区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(5)

Conference:International World Wide Web Conference (WWW)
CCF level:CCF A
Categories:交叉/综合/新兴
Year:2025
Conference time:Sydney, Australia April - 2 May 2025
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(1)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(2)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(3)
区块链论文速读 CCF A--WWW 2025(4)
17
Title:
Private Order Flows and Builder Bidding Dynamics: The Road to Monopoly in Ethereum's Block Building Market
私人订单流和建造者竞价动态:以太坊区块建造市场的垄断之路
Authors:

Key words:
Ethereum, Builder market, Private Order Flow, Centralization, Monopoly
以太坊、建造者市场、私人订单流、中心化、垄断
Abstract:
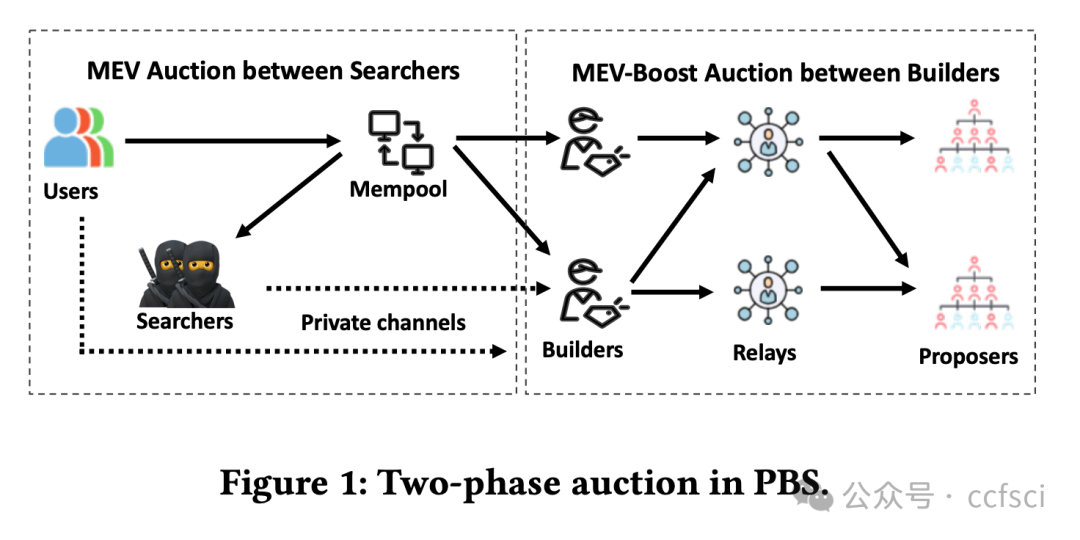
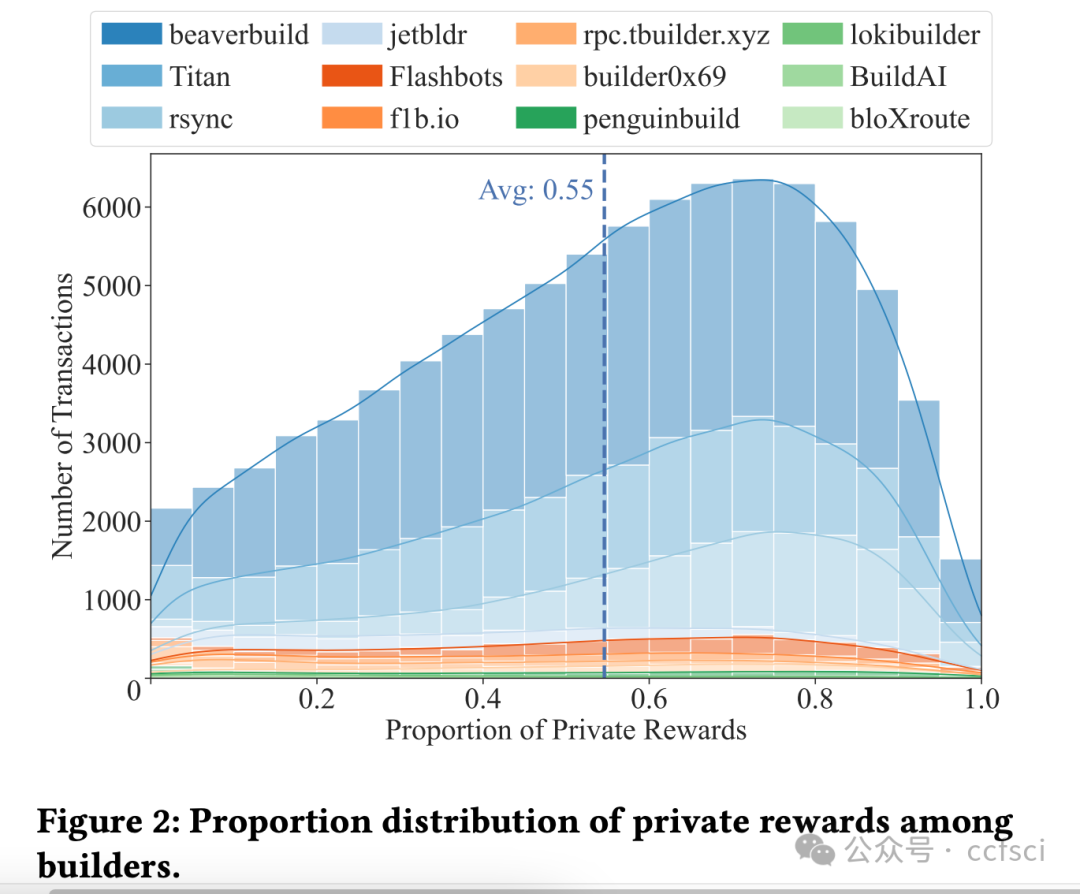
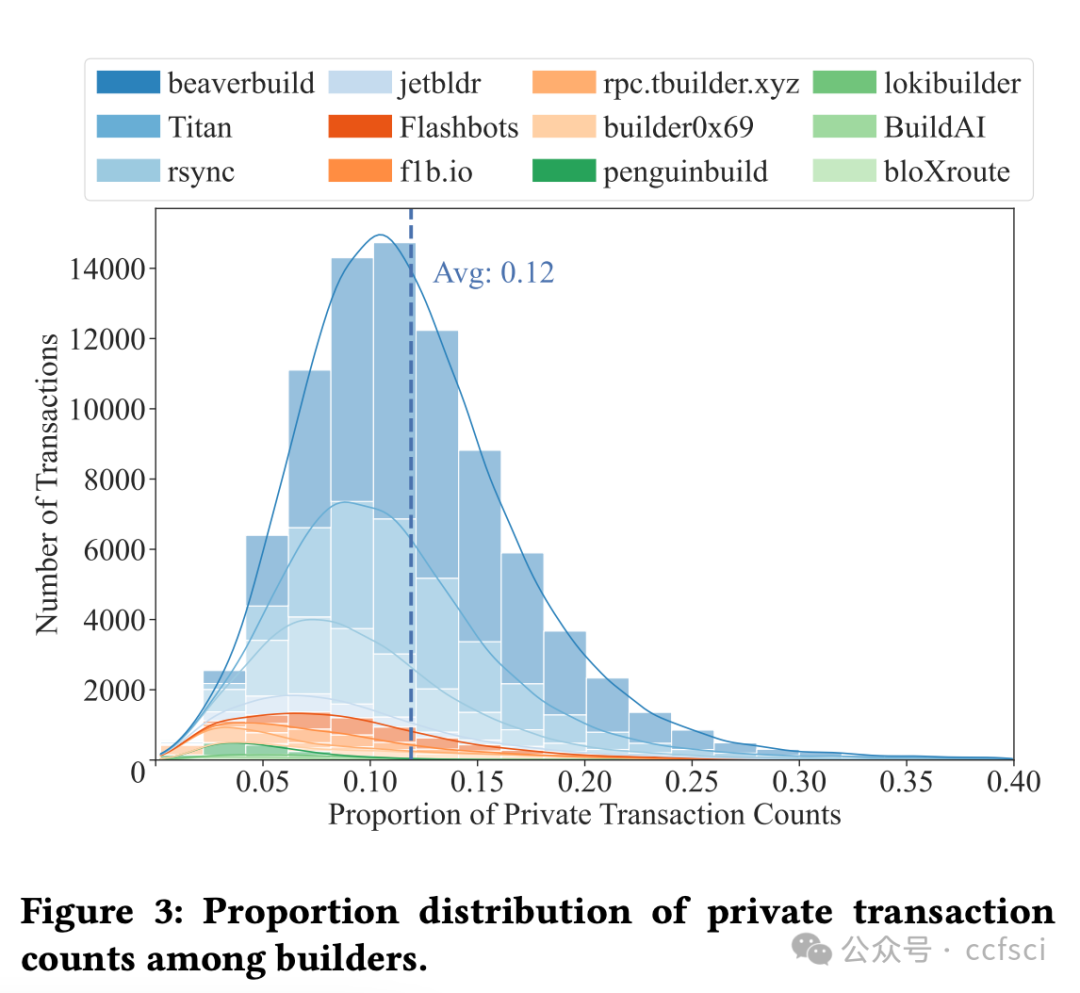
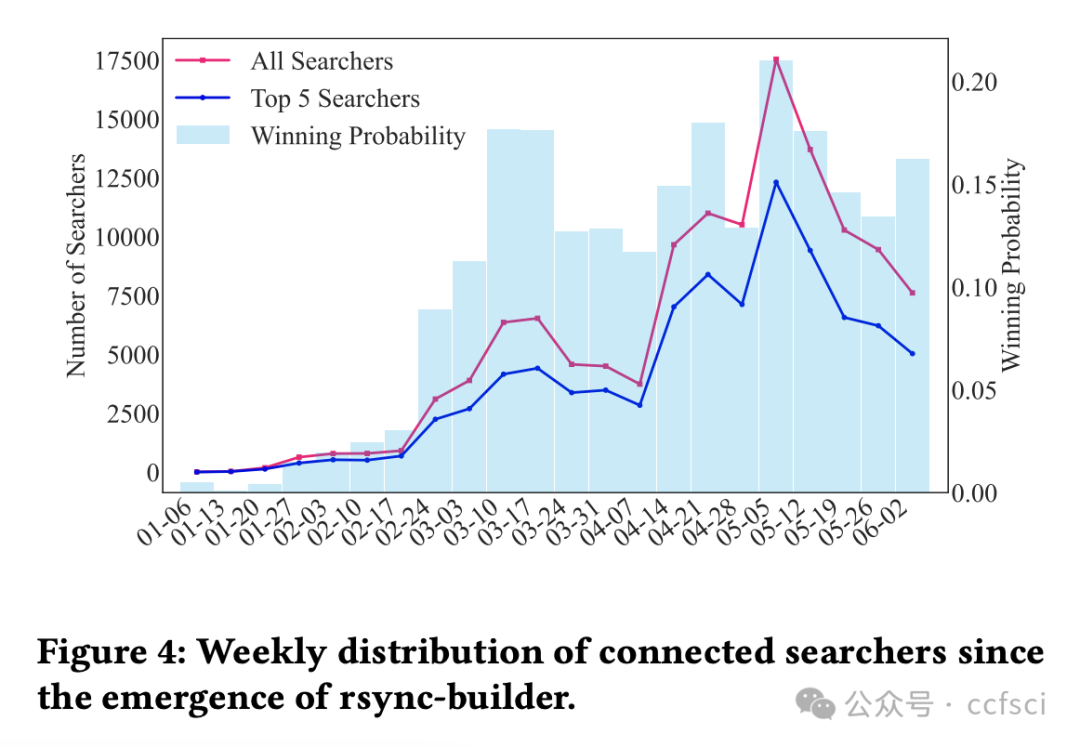
