【JAVA接口自动化】JAVA如何读取Yaml文件
java读取yaml文件 自动化测试中,用例数据存放在yaml文件中
数据存储
我们采用yaml存储数据文件 按照我下面的方式创建
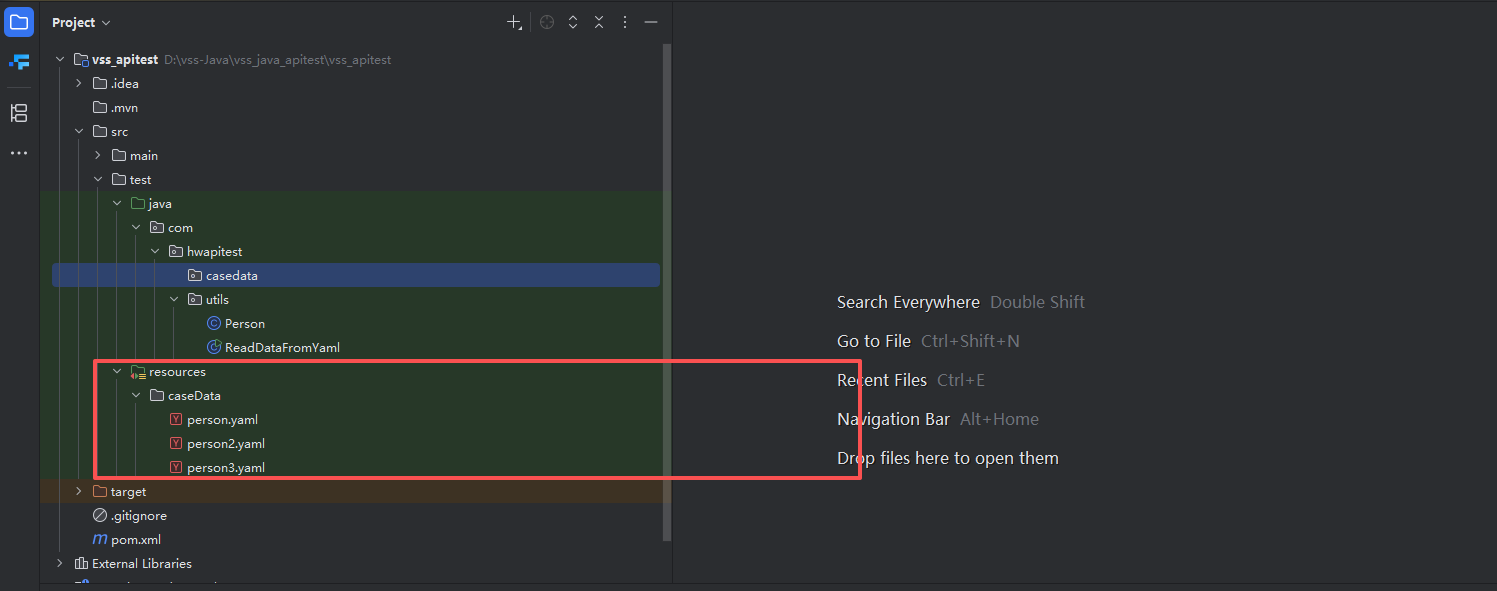
yaml文件数据
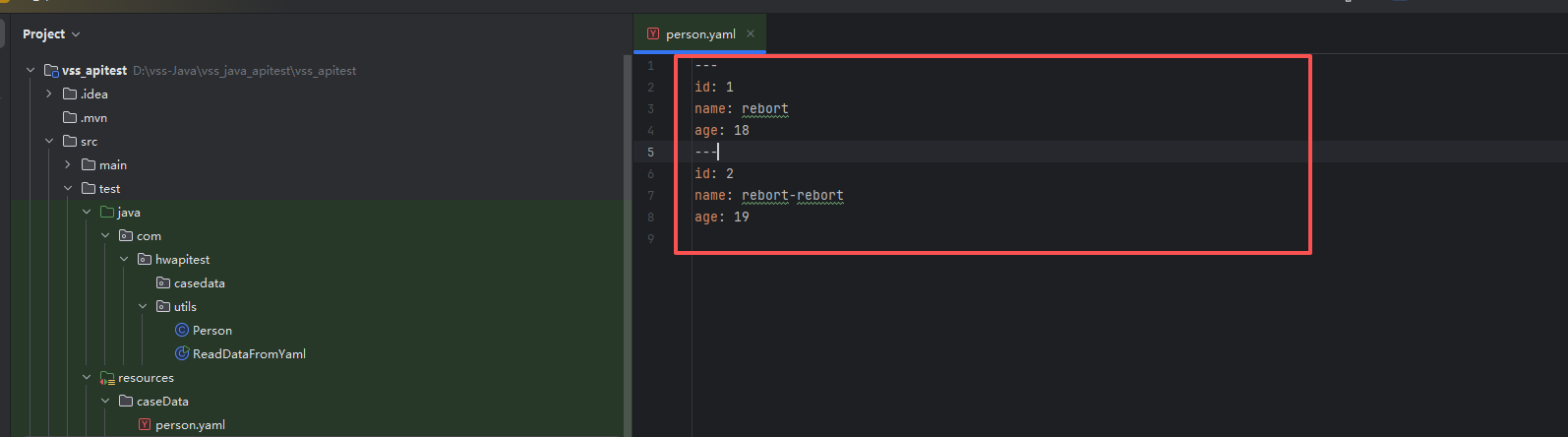
接下来我们创建并构造三个yaml文件,用于我们在JAVA中进行读取yaml文件数据,依次创建yaml文件如下: person.yaml
---
id: 1
name: rebort
age: 18
---
id: 2
name: rebort-rebort
age: 19
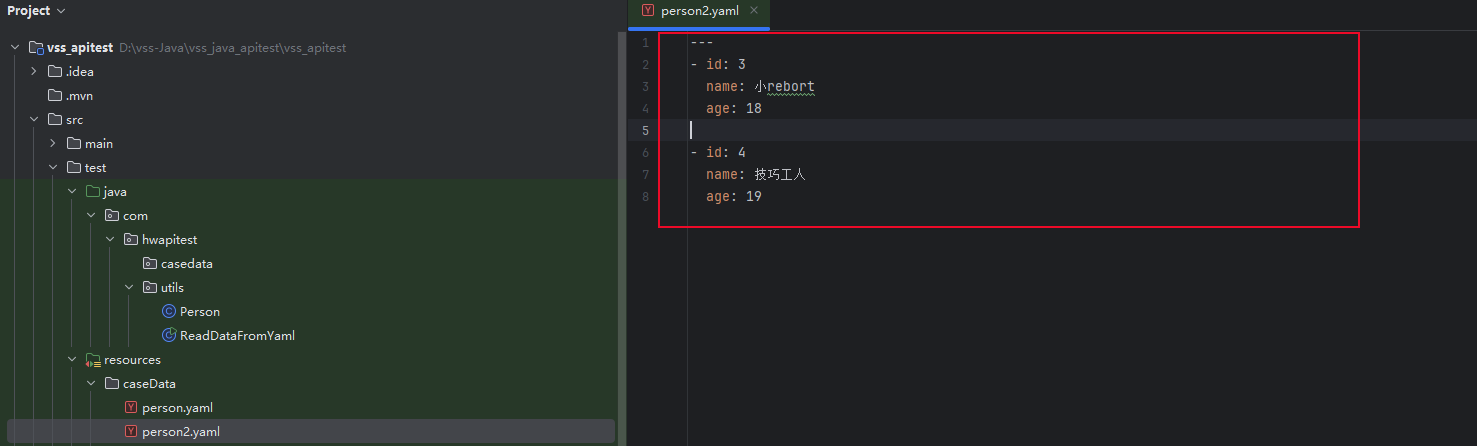
person2.yaml
---
- id: 3name: 小rebortage: 18- id: 4name: 技巧工人age: 19
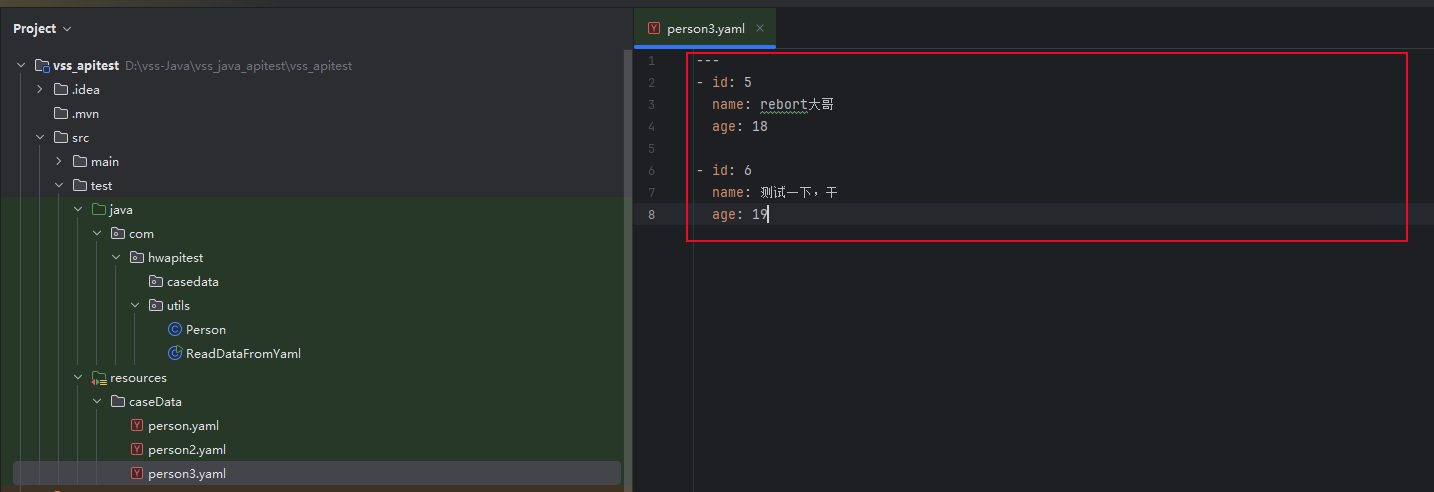
person3.yaml
---
- id: 5name: rebort大哥age: 18- id: 6name: 测试一下,干age: 19
接下来编写读取yaml文件的JAVA代码
public class Person {private String id;private String name;private String age;public String getId() {return id;}public void setId(String id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public String getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(String age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"id='" + id + '\'' +", name='" + name + '\'' +", age='" + age + '\'' +'}';}
}
编写JAVA代码读取yaml文件数据,并返回对象
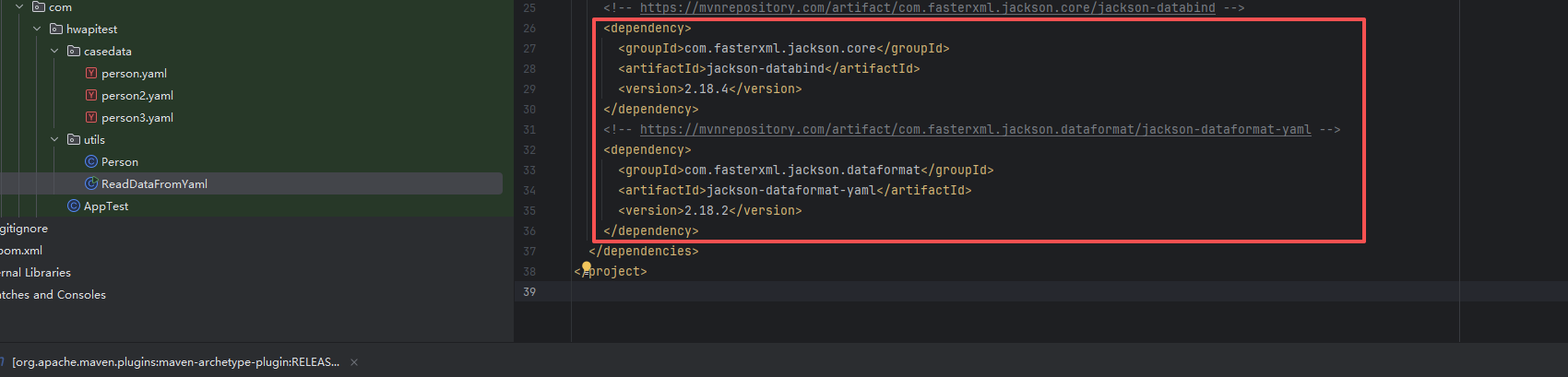
在编写读取文件代码之前,我们先将yaml文件读取所需要的依赖添加一下,我这里使用的是maven,所以我直接在pom.xml中添加 如下:
package com.hwapitest.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
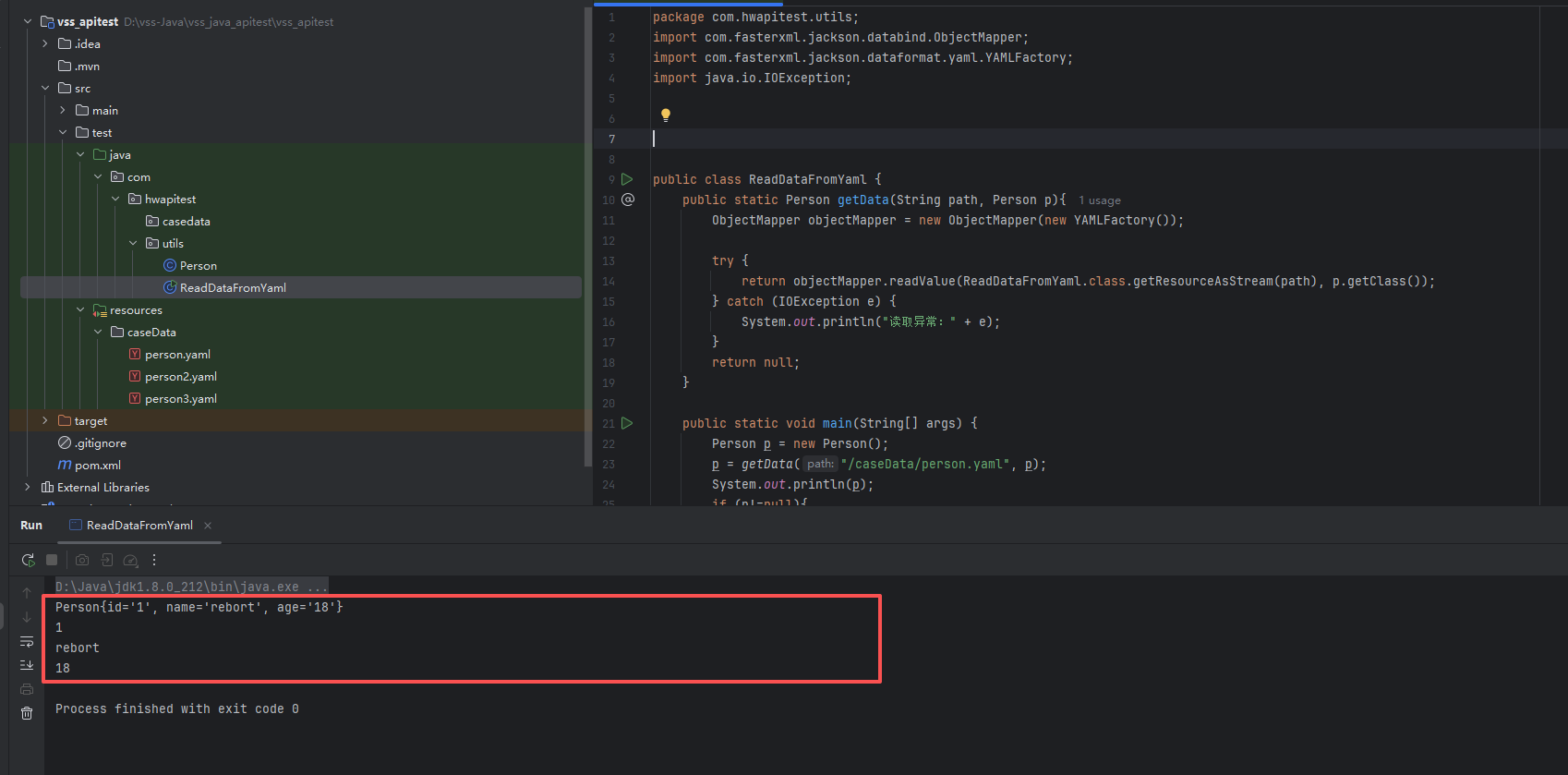
import java.io.IOException;public class ReadDataFromYaml {public static Person getData(String path, Person p){ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());try {return