贴一下Student/Index.cshtml的界面:
@model IEnumerable<WebMVC.Models.Student>@{ViewData["Title"] = "Student";
}<h1>Index</h1><p><a asp-action="Create">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table"><thead><tr><th>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Id)</th><th>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Name)</th><th>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Class)</th><th>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Age)</th><th>@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.Sex)</th></tr></thead><tbody>@foreach (var item in Model) {<tr><td>@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Id)</td><td>@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)</td><td>@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Class)</td><td>@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Age)</td><td>@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Sex)</td><td><a asp-action="Edit" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Edit</a> |<a asp-action="Details" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Details</a> |<a asp-action="Delete" asp-route-id="@item.Id">Delete</a></td></tr>}</tbody>
</table>
其他的界面大同小异,不过要另外学习razor知识
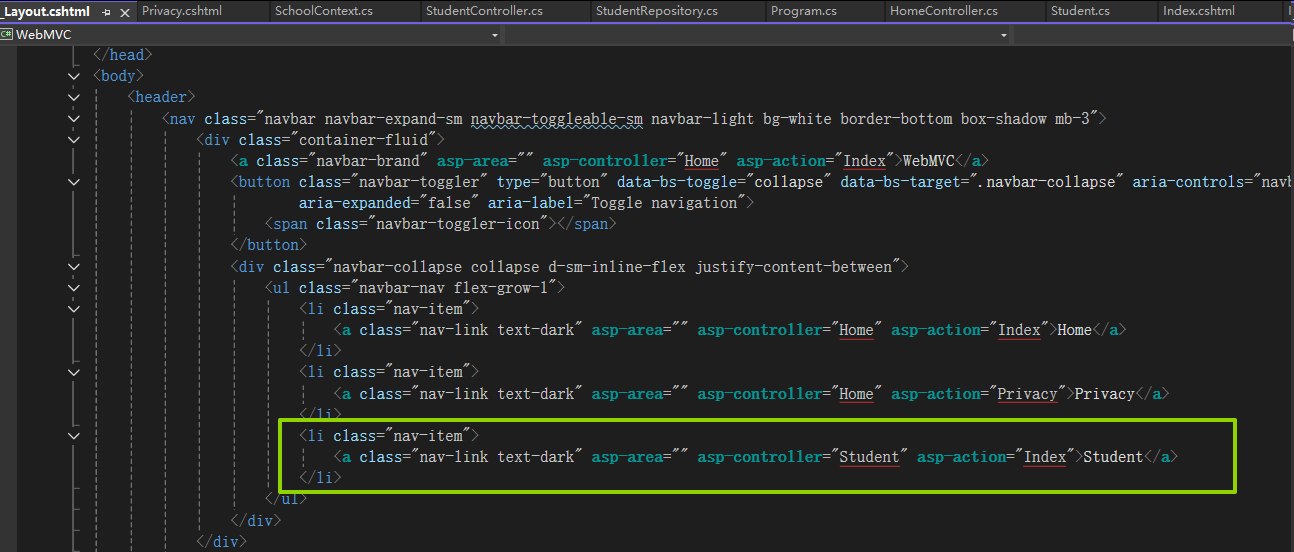
_Layout.cshtml文件添加锚点标签:
到这里项目最后的文件结构:
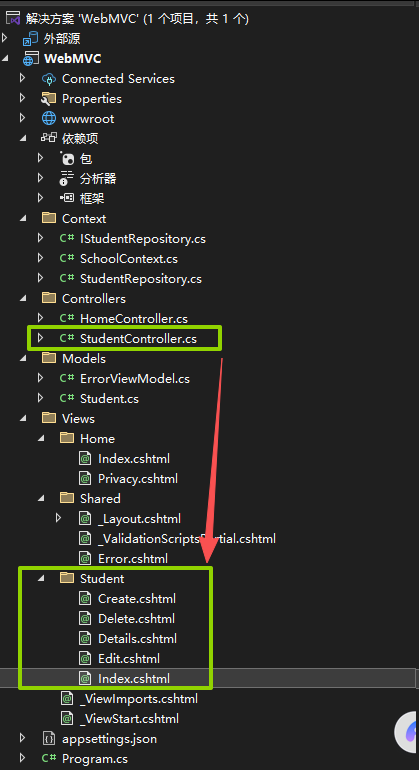
Controller和Views对应,就是MVC中的V和C。
启动:
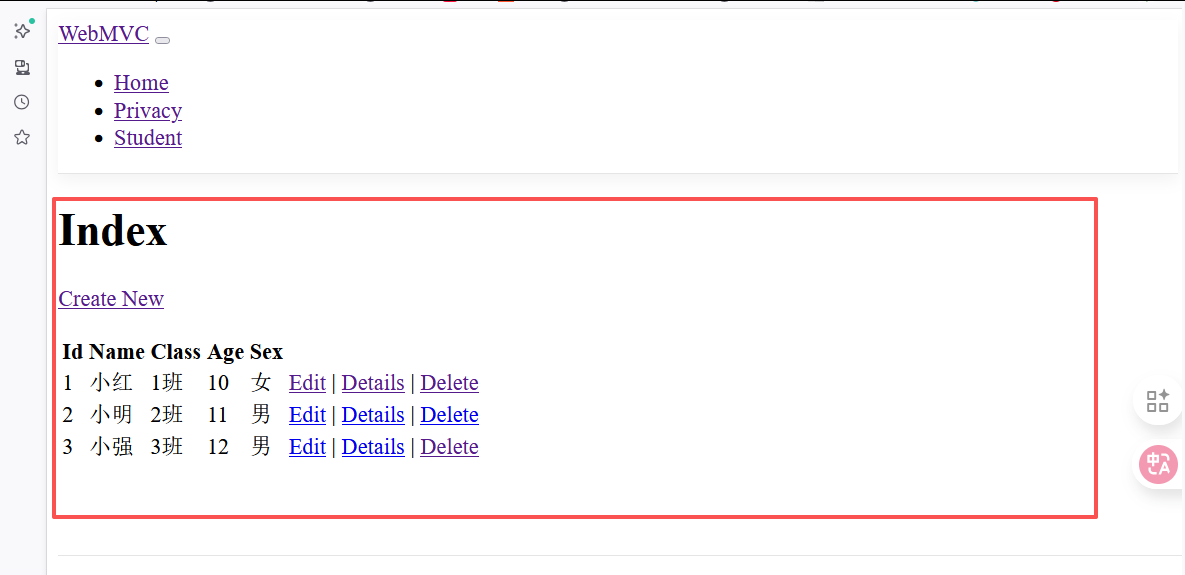
点击Student标签

显示:
一点个人浅见,未必周全,权当抛砖引玉。若有疏漏之处,还请大家一起指正讨论。