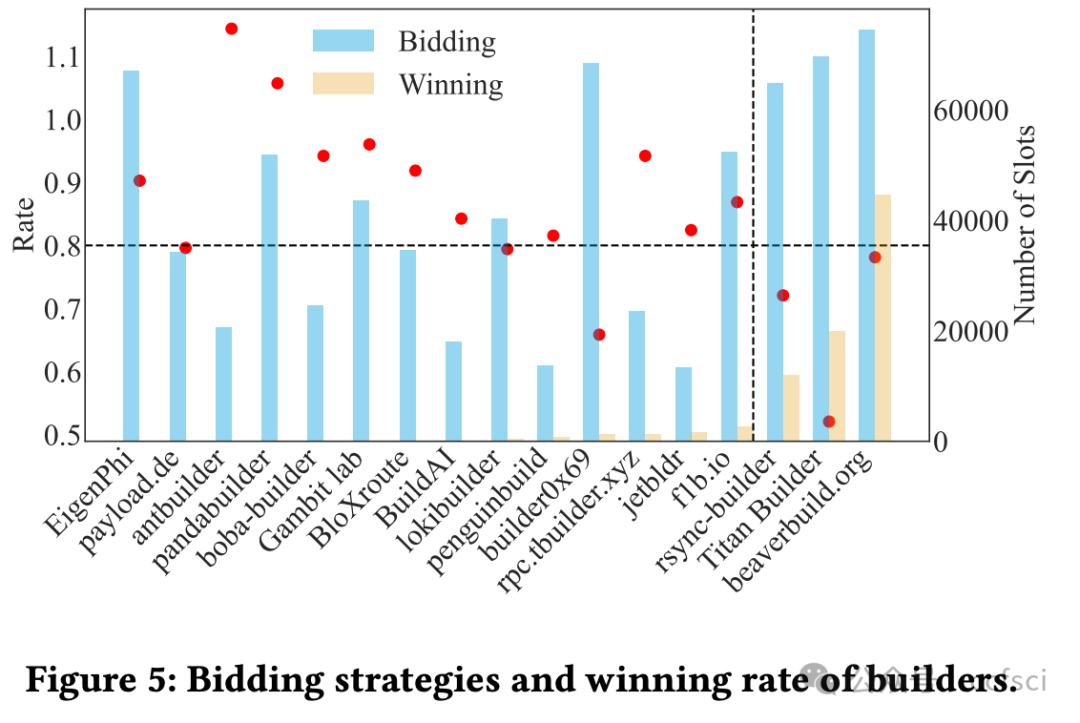
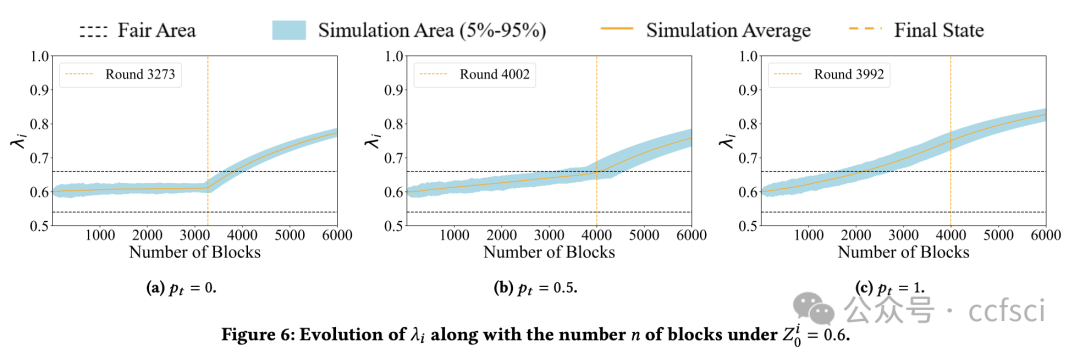
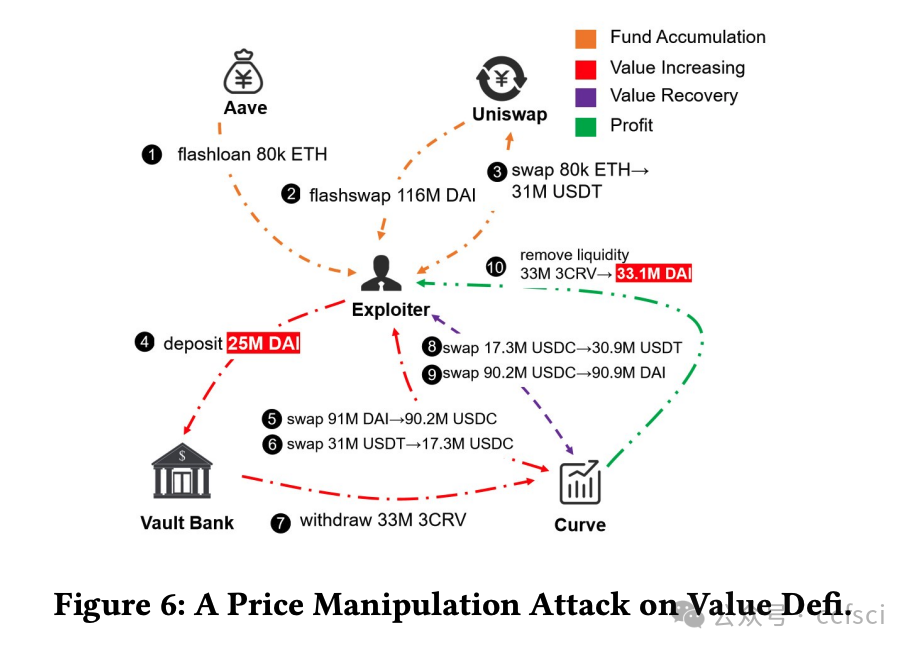
Ethereum, as a representative of Web3, adopts a novel framework called Proposer Builder Separation (PBS) to prevent the centralization of block profits in the hands of institutional Ethereum stakers. Introducing builders to generate blocks based on public transactions, PBS aims to ensure that block profits are distributed among all stakers. Through the auction among builders, only one will win the block in each slot. Ideally, the equilibrium strategy of builders under public information would lead them to bid all block profits. However, builders are now capable of extracting profits from private order flows. In this paper, we explore the effect of PBS with private order flows. Specifically, we propose the asymmetry auction model of MEV-Boost auction. Moreover, we conduct empirical study on Ethereum blocks from January 2023 to May 2024. Our analysis indicates that private order flows contribute to 54.59% of the block value, indicating that different builders will build blocks with different valuations. Interestingly, we find that builders with more private order flows (i.e., higher block valuations) are more likely to win the block, while retain larger proportion of profits. In return, such builders will further attract more private order flows, resulting in a monopolistic market gradually. Our findings reveal that PBS in current stage is unable to balance the profit distribution, which just transits the centralization of block profits from institutional stakers to the monopolistic builder.