objectMapper.readValue(ReadDataFromYaml.class.getResourceAsStream(path), p.getClass());} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("读取异常:" + e);}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {Person p = new Person();p = getData("/caseData/person.yaml", p);System.out.println(p);if (p!=null){System.out.println(p.getId());System.out.println(p.getName());System.out.println(p.getAge());}}
}运行代码后查看此时控制台的输出打印情况
可以看到我们已经读取到了yaml中的数据,并且打印在控制台显示 可以在控制台看到具体的数据信息
接下来我们优化了代码,使用优化:泛型,传字节码
package com.hwapitest.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
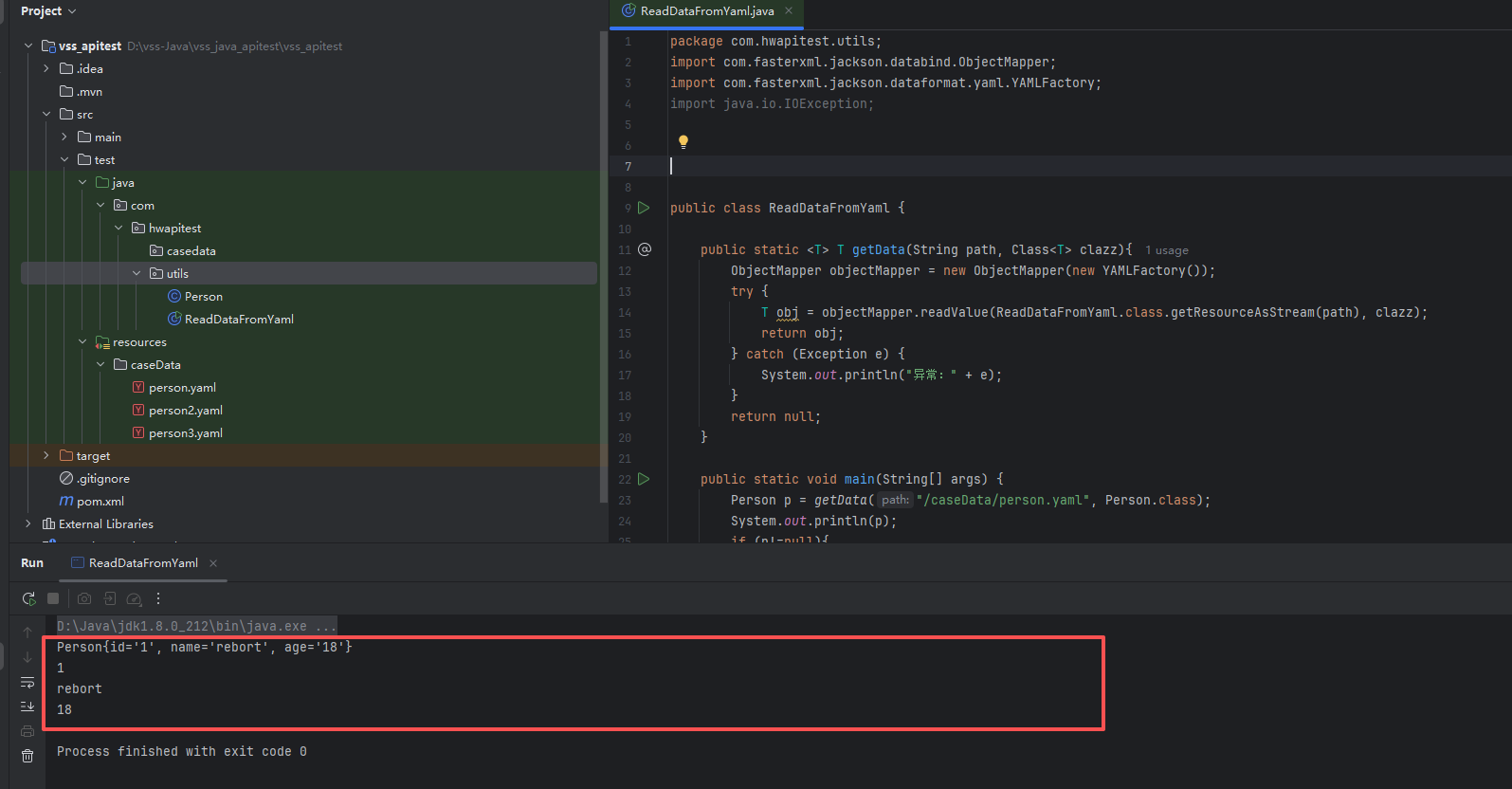
import java.io.IOException;public class ReadDataFromYaml {public static <T> T getData(String path, Class<T> clazz){ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());try {T obj = objectMapper.readValue(ReadDataFromYaml.class.getResourceAsStream(path), clazz);return obj;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("异常:" + e);}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {Person p = getData("/caseData/person.yaml", Person.class);System.out.println(p);if (p!=null){System.out.println(p.getId());System.out.println(p.getName());System.out.println(p.getAge());}}
}
再次查看此时控制台的输出打印,是不是同样也能看到输出的打印信息
如何读取yaml文件,并返回对象list,接下来我们将代码优化为返回list
package com.hwapitest.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
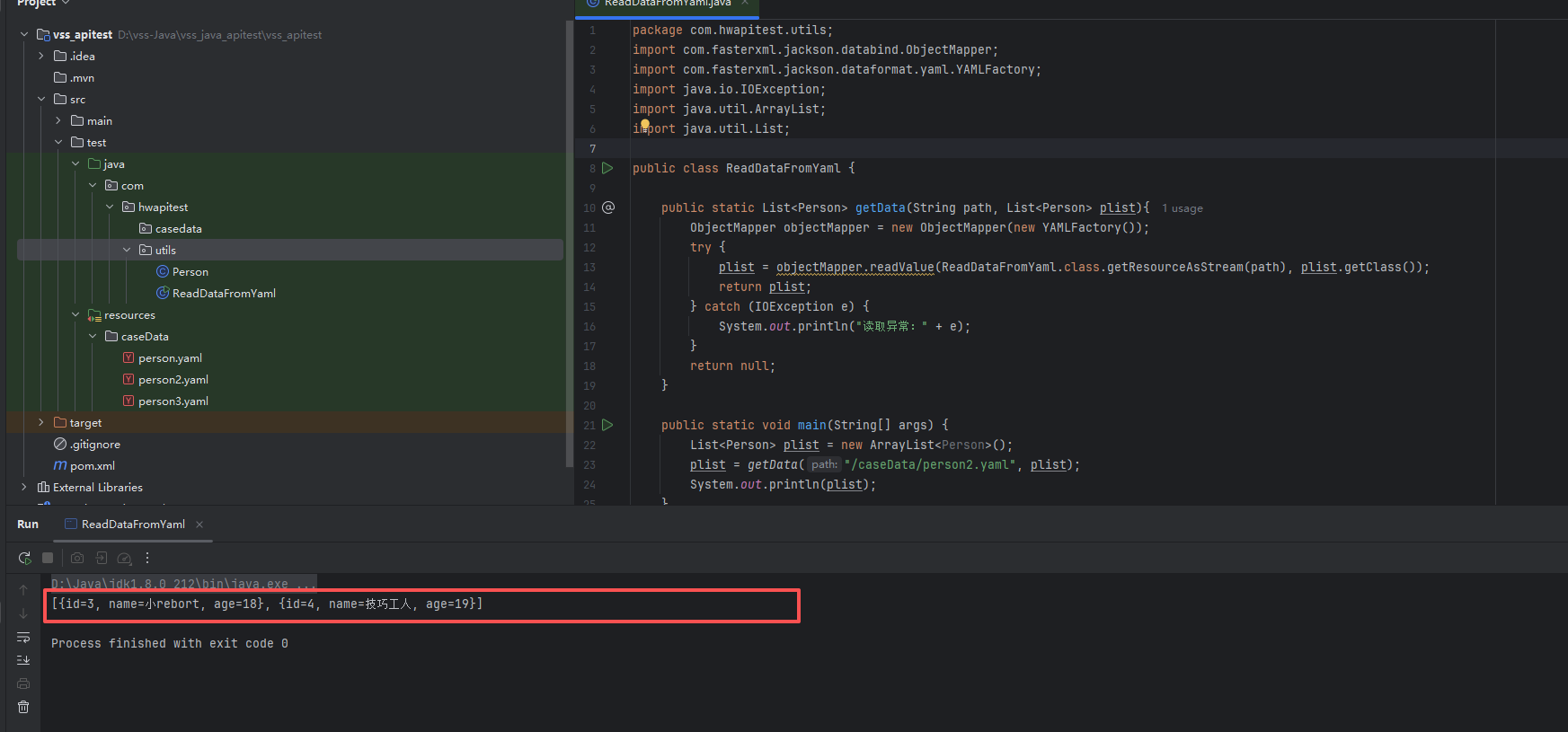
import java.util.List;public class ReadDataFromYaml {public static List<Person> getData(String path, List<Person> plist){ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());try {plist = objectMapper.readValue(ReadDataFromYaml.class.getResourceAsStream(path), plist.getClass());return plist;} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("读取异常:" + e);}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> plist = new ArrayList<Person>();plist = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml", plist);System.out.println(plist);}
}
运行代码此时查看控制台的输出打印情况
再次优化读取返回对象list的代码,使用泛型的方式,返回字节码
package com.hwapitest.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.hwapitest.utils.Person;public class ReadDataFromYaml {public static <T> List<T> getData(String path, Class<T> clazz){ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());try {List<T> list = objectMapper.readValue(ReadDataFromYaml.class.getResourceAsStream(path), List.class);return list;} catch (IOException e) {System.out.println("读取异常:" + e);}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> plist = new ArrayList<Person>();List<Person> plist1 = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml", Person.class);if ( plist1!=null){plist.addAll(plist1);}List<Person> plist2 = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml", Person.class);if ( plist2!=null){plist.addAll(plist2);}System.out.println(plist);}
}
再次运行代码,可以看到控制台输出打印结果
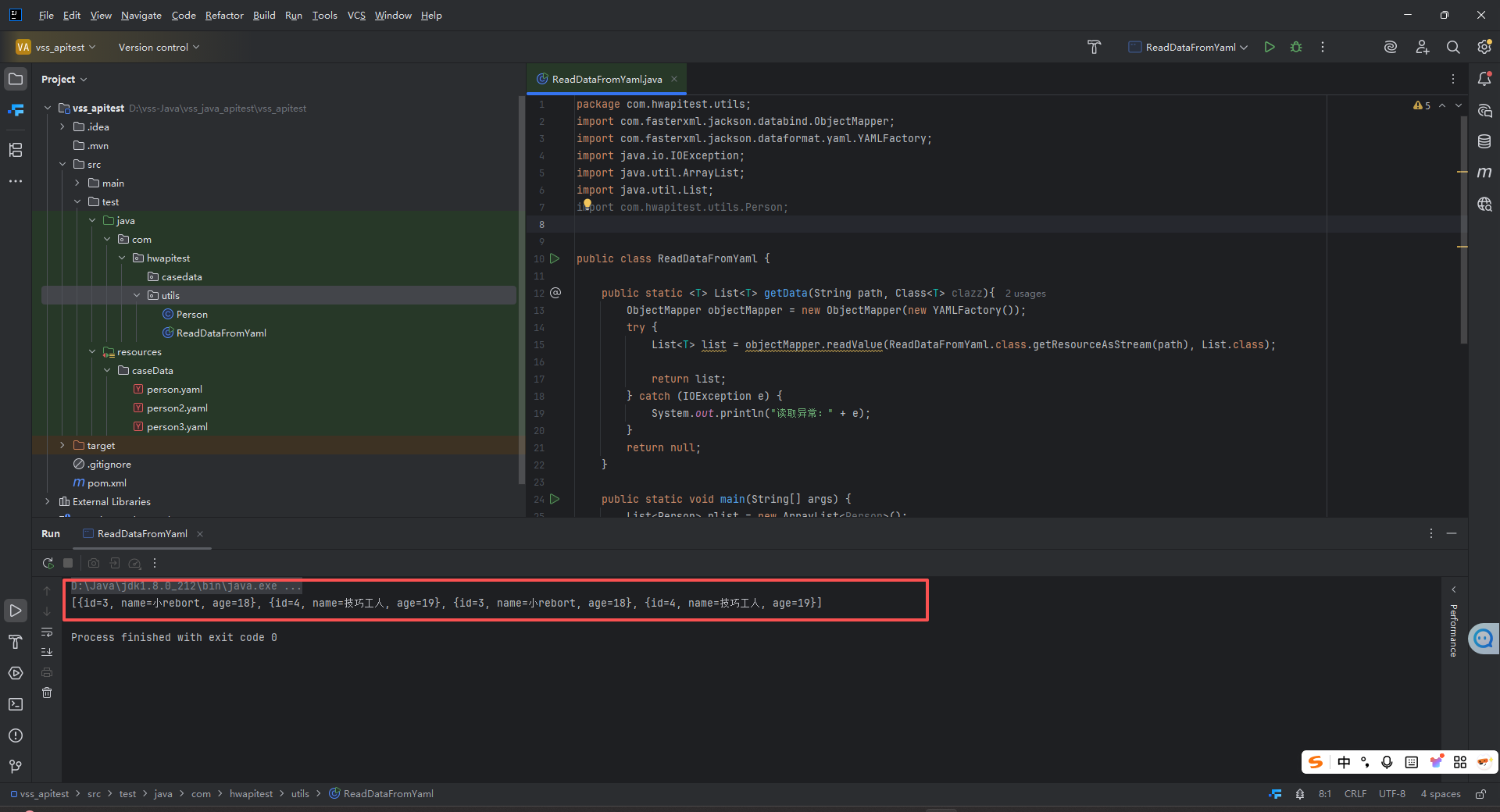
问题
上面可以把多个yaml的数据放到一个list里面
但是,如果打印对象内容(模拟解析测试用例数据)
public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> plist = new ArrayList<Person>();List<Person> plist1 = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml", Person.class);if ( plist1!