作为 Web3 的代表,以太坊采用了一种名为提议者建造者分离 (PBS) 的创新框架,以防止区块收益集中在机构以太坊质押者手中。PBS 引入建造者基于公开交易生成区块,旨在确保区块收益在所有质押者之间分配。通过建造者之间的竞价,每个 slot 中只有一个建造者能够赢得区块。理想情况下,在公开信息下,建造者的均衡策略是竞价所有区块收益。然而,建造者现在能够从隐私订单流中获取收益。本文探讨了 PBS 对隐私订单流的影响。具体而言,我们提出了 MEV-Boost 拍卖的非对称拍卖模型。此外,我们对 2023 年 1 月至 2024 年 5 月的以太坊区块进行了实证研究。我们的分析表明,隐私订单流贡献了 54.59% 的区块价值,这表明不同的建造者会建造具有不同估值的区块。有趣的是,我们发现拥有更多私人订单流(即区块估值更高)的构建者更有可能赢得区块,并获得更大比例的利润。作为回报,这样的构建者会进一步吸引更多私人订单流,最终逐渐形成垄断市场。我们的研究结果表明,现阶段的PBS无法平衡利润分配,只是将区块利润的中心化从机构质押者转移到了垄断的构建者身上。
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3696410.3714754
18
Title:
Quantitative Runtime Monitoring of Ethereum Transaction Attacks
以太坊交易攻击的定量运行时监控
Authors:
Xinyao Xu, Ziyu Mao, Jianzhong Su, Xingwei Lin, David Basin, Jun Sun, Jingyi Wang
Key words:
Ethereum, Runtime Monitoring, Ethereum Attack Detection
以太坊、运行时监控、以太坊攻击检测
Abstract:
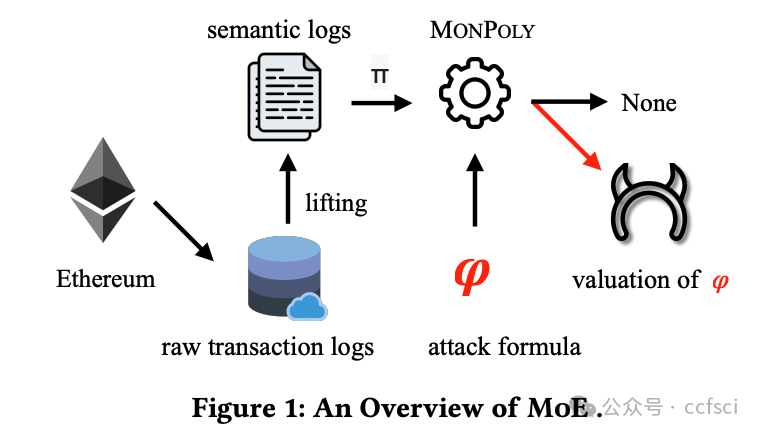
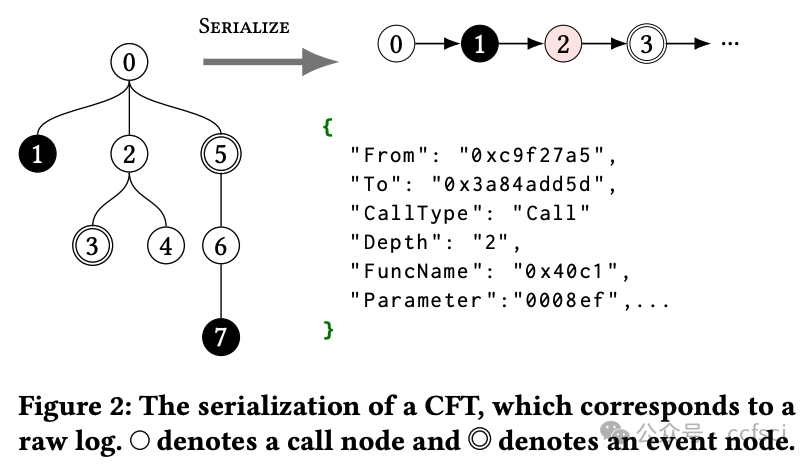
The rapid growth of decentralized applications, while revolutionizing financial transactions, has created an attractive target for malicious attacks. Existing approaches to detecting attacks often rely on predefined rules or simplistic and overly-specialized models, which lack the flexibility to handle the wide spectrum of diverse and dynamically changing attack types. To address this challenge, we present a general and extensible framework, MoE (<u>Mo</u>nitoring <u>E</u>thereum), that leverages runtime verification to detect a wide range of attacks on Ethereum. MoE features an expressive attack modeling language, based on Metric First-order Temporal Logic (MFOTL), that can formalize a wide range of attacks. We integrate a novel semantic lifting approach that extracts system behaviors relevant for various attacks, which can be analyzed using the monitoring tool MonPoly. Furthermore, we also equip MoE with quantitative capabilities to evaluate the similarity between a transaction and an attack formula to enhance its performance in identifying attacks, including near-miss attacks. We carry out extensive experiments with MoE on a labeled benchmark and a large-scale dataset containing over one million transactions. On the labeled benchmark, MoE successfully detects 92.0% attacks and achieves a 45.0% higher recall rate than competing state-of-the-art tool. MoE finds 3,319 attacks with 95.4% precision on the large dataset. Furthermore, MoE uses quantitative analysis to uncover 8% additional attacks. Finally, the average time for monitoring a transaction is less than 23 ms, positioning MoE as a promising practical solution for real-time attack detection for Ethereum.
去中心化应用的快速增长在彻底改变金融交易的同时,也为恶意攻击创造了一个诱人的目标。现有的攻击检测方法通常依赖于预定义规则或过于简单且过于专业的模型,这些模型缺乏处理种类繁多且动态变化的攻击类型的灵活性。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一个通用且可扩展的框架——MoE(Monitoring Ethereum),该框架利用运行时验证来检测针对以太坊的各种攻击。MoE 采用一种基于度量一阶时序逻辑 (MFOTL) 的富有表现力的攻击建模语言,可以形式化各种攻击。我们集成了一种新颖的语义提升方法,该方法可以提取与各种攻击相关的系统行为,并可以使用监控工具 MonPoly 进行分析。此外,我们还为 MoE 提供了量化功能,以评估交易与攻击公式之间的相似性,从而提升其识别攻击(包括近乎失手攻击)的性能。我们利用 MoE 在带标签的基准测试集和包含超过一百万笔交易的大规模数据集上进行了广泛的实验。在带标签的基准测试集上,MoE 成功检测到 92.0% 的攻击,召回率比同类最佳工具高出 45.0%。在大型数据集上,MoE 发现了 3,319 种攻击,准确率高达 95.4%。此外,MoE 还利用定量分析发现了 8% 的额外攻击。最终,MoE 监控每笔交易的平均时间不到 23 毫秒,这使得 MoE 成为以太坊实时攻击检测中极具潜力的实用解决方案。
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3696410.3714682
19
Title:
Distributed Ledger and Text Watermarking for Fine-Grain Provenance Checking of Textual Content
分布式账本和文本水印,用于文本内容的细粒度来源检查
Authors:

Key words:
Distributed ledger, Text watermarking, Text news sealing, Text
provenance checking, Online misinformation
分布式账本、文本水印、文本新闻密封、文本来源检查、在线虚假信息
Abstract:
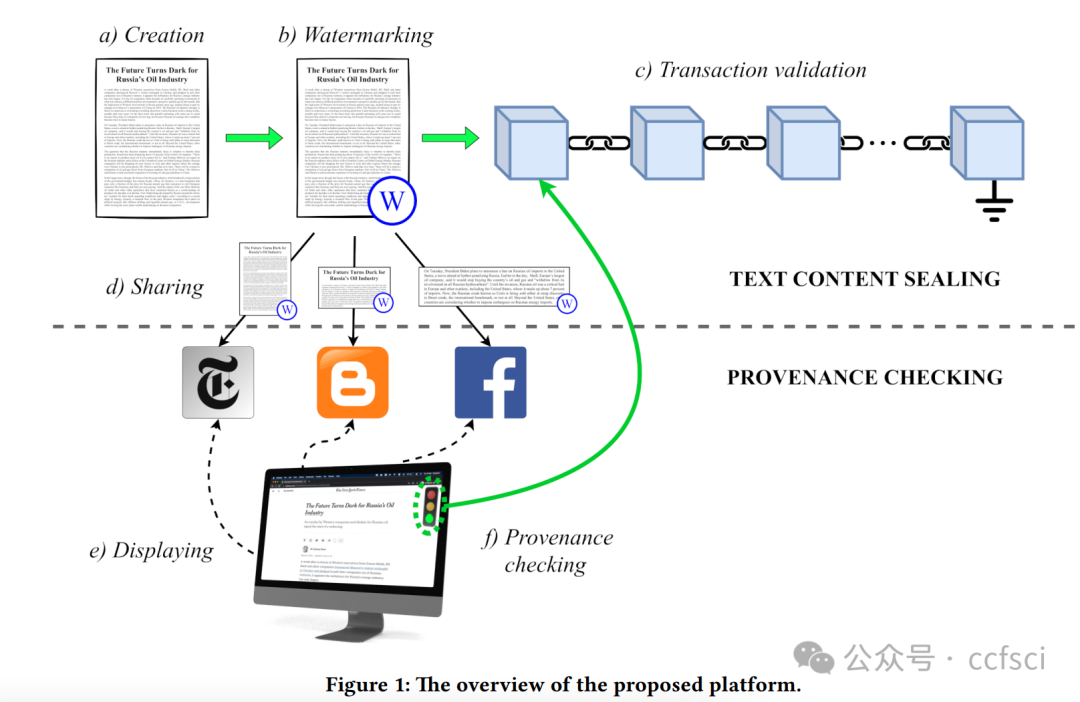
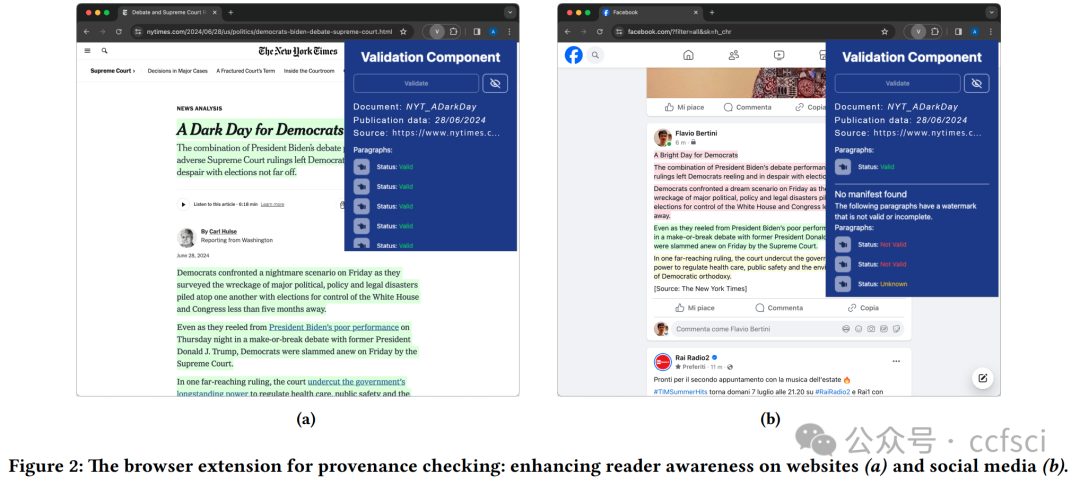
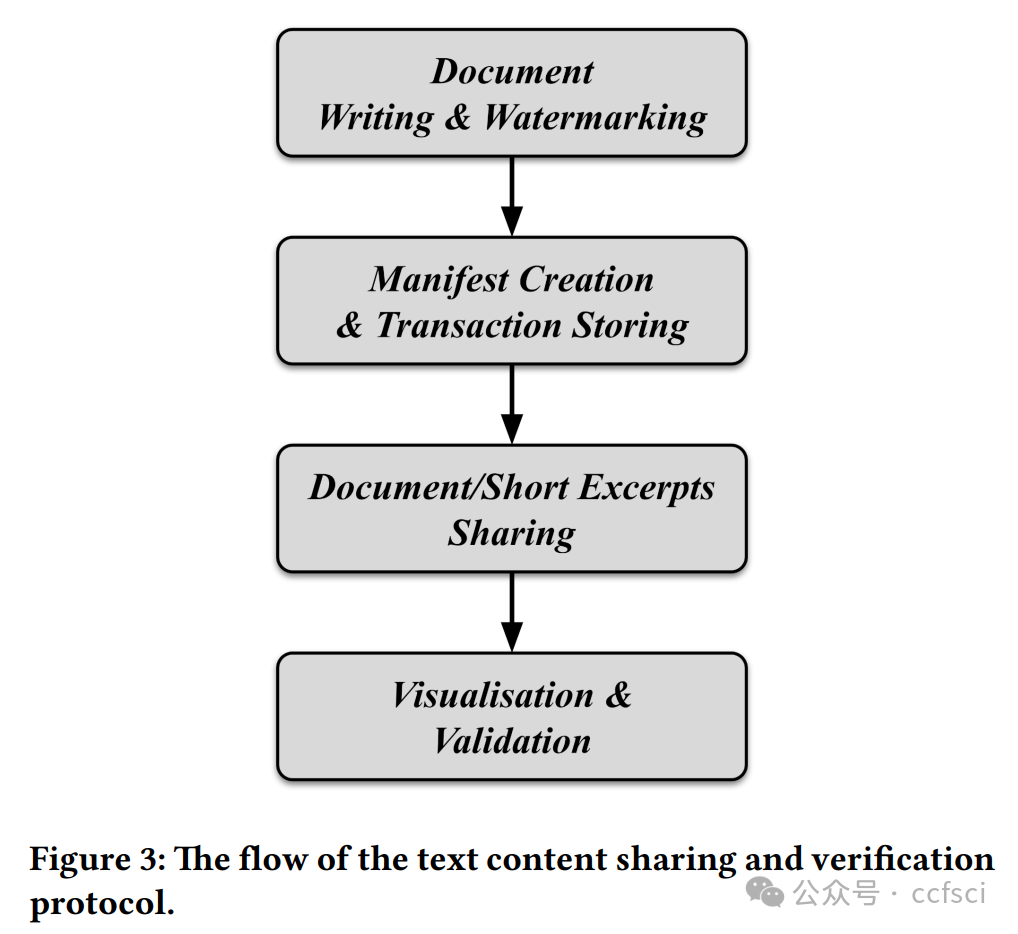