=null){plist.addAll(plist1);}List<Person> plist2 = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml", Person.class);if ( plist2!=null){plist.addAll(plist2);}System.out.println(plist);for (Person person : plist2) {System.out.println(person.getName());}
}
运行结果后会看到如下的报错情况
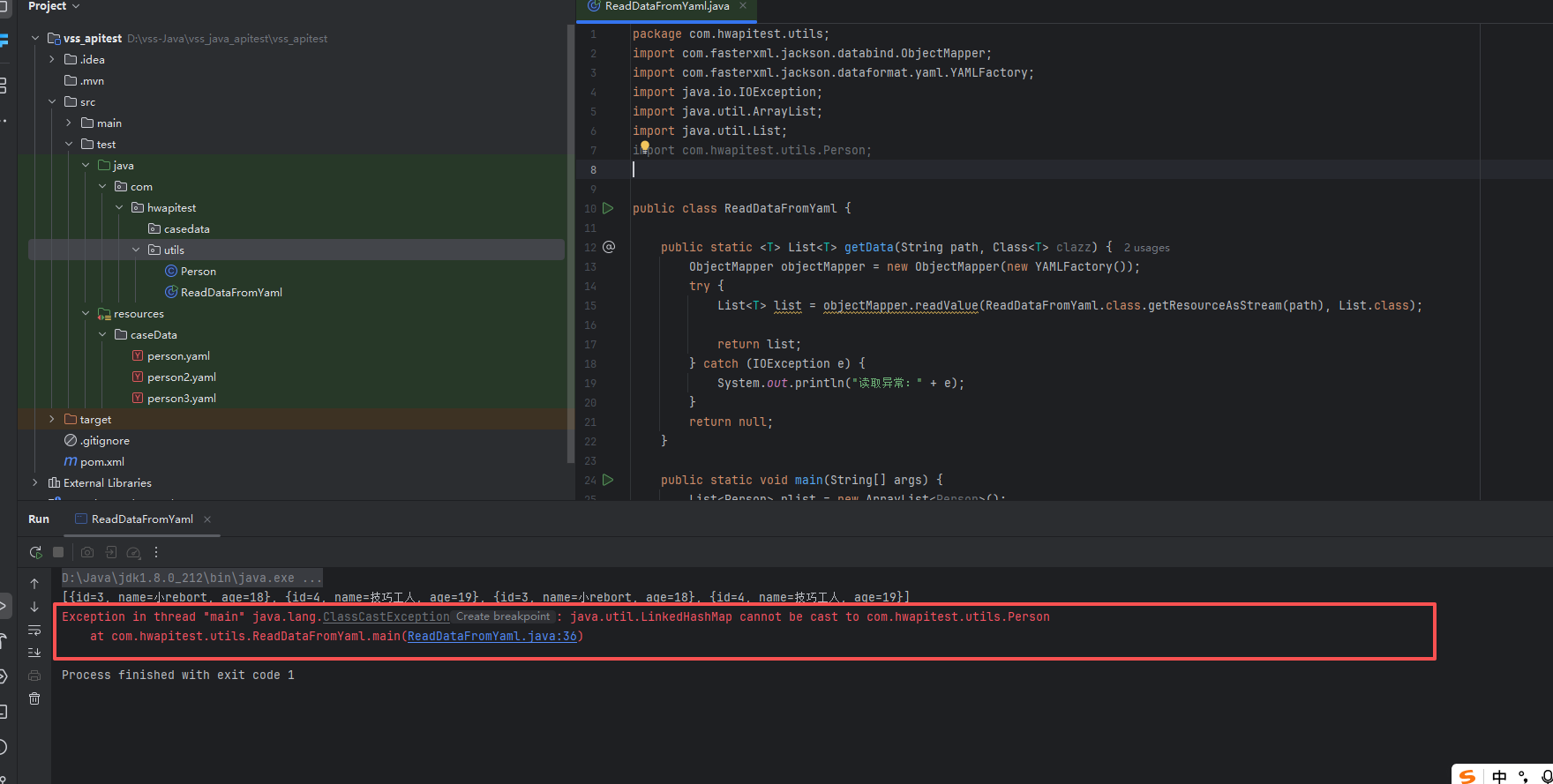
通过debug发现,list的元素是LinkedHashMap类型
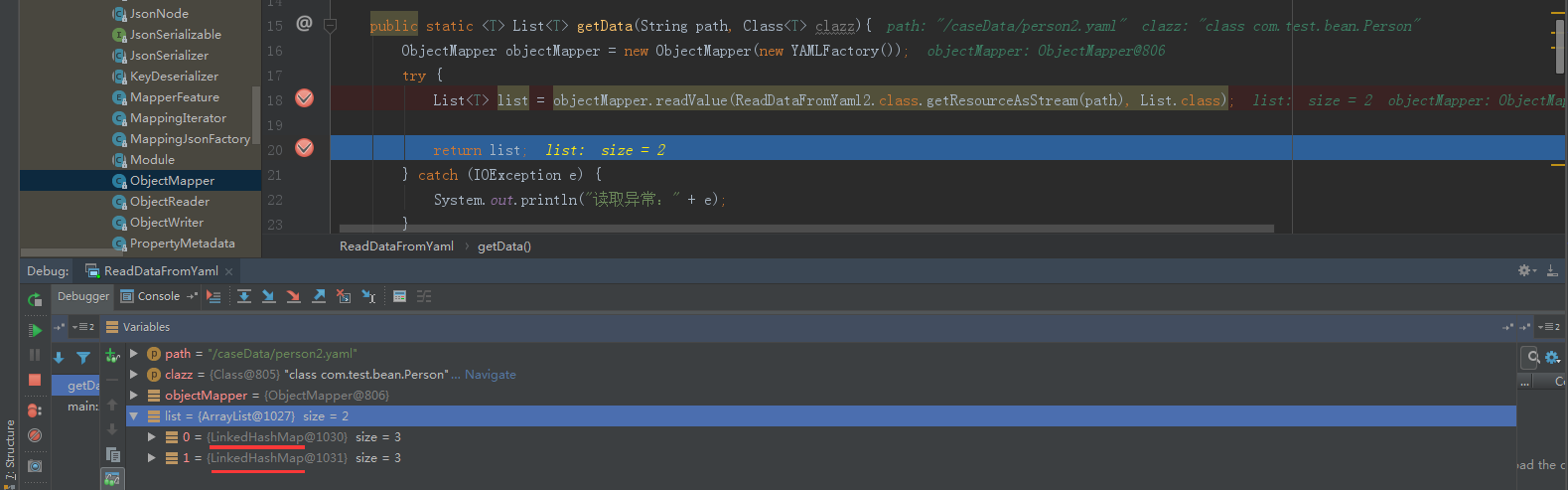
解决方案:
装换位指定的类型
package com.hwapitest.utils;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;public class ReadDataFromYaml {public static List<Person> getData(String path) {ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());try {List list = objectMapper.readValue(ReadDataFromYaml.class.getResourceAsStream(path), List.class);// 转成指定类型的list集合List<Person> list_new = objectMapper.convertValue(list, new TypeReference<List<Person>>() {});return list_new;} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println("异常:" + e);}return null;}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Person> plist = new ArrayList<Person>();List<Person> plist1 = getData("/caseData/person2.yaml");if ( plist1!=null){plist.addAll(plist1);}List<Person> plist2 = getData("/caseData/person3.yaml");if ( plist2!=null){plist.addAll(plist2);for (Person person : plist2) {System.out.println(person.getId());System.out.println(person.getName());System.out.println(person.getAge());}}System.out.println(plist);}
}
再次运行后可以看到打印输出多个文件的yaml数据
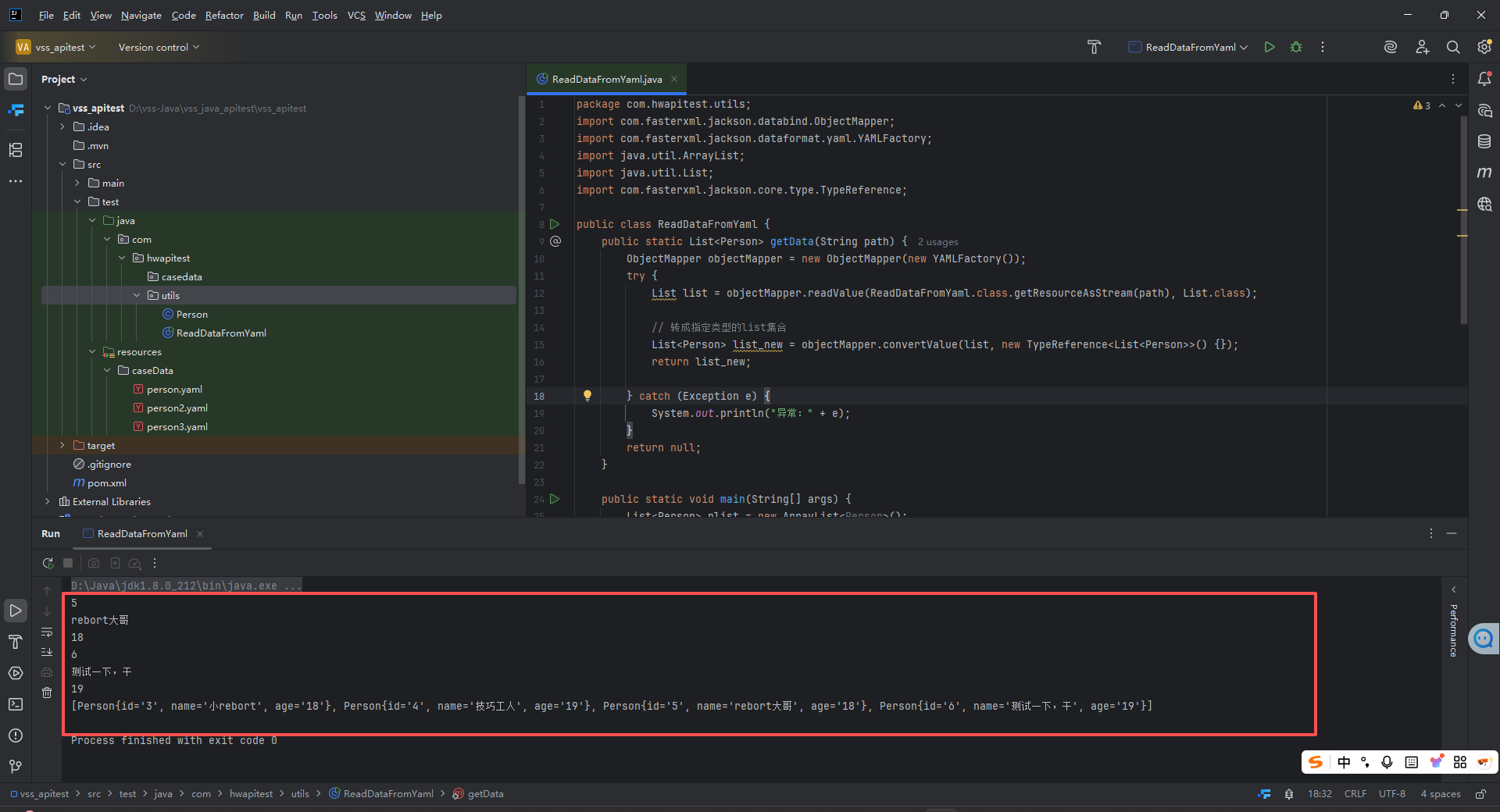
思考
上面解决方案中,我们把类型写死了,如果作为一个工具类,如何实现传任意类型?