Information disorder has become a major societal challenge, impacting public discourse and democracy. This phenomenon has been exacerbated by the spread of social media platforms, affecting various areas, ranging from national elections to public health. Addressing fake news through a manual approach (e.g., human fact-checking) is unfeasible due to the rapid production of textual content. At the same time, applying automatic tools is equally challenging, primarily due to the ambiguity of natural language. In this paper, we addressed online information disorder from a different perspective by proposing a platform that supports trustworthy and reputable news producers and enhances awareness among readers across various social media. Specifically, the proposed platform enables news producers to automatically embed a unique watermark in the text they create, ensuring that the news cannot be manipulated or misattributed. The watermarking is embedded in a fine-grained way, allowing even small extracts of the news to be shared while preserving traceability. Additionally, the association between the watermark and the news item is recorded in a distributed ledger, preventing further manipulation that could arise from centralised management. The aim is to enable readers to make more informed decisions about the content they encounter, even when engaging with excerpts of the original document, minimising reliance on external fact-checking organisations.
信息混乱已成为一项重大的社会挑战,影响着公共话语和民主。社交媒体平台的普及加剧了这一现象,影响了从国家选举到公共卫生等各个领域。由于文本内容的快速生成,通过人工方法(例如人工事实核查)来应对虚假新闻已变得不可行。同时,应用自动化工具也同样具有挑战性,这主要是由于自然语言的模糊性。本文从不同的角度解决了在线信息混乱问题,提出了一个平台,该平台支持值得信赖且信誉良好的新闻制作者,并增强了各社交媒体读者的认知度。具体而言,该平台使新闻制作者能够自动在其创作的文本中嵌入独特的水印,确保新闻不会被篡改或误传。水印以细粒度的方式嵌入,即使是新闻的一小部分片段也可以在保留可追溯性的同时进行共享。此外,水印与新闻内容之间的关联会被记录在分布式账本中,从而防止中心化管理可能造成的进一步操纵。其目的是让读者即使在阅读原文摘录时,也能对所看到的内容做出更明智的判断,最大限度地减少对外部事实核查机构的依赖。
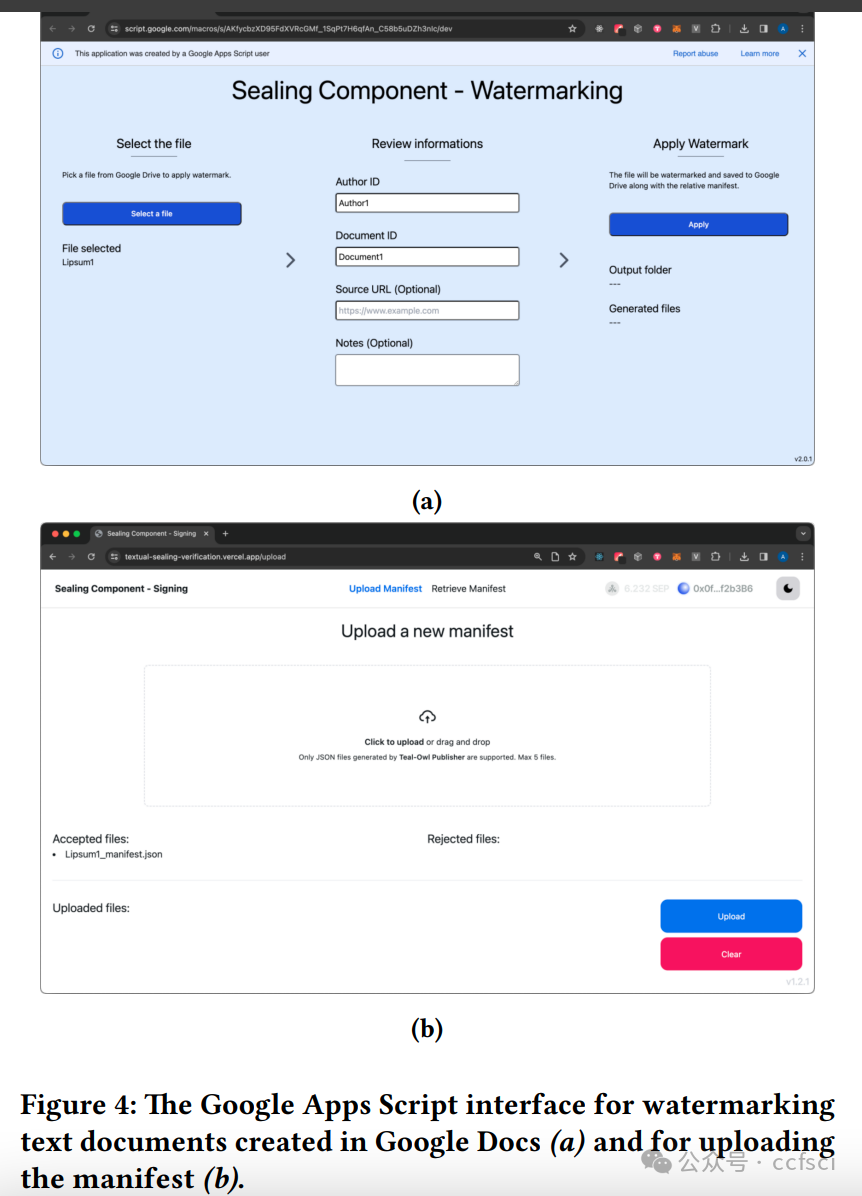
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/pdf/10.1145/3701716.3717536
20
Title:
BeyondLife: Third-Party Digital Will Application
BeyondLife:第三方数字遗嘱申请
Authors:

Abstract:
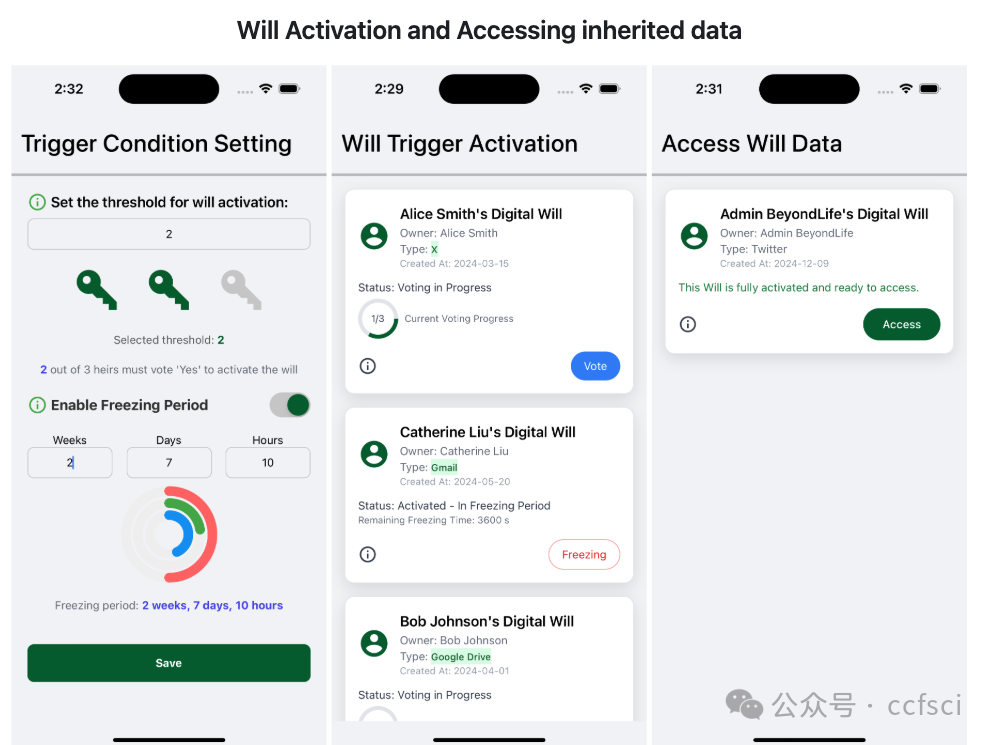
In the digital age, nearly everyone leaves behind a vast array of digital footprints, including social media posts, emails, and files or photos stored in the cloud. Managing these digital assets after death has become an increasingly significant challenge. Major companies like Meta and Google provide limited and rigid options to users that require configuration separately. There are a handful of third-party closed-source services that are complex and do not have features deemed necessary. In this demo paper, we introduce BeyondLife, the first cross-platform solution for managing digital wills and securely handling digital assets after death. It introduces a cross-platform solution for digital wills, addressing limitations in existing services. The system combines a customized encryption scheme, multi-cloud storage, and decentralized architecture to enable secure and granular digital asset management. A prototype is available at https://github.com/Xinzhang-Chen/BeyondLife.
在数字时代,几乎每个人都会留下大量的数字足迹,包括社交媒体帖子、电子邮件以及存储在云端的文件或照片。在人去世后管理这些数字资产已成为一项日益严峻的挑战。像Meta和谷歌这样的大公司为用户提供的选项有限且僵化,需要单独配置。此外,还有一些第三方闭源服务,它们功能复杂,且缺乏必要的功能。在本演示论文中,我们将介绍BeyondLife,这是首个用于管理数字遗嘱并安全处理身后数字资产的跨平台解决方案。它引入了一种跨平台的数字遗嘱解决方案,解决了现有服务的局限性。该系统结合了定制加密方案、多云存储和去中心化架构,以实现安全、精细的数字资产管理。原型可在https://github.com/Xinzhang-Chen/BeyondLife获取。
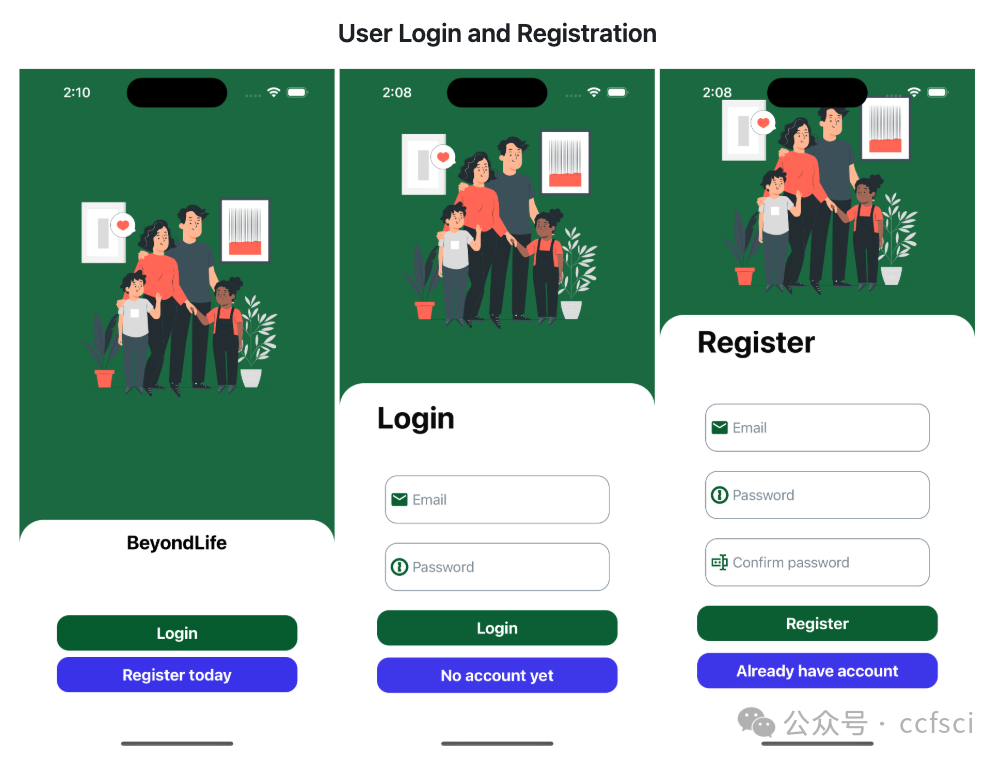
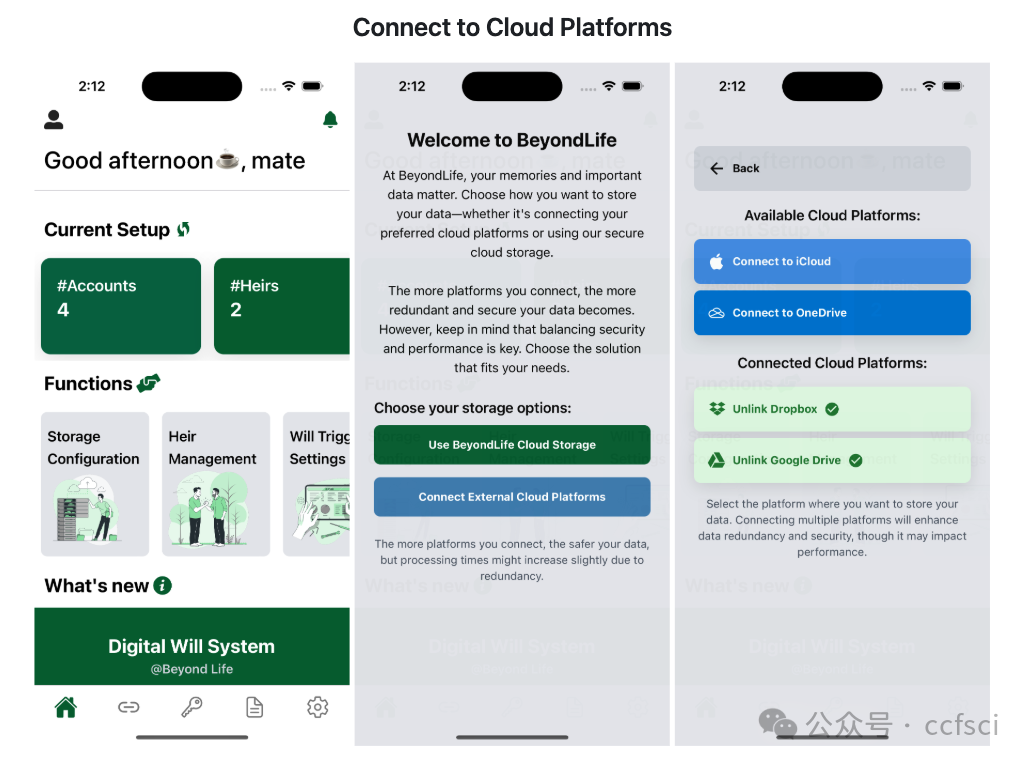
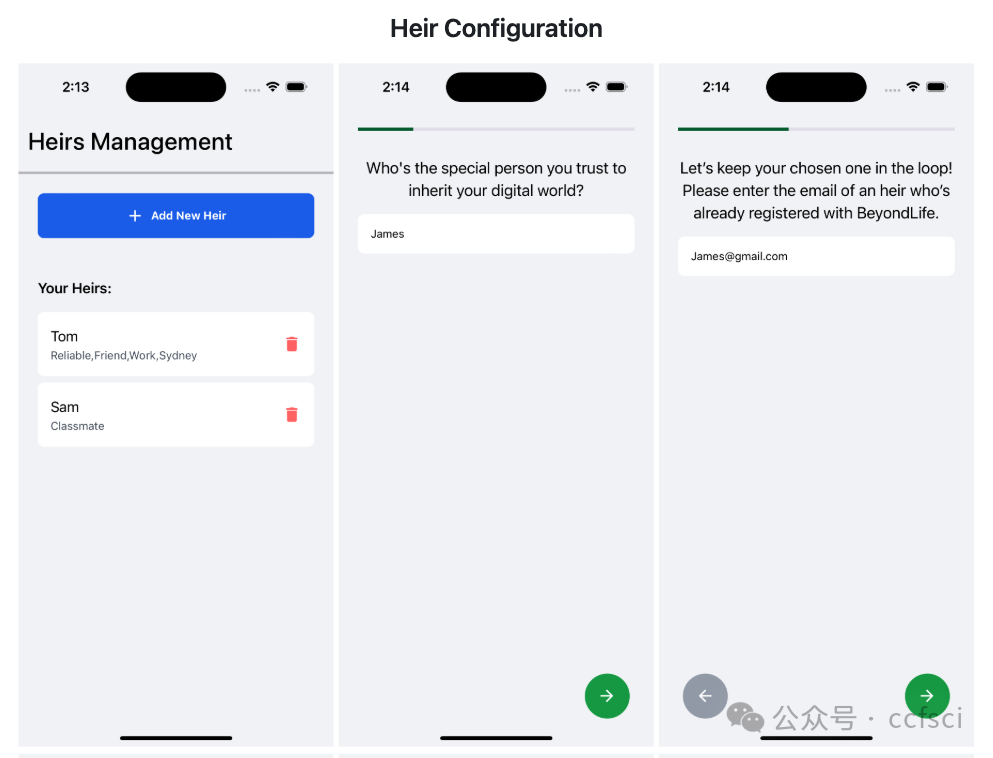
Pdf下载链接:
https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3701716.3715168
